Reinforcement Effects on the Properties of Wood-Veneered Wood Fiber/Fabric/High-Density Polyethylene Laminated Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
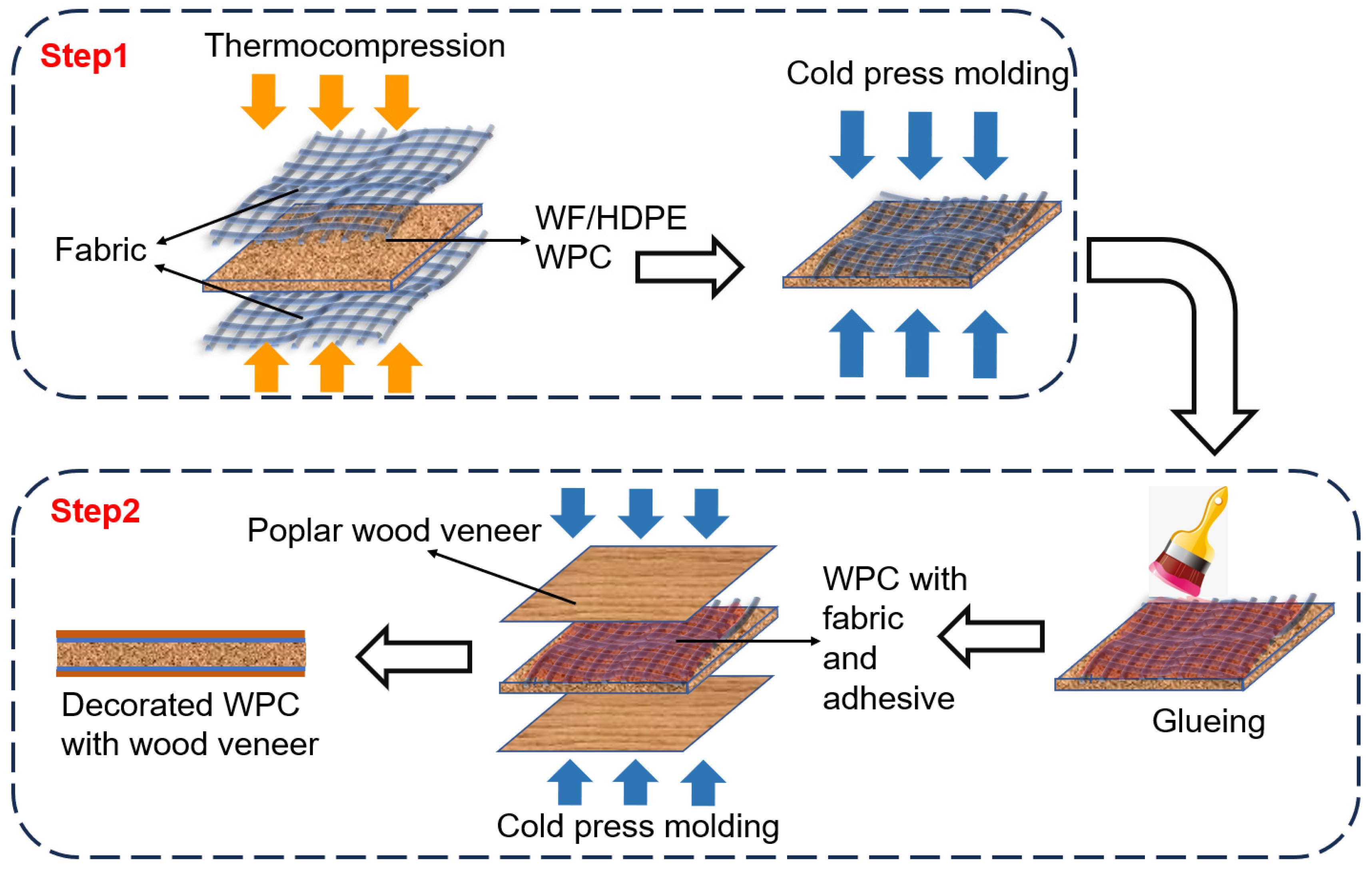
2.2. Preparation Parameters of the Fabric-Decorated WF/HDPE Substrate
2.3. Preparation of Wood-Veneered WF/HDPE Composite Panels
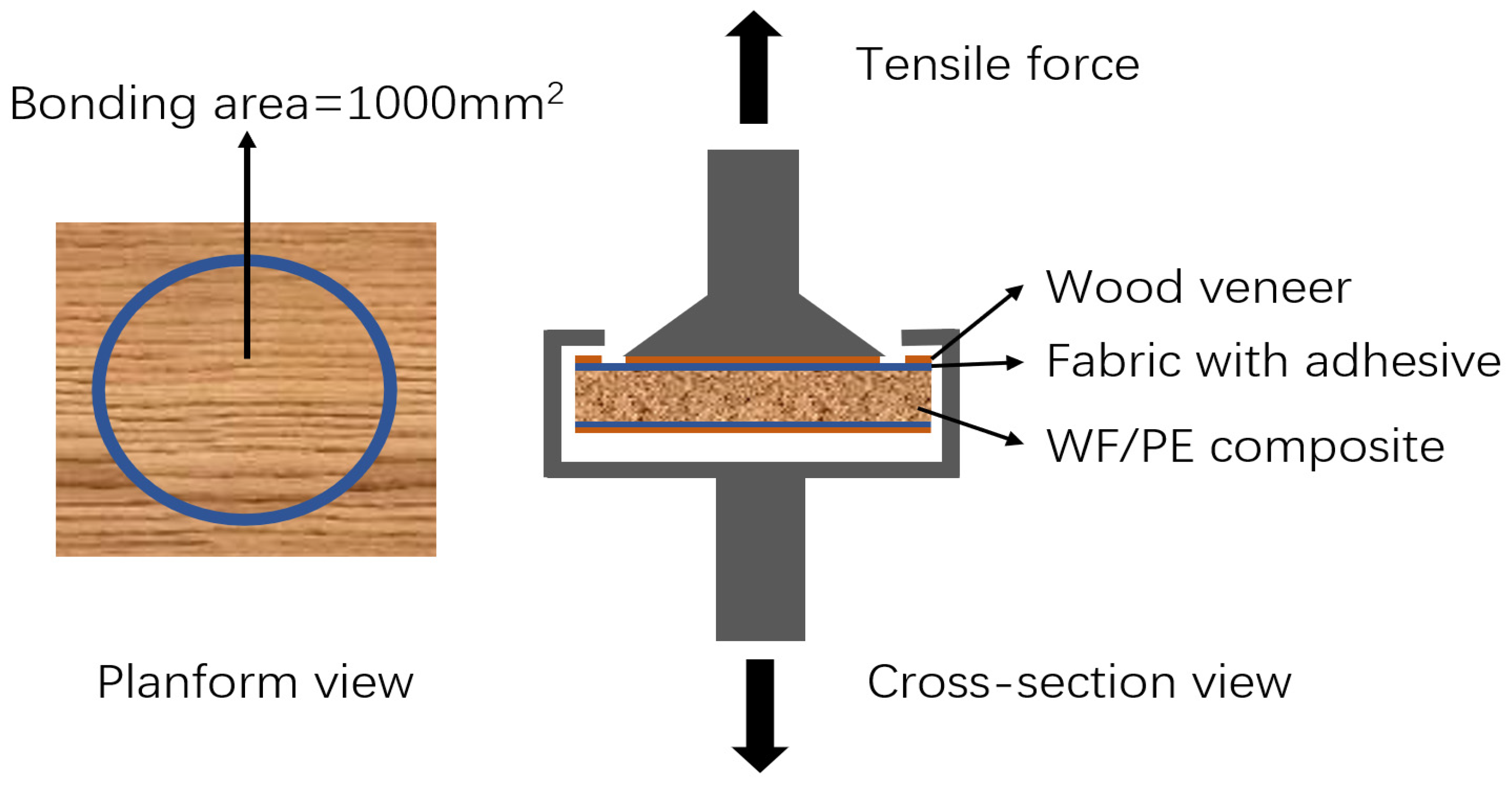
2.4. Surface Bonding Strength Test
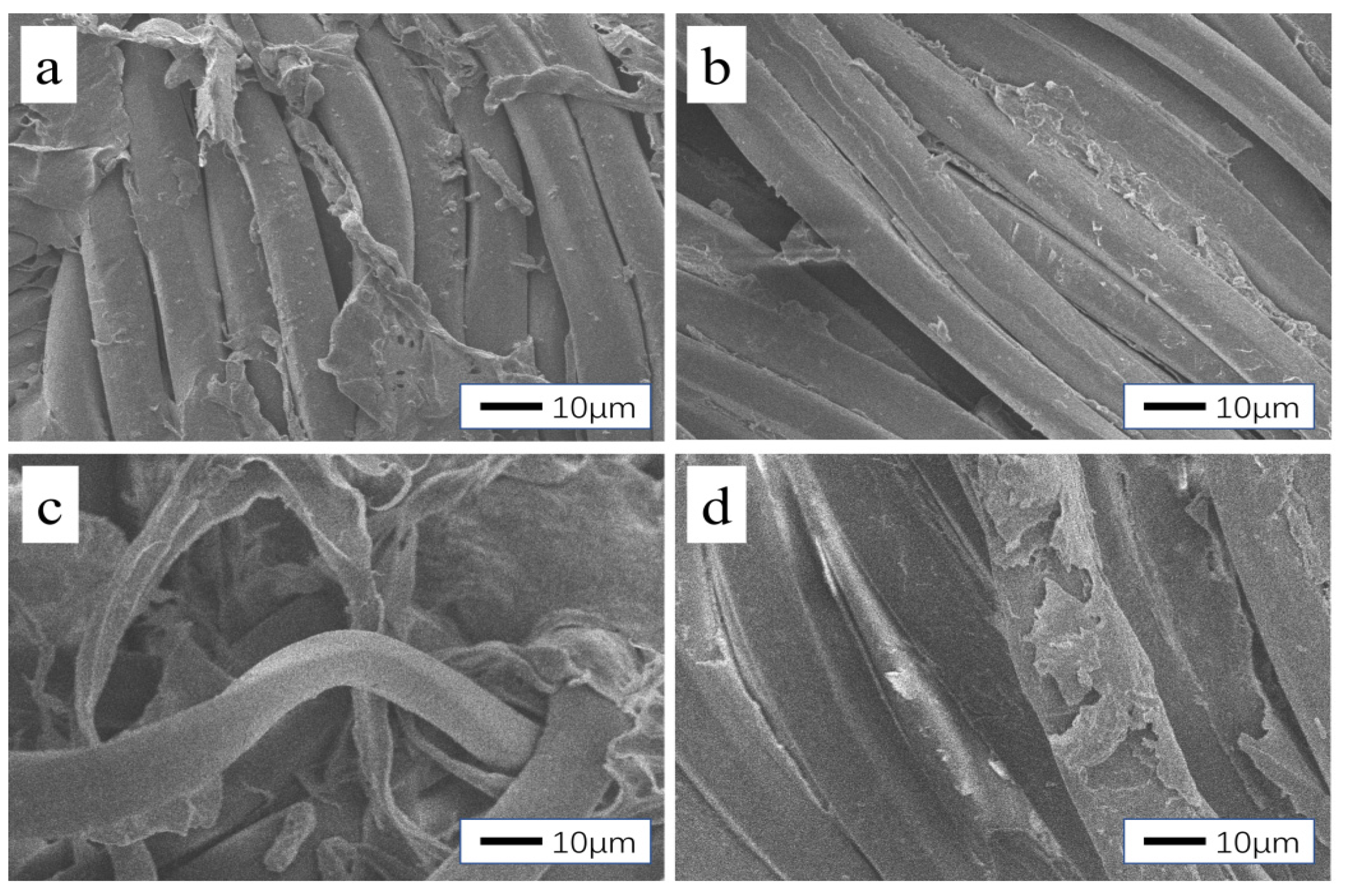
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
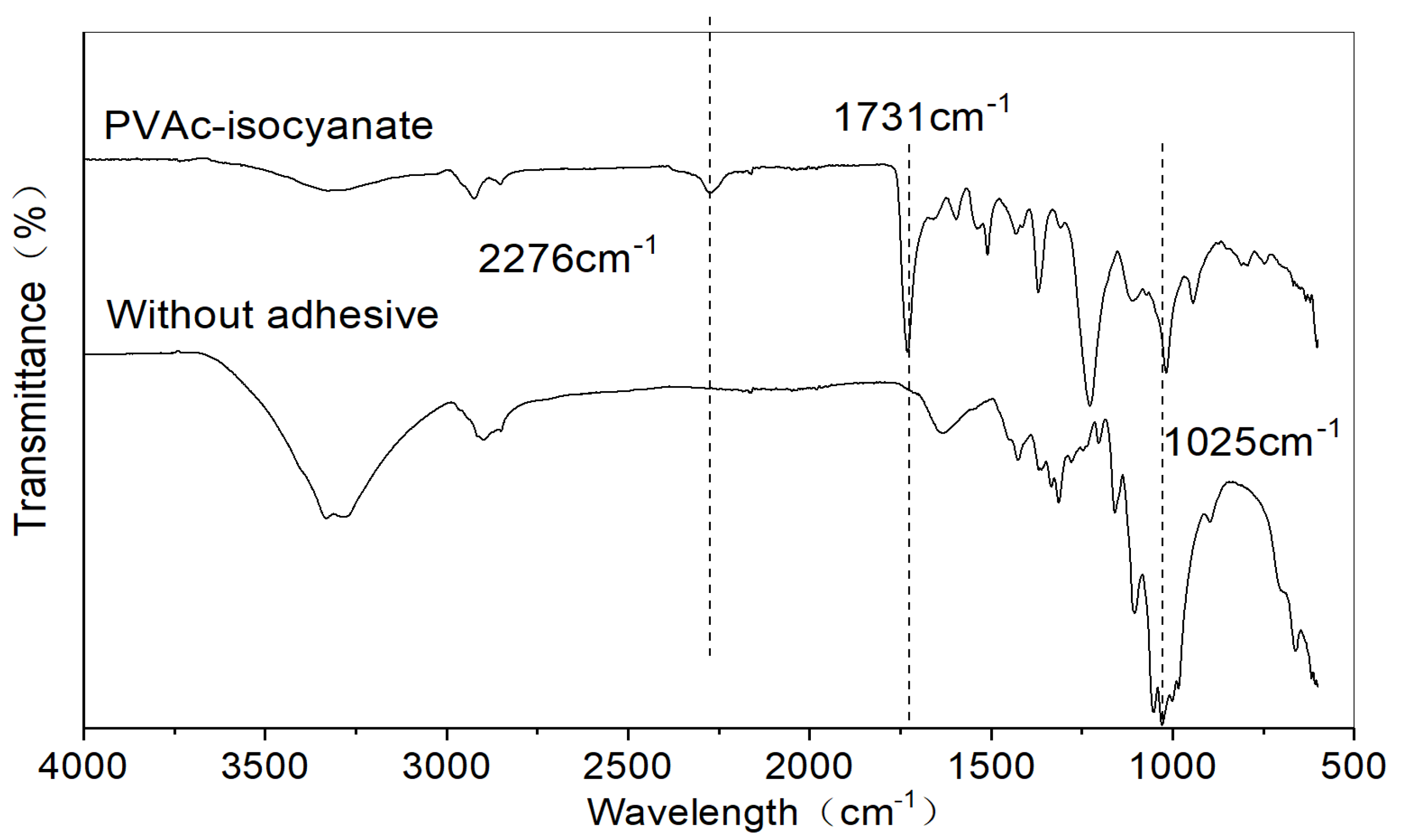
2.6. Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.7. Bending Strength Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Bonding Strength
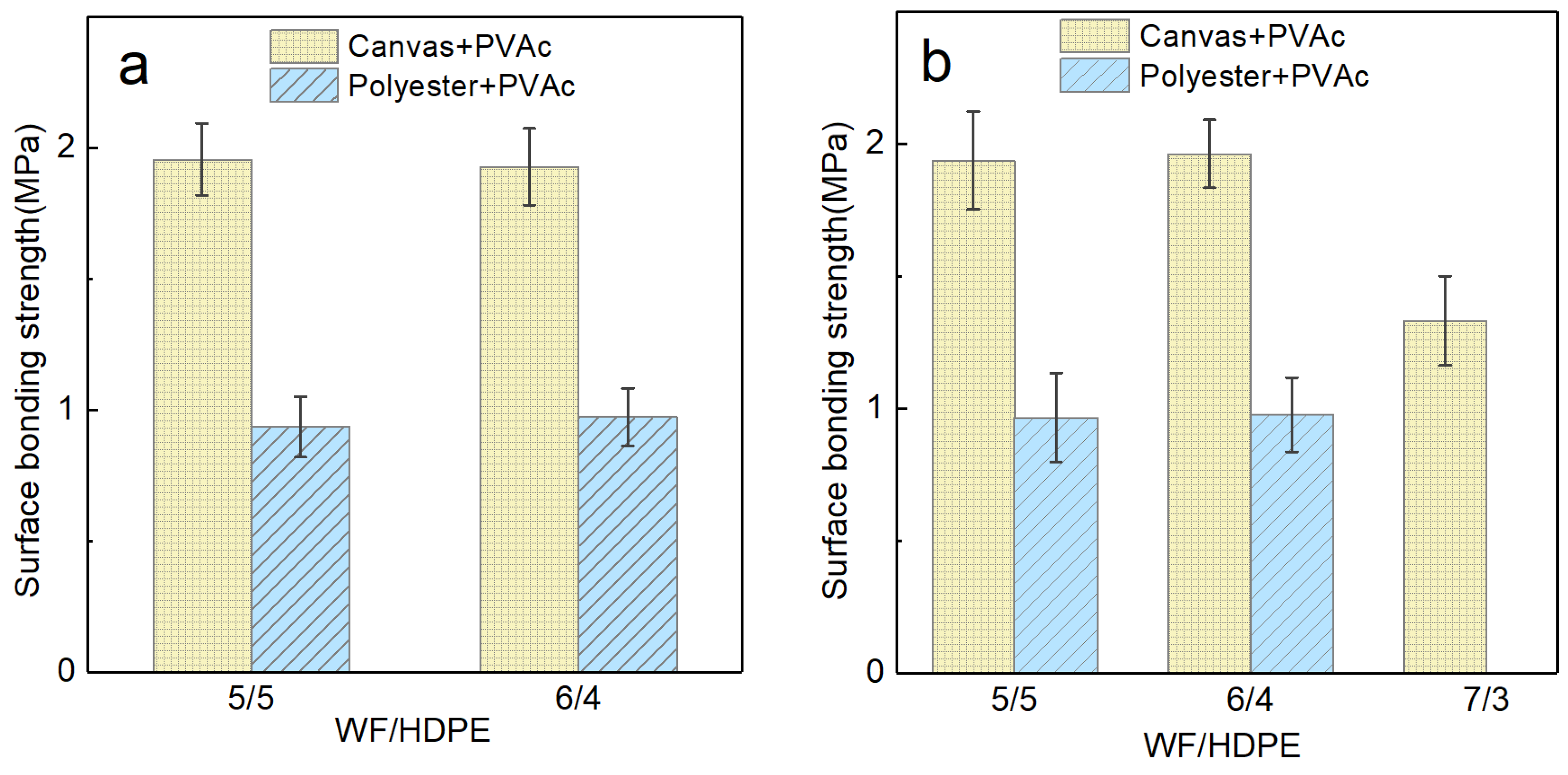
3.1.1. Surface Bonding Strength of Wood Veneered WF/HDPE Composite Board with PVAc
3.1.2. Surface Bonding Strength of Wood Veneered WF/HDPE Composite Board with PVAc-Isocyanate
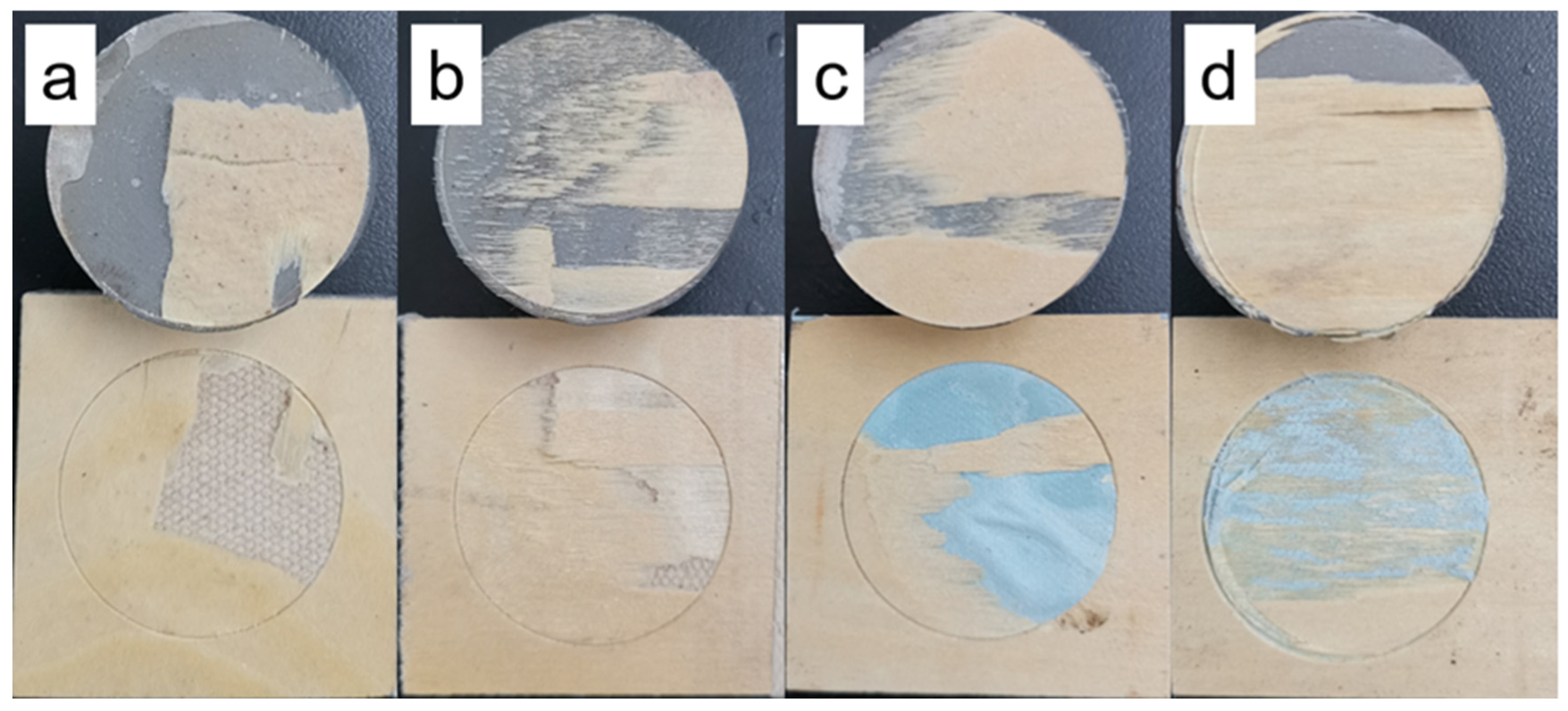
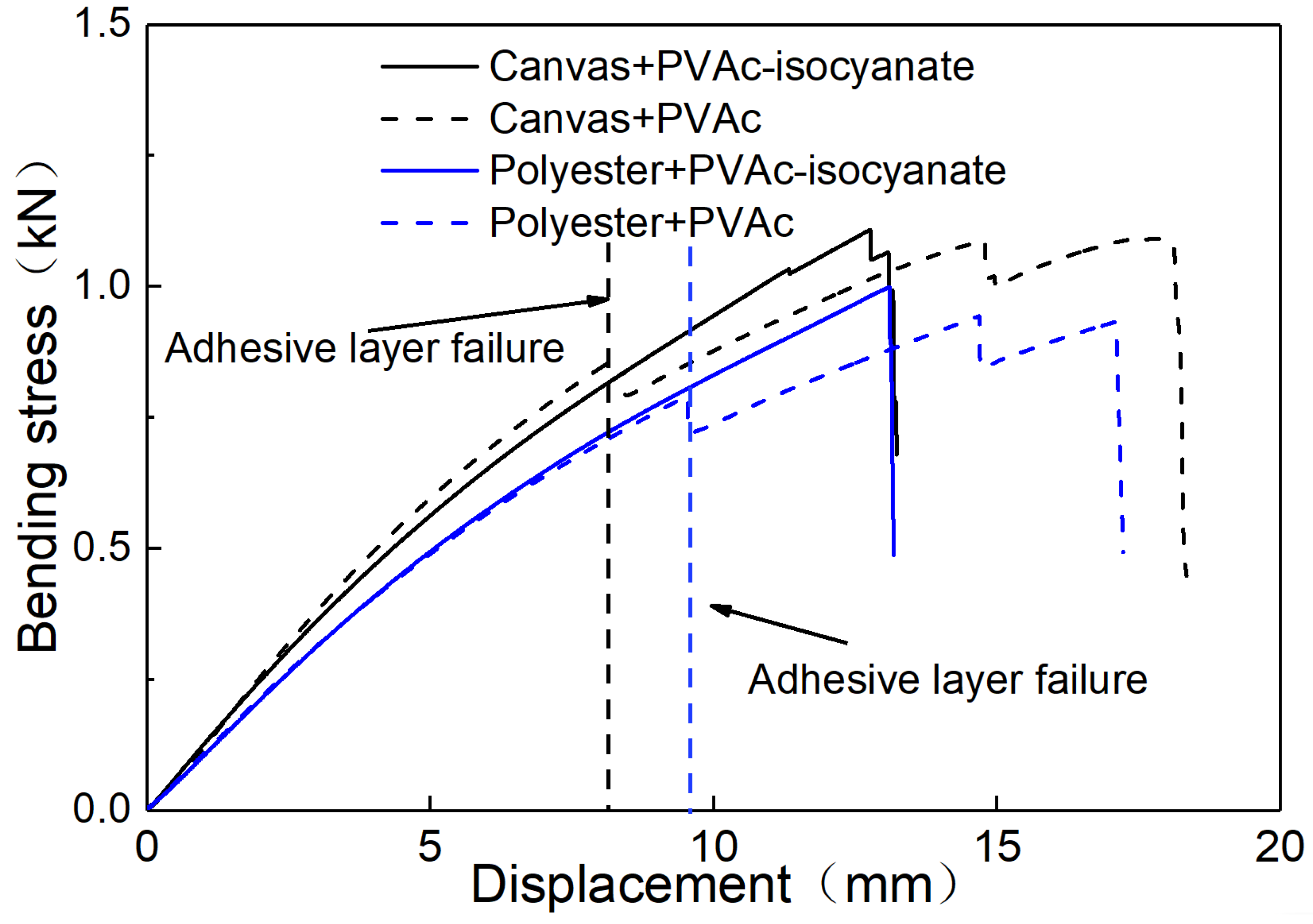
3.2. Bonding Mechanism of the Fabric and Adhesive
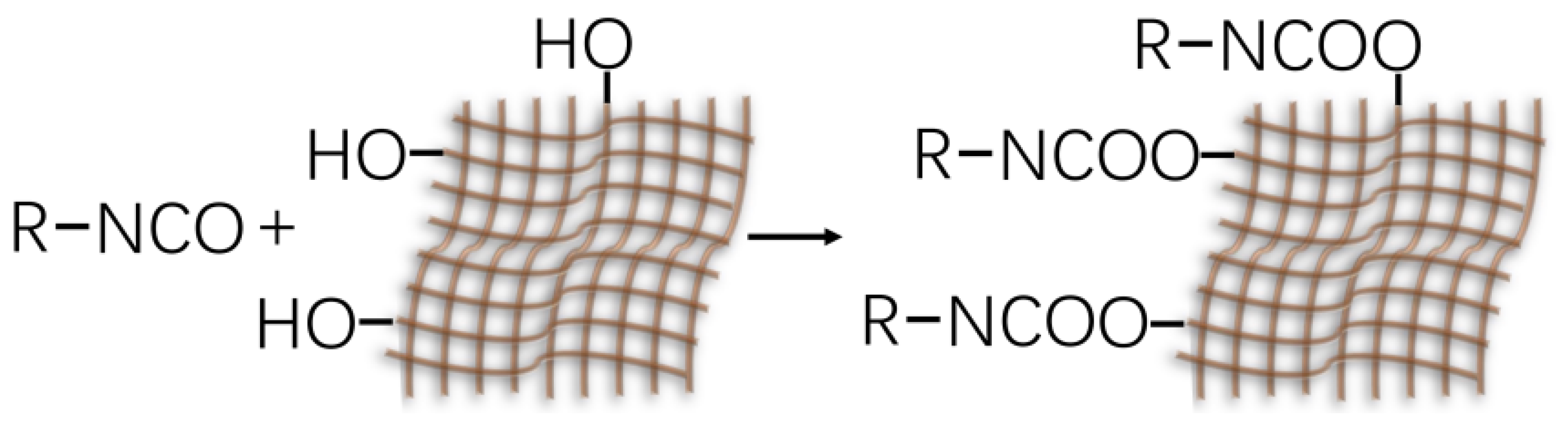
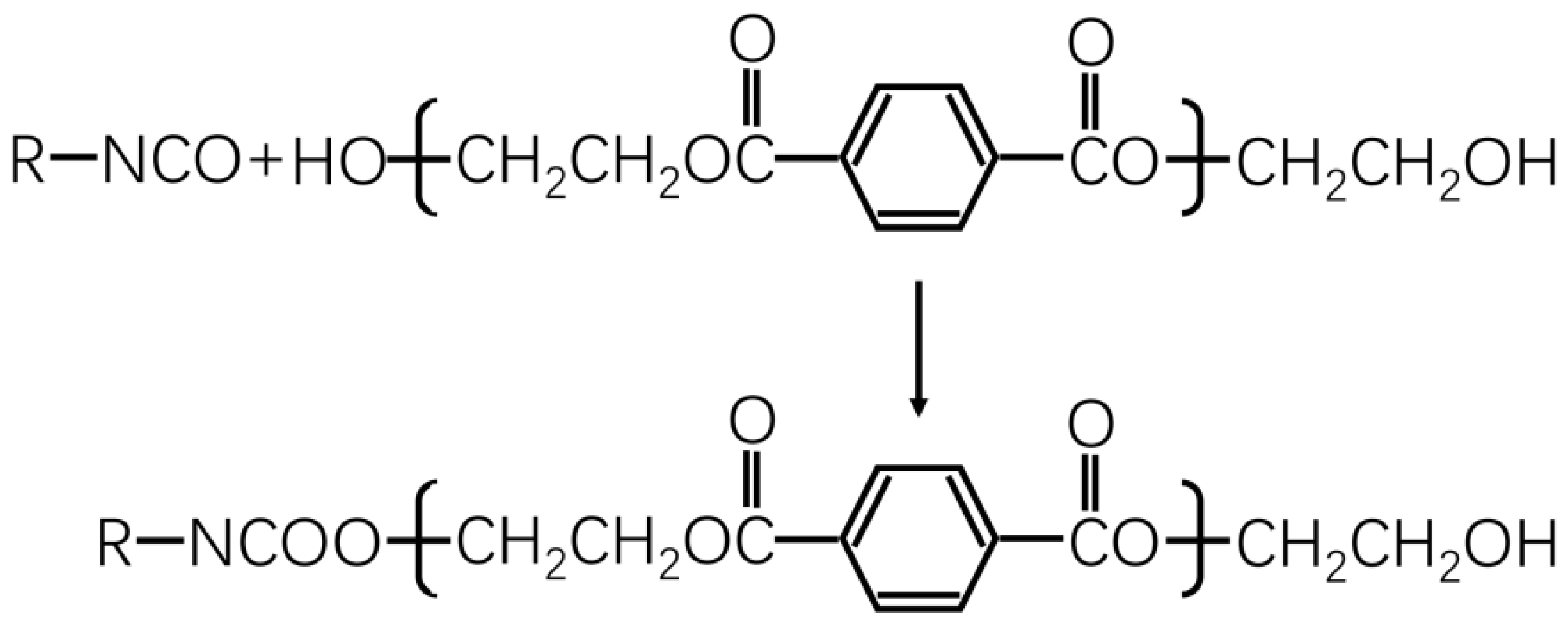
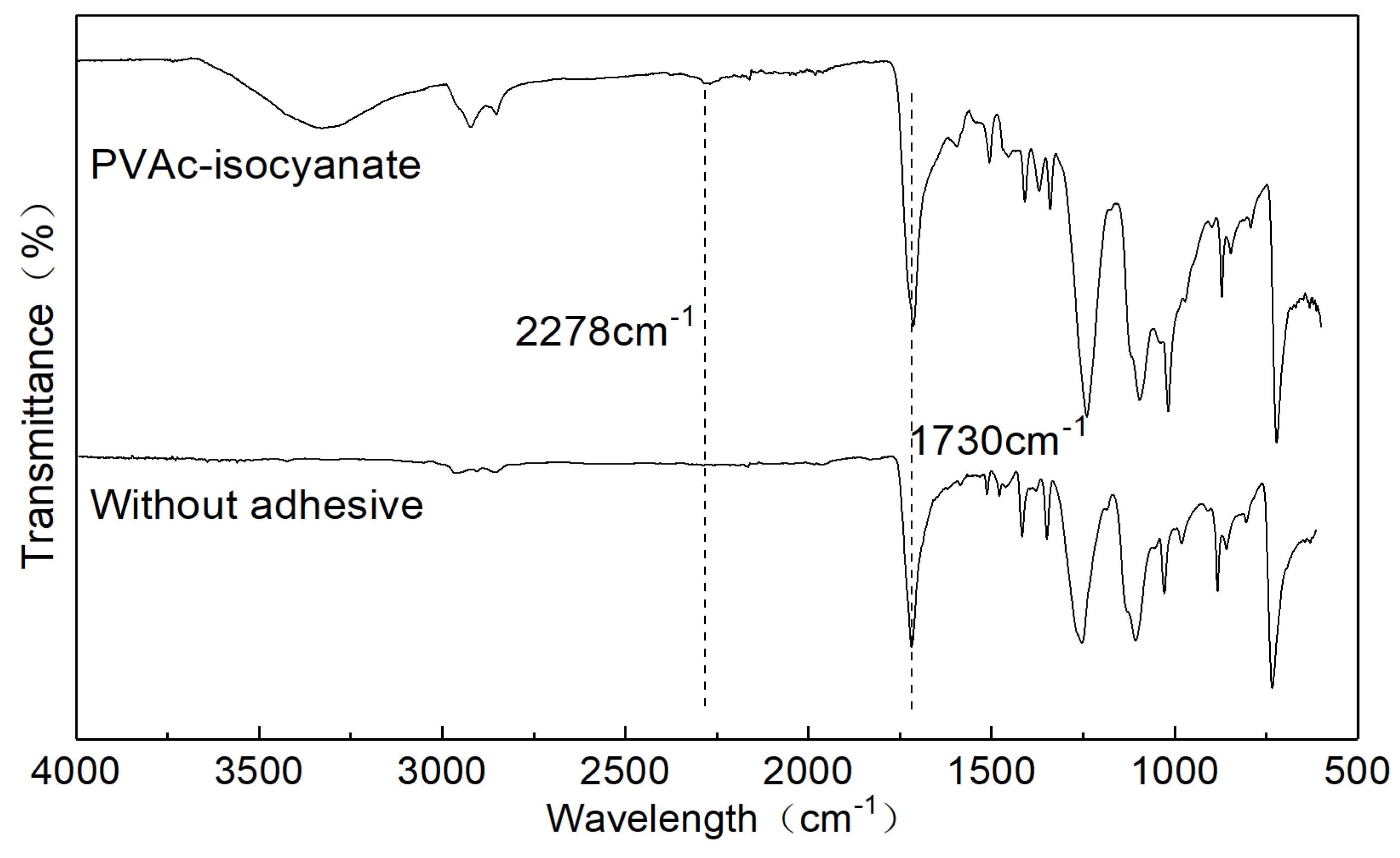
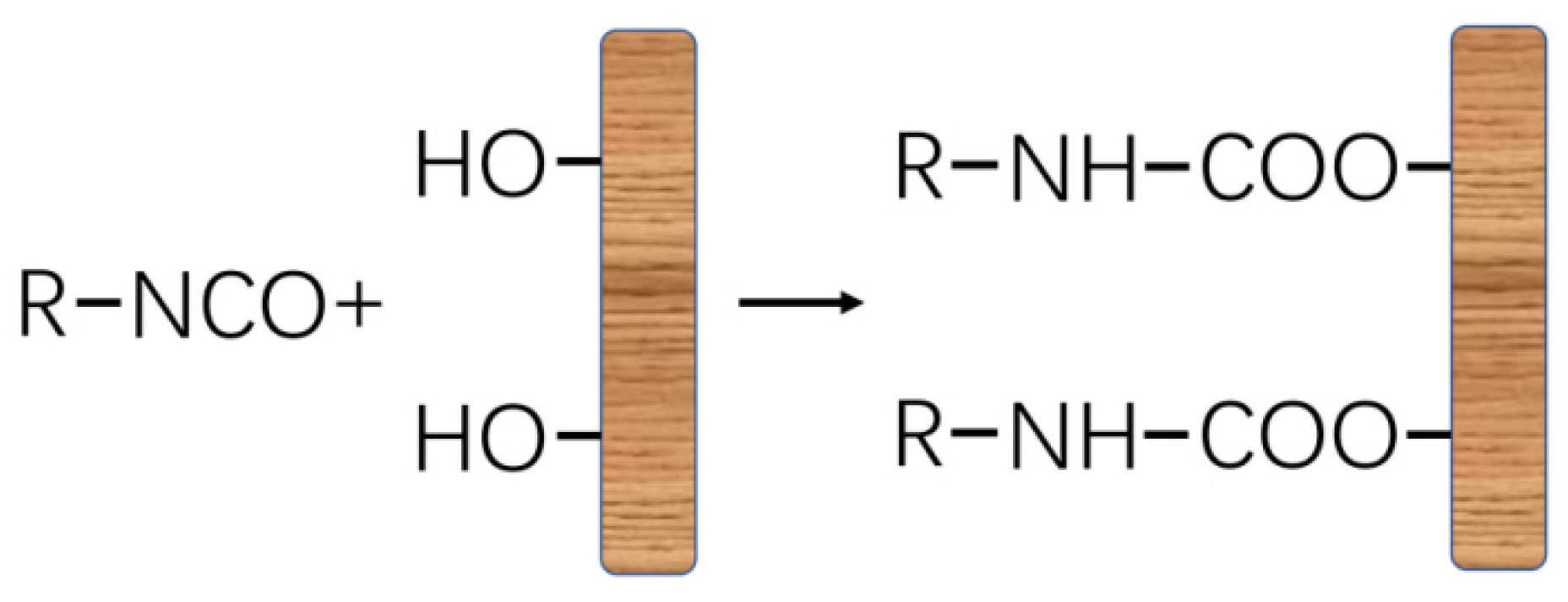
