A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse’s Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Construction of hDPP4-KIMice
2.3. Generation of Pseudoviruses
2.4. In Vitro Neutralization Tests
2.5. MERS-CoV-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies
2.6. Murine Model of MERS-CoV Pseudovirus Infection
2.7. Authentic Virus Infection of Mice and Plaque Assays
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real-Time QuantitativePCR
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
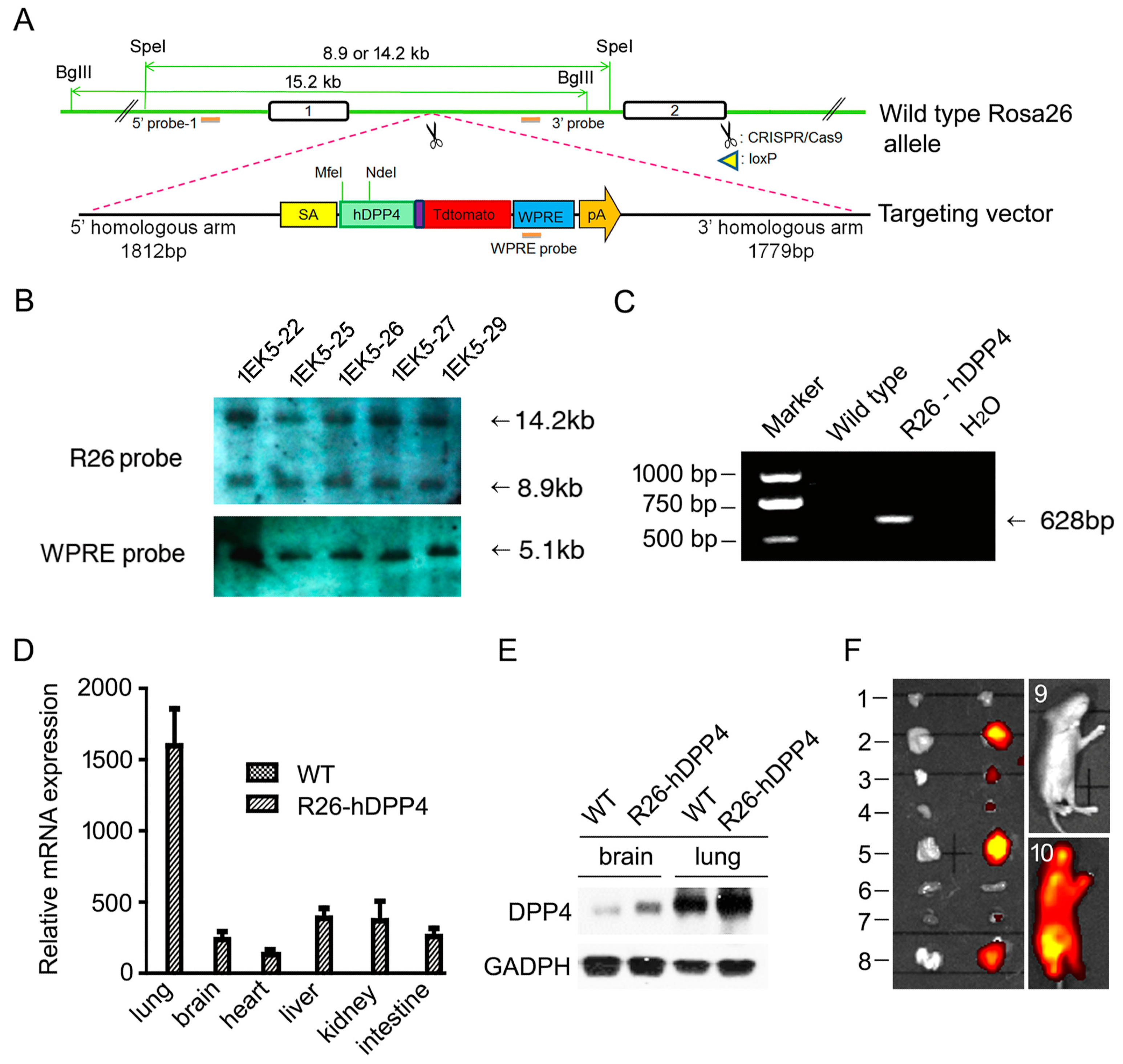
3.1. A HDPP4-Knockin Mouse (R26-hDPP4) Was Established Using CRISPR/Cas9
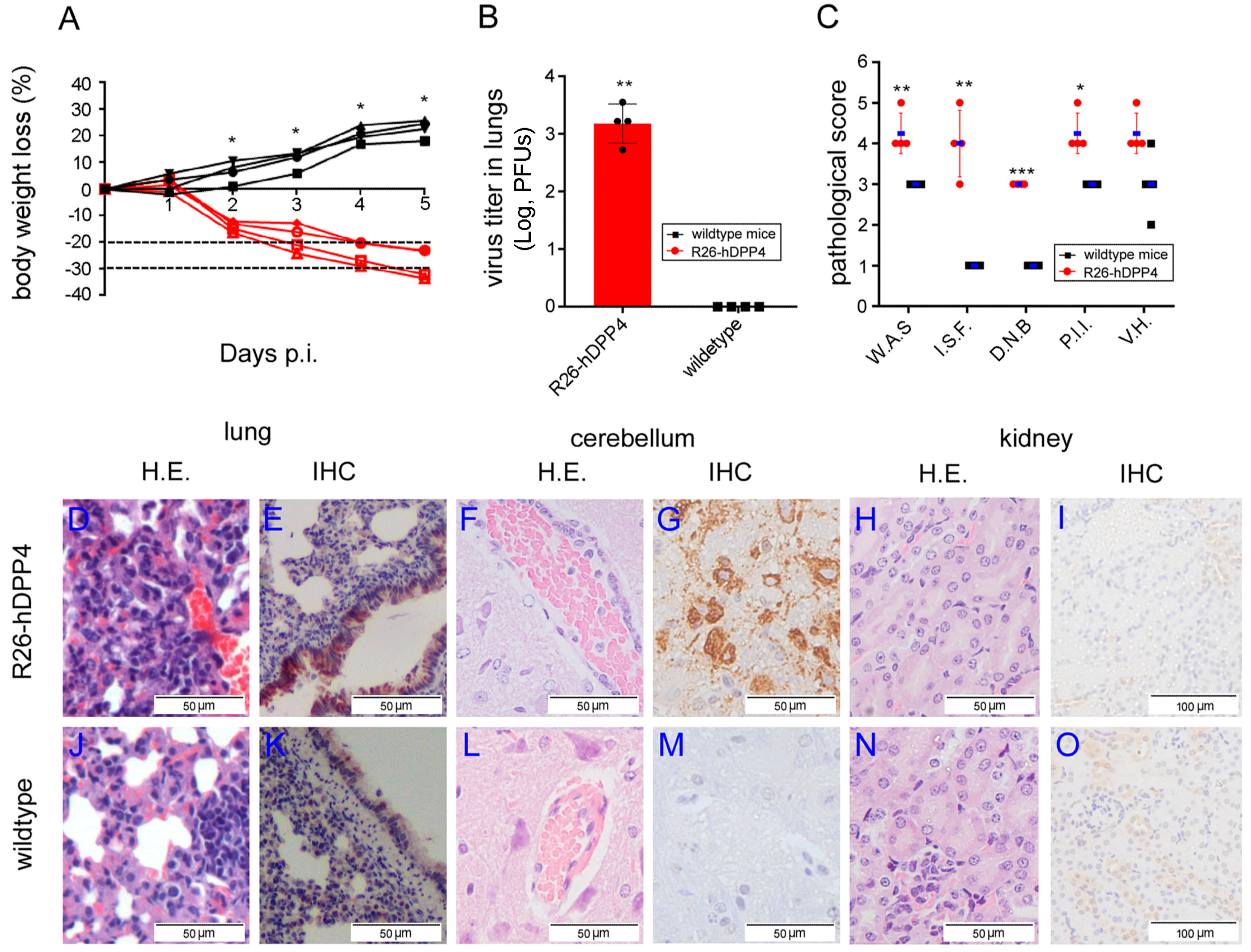
3.2. R26-hDPP4 Mice Were Susceptible to Authentic MERS-CoV Infection, with Infected Mice Exhibiting Disease Symptoms Similar to Those of MERS-CoV-Infected Human Patients
3.3. A MERS-CoV S-RBD-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Protected R26-hDPP4 Mice from Challenge with Authentic MERS-CoV
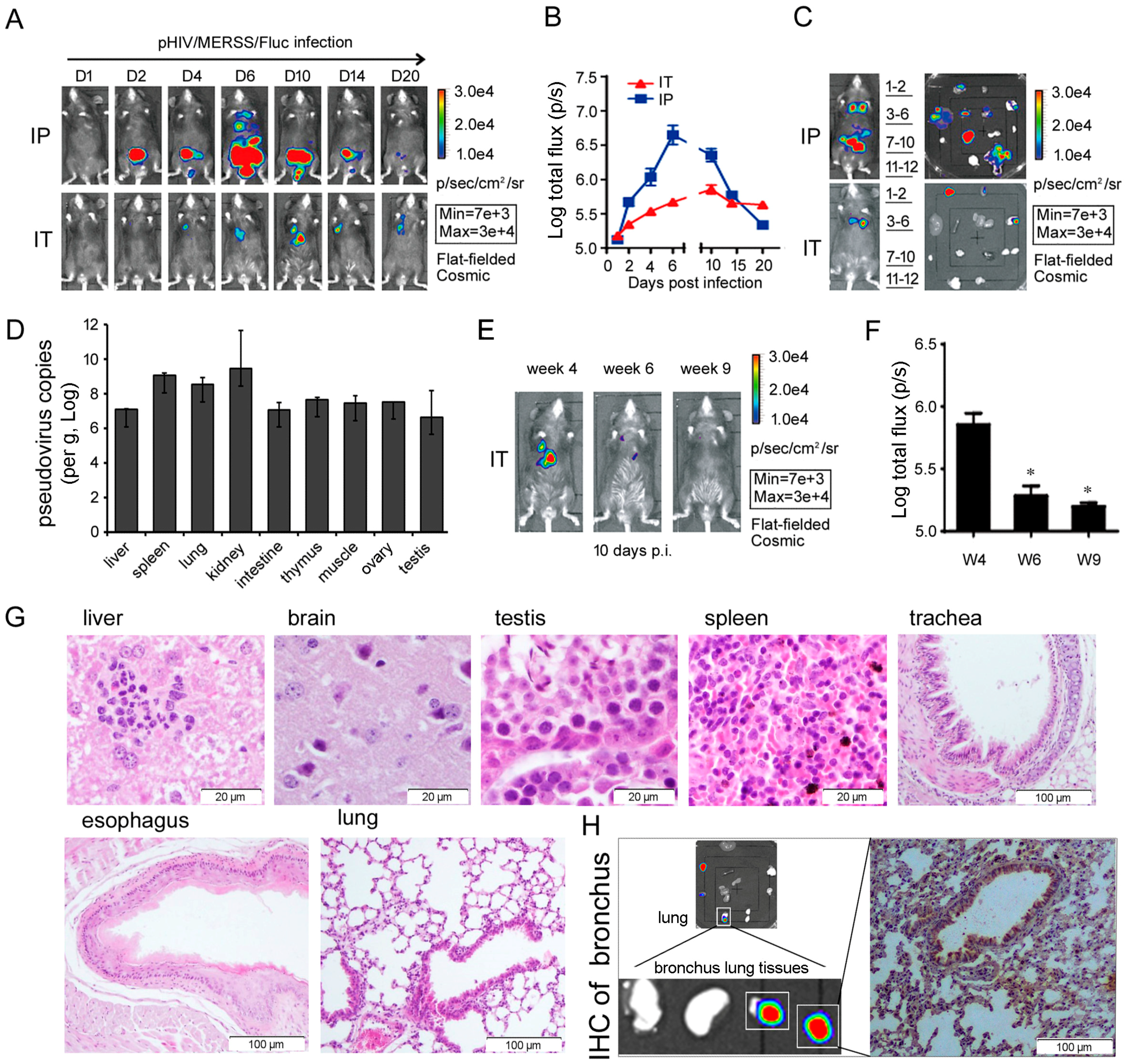
3.4. AMurine Model of Infection with Pseudotyped MERS-CoV was Established Using R26-hDPP4 Mice
3.4.1. Optimization of Pseudotyped MERS-CoV System and Establishment of a Model of Pseudotyped MERS-CoV Infection Using R26-hDPP4 Mice
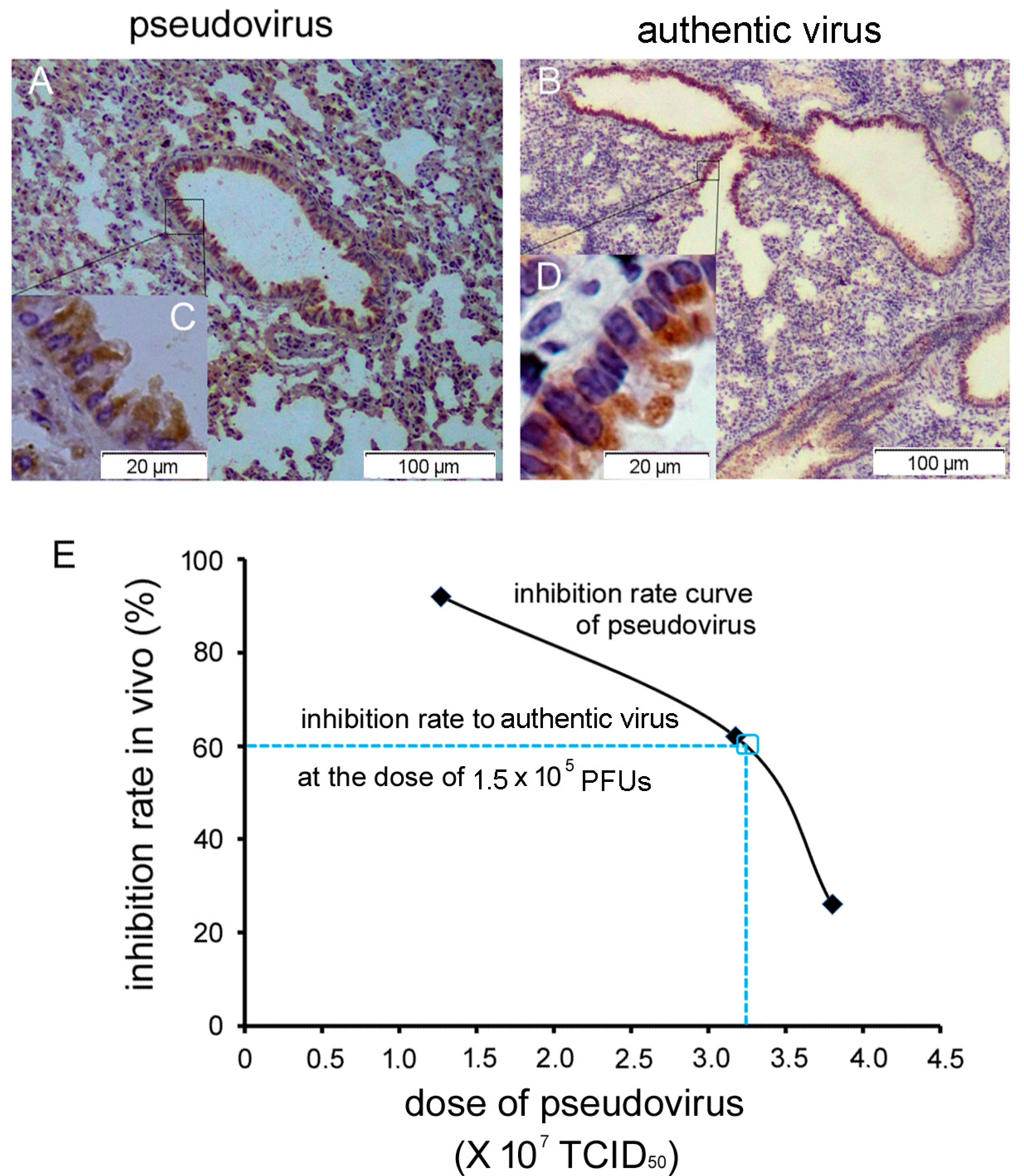
3.4.2. Relevance of the R26-hDPP4 Mouse Model of Infection by Pseudotyped and Authentic MERS-CoV
3.5. MERS-CoV S-RBD-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Protected R26-hDPP4 Mice against Challenge with Pseudotyped MERS-CoV
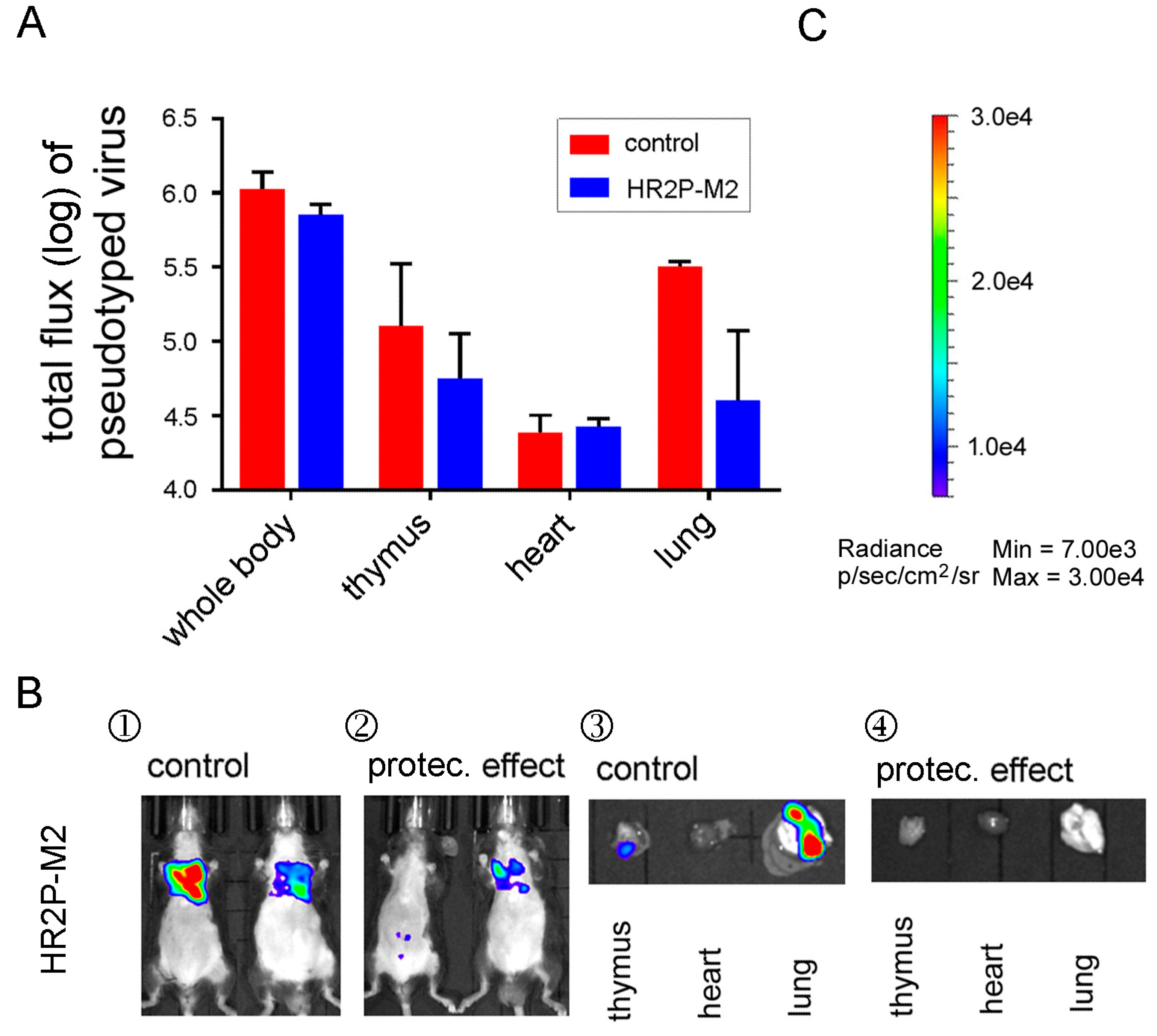
3.6. A MERS-CoV S-HR1-Specific Fusion Inhibitor Peptide Protected R26-DPP4 Mice from Infection by Pseudotyped MERS-CoV
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Chan, C.C.; Sun, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Guo, H.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.-J. Recombinant receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein expressed in mammalian, insect and E. coli cells elicits potent neutralizing antibody and protective immunity. Virology 2009, 393, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Du, L.