Branch Wood Decomposition of Tree Species in a Deciduous Temperate Forest in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Mass Loss Measurements
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition of Branch Wood
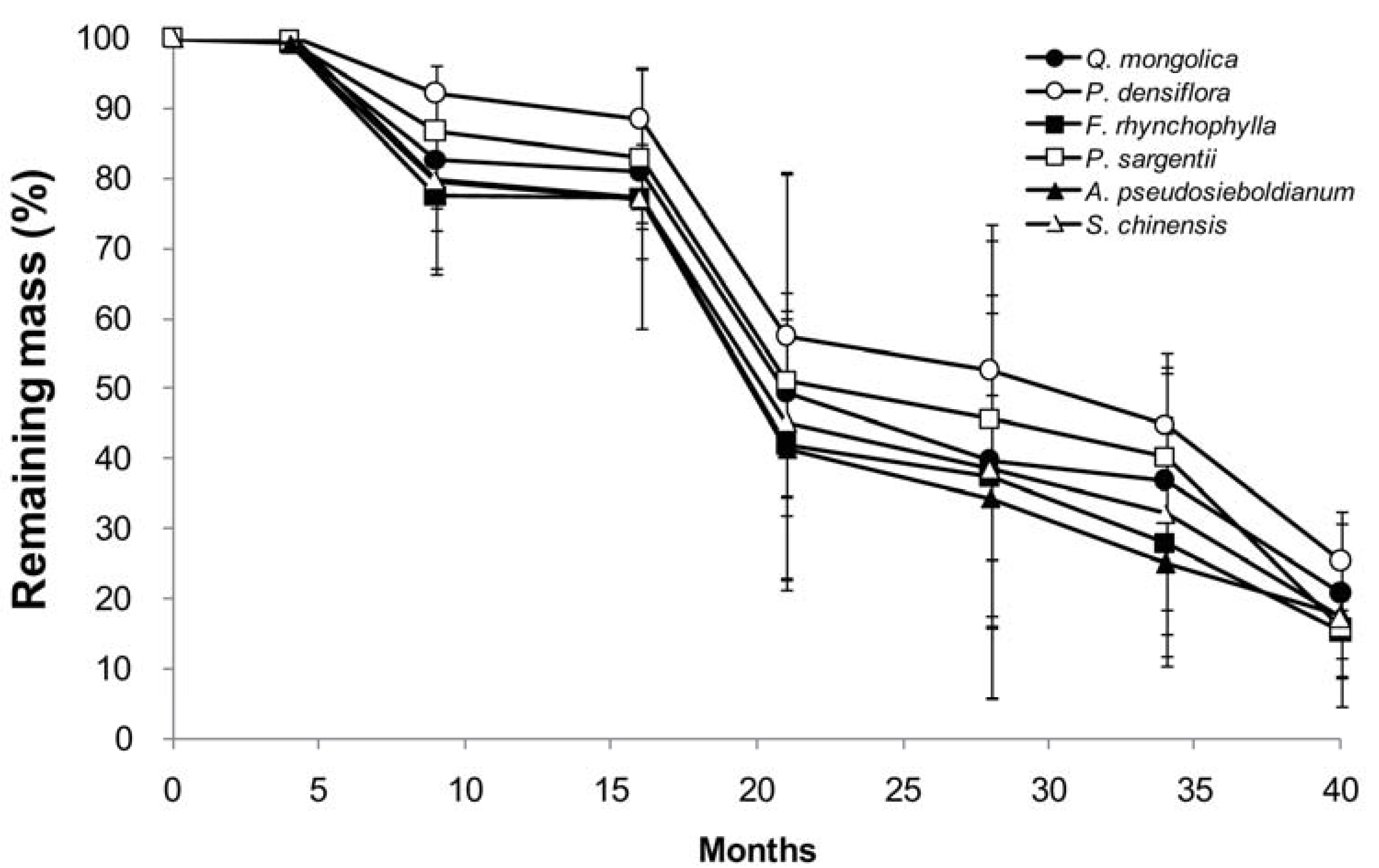
3.2. Mass Loss and Decomposition Rate
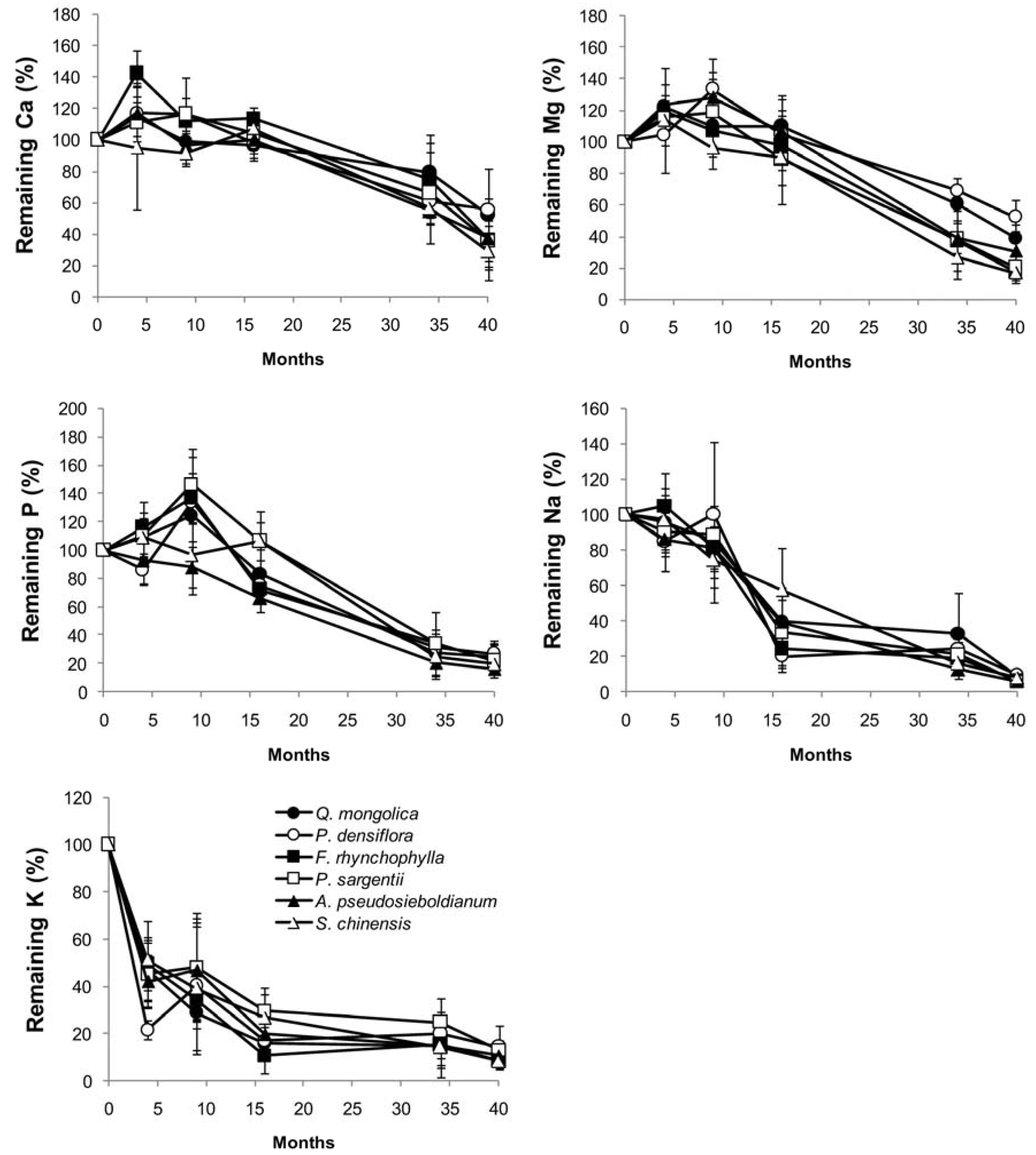
3.3. Changes in Chemical Composition during Decomposition
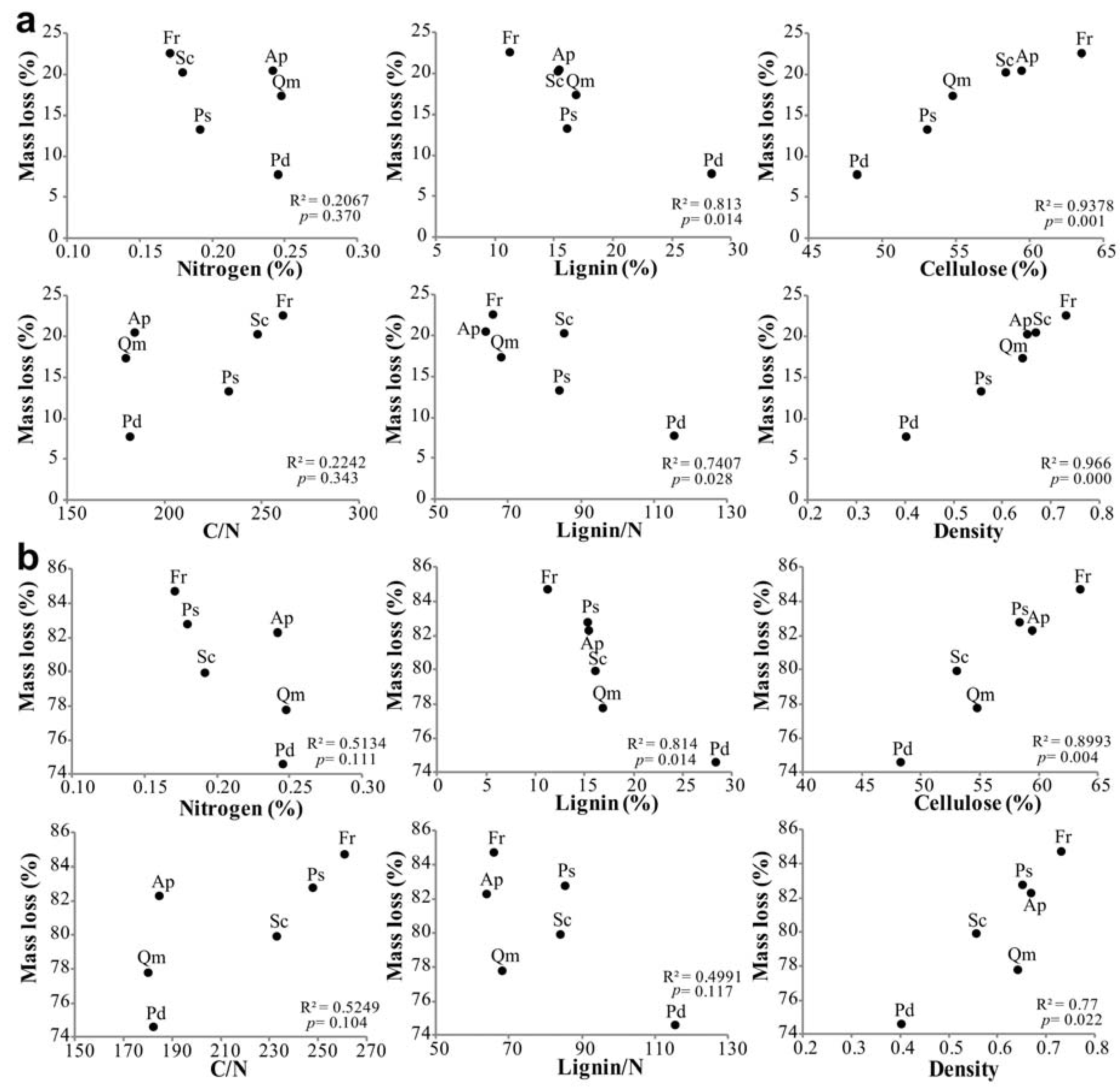
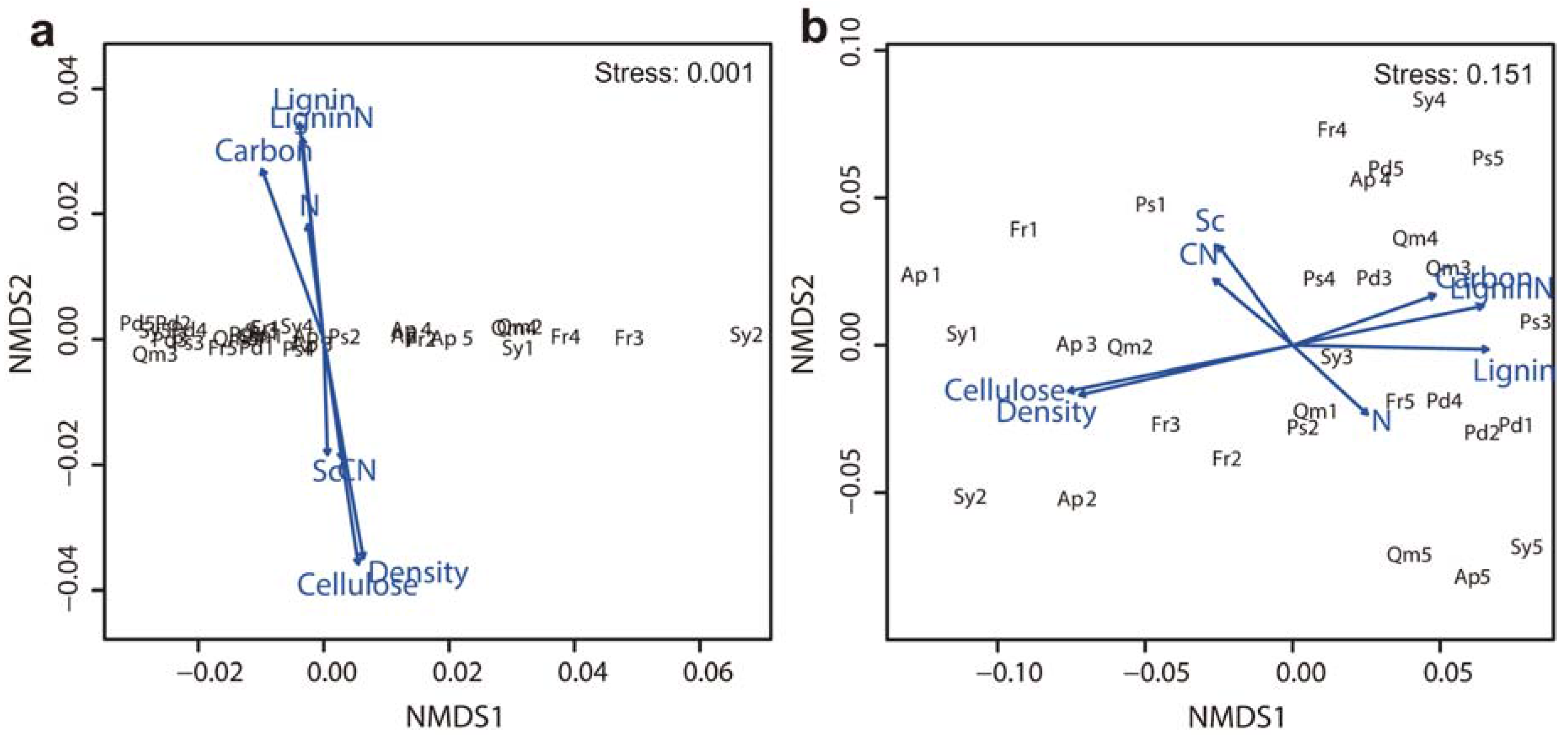
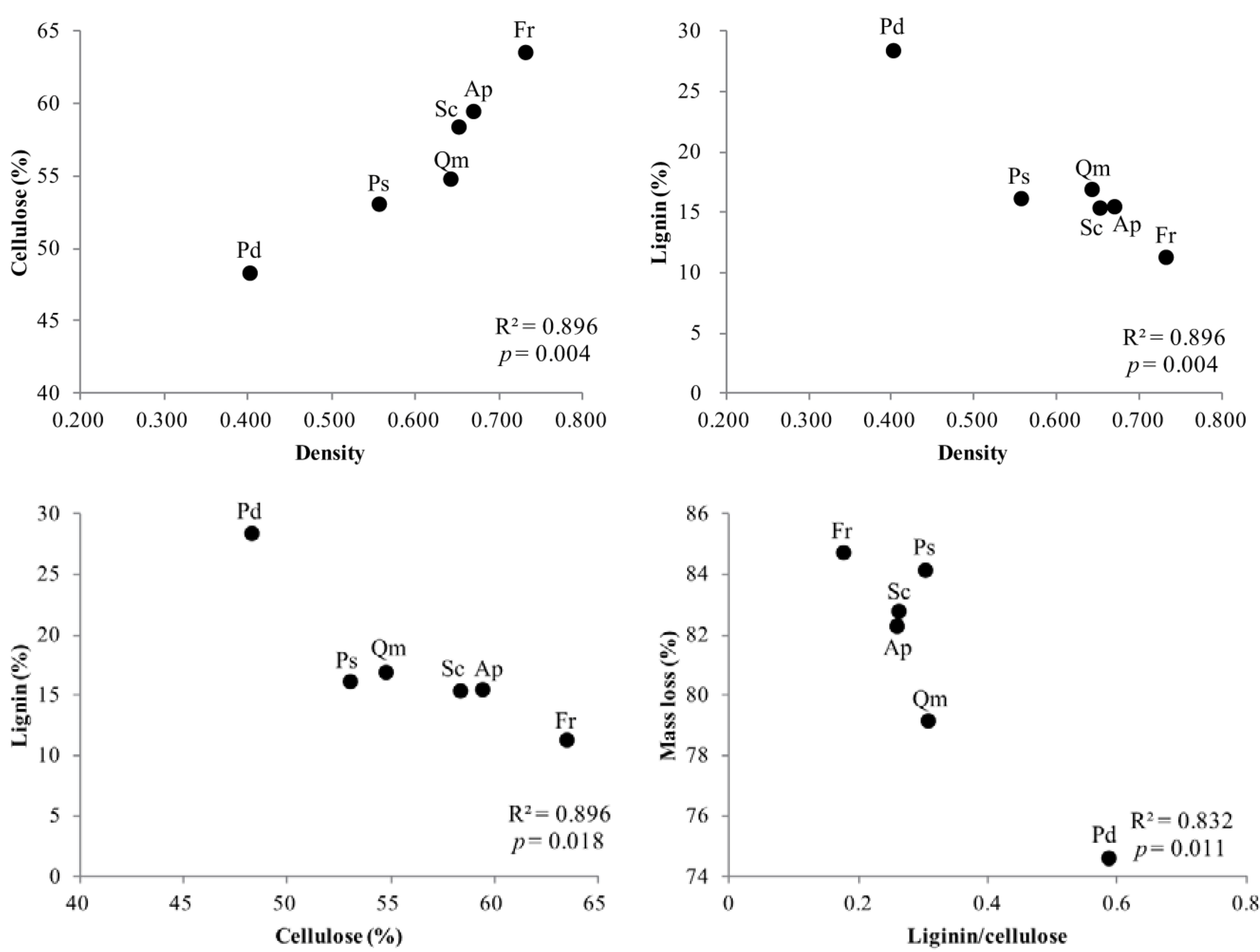
3.4. Factors Affecting Branch Wood Decomposition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harmon, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Swanson, F.J.; Sollins, P.; Gregory, S.; Lattin, J.; Anderson, N.; Cline, S.; Aumen, N.G.; Sedell, J. Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. In Advances in Ecological Research; MacFayden, A., Ford, E., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1986; Volume 15, pp. 133–302. [Google Scholar]
- Laiho, R.; Prescott, C.E. Decay and nutrient dynamics of coarse woody debris in northern coniferous forests: A synthesis. Can. J. For. Res. 2004, 34, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargali, S.S. Weight loss and n release in decomposing wood litter in a eucalypt plantation age series. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Scherer, R. Influence of wildfire and harvest on biomass, carbon pool, and decomposition of large woody debris in forested streams of southern interior British Columbia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 208, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Gorham, E. Litter production in forests of the world. In Advances in Ecological Research; Cragg, J.B., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964; Volume 2, pp. 101–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.G.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, M.J.; Joo, G.J.; Yoo, Y.H.; Min, B.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.S. The Third Stage Report (2010–2013) of KNLTER (Korea National Long Term Ecological Research); National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Korea, 2013; pp. 225–236.
- Ganjegunte, G.K.; Condron, L.M.; Clinton, P.W.; Davis, M.R.; Mahieu, N. Decomposition and nutrient release from radiata pine (Pinus radiata) coarse woody debris. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 187, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, L.-m.; Gu, H.-y.; Zhong, L. Review on the decomposition and influence factors of coarse woody debris in forest ecosystem. J. For. Res. 2007, 18, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, L.; Oliver, G.; Pearce, S.; Davis, M. Decomposition of Pinus radiata coarse woody debris in New Zealand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, D.; Crossley, D. Woody litter decomposition following clear-cutting. Ecology 1982, 63, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.; Zelazny, V.; Beaudette, D.; Fleming, T.; Johnson, G.; Flemming, S.; Gerrow, J.; Forbes, G.; Woodley, S. Biodiversity implications of changes in the quantity of dead organic matter in managed forests. Environ. Rev. 1996, 4, 238–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, F.L.; Houde, I. Down wood and biodiversity—Implications to forest practices. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 397–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.; Merino, J. Leaf decomposition in two Mediterranean ecosystems of southwest Spain: Influence of substrate quality. Ecology 1993, 74, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; McClaugherty, C. Plant Litter. Decomposition Humus Formation. Carbon Sequestration; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, H.M.; Cha, S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, M.J.; Shim, J.K. Age-related decomposition of Quercus mongolica. Plant Ecol. 2016, 217, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Staaf, H. Decomposition rate and chemical changes of scots pine needle litter. II. Influence of chemical composition. Ecol. Bull. 1980, 373–390. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, V.; Singh, J. Decomposition of woody branch litter on an altitudinal transect in the Himalaya. Plant Ecol. 1986, 64, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, A.; Di Nardo, C.; Papa, S.; Fuggi, A. Lignin and cellulose degradation