Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition and Stability in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations in Subtropical China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
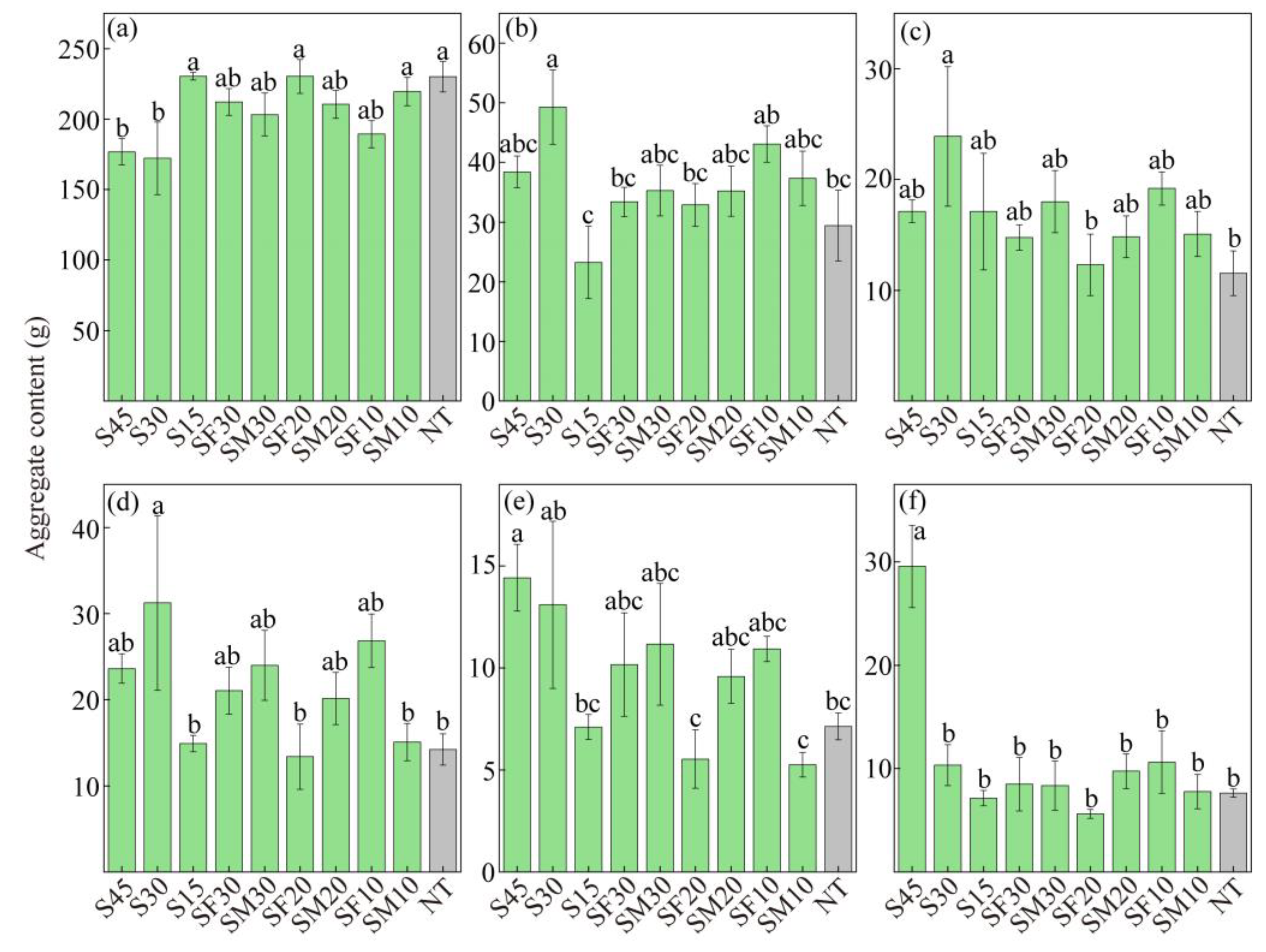
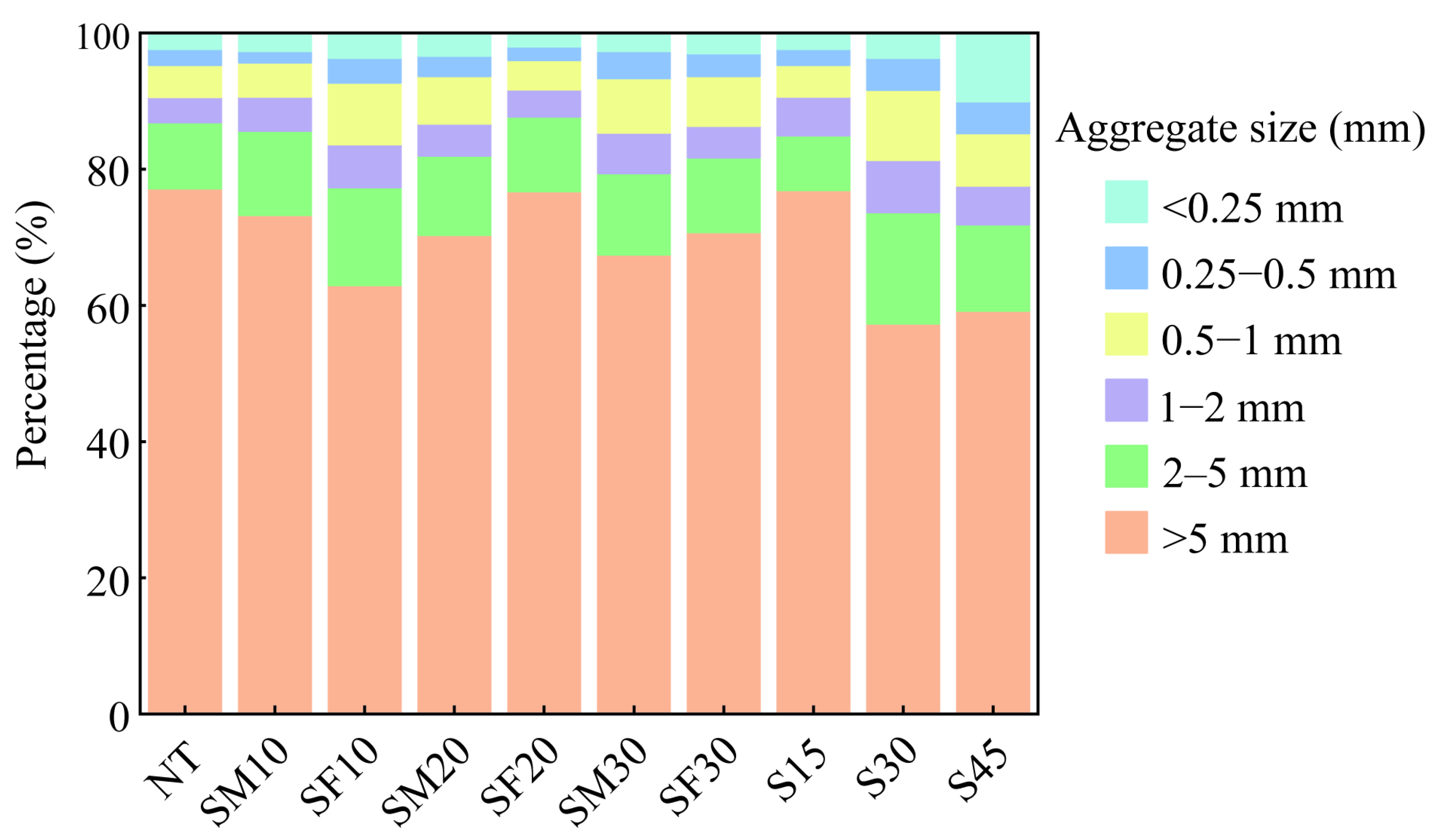
3.1. Changes in Soil Aggregate Composition
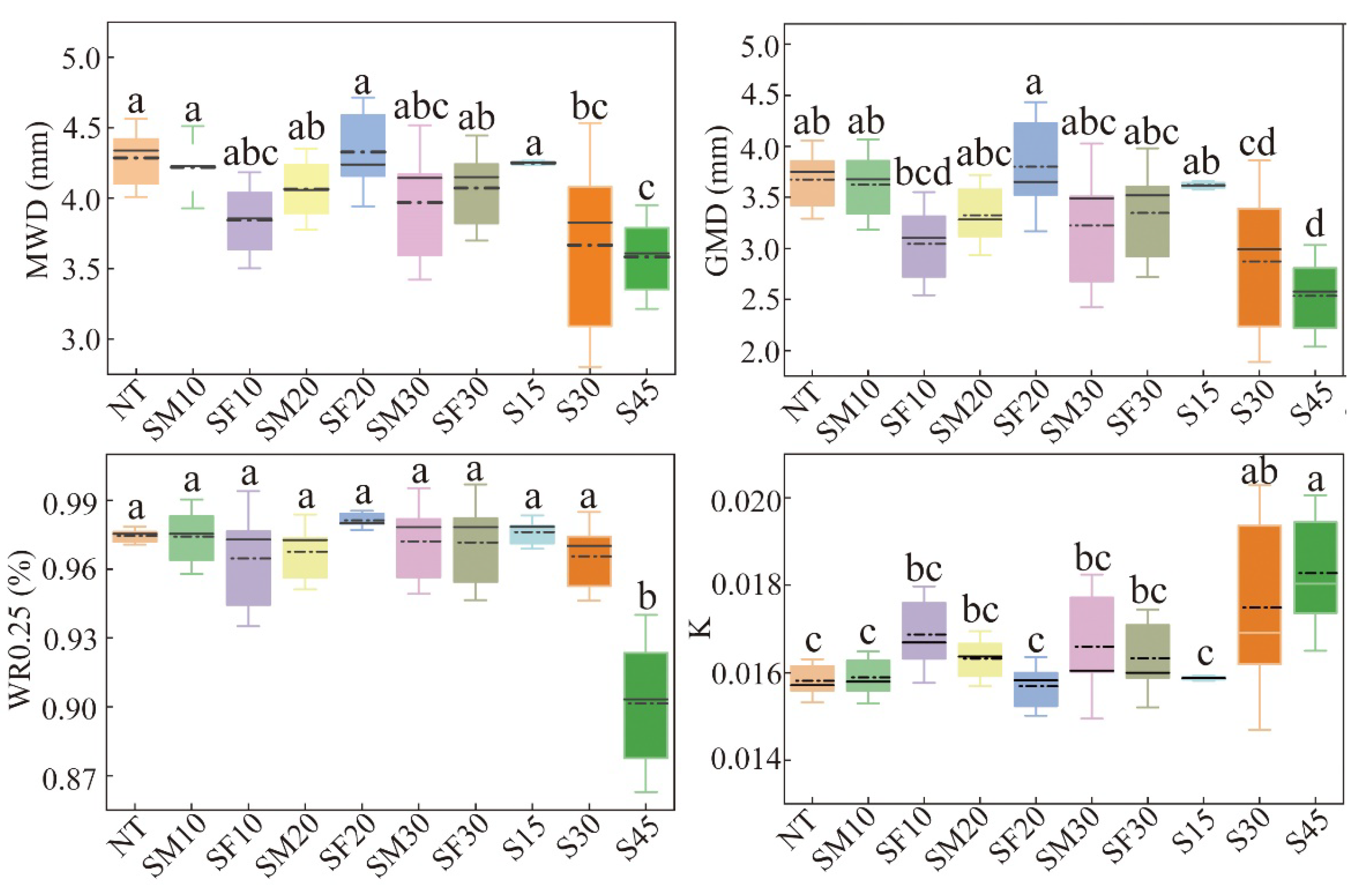
3.2. Changes in Soil Aggregate Stability
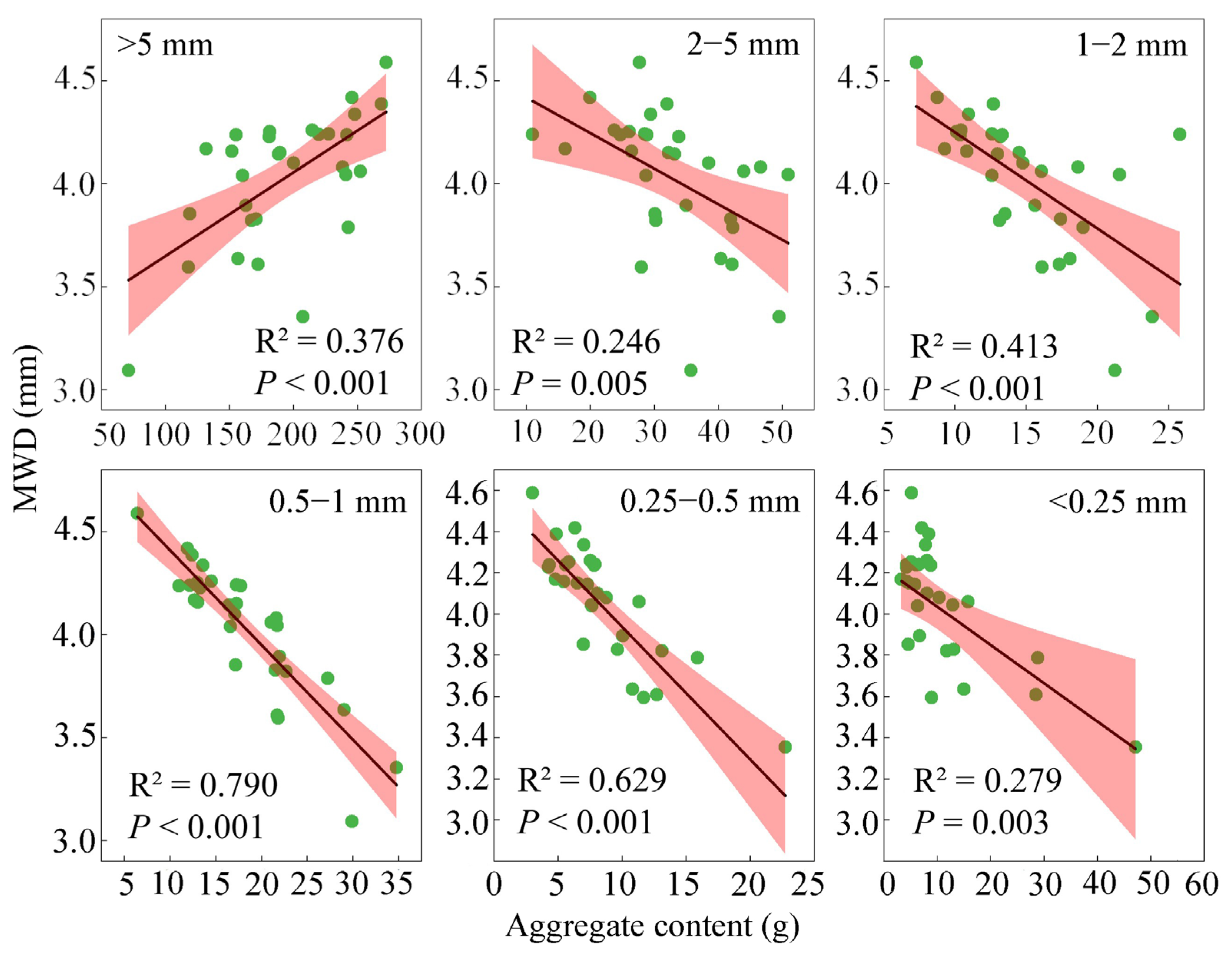
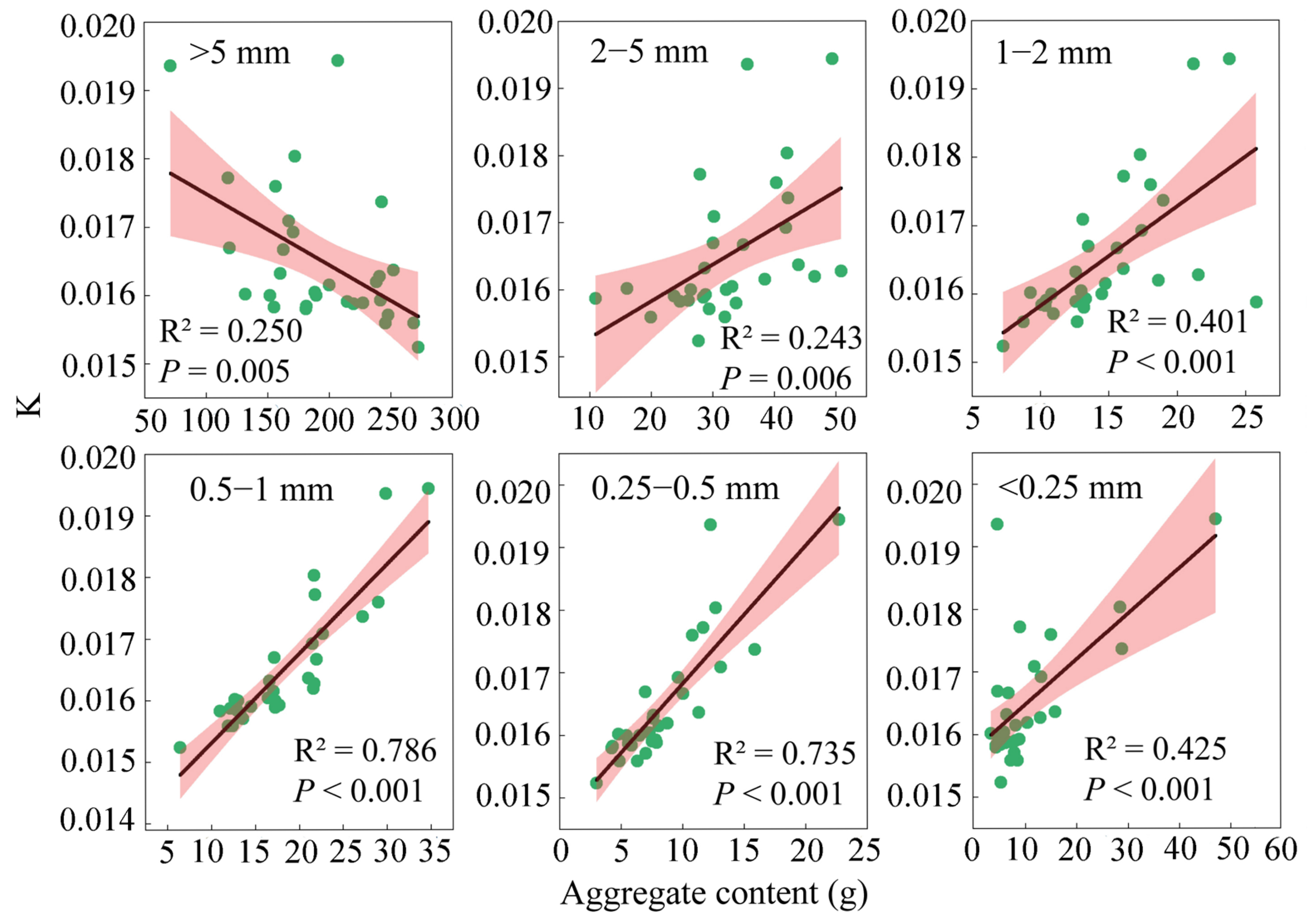
3.3. Correlation Between the Soil Aggregate Content and Aggregate Stability Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition
4.2. Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on Soil Aggregate Stability
4.3. Limitations and Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- da Silva, A.P.; Babujia, L.C.; Franchini, J.C.; Ralisch, R.; Hungria, M.; Guimaraes, M.d.F. Soil structure and its influence on microbial biomass in different soil and crop management systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 142, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ruiz, A.; Linde, N.; Keller, T.; Or, D. A Review of Geophysical Methods for Soil Structure Characterization. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 672–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Roemkens, M.J.M.; Darboux, F. Soil erodibility for water erosion: A perspective and Chinese experiences. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latterini, F.; Dyderski, M.K.K.; Horodecki, P.; Picchio, R.; Venanzi, R.; Lapin, K.; Jagodzinski, A.M.M. The Effects of Forest Operations and Silvicultural Treatments on Litter Decomposition Rate: A Meta-analysis. Curr. For. Rep. 2023, 9, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, G.J.; Baker, P.J.; Mac Nally, R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Thomson, J.R.; Hamilton, F. Forest structure, habitat and carbon benefits from thinning floodplain forests: Managing early stand density makes a difference. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, J. Near-natural conversion of plantations primarily enhances the abundance and functionality of nematodes within medium-sized soil aggregates. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 378, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesinski, J.; Lavigne, M.B.; Kershaw, J.A., Jr.; Krasowski, M.J. Fine-root dynamics change during stand development and in response to thinning in balsam fir (Abies balsamea L. Mill.) forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 286, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F.; Han, H. Effects of thinning on soil aggregation, organic carbon and labile carbon component distribution in Larix principis-rupprechtii plantations in North China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, D.; Phillips, P.; Vidal, E.; Schulze, M.; Grogan, J.; Sales, M.; van Gardingen, P. Adaptation of a spatially explicit individual tree-based growth and yield model and long-term comparison between reduced-impact and conventional logging in eastern Amazonia, Brazil. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 243, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Kang, F.; Cheng, X.; Han, H. Moderate thinning increases soil organic carbon in Larix principis-rupprechtii (Pinaceae) plantations. Geoderma 2018, 329, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.a.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, J. Long-Term Forest Conversion Affects Soil Stability and Humic Substances in Aggregate Fractions in Subtropical China. Forests 2022, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Broadleaf Trees Increase Soil Aggregate Stability in Mixed Forest Stands of Southwest China. Forests 2023, 14, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, H.; You, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; et al. Coniferous-Broadleaf Mixture Increases Soil Microbial Biomass and Functions Accompanied by Improved Stand Biomass and Litter Production in Subtropical China. Forests 