Tree Functional Identity Drives Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Ratios and Microbial Nutrient Limitation Responses to Artificial Forest Conversion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Meta-Analysis and Statistical Approaches
3. Results
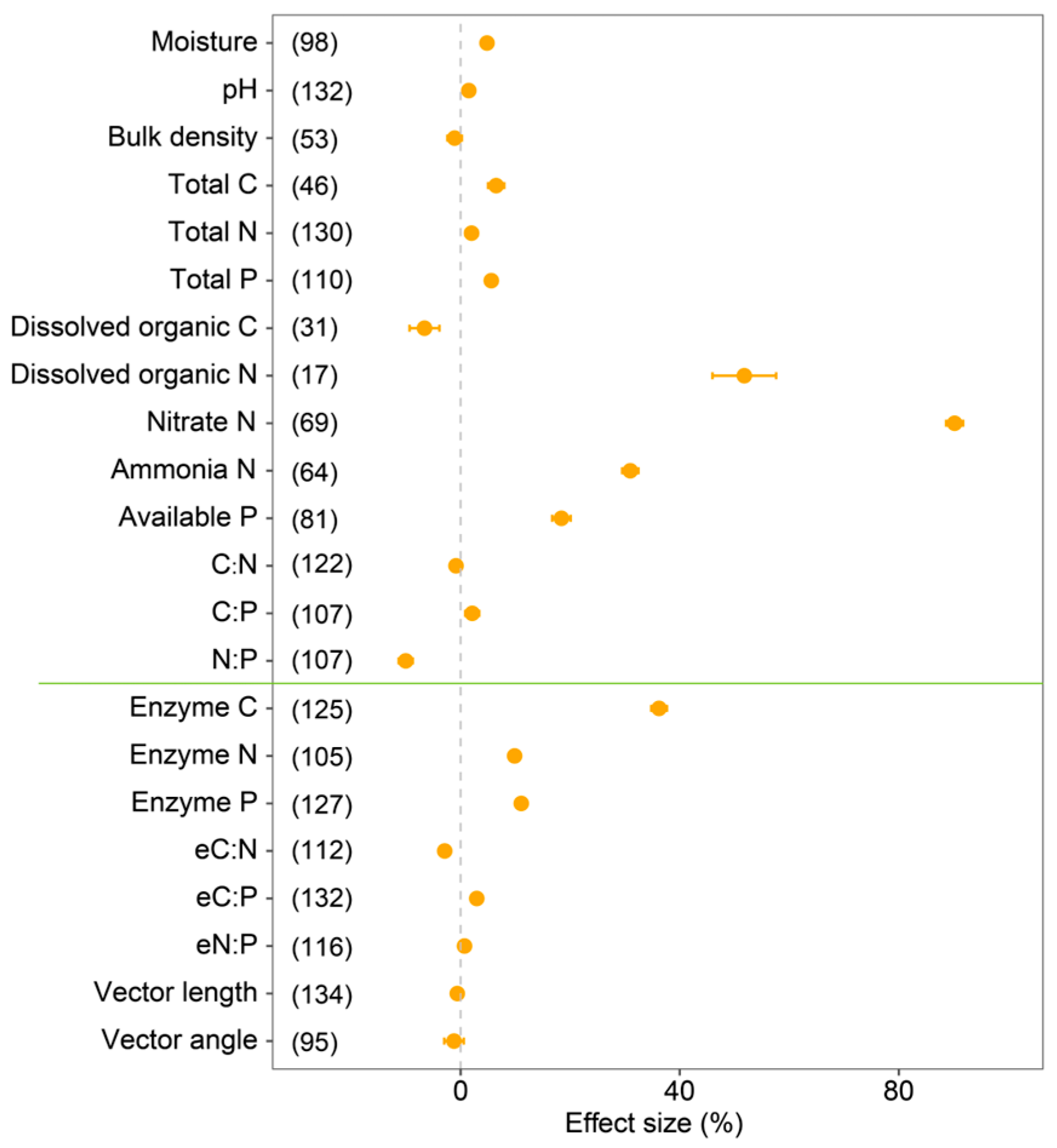
3.1. Effects of Conversion from Monoculture to Mixed Forests on Soil Properties
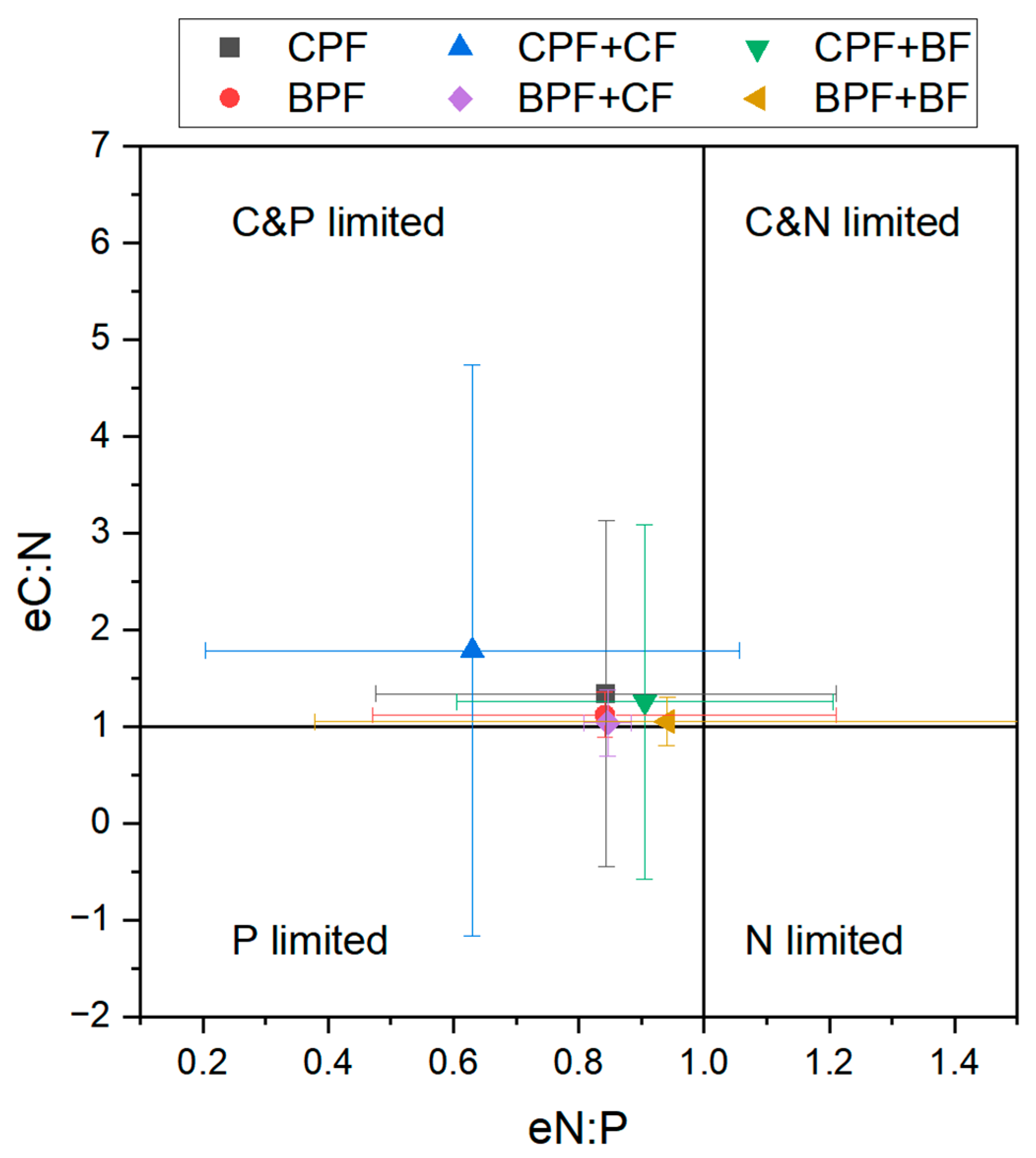
3.2. Differences Between Mixed Forest Patterns
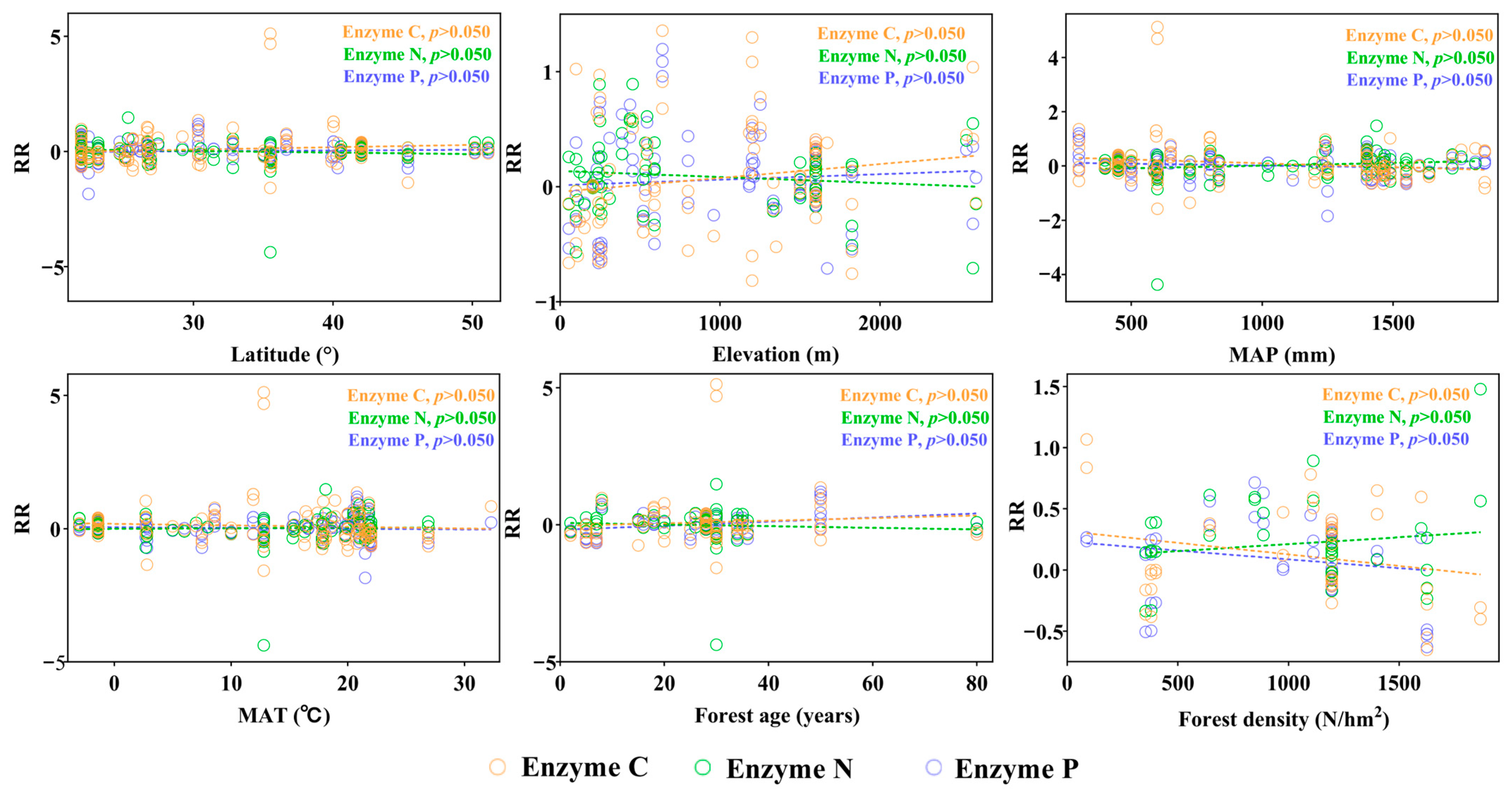
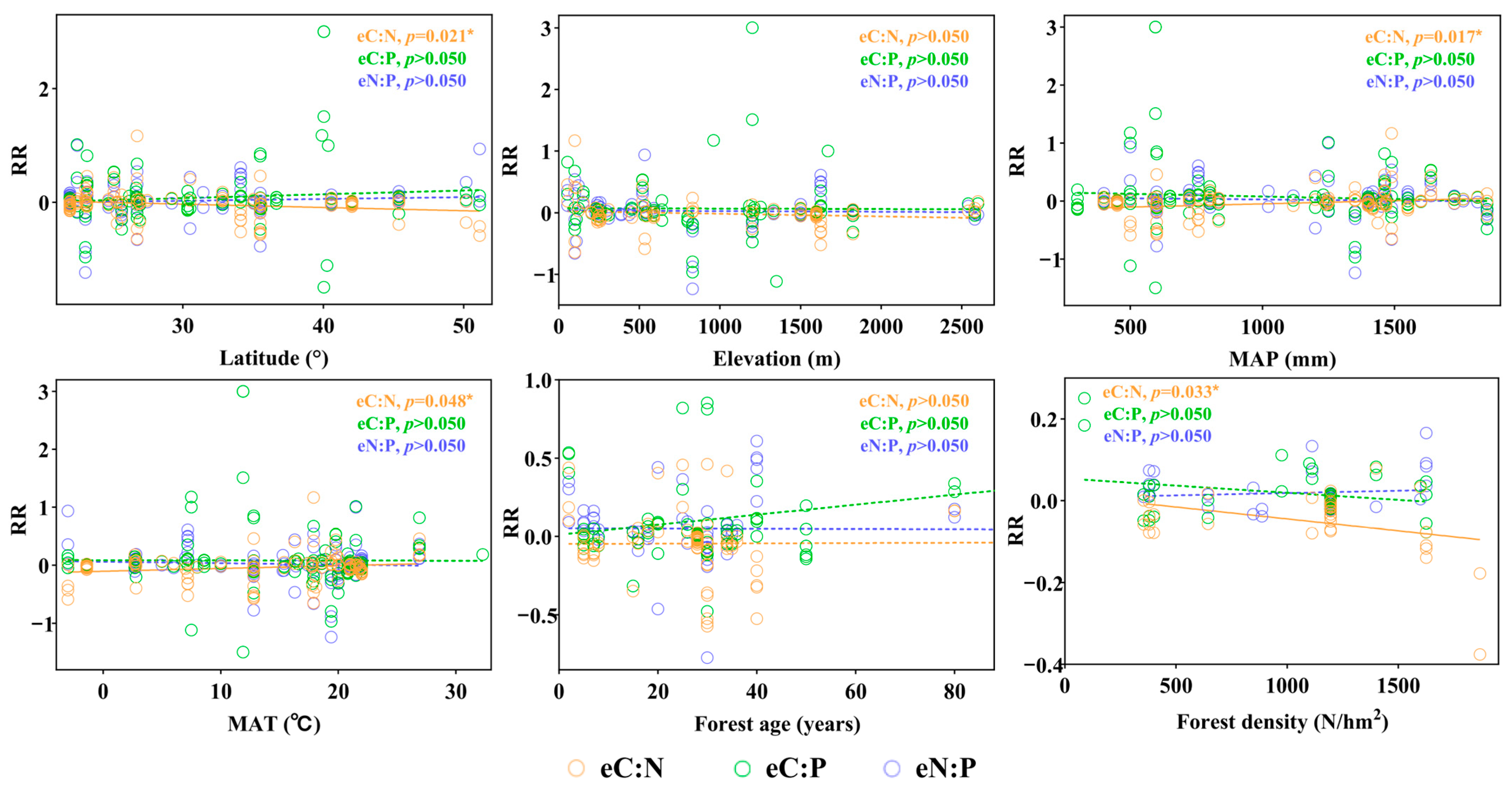
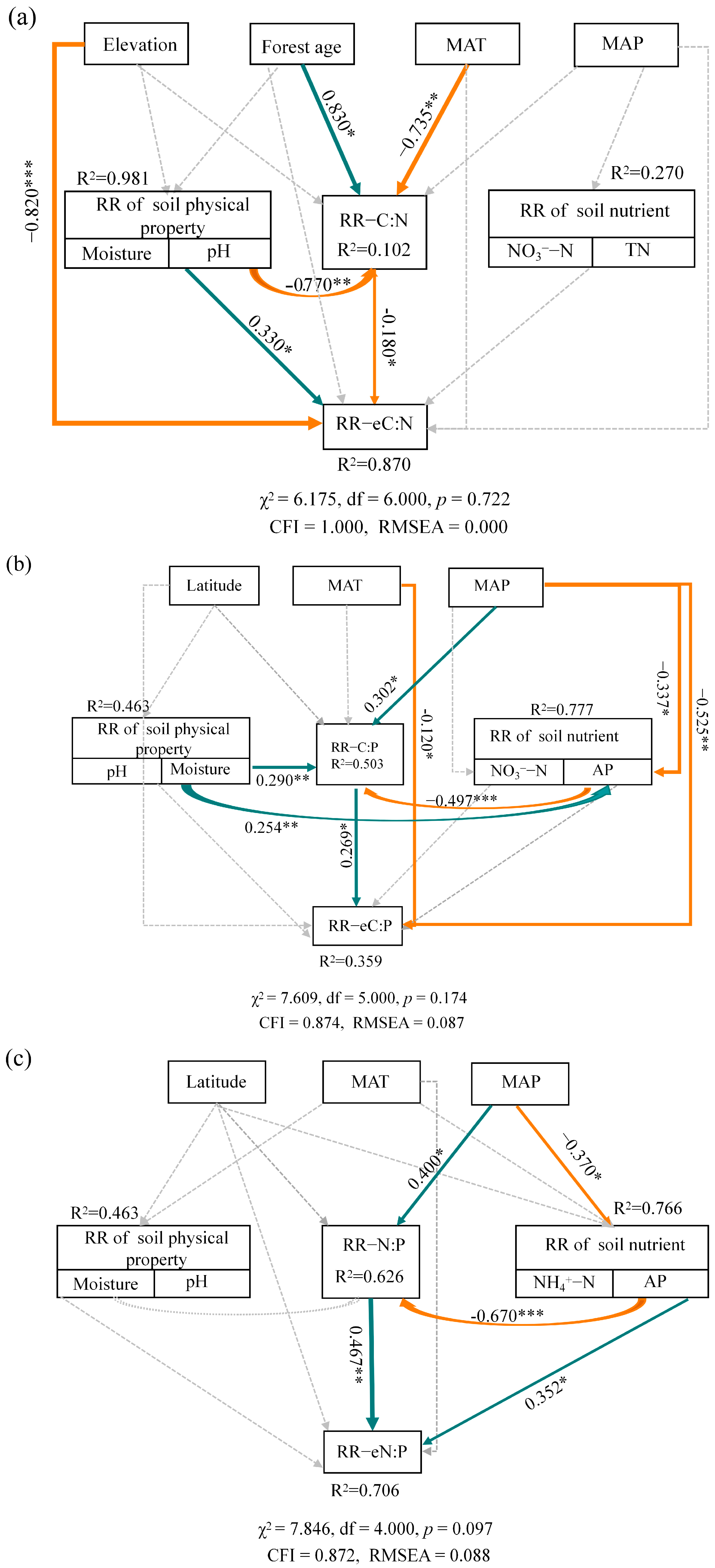
3.3. Factors Influencing the Responses of Soil Enzyme to Forest Mixing
4. Discussion
4.1. Global Pattern Effects of Mixed Artificial Forests
4.2. Differentiated Responses Based on Artificial Forest Origin
4.3. Regulatory Roles of Environmental, Stand Characteristics, and the Artificial Forest Context
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aon, M.A.; Cabello, M.N.; Sarena, D.; Colaneri, A.C.; Franco, M.; Burgos, J.L.; Cortassa, S.I. Spatio-temporal patterns of soil microbial and enzymatic activities in an agricultural soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 18, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Linking microbial functional gene abundance and soil extracellular enzyme activity: Implications for soil carbon dynamics. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Peng, S.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Peñuelas, J. Predicting microbial nutrient limitations from a stoichiometry-based threshold framework. Innov. Geosci. 2024, 2, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gunina, A.; Reich, P.B.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Sun, T. Nutrient cycles in transition: C: N: P stoichiometry by forest conversion to plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 593, 122874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xie, X.; Shao, Q.; Pu, L.; Meadows, M.; Jia, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Xu, F. Differential