The Canine Morbillivirus Strain Associated with An Epizootic in Caspian Seals Provides New Insights into the Evolutionary History of this Virus
Abstract
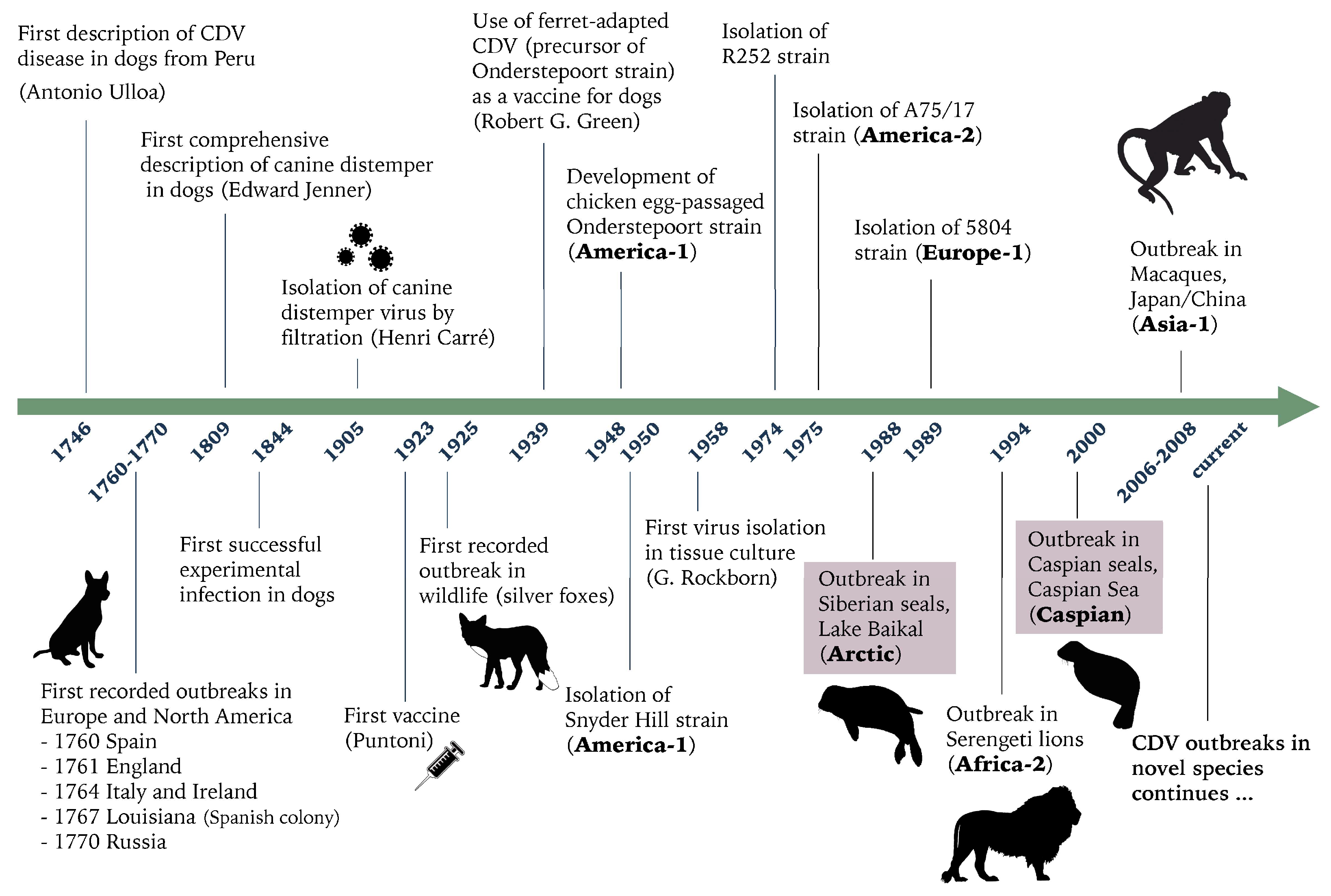
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Generation of Full-Length Genome
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
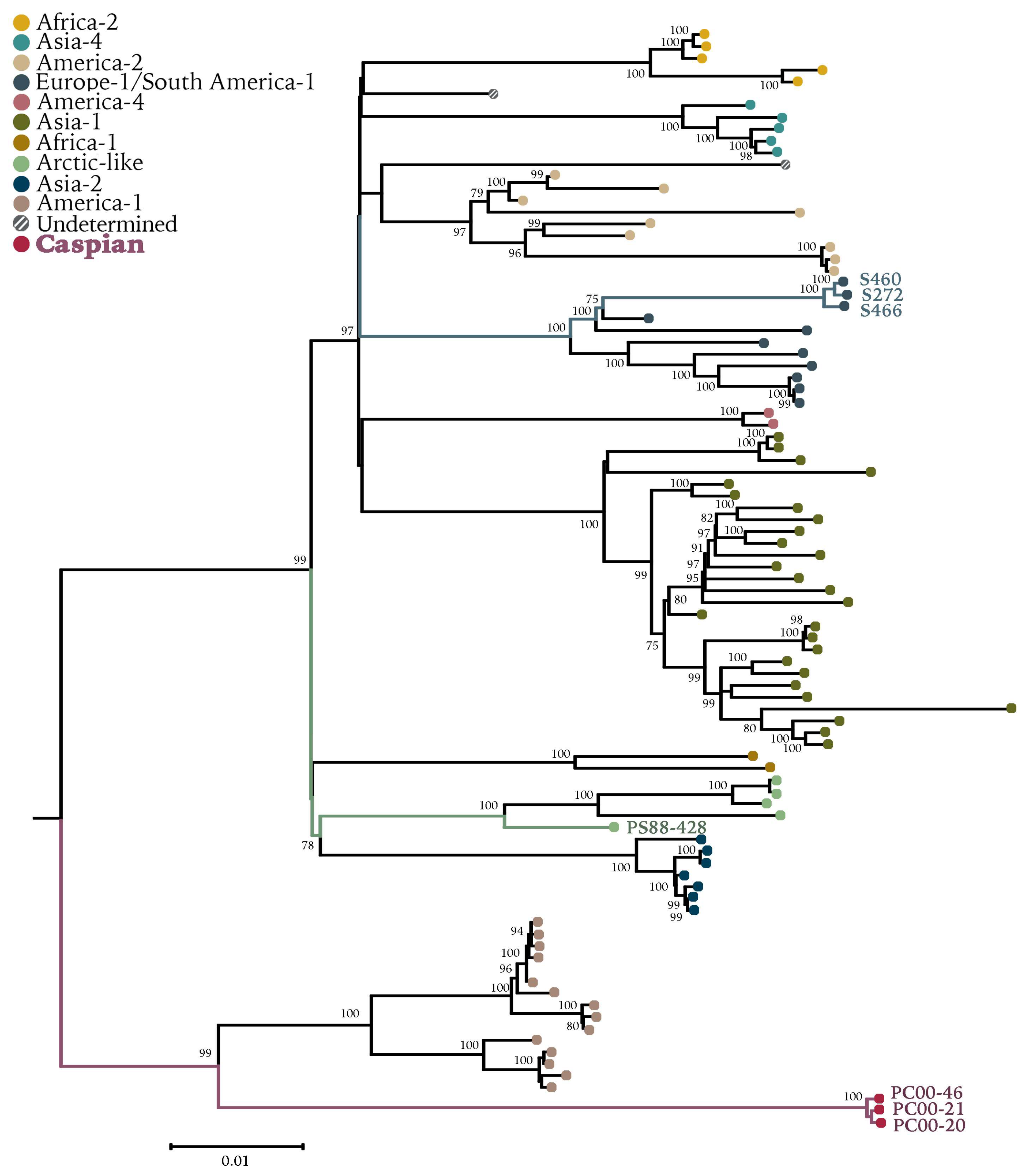
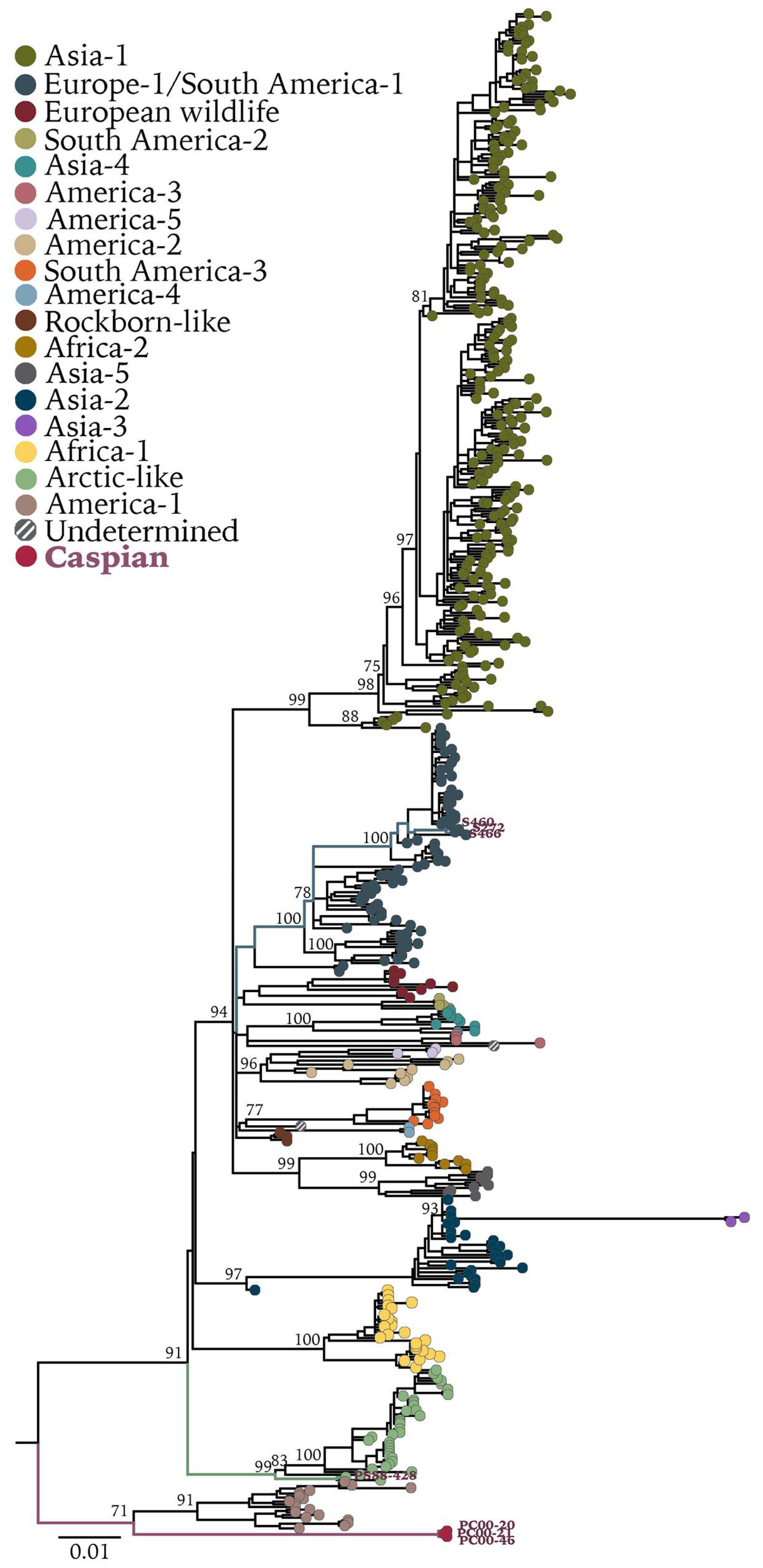
3. Results
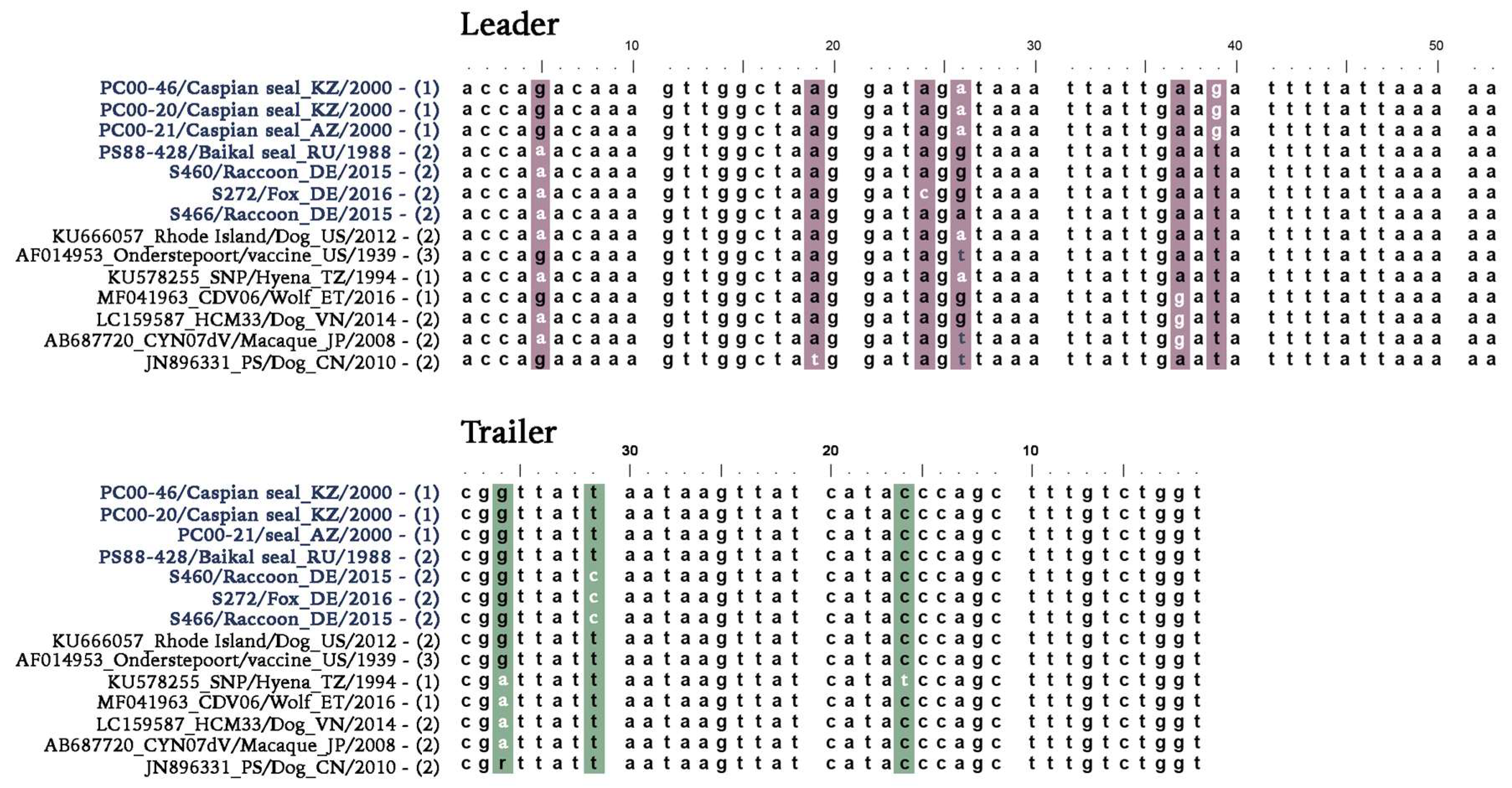
3.1. Identification of a Novel CDV Clade in Caspian Seals
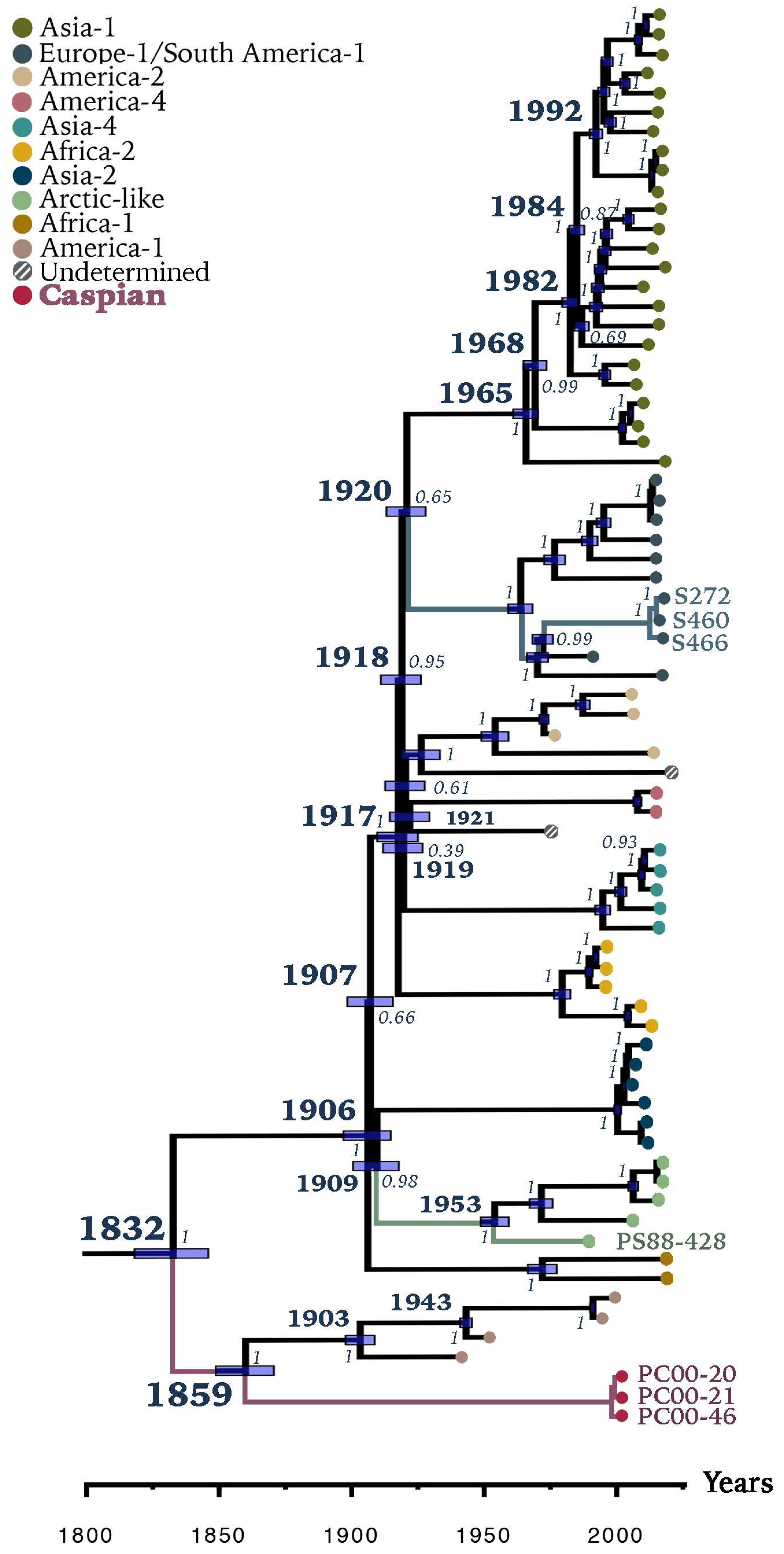
3.2. Divergence Dates between CDV Clades
3.3. Evolutionary Rate of CDV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Diversity of susceptible hosts in canine distemper virus infection: A systematic review and data synthesis. BMC Veter Res. 2016, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Li, A.; Ye, H.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, L. Natural infection with canine distemper virus in hand-feeding Rhesus monkeys in China. Veter Microbiol. 2010, 141, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liao, G.; Hu, R. Canine Distemper Outbreak in Rhesus Monkeys, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Nagata, N.; Ami, Y.; Seki, F.; Suzaki, Y.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Suzuki, T.; Fukushi, S.; Mizutani, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. Lethal canine distemper virus outbreak in cynomolgus monkeys in Japan in 2008. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, M.J.; Reggiardo, C.; Summers, B.A.; Pearce-Kelling, S.; Maré, C.J.; Noon, T.H.; Reed, R.E.; Shively, J.N.; Orvell, C. Canine distemper virus infection and encephalitis in javelinas (collared peccaries). Arch. Virol. 1991, 119, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Origgi, F.C.; Sattler, U.; Pilo, P.; Waldvogel, A.S. Fatal Combined Infection With Canine Distemper Virus and Orthopoxvirus in a Group of Asian Marmots (Marmota caudata). Veter Pathol. 2013, 50, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, M.; Darold, G.M.; Amude, A.M.; Headley, S.A.; Sonne, L.; Yamauchi, K.C.I.; Boabaid, F.M.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Canine distemper virus active infection in order Pilosa, family Myrmecophagidae, species Tamandua tetradactyla. Veter Microbiol. 2018, 220, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, G.