Characterizing the PRRSV nsp2 Deubiquitinase Reveals Dispensability of Cis-Activity for Replication and a Link of nsp2 to Inflammation Induction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Virus, and Antibodies
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. E. coli-Based Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. In Vitro Fluorescent DUB Assay
2.5. In Vitro Cleavage of K48 and K64-Linked Polyubiquitin Chains
2.6. Cell-Based DUB Assay
2.7. Cell-Based Trans- and Cis-Cleavage Assay
2.8. Construction of PRRSV Mutants and Growth Kinetics Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Measurement of Secreted TNFα
2.11. Bioinformatics Prediction
2.12. Quantitative Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
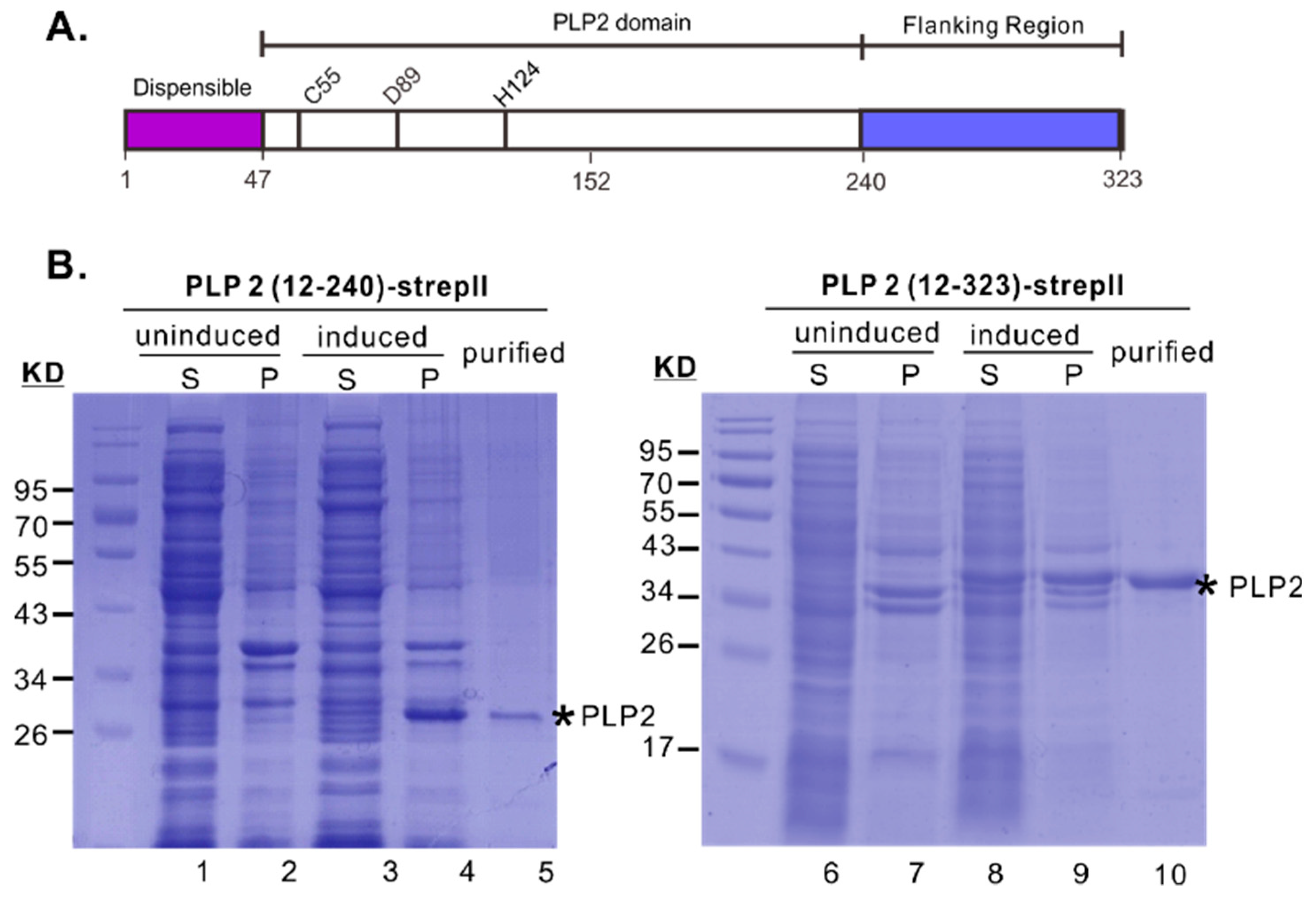
3.1. The Downstream Flanking Sequence is Critical for the Yield and Solubility of PRRSV PLP2 Protease Domain in E. coli
3.2. The In Vitro Purified PRRSV PLP2 Can Efficiently Cleave Both K63 and K48-Linked Polyubiquitin Chains Ub3-7 but Displays a Differential Activity in Converting the Respective Ubiquitin Dimers to Monomer
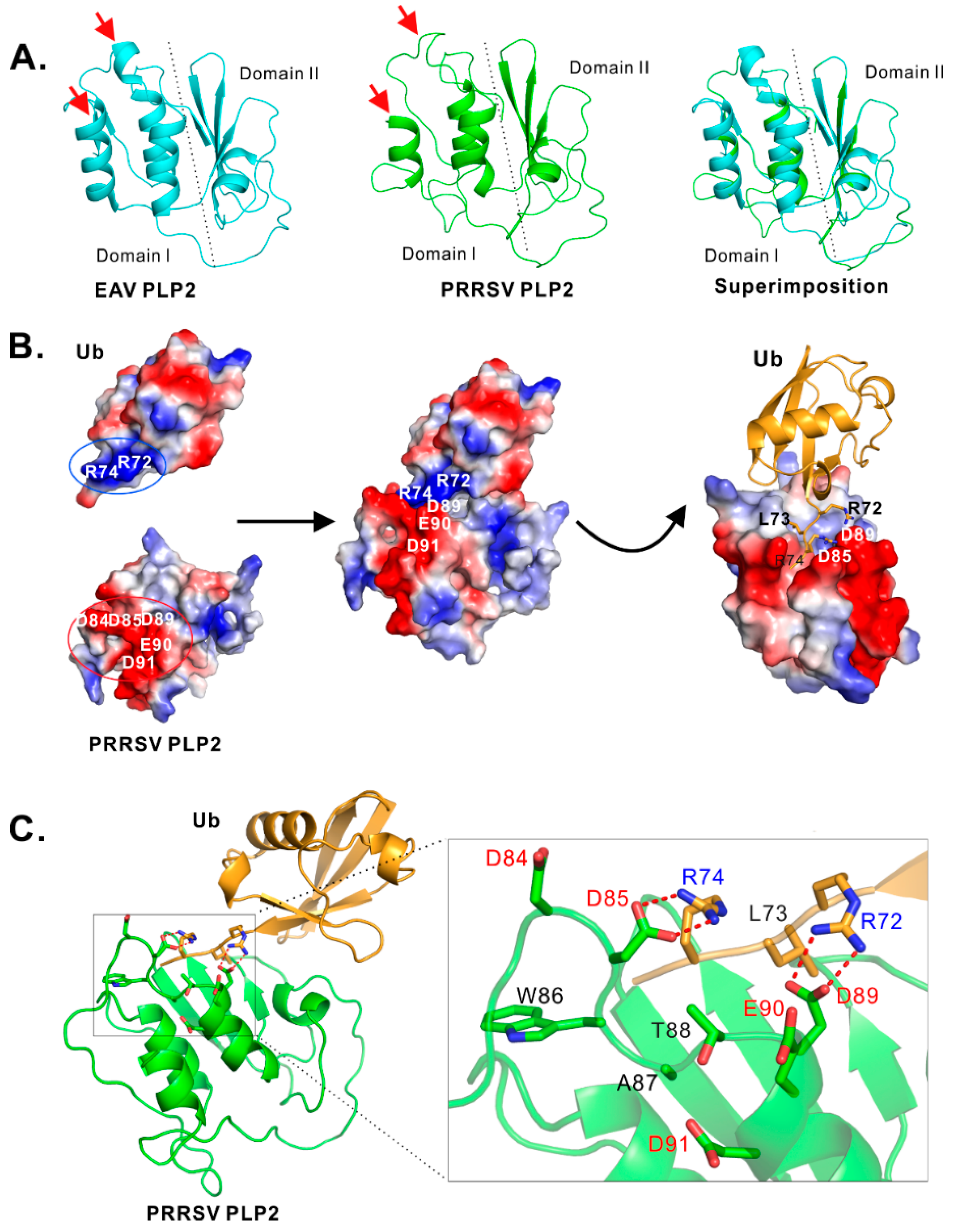
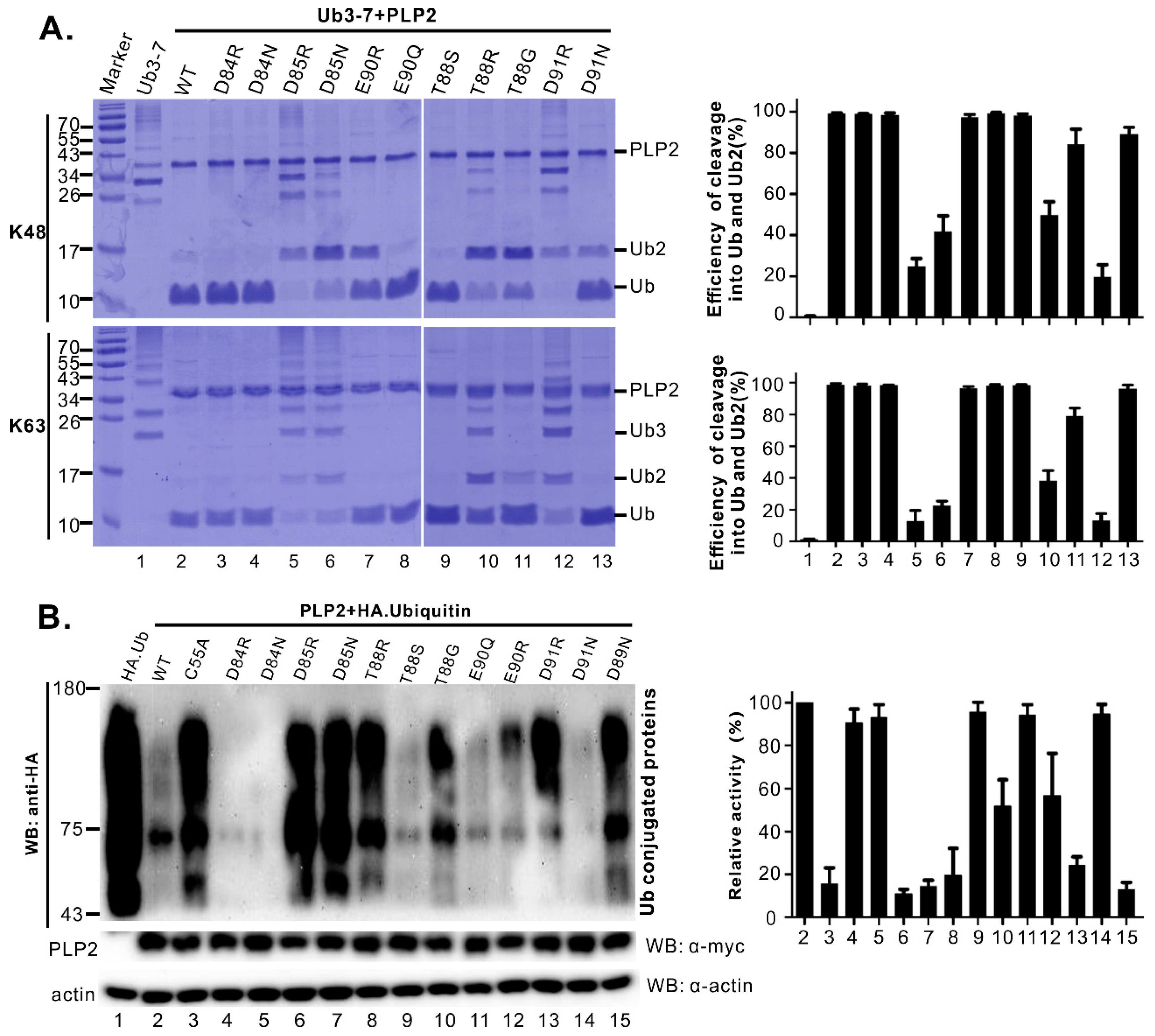
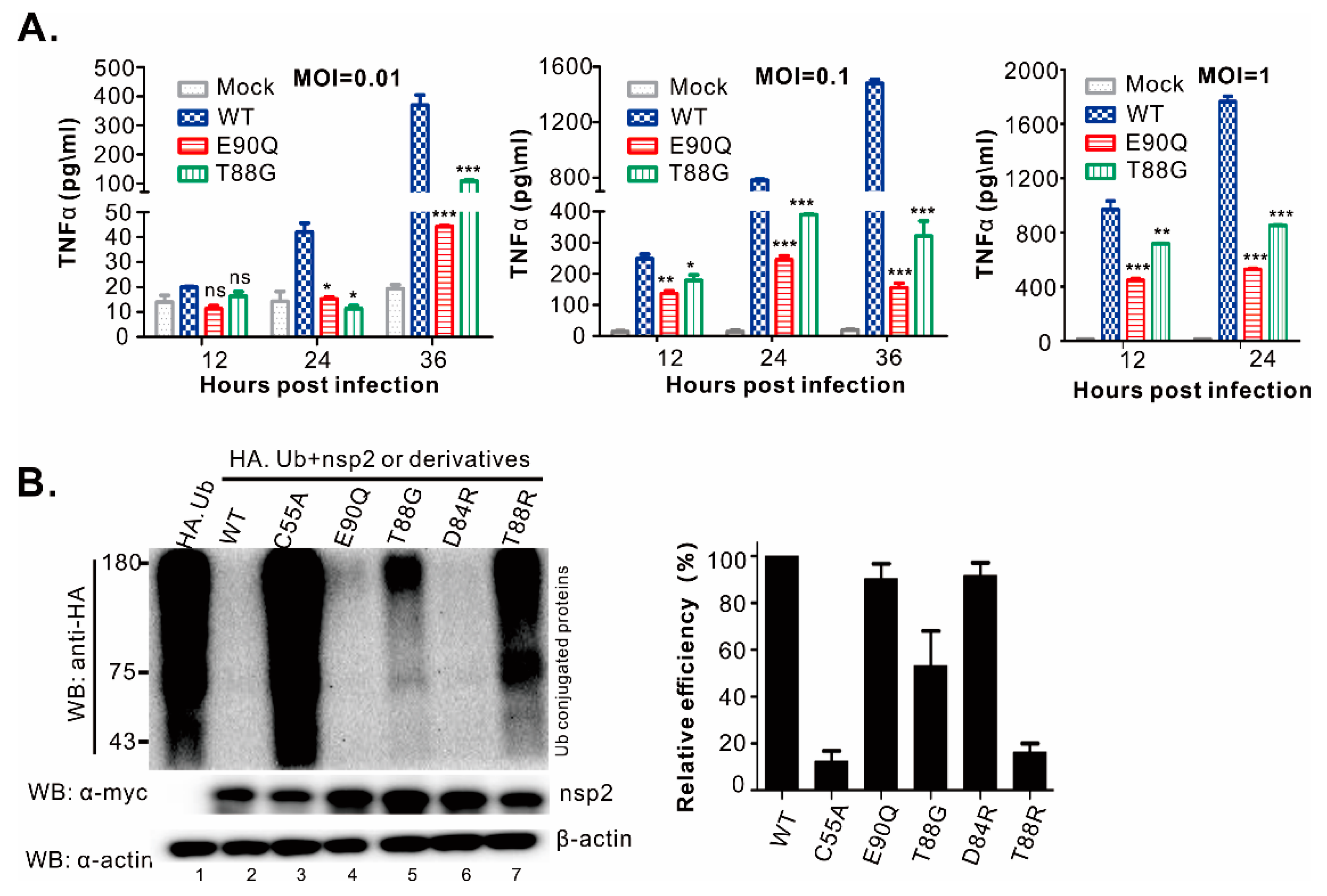
3.3. Identification of Residues Critical for the PLP2 DUB Activity
3.4. Differentiation of DUB Activity from Trans- and Cis-Cleavage Activity
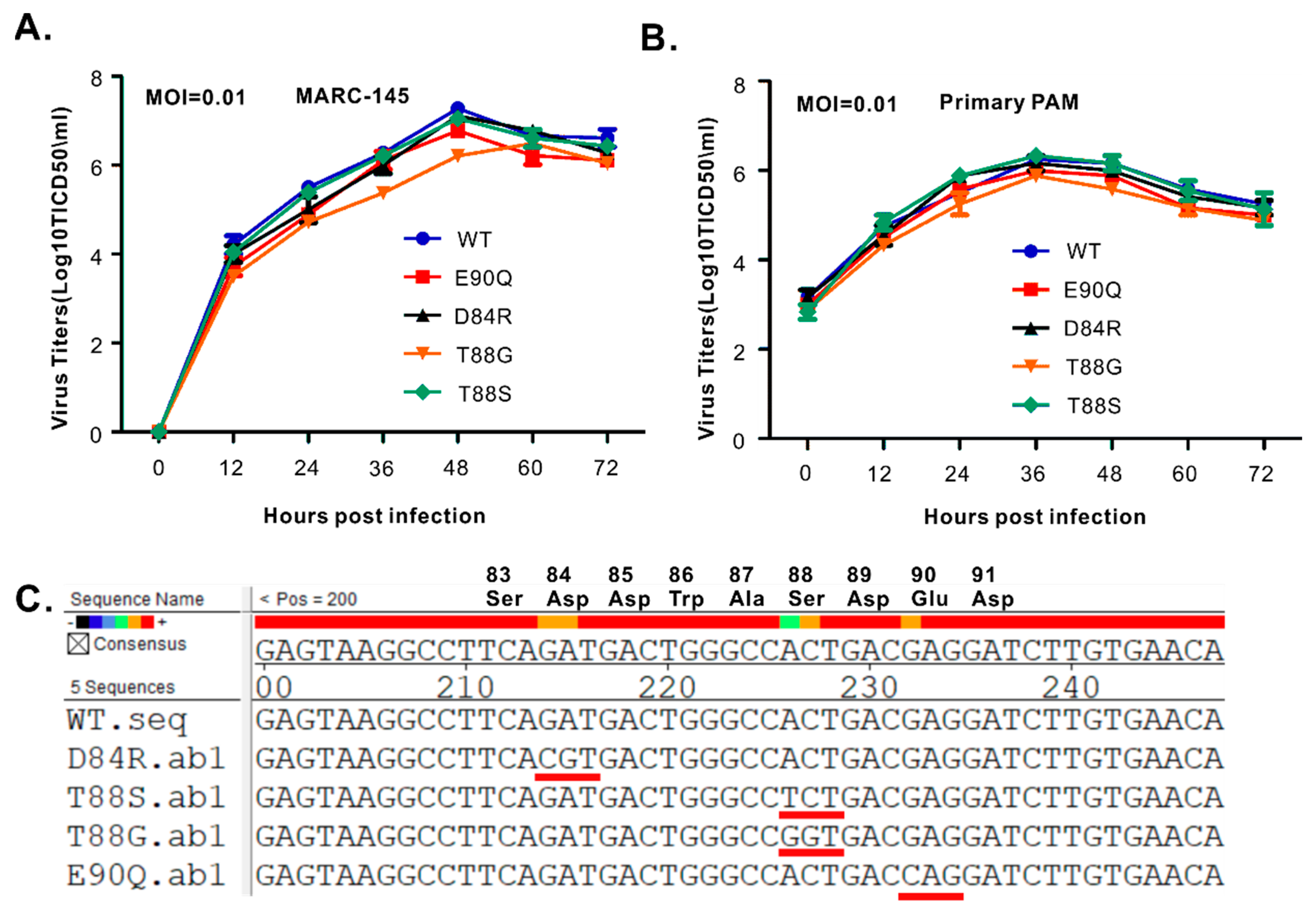
3.5. The PLP2 Cis-Cleavage Activity is Dispensable for HP-PRRSV Strain JXwn06 Viability in Cell Culture
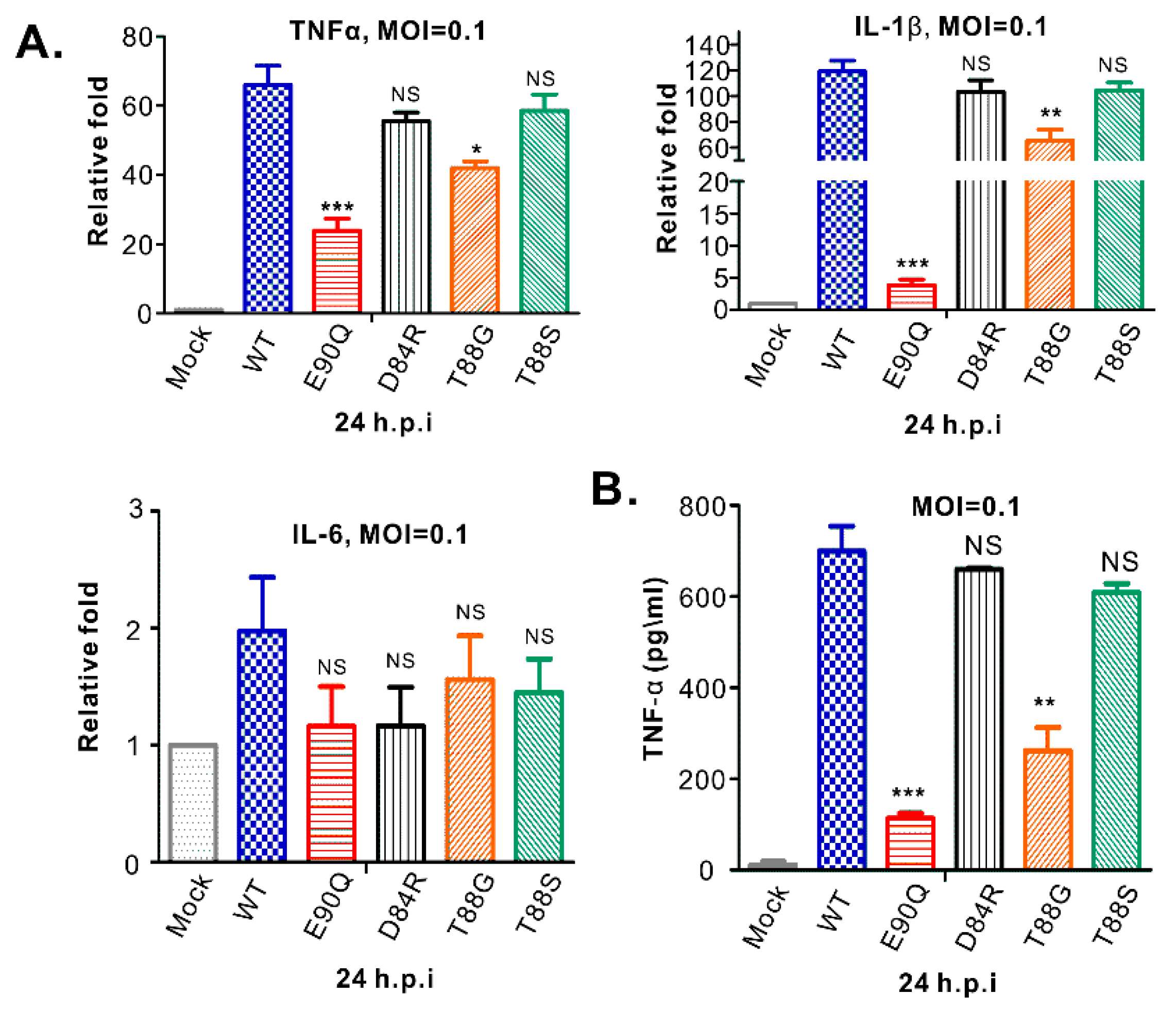
3.6. HP-PRRSV-Induced Production of TNF-α and IL-1β is Strongly Associated with nsp2 that is Independent of PLP2 DUB Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Insight into the Biochemical Properties of PRRSV PLP2
4.2. The Role of Cis-Cleavage and DUB Activities of PLP2 in PRRSV Infection
4.3. Insight into the Induction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production During PRRSV Infection
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komander, D.; Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Breaking the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulathu, Y.; Komander, D. Atypical ubiquitylation—The unexplored world of polyubiquitin beyond Lys48 and Lys63 linkages. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Skaug, B.