response of soil characteristics and extracellular enzyme activities along an altitude gradient in a subtropical forest ecosystem, eastern China. Catena 2025, 256, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Hu, H.; Kuai, J.; Wang, X.; Chu, L. Effects of Soil Warming on Soil Microbial Metabolism Limitation in a Quercus acutissima Forest in North Subtropical China. Forests 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Peng, S.; Rillig, M.C.; Camenzind, T.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Terrer, C.; Xu, X.; Feng, M.; Wang, M.; Fang, L. Global patterns of nutrient limitation in soil microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2424552122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, M.; Mao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Cropland conversion changes the status of microbial resource limitation in degraded karst soil. Geoderma 2019, 352, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ning, P.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Ge, T.; Cui, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, W. Responses of soil microbial community composition and enzyme activities to long-term organic amendments in a continuous tobacco cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020—Key Findings; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Development strategy and management countermeasures of planted forests in China: Transforming from timber-centered single objective management towards multi-purpose management for enhancing quality and benefits of ecosystem services. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Advantage of mixed trees in the trade-off between soil water storage and tree biomass: A meta-analysis from artificially planted forests in Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2022, 214, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiong, D.; Xu, C.; Yue, K.; Wu, F. Decline in nutrient inputs from litterfall following forest plantation in subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 496, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Geng, Q.; Jin, C.