Whole Genome Characterization of Orthopoxvirus (OPV) Abatino, a Zoonotic Virus Representing a Putative Novel Clade of Old World Orthopoxviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Whole Genome Assembly
2.2. Genome Annotation
- The pipeline takes the given genome, and searches for all ORFs longer than 93 bp (i.e. the size of the shortest annotated poxvirus gene).
- Next, it translates ORFs into their corresponding amino acid sequences.
- Then, it uses BLASTp to find orthologous genes for every ORF in a previously established database of all the protein sequences belonging to the family of Poxviridae.
- Lastly, it collects the homologous genes of each ORF, together with their similarity values (see below), in a GenBank file.
2.3. Core Gene Set Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Similarity Analysis
3. Results
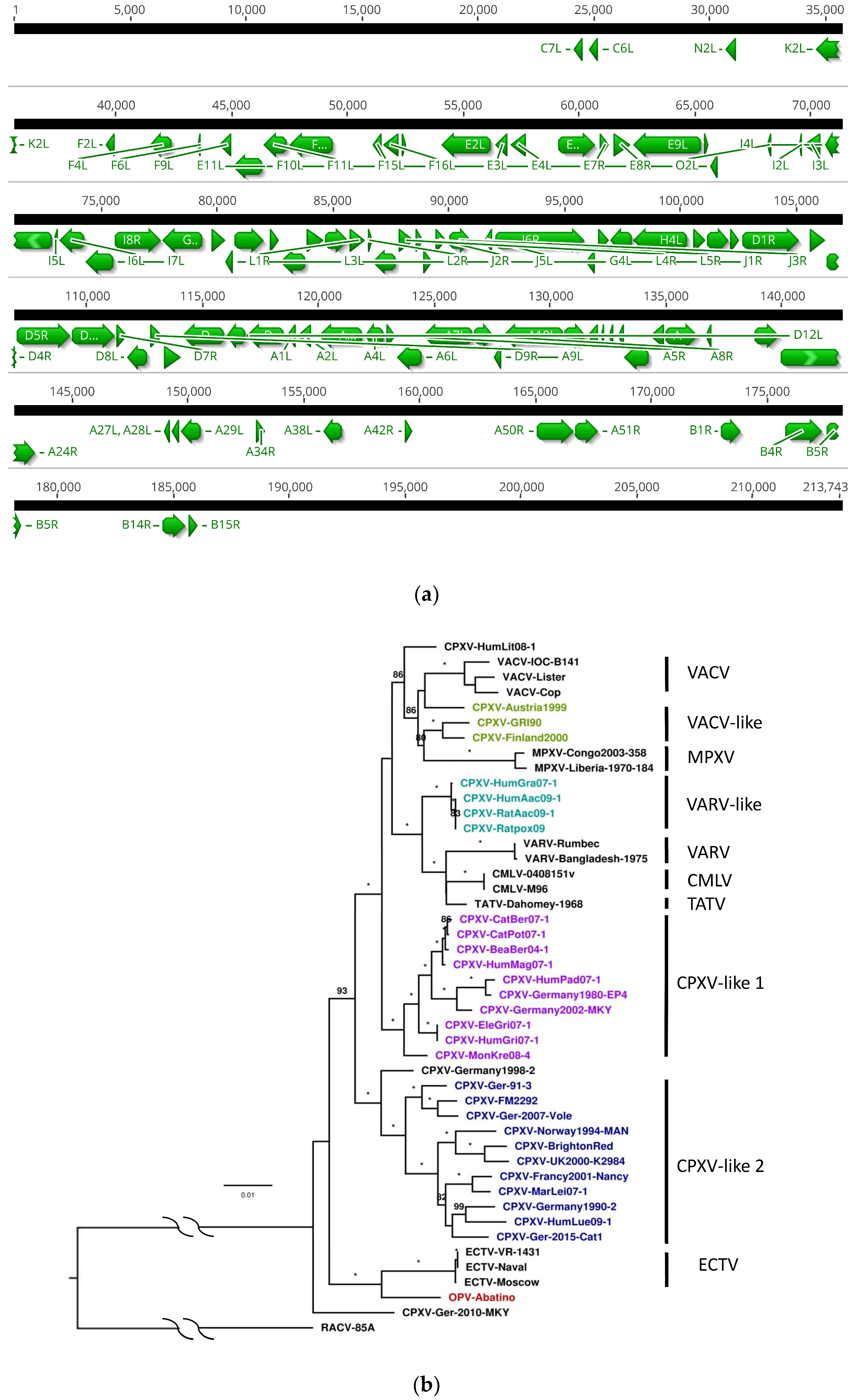
3.1. Whole Genome Assembly
3.2. Genome Annotation
3.3. Core Gene Set Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
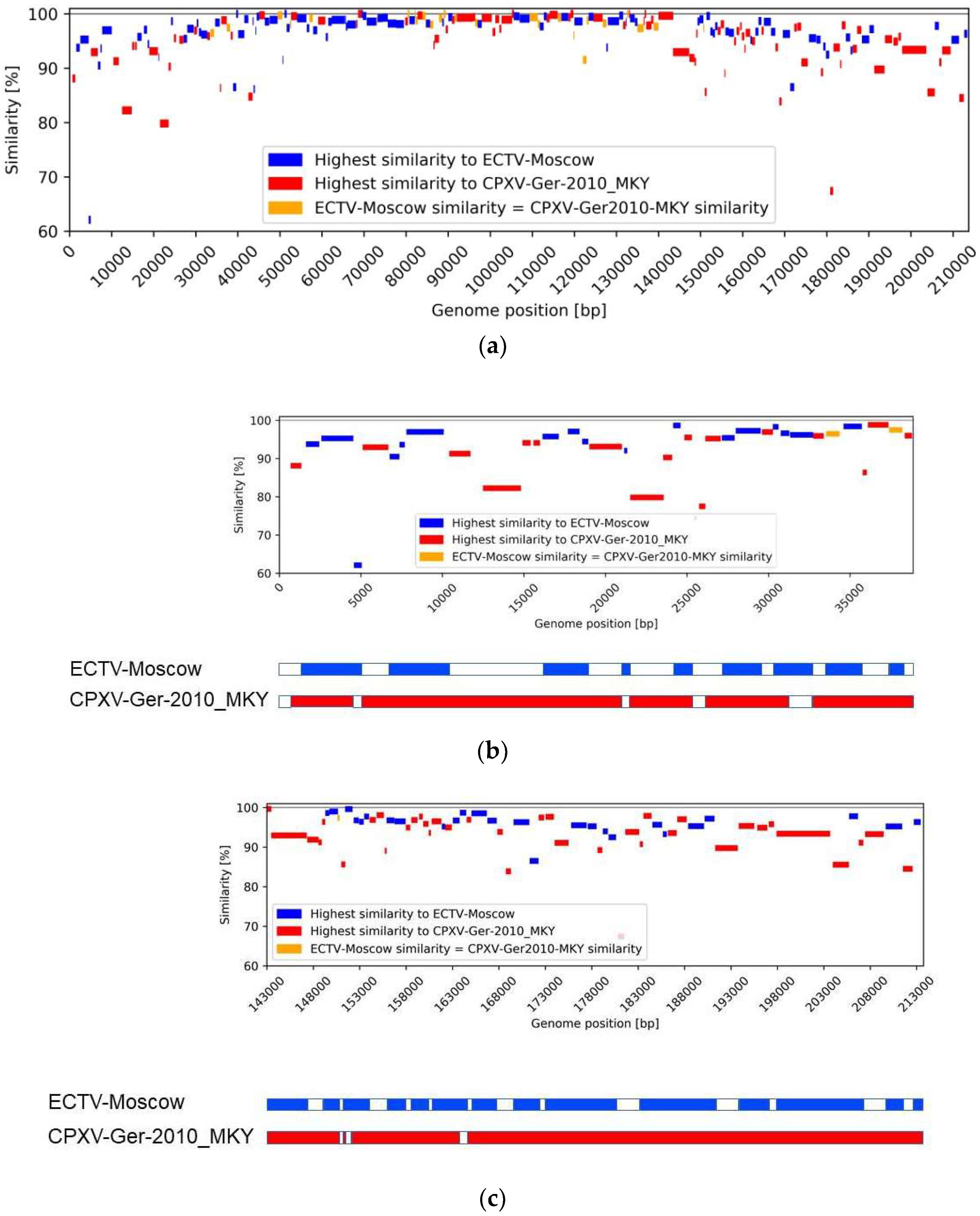
3.4. Similarity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McFadden, G. Poxvirus tropism. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2005, 3, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smithson, C.; Tang, N.; Sammons, S.; Frace, M.; Batra, D.; Li, Y.; Emerson, G.L.; Carroll, D.S.; Upton, C. The genomes of three North American orthopoxviruses. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, D.S.; Emerson, G.L.; Li, Y.; Sammons, S.; Olson, V.; Frace, M.; Nakazawa, Y.; Czerny, C.P.; Tryland, M.; et al. Chasing Jenner’s Vaccine: Revisiting Cowpox Virus Classification. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.G.; Guagliardo, S.A.J.; Nakazawa, Y.J.; Doty, J.B.; Mauldin, M.R. Understanding orthopoxvirus host range and evolution: from the enigmatic to the usual suspects. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 28, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauldin, M.; Antwerpen, M.; Emerson, G.; Li, Y.; Zoeller, G.; Carroll, D.; Meyer, H. Cowpox virus: What’s in a Name? Viruses 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, J.J. Genome Sequence Diversity and Clues to the Evolution of Variola (Smallpox) Virus. Science 2006, 313, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moss, B. Poxvirus DNA Replication. Cold Spr. Harbor Persp. Biol. 2013, 5, a010199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, R.C.; Wang, C.; Hatcher, E.L.