Antiviral and Inflammatory Cellular Signaling Associated with Enterovirus 71 Infection
Abstract
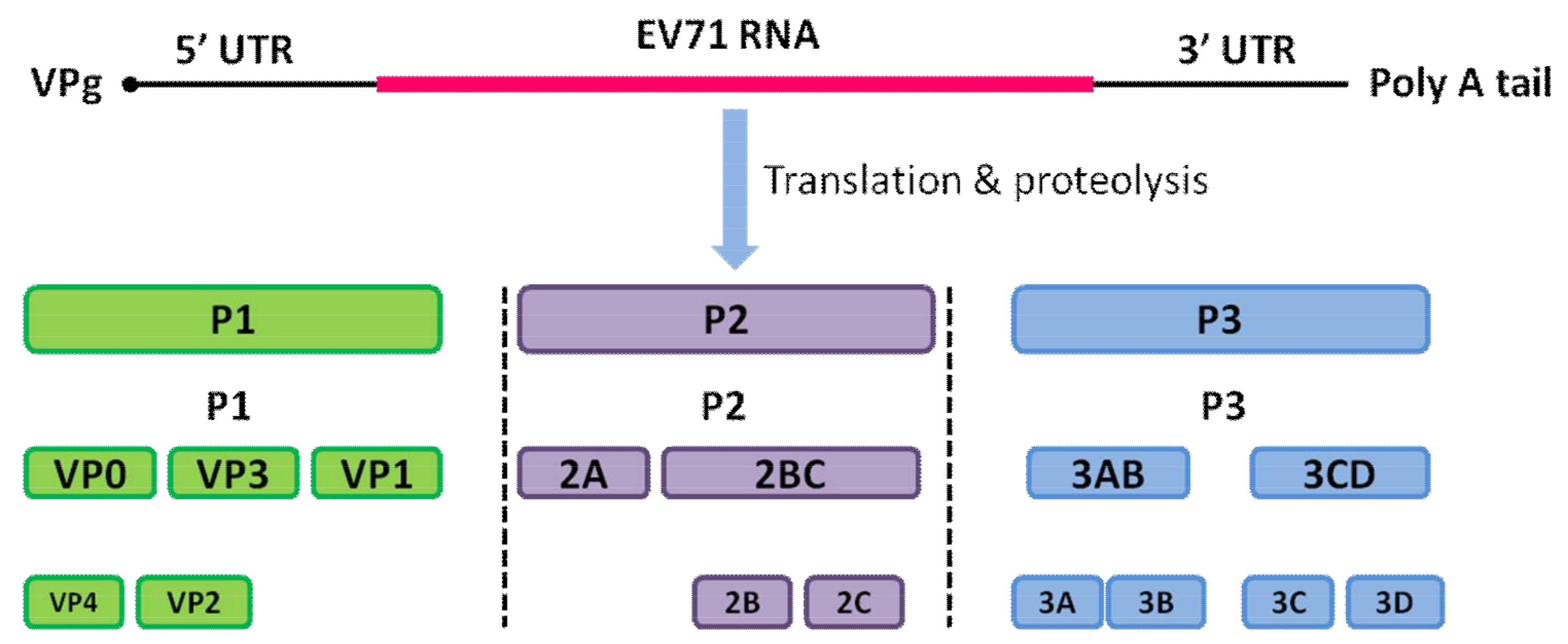
1. Introduction
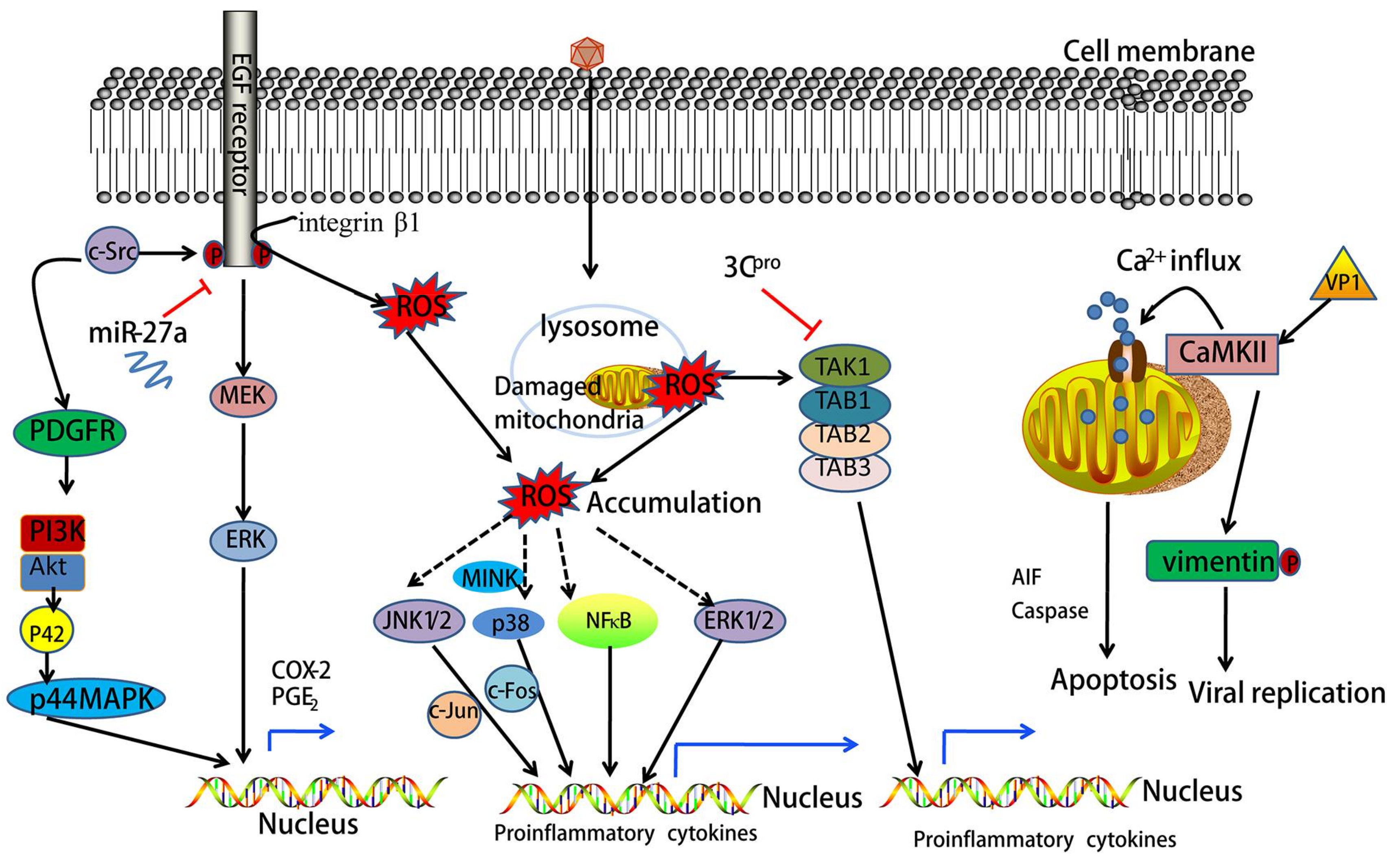
2. Oxidative Stress Mediates EV71-Induced Signaling
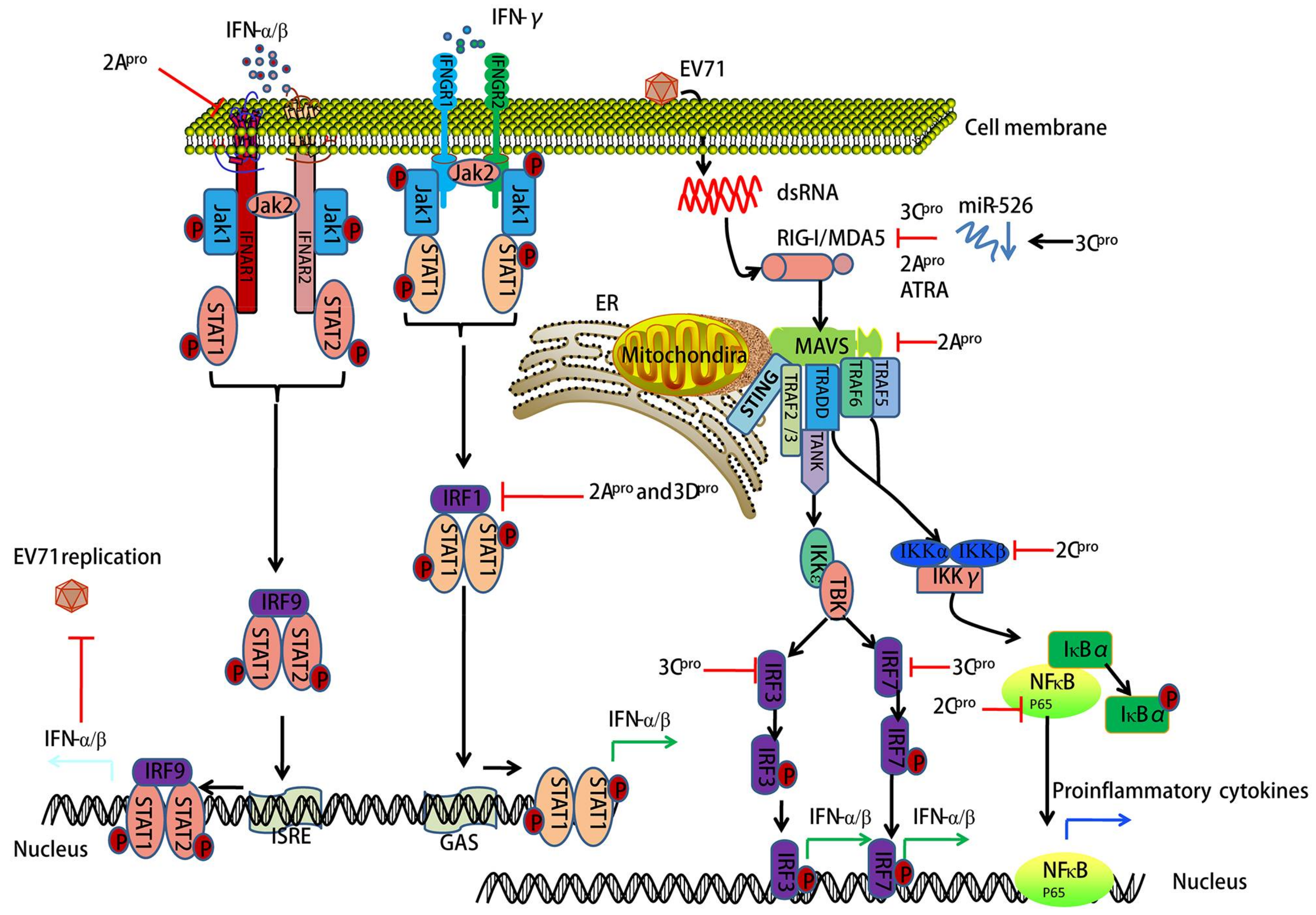
3. EV71-Encoded Proteases Block Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene I (RIG-I)-Like Receptor (RLR)-Dependent Antiviral Signaling
4. EV71-Encoded Proteases Inhibit MAVS-Mediated Antiviral Signaling
5. EV71 Infection-Associated IFN Signaling
6. EV71 Interacts with IRF Signaling
7. EV71 Triggers NF-κB Signaling
8. EV71 Interacts with TLR Signaling
9. EV71-Associated NOD-Like Receptor (NLR) Signaling
10. EV71 Infection Activates Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Signaling
11. EV71 Activates Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling
12. EV71 Induces Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K) Signaling
13. EV71 Activates Calcium (Ca2+)-Dependent Signaling
14. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, M.H.; Wong, S.C.; Lewthwaite, P.; Cardosa, M.J.; Solomon, T. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevka, P.; Perera, R.; Cardosa, J.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Crystal structure of human enterovirus 71. Science 2012, 336, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Peng, W.; Ren, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lou, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, W.; Shen, X.; Porta, C.; et al. A sensor-adaptor mechanism for enterovirus uncoating from structures of EV71. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notkins, A.L.; Oldstone, M. Concepts in Viral Pathogenesis I. Q. Rev. Biol. 1986, 60, 720–721. [Google Scholar]
- Pathinayake, P.S.; Hsu, A.C.; Wark, P.A. Innate immunity and immune evasion by enterovirus 71. Viruses 2015, 7, 6613–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Ren, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, G.; Feng, D.; Sun, T. Involvement of inducible nitric oxide synthase and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 infection. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81014–81026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Liao, Y.; Na, R.; Dong, C.; Wang, L.; Xie, Z.; et al. Pathogenesis study of enterovirus 71 infection in rhesus monkeys. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Yang, H.; Shi, L.; Sun, W.; Sui, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Xi, Y.; et al. Serum inflammatory cytokine levels correlate with hand-foot-mouth disease severity: A nested serial case-control study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Ren, J.; Chen, S.; Sui, M.; Zhou, G.; Dang, D.; Zhu, J.; Feng, H.; et al. Pulmonary edema following central nervous system lesions induced by a non- mouse-adapted EV71 strain in neonatal BALB/c mice. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Chen, W. Pd169316, a specific p38 inhibitor, shows antiviral activity against enterovirus71. Virology 2017, 508, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Xu, W.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Lv, A.; Li, X. Clinical efficacy of andrographolide sulfonate in the treatment of severe hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is dependent upon inhibition of neutrophil activation. Phytother. Res. PTR 2015, 29, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, H.B.; Chou, A.H.; Lin, S.I.; Chen, I.H.; Lien, S.P.; Liu, C.C.; Chong, P.; Liu, S.J. Toll-like receptor 9-mediated protection of enterovirus 71 infection in mice is due to the release of danger-associated molecular patterns. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11658–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Yang, J.; Luo, K.; Yang, C.; Zhang, N.; Xu, R.; Chen, J.; Jin, M.; Xu, B.; Guo, N.; et al. TLR3 signaling in macrophages is indispensable for the protective immunity of invariant natural killer T cells against enterovirus 71 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gomez, A.M.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, H. Ros regulation of microdomain Ca2+ signalling at the dyads. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. Ros and ros-mediated cellular signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.L.; Weng, S.F.; Kuo, C.H.; Ho, H.Y. Enterovirus 71 induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation that is required for efficient replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Weng, S.F.; Chang, L.; Yeh, T.T.; Shih, S.R.; Chiu, D.T. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency enhances enterovirus 71 infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.G.; Cheng, M.L.; Chen, K.H.; Horng, J.T.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, S.M.; Sakurai, H.; Leu, Y.L.; Wang, S.D.; Ho, H.Y. Antiviral activities of schizonepeta tenuifolia briq. against enterovirus 71 in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Si, X.; Wu, H.; Zhai, X.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Pan, B.; et al. Curcumin inhibits the replication of enterovirus 71 in vitro. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Qiu, M.; Chen, D.; Zheng, N.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Z. Apigenin inhibits enterovirus 71 replication through suppressing viral ires activity and modulating cellular JNK pathway. Antivir. Res. 2014, 109, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Natsukawa, T.; Shinobu, N.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Akira, S.; Fujita, T. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.K.; Gack, M.U. RIG-I-like receptor regulation in virus infection and immunity. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 12, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goubau, D.; Deddouche, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. Cytosolic sensing of viruses. Immunity 2013, 38, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. The 3C protein of enterovirus 71 inhibits retinoid acid-inducible gene I-mediated interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and type i interferon responses. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8051–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Cleavage of the adaptor protein trif by enterovirus 71 3C inhibits antiviral responses mediated by toll-like receptor 3. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8811–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Guan, K.; Hou, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; Cao, Y.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA miR-526a by enterovirus inhibits RIG-I-dependent innate immune response. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11356–11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, R.L.; Kao, L.T.; Lin, S.J.; Wang, R.Y.; Shih, S.R. MDA5 plays a crucial role in enterovirus 71 RNA-mediated IRF3 activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Langereis, M.A.; Lork, M.; Nguyen, M.; Hato, S.V.; Lanke, K.; Emdad, L.; Bhoopathi, P.; Fisher, P.B.; Lloyd, R.E.; et al. Enterovirus 2Apro targets MDA5 and MAVS in infected cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3369–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisch, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Su, L.; Wang, W. Effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on enterovirus 71 infection in vitro. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, C.E. On the origins of arrestin and rhodopsin. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2008, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Yao, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. ARRDC4 regulates enterovirus 71-induced innate immune response by promoting K63 polyubiquitination of MDA5 through TRIM65. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Ea, C.K.; Chen, Z.J. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-κB and IRF 3. Cell 2005, 122, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xi, X.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, Z. Enterovirus 71 protease 2Apro targets MAVS to inhibit anti-viral type i interferon responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-i- and type-ii-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Yi, L.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, M.C.; Kung, H.F.; He, M.L. Enterovirus 71 disrupts interferon signaling by reducing the level of interferon receptor 1. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3767–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.C.; Chen, S.O.; Chang, S.P.; Lee, Y.P.; Yu, C.K.; Chen, C.L.; Tseng, P.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Lin, C.F. Enterovirus 71 proteins 2A and 3D antagonize the antiviral activity of γ interferon via signaling attenuation. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7028–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.C.; Liou, A.T.; Chang, Y.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Chang, C.S.; Lee, C.K.; Kung, J.T.; Tu, P.H.; Yu, Y.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; et al. Immunodeficient mouse models with different disease profiles by in vivo infection with the same clinical isolate of enterovirus 71. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12485–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Shi, H.; Liu, L. Suppression of the toll-like receptor 7-dependent type i interferon production pathway by autophagy resulting from enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 infections facilitates their replication. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Yanai, H.; Savitsky, D.; Taniguchi, T. The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 535–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ji, L.; Yuan, X.; Jin, Y.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Differential regulation of TLR signaling on the induction of antiviral interferons in human intestinal epithelial cells infected with enterovirus 71. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Xiao, X.; Xue, Q.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Cleavage of interferon regulatory factor 7 by enterovirus 71 3C suppresses cellular responses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: New discoveries and insights. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.M.; Tergaonkar, V. NF-κB signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, F.D.; Carmody, R.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Modulation of NF-κB signaling as a therapeutic target in autoimmunity. J. Biomol. Screen. 