Impact of Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Function in Pinus densata Forest, Southeastern Tibet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Site Selection and Sampling Acquisition
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Indicators Determination
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing of Soil Bacterial Communities
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Structure
3.2. Soil Environmental Factors
3.3. Soil Bacterial Community Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Forest Fire Severity on the Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities
4.2. Effects of Forest Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Composition
4.3. Impact of Forest Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Functions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flannigan, M.D.; Krawchuk, M.A.; de Groot, W.J.; Wotton, B.M.; Gowman, L.M. Implications of changing climate for global wildland fire. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jia, G.; Zhang, X.; Riley, W.J.; Xue, Y. Climate regime shift and forest loss amplify fire in Amazonian forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5874–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Lin, H.; Hu, H.; Song, H. A review of models of forest fire occurrence prediction in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3227–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Wei, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, M. Research Progress on the Effects of Forest Fire Disturbance on Soil Carbon Release in High-latitude Permafrost Regions. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1278. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Noack, A.G. Black carbon in soils and sediments: Analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbeshie, A.A.; Abugre, S.; Atta-Darkwa, T.; Awuah, R. A review of the effects of forest fire on soil properties. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Birch, P. Soil microbial activity in opencast coal mine restorations. Soil Use Manag. 1989, 5, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Li, Z.; Cai, Z. Effects of long-term different fertilization on soil enzyme activity and microbial community functional diversity in paddy soil derived from Quaternary red clay. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2006, 22, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Perrault-Hébert, M.; Boucher, Y.; Fournier, R.; Girard, F.; Auger, I.; Thiffault, N.; Grenon, F. Ecological drivers of post-fire regeneration in a recently managed boreal forest landscape of eastern Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 399, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincă, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Onet, C.; Onet, A. Fertilization and soil microbial community: A review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knelman, J.E.; Graham, E.B.; Trahan, N.A.; Schmidt, S.K.; Nemergut, D.R. Fire severity shapes plant colonization effects on bacterial community structure, microbial biomass, and soil enzyme activity in secondary succession of a burned forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwerth, K.L.; Jackson, L.E.; Calderón, F.J.; Stromberg, M.R.; Scow, K.M. Soil microbial community composition and land use history in cultivated and grassland ecosystems of coastal California. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontúrbel, M.; Barreiro, A.; Vega, J.; Martín, A.; Jiménez, E.; Carballas, T.; Fernández, C.; Díaz-Raviña, M. Effects of an experimental fire and post-fire stabilization treatments on soil microbial communities. Geoderma 2012, 191, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Cui, X.; Di, X.; Jin, S. Effects of different forest fire intensities on microbial community functional diversity in forest soil in Daxing’anling. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 48, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bowd, E.J.; Egidi, E.