The Influence of Slope Aspect on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Point Setting
2.3. Vegetation Investigation
2.4. Determination of Environmental Factors
2.5. Determination of Soil Factors
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microenvironment and Soil in Regard to Different Slope Aspects
3.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients in Regard to Different Slope Aspects
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Slope Aspect on Soil Spatial Heterogeneity
4.2. Effects of Slope Aspect on Seedling Regeneration Pattern
4.3. Effects of Soil Nutrients on Seedling Regeneration
4.4. Research Limitations and Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrivastav, P.; Prasad, M.; Singh, T.B.; Yadav, A.; Goyal, D.; Ali, A.; Dantu, P.K. Role of nutrients in plant growth and development. In Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management; Naeem, M., Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 43–59. ISBN 978-3-030-41552-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gazol, A.; Tamme, R.; Price, J.N.; Hiiesalu, I.; Laanisto, L.; Pärtel, M. A negative heterogeneity–diversity relationship found in experimental grassland communities. Oecologia 2013, 173, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Lv, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C. Spatial multi-scale relationships of ecosystem services: A case study using a geostatistical methodology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichami, S.M.; Shepherd, K.D.; Hoffland, E.; Karuku, G.N.; Stoorvogel, J.J. Soil spatial variation to guide the development of fertilizer use recommendations for smallholder farms in western Kenya. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 22, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Cortina, J.; Bautista, S.; Bellot, J.; Vallejo, R. Small-scale environmental heterogeneity and spatiotemporal dynamics of seedling establishment in a semiarid degraded ecosystem. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.T.; Harms, K.E.; Connell, J.H. Nonrandom, diversifying processes are disproportionately strong in the smallest size classes of a tropical forest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18649–18654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Xia, S.; Zou, C.; Goodale, U.M. Seedling growth and survival responses to multiple soil properties in subtropical forests of south