1. Introduction
Hickory (
Carya cathayensis), a characteristic economic tree species native to China, is highly valued for its kernels, which are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, proteins, and various mineral elements, offering both nutritional and health benefits [
1]. In key production areas such as the border regions of Zhejiang and Anhui provinces, the hickory industry has become a pillar of the local economy, underscoring its critical role in rural revitalization. Tree architecture, as a vital morphological indicator of growth and development in forest trees, not only reflects physiological and ecological adaptability but also profoundly influences reproductive growth through mechanisms such as light interception efficiency and nutrient transport pathways [
2]. Studies have shown that an optimized canopy structure can significantly enhance light utilization efficiency and fruit yield [
3,
4,
5]. While canopy structure research is relatively mature for fruit trees like peach, pear, and walnut, studies focusing on hickory remain limited. Moreover, existing investigations primarily rely on traditional morphological observations and manual measurements, lacking systematic, quantitative methods based on digital technologies. This technical limitation has resulted in hickory forest management practices that still heavily depend on subjective experience, with no established digital decision support systems, thereby hindering the implementation of precision forestry.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), as a revolutionary remote sensing technology, enables efficient acquisition of three-dimensional spatial coordinates of target objects and holds significant potential for forest management and ecosystem research [
6,
7,
8]. However, hickory forests are typically located in hilly and mountainous regions with steep slopes, where UAV-mounted (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle mounted) LiDAR systems are often affected by complex terrain and canopy occlusion, leading to point cloud data gaps and increased difficulty in reconstructing complete tree structures [
9]. Although LiDAR has been successfully applied in forest parameter retrieval, these challenges have impeded its application in structural analysis of economic tree species, resulting in a noticeable research gap in this area.
Terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) technology enables rapid acquisition of three-dimensional spatial coordinates of target objects and has emerged as a crucial surveying tool in agriculture and forestry. It demonstrates significant advantages in the efficient collection of 3D point cloud data of trees and in the extraction of structural parameters across multiple scales [
10]. Kukenbrink et al. compared TLS with terrestrial photogrammetry in temperate forests and confirmed the superior accuracy of TLS in measuring tree height, diameter at breast height (DBH), and related parameters [
11]. Brolly et al. proposed a voxel-based, fully automated single-tree detection method capable of extracting DBH, tree height, and stem curvature [
12]. In validation trials conducted in southern Finland, the method achieved a root mean square error (RMSE) of ±1.7 cm for DBH and ±2.3 cm for broad-leaved forests. Tuomas et al. were the first to demonstrate that TLS could detect significant changes in DBH at the plot level (average correlation r = 0.46,
p = 0.04), establishing a technical benchmark for non-destructive monitoring of growth dynamics in boreal forests [
13]. Shen et al. introduced a deep learning framework combining energy-based segmentation and PointCNN, further optimized by a Geometric Feature Balance Model (GFBM), enabling high-precision extraction of tree height (RMSE = 0.21–0.30 m) and DBH (RMSE = 0.012–0.014 m) from TLS point clouds, effectively addressing modeling errors caused by occlusions in dense forest stands [
14].
In terms of biomass estimation, Krause et al. used TLS combined with a quantitative structure model to derive the 3D volume of 282 individual trees and estimate aboveground biomass (AGB) [
15]. By comparing results with those from traditional allometric equations, they demonstrated the potential of TLS to replace destructive sampling in complex forest ecosystems. Zimbres et al. built an AGB estimation model for Brazilian Cerrado vegetation using single-scan TLS point clouds, confirming the method’s suitability for sparse vegetation [
16]. Goodbody et al. integrated post-harvest digital aerial photogrammetry (DAP) point clouds acquired via UAVs with airborne LiDAR scanning (ALS) data, constructing a residual volume prediction model with field measurements, thus providing a semi-automated solution for dynamic forest monitoring [
17]. Jiang et al. extracted culm lengths of Phyllostachys edulis (Moso bamboo) from TLS point clouds and combined them with DBH to build an allometric model, reducing biomass estimation error by 2.85% [
18]. Yusup et al. proposed a stem–leaf separation algorithm based on reflectance intensity, reducing RMSE in stem volume estimation by 18% compared to conventional models [
19].
In the field of ecological research, Terryn et al. constructed quantitative structural models from TLS point clouds to extract 17 geometric and topological features, including branch angle and canopy density [
20]. Using k-nearest neighbors, multinomial logistic regression, and support vector machine algorithms, they classified 758 individual trees from five species, achieving an overall accuracy of 80%. Gao et al. combined TLS point clouds with genetic analysis to extract structural growth traits of individual Ginkgo biloba trees, such as leaf area index and canopy width [
21]. Principal component analysis was used to screen superior individuals, demonstrating the potential of TLS point clouds in quantifying tree phenotypes and providing phenotypic support for species classification. Dai et al. proposed MDC-Net, a deep learning network integrating multi-directional constraints and prior features, which effectively separated branches and leaves in TLS point clouds of subtropical plantations, significantly improving classification accuracy in fine-scale regions such as twigs and foliage [
22].
Current methods for 3D tree reconstruction can be categorized into image-based and LiDAR-based approaches. Image-based methods rely on multi-view photogrammetry, which is cost-effective and data-rich but often suffers from missing depth information and susceptibility to environmental interference [
23,
24]. Huang et al. applied the Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) method to generate single-tree point clouds from multi-source camera images and compared the results with those from conventional photogrammetry and LiDAR, demonstrating NeRF’s potential in single-tree 3D reconstruction [
25]. However, the output point clouds tend to be noisy and have relatively low resolution. Wu et al. developed a portable platform, MVS-Pheno, based on multi-view stereo (MVS), which reconstructed 3D models of maize plants from multi-angle images and enabled the extraction of phenotypic parameters [
26]. Nevertheless, the reconstruction stability was affected by dynamic field environments. Isokane et al. proposed a probabilistic model for image-to-image transformation using multi-view images, generating 3D plant structures through probabilistic inference, although the model required optimization with geometric constraints [
27]. Gao et al. introduced an integrated 3D imaging system that automatically extracts plant phenotypic parameters using point cloud processing algorithms, but the approach remains sensitive to environmental factors such as dynamic lighting [
28].