2015, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.C.; Guo, N.J.; Grenman, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Vuorenmma, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.Y.; Pang, L.L.; et al. Susceptibility of human tonsillar epithelial cells to enterovirus 71 with normal cytokine response. Virology 2016, 494, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Hsieh, H.L.; Yang, C.M. Enterovirus 71 induces COX-2 expression via mapks, NF-κB, and AP-1 in SK-N-SH cells: Role of PGE2 in viral replication. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Lee, I.T.; Hsieh, H.L.; Yang, C.M. EV71 induces COX-2 expression via c-Src/PDGFR/PI3K/Akt/p42/p44 MAPK/AP-1 and NF-κB in rat brain astrocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Sun, C.C.; Hsieh, H.L.; Wang, S.W.; Horng, J.T.; Yang, C.M. EV71 induces VCAM-1 expression via PDGF receptor, PI3-K/AKT, p38 MAPK, JNK and NF-κB in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Li, J.R.; Ou, Y.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Hsiao, A.L.; Chen, C.J. Enterovirus 71 infection caused neuronal cell death and cytokine expression in cultured rat neural cells. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yin, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, G. Enterovirus 71 2C protein inhibits NF-κB activation by binding to RelA(p65). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Ji, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Shi, W. Resveratrol inhibits enterovirus 71 replication and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in rhabdosarcoma cells through blocking IKKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116879. [Google Scholar]
- Baccala, R.; Hoebe, K.; Kono, D.H.; Beutler, B.; Theofilopoulos, A.N. TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways of type i interferon induction in systemic autoimmunity. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.L.; Hu, Y.C.; Liang, C.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Liang, Y.C.; Yuan, H.P.; Chiang, B.L. Enterovirus-71 virus-like particles induce the activation and maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells through TLR4 signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Ge, M.; Chen, J.; Geng, Q.; Tian, M.; Qiao, Z.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, Y.; et al. HRS plays an important role for TLR7 signaling to orchestrate inflammation and innate immunity upon EV71 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Qi, G.; Liu, N.; Sheng, L.; Shang, L.; Qi, B. The immune mechanism of intestinal tract toll-like receptor in mediating EV71 virus type severe hand-foot-and-mouth disease and the mapk pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2263–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Jin, Y.; Duan, Z. Excessive proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine responses of human monocyte-derived macrophages to enterovirus 71 infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.J.; McDermott, M.F.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammasomes and autoimmunity. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, F.; Wan, P.; Pan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. EV71 3D protein binds with NLRP3 and enhances the assembly of inflammasome complex. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Niu, J.; Guo, Q.; Leng, Q.