2019, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Mentler, A.; Mayer, H.; Blum, W.E.H. Soil aggregation, aggregate stability, organic carbon and nitrogen in different soil aggregate fractions under forest and shrub vegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2010, 81, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Sheng, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z. Land use conversion and lithology impacts soil aggregate stability in subtropical China. Geoderma 2021, 389, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Su, X.; Liao, S.; You, Y. Conversion of pure Chinese fir plantation to multi-layered mixed plantation enhances the soil aggregate stability by regulating microbial communities in subtropical China. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.-H.; Wu, F.-Z.; Zhang, H.-L.; Peng, Q.-Q.; Qiu, D.-N.; Peng, Y. Community structure of soil fauna under different tree species in subtropical forests. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2023, 34, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar]
- Babur, E.; Kara, O.; Fathi, R.A.; Susam, Y.E.; Riaz, M.; Arif, M.; Akhtar, K. Wattle fencing improved soil aggregate stability, organic carbon stocks and biochemical quality by restoring highly eroded mountain region soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.-M.; Chen, F.-S.; Wan, S.-Z.; Yang, Q.-P.; Shi, J.-M. Topsoil and Deep Soil Organic Carbon Concentration and Stability Vary with Aggregate Size and Vegetation Type in Subtropical China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomin, D.; Timofeeva, M.; Ovchinnikova, O.; Valdes-Korovkin, I.; Holub, A.; Yudina, A. Energy-based indicators of soil structure by automatic dry sieving. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Zhou, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. Effects of Shelterbelt Transformation on Soil Aggregates Characterization and Erodibility in China Black Soil Farmland. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Soil aggregate size distribution and stability of farmland as affected by dry and wet sieving methods. Zemdirb. -Agric. 