-M.; Ho, C.-H.; Chiang, M.-J.; Sanno-Duanda, B.; Chung, C.-S.; Lin, M.-Y.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C.; Liao, P.-C.; et al. Phylodynamic analysis of the canine distemper virus hemagglutinin gene. BMC Veter Res. 2015, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, M.C.; Wilkes, R.P. Sequencing of emerging canine distemper virus strain reveals new distinct genetic lineage in the United States associated with disease in wildlife and domestic canine populations. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.M.; Gabriel, M.; Terio, K.A.; Dubovi, E.J.; VanWormer, E.; Sweitzer, R.; Barret, R.; Thompson, C.; Purcell, K.; Munson, L. Canine distemper in an isolated population of fishers (Martes pennanti) from California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, E.; Newell, T.K.; Dyer, N.; Wilkes, R.P. Phylogenetic analysis of the wild-type strains of canine distemper virus circulating in the United States. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzera, Y.; Calderón, M.G.; Sarute, N.; Guasco, S.; Cardeillac, A.; Bonilla, B.; Hernández, M.; Francia, L.; Bedó, G.; La Torre, J.; et al. Evidence of two co-circulating genetic lineages of canine distemper virus in South America. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinal, M.A.; Díaz, F.J.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Phylogenetic evidence of a new canine distemper virus lineage among domestic dogs in Colombia, South America. Veter Microbiol. 2014, 172, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewbang, C.; Radtanakatikanon, A.; Puenpa, J.; Poovorawan, Y.; Techangamsuwan, S. Genetic and evolutionary analysis of a new Asia-4 lineage and naturally recombinant canine distemper virus strains from Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, M.; Rajak, K.K.; Chakravarti, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.; Chander, V.; Mathesh, K.; Chandramohan, S.; Sharma, A.K.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of haemagglutinin gene deciphering a new genetically distinct lineage of canine distemper virus circulating among domestic dogs in India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-J.; Yan, X.-J.; Chai, X.-L.; Martella, V.; Luo, G.-L.; Zhang, H.-L.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.