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, H.; Xu, X. The roles of initial litter traits in regulating litter decomposition: A “common plot” experiment in a subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest. Plant Soil 2020, 452, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonghuloo, I.; Kharbhih, S.; Suchiang, B.; Adhikari, D.; Upadhaya, K.; Barik, S. Production, decomposition and nutrient contents of litter in subtropical broadleaved forest surpass those in coniferous forest, Meghalaya. Trop. Ecol. 2020, 61, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; An, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, J.; Chang, S.X. Tree species composition alters the decomposition of mixed litter and the associated microbial community composition and function in subtropical plantations in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Xi, W. Multiple ecosystem services of monoculture and mixed plantations: A case study of the Huitong experimental forest of Southern China. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Schmid, B.; Loreau, M.; Forrester, D.I.; Fei, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hong, P.; Ji, C. Multispecies forest plantations outyield monocultures across a broad range of conditions. Science 2022, 376, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Reich, P.B.; Taylor, A.R.; An, Z.; Chang, S.X. Resource availability enhances positive tree functional diversity effects on carbon and nitrogen accrual in natural forests. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Yang, Y.; Macartney, E.L.; Spake, R.; Lagisz, M. Quantitative evidence synthesis: A practical guide on meta-analysis, meta-regression, and publication bias tests for environmental sciences. Environ. Evid. 2023, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Feng, H.; McNie, P.