Abstract
The ecological impacts of dam and reservoir construction necessitate systematic environmental quality evaluation (EEQ) to reconcile ecological protection with sustainable development. To address this need, we integrated the Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI)—a comprehensive metric synthesizing greenness, humidity, heat, and dryness—with a Land Use Change Ecological Response (LUCER) model to quantify the long-term EEQ dynamics in reservoir-affected regions. This study utilized Landsat and Sentinel-2 remote sensing imagery with a 10 m resolution from the years 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 to compute the RSEI for the Qianping Reservoir area in Henan Province, investigating the spatiotemporal variations in EEQ. Key findings reveal: (1) Temporal trend: EEQ showed fluctuating improvement, with RSEI projected to rise gradually until 2030. (2) Spatial pattern: A lower ecological quality in central reservoir zones contrasts with higher quality in surrounding mountainous areas. (3) Mechanism: The Land Use Change Ecological Response (LUCER) model reveals that the conversion of cultivated land to forestland and grassland drives significant EEQ improvements, counterbalancing the negative impacts of hydrological fragmentation caused by reservoir construction and urbanization. This study advances RSEI applications in reservoir ecology by establishing a coupled monitoring–prediction framework, providing actionable insights for dam-related ecological restoration and governance.
1. Introduction
Rapid development and urbanization have led to dramatic changes in land use and land cover types. The resulting ecological and environmental issues, such as soil erosion and land desertification, have raised widespread concerns among researchers [1,2]. Ecological and environmental quality (EEQ), defined as the integrated assessment of ecosystem health and environmental protection status, requires timely monitoring and evaluation to promote sustainable socio-economic development and natural resource utilization [3]. While changes in land use usually require some time to show measurable effects on EEQ, the construction of dams and reservoirs—exemplified by the Qianping Reservoir in Henan Province studied here—as a typical type of grey infrastructure, can have immediate impacts on the ecological environment [4]. Specifically, building dams offers benefits such as flow regulation, flood control, and water storage for irrigation, etc. [5,6]. However, our findings reveal a dual effect: short-term benefits are counterbalanced by long-term ecological risks, including altered river flow regimes [7], landscape fragmentation, and biodiversity loss [8]. Recent years have seen increasing attention paid to these impacts on EEQ and ecological restoration after reservoir construction [9].
While the demand for timely EEQ monitoring is evident in addressing rapid anthropogenic disturbances (e.g., reservoir construction mentioned above), methodological limitations persisted in early assessment approaches. Traditional EEQ assessments relied predominantly on mathematical statistics constrained by single-source data, facing challenges such as subjective indicator weighting and limited spatial resolution. However, advancements in remote sensing (RS) technology have enabled multidimensional ecosystem monitoring through vegetation indices [10], land surface temperature, and impervious surface coverage [11], thereby facilitating spatially explicit EEQ evaluation [12]. This approach is particularly critical for assessing the immediate ecological impacts of grey infrastructure, such as the Qianping Reservoir.
While existing studies have applied Sen slope analysis, MK tests, and CA-Markov models to general EEQ trend prediction, their integration for assessing the dynamic ecological impacts of reservoir construction remains underexplored. Specifically, the rapid ecological transitions induced by grey infrastructure (e.g., dam projects like Qianping Reservoir) demand methods capable of resolving both short-term disturbances (via Sen-MK trend detection) and long-term spatiotemporal patterns (via CA-Markov simulation). Our work addresses this gap by coupling these approaches to quantify how reservoir-driven land use changes propagate non-linear EEQ degradation, thereby providing a methodological framework tailored to infrastructure ecology monitoring.
In [13], it was found that anthropogenic activities exert a more pronounced impact on ecological degradation compared to natural drivers, with land-use change directly contributing to the deterioration of EEQ. Analyzing the driving factors behind changes in EEQ within reservoir areas is crucial for understanding the causes of EEQ deterioration and providing a scientific foundation for its improvement.
Qianping Reservoir is located on the mainstream of the Beiru River in central and northern China (Henan Province). It is a low mountainous and hilly area. Its key ecological characteristics include biodiversity hotspots, hydrological complexity, and interactions between humans and nature. These characteristics make Qianping an ideal model system for studying reservoir EEQ dynamics under combined natural and anthropogenic pressures. The region serves as an important distribution area of natural forests in Henan, boasting a vegetation coverage rate of 30%. However, the construction of the reservoir project, initiated in 2015, resulted in the occupation of a significant amount of cultivated land, the destruction of surface vegetation, and an increased risk of soil erosion. Certain engineering activities such as blasting, the excavation of roads, road slope cutting, and diversion tunnels have exacerbated soil erosion and inflicted severe damage on the local native ecological environment [14]. Ecological restoration following reservoir construction is paramount to the completion of the reservoir area’s ecological environment and plays an irreplaceable role in connecting the hydrological and ecological environments. Thus, it is crucial to monitor and evaluate the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir.
Utilizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 RS images, digital elevation model (DEM) data, meteorological data, and other sources, this study employed the RSEI, CA-Markov, and LUCER to investigate the dynamic characteristics of EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir area in the years 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. The primary objectives are to (1) clarify the spatiotemporal distribution and identify interannual changes and trends in EEQ, (2) employ trend analysis methods and the CA-Markov model to simulate and predict its development, and (3) quantitatively evaluate the process of land use change and ecological response. The research findings will not only provide an effective method for monitoring and evaluating changes in ecological quality in reservoir areas but also offer a scientific basis and theoretical support for ecological environment monitoring, ecological restoration, biodiversity conservation, and the sustainable development of dam-affected areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The Qianping Reservoir is located in Ruyang County, Luoyang City, Henan Province, situated between 112°13′15″ to 112°25′7″ E and 34°1′45″ to 34°8′22″ N (see Figure 1). The study area encompasses 38.57 km2 (3857 hm2), with the reservoir-controlled watershed covering an area of 1325 km2. The region experiences a temperate monsoon climate, with an average annual rainfall of 761.7 mm and an average temperature of 14.2 °C (Source: https://www.weather.com.cn/) accessed on 9 October 2023. It falls within the National Key Water and Soil Erosion Control Area of Zhongtiao and Funiu Mountains, as well as the Water and Soil Erosion Prevention Protection Zone and Key Control Area of Henan Province. Portions of the Beiru River’s source above the dam site are covered by virgin forest, while sparse vegetation and steep slopes characterize the watershed below the dam site. Land reclamation activities have led to severe water and soil erosion, rendering the area ecologically fragile. The construction of the reservoir resulted in numerous exposed slopes, altering natural flood and drought patterns in the surrounding water flow area. Additionally, it caused significant damage to beach land vegetation, disrupted ecosystems and natural habitats, and impacted the ecology in both the project disturbance area and its surrounding zones. These effects are evident in photographs shown in Figure 1d. However, nearing the completion of reservoir construction, improvements were observed, as depicted in Figure 1e, which were attributed to the implementation of slope restoration measures.
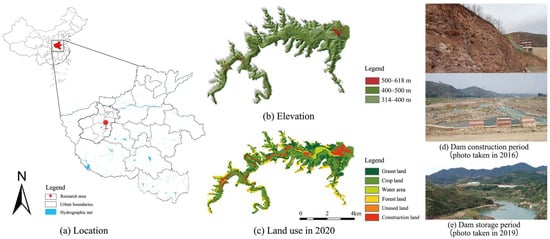
Figure 1.
Location and conditions of the study area.
2.2. Data and Research Framework
2.2.1. Data Source and Processing
The data sources utilized in this study are outlined in Table 1. Five Landsat and Sentinel-2 datasets of the reservoir area from 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were chosen for calculating the RSEI. To mitigate the impact of the inter-annual growth variations of different vegetation types on the RSEI, images taken in August and September with cloud coverage below 5% were selected. Mean synthesis technology was applied to generate year-by-year images. The RS imagery, digital elevation model (DEM), and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data were derived from geospatial data clouds, while land use data were acquired from the Global Land Cover website.

Table 1.
Data sources and descriptions.
2.2.2. Research Framework
This study comprises four main parts, as shown in Figure 2. Firstly, four indicators, namely NDVI, WET, LST, and NDBSI, were calculated for the years 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 based on Landsat and Sentinel-2 data. Subsequently, the spatial distribution map of the RSEI for each of these five years was generated through normalization and principal component analysis (PCA). Secondly, the Sen slope and MK trend analysis methods were employed to analyze the changes in ecological quality. Thirdly, the CA-Markov model was utilized to simulate and predict EEQ. Finally, the LUCER model was used to analyze the impact of land type conversion on the EEQ of the Qianping Reservoir.
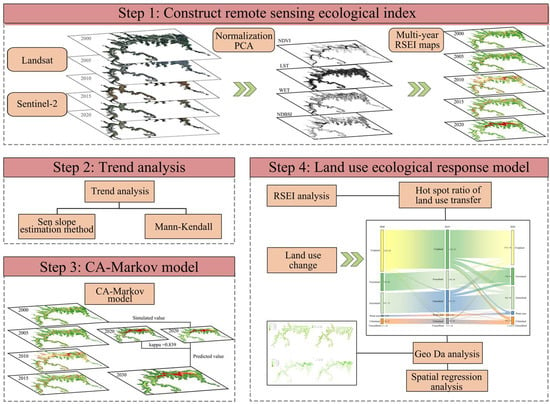
Figure 2.