-X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the haemagglutinin gene of canine distemper virus strains detected from breeding foxes, raccoon dogs and minks in China. Veter Microbiol. 2010, 140, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Miyashita, N.; Yoshida, E.; Gemma, T.; Shin, Y.S.; Mori, T.; Hirayama, N.; Kai, C.; Mikami, T. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the haemagglutinin (H) proteins of field isolates of canine distemper virus from naturally infected dogs. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.D.R.; Johnson, G.C.; Kleiboeker, S.B. Phylogenetic characterization of canine distemper viruses detected in naturally infected dogs in North America. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5009–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarute, N.; Calderón, M.G.; Pérez, R.; La Torre, J.; Hernández, M.; Francia, L.; Panzera, Y. The fusion protein signal-peptide-coding region of canine distemper virus: A useful tool for phylogenetic reconstruction and lineage identification. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, M.; Rennick, L.J.; Nambulli, S.; De Swart, R.L.; Paul Duprex, W. Using the ferret model to study morbillivirus entry, spread, transmission and cross-species infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, K.; de Vries, R.D.; Mesman, A.W.; McQuaid, S.; van Amerongen, G.; Yüksel, S.; Ludlow, M.; Rennick, L.J.; Kuiken, T.; Rima, B.K.; et al. Early target cells of measles virus after aerosol infection of non-human primates. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Messling, V.; Milosevic, D.; Cattaneo, R. Tropism illuminated: Lymphocyte-based pathways blazed by lethal morbillivirus through the host immune system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14216–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsuo, H.; Ono, N.; Yanagi, Y. Morbilliviruses use signaling lymphocyte activation molecules (CD150) as cellular receptors. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Messling, V.; Springfeld, C.; Devaux, P.; Cattaneo, R. A ferret model of canine distemper virus virulence and immunosuppression. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12579–12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyce, R.S.; Delpeut, S.; Richardson, C.D. Dog nectin-4 is an epithelial cell receptor for canine distemper virus that facilitates virus entry and syncytia formation. Virology 2013, 436, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawatsky, B.; Wong, X.