Caerin1.1 Suppresses the Growth of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro via Direct Binding to the Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses and Antimicrobial Peptides
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. Plaque Forming Assay
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assays (IFA)
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
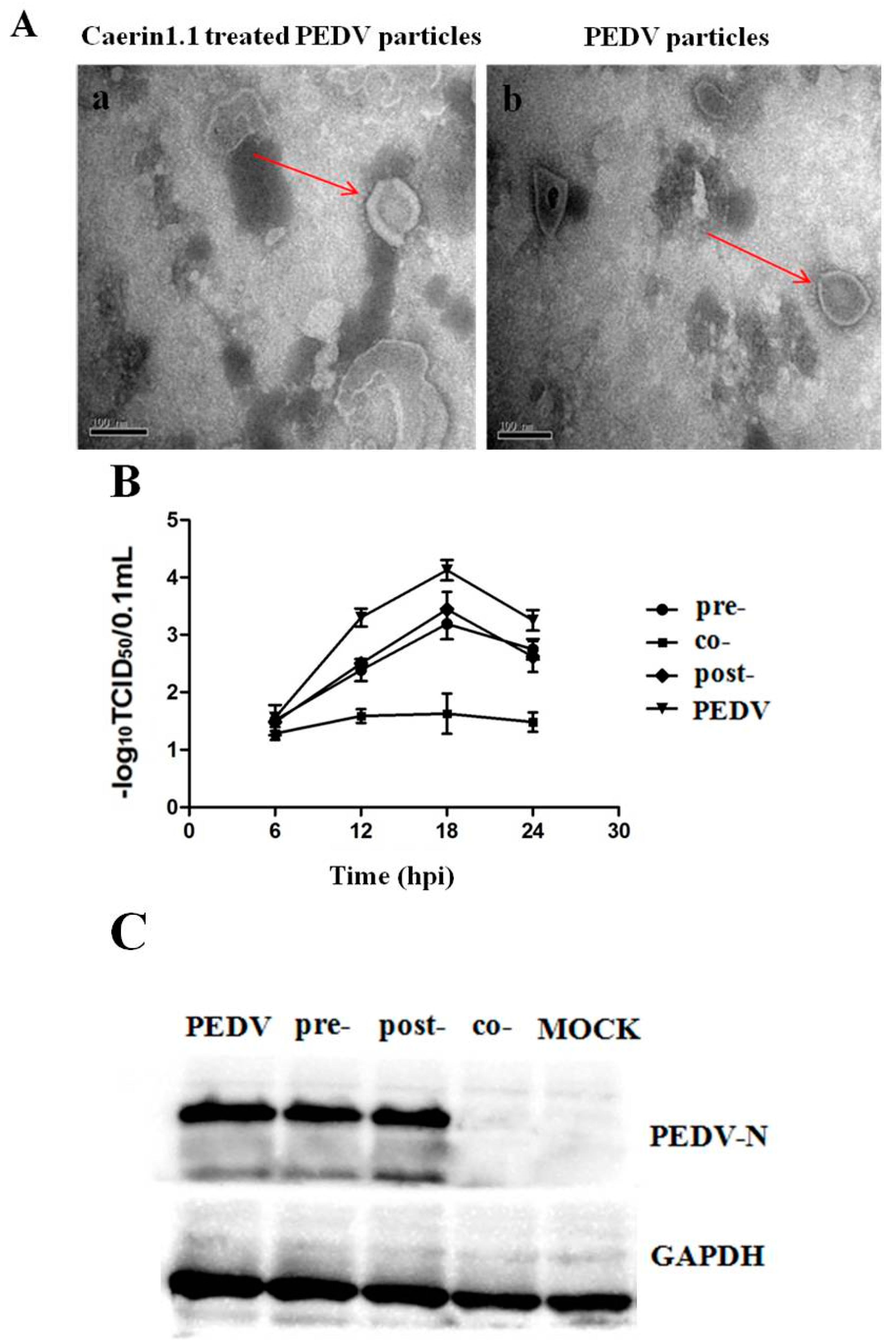
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy Observation
2.7. Assays of Antiviral Activity
2.7.1. Viral Inhibition Assays
2.7.2. Infectious Virus Yield Reduction Assay
2.7.3. Time of Addition Assay by TCID50
2.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
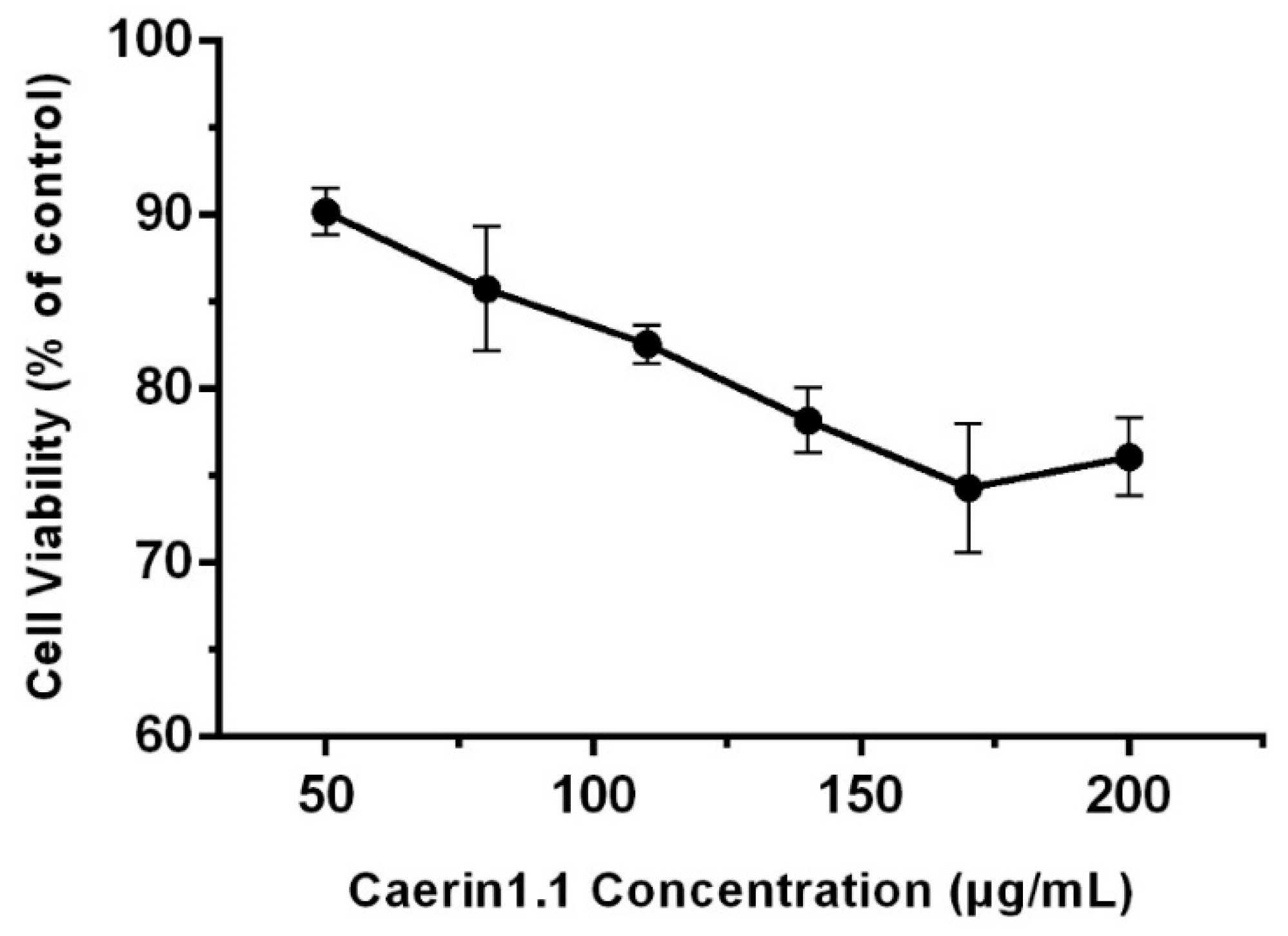
3.1. Cytotoxicity of Caerin1.1
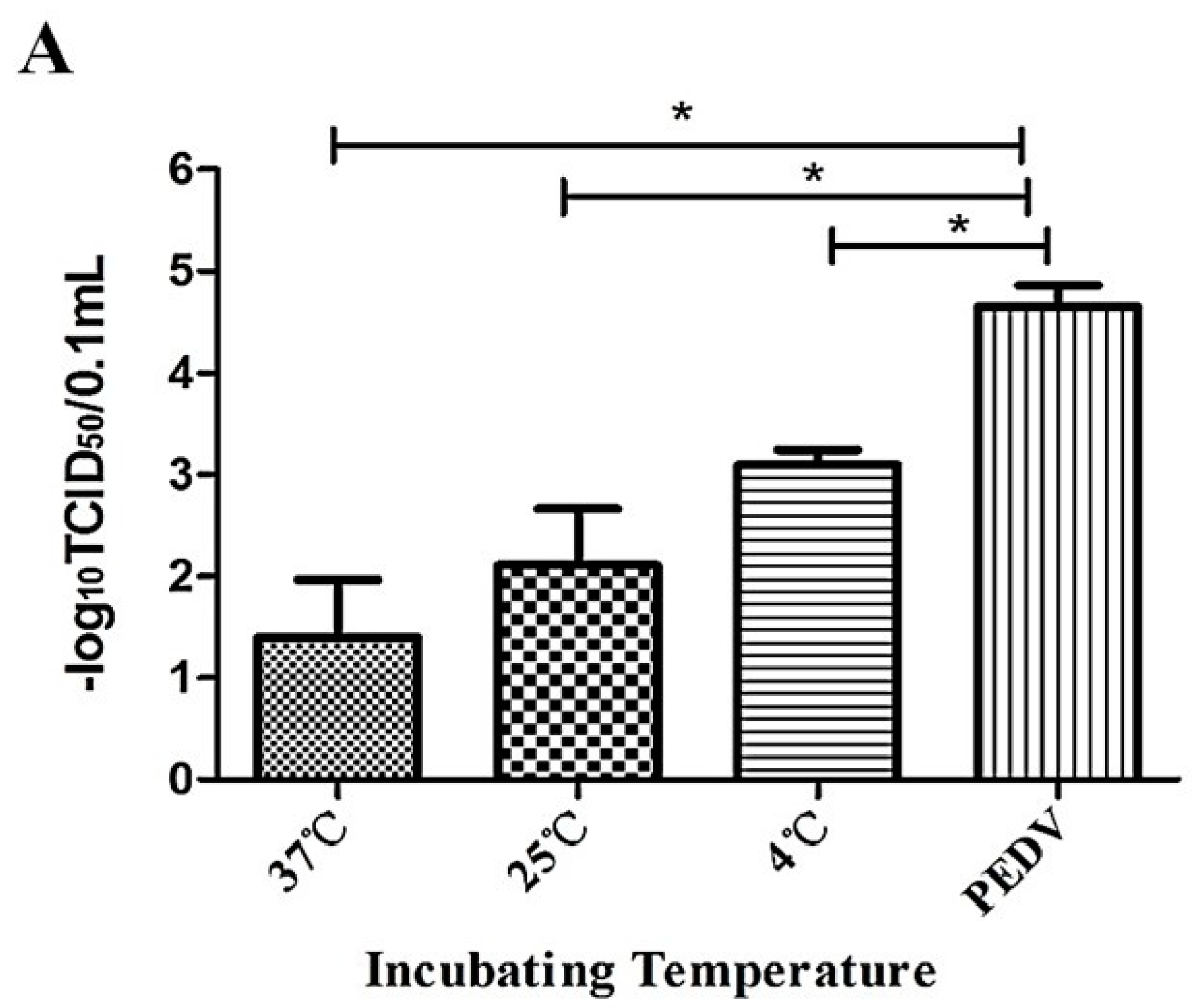
3.2. Optimization of Suitable Incubation Condition of PEDV and Caerin1.1
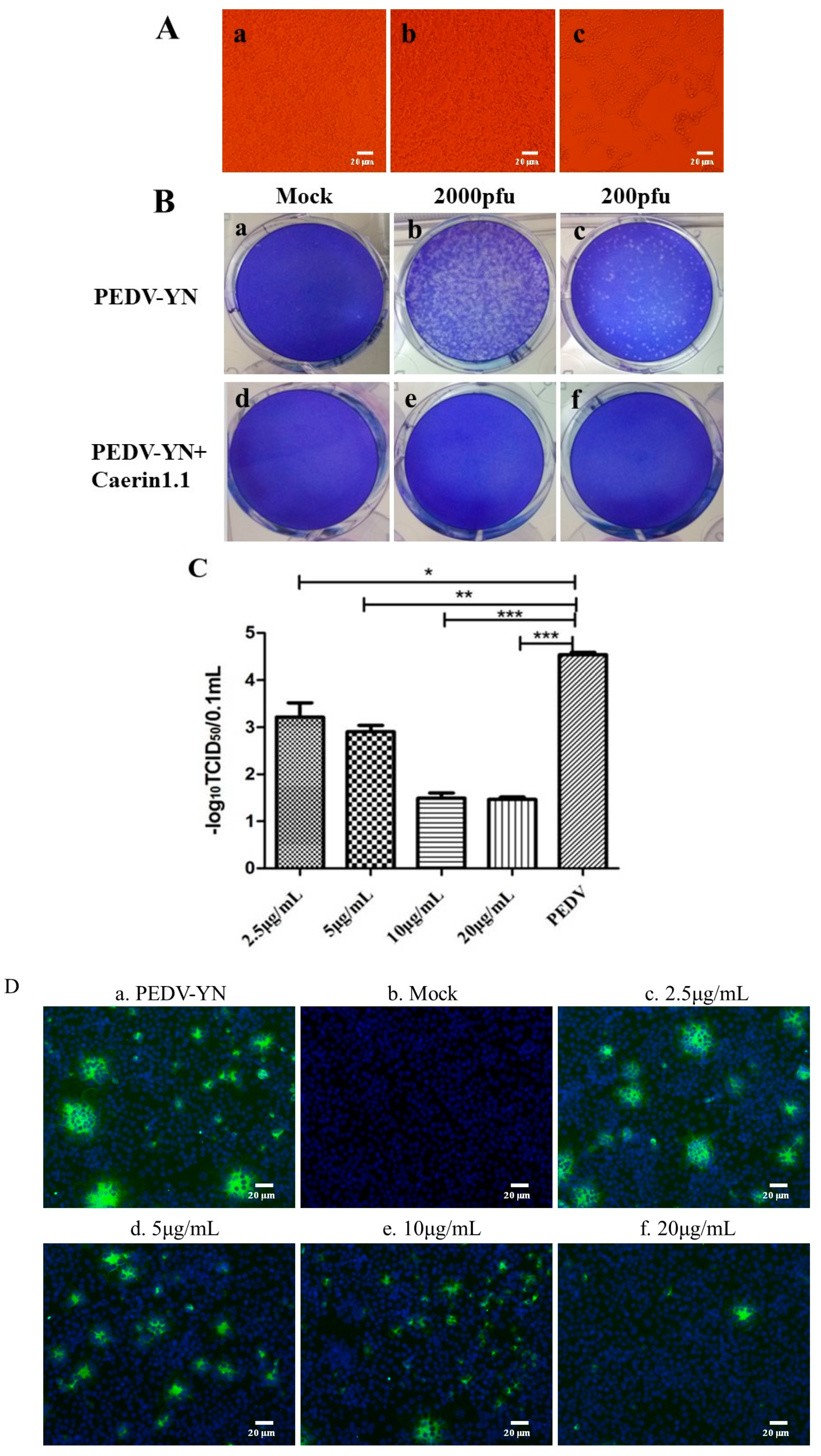
3.3. The Inhibitory Effect of Caerin1.1 against PEDV-YN Strain
3.4. The Inhibitory Effect of Caerin1.1 against Another Two PEDV Strains
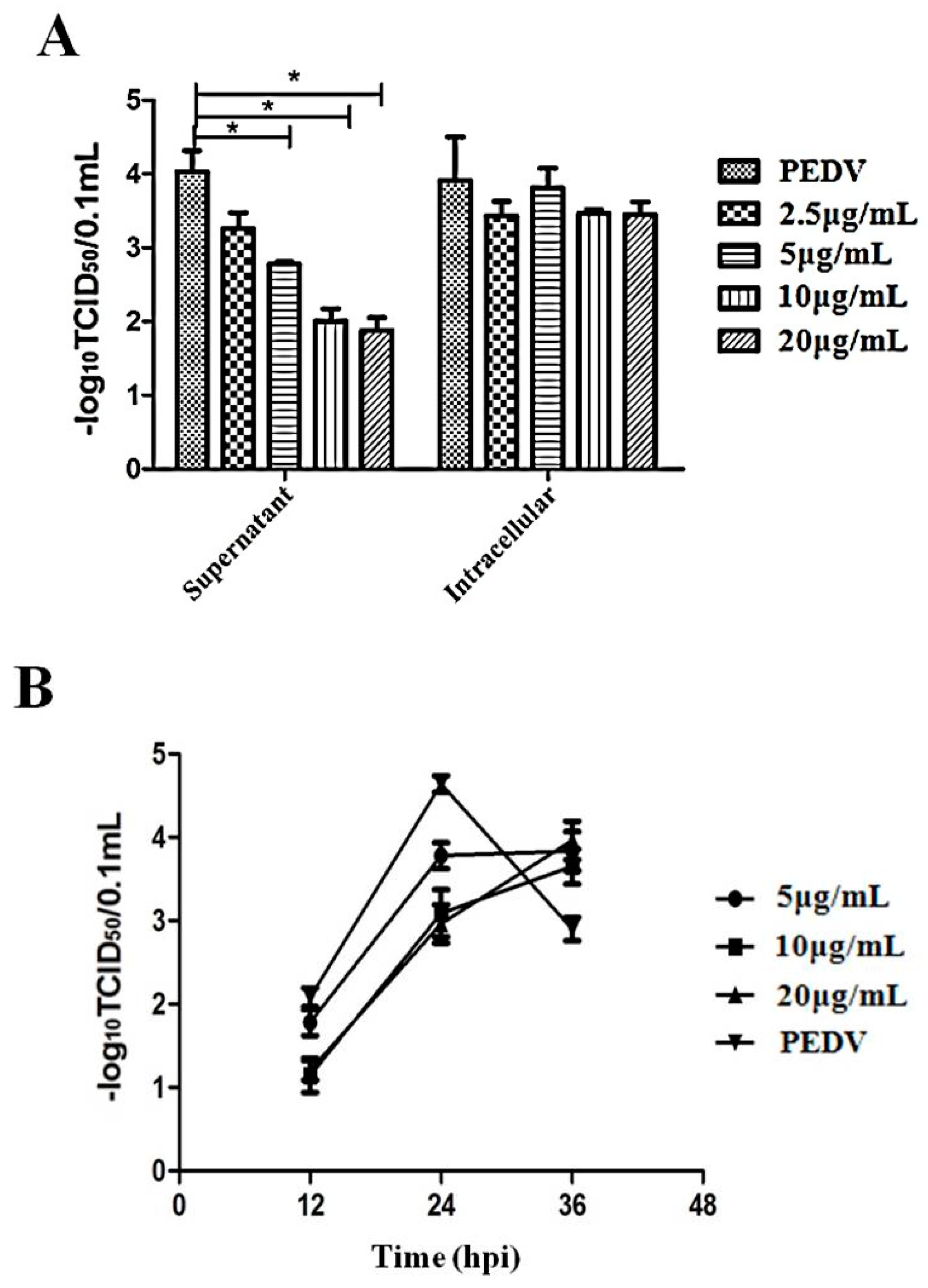
3.5. The Suppression of Virus Propagation
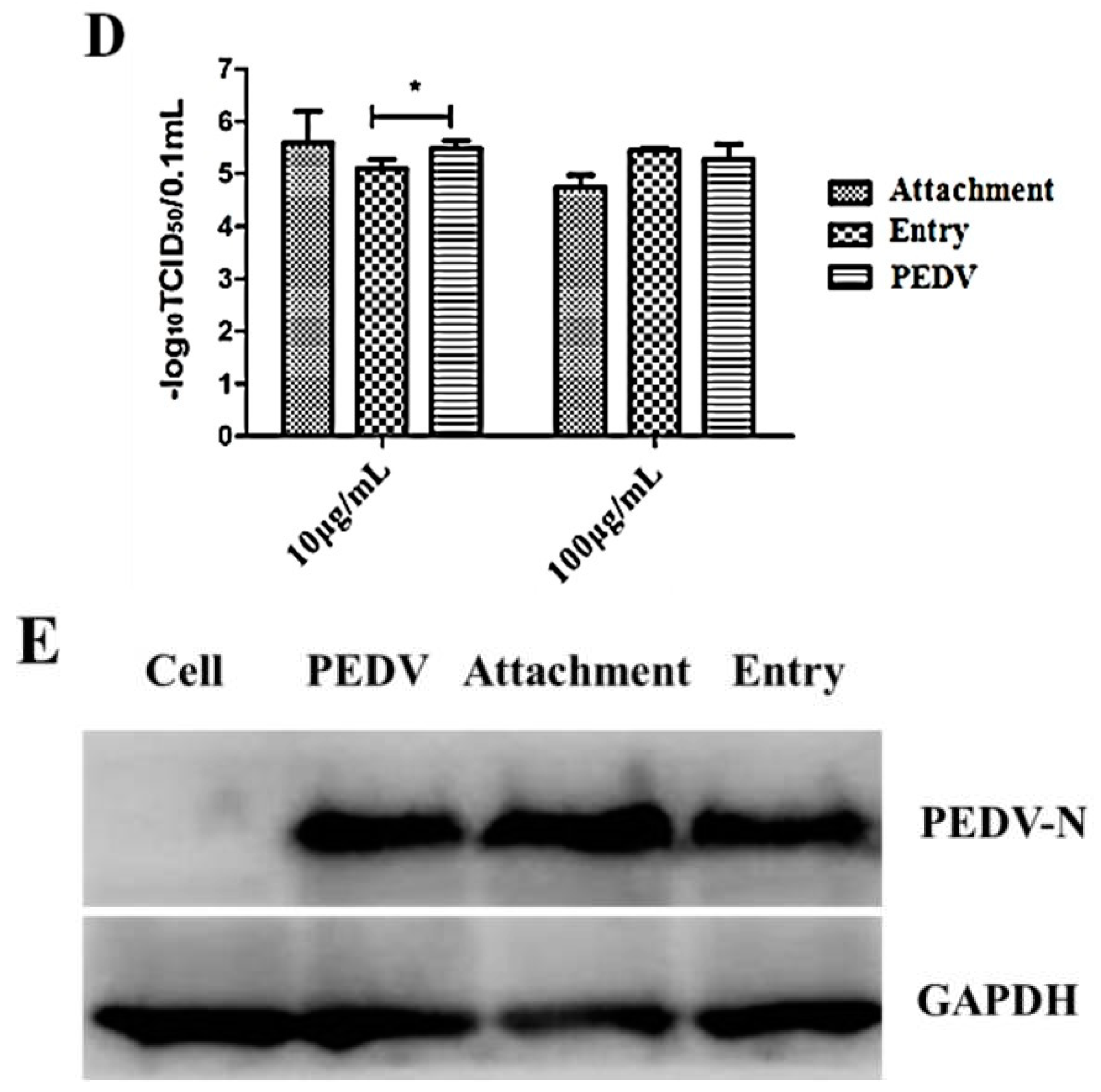
3.6. Caerin1.1 Acts Mainly by Direct Inactivation of Viral Particles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMP | Antimicrobial peptide |