and nitrogen dynamics during decomposition of three leaf litter species in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alban, D.H.; Pastor, J. Decomposition of aspen, spruce, and pine boles on two sites in Minnesota. Can. J. For. Res. 1993, 23, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Prescott, C.E. Mass loss and nutrient dynamics of coarse woody debris in three rocky mountain coniferous forests: 21 year results. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.R.; Fraver, S.; Wagner, R.G. Nutrient concentration of down woody debris in mixedwood forests in central Maine, USA. Silva Fennica 2011, 45, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M.; Aber, J.D.; Muratore, J.F. Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 1982, 63, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Ekbohm, G. Litter mass-loss rates and decomposition patterns in some needle and leaf litter types. Long-term decomposition in a scots pine forest. VII. Can. J. Bot. 1991, 69, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Chae, H.M.; Lee, S.H.; Shim, J.K. Effect of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on growth and leaf litter decomposition of Quercus acutissima and Fraxinus rhynchphylla. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aber, J.; Melillo, J.M. Terrestrial Ecosystems, 2nd ed.; Brooks/Cole Publishing: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, F., III; Matson, P.; Mooney, H. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, M.J.; Heal, O.W.; Anderson, J.M. Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Univ of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1979; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, J.; Bockheim, J. Distribution and cycling of nutrients in an aspen-mixed-hardwood-spodosol ecosystem in northern Wisconsin. Ecology 1984, 65, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallardy, S.G. Physiology of Woody Plants; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maser, C.; Trappe, J.M. The Seen and Unseen World of the Fallen Tree; USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Forest Experiment Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Brais, S.; Paré, D.; Lierman, C. Tree bole mineralization rates of four species of the Canadian eastern boreal forest: Implications for nutrient dynamics following stand-replacing disturbances. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 36, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, C.; Donath, C.; Müller-Using, S.; Bartsch, N. Nutrient fluxes via leaching from coarse woody debris in a Fagus sylvatica forest in the Solling mountains, Germany. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Bauhus, J. Effects of moisture, temperature and decomposition stage on respirational carbon loss from coarse woody debris (CWD) of important European tree species. Scand. J. For. Res. 2013, 28, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Polo, M.; Fernández-Souto, A.; Austin, A.T. Coarse woody debris stimulates soil enzymatic activity and litter decomposition in an old-growth temperate forest of Patagonia, Argentina. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Cherubini, P.; Tognetti, R.; Cocozza, C.; Lasserre, B.; Marchetti, M. Investigating biochemical processes to assess deadwood decay of beech and silver fir in Mediterranean mountain forests. Ann. For. Sci. 2013, 70, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, M.; Laiho, R.; Repo, A.; Liski, J. Wood decomposition model for boreal forests. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Youn, Y. A basic survey about dead tree of old Korean fir stands in Mt. Sorak. Kor. J. Environ. Biol. 2003, 21, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, R.H.; Son, Y.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, I.K.; Seo, K.W.; Koo, J.W.; Noh, N.J.; Ryu, S.-R.; Hong, S.K.; Ihm, B.S. Coarse woody debris mass and nutrients in forest ecosystems of Korea. Ecol. Res. 2006, 21, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, N.J.; Son, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Seo, K.W.; Heo, S.J.; Yi, M.J.; Park, P.S.; Kim, R.H.; Son, Y.M.; Lee, K.H. Carbon and nitrogen storage in an age-sequence of Pinus densiflora stands in Korea. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources. Available online: http://mgeo.kigam.re.kr/map/geology.jsp (accessed on 4 April 2017).