-X.; Hinkelmann, S.; Cattaneo, R.; von Messling, V. Canine distemper virus epithelial cell infection is required for clinical disease but not for immunosuppression. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3658–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, B.A.; Greisen, H.A.; Appel, M.J. Canine distemper encephalomyelitis: Variation with virus strain. J. Comp. Pathol. 1984, 94, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axthelm, M.K.; Krakowka, S. Experimental old dog encephalitis (ODE) in a gnotobiotic dog. Veter Pathol. 1998, 35, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachev, M.A.; Kumarev, V.P.; Mamaev, L.V.; Zoryn, V.L.; Baranova, L.; Denikina, N.N.; Belikov, S.I.; Petrov, E.A.; Kolesnik, V.S.; Kolesnik, R.S.; et al. Distemper virus in Baikal seals. Nature 1989, 338, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, M.A.; Kennedy, S.; Wilson, S.; Eybatov, T.; Barrett, T. Canine distemper virus in a Caspian seal. Veter Rec. 1998, 143, 662–664. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, S.; Kuiken, T.; Jepson, P.; Deaville, R.; Forsyth, M.; Barrett, T.; van de Bildt, M.; Osterhaus, A.; Eybatov, T.; Duck, C.; et al. Mass Die-Off of Caspian Seals Caused by Canine Distemper Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.J.; Dmitrieva, L. Pusa Caspica. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/41669/0 (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Mamaev, L.V.; Denikina, N.N.; Belikov, S.I.; Volchkov, V.E.; Visser, I.K.; Fleming, M.; Kai, C.; Harder, T.C.; Liess, B.; Osterhaus, A.D. Characterisation of morbilliviruses isolated from Lake Baikal seals (Phoca sibirica). Veter Microbiol. 1995, 44, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, J.B.; Brown, C.C.; Poet, S.; Lipscomb, T.P.; Saliki, J.; Frasca, S. Retrospective differentiation of canine distemper virus and phocine distemper virus in phocids. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, W.K.; Kruppa, J.; Habierski, A.; van de Bildt, M.; Mazzariol, S.; Di Guardo, G.; Siebert, U.; Kuiken, T.; Jung, K.; Osterhaus, A.; et al. Evolutionary evidence for multi-host transmission of cetacean morbillivirus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.; Bouckaert, R. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis with BEAST; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, T.; Ose, T.; Kubota, M.; Maita, N.; Kamishikiryo, J.; Maenaka, K.; Yanagi, Y. Structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin bound to its cellular receptor SLAM. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.W.-H.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F. Structure of measles virus hemagglutinin bound to its epithelial receptor nectin-4. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieux, A.; Balloux, F. Inferences from tip-calibrated phylogenies: A review and a practical guide. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámiz, C.; Martella, V.; Ulloa, R.; Fajardo, R.; Quijano-Hernandéz, I.; Martínez, S.; Martella, V. Identification of a new genotype of canine distemper virus circulating in America. Veter Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudas, G.; Bedford, T. The ability of single genes vs full genomes to resolve time and space in outbreak analysis. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Homologous recombination is a force in the evolution of canine distemper virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fontoura Budaszewski, R.; Streck, A.F.; Nunes Weber, M.; Maboni Siqueira, F.; Muniz Guedes, R.L.; Wageck Canal, C. Influence of vaccine strains on the evolution of canine distemper virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancou, J. Dog distemper: Imported into Europe from South America? Hist. Med. Veter 2004, 29, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, H. Canine Distemper: Its Complications, Sequelae, and Treatment; Baillière, Tindall & Cox: London, UK, 1922. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.G. Distemper in the silver fox (Culpes vulpes). Exp. Biol. Med. 1925, 22, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntoni, V. Saggio di vaccinazione anticimurrosa preventiva eseguita per mezzo del virus specifico. Ann. Igiene 1923, 33, 553. [Google Scholar]