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Pan, C.; Yan, K.; Feng, L.; Goitom, E.A.; Yu, Y. Species mixing improves soil properties and enzymatic activities in Chinese fir plantations: A meta-analysis. Catena 2023, 220, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.Y. Plant mixture balances terrestrial ecosystem C: N: P stoichiometry. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Duan, B.; Dai, C.; Wu, Y. Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrient Limitation of Various Temperate Forest Types in Northeastern China. Forests 2024, 15, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Moorhead, D.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ye, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals widespread soil phosphorus limitation to microbial metabolism across Chinese forests. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; You, Y. Effects of mixing Eucalyptus and Castanopsis hystrix on soil hydrolytic enzyme activities and ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Guihaia 2022, 42, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Linhui, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Tan, B.; Li, Z. Effects of seasonal changes on soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometric characteristics of subalpine forests in Western Sichuan. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2023, 41, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, W.; Fan, Y.; Chong, Y.; Xiong, J.; Yu, W. Restoring subtropical forests: Alleviating P limitation and introducing C limitation using evergreen broad-leaved tree species. Forests 2024, 15, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wu, Z.J.; Zong, Y.Y.; Wang, G.G.; Chen, F.S.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, J.J.; Fang, X.M. Tree species mixing enhances rhizosphere soil organic carbon mineralization of conifers in subtropical plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 516, 120238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zong, Y.; Wu, G.; Yu, Z.; Fang, X. Mixing with broad-leaved trees shapes the rhizosphere soil fungal communities of coniferous