In comparison, LiDAR-based methods offer clear advantages in representing branch-stem geometry and ensuring topological consistency [
29,
30,
31]. Du et al. proposed the AdTree algorithm, which integrates hierarchical clustering with cylindrical fitting to enable automated modeling of laser-scanned trees [
32]. For the first time, hierarchical clustering was introduced to address uneven point cloud density, significantly improving the accuracy of branch topology reconstruction, with an overall fitting error of less than 10 cm. Xie et al. developed a voxel-based method capable of reconstructing individual tree leaf distributions, achieving a relative gap fraction error (for virtual trees) of less than 4.1% [
33]. Bailey et al. designed a semi-direct tree reconstruction framework combining point cloud segmentation with morphological optimization, achieving 92% reliability across various environmental conditions [
34]. These approaches, integrating computer graphics with vision algorithms, have driven tree modeling toward higher fidelity and multi-scale representation. Currently, TLS technology is increasingly integrated with artificial intelligence. Zhang et al. applied the PointNet++ network for semantic segmentation of point cloud data from quarry sites, combining quantitative analysis and clustering algorithms to interpret spatial structures [
35]. This work enabled, for the first time, automated recognition of complex quarry elements and quantification of cultural heritage values, providing high-precision 3D data for heritage conservation. Jaafar et al. introduced a novel method combining TLS with generalized Procrustes analysis to monitor historical and heritage buildings [
36]. This approach offered a new technical pathway for detecting subtle deformations in architectural structures with high precision. Although image-based methods are generally more cost-effective in terms of equipment, the superior accuracy of TLS in complex scenarios makes it an irreplaceable tool in precision forestry and related applications [
37,
38].
The investigation of LiDAR point clouds in the context of timber forests primarily emphasizes the extraction of extensive forest parameters for the purpose of biomass inversion on a large scale. This approach markedly contrasts with the focus of the current study, which centers on the management of individual trees within economic forests. Given that the morphology of different tree species correlates with their respective yields, it is imperative to acquire detailed structural parameters of individual trees to facilitate quantitative analysis. The objective of our research is to reconcile the disparities between these two distinct areas of study.
To address key challenges in the application of terrestrial LiDAR technology for hickory forest management, this study makes the following contributions:
- 1.
A field data acquisition and processing workflow is established for TLS under complex mountainous conditions;
- 2.