| IFA | Indirect immunofluorescent assay |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PED | Porcine epidemic diarrhea |
| PEDV | Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus |
| TCID50 | Tissue Culture Infectious Dose 50 |
References
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, M.; Ku, X.; Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; He, Q. Comparative genomic analysis of classical and variant virulent parental/attenuated strains of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Viruses 2015, 7, 5525–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensaert, M.; de Bouck, P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch. Virol. 1978, 58, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Stasko, J.; Thomas, J.T.; Stensland, W.R.; Pillatzki, A.E.; Gauger, P.C.; Schwartz, K.J.; Madson, D.; Yoon, K.-J. Isolation and characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses associated with the 2013 disease outbreak among swine in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; He, Q. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Kou, Q.; Ge, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Phylogenetic analysis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus field strains prevailing recently in China. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrell, D.A.; Beutler, B. The evolution and genetics of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, A.C. Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin: An expanding scenario: Commentary. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanCompernolle, S.E.; Taylor, R.J.; Oswald-Richter, K.; Jiang, J.; Youree, B.E.; Bowie, J.H.; Tyler, M.J.; Conlon, J.M.; Wade, D.; Aiken, C. Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus infection and transfer of virus from dendritic cells to T cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11598–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Li, A.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liao, Y.-S.; Lin, T.-H. Antimicrobial peptide m2163 or m2386 identified from Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 can trigger apoptosis in the human colorectal cancer cell line SW480. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Mishra, B.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M. High-quality 3D structures shine light on antibacterial, anti-biofilm and antiviral activities of human cathelicidin LL-37 and its fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Sahl, H.-G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) with dual mechanisms: Membrane disruption and apoptosis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K. Control of cell selectivity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Shao, F.; Wu, M.; Ren, W.; Xiong, X.