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Wardle, D.A.; Kardol, P.; Cary, G.J.; Foster, C. Direct and indirect effects of fire on microbial communities in a pyrodiverse dry-sclerophyll forest. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, G.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.; Shu, L. Effects of fire disturbance on soil bacterial community in Pinus tabuliformis forest. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Geilfus, C.-M.; Wei, J.; Zheng, F.; Liu, Z.; Tan, D. Managing nitrogen for sustainable crop production with reduced hydrological nitrogen losses under a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system: An eight-season field study. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1274943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Fu, B.; Lu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Hu, W. Exogenous organic materials applied to paddy field improving soil microbial biomass C, N and dissolved organic C, N. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.; Dexter, M.; Perrott, K. Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: A sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilisation, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; DiCuccio, M.; Edgar, R.; Federhen, S. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D13–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, L.; Feeney, B. A Simple Guide to IBM SPSS: For Version 20.0; Nelson Education: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Dynamics of Soil Microbial Community During Fire Chronosequences in Pinus yunnanensis Forest in Central Yunnan. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Hao, M.; Zang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of long-term fertilization on microbial diversity of black loessial soil based on 454 sequencing technology. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2015, 29, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, A.; Di, X. Immediate changes in soil organic carbon and microbial biomassc arbon after an experimental fire in Great Xing’an Mountains. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2011, 39, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zheng, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C. Effects of Catastrophic forest fire in the Great Xingan Mountains on soil microorganisms. Chin. J. Ecol. 1988, 7, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Review on Biochar decomposition and priming effect. Earth Environ. 2017, 45, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certini, G. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: A review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wu, S.; Du, J.; Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. Variations in the diversity and biomass of soil bacteria and fungi under different fire disturbances in the taiga forests of northeastern China. Forests 2023, 14, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neary, D.G.; Klopatek, C.C.; DeBano, L.F.; Ffolliott, P.F. Fire effects on belowground sustainability: A review and synthesis. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 122, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F. Effects of Fire Disturbance on Soil Microbial Diversity and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Xing’an Larch Forest. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, O.; Bolat, I. Short-term effects of wildfire on microbial biomass and abundance in black pine plantation soils in Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, D. Soil phosphorus forms and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria distribution after restoration from seriously burning in Greater Khingan Mountain areas, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.C.; DeLuca, T.H.; Newman, G.S.