Research framework.
2.3. Calculation of RSEI
EEQ assessment is primarily categorized into single-factor change analysis and multi-factor comprehensive analysis [14]. Assessing complex ecological environments comprehensively with a single factor is typically challenging [15]. To address this issue, Xu introduced the RSEI, which was designed for swiftly monitoring and evaluating urban ecological conditions [12]. The RSEI amalgamates four natural indicators that most intuitively reflect the ecological environment. It not only avoids the one-sidedness of a single RS index and the subjectivity of the indicator weight assignment used in earlier studies but also facilitates spatiotemporal analysis and visual representation of the ecological environment’s evolution. Compared to the Ecological Index (EI), the RSEI resolves issues concerning the rationality of weight setting and visualization of EEQ [16] and is now extensively employed in the dynamic monitoring and evaluation of EEQ in diverse areas such as cities [17,18], nature reserves, and rural areas [19,20].
The calculation of the RSEI involves four ecological variables: NDVI, WET, LST, and NDBSI. These variables intuitively reflect the quality of the regional ecological environment.
- (1)
- NDVI
This index serves as a quantitative indicator for studying vegetation coverage on Earth’s land surface, representing the best measure of plant growth status and nutritional information. It is closely associated with parameters such as leaf area index, vegetation coverage, and plant biomass [21]. The NDVI is commonly employed in the RS monitoring of forests, grasslands, and other types of vegetation. The calculation formula is as follows [22]:
where N represents the reflectance of the near-infrared band of Sentinel-2 and Landsat data and R represents the reflectance of the red band.
- (2)
- WET
WET serves as a crucial indicator in ecological environment research, reflecting the moisture content in vegetation, water, and soil, and is linked to ecological and environmental changes such as soil degradation. The expressions are as follows [23]:
where B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, and B7 represent the reflectance values of Bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 7 from the Landsat data.
where B2, B3, B4, B8, B11, and B12 correspond to the blue, green, red, near-infrared, short-wave infrared (1610 nm), and short-wave infrared (2190 nm) bands of Sentinel-2, respectively.
- (3)
- LST
While studies examining thermal–ecological relationships in reservoir areas remain limited [24,25,26], the surface temperature (LST) inversion method of Qianping Reservoir was studied and partially verified. Using the local atmospheric correction parameters of the Henan Province Meteorological Bureau and conducting 28 on-site temperature measurements for calibration, it showed a high degree of consistency (R2 = 0.89, RSSE = 1.4 °C). The modified heat index formula [27]:
where B1 represents the thermal infrared radiance value. Since the Sentinel-2 sensor lacks a thermal infrared band, it is necessary to use Landsat data to invert the true surface temperature and then resample the spatial data into Sentinel-2’s 10 m resolution data for later band fusion.
- (4)
- NDBSI
Soil drying can lead to severe damage to the regional ecological environment. In [28], NDBSI, calculated by combining the Soil Index (SI) and Index-based Built-up Index (IBI), was utilized to represent the degree of soil drying in the study area. The study modifies the standard NDBSI calculation through on-site observation of crack strength in the Qianping Reservoir area. The formulas are as follows:
where B2, B3, B4, and B5 represent the reflectance values of Bands 2, 3, 4, and 5 from the Landsat data, as well as the reflectance of Bands 2, 4, 8, and 11 from Sentinel-2.
- (5)
- Construction of the RSEI
To construct the RSEI, this study adopted the PCA method to synthesize the four ecological variables, fully considering their characteristics. This approach helps eliminate biases that can rise from the subjective weight-setting process [29]. First, the four ecological variables were normalized. Next, PCA transformation was performed to obtain the first principal component result (PCA1). By subtracting PCA1 from 1, the initial RSEI was derived, which was then normalized to produce the final RSEI. The calculation formulas are as follows [30]:
where NIi represents the normalized result of each index; Ii represents the value of each index at the i-th pixel; Imax and Imin represent the maximum and minimum values of each index, respectively; RSEI0 represents the initial RSEI value; and RSEI represents the final RSEI.