A 3D structural reconstruction approach is developed to model hickory tree architecture from point clouds, enabling the extraction of structural parameters such as tree volume and branch angles that are difficult to obtain using conventional methods;
- 3.
By integrating 3D structural data, expert knowledge from forest practitioners, and machine learning techniques, a quantitative model is constructed to identify optimal tree architectures. Model interpretability techniques are further applied to identify the key structural features influencing tree form dominance.
The resulting dataset of hickory tree structural models covers a range of tree ages and structural types, providing a foundation for future quantitative research. More importantly, this study presents a novel approach for translating empirical forestry knowledge into quantitative, scientifically interpretable models, offering a practical pathway for bridging experience-based management and theoretical understanding. Overall, this work contributes both data and methodological support for advancing economic forest management toward digitalization and precision forestry.
The structure of this paper is delineated as follows.
Section 2 will primarily focus on the selection criteria for research plots, the methodologies employed for scanning and processing laser point clouds, the techniques for single tree extraction and reconstruction, the acquisition of empirical data for the optimization and assessment of tree structure, as well as the foundational principles underlying the construction of the corresponding classification machine learning models. Building upon this foundation,
Section 3 will present and analyze the results of the proposed methods from various perspectives. Finally,
Section 4 will provide a summary of the contributions made in this article.
3. Results and Analysis
In order to comprehensively assess our methodology, we will present a range of results from diverse analytical perspectives. Initially, we will focus on the evaluation of the accuracy of the reconstructed 3D point clouds of hickory trees, as this aspect is crucial for establishing the reliability of our primary findings. Subsequently, utilizing the dataset derived from the reconstructed Quantitative Structure Model (QSM), we will employ PCA and clustering techniques to statistically examine the spatial characteristics of hickory tree structures. Following this analysis, we will design a survey experiment aimed at gathering expert insights from forest farmers, which will facilitate the acquisition of empirical classification data pertaining to inferior and superior hickory tree structures. This classification is essential for the development of the GBDT machine learning model. Consequently, we will provide a detailed account of the construction of the GBDT model, encompassing the training and evaluation processes for both individual and crowd models. Finally, we will elucidate the constructed GBDT model and analyze the critical structural parameters that influence the quality of hickory tree structures. Additionally, we will identify two exemplary hickory trees, deemed “tree kings” based on natural selection criteria, and calculate the similarity between these trees and other hickory specimens using the aforementioned distance metrics, thereby further validating the efficacy of the optimal tree structure identified through our methodology.