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Boyle, S.I. Post-fire vegetative dynamics as drivers of microbial community structure and function in forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 220, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, P.H.; Barro, S.C.; Poth, M. Soil moisture affects survival of microorganisms in heated chaparral soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Uwiragiye, Y.; Dan, X.; Tang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Meng, L. Fire Reduces Soil Nitrate Retention While Increasing Soil Nitrogen Production and Loss Globally. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 23004–23017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, Q.; Xu, J. Soil Biochemistry; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J. Effects of wildfire and topography on soil nutrients in a semiarid restored grassland. Plant Soil 2018, 428, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
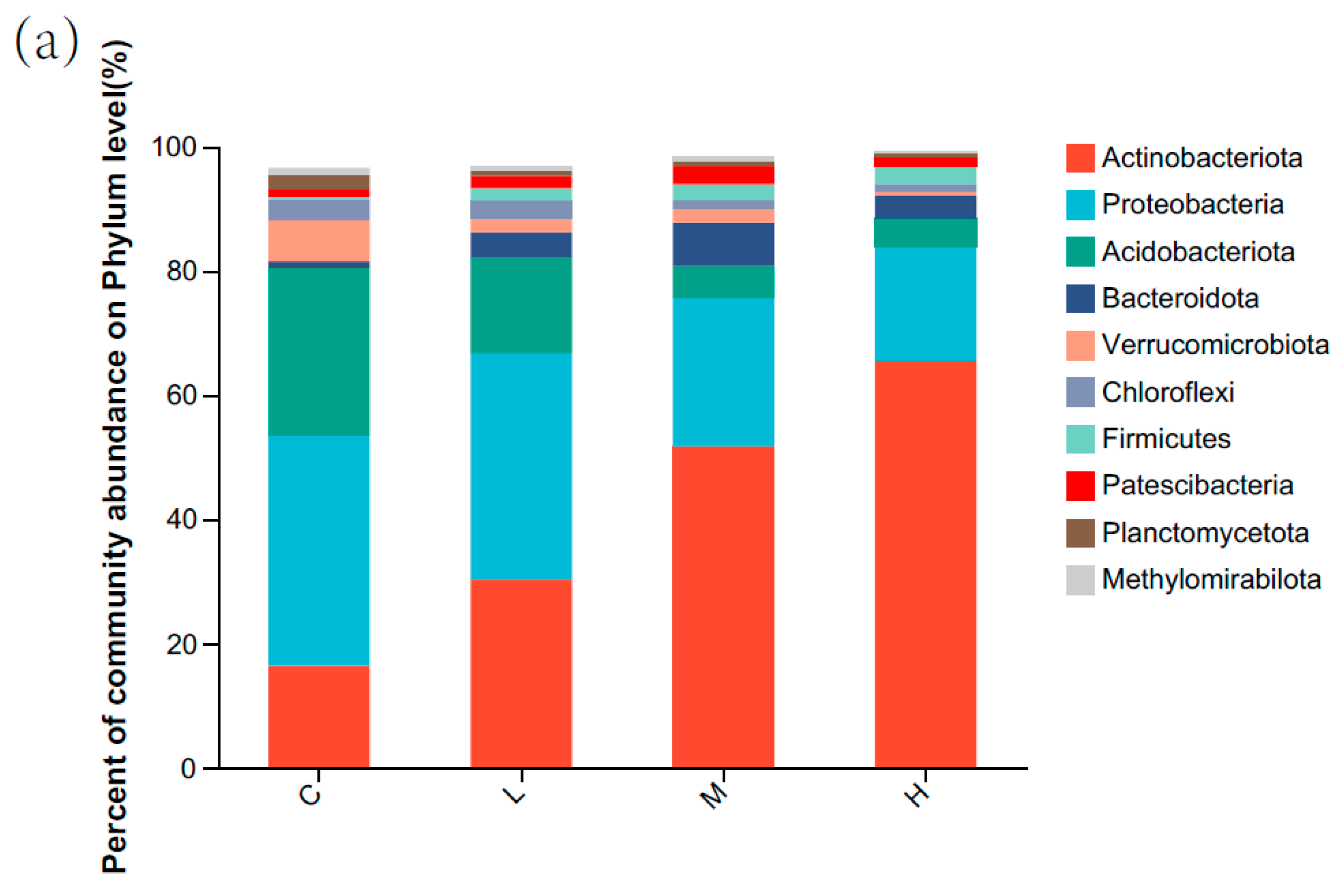
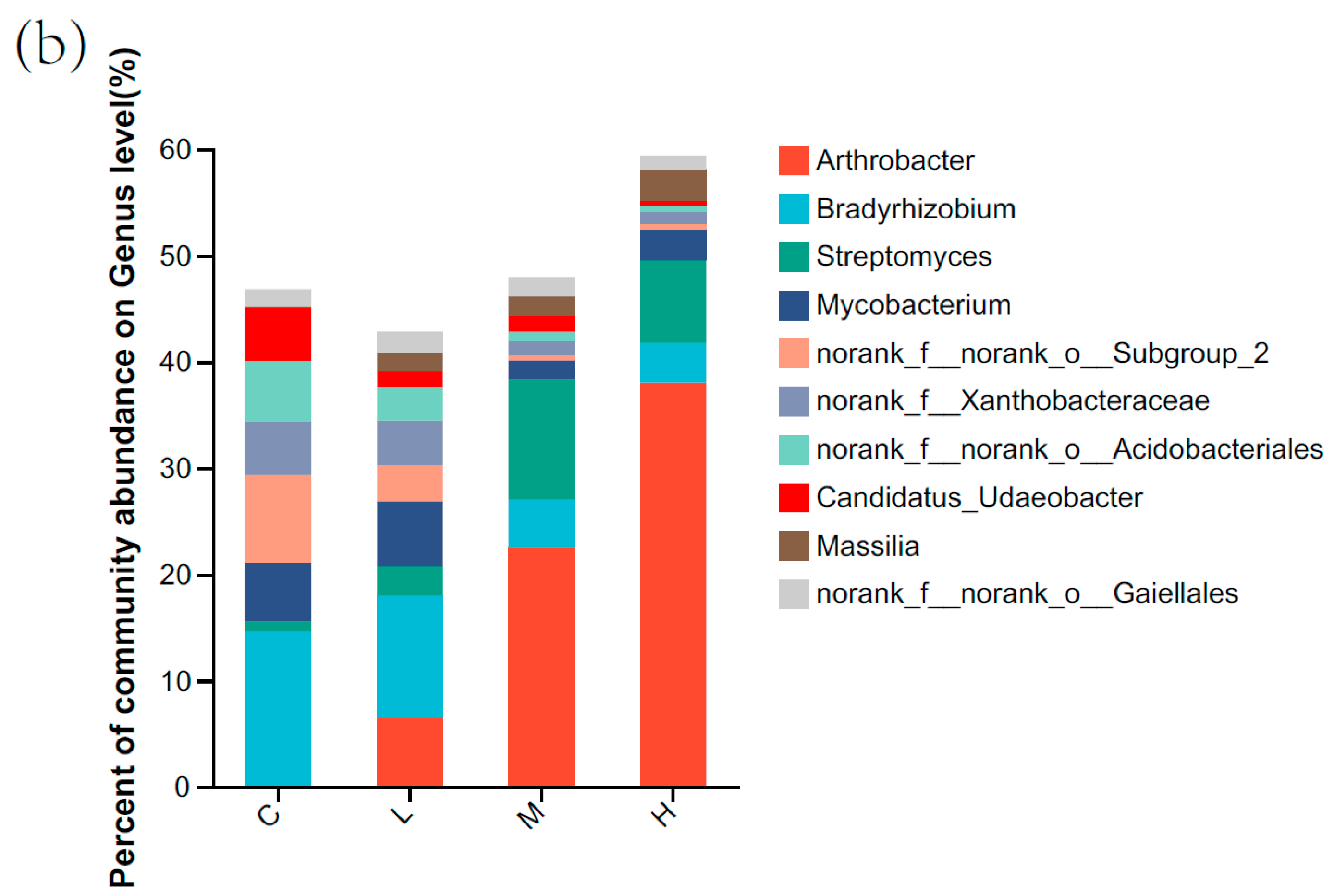

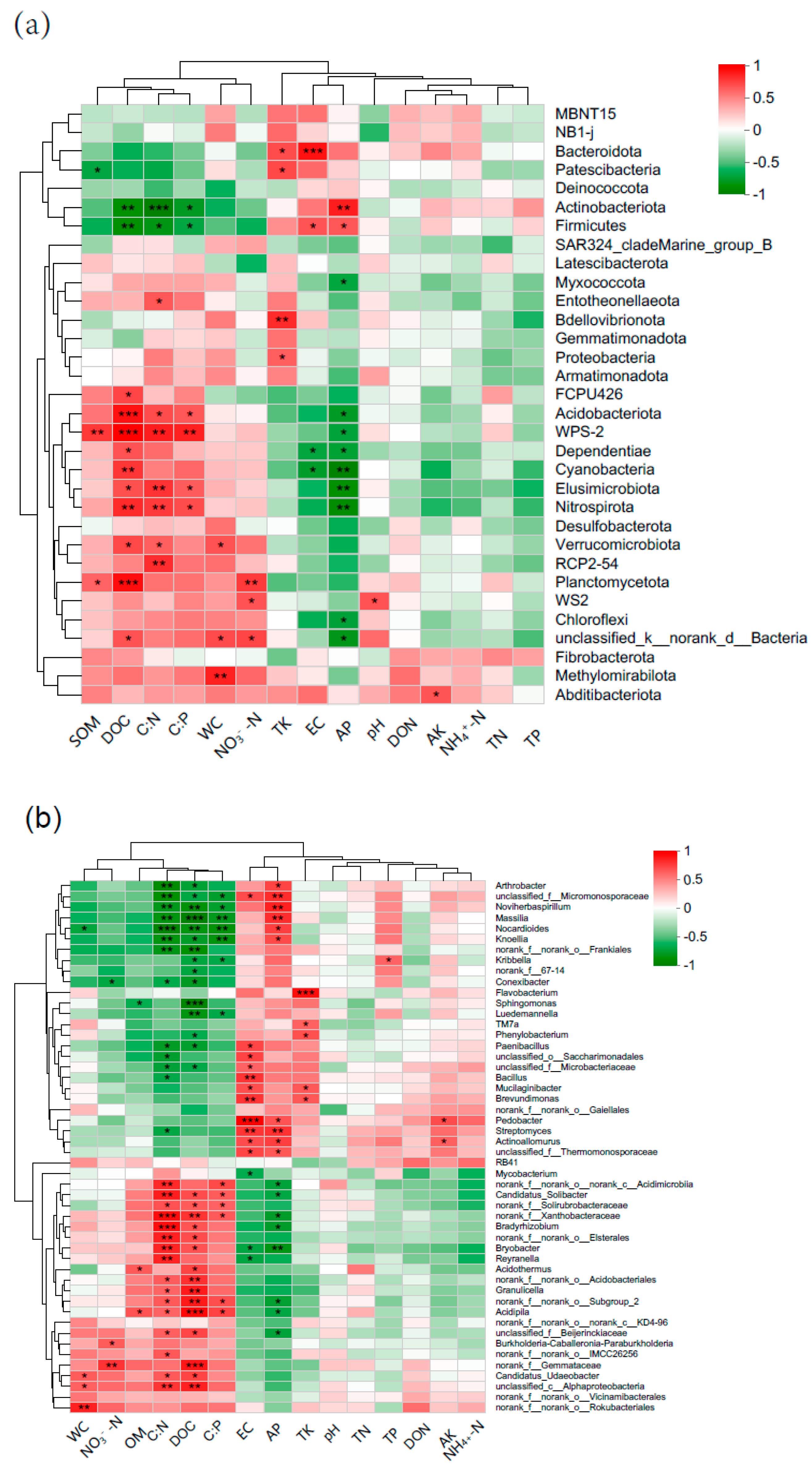
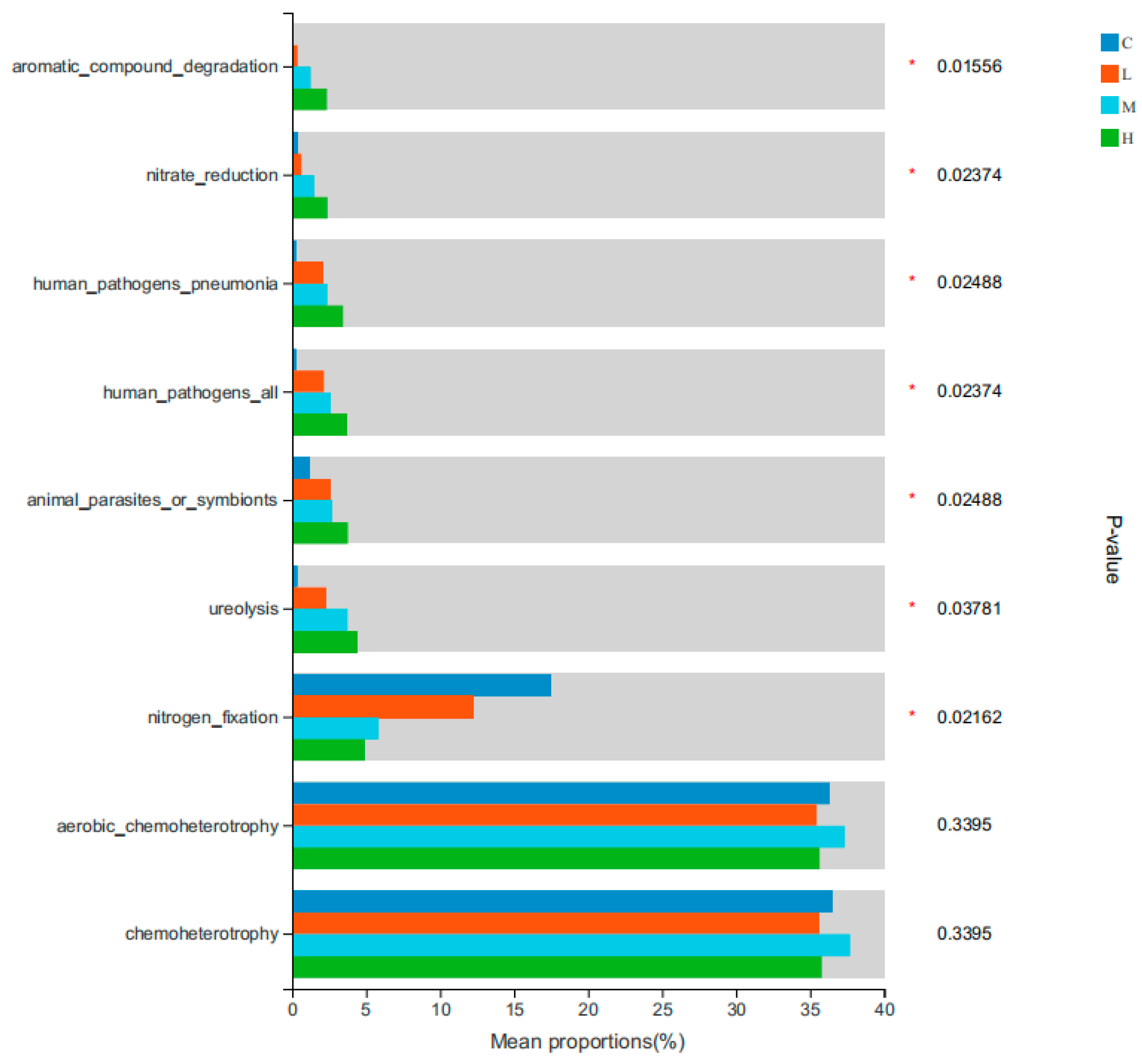
| Sample | CK | L | M | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.17 ± 0.43 a | 5.97 ± 0.37 a | 5.91 ± 0.22 a | 6.02 ± 0.16 a |
| EC/(μs/cm) | 33.14 ± 10.22 a | 41.55 ± 2.99 a | 62.21 ± 23.20 a | 44.26 ± 19.67 a |
| WC/% | 24.96 ± 4.46 a | 18.04 ± 5.04 ab | 22.89 ± 3.01 ab | 11.36 ± 2.68 b |
| SOM/% | 4.96 ± 0.84 a | 5.25 ± 0.80 a | 5.02 ± 1.37 a | 4.27 ± 0.91 a |
| TN/% | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.13 ± 0.03 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 a |
| TP/% | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a |
| TK/% | 1.04 ± 0.03 a | 1.08 ± 0.06 a | 1.08 ± 0.05 a | 1.02 ± 0.02 a |
| AP/(mg/kg) | 19.65 ± 3.33 b | 33.09 ± 9.08 b | 61.84 ± 22.34 a | 61.84 ± 10.91 a |
| AK/(mg/kg) | 179.65 ± 24.94 a | 189.52 ± 20.53 a | 304.68 ± 123.67 a | 201.37 ± 26.56 a |
| NO3−-N/(mg/kg) | 0.24 ± 0.06 a | 0.16 ± 0.03 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.18 ± 0.04 a |