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y. The application of antimicrobial peptides as growth and health promoters for swine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowdish, D.M.; Davidson, D.J.; Scott, M.G.; Hancock, R.E. Immunomodulatory activities of small host defense peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölzl, M.A.; Hofer, J.; Steinberger, P.; Pfistershammer, K.; Zlabinger, G.J. Host antimicrobial proteins as endogenous immunomodulators. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 119, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, E.F.; Hunter, H.N.; Matsuzaki, K.; Vogel, H.J. Solution NMR studies of amphibian antimicrobial peptides: Linking structure to function? Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 1639–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukala, T.L.; Brinkworth, C.S.; Carver, J.A.; Bowie, J.H. Investigating the importance of the flexible hinge in caerin 1.1: Solution structures and activity of two synthetically modified caerin peptides. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechler, A.; Praporski, S.; Atmuri, K.; Boland, M.; Separovic, F.; Martin, L.L. Specific and selective peptide-membrane interactions revealed using quartz crystal microbalance. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanCompernolle, S.; Smith, P.B.; Bowie, J.H.; Tyler, M.J.; Unutmaz, D.; Rollins-Smith, L.A. Inhibition of HIV infection by caerin 1 antimicrobial peptides. Peptides 2015, 71, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Ruchala, P.; Lehrer, R.I.; Ross, C.R.; Rowland, R.R.; Blecha, F. Antimicrobial host defense peptides in an arteriviral infection: Differential peptide expression and virus inactivation. Viral Immunol. 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Yan, W.; Gu, W.; He, Q. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is required for the early stages of porcine circovirus type 2 replication. Virology 2014, 456, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsuan, S.-L.; Chang, S.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liao, T.-L.; Jong, T.-T.; Chien, M.-S.; Lee, W.-C.; Chen, S.-S.; Liao, J.-W. The cytotoxicity to leukemia cells and antiviral effects of Isatis indigotica extracts on pseudorabies virus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Z.; Luo, R.; An, K.; Liu, L.; Bi, J.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S.; Fang, L. Proteome analysis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV)-infected Vero cells. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, C. Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles against adenovirus type 3 in vitro. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana, V.M.; Torres, N.I.; Wachsman, M.B.; Sinko, P.J.; Castilla, V.; Chikindas, M. Antiherpes simplex virus type 2 activity of the antimicrobial peptide subtilosin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, Z. Inhibitory activity and mechanism of two scorpion venom peptides against herpes simplex virus type 1. Antivir. Res. 2014, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Guo, H.; Zeng, W.; Yan, G.; Memon, A.M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Induces Autophagy to Benefit Its Replication. Viruses 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulagina, N.V.; Shaffer, K.M.; Ligler, F.S.; Taitt, C.R. Antimicrobial peptides as new recognition molecules for screening challenging species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by Cecropin D in vitro. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 34, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Shao, K.; Li, Z.; Guo, N.; Zuo, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; He, Q.; Han, H. Antiviral activity of graphene oxide: How sharp edged structure and charge matter. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21571–21579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, B.; Khaliq, H.; Sun, A.; Qi, Y.; Moku, G.K.; Su, Y.; Wang, J. Comparative Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Pharmacodynamics Evaluation of Piscidin 1 Against PRV and PEDV in Rats. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, N.; Zhang, B.; Hu, H.; Ye, S.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, C.; He, Q. Caerin1.1 Suppresses the Growth of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro via Direct Binding to the Virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090507
Guo N, Zhang B, Hu H, Ye S, Chen F, Li Z, Chen P, Wang C, He Q. Caerin1.1 Suppresses the Growth of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro via Direct Binding to the Virus. Viruses. 2018; 10(9):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090507
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Nan, Bingzhou Zhang, Han Hu, Shiyi Ye, Fangzhou Chen, Zhonghua Li, Pin Chen, Chunmei Wang, and Qigai He. 2018. "Caerin1.1 Suppresses the Growth of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro via Direct Binding to the Virus" Viruses 10, no. 9: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090507
APA StyleGuo, N., Zhang, B., Hu, H., Ye, S., Chen, F., Li, Z., Chen, P., Wang, C., & He, Q. (2018). Caerin1.1 Suppresses the Growth of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro via Direct Binding to the Virus. Viruses, 10(9), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090507