2020, 107, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Qi, J.; Yang, J.; Lv, M.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Li, C. The conversion of tropical natural forests alters soil carbon fractions in aggregates and reduces aggregates stability. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J. Soil. Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Xiao, W.; Yang, S. Effects of understory removal and thinning on soil aggregation, and organic carbon distribution in Pinus massoniana plantations in the three Gorges Reservoir area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, J.; del Rio, M.; Cattaneo, N.; Riofrio, J.; Ordonez, C.; Uzquiano, S.; Bravo, F. Short-term effect of thinning on inter- and intra-annual radial increment in Mediterranean Scots pine-oak mixed forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 549, 121462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, G.; Wang, L.; Yu, X. Contributions of biotic and abiotic factors to soil aggregation under different intensities. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Rhizosphere effects promote soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration in rocky areas of desertification. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gan, Q.; Huang, L.; Pan, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Effects of forest thinning on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity. Catena 2024, 239, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhang, J.; Fan, C.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. Stand Density Management of Cypress Plantations Based on the Influence of Soil Hydrothermal Conditions on Fine Root Dynamics in Southwestern China. Forests 2025, 16, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt Ferreira dos Santos, V.A.; Modolo, G.S.; Ferreira, M.J. How do silvicultural treatments alter the microclimate in a Central Amazon secondary forest? A focus on light changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aun, K.; Kukumagi, M.; Varik, M.; Becker, H.; Aosaar, J.; Uri, M.; Morozov, G.; Buht, M.; Uri, V. Short-term effect of thinning on the carbon budget of young and middle-aged Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 492, 119241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yang, Y.; An, S.; Zhu, Z. Effects of different vegetation restoration measures on soil aggregate stability and erodibility on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2020, 185, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, L.; Leppa, K.; Launiainen, S.; Lauren, A.; Hokka, H.; Sarkkola, S.; Saarinen, M.; Nieminen, M. Measuring and Modeling the Effect of Strip Cutting on the Water Table in Boreal Drained Peatland Pine Forests. Forests 2022, 13, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Qu, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Xue, S. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil microbial necromass carbon and organic carbon in grazed and degraded sandy land. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sui, Y.; Xiao, L.; Lin, J.; Cruse, R.M.; Ding, G.; Liu, X. Warming-dominated climate change impacts on soil organic carbon fractions and aggregate stability in Mollisols. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dor, M.; Emmanuel, S.; Brumfeld, V.; Levy, G.J.; Mishael, Y.G. Microstructural changes in soils induced by wetting and drying: Effects on atrazine mobility. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Mao, Q.; Li, C.; Tu, B.; Li, X. Natural factors outweigh anthropogenic impact on aquatic phoD-harboring communities along Yangtze River basin. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Zheng, W.; Rillig, M.C. Soil biota contributions to soil aggregation. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kou, Y.; Mao, Q.