| NH4+-N/(mg/kg) | 9.15 ± 1.88 a | 9.21 ± 3.16 a | 21.60 ± 7.94 b | 9.06 ± 5.71 a |
| DON | 27.04 ± 6.03 ab | 25.69 ± 4.73 b | 39.73 ± 9.79 a | 21.61 ± 5.75 b |
| DOC | 250.05 ± 42.38 a | 205.31 ± 59.66 ab | 167.03 ± 39.58 ab | 144.05 ± 52.22 b |
| C/N | 25.33 ± 1.86 a | 24.59 ± 2.33 a | 21.16 ± 2.84 ab | 19.64 ± 1.86 b |
| C/P | 57.94 ± 15.64 a | 57.04 ± 7.87 a | 48.14 ± 6.13 a | 39.25 ± 11.62 a |
| Sample | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 3.92 ± 0.23 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 327.39 ± 20.55 a | 329.84 ± 23.68 c |
| L | 4.24 ± 0.16 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 394.95 ± 18.75 b | 393.50 ± 17.64 a |
| M | 3.83 ± 0.06 a | 0.08 ± 0.02 a | 346.85 ± 10.55 a | 351.25 ± 5.95 b |
| H | 3.20 ± 0.42 b | 0.17 ± 0.07 b | 305.79 ± 30.48 a | 320.11 ± 27.66 c |
| Soil Environmental Factors | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.095 | −0.051 | −0.181 | −0.205 |
| EC | −0.14 | 0.175 | −0.08 | −0.056 |
| WC | 0.5 | −0.521 | 0.039 | −0.048 |
| SOM | 0.304 | −0.334 | 0.3 | 0.166 |
| TN | −0.114 | 0.102 | 0.043 | −0.02 |
| TP | −0.139 | 0.09 | 0.034 | 0.048 |
| TK | 0.372 | −0.241 | 0.299 | 0.298 |
| AP | −0.377 | 0.398 | −0.152 | −0.104 |
| AK | 0.084 | −0.099 | 0.092 | 0.053 |
| NO−3-N | 0.109 | −0.145 | −0.376 | −0.514 |
| NH+4-N | −0.015 | 0.014 | −0.042 | −0.056 |
| DON | 0.131 | −0.134 | 0.014 | −0.055 |
| DOC | 0.283 | −0.393 | 0.104 | −0.028 |
| C/N | 0.585 * | −0.611 * | 0.414 | 0.295 |
| C/P | 0.383 | −0.38 | 0.198 | 0.084 |
| Functional Gene | pH | EC | WC | SOM | TN | TP | TK | AP | AK | NO3-N | DON | DOC | C/P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemoheterotrophy | −0.111 | 0.676 * | −0.252 | −0.186 | 0.140 | 0.415 | 0.408 | 0.676 * | 0.539 | −0.472 | 0.240 | 0.095 | −0.493 | −0.491 |
| aerobic_chemoheterotrophy | −0.108 | 0.676 * | −0.255 | −0.185 | 0.136 | 0.422 | 0.405 | 0.679 * | 0.544 | −0.472 | 0.237 | 0.091 | −0.493 | −0.493 |
| nitrogen_fixation | −0.044 | −0.552 | 0.345 | 0.361 | −0.256 | −0.251 | −0.081 | −0.677 * | −0.258 | 0.165 | −0.320 | −0.160 | 0.610 * | 0.513 |