2.4. Trend Analysis and Consistency Test
Research on EEQ prediction often employs the Sen slope [31] and Mann–Kendall (MK) test [32] methods to analyze the trend of ecological quality change and the CA-Markov model to simulate and predict spatiotemporal evolution [33]. The Sen slope estimation method is insensitive to measurement errors and demonstrates high computational efficiency for discrete data [31]. It finds extensive application in the time trend analysis of sequences at the pixel scale [34]. In the study by Qin [35], the Sen slope method was employed to illustrate the changing trend of each pixel of RSEI. The MK test, a non-parametric test method, does not necessitate the data to be normally distributed and is unaffected by a few outliers and missing values. Therefore, it is suitable for the trend significance testing of long-term series data [36]. This study employed the Sen’s slope estimator method to analyze the RSEI’s spatial and temporal trends. The calculation formula is as follows:
where xj and xi represent the RSEI values in the j-th and i-th years, respectively, where j > i. A positive slope (β > 0) indicates an increasing trend in RSEI, while a negative slope (β < 0) indicates a decreasing trend.
Statistical significance in trend analysis is commonly utilized to indicate the degree of correlation between various geographical elements. In this study, the relationship between the EEQ of Qianping Reservoir and its influencing factors was assessed using a grid-by-grid spatial analysis method. The calculation formulas are presented below [36]:
where Z represents the statistical significance of the RSEI trend and n represents the number of time series, which is 20. An absolute value of Z that is greater than 1.96 indicates that the trend of the RSEI has passed the 95% confidence test.
The MK trend test is a common method in land use accuracy analysis. It involves comparing two land uses pixel by pixel to generate an error matrix. Subsequently, the Kappa coefficient (K) of the two land uses is calculated to assess their spatial consistency using the following formula [37]:
where K represents the land use/cover type of the product; nkk represents the number of correctly classified pixels in type K; n+k represents the number of pixels of type K in the reference product; nk+ represents the number of pixels of type K in the product to be evaluated; and N represents the total number of pixels in the product.
2.5. CA-Markov Model
The CA-Markov model integrates the spatial simulation advantages of the cellular automaton (CA) model with the temporal prediction advantages of the Markov model [38,39], making it generally suitable for simulating and predicting land use changes [40,41]. Currently, only a few studies have utilized the coupled CA-Markov model in predicting EEQ [42]. Researchers attempt to use this model to simulate the spatio-temporal evolution process of complex systems. The formula is as follows:
where S represents the cellular state; f represents the cellular transformation rules in local space; t and t + 1 represent different cellular moments; and n represents the time interval between the two moments.
The Markov model operates under the assumption that changes in phenomena adhere to a Markov process, wherein the next state of a phenomenon is solely dependent on its preceding state and the transition probability matrix. The calculation formulas are as follows:
where X(t+1) and X(t) represent the states at time t + 1 and t, respectively, and Pij represents the transition probability matrix.
2.6. Land Use Ecological Response Model
Researchers have applied the quantitative evaluation capabilities of the LUCER model to assess the impact of land use on the ecological environment [43,44]. In this study, the LUCER model was utilized to investigate the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and land use patterns influenced by the habitat quality dynamics behind the reservoir dam. Based on the RSEI and land use transition matrix, a LUCER model was constructed with Geo Da software, following prescribed processes and calculation protocols outlined as follows (Table 2):

Table 2.
LUCER model implementation workflow.
3. Results
3.1. Quality Evaluation of the RSEI
3.1.1. Principal Component Analysis
Using ENVI 5.3 software, the four normalized indicator layers were combined, followed by PCA analysis. The results are presented in Table 3. The contribution rate of the first principal component (PC1) in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 was 80.47%, 76.61%, 70.38%, 76.43%, and 65.29%, respectively, indicating that PC1 encompasses most of the characteristics of the four indicators. Additionally, the contribution rates of each indicator to PC1 across these five years are relatively consistent, with similar positive/negative distributions. Specifically, the NDVI and WET positively contribute to PC1, while LST and NDBSI make negative contributions. In contrast, the other three principal components (PC2–PC4) exhibit no apparent regularity and fail to unveil the internal mechanism of superior or poor EEQ. Therefore, this study opted for the results of the first principal component when calculating the RSEI.

Table 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) results.