China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 474, 118382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Graciano, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.; Hughes, A.C.; Ahmed, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, S.; Gao, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Plant root mechanisms and their effects on carbon and nutrient accumulation in desert ecosystems under changes in land use and climate. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil. 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabzems, R. Aspen and white spruce productivity is reduced by organic matter removal and soil compaction. For. Chron. 2012, 88, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Huang, G.; Lin, S.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Su, Y. Changes in soil organic carbon stocks and its physical fractions along an elevation in a subtropical mountain forest. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortina, J.; Vilagrosa, A.; Trubat, R. The role of nutrients for improving seedling quality in drylands. New For. 2013, 44, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako, M.O.; Xue, W.; Du, D.; Yu, F. Soil biota and soil substrates influence responses of the rhizomatous clonal grass Leymus chinensis to nutrient heterogeneity. Plant Soil. 2021, 465, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roem, W.J.; Klees, H.; Berendse, F. Effects of nutrient addition and acidification on plant species diversity and seed germination in heathland. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, K.M.; Snively, A.E.K.; Landhäusser, S.M.; Pinno, B.D. Nutrient loaded seedlings reduce the need for field fertilization and vegetation management on boreal forest reclamation sites. New For. 2016, 47, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Chen, J.; Schaefer, D.; Goodale, U.M. Effect of topography and litterfall input on fine-scale patch consistency of soil chemical properties in a tropical rainforest. Plant Soil. 2016, 404, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. Draft of major function oriented zoning of China. Dili Xuebao/Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Water use strategies of natural Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica trees of different ages in Hulunbuir Sandy Land of Inner Mongolia, China, based on stable isotope analysis. Trees 2018, 32, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jia, Z.; Lu, Q. Integrated desert control pattern in hunshandaka sand land and its benefit Evaluation—A case study of duolun county. For. Res. 2006, 19, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Guignabert, A.; Augusto, L.; Delerue, F.; Maugard, F.; Gire, C.; Magnin, C.; Niollet, S.; Gonzalez, M. Combining partial cutting and direct seeding to overcome regeneration failures in dune forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 476, 118466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 0429126220. [Google Scholar]
- Trangmar, B.B.; Yost, R.S.; Uehara, G. Application of geostatistics to spatial studies of soil properties. In Advances in Agronomy; Brady, N.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 38, pp. 45–94. ISBN 0065-2113. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, E.M.; Cannon, J.B.; Ex, S.; Ocheltree, T.W.; Redmond, M.D. Canopy-mediated microclimate refugia do not match narrow regeneration niches in a managed dry conifer forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 553, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, T.S.; Wardle, D.A.; Gundale, M.J.; Nilsson, M. Effects of soil abiotic and biotic factors on tree seedling regeneration following a boreal forest wildfire. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshof, C.M.; Spasojevic, M.J. The edaphic control of plant diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1634–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holste, E.K.; Kobe, R.K.; Vriesendorp, C.F. Seedling growth responses to soil resources in the understory of a wet tropical forest. Ecology 2011, 92, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; He, L.; Xin, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Slope aspect affects the non-structural carbohydrates and C:N:P stoichiometry of Artemisia sacrorum on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2017, 152, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, S.; Ninkov, J.; Milić, S.; Vasin, J.; Živanov, M.; Jakšić, D.; Komlen, V. Influence of slope gradient and aspect on soil organic carbon content in the region of Niš, Serbia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, O.J.; Luo, Z.; Jin, H.; Chen, Q.; Han, X. Variation in small-scale spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation with different land use in semiarid grassland ecosystem. Plant Soil. 2008, 310, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Cao, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Goodale, U.M. Fine scale heterogeneity of soil properties causes seedling spatial niche separation in a tropical rainforest. Plant Soil. 2019, 438, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Lei, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, F. Spatial heterogeneity and affecting factors of litter organic carbon and total nitrogen over natural spruce-fir mixed forests in northeastern China. Catena 2019, 174, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Kong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, M.; Wei, X. Effects of slope morphology and position on soil nutrients after deforestation in the hilly loess region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 321, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, S.; He, Z.; Jiang, L.; Gu, X.; Xu, D.; Ma, R.; Hong, W. Relationship between Pinus taiwanensis seedling regeneration and the spatial heterogeneity of soil nitrogen in Daiyun Mountain, southeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H.; Steckel, M.; Heym, M.; Biber, P.; Ammer, C.; Ehbrecht, M.; Bielak, K.; Bravo, F.; Ordóñez, C.; Collet, C.; et al. Stand growth and structure of mixed-species and monospecific stands of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and oak (Q. Robur L., Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl.) analysed along a productivity gradient through Europe. Eur. J. For. Res. 2020, 139, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, D. High adaptability of Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica to drought-induced soil nutrient deficiency. Ecol. Process 2022, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.; Fan, S.; Shen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Unraveling the roles of various ecological factors in seedling recruitment to facilitate plant regeneration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 492, 119219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmaster, D.R.J.; Iwasa, Y. Resource competition and coexistence in heterogeneous metacommunities: Many-species coexistence is unlikely to be facilitated by spatial variation in resources. PeerJ 2013, 1, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, D.H. Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. Am. Nat. 1970, 104, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comita, L.S.; Queenborough, S.A.; Murphy, S.J.; Eck, J.L.; Xu, K.; Krishnadas, M.; Beckman, N.; Zhu, Y. Testing predictions of the Janzen–Connell hypothesis: A meta-analysis of experimental evidence for distance- and density-dependent seed and seedling survival. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shen, N.; Yu, D.; Liu, C. Effects of Temporal Heterogeneity of Water Supply and Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients on the Growth and Intraspecific Competition of Bolboschoenus yagara Depend on Plant Density. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.F.; McNickle, G.G.; Haag, J.J.; Lamb, E.G.; Nyanumba, S.M.; St. Clair, C.C. Plants integrate information about nutrients and neighbors. Science 2010, 328, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, M.; Ravenek, J.M.; Smit-Tiekstra, A.E.; van der Paauw, J.W.; de Caluwe, H.; van der Putten, W.H.; de Kroon, H.; Mommer, L. Spatial heterogeneity of plant–soil feedback affects root interactions and interspecific competition. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil pH affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Han, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, M.; Liu, C. Key Strategies Underlying the Adaptation of Mongolian Scots Pine (Pinussylvestris var. Mongolica) in Sandy Land under Climate Change: A Review. Forests 2022, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolander, A.; Saarsalmi, A.; Tamminen, P. Response of soil nutrient content, organic matter characteristics and growth of pine and spruce seedlings to logging residues. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 357, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Xi, N.; Zhu, X.; Lin, W.; He, Q.; Luo, W.; et al. Neighborhood effects and environmental variables drive sapling growth in a young subtropical tree plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 483, 118929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, C.; Pyttel, P.; Modrow, T.; Kohnle, U.; Bauhus, J. Seedling development and regeneration success after 10 years following group selection harvesting in a sessile oak (Quercus petraea [Mattuschka] Liebl.) stand. Ann. For. Sci. 2020, 77, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.R.; Wright, S.J.; Zimmerman, J.K.; Hernandéz, A.; Smith, S.M.; Swenson, N.G.; Umaña, M.N.; Valencia, L.R.; Waring-Enriquez, I.; Wordell, M.; et al. Functional traits of young seedlings predict trade-offs in seedling performance in three neotropical forests. J. Ecol. 2023, 111, 2568–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, M.A.; Ninot, J.M.; Peñuelas, J.