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Meng, G. Interleukin-18 protects mice from enterovirus 71 infection. Cytokine 2017, 96, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lei, X.; Xiao, X.; Yang, C.; Lu, W.; Huang, Z.; Leng, Q.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Meng, G.; et al. Reciprocal regulation between enterovirus 71 and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polosa, R.; Sapsford, R.J.; Dokic, D.; Cacciola, R.R.; Prosperini, G.; Devalia, J.L.; Holgate, S.T.; Howarth, P.H.; Davies, D.E. Induction of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in nasal epithelium by ozone. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wages, P.A.; Devlin, R.B.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Peden, D.B.; Samet, J.M. SRC-mediated EGF receptor activation regulates ozone-induced interleukin 8 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Jin, Y.; Duan, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Samet, J.M.; Wu, W. Regulation of ozone-induced lung inflammation by the epidermal growth factor receptor in mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Hsieh, H.L.; Lee, I.T.; Yang, C.M. Enterovirus 71 modulates a COX-2/PGE2/cAMP-dependent viral replication in human neuroblastoma cells: Role of the c-Src/EGFR/p42/p44 MAPK/CREB signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Hsieh, H.L.; Lee, I.T.; Yang, C.M. Enterovirus 71 induces integrin β1/EGFR-Rac1-dependent oxidative stress in SK-N-SH cells: Role of HO-1/CO in viral replication. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 3316–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, B.; Du, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yin, J.; Peng, B.; He, X.; et al. mir-27a suppresses EV71 replication by directly targeting EGFR. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Kobe, B. Uses for JNK: The many and varied substrates of the c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 1061–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.; Narang, H. The complexity of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) made simple. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3525–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xia, J.; Long, J.E. Prediction of signaling pathways involved in enterovirus 71 infection by algorithm analysis based on miRNA profiles and their target genes. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Shi, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Ji, Y.; et al. Activation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways promotes enterovirus 71 infection in immature dendritic cells. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.Y.; Ong, B.K.; Chu, J.J. The role of misshapen NCK-related kinase (MINK), a novel Ste20 family kinase, in the IRES-mediated protein translation of human enterovirus 71. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, L.; Jin, Y.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Regulation of host responses and viral replication by the mitogen-activated protein kinases in intestinal epithelial cells infected with enterovirus 71. Virus Res. 2015, 197, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Cardona, C.J.; Xing, Z. Intrinsic apoptosis and proinflammatory cytokines regulated in human astrocytes infected with enterovirus 71. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Ohtomo, T.; Sato, S.; Sugamata, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Hisamoto, N.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Tsuchiya, M.; Matsumoto, K. An evolutionarily conserved motif in the TAB1 C-terminal region is necessary for interaction with and activation of TAK1 MAPKKK. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24396–24400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Han, N.; Xiao, X.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Enterovirus 71 3C inhibits cytokine expression through cleavage of the TAK1/TAB1/TAB2/TAB3 complex. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9830–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.K.; Mohan, C. PI3K/AKT signaling and systemic autoimmunity. Immunol. Res. 2005, 31, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.T.; Stephens, L.R. PI3K signalling in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Peng, H.; Shi, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Ji, Y.; Yao, Y.; He, C.; et al. Differential gene expressions of the MAPK signaling pathway in enterovirus 71-infected rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Li, X.; Hou, X.; Peng, H.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, M.; Ji, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Differential apoptosis gene expressions of rhabdomyosarcoma cells in response to enterovirus 71 infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y. Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway limits JNK-mediated apoptosis during EV71 infection. Virus Res. 2014, 192, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pchitskaya, E.; Popugaeva, E.; Bezprozvanny, I. Calcium signaling and molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Calcium 2018, 70, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.R.; Lu, W.W.; Lai, J.Z.; Tsai, F.L.; Wu, S.H.; Lin, C.W.; Kung, S.H. Calcium flux and calpain-mediated activation of the apoptosis-inducing factor contribute to enterovirus 71-induced apoptosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haolong, C.; Du, N.; Hongchao, T.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Hua, Z.; Wenliang, Z.; Lei, S.; Po, T. Enterovirus 71 VP1 activates calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ii and results in the rearrangement of vimentin in human astrocyte cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| TLRs | Ligand | Cell Type | Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR? | No data | Intestinal epithelial cells | Human | [44] |
| TLR2 | No data | MDMs | Human | [60] |
| TLR3 | No data | DCs, PBMCs | Mouse, Human | [26,60] |
| TLR4 | PAMPs (dsRNA?) | DCs, PBMCs | Mammalian cells, Human | [57,60] |
| TLR7 | DAMPs? | 16HBE, MDMs, PBMCs | Human | [41,58,60] |
| TLR8 | No data | MDMs | Human | [60] |
| TLR9 | Endogenous DNA | pDCs | Mouse | [13] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; Duan, G. Antiviral and Inflammatory Cellular Signaling Associated with Enterovirus 71 Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040155
Jin Y, Zhang R, Wu W, Duan G. Antiviral and Inflammatory Cellular Signaling Associated with Enterovirus 71 Infection. Viruses. 2018; 10(4):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040155
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yuefei, Rongguang Zhang, Weidong Wu, and Guangcai Duan. 2018. "Antiviral and Inflammatory Cellular Signaling Associated with Enterovirus 71 Infection" Viruses 10, no. 4: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040155
APA StyleJin, Y., Zhang, R., Wu, W., & Duan, G. (2018). Antiviral and Inflammatory Cellular Signaling Associated with Enterovirus 71 Infection. Viruses, 10(4), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040155