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.J. A ubiquitin replacement strategy in human cells reveals distinct mechanisms of IKK activation by TNFalpha and IL-1beta. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, V.; Tobias, J.W.; Bachmair, A.; Marriott, D.; Ecker, D.J.; Gonda, D.K.; Varshavsky, A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science 1989, 243, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.L.; Wickliffe, K.E.; Dong, K.C.; Yu, C.; Bosanac, I.; Bustos, D.; Phu, L.; Kirkpatrick, D.S.; Hymowitz, S.G.; Rape, M.; et al. K11-linked polyubiquitination in cell cycle control revealed by a K11 linkage-specific antibody. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palombella, V.J.; Rando, O.J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Maniatis, T. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway Is Required for Processing the Nf-Kappa-B1 Precursor Protein and the Activation of Nf-Kappa-B. Cell 1994, 78, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.J. The role of ubiquitylation in immune defence and pathogen evasion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 12, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijman, S.M.; Luna-Vargas, M.P.; Velds, A.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Dirac, A.M.; Sixma, T.K.; Bernards, R. A genomic and functional inventory of deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell 2005, 123, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey-Elkin, B.A.; van Kasteren, P.B.; Snijder, E.J.; Kikkert, M.; Mark, B.L. Viral OTU deubiquitinases: A structural and functional comparison. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ratia, K.; Mesecar, A.D.; Wilkinson, K.D.; Baker, S.C. Proteolytic processing and deubiquitinating activity of papain-like proteases of human coronavirus NL63. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6007–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementz, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Banach, B.S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Ratia, K.; Baez-Santos, Y.M.; Wang, J.; Takayama, J.; Ghosh, A.K.; et al. Deubiquitinating and interferon antagonism activities of coronavirus papain-like proteases. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4619–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattenhorn, L.M.; Korbel, G.A.; Kessler, B.M.; Spooner, E.; Ploegh, H.L. A deubiquitinating enzyme encoded by HSV-1 belongs to a family of cysteine proteases that is conserved across the family Herpesviridae. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottcher, S.; Maresch, C.; Granzow, H.; Klupp, B.G.; Teifke, J.P.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Mutagenesis of the active-site cysteine in the ubiquitin-specific protease contained in large tegument protein pUL36 of pseudorabies virus impairs viral replication in vitro and neuroinvasion in vivo. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6009–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Li, P.; Sun, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, R.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; et al. The leader proteinase of foot-and-mouth disease virus negatively regulates the type I interferon pathway by acting as a viral deubiquitinase. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3758–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias-Staheli, N.; Giannakopoulos, N.V.; Kikkert, M.; Taylor, S.L.; Bridgen, A.; Paragas, J.; Richt, J.A.; Rowland, R.R.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Lenschow, D.J.; et al. Ovarian tumor domain-containing viral proteases evade ubiquitin- and ISG15-dependent innate immune responses. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kasteren, P.B.; Beugeling, C.; Ninaber, D.K.; Frias-Staheli, N.; van Boheemen, S.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Snijder, E.J.; Kikkert, M. Arterivirus and nairovirus ovarian tumor domain-containing Deubiquitinases target activated RIG-I to control innate immune signaling. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenon, M.; Camborde, L.; Cheminant, S.; Jupin, I. A viral deubiquitylating enzyme targets viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and affects viral infectivity. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kasteren, P.B.; Bailey-Elkin, B.A.; James, T.W.; Ninaber, D.K.; Beugeling, C.; Khajehpour, M.; Snijder, E.J.; Mark, B.L.; Kikkert, M. Deubiquitinase function of arterivirus papain-like protease 2 suppresses the innate immune response in infected host cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E838–E847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lawson, S.R.; Fang, Y. The cysteine protease domain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 2 possesses deubiquitinating and interferon antagonism functions. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7832–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Ransburgh, R.; Snijder, E.J.; Fang, Y. Nonstructural protein 2 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus inhibits the antiviral function of interferon-stimulated gene 15. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimianski, J.V.; Beldon, B.S.; Daczkowski, C.M.; Goodwin, O.Y.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Bergeron, E.; Pegan, S.D. Probing the impact of nairovirus genomic diversity on viral ovarian tumor domain protease (vOTU) structure and deubiquitinase activity. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholte, F.E.M.; Zivcec, M.; Dzimianski, J.V.; Deaton, M.K.; Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Nichol, S.T.; Pegan, S.D.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bergeron, E. Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Suppresses Innate Immune Responses via a Ubiquitin and ISG15 Specific Protease. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randow, F.; Lehner, P.J. Viral avoidance and exploitation of the ubiquitin system. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Nidovirales: A new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Lauck, M.; Bailey, A.L.; Shchetinin, A.M.; Vishnevskaya, T.V.; Bao, Y.; Ng, T.F.; LeBreton, M.; Schneider, B.S.; Gillis, A.; et al. Reorganization and expansion of the nidoviral family Arteriviridae. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.E.; Benfield, D.A.; Christianson, W.T.; Harris, L.; Hennings, J.C.; Shaw, D.P.; Goyal, S.M.; McCullough, S.; Morrison, R.B.; Joo, H.S.; et al. Isolation of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) in North America and experimental reproduction of the disease in gnotobiotic pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992, 4, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfield, D.A.; Nelson, E.; Collins, J.E.; Harris, L.; Goyal, S.M.; Robison, D.; Christianson, W.T.; Morrison, R.B.; Gorcyca, D.; Chladek, D. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992, 4, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, W.T.; Collins, J.E.; Benfield, D.A.; Harris, L.; Gorcyca, D.E.; Chladek, D.W.; Morrison, R.B.; Joo, H.S. Experimental reproduction of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome in pregnant sows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 53, 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, K.; Yu, X.; Zhao, T.; Feng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, D.; Tian, X.; et al. Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: Unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.L.; Zeng, J.W.; Yin, S.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zheng, L.Y.; Guo, X.; Ge, X.N.; Yang, H.C. The 30-Amino-Acid Deletion in the Nsp2 of Highly Pathogenic Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Emerging in China Is Not Related to Its Virulence. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5156–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Faaberg, K.S. Identification of nonessential regions of the nsp2 replicase protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain VR-2332 for replication in cell culture. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9878–9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Faaberg, K.S. Complete genome analysis of RFLP 184 isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2006, 122, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Rutherford, M.S.; Faaberg, K.S. The porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nsp2 cysteine protease domain possesses both trans- and cis-cleavage activities. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9449–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 2 contributes to NF-kappaB activation. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P. Effect of amino acids residues 323-433 and 628-747 in Nsp2 of representative porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strains on inflammatory response in vitro. Virus Res. 2015, 208, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Boon, J.A.; Faaberg, K.S.; Meulenberg, J.J.; Wassenaar, A.L.; Plagemann, P.G.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Snijder, E.J. Processing and evolution of the N-terminal region of the arterivirus replicase ORF1a protein: Identification of two papainlike cysteine proteases. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4500–4505. [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty, W.G.; Semler, B.L. Expression of virus-encoded proteinases: Functional and structural similarities with cellular enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 781–822. [Google Scholar]