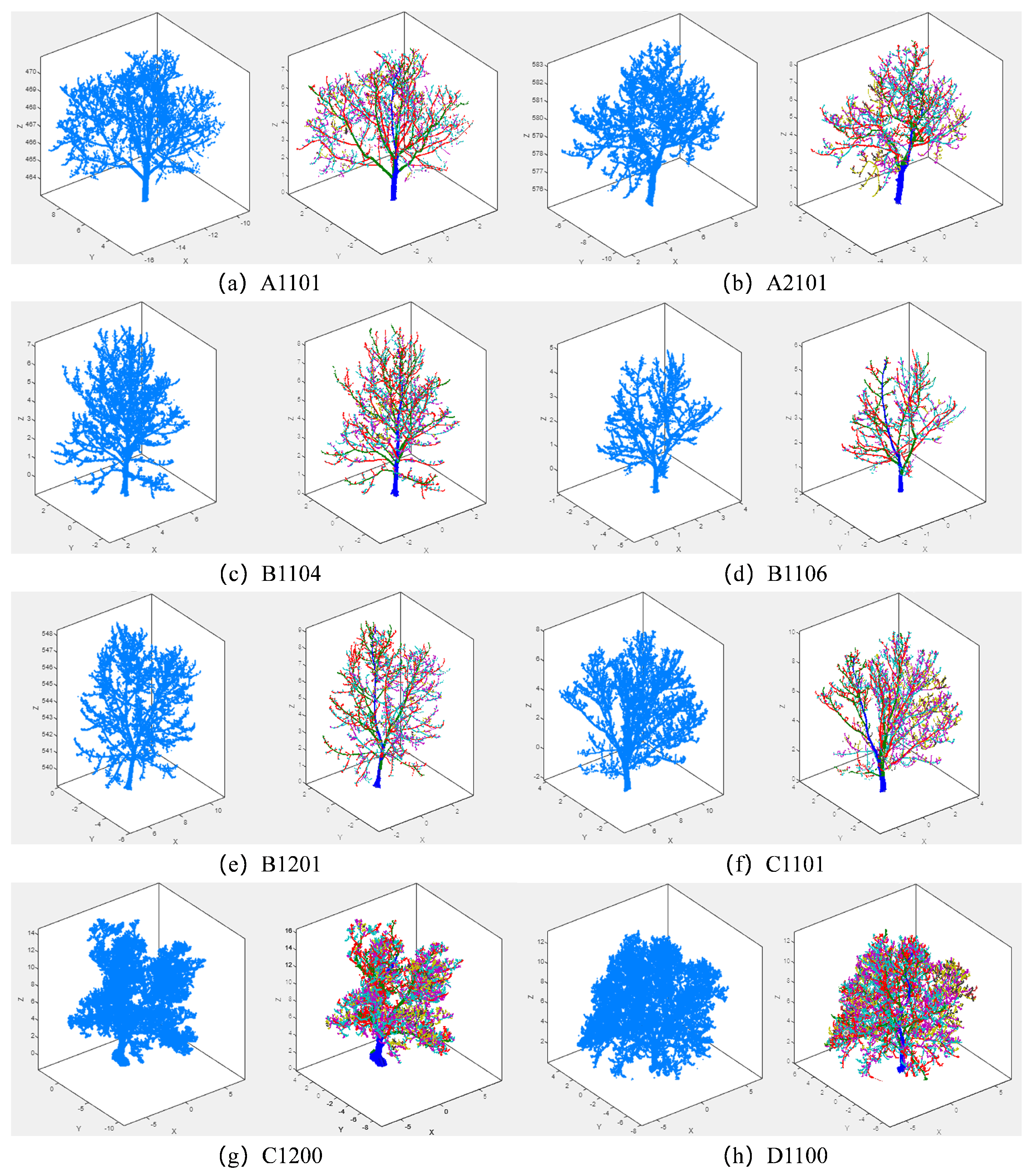
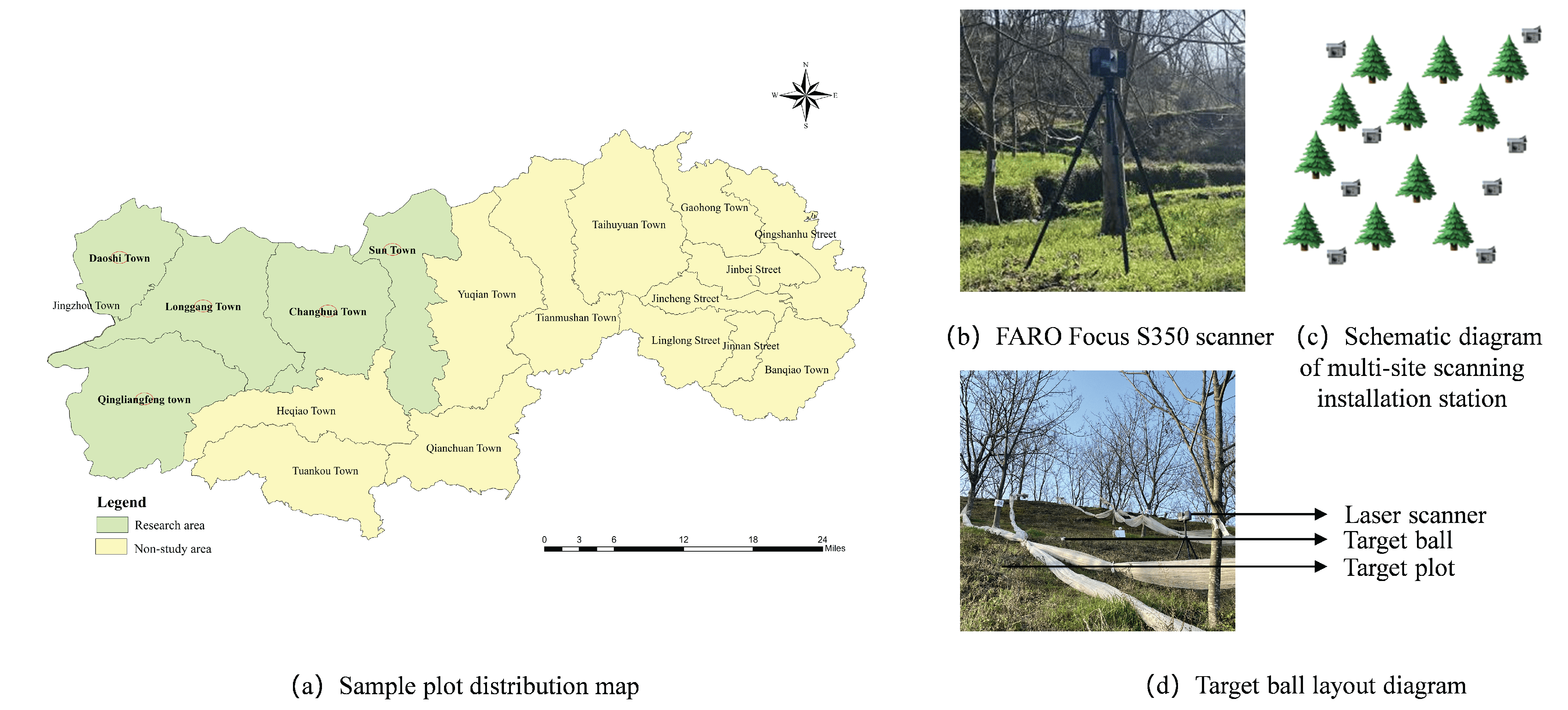
3.1. 3D Reconstruction Accuracy Analysis
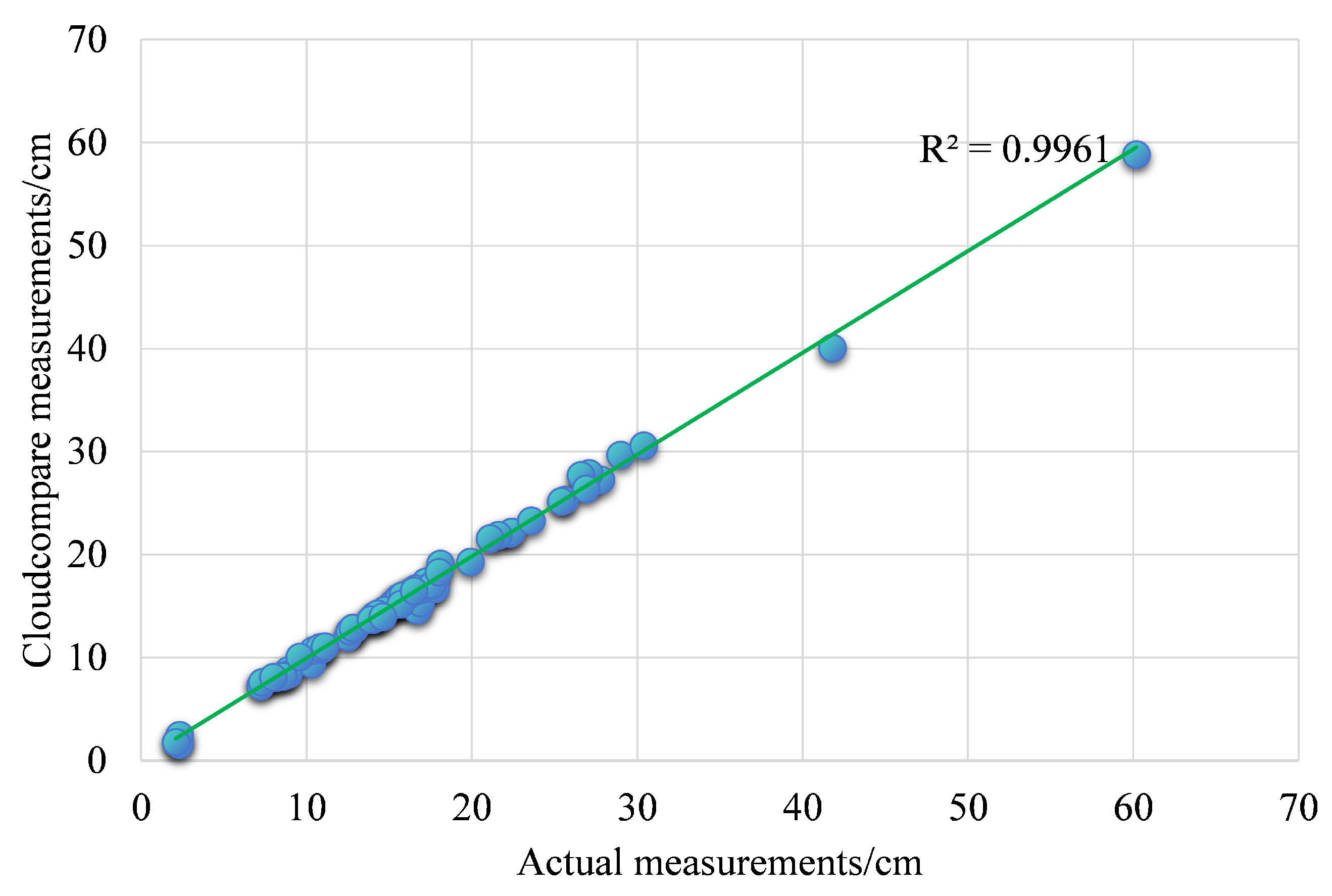
In the data acquisition phase, a tree diameter measurement method is employed to measure the diameter at breast height (DBH). At a height of 1.3 m above the ground, a tape measure is tightly wrapped around the tree trunk to measure the circumference, with three measurements taken to calculate the average. The corresponding diameter is then derived, resulting in a total of 65 valid DBH data points. After individual tree segmentation, CloudCompare software, Version 2.13.beta, is used to measure the 65 trees with accurate DBH data. The real DBH values are compared with those measured by the software to verify the accuracy of the ground-based laser scanner. To quantify this error, the study calculates the mean absolute relative error as in Equation (
16).
where,
n represents the total number of samples, and
i is the index of the data points.
The relative errors of various samples are shown in
Table 3. The calculated overall average relative error is only 0.28 mm. The accuracy of the full scanner has reached the millimeter level, ensuring that a quantitative structural model based on high-precision point cloud data can be constructed. The comparison results are shown in
Figure 6, and R
2 reaches above 0.99.
3.2. Clustering Results of Hickory Tree Structure
3.2.1. Principal Component Analysis
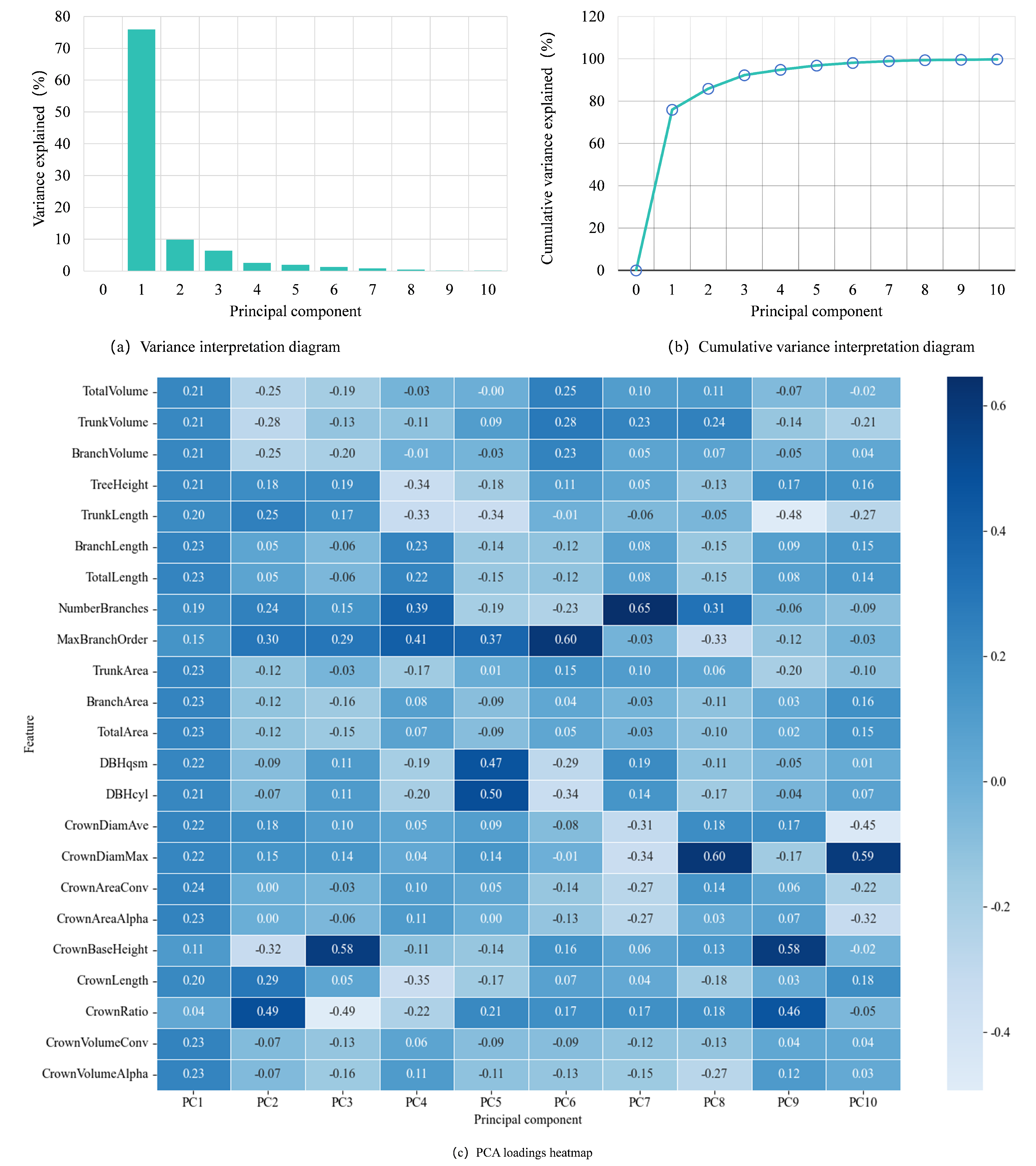
PCA was first applied to the original dataset to reduce its dimensionality. By analyzing the variance contributions of each principal component, as shown in
Figure 7, it is observed that the first principal component explains 75.96% of the total variance, indicating that it is the primary source of variation in the data. The second principal component explains an additional 9.90% of the total variance, a relatively small proportion, but it still provides insight into the secondary variation in the data. Together, the first two principal components account for 85.86% of the total variance, a significant proportion that suggests these components capture the most crucial information in the data. By selecting these two principal components for dimensionality reduction, not only is the complexity of the data significantly reduced, which eases the computational burden of the model, but the most valuable features of the data are retained, providing a clearer and more streamlined feature space for subsequent data analysis and model development.
