Rapid Construction of a Replication-Competent Infectious Clone of Human Adenovirus Type 14 by Gibson Assembly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Bacteria, Viruses, Plasmid and Enzymes
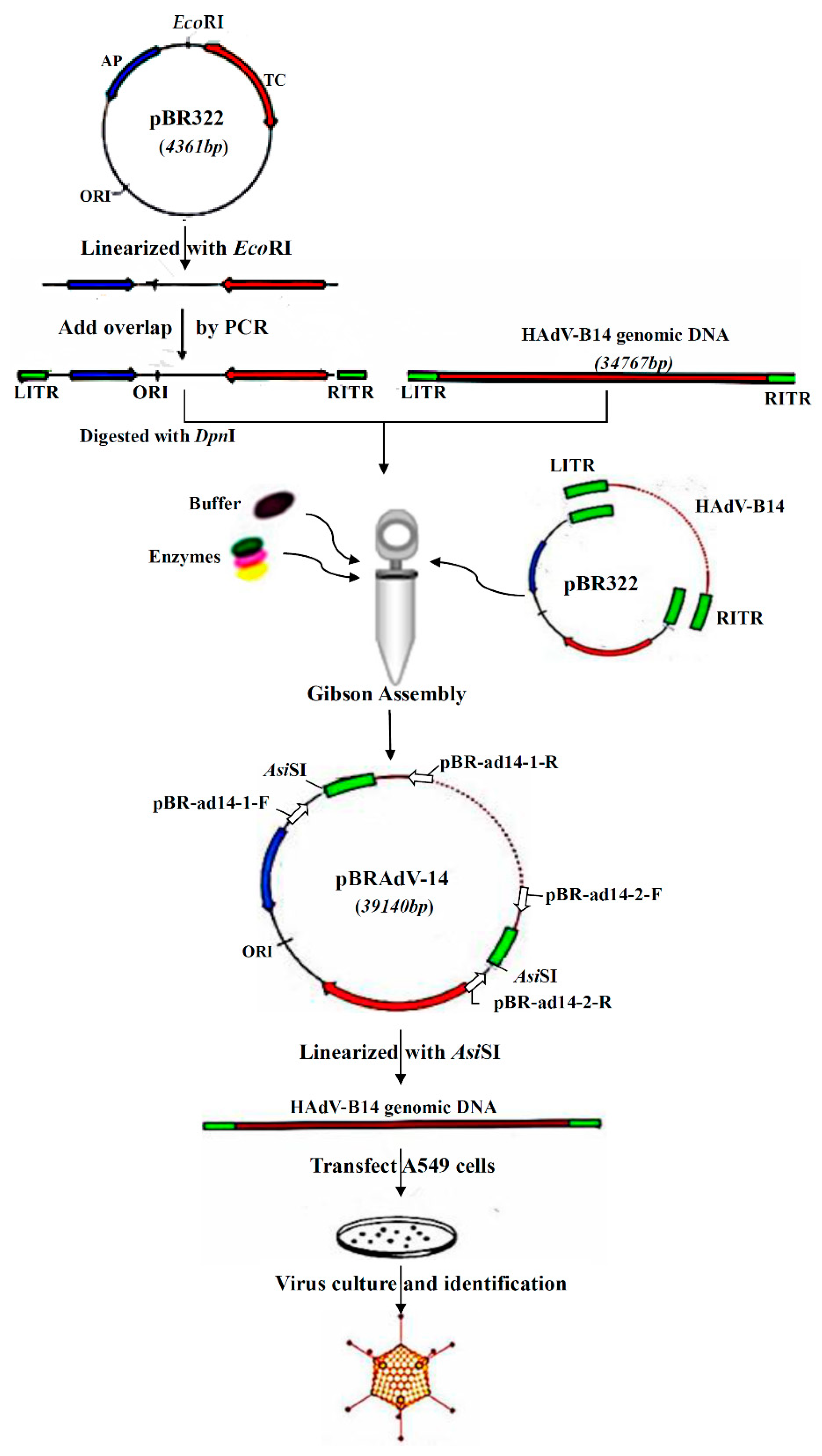
2.2. Construction and Screening of Recombinant Infectious Clones of HAdV-B14 by Gibson Assembly Method
2.3. Rescue and Amplification of HAdV-B14 Infectious Viral Particles
2.4. Restriction Enzyme and Complete Plasmid Sequencing Analysis of the Infectious Clone pBRAdV14 and the Adenoviral Genome
2.5. Direct Immunofluorescence and Fluorescence Forming Assay
2.6. One-Step Growth Curves of HAdV-B14
2.7. Electron Microscopic Observation
3. Results
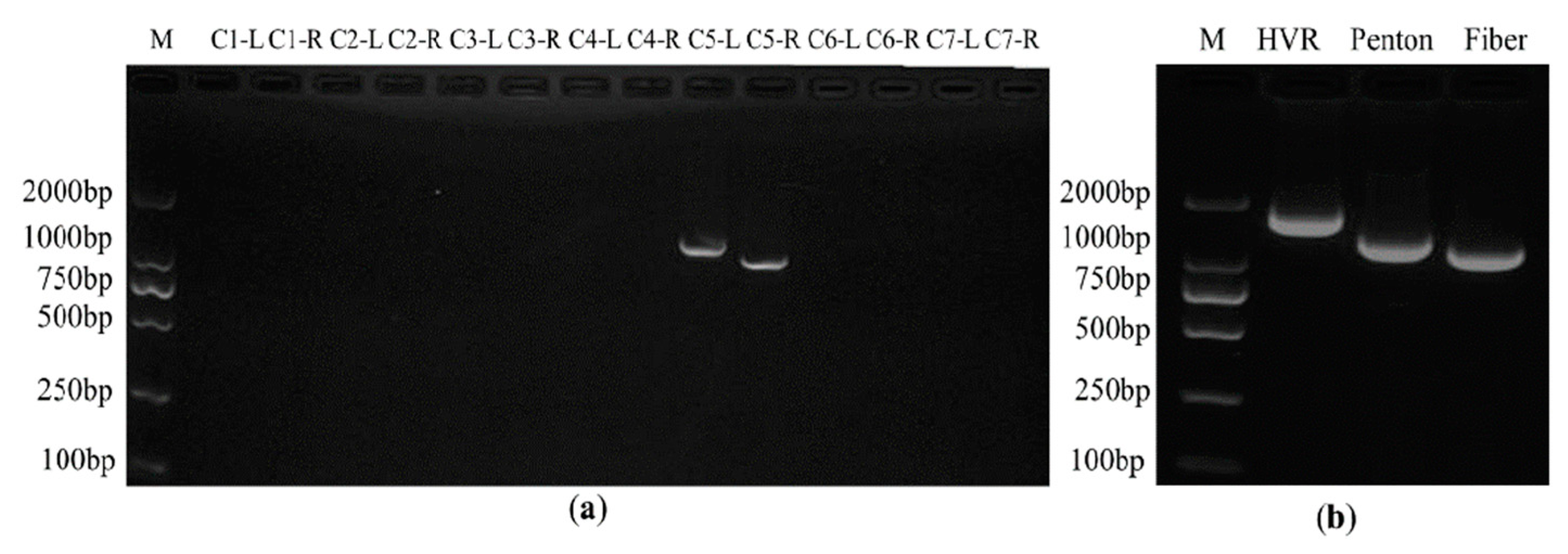
3.1. Identification of Infectious Clones of HAdV-B14 and Rescue of the Viral Particles
3.2. The Identification of the Genomic Sequences of pBRAdV14 and Plasmid Derived Viruses
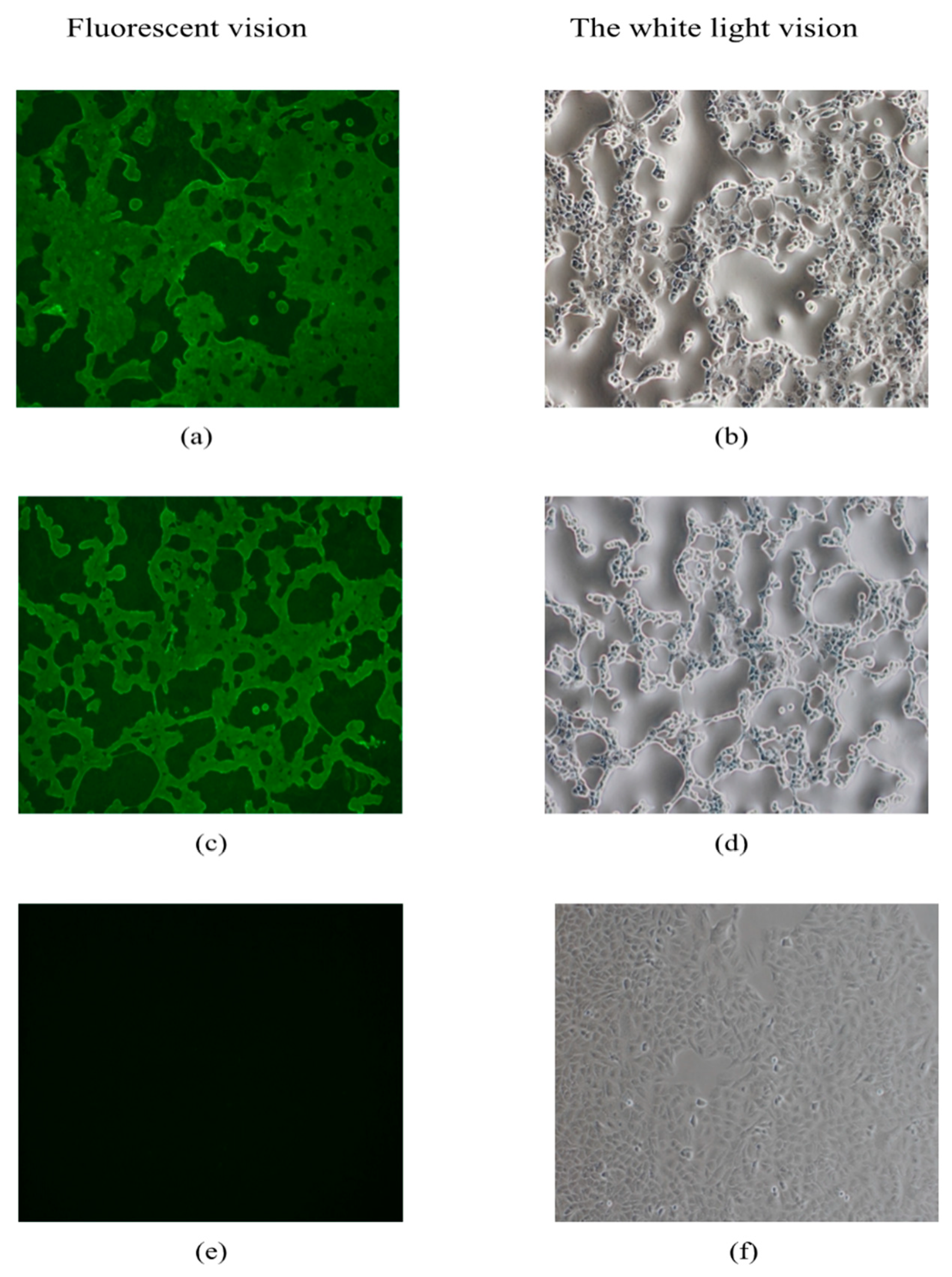
3.3. Direct Immunofluorescence Assay
3.4. Growth Characteristics of pBRAdV14 Derived Virus
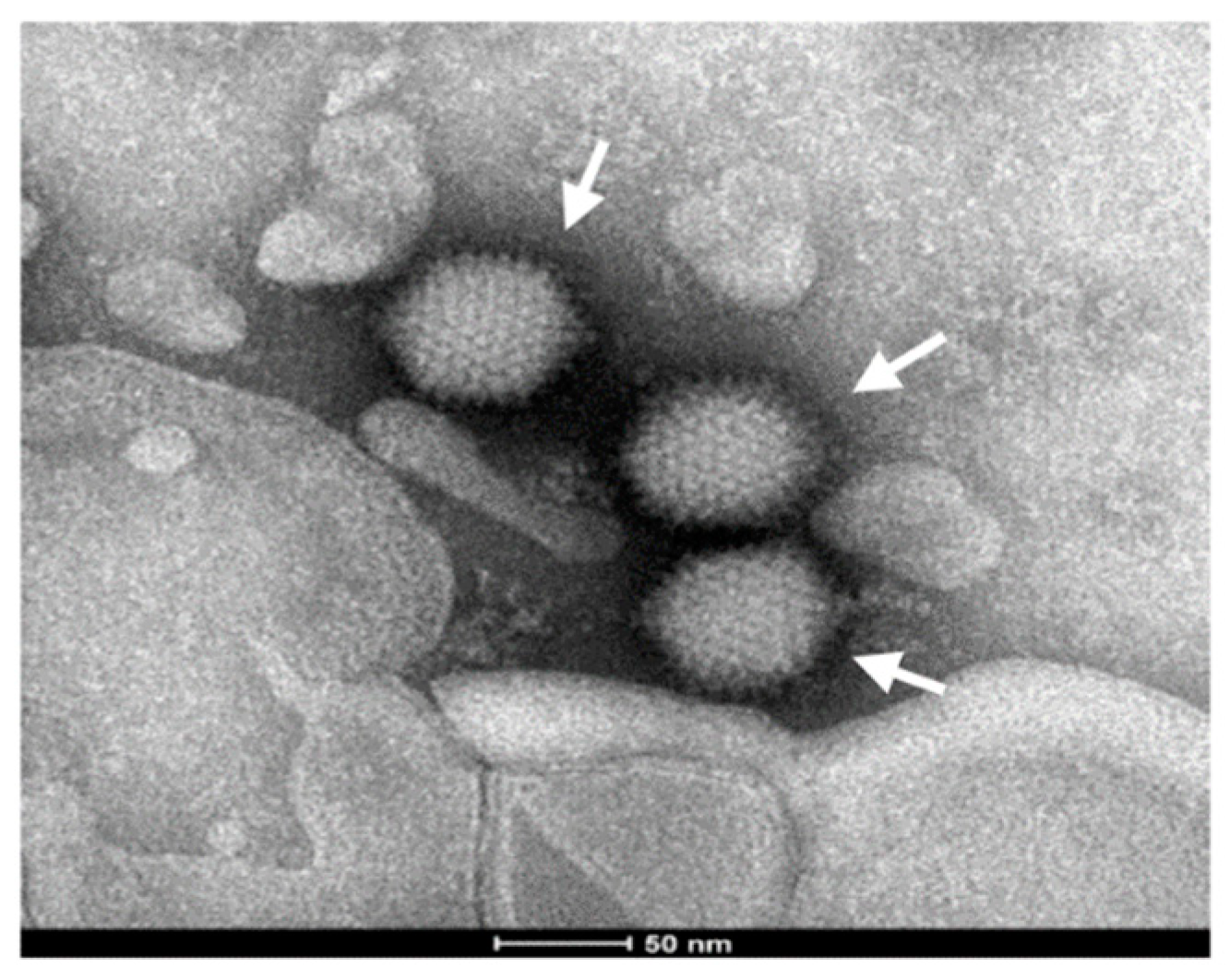
3.5. Electron Microscopic Observation
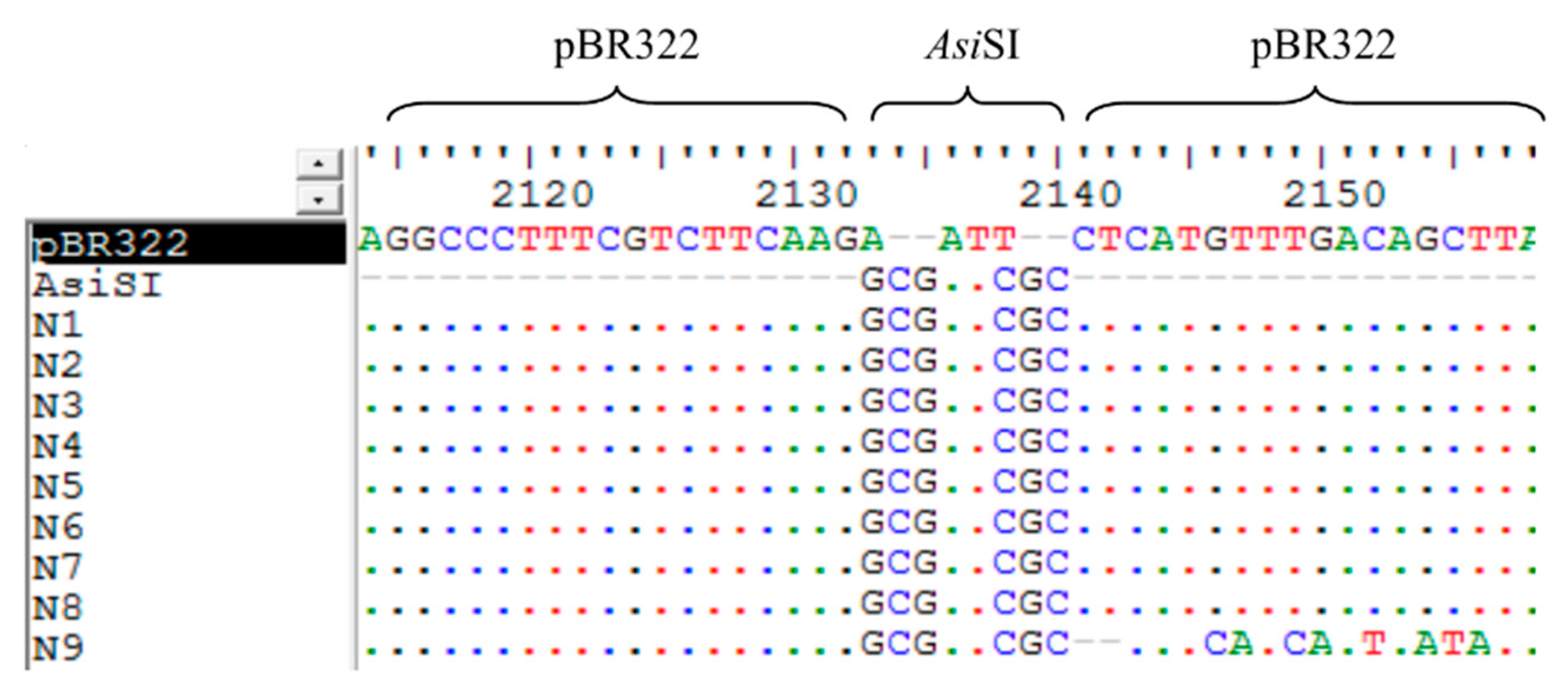
3.6. The Analysis of the Sequences of False Positive Infectious Clones
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kajan, G.L.; Kajon, A.E.; Pinto, A.C.; Bartha, D.; Arnberg, N. The complete genome sequence of human adenovirus 84, a highly recombinant new Human mastadenovirus D type with a unique fiber gene. Virus Res. 2017, 242, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, H.; Aoki, K.; Ishida, S.; Ohno, S.; Kitaichi, N.; Ishiko, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Gonzalez, G.; et al. Recombination analysis of intermediate human adenovirus type 53 in Japan by complete genome sequence. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seto, D.; Chodosh, J.; Brister, J.R.; Jones, M.S. Using the whole-genome sequence to characterize and name human adenoviruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5701–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushima, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Kano, A.; Nakajima, E.; Ishimaru, Y.; Dey, S.K.; Watanabe, Y.; Adachi, F.; Suzuki, K.; Mitani, K.; et al. Novel human adenovirus strain, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.N.; Harrach, B.; Ganac, R.D.; Gozum, M.M.; Dela, C.W.; Riedel, B.; Pan, C.; Delwart, E.L.; Schnurr, D.P. New adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5978–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, E.; Dhingra, A.; Liebert, U.G.; Bergs, S.; Ganzenmueller, T.; Heim, A. Three novel, multiple recombinant types of species of human mastadenovirus D (HAdV-D 73, 74 & 75) isolated from diarrhoeal faeces of immunocompromised patients. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.M.; Singh, G.; Lee, J.Y.; Dehghan, S.; Rajaiya, J.; Liu, E.B.; Yousuf, M.A.; Betensky, R.A.; Jones, M.S.; Dyer, D.W.; et al. Molecular evolution of human adenoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Jing, S.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dehghan, S.; Shamsaddini, A.; Yan, Y.; Li, M.; Seto, D. Comparative genomic analysis of two emergent human adenovirus type 14 respiratory pathogen isolates in China reveals similar yet divergent genomes. Emerg. Microbes & Infect. 2017, 6, e92. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Dehghan, S.; Seto, D. Pitfalls of restriction enzyme analysis in identifying, characterizing, typing, and naming viral pathogens in the era of whole genome data, as illustrated by HAdV type 55. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, D.; Cao, B.; Zhao, S.; Wan, C. Genome Sequence of Human Adenovirus Type 55, a Re-Emergent Acute Respiratory Disease Pathogen in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12441–12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, W.; Wan, C. Genome sequence of the first human adenovirus type 14 isolated in China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7019–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Yan, Y.; Jing, S.; Li, W.-G.; Chen, W.-W.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, S.; Cao, N.; Ou, J.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Re-emergent Human Adenovirus Type 55 Pathogens Associated With Adult Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia Reveals Conserved Genomes and Capsid Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Veen, J.; Kok, G. Isolation and typing of adenoviruses recovered from military recruits with acute respiratory disease in The Netherlands. Am. J. Hyg. 1957, 65, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kendall, E.J.; Riddle, R.W.; Tuck, H.A.; Rodan, K.S.; Andrews, B.E.; McDonald, J.C. Pharyngo-conjunctival fever; school outbreaks in England during the summer of 1955 associated with adenovirus types 3, 7, and 14. Br. Med. J. 1957, 2, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houng, H.S.; Gong, H.; Kajon, A.E.; Jones, M.S.; Kuschner, R.A.; Lyons, A.; Lott, L.; Lin, K.H.; Metzgar, D. Genome sequences of human adenovirus 14 isolates from mild respiratory cases and a fatal pneumonia, isolated during 2006–2007 epidemics in North America. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flanagan, D.; O’Donnell, J.; Domegan, L.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Connell, J.; Coughlan, S.; De Gascun, C.; Carr, M.J. First reported cases of human adenovirus serotype 14p1 infection, Ireland, October 2009 to July 2010. Eur. Surveill. 2011, 16, 19801. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.J.; Kajon, A.E.; Lu, X.; Dunford, L.; O’Reilly, P.; Holder, P.; De Gascun, C.F.; Coughlan, S.; Connell, J.; Erdman, D.D.; et al. Deaths associated with human adenovirus-14p1 infections, Europe, 2009–2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parcell, B.J.; McIntyre, P.G.; Yirrell, D.L.; Fraser, A.; Quinn, M.; Templeton, K.; Christie, S.; Romanes, F. Prison and community outbreak of severe respiratory infection due to adenovirus type 14p1 in Tayside, UK. J. Public Health 2015, 37, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzgar, D.; Osuna, M.; Kajon, A.E.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Irvine, M.; Russell, K.L. Abrupt emergence of diverse species B adenoviruses at US military recruit training centers. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Yu, D.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, P.; Gray, G.C.; Meng, L.; Xu, W. Outbreak of febrile respiratory illness associated with human adenovirus type 14p1 in Gansu Province, China. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binn, L.N.; Sanchez, J.L.; Gaydos, J.C. Emergence of adenovirus type 14 in US military recruits—A new challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.F.; Schmidt, M.A.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Campbell, M.; Thomas, A.; Cieslak, P.R.; Grenz, L.D.; Tsaknardis, L.; Gleaves, C.; et al. A community-based outbreak of severe respiratory illness caused by human adenovirus serotype 14. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girouard, G.; Garceau, R.; Thibault, L.; Oussedik, Y.; Bastien, N.; Li, Y. Adenovirus serotype 14 infection, New Brunswick, Canada, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Z.; Butt, A.M.; An, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, W.; Qin, C.; Cao, W.C.; Tong, Y. Genomic analysis of HAdV-B14 isolate from the outbreak of febrile respiratory infection in China. Genomics 2013, 102, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Kong, W.; Yu, X. Trimeric knob protein specifically distinguishes neutralizing antibodies to different human adenovirus species: Potential application for adenovirus seroepidemiology. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.R.; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.G. Synthesis of DNA fragments in yeast by one-step assembly of overlapping oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 6984–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merryman, C.; Gibson, D.G. Methods and applications for assembling large DNA constructs. Metab. Eng. 2012, 14, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.T.; Gray, G.C.; Poddar, S.K. A modified rapid method of nucleic acid isolation from suspension of matured virus: Applied in restriction analysis of DNA from an adenovirus prototype strain and a patient isolate. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagawa, M.; Matsuda, A.; Ishiyama, T.; Goto, H.; Sato, G. A rapid and simple method for preparation of adenovirus DNA from infected cells. Microbiol. Immunol. 1983, 27, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Acute respiratory disease associated with adenovirus serotype 14-four states, 2006–2007. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2007, 56, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Kajon, A.E.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Louie, J.; Schnurr, D.; George, K.S.; Koopmans, M.P.; Allibhai, T.; Metzgar, D. Molecular epidemiology and brief history of emerging adenovirus 14-associated respiratory disease in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, J.K.; Kajon, A.E.; Holodniy, M.; Guardia-LaBar, L.; Lee, B.; Petru, A.M.; Hacker, J.K.; Schnurr, D.P. Severe pneumonia due to adenovirus serotype 14: A new respiratory threat? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Olphen, A.L.; Mittal, S.K. Generation of infectious genome of bovine adenovirus type 3 by homologous recombination in bacteria. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 77, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Corredor, J.C.; Griffin, B.D.; Krell, P.J.; Nagy, E. Fowl Adenovirus 4 (FAdV-4)-Based Infectious Clone for Vaccine Vector Development and Viral Gene Function Studies. Viruses 2018, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirena, D.; Ruzsics, Z.; Schaffner, W.; Greber, U.F.; Hemmi, S. The nucleotide sequence and a first generation gene transfer vector of species B human adenovirus serotype 3. Virology 2005, 343, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, J.; Ehrhardt, A. Novel Vector Construction Based on Alternative Adenovirus Types via Homologous Recombination. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2018, 29, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, X.; Seto, D.; Zheng, B.-J.; Tian, X.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R. Construction and characterization of a replication-competent human adenovirus type 3-based vector as a live-vaccine candidate and a viral delivery vector. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z. Rapid Construction of Complex Plant RNA Virus Infectious cDNA Clones for Agroinfection Using a Yeast-E. coli-Agrobacterium Shuttle Vector. Viruses 2017, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuo, D.; Shen, W.; Yan, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, P. Rapid Construction of Stable Infectious Full-Length cDNA Clone of Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus Using In-Fusion Cloning. Viruses 2015, 7, 6241–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miciak, J.J.; Hirshberg, J.; Bunz, F. Seamless assembly of recombinant adenoviral genomes from high-copy plasmids. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijora, T.; Blawid, R.; Costa, D.K.T.; Aragao, F.J.L.; Souto, E.R.; Nagata, T. Construction of an agroinfectious clone of bean rugose mosaic virus using Gibson Assembly. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordat, A.; Houvenaghel, M.C.; German-Retana, S. Gibson assembly: An easy way to clone potyviral full-length infectious cDNA clones expressing an ectopic VPg. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blawid, R.; Nagata, T. Construction of an infectious clone of a plant RNA virus in a binary vector using one-step Gibson Assembly. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 222, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, T.C.; Kierstead, L.; Gupta, S.B.; Nikas, A.A.; Kallas, E.G.; Novitsky, V.; Mbewe, B.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Schechter, M.; Vardas, E.; et al. International epidemiology of human pre-existing adenovirus (Ad) type-5, type-6, type-26 and type-36 neutralizing antibodies: Correlates of high Ad5 titers and implications for potential HIV vaccine trials. Vaccine 2010, 28, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, K.M.; Da Costa, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Berry, D.; Lindsay, R.W.; Darrah, P.A.; Wang, L.; Cheng, C.; Kong, W.P.; Gall, J.G.; et al. Comparative analysis of the magnitude, quality, phenotype, and protective capacity of simian immunodeficiency virus gag-specific CD8+ T cells following human-, simian-, and chimpanzee-derived recombinant adenoviral vector immunization. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2720–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | PCR Product (bp) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| pBR-ITR-F | ATTGGCACCATTCCATCTATAAGGTAT ATTATTGATGATGgcgatcgcctcatgtttgaca gcttatcatcg | 4453 | Amplification of pBR322 and addition of 5′ ITR homologous arm (40 bp) and AsiSI restriction site at both ends |
| pBR-ITR-R | ATTGGCACCATTCCATCTATAAGGTAT ATTATTGATGATGgcgatcgccttgaagacga aagggcctcg | ||