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss. Viruses 2010, 2, 1933–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Wang, C.; Upton, C. Poxviruses: past, present and future. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, M.M.; McFadden, G.; Karupiah, G.; Chaudhri, G. Immunopathogenesis of poxvirus infections: forecasting the impending storm. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bratke, K.A.; McLysaght, A. Identification of multiple independent horizontal gene transfers into poxviruses using a comparative genomics approach. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2008, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLysaght, A.; Baldi, P.F.; Gaut, B.S. Extensive gene gain associated with adaptive evolution of poxviruses. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratke, K.A.; McLysaght, A.; Rothenburg, S. A survey of host range genes in poxvirus genomes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.L.; Irausquin, S.; Friedman, R. The evolutionary biology of poxviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mavian, C.; López-Bueno, A.; Bryant, N.A.; Seeger, K.; Quail, M.A.; Harris, D.; Barrell, B.; Alcami, A. The genome sequence of ectromelia virus Naval and Cornell isolates from outbreaks in North America. Virology 2014, 462–463, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Ulrich, R.; Weber, S.; Osterrieder, N.; Keller, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Beer, M. Experimental Cowpox Virus (CPXV) Infections of Bank Voles: Exceptional Clinical Resistance and Variable Reservoir Competence. Viruses 2017, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, P.W.; Radonić, A.; Kurth, A.; Nitsche, A. Genome-Wide Comparison of Cowpox Viruses Reveals a New Clade Related to Variola Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Pfaff, F.; Jenckel, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Höper, D.; Antwerpen, M.; Meyer, H.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, D. Classification of Cowpox Viruses into Several Distinct Clades and Identification of a Novel Lineage. Viruses 2017, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.; Franke, A.; Jenckel, M.; Tamošiūnaitė, A.; Schluckebier, J.; Granzow, H.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, S.; Ulrich, R.G.; Höper, D.; et al. Out of the Reservoir: Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of a Novel Cowpox Virus Isolated from a Common Vole. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10959–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurth, A.; Wibbelt, G.; Gerber, H.-P.; Petschaelis, A.; Pauli, G.; Nitsche, A. Rat-to-Elephant-to-Human Transmission of Cowpox Virus. Emer. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 670–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stagegaard, J.; Kurth, A.; Stern, D.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Pocknell, A.; Nitsche, A.; Schrick, L. Seasonal recurrence of cowpox virus outbreaks in captive cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prkno, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Goerigk, D.; Kaiser, M.; van Maanen, A.; Jeske, K.; Jenckel, M.; Pfaff, F.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Beer, M.; et al. Epidemiological Investigations of Four Cowpox Virus Outbreaks in Alpaca Herds, Germany. Viruses 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, Y.P.; Hsu, C.H.; Werle, Z.R.; Olson, L.E.; Cooper, M.P.; Castrodale, L.J.; Fowler, N.; McCollum, A.M.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Emerson, G.L.; et al. Novel Orthopoxvirus Infection in an Alaska Resident. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gigante, C.; Khmaladze, E.; Liu, P.; Tang, S.; Wilkins, K.; Zhao, K.; Davidson, W.; Nakazawa, Y.; Maghlakelidze, G.; et al. Genome Sequences of Akhmeta Virus, an Early Divergent Old World Orthopoxvirus. Viruses 2018, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canese, M.G.; Lavazza, A.; Massone, A.; Galeano, F.; Boldini, M. Feline Poxvirus Infection: A case report. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 1997, 139, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scagliarini, A.; Casà, G.; Trentin, B.; Gallina, L.; Savini, F.; Morent, M.; Lavazza, A.; Puleio, R.; Buttaci, C.; Cannella, V.; et al. Evidence of zoonotic Poxviridae coinfections in clinically diagnosed papillomas using a newly developed mini-array test. J. Vet. Diag. Invest. 2016, 28, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardeti, G.; Brozzi, A.; Eleni, C.; Polici, N.; D’Alterio, G.; Carletti, F.; Scicluna, M.T.; Castilletti, C.; di Caro, A.; Autorino, G.L.; et al. Cowpox Virus in Llama, Italy. Emer. Infect. Dis. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carletti, F.; Bordi, L.; Castilletti, C.; di Caro, A.; Falasca, L.; Gioia, C.; Ippolito, G.; Zaniratti, S.; Beltrame, A.; Viale, P.; et al. Cat-to-Human Orthopoxvirus Transmission, Northeastern Italy. Emer. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardeti, G.; Gruber, C.E.M.; Eleni, C.; Carletti, F.; Castilletti, C.; Manna, G.; Rosone, F.; Giombini, E.; Selleri, M.; Lapa, D.; et al. Fatal Outbreak in Tonkean Macaques Caused by Possibly Novel Orthopoxvirus, Italy, January 20151. Emer. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puro, V.; Fusco, F.M.; Castilletti, C.; Carletti, F.; Colavita, F.; Agrati, C.; Di Caro, A.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Ippolito, G. Occupational transmission of an Orthopoxvirus infection during an outbreak in a colony of Macaca. tonkeana in Lazio Region, Italy, 2015. Zoonoses. Public Health 2018, 65, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanave, G.; Dowgier, G.; Decaro, N.; Albanese, F.; Brogi, E.; Parisi, A.; Losurdo, M.; Lavazza, A.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, C.; Elia, G. Novel Orthopoxvirus and Lethal Disease in Cat, Italy. EID 2018, 24, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tausch, S.H.; Renard, B.Y.; Nitsche, A.; Dabrowski, P.W. RAMBO-K: Rapid and Sensitive Removal of Background Sequences from Next Generation Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Gen. Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinfor. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl. Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emerson, G.L.; Li, Y.; Frace, M.A.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.A.; Khristova, M.L.; Govil, D.; Sammons, S.A.; Regnery, R.L.; Karem, K.L.; Damon, I.K.; et al. The phylogenetics and ecology of the orthopoxviruses endemic to North America. PLoS ONE 2009, 29, e7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| OPV Abatino CDS | OPV Genome with Highest Identity in the Homologous CDS* | Phylogenetic Cluster ** | % Identity with Homologous CDS in OPV Abatino |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPVA001 | CPXV-Ratpox09 | VARV-like | 98.05 |
| OPVA002 | CPXV-HumLit08-1 | *** | 99.09 |
| OPVA005 | CPXV-HumLue09-1 | CPXV-like2 | 98.13 |
| OPVA011 | CPXV-GRI90 | VACV-like | 97.02 |
| OPVA012 | CPXV-GRI90 | VACV-like | 98.03 |
| OPVA020 | CPXV-Ratpox09 | VARV-like | 94.87 |
| OPVA024 | CPXV-Ratpox09 | VARV-like | 95.20 |
| OPVA025 | ECTV-VR-1431 | ECTV | 99.07 |