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Grau, O. Tree sapling responses to 10 years of experimental manipulation of temperature, nutrient availability, and shrub cover at the pyrenean treeline. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
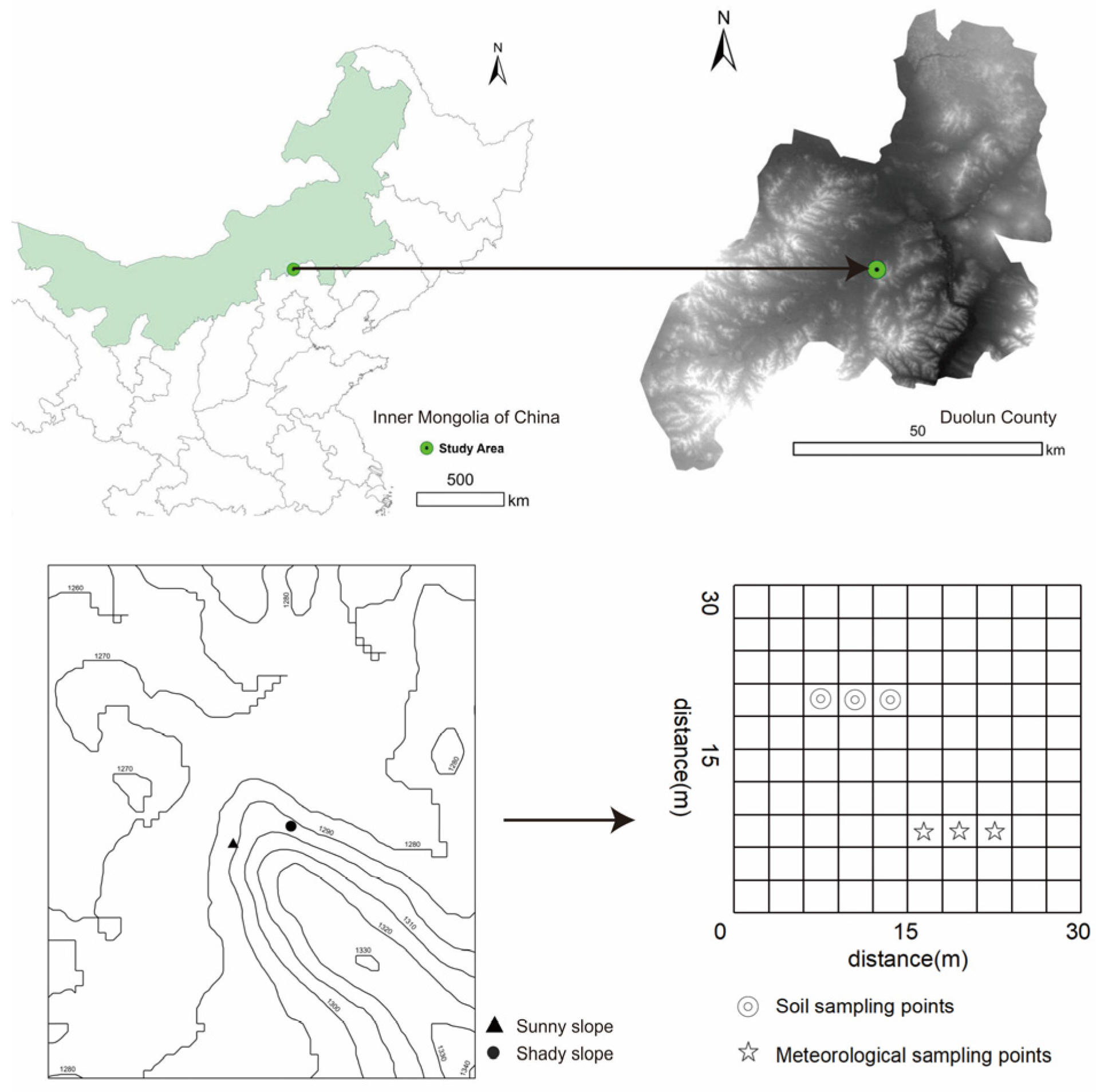
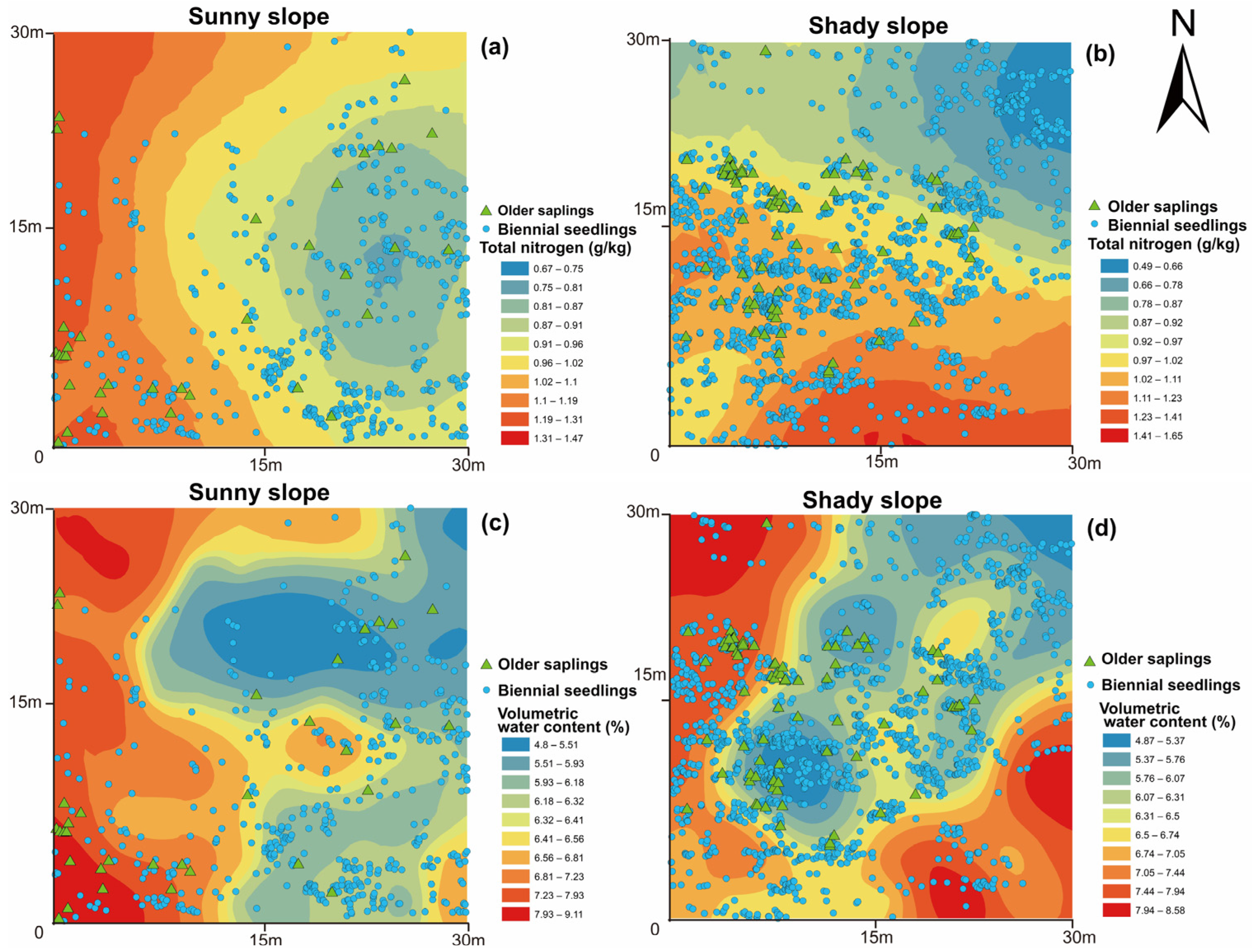
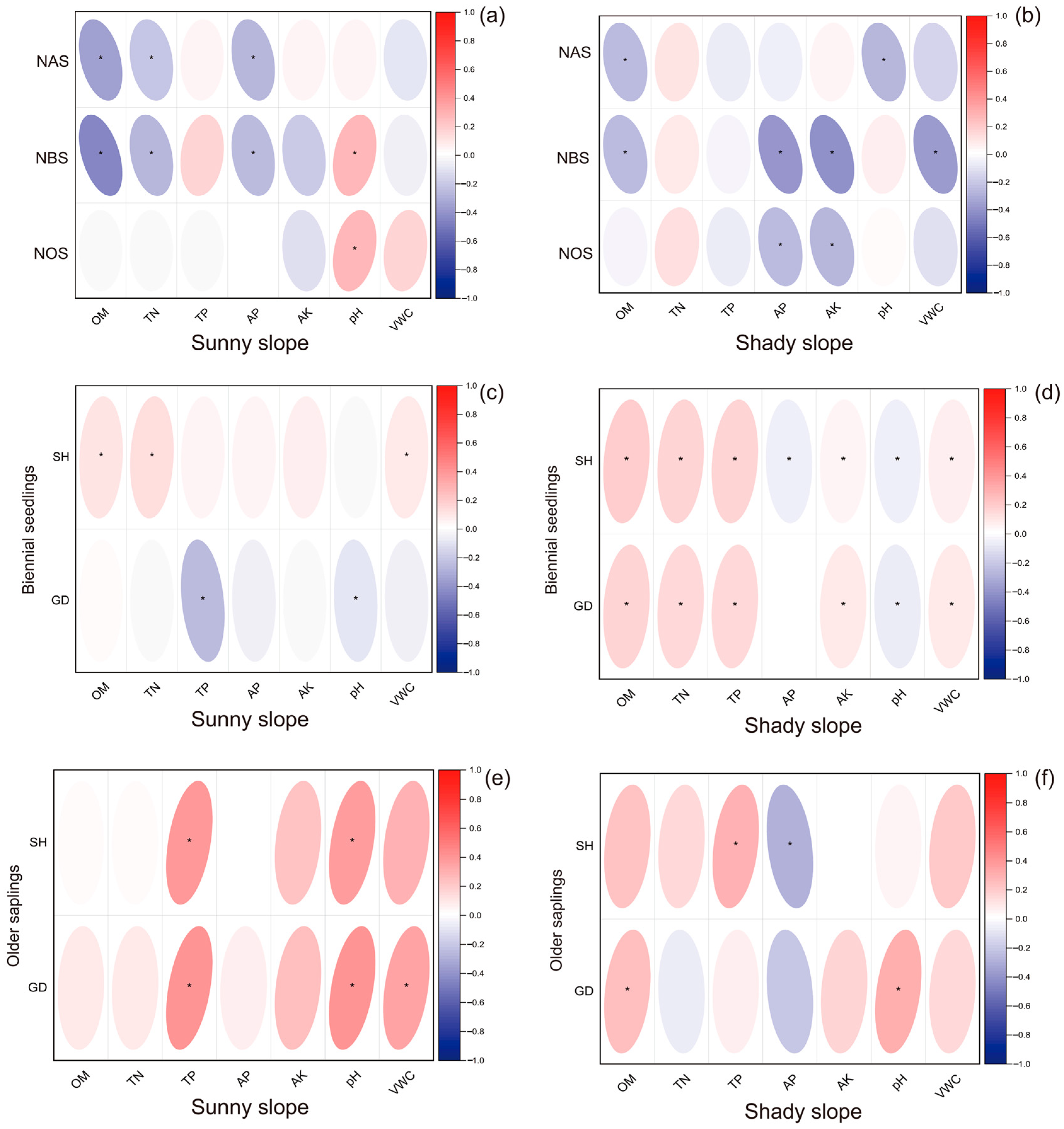
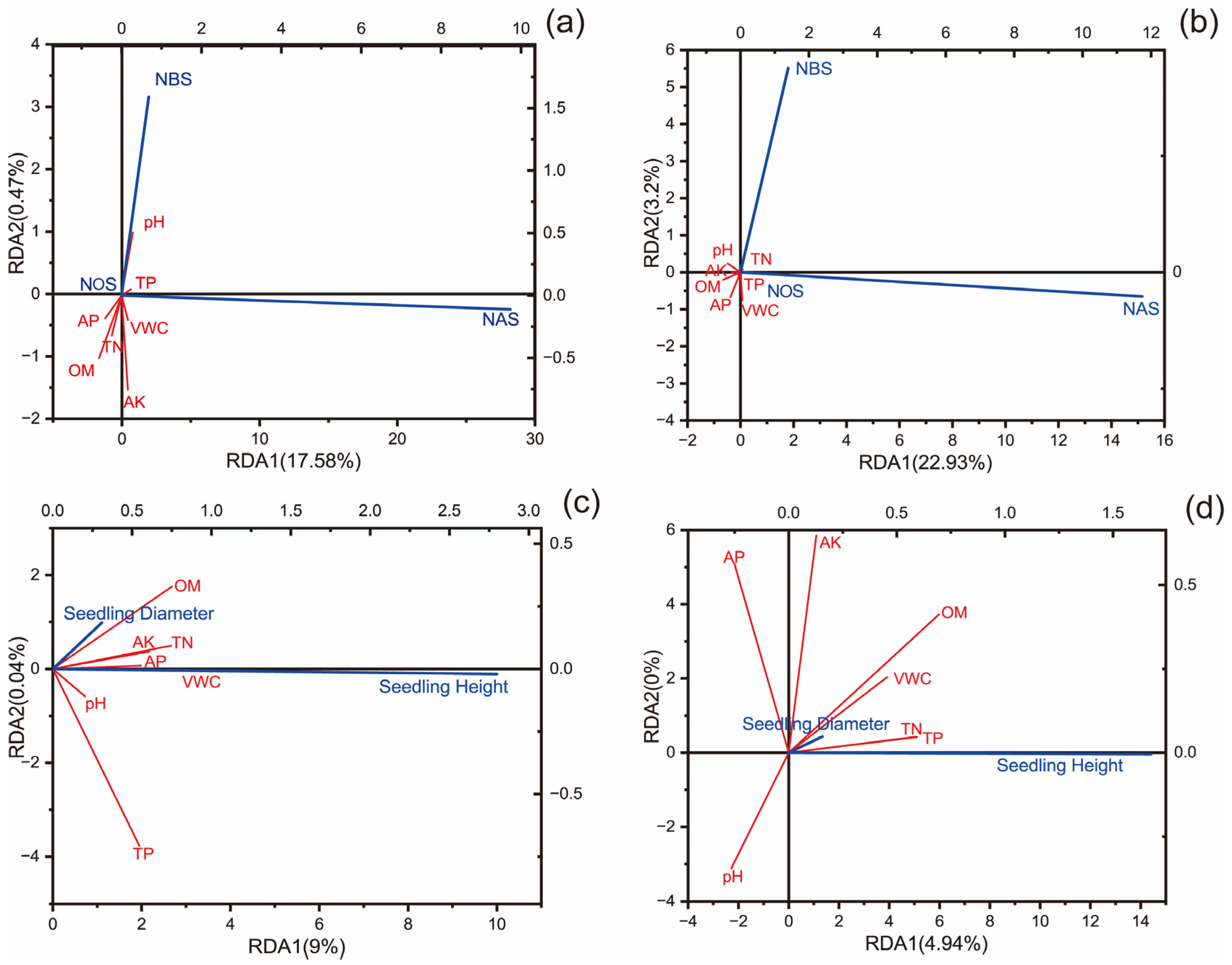
| Stand | Slope Aspect | Area (m2) | Slope (°) | Altitude (m) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Density (Stems·hm2) | Crown Density | Mean Height (m) | Mean DBH (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | sunny slope | 900 | 12 | 1287.519 | 116.489197 N | 42.139612 E | 1667 | 0.6 | 9.39 ± 1.93 | 9.97 ± 2.81 |
| II | shady slope | 900 | 11 | 1298.317 | 116.490558 N | 42.140400 E | 1722 | 0.7 | 9.37 ± 2.00 | 10.00 ± 3.07 |
| Index | Months | Sunny Slope | Shady Slope |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPFD (μmol/m2∙s) | 7 | 498.47 ± 334.58 | 359.16 ± 248.19 |
| 8 | 416.54 ± 292.51 | 460.87 ± 371.99 | |
| 9 | 225.80 ± 163.83 | 129.96 ± 120.01 | |
| 10 | 167.45 ± 134 | 62.00 ± 59.63 | |
| Total | 327.07 ± 184.29 | 253.00 ± 130.04 | |
| Air temperature (°C) | 7 | 25.20 ± 0.59 | 26.73 ± 4.81 |
| 8 | 23.06 ± 0.31 | 24.42 ± 0.45 | |
| 9 | 17.74 ± 0.17 | 17.70 ± 0.16 | |
| 10 | 9.31 ± 0.28 | 9.00 ± 0.19 | |
| Total | 18.83 ± 0.26 | 19.40 ± 1.21 | |
| Relative air humidity (%) | 7 | 49.22 ± 1.19 | 55.91 ± 63.62 |
| 8 | 43.8 ± 1.86 | 39.92 ± 5.30 | |
| 9 | 64.66 ± 18.69 | 60.14 ± 6.23 | |
| 10 | 25.2 ± 2.86 | 23.9 ± 0.52 | |
| Total | 45.72 ± 4.79 | 44.97 ± 15.98 |
| Slope Aspect | Items | Min. | Max. | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Kurtosis | Skewness | K-S D | K-S P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny slope | OM (g/kg) | 3.50 | 21.24 | 8.14 | 4.02 | 49% | 0.46 | 0.93 | 0.12 | 0.001 |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.67 | 1.47 | 0.97 | 0.18 | 18% | −0.29 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 0.010 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | 58.55 | 222.49 | 103.25 | 22.59 | 22% | 10.60 | 2.35 | 0.15 | 0.000 | |
| AP (mg/kg) | 14.77 | 62.43 | 31.59 | 7.48 | 24% | 1.72 | 0.82 | 0.08 | 0.117 | |