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Tu, B.; Li, J.; Tu, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Climate outweighs fertiliser effects on soil phoD-harbouring communities in agroecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 202, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Kongsurakan, P.; Iwai, C.B.; Yuttitham, M.; Hatano, R. Post-fire recovery of soil organic carbon, soil total nitrogen, soil nutrients, and soil erodibility in rotational shifting cultivation in Northern Thailand. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1117427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zha, T.-G.; Wang, Y.-K.; Wang, G.-M. Soil aggregate stability and soil organic carbon characteristics in Quercus variabilis and Pinus tabulaeformis plantations in Beijing area. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, W.; Huang, L.; Zhu, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; You, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Dynamics of soil phosphorus fractions during the early recovery stage of two typical plantations in China after strip clearcutting. Catena 2025, 250, 108767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, T.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Liu, W. Reforestation Increases the Aggregate Organic Carbon Concentration Induced by Soil Microorganisms in a Degraded Red Soil, Subtropical China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Q.; Daryanto, S.; Guo, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Ma, X. Responses of Chinese fir and Schima superba seedlings to light gradients: Implications for the restoration of mixed broadleaf-conifer forests from Chinese fir monocultures. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 419, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Luo, L.; Tao, L.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Y. The Carbon Storage of Reforestation Plantings on Degraded Lands of the Red Soil Region, Jiangxi Province, China. Forests 2024, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Damour, G.; Gary, C.; Follain, S.