3.1.2. Indicator Correlation Analysis
Figure 3 illustrates the correlation between the RSEI and the four indicators based on the 2020 data for the study area. As illustrated in the graph, both the NDVI and WET exhibit strong correlations with the RSEI, with high correlation coefficients of 0.81 and 0.84, respectively. In contrast, the correlations of LST and NDBSI with the RSEI are much lower, with coefficients of −0.22 and −0.19, respectively. Furthermore, there is a correlation coefficient of −0.62 between the NDVI and LST and one of 0.77 between the NDVI and WET, indicating a strong correlation among these three indicators. Conversely, NDBSI shows low correlations with the RSEI and the other three indicators, likely due to the relatively small area occupied by construction land in the study area, which accounts for only 8.9% of the total area. Therefore, it can be inferred that the RSEI exhibits a strong correlation with the four indicator components. This index is more representative than any single indicator and provides a more comprehensive reflection of the EEQ of the Qianping Reservoir.
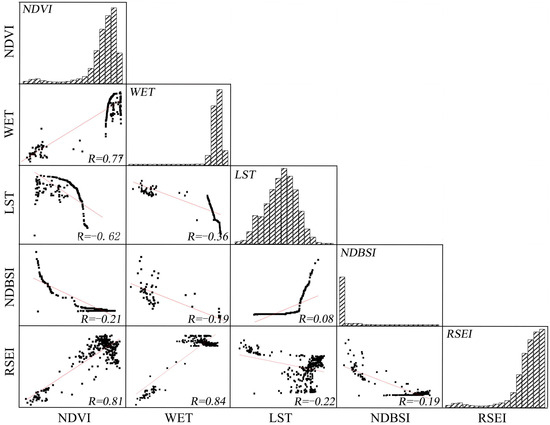
Figure 3.
Scatter plots for correlation analysis (Red lines represent slope).
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir
3.2.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics
Figure 4 illustrates the changes in the RSEI in the Qianping Reservoir area over the past 20 years. Overall, the EEQ of the reservoir area has shown significant improvement, with RSEI values rising from a low of 0.412 in 2000 to a high of 0.820 in 2020, achieving an average RSEI of 0.71. Throughout the 20-year period, the upward trend of the RSEI fluctuated alongside changes in ecological factors, with an average annual change rate of 0.0204. The RSEI experienced rapid growth between 2000 and 2010 but witnessed a slight decline between 2010 and 2015 (from 0.817 to 0.722) due to reservoir construction activities. However, between 2015 and 2020, the EEQ of the study area gradually recovered, with the RSEI value rebounding. From 2000 to 2020, the NDVI remained high, with minor fluctuations in the average value (ranging from 0.78 to 0.88), while WET demonstrated an overall upward trend, despite a sudden drop in 2010. Conversely, LST showed a slight downward trend, with a sharp rise occurring in the same year. NDBSI experienced a slight increase between 2000 and 2005, followed by a downward trend with minimal changes. The stacked diagram indicates that the primary ecological factors influencing the RSEI are the NDVI, WET, and LST, while the impact of NDBSI is relatively small and almost negligible.
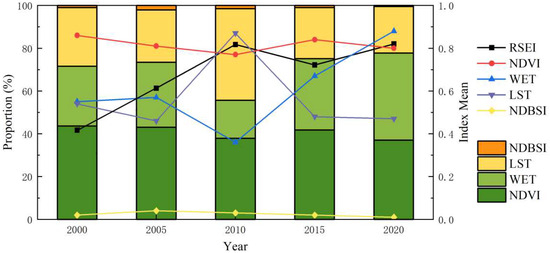
Figure 4.
Stacked bar chart and mean values of each indicator from 2000 to 2020.
This study classified the RSEI into five levels: poor [0–0.2], fair (0.2–0.4], moderate (0.4–0.6], good (0.6–0.8], and excellent (0.8–1], as described by Han et al. [9]. Arcgis10.5 software was utilized to compile statistics on the ecological status of the Qianping Reservoir area. The results are presented in Figure 5, using color-coding: red indicates a poor EEQ level, while dark green represents an excellent level. From 2000 to 2020, there was an increasing trend in the areas classified as having poor and excellent EEQ levels. Specifically, the excellent EEQ area exhibited the most significant increase, expanding by 7.91 km2, while the poor EEQ area grew by 1.43 km2. In contrast, areas categorized as good, moderate, and fair EEQ showed a declining trend, with the moderate EEQ area experiencing the largest decrease of 4.01 km2, the good EEQ area decreasing by 3.63 km2, and the fair EEQ area decreasing by 1.7 km2. Overall, the EEQ of the Qianping Reservoir area has demonstrated steady improvement over the past 20 years, with areas previously categorized as good and moderate transitioning to the excellent EEQ level. However, reservoir construction has contributed to an increase in the area classified as poor.
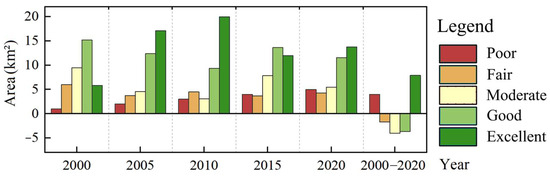
Figure 5.