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Poon, V.K.; Wang, L.; Yu, F.; Zheng, B.-J.; Jiang, S. A safe and convenient pseudovirus-based inhibition assay to detect neutralizing antibodies and screen for viral entry inhibitors against the novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.M.; Matthews, K.L.; Goicochea, L.; Frieman, M.B. Wild-type and innate immune-deficient mice are not susceptible to the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, E.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Falzarano, D.; Bushmaker, T.; Feldmann, F.; Brining, D.L.; Fischer, E.R.; Martellaro, C.; Okumura, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes transient lower respiratory tract infection in rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16598–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Smits, S.L.; Provacia, L.B.; van den Brand, J.M.; Wiersma, L.; Ouwendijk, W.J.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Spronken, M.I.; van Amerongen, G.; Rottier, P.J.; et al. Adenosine deaminase acts as a natural antagonist for dipeptidyl peptidase 4-mediated entry of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1834–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzarano, D.; de Wit, E.; Feldmann, F.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Okumura, A.; Peng, X.; Thomas, M.J.; van Doremalen, N.; Haddock, E.; Nagy, L.; et al. Infection with MERS-CoV causes lethal pneumonia in the common marmoset. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; Dekkers, D.H.; Müller, M.A.; Dijkman, R.; Muth, D.; Demmers, J.A.; Zaki, A.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockrell, A.S.; Yount, B.L.; Scobey, T.; Jensen, K.; Douglas, M.; Beall, A.; Tang, X.-C.; Marasco, W.A.; Heise, M.T.; Baric, R.S. A mouse model for MERS coronavirus-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, K.