- Bresalier, M.; Worboys, M. ‘Saving the lives of our dogs’: The development of canine distemper vaccine in interwar Britain. Br. J. Hist. Sci. 2014, 47, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek-Kommonen, C.; Sihvonen, L.; Pekkanen, K.; Rikula, U.; Nuotio, L. Outbreak of canine distemper in vaccinated dogs in Finland. Veter Rec. 1997, 141, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Cirone, F.; Elia, G.; Lorusso, E.; Decaro, N.; Campolo, M.; Desario, C.; Lucente, M.S.; Bellacicco, A.L.; Blixenkrone-Møller, M.; et al. Heterogeneity within the hemagglutinin genes of canine distemper virus (CDV) strains detected in Italy. Veter Microbiol. 2006, 116, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wilker, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gao, Y.; Xia, X. Fatal canine distemper virus infection of giant pandas in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulikhan, N.S.; Gilbert, M.; Blidchenko, E.Y.; Naidenko, S.V.; Ivanchuk, G.V.; Gorpenchenko, T.Y.; Alshinetskiy, M.V.; Shevtsova, E.I.; Goodrich, J.M.; Lewis, J.C.M.; et al. Canine Distemper Virus in a Wild Far Eastern Leopard Panthera pardus orientalis. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 54, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, G.; Jensen, T.D.; Gottschalck, E.; Arctander, P.; Appel, M.J.G.; Buckland, R.; Blixenkrone-Møller, M. Genetic diversity of the attachment (H) protein gene of current field isolates of canine distemper virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, S.; Allison, R.W.; Johnston, L.; Murray, B.L.; Holland, S.; Meinkoth, J.; Johnson, B. Canine Distemper Virus Strains Circulating among North American Dogs. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namroodi, S.; Rostami, A.; Majidzadeh-Ardebili, K.; Ghalyanchi Langroudi, A.; Morovvati, A. Detection of Arctic and European cluster of canine distemper virus in north and center of Iran. Vet. Res. Forum 2015, 6, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sabatino, D.; Di Francesco, G.; Zaccaria, G.; Malatesta, D.; Brugnola, L.; Marcacci, M.; Portanti, O.; De Massis, F.; Savini, G.; Teodori, L.; et al. Lethal distemper in badgers (Meles meles) following epidemic in dogs and wolves. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 46, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butina, T.V.; Denikina, N.N.; Belikov, S.I. Canine distemper virus diversity in Lake Baikal seal (Phoca sibirica) population. Veter Microbiol. 2010, 144, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, Y.; Sarute, N.; Iraola, G.; Hernández, M.; Pérez, R. Molecular phylogeography of canine distemper virus: Geographic origin and global spreading. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 92, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.W.; Bjørnstad, O.N.; Holmes, E.C. The Evolutionary and Epidemiological Dynamics of the Paramyxoviridae. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 66, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque-Valencia, J.; Sarute, N.; Olarte-Castillo, X.A.; Ruíz-Sáenz, J. Evolution and Interspecies Transmission of Canine Distemper Virus—An Outlook of the Diverse Evolutionary Landscapes of a Multi-Host Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Clade | Strain Variant | Stranding Year | Location | Host | Sample Material | Coverage | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caspian | PC00-46 | 2000 | Kazakhstan | Caspian seal | Kidney | 393x | MN267064 |
| Caspian | PC00-20 | 2000 | Kazakhstan | Caspian seal | Kidney | 547x | -- |
| Caspian | PC00-20 | 2000 | Kazakhstan | Caspian seal | Lung | 9149x | MN267065 |
| Caspian | PC00-21 | 2000 | Azerbaijan | Caspian seal | Lung | 33184x | MN267066 |
| Caspian | PC00-21 | 2000 | Azerbaijan | Caspian seal | Kidney | 0.3x | -- |
| Arctic | PS88-428 | 1988 | Russia | Baikal seal | Lung | 2572x | MN267063 |
| Arctic | PS88-428 | 1988 | Russia | Baikal seal | Spleen | 247x | -- |
| Europe-1 | S466 | 2015 | Germany | Raccoon | Lung | 19505x | MN267062 |
| Europe-1 | S460 | 2015 | Germany | Raccoon | Lung | 9922x | MN267060 |
| Europe-1 | S272 | 2016 | Germany | Fox | Tonsils | 157x | MN267061 |
| Protein | PC00-46/20/21 (Caspian seal) | PS88-428 (Baikal seal) | S460/S466/S272 (Europe-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleocapsid | N65S | A140V | D151N | |
| D135N | P/L432S | |||
| S439F | T/A/S434V | |||
| G458E | R438S | |||
| Y459H | L/F/P/V456S | |||
| Y/F/H471P | V463A | |||
| E/G467K | ||||
| Phosphoprotein | I29V | P223S | H/Y75D | E54D |
| N/D46S | S238L | D206E | Q102H | |
| T/I/A48G | S254P | G/S418N | T209I | |
| M/V/K51I | V272A | D443N | ||
| K/R/E68T | A458P | |||
| N/S138D | ||||
| Matrix | No unique changes | No unique changes | S202L | |
| Fusion | K/N/E/R3G | R/K73G | V/A/T32I | I/T/S/V30A |
| E/K7T | S/L74P | R/M/G65I | I/T33V/A | |
| Q/R22H | V/I/F87T | S/T91P | V/I/D57T | |
| V/A/T32I | V/I94A | I/T/V110F | A/G85C | |
| Q/H/R/L43K | I/L124F | I515M | ||
| H/R/Y47D | P161S | N517S | ||