| AK (mg/kg) | 2.47 | 27.22 | 9.13 | 4.32 | 47% | 2.18 | 1.09 | 0.18 | 0.000 | |
| pH | 5.80 | 6.22 | 6.01 | 0.09 | 1% | −0.11 | −0.02 | 0.07 | 0.200 * | |
| VWC (%) | 4.80 | 9.11 | 6.38 | 0.82 | 13% | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.009 | |
| Shady slope | OM (g/kg) | 3.41 | 27.24 | 9.05 | 4.65 | 51% | 2.68 | 1.52 | 0.16 | 0.000 |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.49 | 1.65 | 0.97 | 0.24 | 25% | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.102 | |
| TP (mg/kg) | 83.90 | 139.28 | 101.46 | 9.31 | 9% | 3.05 | 1.12 | 0.09 | 0.039 | |
| AP (mg/kg) | 17.00 | 62.56 | 33.55 | 8.45 | 25% | 1.20 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.000 | |
| AK (mg/kg) | 2.47 | 32.17 | 10.34 | 5.69 | 55% | 1.51 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 0.000 | |
| pH | 5.73 | 6.18 | 5.95 | 0.09 | 2% | −0.30 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.200 * | |
| VWC (%) | 4.87 | 8.58 | 6.57 | 0.87 | 13% | −0.85 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.015 |
| Slope Aspect | Seedling Type | Number | Density (Plant/m2) | Height of Seedlings (cm) | Ground Diameter of Seedlings (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny slope | Annual seedlings | 7308 | 8.12 | no data | no data |
| Biennial seedlings | 556 | 0.62 | 4.45 ± 2.55 | 0.72 ± 0.31 | |
| Older saplings | 34 | 0.04 | 13.62 ± 7.68 | 2.14 ± 0.82 | |
| Shady slope | Annual seedlings | 7378 | 8.20 | no data | no data |
| Biennial seedlings | 1910 | 2.12 | 3.8 ± 1.1 | 0.64 ± 0.13 | |
| Older saplings | 78 | 0.09 | 6.69 ± 3.1 | 0.96 ± 0.38 |
| Slope Aspect | Soil Property | C0 | Sill (C0 + C) | A0 (m) | C0/(C0 + C) | Theoretical Model | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny slope | OM | 0.0122 | 0.1156 | 55.69 | 10.55% | Gaussian | 0.989 | 3.27 × 10−5 |
| TN | 0.00192 | 0.01012 | 35.47 | 18.97% | Gaussian | 0.981 | 8.99 × 10−7 | |
| TP | 0.00559 | 0.01198 | 170.82 | 46.66% | Exponential | 0.683 | 1.89 × 10−6 | |
| AP | 0.00605 | 0.029 | 70.17 | 20.86% | Gaussian | 0.932 | 5.40 × 10−6 | |
| AK | 0.036 | 0.0906 | 213.00 | 39.74% | Exponential | 0.830 | 4.30 × 10−5 | |
| pH | 0.00497 | 0.01563 | 163.38 | 31.80% | Exponential | 0.715 | 4.91 × 10−6 | |
| VWC | 0.00045 | 0.00692 | 60.02 | 6.50% | Spherical | 0.975 | 3.18 × 10−7 | |
| Shady slope | OM | 0.01386 | 0.04052 | 27.46 | 34.21% | Spherical | 0.931 | 3.49 × 10−5 |
| TN | 0.00423 | 0.02866 | 46.83 | 14.76% | Gaussian | 0.98 | 5.24 × 10−6 | |