Eco-environmental quality change of the study area from 2000 to 2020.
3.2.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics
The EEQ of Qianping Reservoir shows clear regional differentiation, with overall low ecological quality in the central area associated with the water bodies and high ecological quality in the surrounding mountainous regions. Figure 6 displays the spatial distribution characteristics of EEQ in Qianping Reservoir from 2000 to 2020. To illustrate the variation in water areas over these years, water bodies were coded with a particular color. However, it is important to note that, according to the RSEI calculations, the EEQ of these water areas is generally classified as poor, primarily due to their very low NDVI values. As shown in Figure 6, the spatial distribution characteristics of EEQ in Qianping Reservoir are as follows: (1) The RSEI value in 2000 was only 0.412, falling into the moderate level. Specifically, areas with better EEQ were mainly distributed in valley areas far away from water bodies, while areas with relatively poor EEQ were distributed on both sides of the river. (2) In 2005, the proportion of excellent EEQ areas was the largest (44.4%), followed by the good EEQ areas (32.1%). The south side of the Beiru River had better EEQ than the north side, mainly due to its higher vegetation coverage. The three grades of poor, fair, and excellent accounted for a smaller proportion (a total of 23.5%) and were mainly distributed in valley areas far away from water bodies. The year 2010 saw a significant improvement in the EEQ, accompanied by a notable increase in areas achieving an excellent grade; these were primarily in low-altitude hillside regions. (3) In 2015, the EEQ slightly deteriorated due to the start of reservoir construction, and the excellent grade changed to the good grade, while the moderate grade increased to some degree. From 2015 to 2020, the EEQ gradually returned to the state before reservoir construction, with the largest proportion of excellent grades (35.7%). Improvements continued to extend to the northeast, with poor transforming to moderate. The southwest has relatively complex terrain, high vegetation coverage, less human activity, and a better ecological base, resulting in smaller changes. The dramatic changes in reservoir water levels in 2020 have damaged local native vegetation, thereby impacting the quality of the ecological environment. Consequently, the EEQ in the watershed is significantly lower compared to areas covered by perennial vegetation. The restoration of EEQ should involve the introduction of tree species that are resistant to water and moisture.
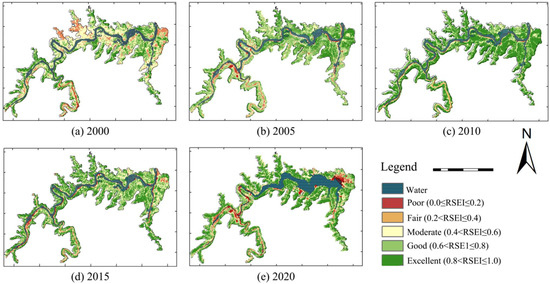
Figure 6.
The spatial distribution of RSEI in the study area during 2000–2020.
3.3. Changing Trends
The Sen slope and MK tests were utilized to detect the changing trend of ecological quality at the 95% confidence level. Building upon existing research [43], this study categorized the RSEI trend changes into five levels: significant improvement (an increase of at least 0.2 in RSEI), slight improvement (an increase of 0.05–0.2), basically stable (a change within ±0.05), slight degradation (a decrease of 0.05–0.2), and significant degradation (a decrease of at least 0.2). Their spatial distribution in the study area during 2000–2020 is presented in Figure 7.
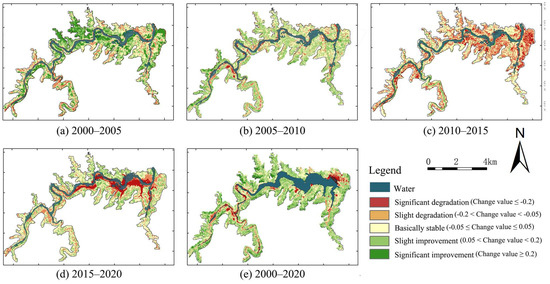
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of RSEI change trends in the study area during 2000–2020.