| Ureolysis | −0.219 | 0.356 | −0.390 | −0.517 | 0.019 | 0.324 | 0.249 | 0.704 * | 0.211 | −0.433 | 0.173 | −0.064 | −0.879 ** | −0.638 * |
| animal_parasites_or_symbionts | −0.226 | 0.359 | −0.479 | −0.533 | −0.075 | 0.396 | 0.272 | 0.735 ** | 0.202 | −0.460 | 0.019 | −0.231 | −0.884 ** | −0.697 * |
| human_pathogens_all | −0.164 | 0.383 | −0.505 | −0.496 | −0.016 | 0.375 | 0.266 | 0.739 ** | 0.213 | −0.481 | 0.053 | −0.190 | −0.874 ** | −0.653 * |
| human_pathogens_pneumonia | −0.170 | 0.353 | −0.507 | −0.492 | −0.033 | 0.390 | 0.258 | 0.735 ** | 0.211 | −0.483 | 0.036 | −0.209 | −0.880 ** | −0.653 * |
| nitrate_reduction | 0.083 | 0.525 | −0.424 | −0.605* | −0.058 | 0.360 | 0.082 | 0.677 * | 0.230 | −0.482 | 0.179 | −0.098 | −0.789 ** | −0.717 ** |
| aromatic_compound_degradation | −0.082 | 0.297 | −0.598* | −0.520 | 0.105 | 0.467 | −0.134 | 0.704 * | 0.127 | −0.426 | 0.088 | −0.164 | −0.745 ** | −0.729 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, W. Impact of Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Function in Pinus densata Forest, Southeastern Tibet. Forests 2025, 16, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060894
Hou L, Chen J, Lin W. Impact of Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Function in Pinus densata Forest, Southeastern Tibet. Forests. 2025; 16(6):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060894
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Lei, Jie Chen, and Wen Lin. 2025. "Impact of Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Function in Pinus densata Forest, Southeastern Tibet" Forests 16, no. 6: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060894
APA StyleHou, L., Chen, J., & Lin, W. (2025). Impact of Fire Severity on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Its Function in Pinus densata Forest, Southeastern Tibet. Forests, 16(6), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060894