3.3. Bonding Mechanism Between Adhesive and Wood Veneer
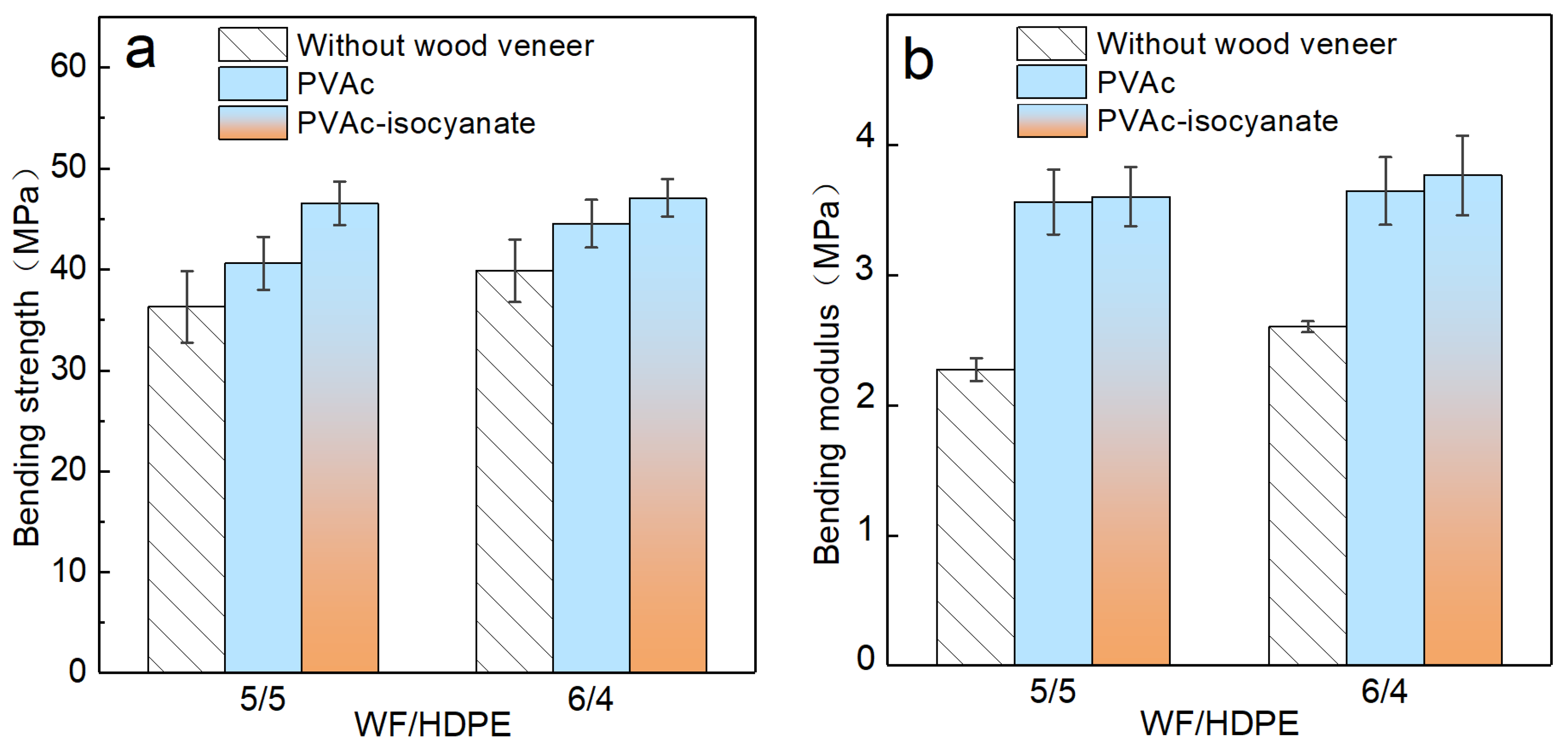
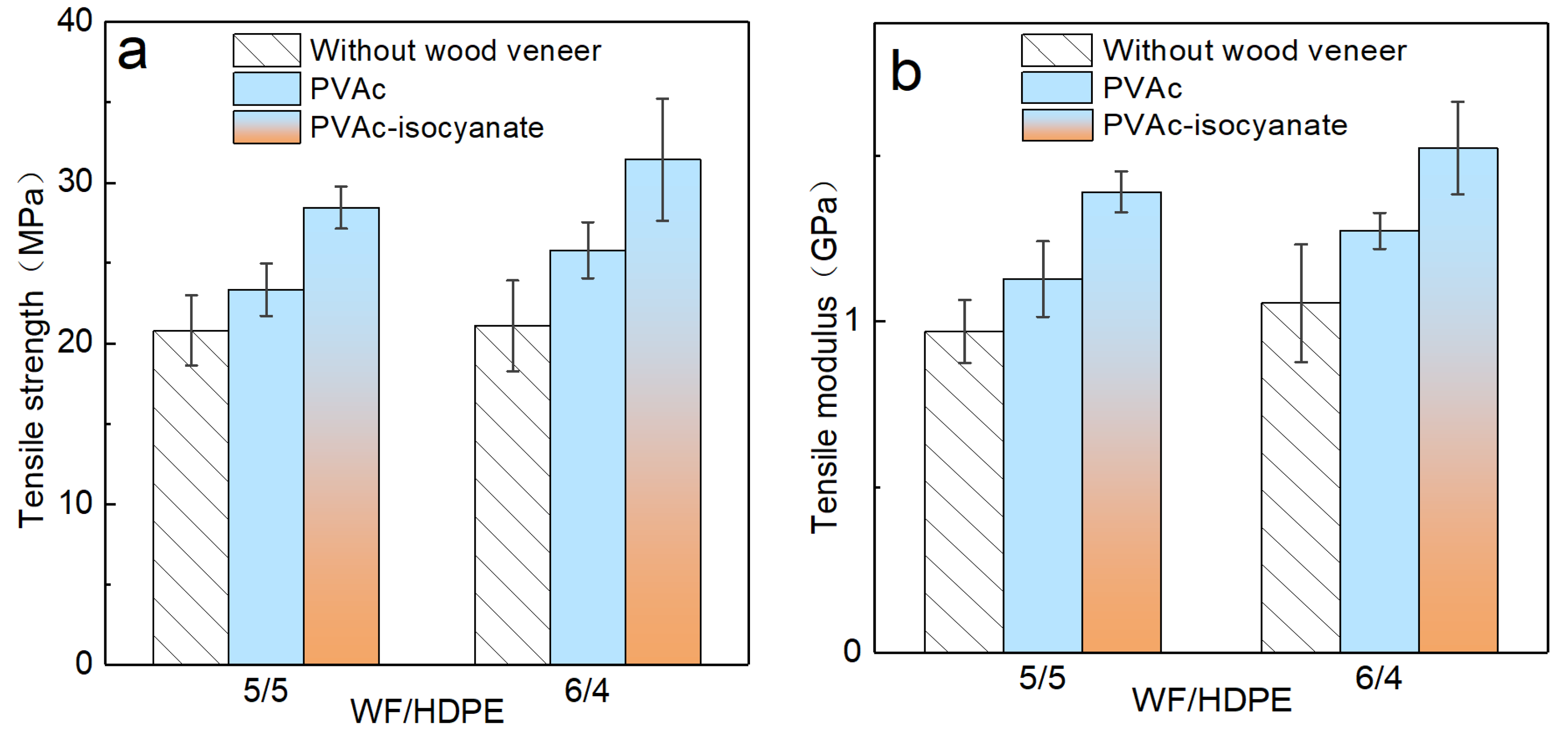
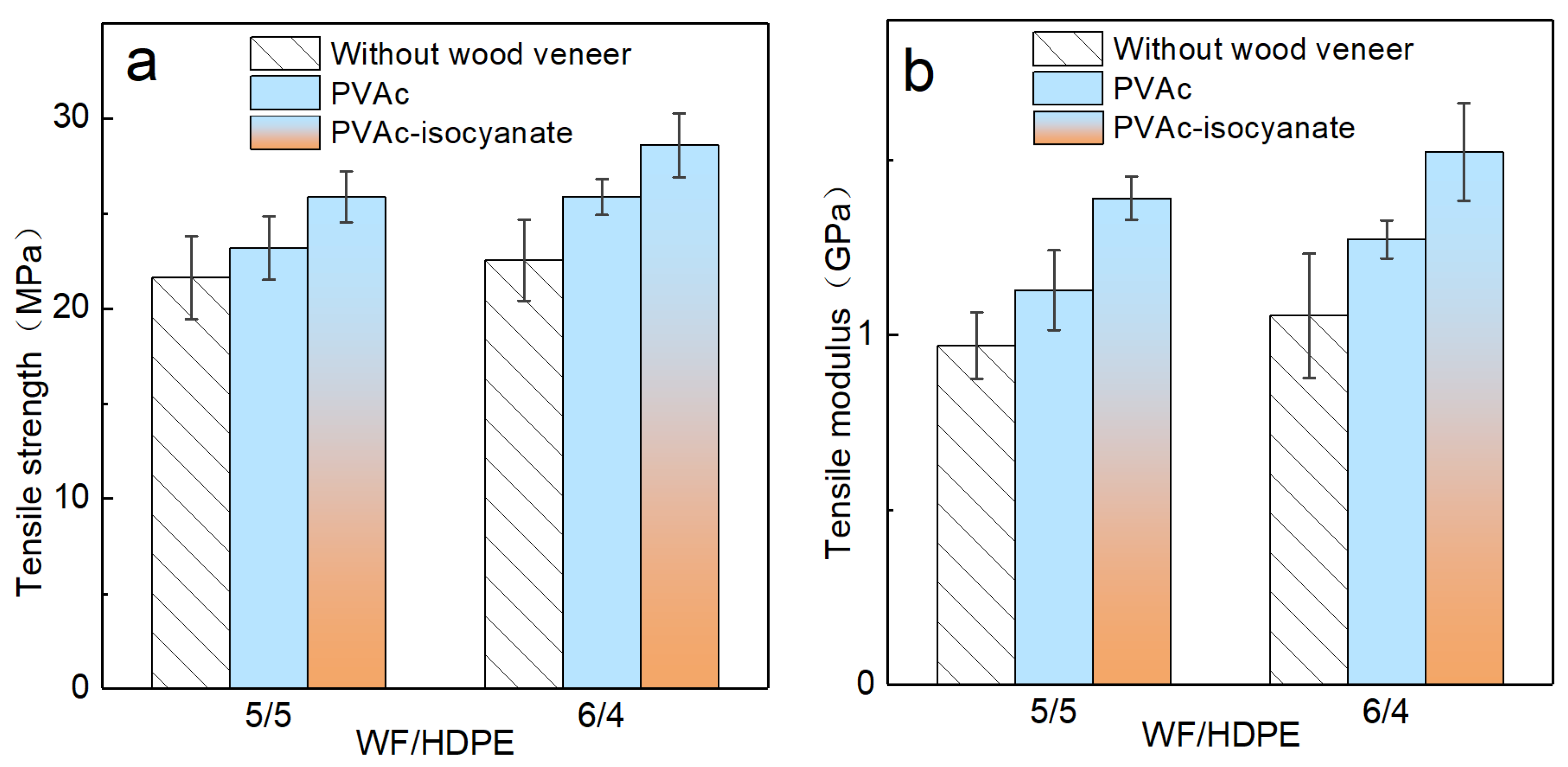
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Decorated Boards
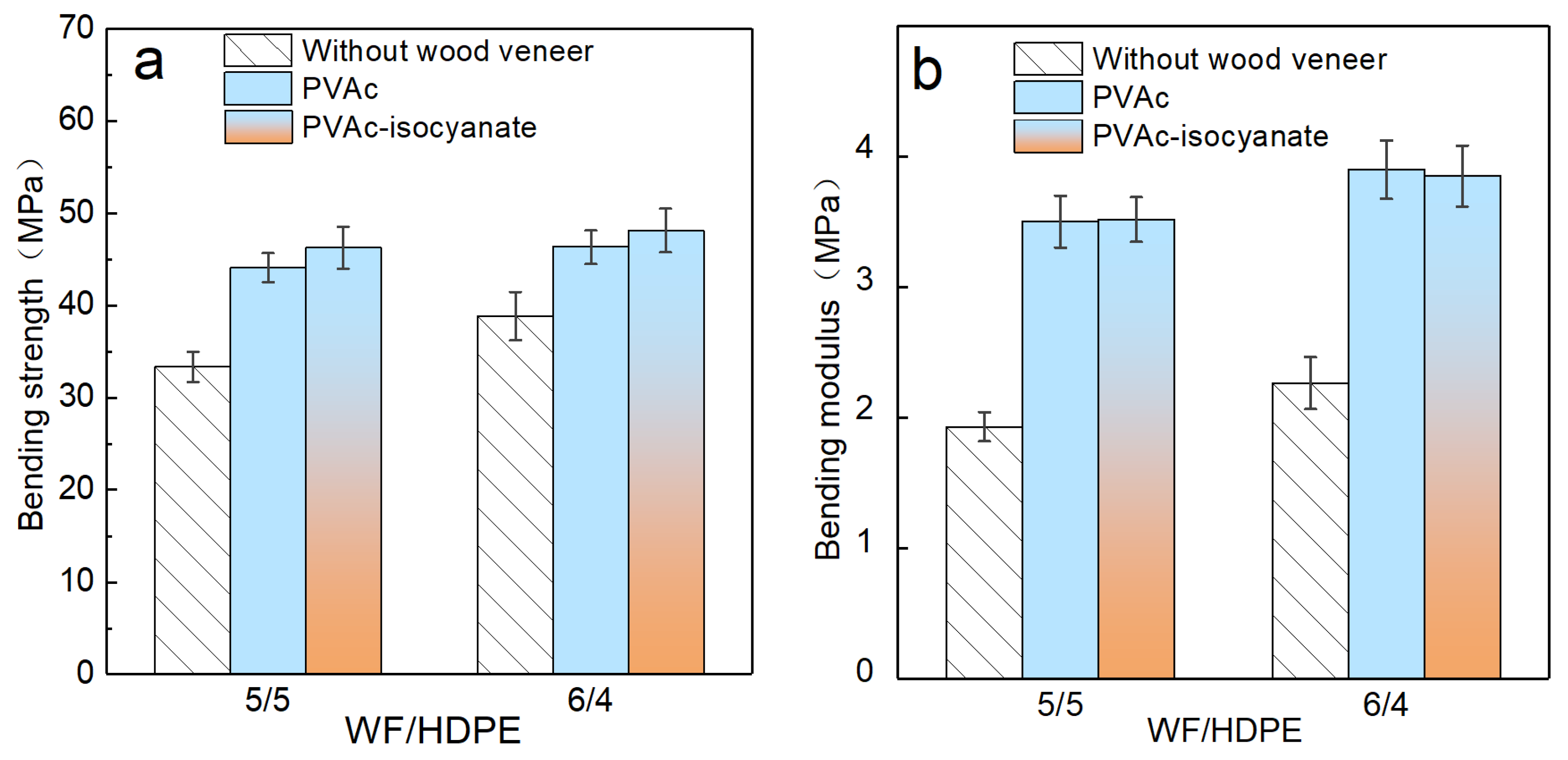
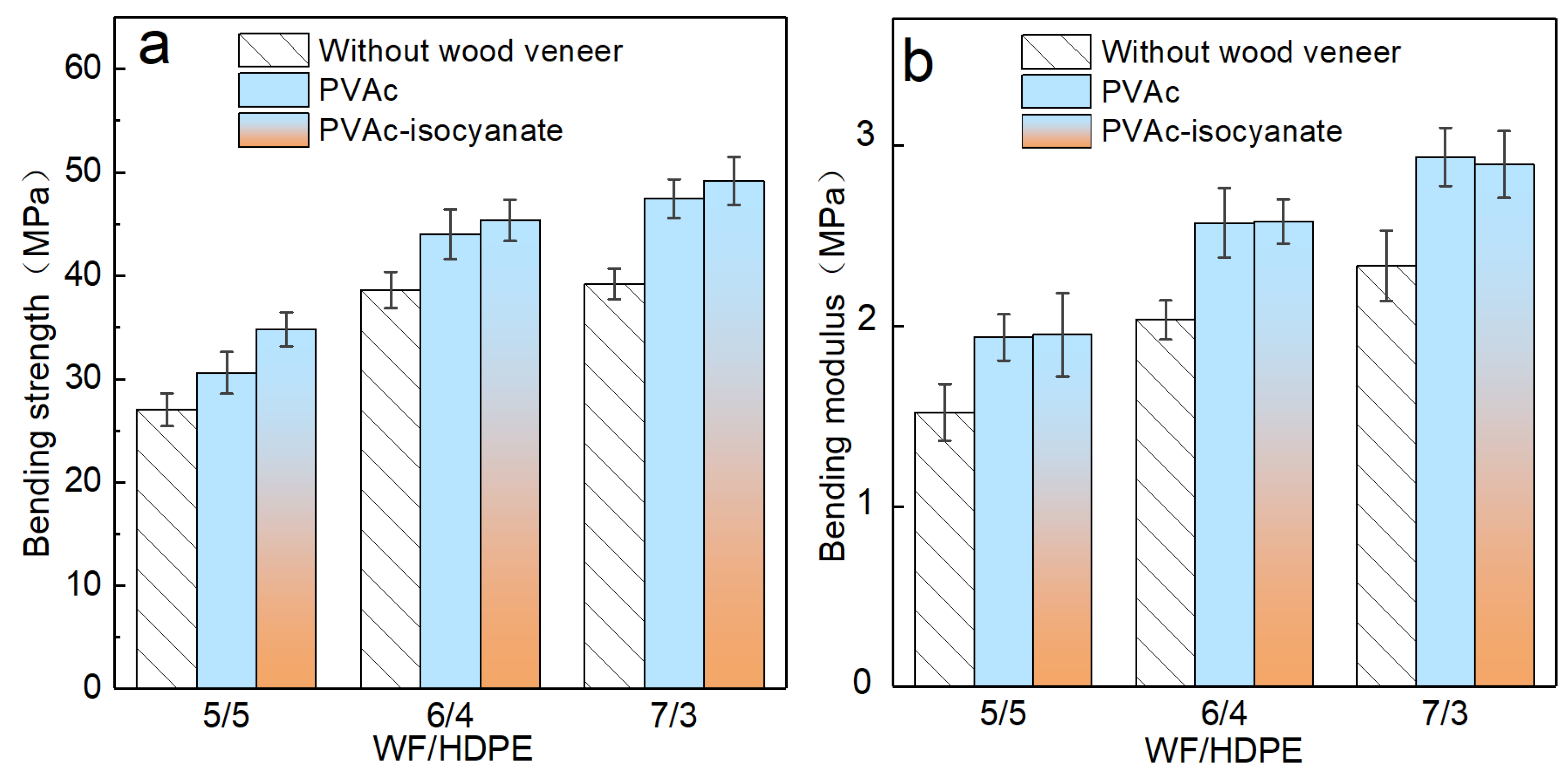
3.4.1. Bending Properties of the Decorated WF/HDPE Board
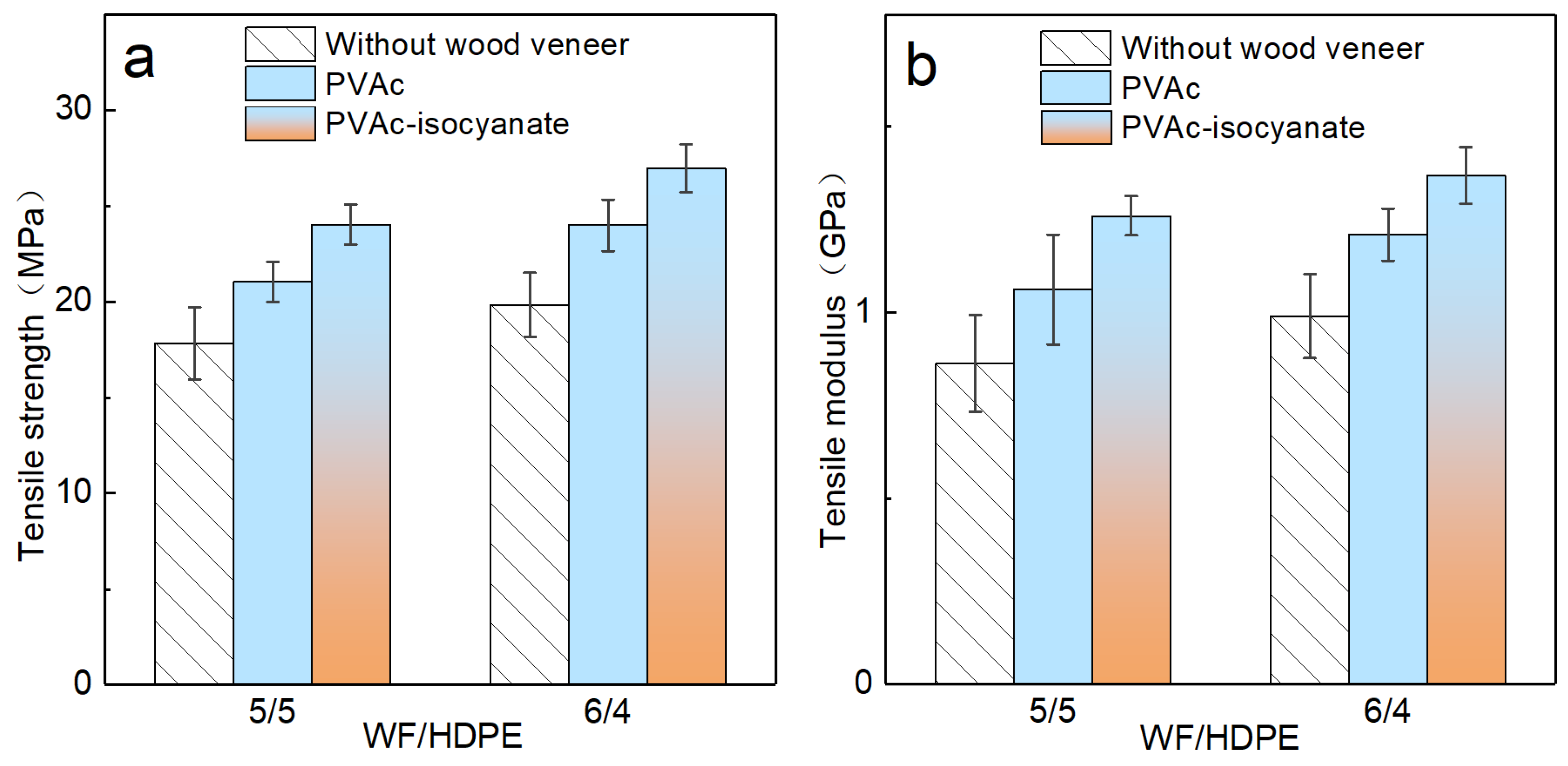
3.4.2. Tensile Properties of Decorated WF/HDPE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, A.C.; Jenkins, D.; Whitty, C.J.M. Hidden harms of indoor air pollution—Five steps to expose them. Nature 2023, 614, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yu, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G.; Feng, G. Study on the Influence of Pollution Source Location on Indoor Pollutant Distribution under Different Air Supply. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.R.; Schoemaecker, C.; Carslaw, N.; Waring, M.S.; Ham, J.E.; Nelissen, I.; Wolkoff, P. Reactive Indoor Air Chemistry and Health—A Workshop Summary. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Dudzińska, M.R.; Gunnarsen, L.; Hgerhed, L.; Maula, H.; Singh, R.; Toyinbo, O.; Haverinen-Shaughnessy, U. Indoor air quality guidelines from across the world: An appraisal considering energy saving, health, productivity, and comfort. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, M.J.; Burnard, M.D. Wood-Plastic Composites—Performance and Environmental Impacts. In Environmental Impacts of Traditional and Innovative Forest-Based Bioproducts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Potkán, M.Y. Circular Economy and Technological Innovation in the Forest-Based Sector: A Study on Wood–Plastic Composites Business Plan and Cost Calculations. Forests 2024, 16, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Cholake, S.T.; Rajarao, R.; Henderson, P.; Rajagopal, R.R.; Sahajwalla, V. Composite Panels Obtained from Automotive Waste Plastics and Agricultural Macadamia Shell Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paletto, A.; Biancolillo, I.; Bersier, J.; Keller, M.; Romagnoli, M. A literature review on forest bioeconomy with a bibliometric network analysis. J. For. Sci. 2020, 66, 265–279. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, E.F.; Jiménez-Sáez, F.; Hontoria, E. Can Industry Counteract the Ecological Crisis? An Approach for the Development of a New Circular Bioeconomic Model Based on Biocomposite Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.S.; Reiniati, I.; Laborie, M.P.G. Surface Properties and Adhesion of Wood Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, E.; Baudrit, B.; Heidemeyer, P.; Bastian, M.; Stoyanov, O.; Starostina, I. Problems in Adhesion Bonding of Wpc. Polym. Res. J. 2015, 9, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.S.; Laborie, M.-P.G. Surface Activation and Adhesion Properties of Wood-Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. J. Adhes. 2007, 83, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborie, M.P.G.; Gupta, B.S. Oxyfluorination of Wood-Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites to Improve Adhesion. J. Adhes. 2008, 84, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihzadeh, S.M.; Dastoorian, F.; Ebrahimi, G. Effect of Wood Species and Coupling Agent on Mechanical Properties of Wood Flour/Hdpe Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Ding, X.Y.; Xu, C. Effect of Compatibilizing Agent on Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Wood-Plastic Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 150, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Effect of a Novel Coupling Agent, Alkyl Ketene Dimer, on the Mechanical Properties of Wood–Plastic Composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Wu, Q.; Negulescu, I.I. Wood-Fiber/High-Density-Polyethylene Composites: Coupling Agent Performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, M.; Bongaers, E. Use of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Technology for Durable Hydrophilicity Enhancement of Polymeric Substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 5036–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Put, S.; Bertels, C.; Vanhulsel, A. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment of Polymeric Powders. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 234, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečasová, B.; Liška, P.; Kelar, J.; Šlanhof, J. Comparison of Adhesive Properties of Polyurethane Adhesive System and Wood-Plastic Composites with Different Polymers after Mechanical, Chemical and Physical Surface Treatment. Polymers 2019, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Easteal, A.J. Aspects of the Performance of Pvac Adhesives in Wood Joints. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2001, 30, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, F.W.; Owen, N.L. Isocyanate-Wood Adhesive Bond. Appl. Spectrosc. 1995, 49, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 16978:2003; Wood-Based Panels—Determination of Modulus of Elasticity in Bending and of Bending Strength. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Motohashi, K.; Tomita, B. Mizumachi. Relationship between Chemical Properties of Poly(Vinyl Acetate) Emulsion Adhesives and Tensile Strength for Cross-Lap Joint of Wood. Holzforsch.-Int. J. Biol. Chem. Phys. Technol. Wood 1982, 36, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, E.B.; Vanderhoff, J.W. Additional Studies of Morphological Changes in Latex Films. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1972, 6, 671–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Wang, J.; Luo, G.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, W.; Huang, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. Healable Super hydrophobicity of Novel Cotton Fabrics Modified Via One-Pot Mist Copolymerization. Cellulose 2016, 23, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qiu, R.; Li, K. Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion in Natural Plant Fiber-Reinforced Unsaturated Polyester Composites: A Critical Review. Rev. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 3, 98–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, K.; Takahashi, A.; Kawai, S. Durability of Isocyanate Resin Adhesives for Wood I: Thermal Properties of Isocyanate Resin Cured with Water. J. Wood Sci. 1998, 44, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A. A Brief, Non-Mathematical Review of Adhesion Theories as Regards Their Applicability to Wood. Holzforsch. Holzverwert. 1992, 44, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, P.R.; Chow, S.; Vadja, S. Interaction of Polyisocyanate Adhesive with Wood. For. Prod. J. 1980, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar]





| Fabric | Thickness | Melting (Decomposition) Temperature | Chemical Composition | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester fiber fabric | 0.48 mm | Melting: 205 °C | HO-CH2-CH2-O [-OC-Ph-COOCH2CH2O-]n |  |
| Canvas | 0.70 mm | Decomposition: 310 °C | Mainly cellulose |  |
| Fabric | WF/HDPE | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Canvas | 5/5 | 140, 160 |
| 6/4 | 140, 160 | |
| 7/3 | 160 | |
| Polyester fiber | 5/5 | 140, 160 |
| 6/4 | 140, 160 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Ni, X.; Zong, G.; Xia, X. Reinforcement Effects on the Properties of Wood-Veneered Wood Fiber/Fabric/High-Density Polyethylene Laminated Composites. Forests 2025, 16, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060877
Liu Y, Zhou J, Ma Y, Chen F, Ni X, Zong G, Xia X. Reinforcement Effects on the Properties of Wood-Veneered Wood Fiber/Fabric/High-Density Polyethylene Laminated Composites. Forests. 2025; 16(6):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yinan, Jinjiang Zhou, Yanqiu Ma, Feng Chen, Xiaohui Ni, Guanggong Zong, and Xinghua Xia. 2025. "Reinforcement Effects on the Properties of Wood-Veneered Wood Fiber/Fabric/High-Density Polyethylene Laminated Composites" Forests 16, no. 6: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060877
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhou, J., Ma, Y., Chen, F., Ni, X., Zong, G., & Xia, X. (2025). Reinforcement Effects on the Properties of Wood-Veneered Wood Fiber/Fabric/High-Density Polyethylene Laminated Composites. Forests, 16(6), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060877