This study yielded the following observations: (1) From 2000 to 2005, significantly improved areas accounted for 32.5% of the study area and were primarily distributed in higher-altitude regions on both sides of the river. Between 2005 and 2010, areas with slightly improved EEQ reached 24.1%. Throughout this decade, most regions experienced improvements in EEQ, with only a relatively small proportion (about 5.8%) showing significant degradation; these areas were primarily concentrated around the river (refer to Figure 7a,b). (2) During the dam construction period from 2010 to 2015, the RSEI was significantly impacted by human activities, with areas experiencing EEQ deterioration accounting for 58.3% and mainly concentrated in valley areas and eastern towns (Figure 7c). Subsequent reservoir filling between 2015 and 2020 led to a notable degradation of EEQ behind the dam (see Figure 7d). (3) Overall, the EEQ of Qianping Reservoir has exhibited a fluctuating upward trend over the past 20 years. Notably, while the Beiru River and surrounding mountains provided some level of EEQ assurance in the study area, they remained vulnerable to human-induced factors such as reservoir construction and changes in land use. Additionally, as depicted in Figure 7e, the ecological restoration of the slope behind the reservoir dam is imperative for enhancing the EEQ of the reservoir area.
3.4. CA-Markov Model Prediction
In this study, the CA-Markov model was utilized to simulate the RSEI levels for the year 2020, building upon the calculated RSEI results from 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015. The RSEI levels for 298 randomly selected points within the study area were simulated and compared with the calculated values for 2020. Subsequently, the kappa coefficient was calculated to assess the model’s applicability. The prediction accuracy is summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Confusion matrix of 2020 simulated and calculated RSEI levels in the study area.
The kappa coefficient between the simulated and calculated results for 2020 was computed as 0.839, indicating a strong agreement between the two sets of results and affirming the reliability of the model in predicting the EEQ of the reservoir area. To further evaluate model reliability, a comprehensive sensitivity analysis was conducted by systematically varying key parameters within ±15% of their baseline values. The results revealed minimal deviations in predicted EEQ classes. Kappa stability: The coefficient ranged between 0.815 and 0.852 under parameter perturbations, confirming insensitivity to minor calibration uncertainties. Spatial consistency: Over 89% of grid cells retained their original EEQ classification (±1 class) across simulations, with variability concentrated in transitional zones near the Beiru River. These findings underscore the model’s suitability for projecting EEQ trends.
Consequently, this study utilized the CA-Markov model to simulate the EEQ of the Qianping Reservoir in 2030. The simulated results are presented in Figure 8. According to the statistics, the proportion of areas rated as good and excellent in 2020 was 29.9% and 35.7%, respectively, while in 2030, these proportions are expected to shift to 27.7% and 50.3%, respectively. Compared to 2020, the proportion of excellent-grade areas in 2030 is projected to increase by 14.6%, with areas rated as fair, moderate, and good continuously transitioning into the excellent grade. The areas rated as poor are also expected to slightly increase. It is anticipated that the improvement in EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir area will continue to expand toward the northeast by 2030. However, given that the northeastern part of the Qianping Reservoir is situated within a densely populated urban area characterized by low vegetation coverage and a poor ecological background value, the future focus of watershed ecological environment management should remain on the urban area in the northeastern part of the study area.
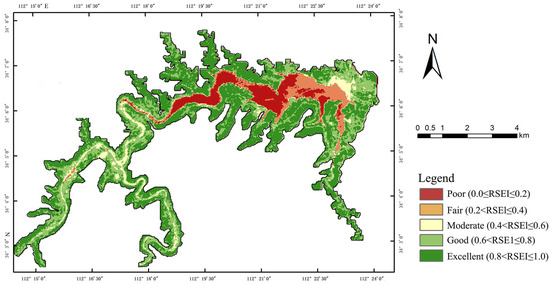
Figure 8.
RSEI simulation results.
3.5. Analysis of Ecological Responses to Land Use Changes
According to the Sankey diagram illustrating land use change in the study area (Figure 9), between 2000 and 2020 the net transfer area of cultivated land in the Qianping Reservoir totaled 279.97 hm2. The key areas of land use transition from 2010 to 2020 were primarily focused on the conversion of cultivated land to grassland, forestland, water areas, and construction land. Notably, 21.9% of cultivated land was transformed into construction land. This study employed GeoDa software to conduct significance analysis on the difference between cultivated land conversion in the study area and the corresponding RSEI of each grid, as well as spatial regression analysis on the process of converting cultivated land into construction land. As depicted in Figure 10a, there exists a significant correlation (i.e., p-value less than 0.05) between cultivated land conversion and the RSEI of the corresponding grid on both sides of the river. Figure 10b illustrates that the conversion of cultivated land to water bodies and construction land yields a negative ecological response, while the conversion to forestland and grassland results in a positive ecological response.