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Fett, C.; Zhao, J.; Gale, M.J.; Baric, R.S.; Enjuanes, L.; Gallagher, T. Rapid generation of a mouse model for Middle East respiratory syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Perlman, S.; Zhao, J.; Jewell, A.K.; Reznikov, L.R.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Meyerholz, D.K.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus causes multiple organ damage and lethal disease in mice transgenic for human dipeptidyl peptidase 4. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 213, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.S.; Garron, T.; Tao, X.; Peng, B.-H.; Wakamiya, M.; Chan, T.-S.; Couch, R.B.; Tseng, C.-T.K. Generation of a transgenic mouse model of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection and disease. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3659–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.L.; Channappanavar, R.; Park, J.-E.; Earnest, J.T.; Bair, T.B.; Bates, A.M.; Brogden, K.A.; Flaherty, H.A.; Gallagher, T.; et al. Mouse-adapted MERS coronavirus causes lethal lung disease in human DPP4 knockin mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3119–E3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeir, A.-M.; Durinx, C.; Scharpé, S.; De Meester, I. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV from bench to bedside: An update on structural properties, functions, and clinical aspects of the enzyme DPP IV. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2003, 40, 209–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, L.; Rufini, A.; Moretti, T.; Forte, P.; Aiuti, A.; Fantoni, A. Human cd26 expression in transgenic mice affects murine t-cell populations and modifies their subset distribution. Hum. Immunol. 2002, 63, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Kou, Z.; Ma, C.; Tao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, F.; Tseng, C.-T.K.; Zhou, Y. A truncated receptor-binding domain of MERS-CoV spike protein potently inhibits MERS-CoV infection and induces strong neutralizing antibody responses: Implication for developing therapeutics and vaccines. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, T.; Du, L.; Ju, T.W.; Prabakaran, P.; Lau, C.C.; Lu, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Exceptionally potent neutralization of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus by human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7796–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Kou, Z.; Tao, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, S.; Tseng, C.-T.K.; et al. A conformation-dependent neutralizing monoclonal antibody specifically targeting receptor-binding domain in Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-C.; Agnihothram, S.S.; Jiao, Y.; Stanhope, J.; Graham, R.L.; Peterson, E.C.; Avnir, Y.; Tallarico, A.S.C.; Sheehan, J.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Identification of human neutralizing antibodies against MERS-CoV and their role in virus adaptive evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2018–E2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, D.; Zhao, J.; Pedotti, M.; Simonelli, L.; Agnihothram, S.; Fett, C.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, B.; Foglierini, M.; Agatic, G.; Vanzetta, F.; et al. Prophylactic and postexposure efficacy of a potent human monoclonal antibody against MERS coronavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10473–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, T.; Prabakaran, P.; Du, L.; Shi, W.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, S.; Dimitrov, D.S.; et al. Junctional and allele-specific residues are critical for MERS-CoV neutralization by an exceptionally potent germline-like antibody. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Garron, T.; Agrawal, A.S.; Algaissi, A.; Peng, B.-H.; Wakamiya, M.; Chan, T.-S.; Lu, L.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; et al. Characterization and demonstration of the value of a lethal mouse model of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection and disease. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Cao, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Development of In Vitro and In Vivo rabies virus neutralization assays based on a high-titer pseudovirus system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grehan, K.; Ferrara, F.; Temperton, N. An optimised method for the production of MERS-CoV spike expressing viral pseudotypes. MethodsX 2015, 2, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, W.; Nie, J.; Zhu, R.; Gao, D.; Song, A.; Meng, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. A novel high-throughput vaccinia virus neutralization assay and preexisting immunity in populations from different geographic regions in china. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.S.; Ying, T.; Tao, X.; Garron, T.; Algaissi, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, B.-H.; Jiang, S.; Dimitrov, D.S.; et al. Passive transfer of a germline-like neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects transgenic mice against lethal Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channappanavar, R.; Lu, L.; Xia, S.; Du, L.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Perlman, S.; Jiang, S. Protective effect of intranasal regimens containing peptidic Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus fusion inhibitor against MERS-CoV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chan, K.-H.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Du, L.; Yu, F.; et al. Structure-based discovery of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus fusion inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberger, P.; Sutton, J.K.; Rader, C.; Elia, M.; Barbas, C.F. Generation and characterization of a recombinant human ccr5-specific antibody a phage display approach for rabbit antibody humanization. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36073–36078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lee, P.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Lee, J.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Chen, J.; Dai, J.; et al. A humanized anti-VEGF rabbit monoclonal antibody inhibits angiogenesis and blocks tumor growth in xenograft models. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, Z.; Fan, C.; Wang, Y. A safe and sensitive enterovirus A71 infection model based on human SCARB2 knock-in mice. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitseva, M.; Kapnick, S.M.; Scott, J.; King, L.R.; Manischewitz, J.; Sirota, L.; Kodihalli, S.; Golding, H. Application of bioluminescence imaging to the prediction of lethality in vaccinia virus-infected mice. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10437–10447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Xu, L.; Li, F.; Lv, Q.; Yu, P.; Chen, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; et al. An animal model of MERS produced by infection of rhesus macaques with MERS coronavirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 209, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrowicz, B.P.; Imamoto, A.; Fiering, S.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Kerr, W.G.; Soriano, P. Disruption of overlapping transcripts in the ROSA βgeo 26 gene trap strain leads to widespread expression of β-galactosidase in mouse embryos and hematopoietic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3789–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.M.; Van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, R.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Moon, K.C.; Joh, J.-S.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, H.-S.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.S. A case report of a Middle East respiratory syndrome survivor with kidney biopsy results. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Fan, C.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Biodistribution and residence time of adenovector serotype 5 in normal and immunodeficient mice and rats detected with bioluminescent imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumla, A.; Hui, D.S.; Perlman, S. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2015, 386, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; de Wit, E.; Feldmann, H. Pneumonia from human coronavirus in a macaque model. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1560–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascal, K.E.; Coleman, C.M.; Mujica, A.O.; Kamat, V.; Badithe, A.; Fairhurst, J.; Hunt, C.; Strein, J.; Berrebi, A.; Sisk, J.M.; et al. Pre-and postexposure efficacy of fully human antibodies against spike protein in a novel humanized mouse model of MERS-CoV infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8738–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.; Harthi, A.; Hussein, J.; Bouchama, A.; Johani, S.; Hajeer, A.; Saeed, B.; Wahbi, A.; Saedy, A.; AlDabbagh, T.; et al. Severe neurologic syndrome associated with Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV). Infection 2015, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Channappanavar, R.; Coleman, C.M.; Jiao, J.-A.; Matsushita, H.; Liu, Y.; Postnikova, E.N.; Ork, B.L.; et al. Human polyclonal immunoglobulin G from transchromosomic bovines inhibits MERS-CoV In Vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 326ra21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Sun, S.; Xiao, H.; Feng, J.; Guo, Y.; Tai, W.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y. Single-dose treatment with a humanized neutralizing antibody affords full protection of a human transgenic mouse model from lethal Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-coronavirus infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 132, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. A humanized neutralizing antibody against MERS-CoV targeting the receptor-binding domain of the spike protein. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, C.; Schlossman, S.F. The structure and function of cd26 in the t-cell immune response. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 161, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauchemez, S.; Fraser, C.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Donnelly, C.A.; Riley, S.; Rambaut, A.; Enouf, V.; van der Werf, S.; Ferguson, N.M. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Quantification of the extent of the epidemic, surveillance biases, and transmissibility. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, T. Pseudovirus-based neuraminidase inhibition assays reveal potential H5N1 drug-resistant mutations. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
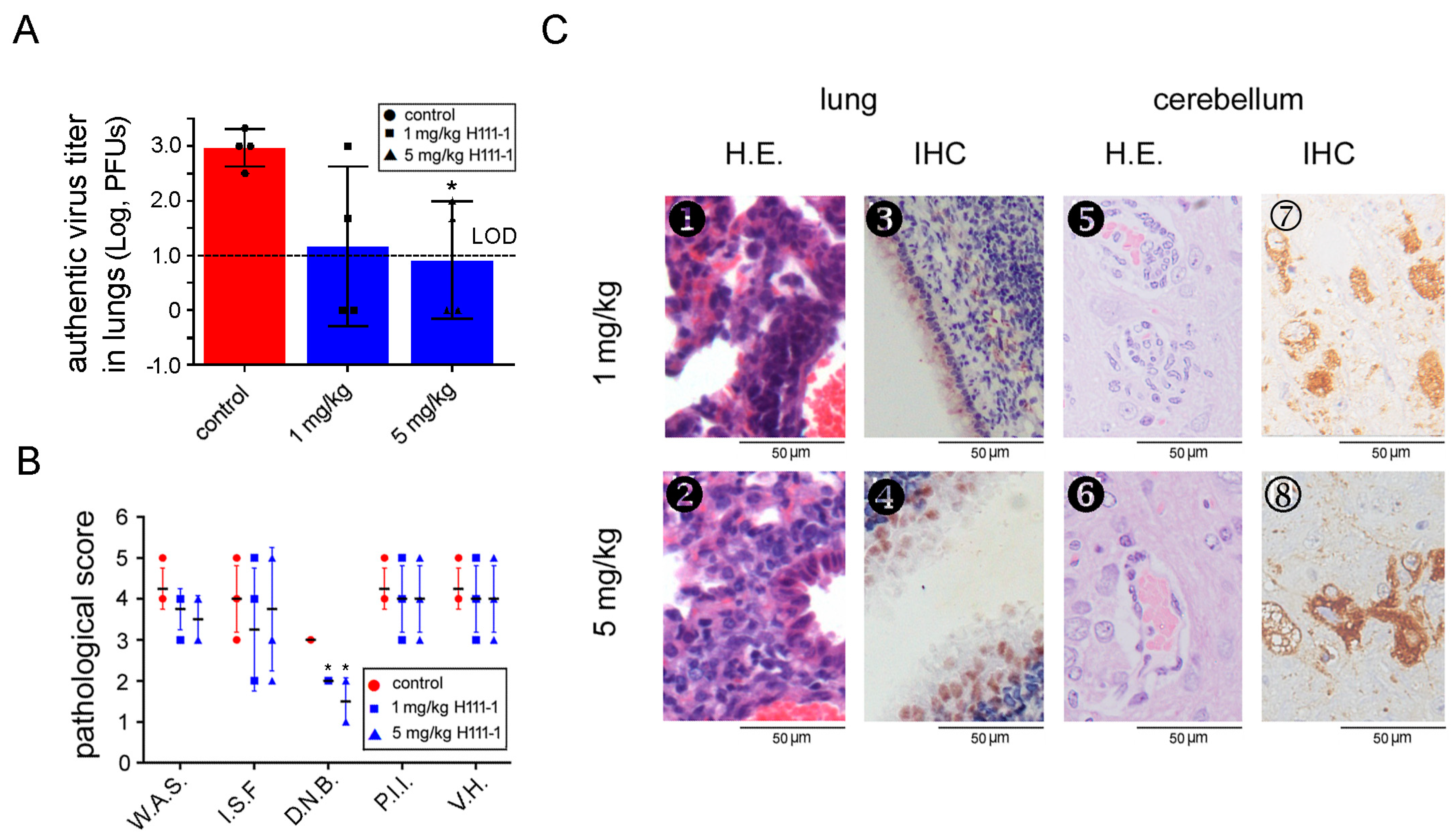

| Days p.i. | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R26-hDPP4 + PBS | 0 | 1.9 ± 2.2 | −14.1 ± 1.9 | −18.5 ± 5.1 | −24.0 ± 4.5 | −28.0 ± 5.6 |
| R26-hDPP4 + 1 mg/kgmAbH111-1 | 0 | −0.5 ± 1.4 | −13.0 ± 3.5 | −17.0 ± 3.0 | −22.9 ± 2.7 | −27.5 ± 1.9 |
| R26-hDPP4 + 5 mg/kgmAbH111-1 | 0 | −0.1 ± 2.3 | −7.6 ± 4.8 | −13.1 ± 3.0 | −19.0 ± 3.6 | −24.8 ± 3.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huang, W.; Liang, C.; et al. A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse’s Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV. Viruses 2018, 10, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090448
Fan C, Wu X, Liu Q, Li Q, Liu S, Lu J, Yang Y, Cao Y, Huang W, Liang C, et al. A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse’s Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV. Viruses. 2018; 10(9):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090448
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Changfa, Xi Wu, Qiang Liu, Qianqian Li, Susu Liu, Jianjun Lu, Yanwei Yang, Yuan Cao, Weijin Huang, Chunnan Liang, and et al. 2018. "A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse’s Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV" Viruses 10, no. 9: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090448
APA StyleFan, C., Wu, X., Liu, Q., Li, Q., Liu, S., Lu, J., Yang, Y., Cao, Y., Huang, W., Liang, C., Ying, T., Jiang, S., & Wang, Y. (2018). A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse’s Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV. Viruses, 10(9), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090448