| T/I/A52K | K211R | P613L | ||
| C/R67H | P/L212S | |||
| Q69H | D/A644N | |||
| A/T70I | ||||
| Hemagglutinin | P35S | T360I | A191V | S311P |
| K/R161N | E379K | R/K197E | D/N313S | |
| L175I | S394A | D571G | V334M | |
| G/R177E | I/T/V417A | M362V | ||
| G/D/A178S | E/D441K | M/V389I | ||
| V/I/S198G | S/P447F | Q516R | ||
| P/S200L | G488R | T590I | ||
| I210V | S497P | R/C/H/S597Y | ||
| D/N237Y | R/I519K | |||
| T/S245A | E/D560N | |||
| T268I | D/N584T | |||
| Y/S305H | K/N606S | |||
| N/S/D/R309K | ||||
| Large | A32S | K1229R | N319T | V6I |
| N/S37R | N/H1391I | R699K | C/R65Y | |
| T43A | S/I/V1392T | V/I975M | V85M | |
| R47C | V1445I | V/A256G | ||
| I66V | Q/R1701S | D318V | ||
| S/A/P252T | S/P1702L | Y400F | ||
| M/I385L | S1995T | T/A/S/I622G | ||
| R/C/Y/S/W611H | S2023G | D717N | ||
| K/R615Q | N2141H | I917V | ||
| L1179I | F1718L | |||
| N/T1776K | ||||
| I2024M | ||||
| L2175V | ||||
| Total | 80 changes | 15 changes | 39 changes | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, W.K.; Peters, M.; Kydyrmanov, A.; van de Bildt, M.W.G.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A.; Ludlow, M. The Canine Morbillivirus Strain Associated with An Epizootic in Caspian Seals Provides New Insights into the Evolutionary History of this Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100894
Jo WK, Peters M, Kydyrmanov A, van de Bildt MWG, Kuiken T, Osterhaus A, Ludlow M. The Canine Morbillivirus Strain Associated with An Epizootic in Caspian Seals Provides New Insights into the Evolutionary History of this Virus. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100894
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Wendy K., Martin Peters, Aidyn Kydyrmanov, Marco W. G. van de Bildt, Thijs Kuiken, Albert Osterhaus, and Martin Ludlow. 2019. "The Canine Morbillivirus Strain Associated with An Epizootic in Caspian Seals Provides New Insights into the Evolutionary History of this Virus" Viruses 11, no. 10: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100894
APA StyleJo, W. K., Peters, M., Kydyrmanov, A., van de Bildt, M. W. G., Kuiken, T., Osterhaus, A., & Ludlow, M. (2019). The Canine Morbillivirus Strain Associated with An Epizootic in Caspian Seals Provides New Insights into the Evolutionary History of this Virus. Viruses, 11(10), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100894