| TP | 0.00093 | 0.00545 | 80.40 | 17.06% | Gaussian | 0.973 | 5.09 × 10−8 | |
| AP | 0.0039 | 0.0127 | 23.57 | 30.71% | Spherical | 0.926 | 3.82 × 10−6 | |
| AK | 0.0054 | 0.066 | 6.39 | 8.18% | Exponential | 0.262 | 2.53 × 10−4 | |
| pH | 0.00292 | 0.02084 | 45.29 | 14.01% | Gaussian | 0.997 | 5.20 × 10−7 | |
| VWC | 0.00001 | 0.00389 | 19.69 | 0.26% | Spherical | 0.967 | 3.05 × 10−7 |
| Slope Aspect | Items | ME | RMSE | MSE | SA | NRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny slope | OM | 0.14 | 2.35 | 2.61 | 0.07 | 0.99 |
| TN | 0 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.98 | |
| TP | 0 | 22.8 | 19.97 | −0.02 | 1.1 | |
| AP | −0.13 | 6.28 | 6.02 | −0.03 | 1.03 | |
| AK | 0.02 | 4.22 | 4.63 | −0.02 | 0.98 | |
| pH | 0 | 0.07 | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.92 | |
| VWC | 0 | 0.31 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.75 | |
| Shady slope | OM | −0.02 | 3.25 | 3.52 | 0.02 | 0.89 |
| TN | 0 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.96 | |
| TP | 0.19 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 0.02 | 1.05 | |
| AP | −0.03 | 6.78 | 6.64 | 0 | 0.99 | |
| AK | 0.14 | 5.05 | 6.57 | 0.02 | 0.78 | |
| pH | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0 | 1.1 | |
| VWC | 0 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, W.; Duan, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Mu, M. The Influence of Slope Aspect on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation Forests. Forests 2025, 16, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071100
Duan W, Duan J, Qu M, Wang Y, Zhu S, Wang H, Mu M. The Influence of Slope Aspect on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation Forests. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071100
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Wenbiao, Jingyue Duan, Meixue Qu, Yafei Wang, Shuaiwei Zhu, Haoyu Wang, and Miaoxian Mu. 2025. "The Influence of Slope Aspect on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation Forests" Forests 16, no. 7: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071100
APA StyleDuan, W., Duan, J., Qu, M., Wang, Y., Zhu, S., Wang, H., & Mu, M. (2025). The Influence of Slope Aspect on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Seedling Regeneration in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation Forests. Forests, 16(7), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071100