- Snijder, E.J.; Wassenaar, A.L.; Spaan, W.J. Proteolytic processing of the replicase ORF1a protein of equine arteritis virus. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5755–5764. [Google Scholar]
- Snijder, E.J.; Wassenaar, A.L.; Spaan, W.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. The arterivirus Nsp2 protease. An unusual cysteine protease with primary structure similarities to both papain-like and chymotrypsin-like proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16671–16676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, M.K.; Spear, A.; Faaberg, K.S.; Pegan, S.D. The vOTU domain of highly-pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus displays a differential substrate preference. Virology 2014, 454, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, S.M.; Daczkowski, C.M.; Faaberg, K.S.; Pegan, S.D. Insights into the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Viral Ovarian Tumor Domain Protease Specificity for Ubiquitin and Interferon Stimulated Gene Product 15. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, X.; Ge, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H. Changes in the cellular proteins of pulmonary alveolar macrophage infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by proteomics analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Miao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Dynamic Gene Expression Profiles in Porcine Alveolar Macrophages in Response to the Chinese Highly Pathogenic Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1538127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; Yang, H. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nsp1β and nsp11 antagonize the antiviral activity of cholesterol-25-hydroxylase via lysosomal degradation. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.U.; Islam, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Tholen, E.; Tesfaye, D.; Looft, C.; Schellander, K. Evaluation of suitable reference genes for gene expression studies in porcine alveolar macrophages in response to LPS and LTA. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Pathogenesis and control of the Chinese highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 209, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, H. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome in China. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, W.H. Regulation and evasion of antiviral immune responses by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2015, 202, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Laguna, J.; Salguero, F.J.; Pallares, F.J.; Carrasco, L. Immunopathogenesis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome in the respiratory tract of pigs. Vet. J. 2013, 195, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.M.; Cha, S.H.; Chittick, W.; Lawson, S.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Nelson, E.A.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Yoon, K.J.; Evans, R.; Rowland, R.R.; et al. Immune response against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus during acute and chronic infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascon-Castelo, E.; Burgara-Estrella, A.; Mateu, E.; Hernandez, J. Immunological features of the non-structural proteins of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses 2015, 7, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Kim, C.; Calvert, J.G.; Yoo, D. Interplay between interferon-mediated innate immunity and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 424–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Du, Y.; Kim, O.; Liu, H.C. Modulation of host cell responses and evasion strategies for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Both Nsp1beta and Nsp11 are responsible for differential TNF-alpha production induced by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strains with different pathogenicity in vitro. Virus Res. 2015, 201, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.K.; Yu, Z.B.; Xu, A.T.; Tang, J.; Feng, W.H. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 4 antagonizes beta interferon expression by targeting the NF-kappaB essential modulator. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10934–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongyanin, P.; Buranapraditkul, S.; Yoo, D.; Thanawongnuwech, R.; Roth, J.A.; Suradhat, S. Role of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein in induction of interleukin-10 and regulatory T-lymphocytes (Treg). J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hou, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wen, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhong, F. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus activates inflammasomes of porcine alveolar macrophages via its small envelope protein E. Virology 2013, 442, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Holzer, B.; Bridgen, A.; McMullan, G.; Quinn, D.G.; Baron, M.D. Dugbe virus ovarian tumour domain interferes with ubiquitin/ISG15-regulated innate immune cell signalling. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PLP2 Mutants | DUB Activity | Cis-Cleavage | Trans-Cleavage | Viral Viability | Cytokine Production |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D84R | Active | √ | √ | viable | No effect |
| D84N | Active | √ | √ | viable | ND |
| D85R | Largely blocked | - | √ | nonviable | |
| D85N | Largely blocked | - | √ | nonviable | |
| T88R | Largely blocked | - | √ | nonviable | |
| T88S | Active | √ | √ | viable | No effect |
| T88G | Partially blocked | - | √ | viable | TNF-α, IL-1β  |
| E90R | Slightly blocked | √ | √ | nonviable | |
| E90Q | Active | √ | √ | viable | TNF-α,IL-1β  |
| D91R | Largely blocked | - | √ | nonviable | |
| D91N | Active | √ | √ | nonviable |
 : downregulation.
: downregulation.© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Ge, X.; Kong, C.; Liu, T.; Liu, A.; Gao, P.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; et al. Characterizing the PRRSV nsp2 Deubiquitinase Reveals Dispensability of Cis-Activity for Replication and a Link of nsp2 to Inflammation Induction. Viruses 2019, 11, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100896
Zhou S, Ge X, Kong C, Liu T, Liu A, Gao P, Song J, Zhou L, Guo X, Han J, et al. Characterizing the PRRSV nsp2 Deubiquitinase Reveals Dispensability of Cis-Activity for Replication and a Link of nsp2 to Inflammation Induction. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100896
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shaochuan, Xinna Ge, Can Kong, Teng Liu, Aijing Liu, Peng Gao, Jiangwei Song, Lei Zhou, Xin Guo, Jun Han, and et al. 2019. "Characterizing the PRRSV nsp2 Deubiquitinase Reveals Dispensability of Cis-Activity for Replication and a Link of nsp2 to Inflammation Induction" Viruses 11, no. 10: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100896
APA StyleZhou, S., Ge, X., Kong, C., Liu, T., Liu, A., Gao, P., Song, J., Zhou, L., Guo, X., Han, J., & Yang, H. (2019). Characterizing the PRRSV nsp2 Deubiquitinase Reveals Dispensability of Cis-Activity for Replication and a Link of nsp2 to Inflammation Induction. Viruses, 11(10), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100896