| pBR-ad14-1-F | CCATCACAAGACAAGCCACA | 1334 | Screening of positive infectious clones (targeting the left ligation region) |
| pBR-ad14-1-R | GCCTCAACCTACTACTGGG | ||
| pBR-ad14-2-F | CTTACTG TCATGCCATCCG | 1113 | Screening of positive infectious clones (targeting the right ligation region) |
| pBR-ad14-2-R | TGAGTGCCAGCGAGAAGA | ||
| HVR-F | CAGGATGCT TCGGAGTAC | 1685 | Hexon amplification |
| HVR-R | TTTCTGAAGTTCCACTCGT | ||
| Fiber-F | CCCTCTTCCCAACTCTGG | 1253 | Fiber amplification |
| Fiber-R | GGGGAGGCAAAATAACT | ||
| Penton-F | CTATCAGAATGACCACAG | 1153 | Penton amplification |
| Penton-R | TCCCGTG ATCTGTGAGAG |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Feng, L.; Ou, J.; Cao, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, W.; Wan, C.; et al. Rapid Construction of a Replication-Competent Infectious Clone of Human Adenovirus Type 14 by Gibson Assembly. Viruses 2018, 10, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100568
Pan H, Yan Y, Zhang J, Zhao S, Feng L, Ou J, Cao N, Li M, Zhao W, Wan C, et al. Rapid Construction of a Replication-Competent Infectious Clone of Human Adenovirus Type 14 by Gibson Assembly. Viruses. 2018; 10(10):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100568
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Haibin, Yuqian Yan, Jing Zhang, Shan Zhao, Liqiang Feng, Junxian Ou, Na Cao, Min Li, Wei Zhao, Chengsong Wan, and et al. 2018. "Rapid Construction of a Replication-Competent Infectious Clone of Human Adenovirus Type 14 by Gibson Assembly" Viruses 10, no. 10: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100568
APA StylePan, H., Yan, Y., Zhang, J., Zhao, S., Feng, L., Ou, J., Cao, N., Li, M., Zhao, W., Wan, C., Ismail, A. M., Rajaiya, J., Chodosh, J., & Zhang, Q. (2018). Rapid Construction of a Replication-Competent Infectious Clone of Human Adenovirus Type 14 by Gibson Assembly. Viruses, 10(10), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100568