The PCA loadings heatmap illustrates the contributions of individual features to principal components, where the magnitude of each loading reflects its relative importance. Features with larger absolute loadings exert stronger influences on component interpretation, effectively highlighting the most influential features in dimensionality reduction. Notably, the heatmap reveals distinct contribution patterns across components. For the first principal component (PC1), features demonstrate relatively balanced contributions, suggesting a collective influence on this axis. For the second principal component (PC2), three features (CrownRatio, MaxBranchOrder, and CrownLength) exhibit significantly larger absolute loadings compared to others, establishing them as dominant drivers of variance captured by PC2.
3.2.2. K-Means Clustering
After determining the appropriate number of principal components, the data was reduced to two-dimensional space, and the K-means clustering algorithm was applied to identify the clustering structure within the data. The dimensionality reduction not only enhances computational efficiency but also, by focusing on the most important features, enables the K-means algorithm to more clearly identify patterns and structures within the data, thereby improving both clustering accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, dimensionality reduction makes the clustering results easier to visualize and interpret, aiding in the understanding of the underlying patterns in the data.
Figure 8 shows the results of applying the K-means algorithm to the data with K values set to 2 and 3. By comparing the clustering results for these three different values of K, significant differences in the clustering outcomes can be observed: when K = 3, the distribution of points among the clusters is uneven, with cluster sizes of 51, 28, and 2, where the smallest cluster contains only 2 points. When K = 2, the point distribution between Cluster 0 and Cluster 1 is more balanced, with 46 and 35 points, respectively, and no extremely small clusters are present. Setting K = 2 leads to a more balanced point distribution and eliminates the issue of very small clusters, which helps improve the stability and interpretability of the clustering results.
3.3. Classification Model of Superior Hickory Trees
3.3.1. Building Individual and Crowd Models
Based on the results of the K-means clustering analysis, the data is divided into two categories, and two models are constructed: the individual model and the consensus model. To convert the 4-point scale into a binary classification, a threshold of 2.5 is selected. Scores higher than 2.5 (i.e., 3 and 4 points) are classified as “superior”, labeled as 0 (False), while scores lower than 2.5 (i.e., 1 and 2 points) are classified as “non-superior”, labeled as 1 (True). The ratings of each forest farmer for 81 trees are then converted into binary classification data. For each forest farmer, a binary classification model is constructed, based on their personal rating data, which primarily captures the individual’s judgment and preference regarding the dominance status of the trees. For each tree, the most frequent category (i.e., the mode) among the ratings from 24 forest farmers is calculated to construct a consensus model. The output of this model reflects the collective judgment of the 24 forest farmers, offering higher reliability and representativeness, and better reflecting the consensus of the forest farming community.
3.3.2. Model Accuracy Analysis
This study employed a randomized search framework combined with LOOCV to select best hyper-parameters for the GBDT model. The hyper-parameter search space encompassed critical parameters including: number of trees (50–300), learning rate (uniformly sampled from 0.01 to 0.2), and maximum depth (3–15). A total of 200 hyper-parameter combinations were randomly sampled from the parameter space. Each combination’s generalization performance was evaluated through LOOCV, with classification accuracy serving as the optimization criterion. The final selection prioritized the hyper-parameter configuration achieving the highest mean LOOCV accuracy.
After processing the 72 training samples using LOOCV and determining the optimal hyperparameters for both the individual model and the consensus model, the overall performance of the models is evaluated using three key metrics: LOOCV average accuracy, the score of the best model on the training set, and accuracy. The results are presented in
Appendix A,
Table A2. The consensus model achieved an LOOCV average accuracy of 87%, a training set accuracy of 100%, and a test set accuracy of 78%. For the individual model, the LOOCV average accuracy reached 75%, with an average training set accuracy exceeding 99%, and an average test set accuracy of over 73%. While the individual model demonstrates a very high average accuracy on the training set, its average accuracy on the test set is relatively lower, indicating some degree of overfitting. However, the objective of constructing the GBDT model in this study is not to develop an accurate classification model, but rather to intentionally allow it to overfit in order to maximize the extraction of information from the data. This approach helps achieve the research goal of identifying commonalities across all individual models and gaining deeper insights into the experiences of the forest farmers.
