Apoptosis Induction by dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase R (PKR) in EPC Cells via Caspase 8 and 9 Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Virus
2.2. Electroporation of Plasmids into EPC and AGK Cells
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Apoptosis Assays
2.5. Measurement of Caspase-8 and -9 Activation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
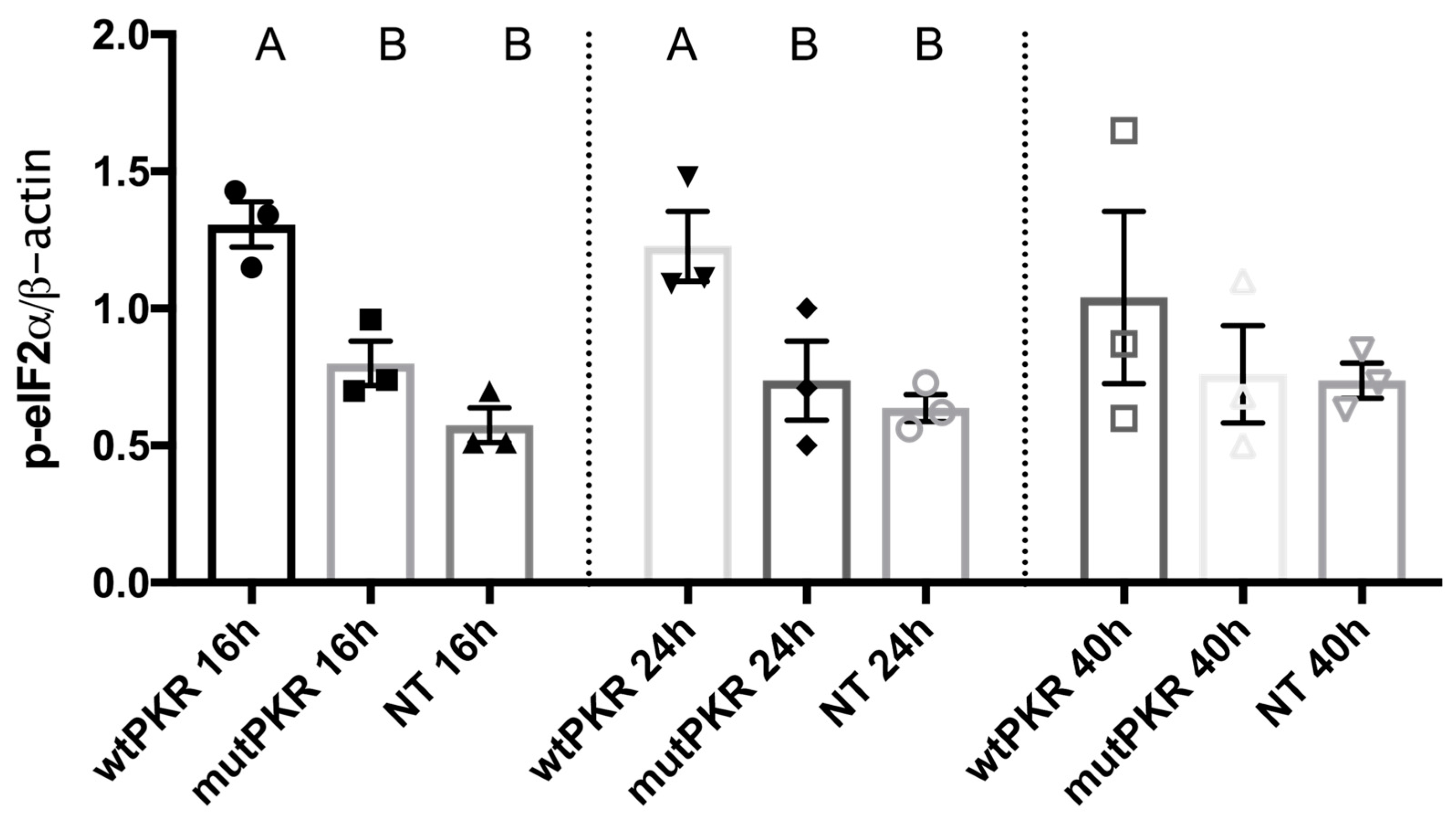
3.1. Carp PKR Overexpression Induce eIF2α Phosphorylation in EPC Cells
3.2. Carp PKR Overexpression Induce Apoptosis in EPC
3.3. Caspas-8 and -9 Are Activated in PKR-Induced Apoptosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perry, A.K.; Gang, C.; Zheng, D.; Hong, T.; Cheng, G. The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Weerd, N.A.; Samarajiwa, S.A.; Hertzog, P.J. Type I interferon receptors: Biochemistry and biological functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20053–20057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Evensen, Ø.; Munang’andu, H.M. A de novo transcriptome analysis shows that modulation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway by salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 favors virus replication in macrophage/dendritic-like TO-cells. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Takaoka, A. The interferon-α/β system in antiviral responses: A multimodal machinery of gene regulation by the IRF family of transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Gil, J.; Ventoso, I.; Guerra, S.; Domingo, E.; Rivas, C.; Esteban, M. Impact of protein kinase PKR in cell biology: From antiviral to antiproliferative action. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 1032–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Chong, K.; Kumar, A.; Williams, B. Identification of double-stranded RNA-binding domains in the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated p68 kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5447–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, S.J.; Thomis, D.C.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action: Identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2α protein kinase. Virology 1992, 188, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Cao, C.; Dar, A.C.; Tamura, T.; Ozato, K.; Sicheri, F.; Dever, T.E. Mechanistic link between PKR dimerization, autophosphorylation, and eIF2α substrate recognition. Cell 2005, 122, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Esteban, M. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated human p68 protein kinase inhibits the replication of vaccinia virus. Virology 1993, 193, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.P.; Kumar, K.U.; Kaufman, R.J. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 mediates apoptosis in response to activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Functional domains and the antiviral effect of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR from Paralichthys olivaceus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6889–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenburg, S.; Deigendesch, N.; Dey, M.; Dever, T.E.; Tazi, L. Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR of fishes and amphibians: Varying the number of double-stranded RNA binding domains and lineage-specific duplications. BMC Biol. 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Huang, G.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, H.F. Molecular cloning and characterisation of a fish PKR-like gene from cultured CAB cells induced by UV-inactivated virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 17, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenke, K.; Nam, Y.K.; Kim, K.H. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) in rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-K.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Gui, J.-F. Cooperative roles of fish protein kinase containing Z-DNA binding domains and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in interferon-mediated antiviral response. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12769–12780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamil, A.A.; Xu, C.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, O. PKR Activation Favors Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Replication in Infected Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.S.; Li, W.; Li, D.M.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.H.; Rao, Z.C.; Lin, G.; Hu, C.Y. Cloning, expression and functional analysis of PKR from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2922–2933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, I.; Kirchhoff, S.; Krammer, P.H. Regulation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kischkel, F.; Hellbardt, S.; Behrmann, I.; Germer, M.; Pawlita, M.; Krammer, P.; Peter, M. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5579–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnaiyan, A.M. The apoptosome: Heart and soul of the cell death machine. Neoplasia 1999, 1, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmer, A.D. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Translating basic knowledge into clinical practice. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7183–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.M. Caspases: The executioners of apoptosis. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slee, E.A.; Adrain, C.; Martin, S.J. Executioner caspase-3,-6, and-7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Evensen, Ø.; Munang’andu, H.M. De novo assembly and transcriptome analysis of Atlantic salmon macrophage/dendritic-like TO cells following type I IFN treatment and Salmonid alphavirus subtype-3 infection. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Ge, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q. Molecular cloning, immunohistochemical localization, characterization and expression analysis of caspase-8 from the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) exposed to ammonia. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espín, R.; Roca, F.J.; Candel, S.; Sepulcre, M.P.; González-Rosa, J.M.; Alcaraz-Pérez, F.; Meseguer, J.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mercader, N.; Mulero, V. TNF receptors regulate vascular homeostasis in zebrafish through a caspase-8, caspase-2 and P53 apoptotic program that bypasses caspase-3. Dis. Model Mech. 2013, 6, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.-L.; Yuan, J.-M.; Yang, L.-Y.; Xie, J.-F.; Weng, S.-P.; Yu, X.-Q.; He, J.-G. The viral TRAF protein (ORF111L) from infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus interacts with TRADD and induces caspase 8-mediated apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Evensen, O.; Mutoloki, S. Delayed protein shut down and cytopathic changes lead to high yields of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus cultured in Asian Grouper cells. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 195, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagon, Y.; Dovrat, S.; Vilchik, S.; Hacohen, D.; Shlomo, G.; Sredni, B.; Salzberg, S.; Nir, U. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR, down-regulates CDC 2/cyclin B 1 and induces apoptosis in non-transformed but not in v-mos transformed cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koromilas, A.E.; Roy, S.; Barber, G.N.; Katze, M.G.; Sonenberg, N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-Inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science 1992, 257, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, K.; Feng, L.; Schappert, K.; Meurs, E.; Donahue, T.; Friesen, J.; Hovanessian, A.; Williams, B. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, S.J.; Ortega, L.G.; Doohan, J.P.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action motif I of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is sufficient to mediate RNA-binding activity. Virology 1994, 198, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomis, D.C.; Samuel, C.E. Mechanism of interferon action: Evidence for intermolecular autophosphorylation and autoactivation of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7695–7700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, N.; Samuel, C.E. RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR and the Z-DNA binding orthologue PKZ differ in their capacity to mediate initiation factor eIF2α-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis and virus-induced stress granule formation. Virology 2013, 443, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamil, A.A.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø. A piscine birnavirus induces inhibition of protein synthesis in CHSE-214 cells primarily through the induction of eIF2α phosphorylation. Viruses 2015, 7, 1987–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takizawa, T.; Ohashi, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Possible involvement of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase in cell death by influenza virus infection. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8128–8132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.C.; Chang, D.L.; Camantigue, R.E.; Lau, A.S. Inhibitory role of the host apoptogenic gene PKR in the establishment of persistent infection by encephalomyocarditis virus in U937 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11860–11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil, J.; Alcami, J.; Esteban, M. Induction of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) involves the a subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and NF-kappa B. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 4653–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.; García, M.A.; Esteban, M. Caspase 9 activation by the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR: molecular mechanism and relevance. FEBS Lett. 2002, 529, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Gamil, A.A.A.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Apoptosis Induction by dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase R (PKR) in EPC Cells via Caspase 8 and 9 Pathways. Viruses 2018, 10, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100526
Xu C, Gamil AAA, Munang’andu HM, Evensen Ø. Apoptosis Induction by dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase R (PKR) in EPC Cells via Caspase 8 and 9 Pathways. Viruses. 2018; 10(10):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100526
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Cheng, Amr A. A. Gamil, Hetron Mweemba Munang’andu, and Øystein Evensen. 2018. "Apoptosis Induction by dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase R (PKR) in EPC Cells via Caspase 8 and 9 Pathways" Viruses 10, no. 10: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100526
APA StyleXu, C., Gamil, A. A. A., Munang’andu, H. M., & Evensen, Ø. (2018). Apoptosis Induction by dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase R (PKR) in EPC Cells via Caspase 8 and 9 Pathways. Viruses, 10(10), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100526