- Olson, J.S. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 1963, 44, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—Chemical Methods; Bartels, J.M., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—Chemical Methods; Bartels, J.M., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, A.; Roberts, J. Lignin and cellulose fractionation in decomposition studies using acid-detergent fibre methods. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1994, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helrick, K. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.E.; Grimshaw, H.M.; Parkinson, J.A.; Quarmby, C. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Salisbury, F.B.; Ross, C.W. Plant Physiology, 3rd ed.; Wadsworth Publishing Co.: Belmont, CA, USA, 1985; p. 540. [Google Scholar]
- Palviainen, M.; Finér, L.; Kurka, A.M.; Mannerkoski, H.; Piirainen, S.; Starr, M. Release of potassium, calcium, iron and aluminium from Norway spruce, Scots pine and silver birch logging residues. Plant Soil 2004, 259, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Incerti, G.; Antignani, V.; Capodilupo, M.; Mazzoleni, S. Decomposition and nutrient dynamics in mixed litter of Mediterranean species. Plant Soil 2010, 331, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M; Scandellari, F.; Bonora, E.; Tagliavini, M. Nutrient release during decomposition of leaf litter in a peach (Prunus persica L.) orchard. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 87, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto, G; Ventura, M.; Scandellari, F.; Ceretta, C.A.; Kaminski, J.; Melo, G.W.B.; Taglavini, M. Nutrients release during the decomposition of mowed perennial ryegrass and white clover and its contribution to nitrogen nutrition of grapevine. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 90, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini, M.; Tonon, G.; Scandellari, F.; Quiñones, A.; Palmieri, S.; Menarbin, G.; Gioacchini, P.; Masia, A. Nutrient recycling during the decomposition of apple leaves (Malus domestica) and mowed grasses in an orchard. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lizana, A.; Carbonell, R.; González, P.; Ordóñez, R. N, P and K released by the field decomposition of residues of a pea-wheat-sunflower rotation. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.; Healey, I.; Hibberd, J.; Sykes, J.; Bampoe, V.; Nesbitt, M. The decomposition of branch-wood in the canopy and floor of a mixed deciduous woodland. Oecologia 1976, 26, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heal, O.; Anderson, J.; Swift, M. Plant litter quality and decomposition: An historical overview. In Driven by Nature: Plant Litter Quality and Decomposition; Cadisch, G., Ed.; CAB International: Walling Ford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, B.; Laskowski, R. Decomposers: Soil microorganisms and animals. In Advances in Ecological Research; Berg, B., Laskowski, R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 38, pp. 73–100. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Gupta, S. Plant decomposition and soil respiration in terrestrial ecosystems. Bot. Rev. 1977, 43, 449–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zak, J.C. Effects of gap size on litter decomposition and microbial activity in a subtropical forest. Ecology 1995, 76, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B. Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 133, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, R.; Cromack, K., Jr. Effect of habitat and substrate quality on douglas fir litter decomposition in western Oregon. Can. J. Bot. 1977, 55, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Lundmark, J.E. Decomposition of needle litter in Pinus contorta and Pinus sylvestris monocultures—A comparison. Scand. J. For. Res. 1987, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklas, K.J. Mechanical properties of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) wood: Correlations among elastic and rupture moduli, proportional limit, and tissue density and specific gravity. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, U.G.; Sperry, J.S. Functional and ecological xylem anatomy. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2001, 4, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.L.; Ewers, F.W.; Pratt, R.B.; Paddock, W.A.; Davis, S.D. Do xylem fibers affect vessel cavitation resistance? Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, H.; Poorter, L.; Sterck, F. Wood mechanics, allometry, and life-history variation in a tropical rain forest tree community. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, A.L.; Agenbag, L.; Esler, K.J.; Pratt, R.B.; Ewers, F.W.; Davis, S.D. Xylem density, biomechanics and anatomical traits correlate with water stress in 17 evergreen shrub species of the Mediterranean-type climate region of south Africa. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osunkoya, O.O.; Sheng, T.K.; Mahmud, N.A.; Damit, N. Variation in wood density, wood water content, stem growth and mortality among twenty-seven tree species in a tropical rainforest on Borneo island. Austral Ecol. 2007, 32, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, J.; Coomes, D.; Jansen, S.; Lewis, S.L.; Swenson, N.G.; Zanne, A.E. Towards a worldwide wood economics spectrum. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorter, L. The relationships of wood-, gas-and water fractions of tree stems to performance and life history variation in tropical trees. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, J.Q.; Higuchi, N; Schimel, J.P.; Ferreira, L.V.; Melack, J.M. Decomposition and carbon cycling of dead trees in tropical forests of the central Amazon. Oecologia 2000, 122, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemińska, K.; Butler, D.W.; Gleason, S.M.; Wright, I.J.; Westoby, M. Fibre wall and lumen fractions drive wood density variation across 24 Australian angiosperms. AoB Plants 2013, 5, plt046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Matzner, E. The effect of n deposition on the mineralization of c from plant litter and humus. Environ. Rev. 1997, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercus mongolica | 51.97 ± 2.57 | 15.74 ± 2.77 | 0.642 ± 0.015 |
| Pinus densiflora | 36.73 ± 5.10 | 14.92 ± 1.22 | 0.403 ± 0.038 |
| Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 29.93 ± 2.72 | 15.57 ± 1.27 | 0.731 ± 0.026 |
| Prunus sargentii | 46.92 ± 3.21 | 14.53 ± 1.24 | 0.557 ± 0.023 |
| Acer pseudosieboldianum | 33.31 ± 2.19 | 14.73 ± 1.44 | 0.669 ± 0.020 |
| Symplocos chinensis | 30.15 ± 2.54 | 16.06 ± 1.83 | 0.652 ± 0.028 |
| Q. mongolica | P. densiflora | F. rhynchophylla | P. sargentii | A. pseudosieboldianum | S. chinensis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (%) | 44.6 ± 0.09 a 1 | 44.7 ± 0.16 a | 44.6 ± 0.10 a | 44.7 ± 0.04 a | 44.7 ± 0.22 a | 44.5 ± 0.23 a |
| Nitrogen (%) | 0.25 ± 0.03 a | 0.25 ± 0.07 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 0.19 ± 0.03 ab | 0.24 ± 0.05 a | 0.18 ± 0.05 b |
| Lignin (%) | 16.2 ± 1.75 b | 28.4 ± 1.46 a | 10.6 ± 1.85 c | 16.1 ± 1.89 b | 15.5 ± 0.58 b | 16.3 ± 1.88 b |
| Cellulose (%) | 54.8 ± 6.34 bc | 48.3 ± 1.85 d | 63.5 ± 3.18 a | 53.0 ± 4.58 cd | 59.4 ± 2.43 ab | 58.4 ± 3.40 abc |
| SC 2 (%) | 1.54 ± 0.69 a | 1.42 ± 0.87 a | 2.22 ± 0.71 a | 2.58 ± 1.10 a | 2.08 ± 0.65 a | 1.76 ± 0.56 a |
| C/N | 180.1 ± 24.6 c | 182.3 ± 65.6 c | 261.0 ± 29.1 a | 233.1 ± 33.4 ab | 184.7 ± 33.1 bc | 247.9 ± 74.9 ab |
| Lignin/N | 65.6 ± 9.3 b | 115.6 ± 46.7 a | 61.8 ± 9.7 b | 84.1 ± 15.9 b | 63.9 ± 14.2 b | 90.6 ± 26.2 b |
| Ca (μg /g) | 3722 ± 235 b | 1913 ± 257 e | 2678 ± 442 d | 3098 ± 604 cd | 3485 ± 298 bc | 5371 ± 448 a |
| P (μg /g) | 193 ± 46 b | 280 ± 138 ab | 212 ± 56 ab | 201 ± 46 b | 312 ± 45 a | 236 ± 83 ab |
| K (μg /g) | 815± 246 a | 865 ± 776 a | 921 ± 361 a | 562 ± 72 a | 680 ± 58 a | 821 ± 134 a |
| Mg (μg /g) | 219 ± 21 cd | 281 ± 68 cd | 443 ± 105 a | 301 ± 54 bc | 190 ± 27 d | 374 ± 99 ab |
| Na (μg /g) | 461 ± 126 a | 495 ± 145 a | 452 ± 57 a | 501 ± 98 a | 513 ± 64 a | 506 ± 118 a |
| Q. mongolica | P. densiflora | F. rhynchophylla | P. sargentii | A. pseudosieboldianum | S. chinensis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | 0.478 ± 0.077 | 0.420 ± 0.079 | 0.586 ± 0.138 | 0.560 ± 0.078 | 0.575 ± 0.193 | 0.561 ± 0.166 |
| Half-life (year) | 1.479 ± 0.214 | 1.705 ± 0.355 | 1.233 ± 0.289 | 1.257 ± 0.179 | 1.384 ± 0.675 | 1.321 ± 0.365 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, S.; Chae, H.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Shim, J.-K. Branch Wood Decomposition of Tree Species in a Deciduous Temperate Forest in Korea. Forests 2017, 8, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8050176
Cha S, Chae H-M, Lee S-H, Shim J-K. Branch Wood Decomposition of Tree Species in a Deciduous Temperate Forest in Korea. Forests. 2017; 8(5):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8050176
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Sangsub, Hee-Myung Chae, Sang-Hoon Lee, and Jae-Kuk Shim. 2017. "Branch Wood Decomposition of Tree Species in a Deciduous Temperate Forest in Korea" Forests 8, no. 5: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8050176
APA StyleCha, S., Chae, H.-M., Lee, S.-H., & Shim, J.-K. (2017). Branch Wood Decomposition of Tree Species in a Deciduous Temperate Forest in Korea. Forests, 8(5), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8050176