3.3.3. Analysis and Comparison Based on Crowd Model
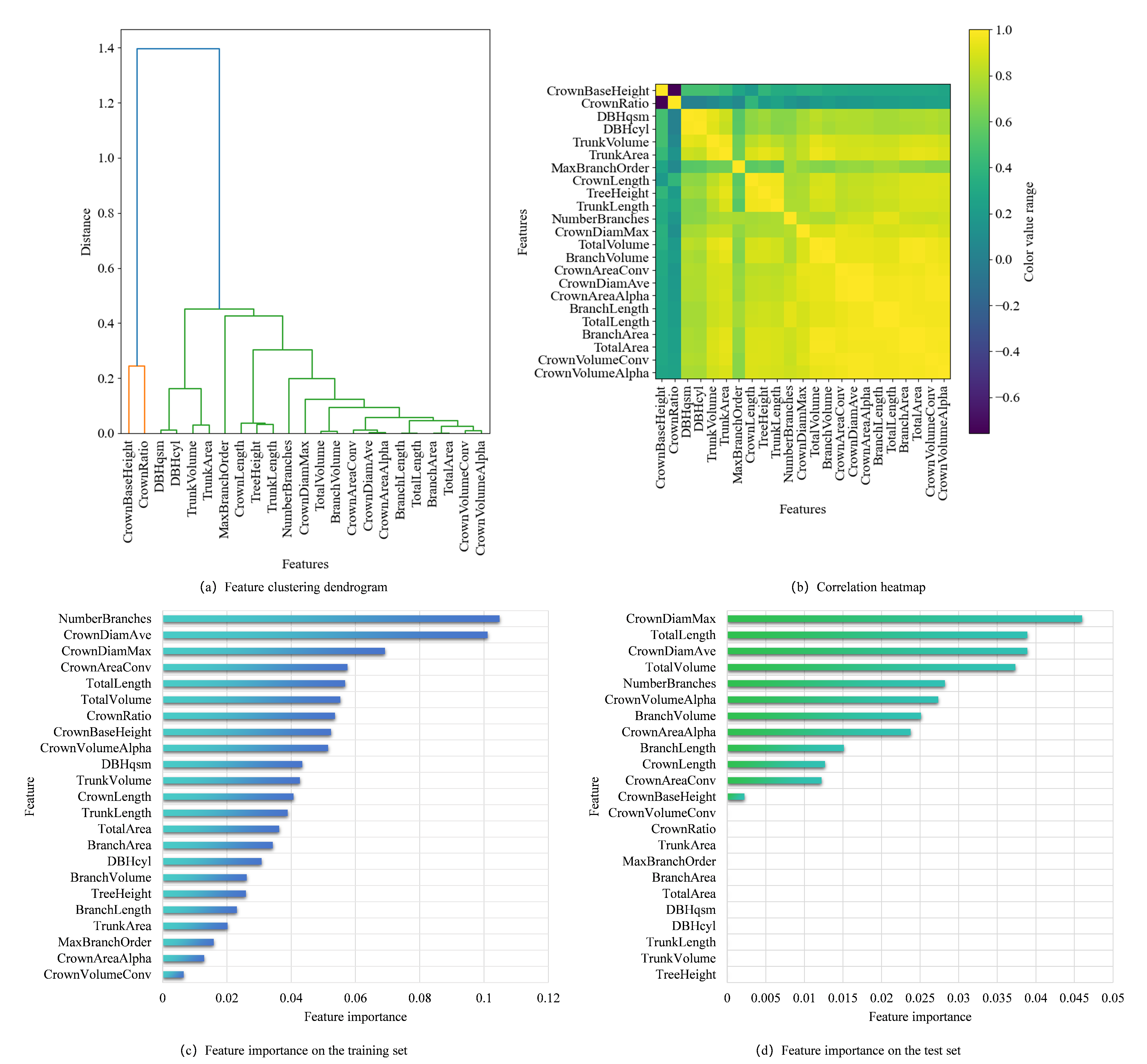
Figure 9 combines hierarchical clustering, correlation patterns, and consensus model-driven importance rankings to holistically evaluate feature relationships and predictive relevance. The dendrogram reveals distinct groupings: CrownBaseHeight forms an isolated cluster, indicating uniqueness, while TrunkVolume and TrunkArea cluster tightly, suggesting shared attributes. The heatmap identifies TrunkVolume and TotalVolume as perfectly correlated, CrownBaseHeight and BranchArea as negatively correlated, and crown-related features (CrownDiamMax, CrownDiamAve) with moderate-to-strong positive correlations (0.6–0.8).
From
Figure 9, based on the feature importance ranking in the consensus model for the training set according to the Gini importance metric, the top five features are branch count, average crown diameter, maximum horizontal crown diameter, total length of all branches, and the overall tree volume. Based on the feature importance ranking in the consensus model for the test set according to the permutation importance metric, the top five features are maximum horizontal crown diameter, total length of all branches, average crown diameter, branch count, and overall tree volume.
After calculating the feature importance, the decision nodes of each tree in the GBDT model were analyzed (see
Table 4). The frequency of each feature’s occurrence across all trees, along with their corresponding thresholds, were recorded. The average, median, mode, maximum, and minimum values of these thresholds were then computed. These values provide a general understanding of the importance of each feature. If a feature frequently appears in many decision trees, it likely plays an important role in the model’s decision-making process. The average and median of the thresholds provide typical values for feature-based data splits, while the mode represents the most frequent threshold in the decision trees, indicating the model’s decisions at specific feature values. The maximum and minimum threshold values offer insights into the range of feature values, helping to understand the feature’s distribution. Specifically, if the threshold range for a feature is narrow, with the maximum and minimum values being close, it may suggest that the feature has a stable decision boundary, significantly influencing the model’s predictions. In contrast, a broad threshold range may indicate that the feature is used to capture different data patterns in various decision trees.
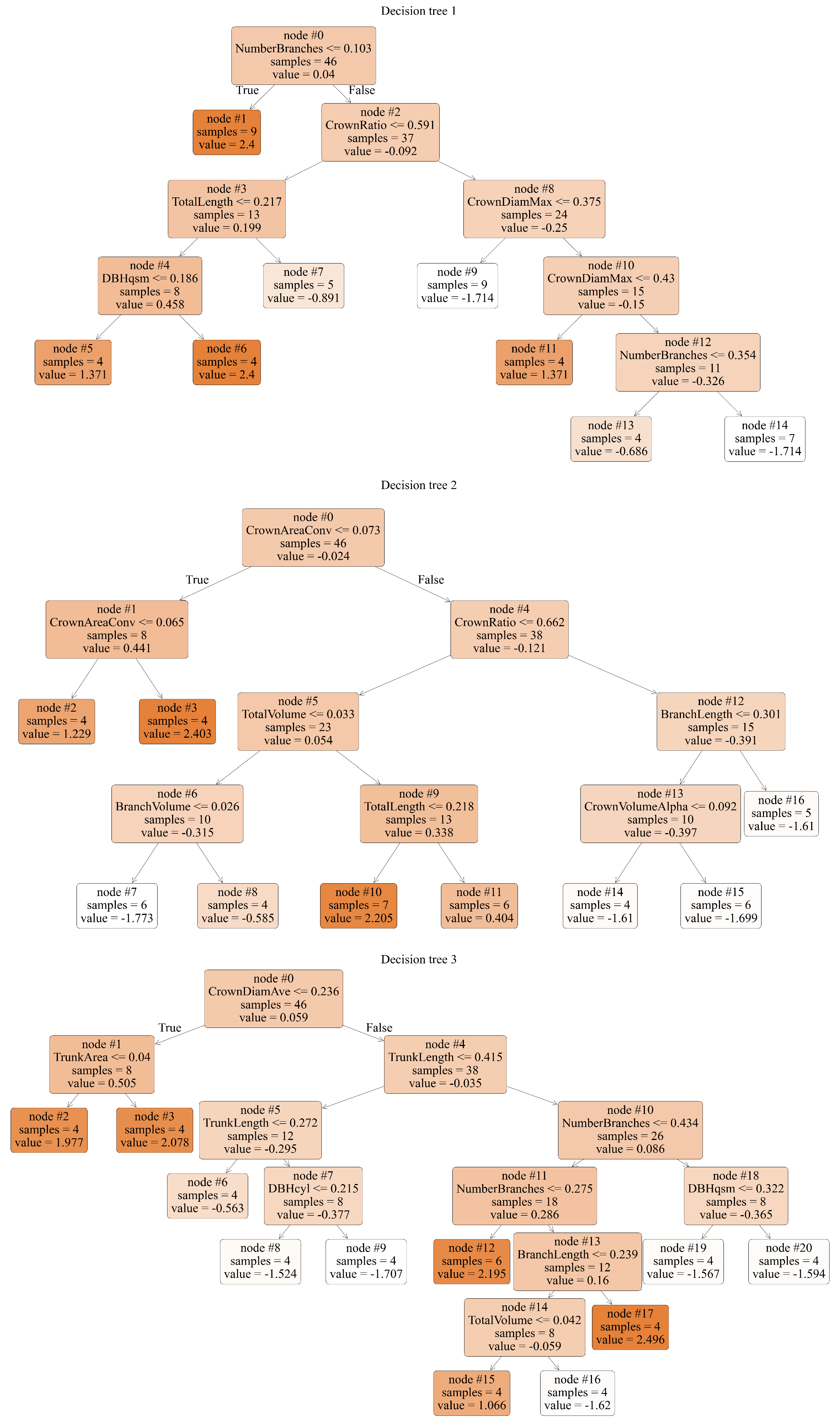
To effectively illustrate the decision process and internal structure of the GBDT model,
Figure 10 selectively shows the first three decision trees. As the GBDT model consists of multiple decision trees, each tree corrects the errors of the previous one. The first three trees reveal both the initial predictions made by the model and the subsequent error correction process. These three trees not only represent the model’s initial state but also demonstrate how the model gradually improves its predictive ability. In the visualization of the decision trees, nodes labeled “False” represent superior trees, while nodes labeled “True” are identified as non-superior trees. The node parameter represents decision points in the process, containing the feature and threshold used to split the data. The value parameter indicates the number of samples for each category at each node, aiding in the identification of the data distribution in the tree. The samples parameter shows the total number of samples at each node, reflecting the degree of data segmentation and concentration in the tree.