| OPVA036 | CPXV-HumLue09-1 | CPXV-like2 | 97.00 |
| OPVA040 | CPXV-Germany1990-2 | CPXV-like2 | 93.46 |
| OPVA044 | VACV-Cop | VACV | 94.55 |
| OPVA046 | CPXV-MarLei07-1 | CPXV-like2 | 95.79 |
| OPVA054 | ECTV-VR-1431 | ECTV | 99.33 |
| OPVA151 | ECTV-VR-1431 | ECTV | 99.22 |
| OPVA152 | CPXV-Ratpox09 | VARV-like | 94.85 |
| OPVA159 | CPXV-HumMag07-1 | CPXV-like1 | 93.85 |
| OPVA176 | CPXV-Austria1999 | VACV-like | 97.15 |
| OPVA178 | CPXV-Germany1998-2 | *** | 96.04 |
| OPVA184 | CPXV-Ger-2010-MKY | *** | 93.52 |
| OPVA187 | CPXV-GRI90 | VARV-like | 98.65 |
| OPVA197 | CPXV-Francy2001-Nancy | CPXV-like2 | 95.52 |
| OPVA202 | CPXV-GRI90 | VACV-like | 97.60 |
| OPVA207 | MPXV-Congo2003-358 | MPXV | 96.36 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruber, C.E.M.; Giombini, E.; Selleri, M.; Tausch, S.H.; Andrusch, A.; Tyshaieva, A.; Cardeti, G.; Lorenzetti, R.; De Marco, L.; Carletti, F.; et al. Whole Genome Characterization of Orthopoxvirus (OPV) Abatino, a Zoonotic Virus Representing a Putative Novel Clade of Old World Orthopoxviruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100546
Gruber CEM, Giombini E, Selleri M, Tausch SH, Andrusch A, Tyshaieva A, Cardeti G, Lorenzetti R, De Marco L, Carletti F, et al. Whole Genome Characterization of Orthopoxvirus (OPV) Abatino, a Zoonotic Virus Representing a Putative Novel Clade of Old World Orthopoxviruses. Viruses. 2018; 10(10):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100546
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruber, Cesare E. M., Emanuela Giombini, Marina Selleri, Simon H. Tausch, Andreas Andrusch, Alona Tyshaieva, Giusy Cardeti, Raniero Lorenzetti, Lorenzo De Marco, Fabrizio Carletti, and et al. 2018. "Whole Genome Characterization of Orthopoxvirus (OPV) Abatino, a Zoonotic Virus Representing a Putative Novel Clade of Old World Orthopoxviruses" Viruses 10, no. 10: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100546
APA StyleGruber, C. E. M., Giombini, E., Selleri, M., Tausch, S. H., Andrusch, A., Tyshaieva, A., Cardeti, G., Lorenzetti, R., De Marco, L., Carletti, F., Nitsche, A., Capobianchi, M. R., Ippolito, G., Autorino, G. L., & Castilletti, C. (2018). Whole Genome Characterization of Orthopoxvirus (OPV) Abatino, a Zoonotic Virus Representing a Putative Novel Clade of Old World Orthopoxviruses. Viruses, 10(10), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100546