tree species in subtropical forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 480, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Prażuch, W.; Ilek, A. Vertical variations in enzymatic activity and C: N: P stoichiometry in forest soils under the influence of different tree species. Euro. J. For. Resea. 2025, 144, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gan, Q.; Huang, L.; Pan, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Effects of forest thinning on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity. Catena 2024, 239, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lull, C.; Gil-Ortiz, R.; Bautista, I.; Lidón, A. Seasonal variation and soil texture-related thinning effects on soil microbial and enzymatic properties in a semi-arid pine forest. Forests 2023, 14, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, P.; Gong, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Z. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the nutrient limitations in soil microbial metabolism under different carbon input manipulations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, B.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Kumaran, S.; Wilson, A. Impacts of global warming on marine microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 147905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, P.A.; Juhos, K.; Prettl, N.; Madarász, B.; Kotroczó, Z. Long-term conservation tillage results in a more balanced soil microbiological activity and higher nutrient supply capacity. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.S.; Wang, X. A meta-analysis of elevated CO2 effects on woody plant mass, form, and physiology. Oecologia 1998, 113, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.S.; Adams, D.C.; Gurevitch, J. MetaWin: Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis with Resampling Tests; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil organic matter priming: The pH effects. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A’Bear, A.D.; Jones, T.H.; Kandeler, E.; Boddy, L. Interactive effects of temperature and soil moisture on fungal-mediated wood decomposition and extracellular enzyme activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Dong, M.; Chen, W. Effects of Forest Conversion on Soil Ecosystem Services in Liuxihe National Forest Park, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Niu, S. Critical role of multidimensional biodiversity in contributing to ecosystem sustainability under global change. Geogr. Sustain. 2023, 4, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetterl, S.; Stevens, A.; Six, J.; Merckx, R.; Van Oost, K.; Casanova Pinto, M.; Casanova-Katny, A.; Muñoz, C.; Boudin, M.; Zagal Venegas, E. Soil carbon storage controlled by interactions between geochemistry and climate. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.; Luo, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Jiang, L.; Luo, X.; Wen, D. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Chen, D.; Insam, H.; Koide, R.T.; Zhang, S. Effects of mixed-species litter on bacterial and fungal lignocellulose degradation functions during litter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinya, F.; Kovács, B.; Bidló, A.; Dima, B.; Király, I.; Kutszegi, G.; Lakatos, F.; Mag, Z.; Márialigeti, S.; Nascimbene, J. Environmental drivers of forest biodiversity in temperate mixed forests–A multi-taxon approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; You, Y.; Tan, X.; Wen, Y.; Yu, S.; Xiao, N.; Shen, W.; Huang, X. Mixture of N2-fixing tree species promotes organic phosphorus accumulation and transformation in topsoil aggregates in a degraded karst region of subtropical China. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszel-Szlachta, K.; Lasota, J.; Szlachta, A.; Błońska, E. The impact of root systems and their exudates in different tree species on soil properties and microorganisms in a temperate forest ecosystem. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Soong, J.L.; Horton, A.J.; Campbell, E.E.; Haddix, M.L.; Wall, D.H.; Parton, W.J. Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Yang, G.; Ren, C.; Han, X. Effects of Farmland Abandonment on Soil Enzymatic Activity and Enzymatic Stoichiometry in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Chu, H. Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Ji, C.; Shen, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, B. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Jiang, J.; Classen, A.T.; Ullah, S.; Wang, G. Disentangling the contribution of mycorrhizal fungi to soil organic carbon storage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 209, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbur, P.; Wrzesiński, P.; Klisz, M.; Jevšenak, J.; Niemczyk, M.; Drozdowski, S. Consistent growth responses of silver fir (Abies alba Mill.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) to drought in mixed and monospecific forests: Insights from Central European forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 577, 122415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M. Increasing the Proportion of Broadleaf Species in Mixed Conifer-Broadleaf Forests Improves Understory Plant Composition and Promotes Soil Carbon Fixation. Plants 2025, 14, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Holloway, J.; Smith, D.B.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Drenovsky, R.E.; Scow, K.; Dick, R.; Howard, D.; Wylie, B.; Grace, J.B. The interacting roles of climate, soils, and plant production on soil microbial communities at a continental scale. Ecology 2017, 98, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in response to precipitation changes in terrestrial ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Jiajia, L.; Zhenhao, W.; Miaochun, F.; Zhouping, S. Revealing nutrient limitation status of microorganisms in the soil of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation through soil stoichiometry and enzyme metrology. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2024, 35, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Peng, X.; Shang, T.; Han, H. Soil microbial community and soil abiotic factors are linked to microorganisms’ C:N:P stoichiometry in Larix plantations. Forests 2023, 14, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Eziz, A.; Halik, Ü.; Abliz, A.; Kurban, A. Precipitation and temperature influence the relationship between stand structural characteristics and aboveground biomass of forests—A meta-analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Xia, X. Microbial community and enzyme activity respond differently to seasonal and edaphic factors in forest and grassland ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Wu, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, T.; Mao, C.; Huang, W.; Zhou, S. Tree Functional Identity Drives Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Ratios and Microbial Nutrient Limitation Responses to Artificial Forest Conversion. Forests 2025, 16, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081327
Fan Y, Wu F, Yang Y, Wang Y, Liu T, Yang T, Mao C, Huang W, Zhou S. Tree Functional Identity Drives Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Ratios and Microbial Nutrient Limitation Responses to Artificial Forest Conversion. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081327
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yixuan, Feng Wu, Yujing Yang, Yanan Wang, Tian Liu, Tao Yang, Cong Mao, Wubiao Huang, and Shuangshi Zhou. 2025. "Tree Functional Identity Drives Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Ratios and Microbial Nutrient Limitation Responses to Artificial Forest Conversion" Forests 16, no. 8: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081327
APA StyleFan, Y., Wu, F., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, T., Yang, T., Mao, C., Huang, W., & Zhou, S. (2025). Tree Functional Identity Drives Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Ratios and Microbial Nutrient Limitation Responses to Artificial Forest Conversion. Forests, 16(8), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081327