The most accurate method for determining feature importance is to directly extract feature importance indicators from the model. Based on the frequency of occurrences and threshold statistics, the dominance or non-dominance of trees is then determined. The top five features for both the training and test set rankings in the consensus model are branch count, average crown diameter, maximum horizontal crown diameter, total length of all branches, and overall tree volume. The maximum horizontal crown diameter and average crown diameter appear most frequently in the GBDT model, followed by branch count and total length of all branches. The threshold range (difference between the maximum and minimum values) for the maximum horizontal crown diameter, average crown diameter, branch count, and total length of all branches shows a larger variation compared to the overall tree volume. Although the overall tree volume does not appear the most frequently, its average, median, and mode threshold values are relatively low, suggesting that it may be an important decision factor.
3.3.4. Analysis and Comparison Based on Personal Models
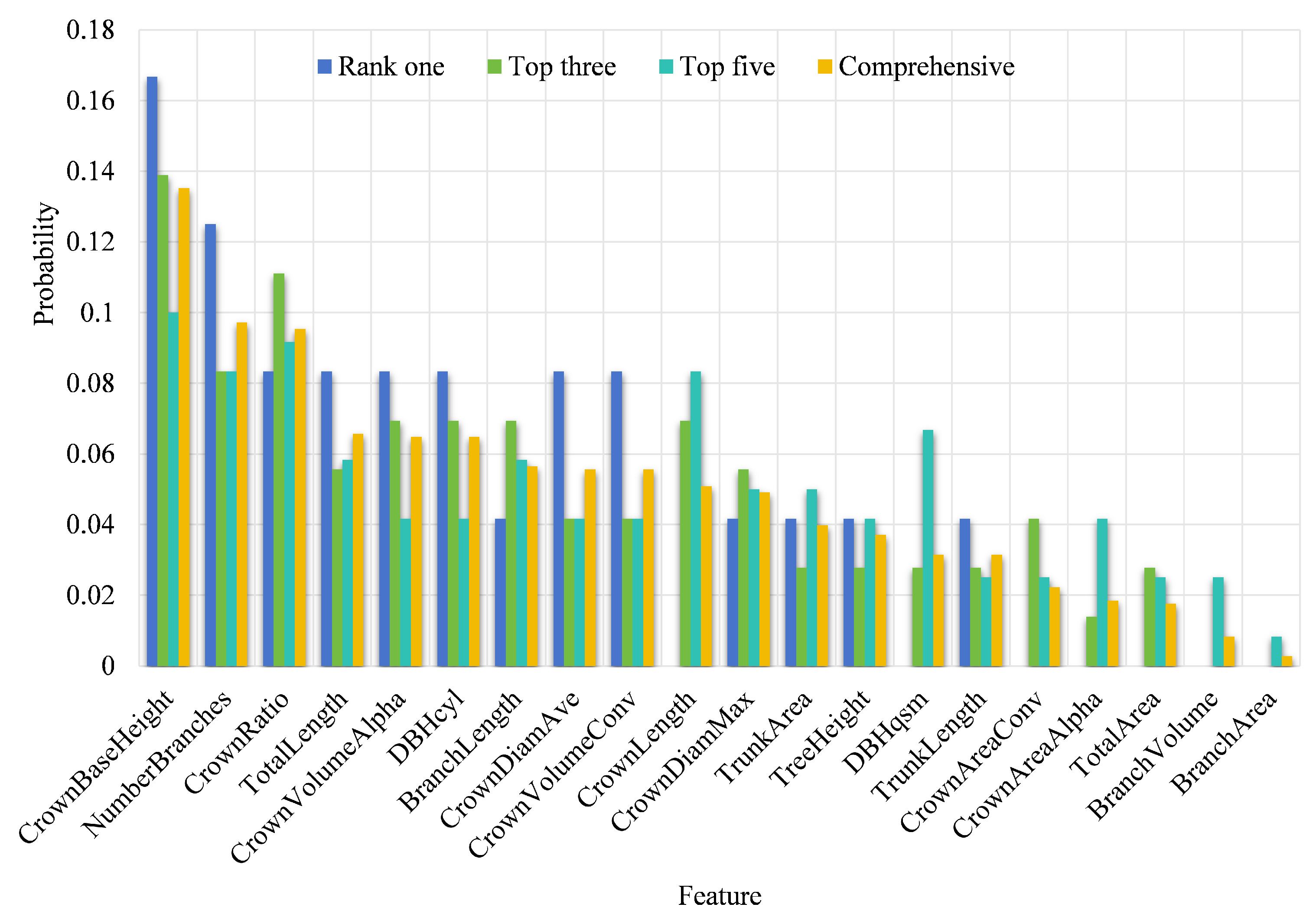
To conduct a more in-depth examination of the distinctions among various features within individual models, we evaluated the first, top three, and top five features for each model. Subsequently, we computed the proportion of these features across all individual models, designating this proportion as the probability value of the feature. Consequently, each feature will yield three aforementioned probability values, and the average of these values will be utilized to derive a comprehensive probability.