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Metay, A. Trait-based approach for agroecology: Contribution of service crop root traits to explain soil aggregate stability in vineyards. Plant Soil 2019, 435, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Kou, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, C.; Kong, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X. The distribution of soil alkaline phosphatase (phoD) gene harbouring bacteria across Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2025, 7, 240282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Yang, M.; Long, Q.; Hussain, S.; Chen, J.; Clay, D.; He, Y. Different fall/winter cover crop root patterns induce contrasting red soil (Ultisols) mechanical resistance through aggregate properties. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Tan, B.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition and Stability in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations in Subtropical China. Forests 2025, 16, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060873
Huang L, Zhou X, Zhao X, Zhang L, Tan B, Li J, Xu H. Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition and Stability in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations in Subtropical China. Forests. 2025; 16(6):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060873
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lulu, Xiaohan Zhou, Xinran Zhao, Li Zhang, Bo Tan, Jiao Li, and Hongwei Xu. 2025. "Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition and Stability in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations in Subtropical China" Forests 16, no. 6: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060873
APA StyleHuang, L., Zhou, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Tan, B., Li, J., & Xu, H. (2025). Effects of Strip Clearcutting and Replanting on the Soil Aggregate Composition and Stability in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations in Subtropical China. Forests, 16(6), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060873