Figure 11 illustrates the ranking of features based on the comprehensive probability values (represented by the yellow bar chart), arranged in descending order. According to
Figure 11, the top four features are height from the ground to crown base, branch count, the ratio of crown length to tree height, and total length of all branches. The fifth position is shared by the volume of the tree’s crown Alpha shape and the tree diameter at 1.1–1.5 m.
When sorted by the probability for the first rank, the top two features are height from the ground to crown base and branch count, followed by the ratio of crown length to tree height, total length of all branches, volume of the tree’s crown Alpha shape, tree diameter at 1.1–1.5 m, average crown diameter, and the volume of the tree crown convex hull.
3.3.5. Analysis of the Differences Between the Crowd Model and the Individual Model
To obtain the expert rating data, this study presented the QSM reconstruction results of individual tree point clouds to experts, displaying images from four different angles. This survey format allows for an intuitive presentation of tree shape features, but it also has limitations. The display angles and visual effects may influence the experts’ ratings, which could, to some extent, affect the assessment of feature importance in the model. The results from both the consensus model and the individual model indicate that tree structural parameters are important for prediction, but there are differences in which specific parameters are most important and to what extent.
On the common aspects, branch count and total length of all branches were identified as important features in both models. This suggests that these features are universally significant for the model’s predictions and are clearly reflected in the images from various angles. Consequently, experts generally rated their importance as high. On the differing aspects, features such as the height from the ground to the crown base, the ratio of crown length to tree height, the volume of the tree’s crown Alpha shape, and the diameter of the tree at 1.1–1.5 m were considered more important in the individual model. However, they did not make it into the top five in the consensus model. This could be because the visual differences of these features across the four image angles were not prominent enough, which led experts to assign them lower importance during individual rating. As a result, they were not frequently rated as important features in the mode-based statistic. In contrast, features such as average crown diameter, maximum horizontal crown diameter, and overall tree volume were considered highly important in the consensus model but did not appear in the individual model. This may be because these features were more consistently and prominently displayed across different image angles, which allowed experts to better recognize their predictive value for tree dominance status, leading them to be frequently rated as important features in the consensus model.
The limitations of the survey data collection format influenced the evaluation of feature importance to some extent, resulting in differences in feature importance rankings between the individual and consensus models. Branch count and total length of all branches were recognized as important features in both models and significantly impacted the model’s prediction results. The height from the ground to crown base exhibited strong predictive capability in the individual model’s dataset. In conclusion, branch count, total length of all branches, and height from the ground to the crown base are the three most significant features affecting the dominance status of Carya cathayensis trees. Combining the decision tree thresholds, a tree can be considered superior if the branch count is greater than 1100.80, the total length of all branches exceeds 378.25 m, and the height from the ground to the crown base is greater than 1.13 m.
3.4. Analysis of Superior Tree Structure Based on Natural Selection
According to the results of the “Carya Cathayensis Tree King” selection event organized by the Lin’an District Agricultural and Rural Bureau and the District Media Center, the first “Carya Cathayensis Tree King” is located in YinKeng Village, Daoshi Town, with the tree numbered C1200 and an age of 152 years. D1100 is another Tree King located in Longgang Town, with a tree age of 40 years. The location of these Tree Kings has deep soil layers and good soil quality, combined with proper management, allowing them to remain vigorous and productive year after year. They have significant reference value for analyzing optimal tree structure and can be considered as the ideal tree form.
Table 5 presents the analysis results of the two optimal trees’ structural parameters compared to other trees, based on distance metrics. Specifically, it calculates the Euclidean and Manhattan distances using expert classification labels (excluding the two optimal trees, with 45 remaining superior trees and 34 non-superior trees). By observing the Euclidean and Manhattan distance data between the two optimal trees and the superior and non-superior trees, it is apparent that the distance range between the superior trees and the optimal trees is generally lower than that between the non-superior trees and the optimal trees.
Therefore, a threshold can be set to classify trees within a certain range as superior, while those exceeding this range can be classified as non-superior. For the second optimal tree, the threshold can be set between the two average values; for the first optimal tree, a lower threshold can be considered. After comprehensive consideration, the Euclidean distance threshold is set between 3.0 and 3.5, while the Manhattan distance threshold is set between 13.0 and 16.0. Trees within this range can be considered superior, while those outside this range are considered non-superior. This threshold is determined based on the middle value of the average distances between the two optimal trees and the superior and non-superior trees.
4. Conclusions
This study, based on a comparative analysis of the individual and consensus models, delves deeply into the key structural parameters that influence the Carya cathayensis tree form. Branch count and total branch length, identified as important features by both models, significantly impact prediction results, highlighting the critical role of branch structure in the complexity of tree growth. The height from the ground to the crown base ranked first in probability and combined probability in the individual model, demonstrating a stronger predictive ability within the dataset of the individual model. Branch count, total branch length, and the height from the ground to the crown base can be regarded as the most significant structural parameters affecting the Carya cathayensis tree form. Specifically, when the branch count exceeds 1101, the total branch length exceeds 378 m, and the height from the ground to the crown base exceeds 1 m, these trees can be marked as superior. These findings provide a scientific basis for the accurate assessment and management of Carya cathayensis trees, contributing to more efficient resource allocation and tree care strategies. With these quantifiable standards, researchers and managers can more precisely identify and cultivate trees with growth advantages, thereby improving overall forestry production efficiency and ecological value.
This study also cleverly extends the application of two traditional vector space distance metrics, Euclidean distance and Manhattan distance, to tree structure similarity assessment. By setting thresholds—Euclidean distance between 3.0 and 3.5 and Manhattan distance between 13.0 and 16.0—a clear boundary is established for tree classification. Trees within this range are considered superior, while those outside the range are classified as non-superior. This innovative approach breaks the conventional limitation of distance metrics, which typically apply only to regular vector spaces. Through appropriate transformation and method optimization, these metrics were successfully adapted to the complex and variable characteristics of tree structures. This opens a new perspective for tree shape structure comparison and expands the application boundaries of distance metrics, showcasing the tremendous potential and value of cross-disciplinary knowledge integration.
This study has several limitations and future directions. First, the current survey method using 2D images limits the comprehensive understanding of tree shape features, and future work could use 3D models or cross-sectional views for clearer feature evaluation. Second, the reliance on Euclidean and Manhattan distances for tree structure similarity analysis may not fully capture complex similarities, so future research could incorporate multidimensional metrics like cosine similarity. Third, the model’s predictions lack sufficient real-world validation, and field investigations could help compare predicted and actual yields for improved model accuracy. Lastly, developing intuitive visualization tools to present complex data and enhance model interpretability would make the results more accessible to non-experts and support more efficient forestry management.