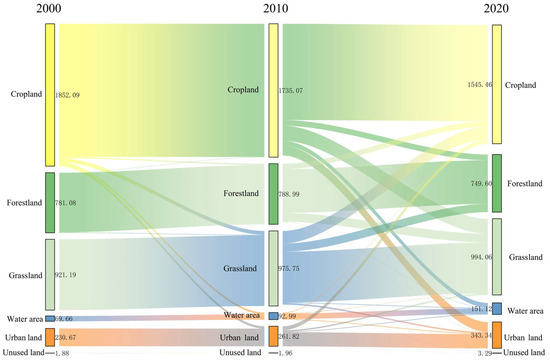
Figure 9.
Sankey diagram of land use change (hm2) in the study area from 2000 to 2020.
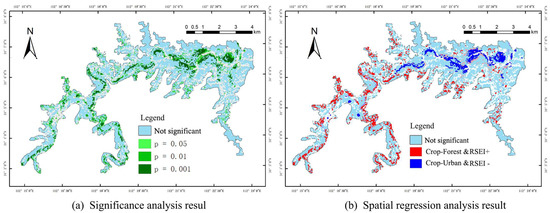
Figure 10.
Cultivated land conversion vs. RSEI change from 2010 to 2020.
The research findings reveal that the loss of cultivated land is widespread across the study area but primarily concentrated around the water and construction land in the eastern section of the reservoir area. In contrast, the conversion of cultivated land to grassland and forestland is relatively scattered. The changes in the RSEI in the study area exhibit a strong correlation with the conversion of cultivated land. During the reservoir construction period from 2010 to 2020, cultivated land was overtaken by construction land, resulting in alterations to the structure and function of the ecosystem, a decrease in land maintenance capacity, and a weakening of its adaptive capacity. Consequently, this led to a deterioration in the EEQ of the study area. Consistent with the findings of [44], a larger area of cultivated land converted to construction land and water bodies corresponds to a more pronounced decline in the EEQ of the study area. Given the substantial impact of reservoir construction and urbanization in the study area, continued conversion of cultivated land into construction land would result in even greater losses in EEQ.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness and Suitability of the RSEI for Analyzing EEQ in Reservoir Areas
Principal component analysis suggests that the NDVI and WET are inversely related to LST and NDBSI, impacting EEQ positively and negatively. This finding aligns with the real-world influence of these four indicators on the ecological environment.
The reservoir area serves as a critical node in the basin’s ecological environment. Real-time and accurate monitoring of the ecological conditions in reservoir areas can provide essential data and theoretical support for basin development and protection, as well as for urban economic growth [45]. Currently, the RSEI is primarily used to assess the ecological quality of urban areas and river basins. However, applying it to reservoir areas poses challenges due to their smaller spatial scale compared to basins, necessitating higher data accuracy. Although RS technology has been employed in reservoir studies, most research has focused on specific topics such as land use [46], vegetation change, and hydrological factors [47]. RSEI monitoring was utilized to analyze the regional changes in the Dongzhuang and Cen Tianhe reservoirs in China, respectively, over an extended period [45,48]. Accordingly, corresponding ecological and environmental protection measures for each region were proposed. The RSEI calculation results based on 10 m resolution RS imagery presented in this paper over the past 20 years align with the observed changes in EEQ before and after the implementation of the reservoir construction project. In addition, the research results show that the RSEI value of Qianping Reservoir has increased from the lowest value of 0.412 in 2000 to the highest value of 0.820 in 2020, indicating that the ecological conditions are generally fluctuating and increasing. This is consistent with the reported overall trend of increasing vegetation coverage in Qianping Reservoir, indicating that RSEI monitoring of EEQ is suitable for reservoir areas.
Qianping Reservoir has a total storage capacity of 584 million cubic meters, with the water in the study area accounting for approximately 12.5%; the water level is subject to constant fluctuations (Figure 6e). In previous studies, extensive areas of water were often masked during RS imagery processing to minimize their significant impact on the assessment of ground humidity and other terrestrial features [45]. Given the substantial changes in water surface levels before and after the reservoir’s construction in 2015, this study calculated the RSEI for the water area. The results indicate that the ecological quality of both the water area and surrounding land was generally poor. It was speculated that the fluctuations in water levels, which caused damage to vegetation, indirectly affected the EEQ of reservoir areas [48].
4.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Changes in EEQ
The RSEI values of the Qianping Reservoir increased from the lowest value of 0.412 in 2000 to the highest value of 0.820 in 2020, suggesting a generally fluctuating upward trend in ecological conditions. As shown in Figure 7c, the impact of reservoir construction on the EEQ is more pronounced than that observed in watershed studies [40]. In 2000, the highest proportion of moderate ecological quality was found in the study area, with the southern side of the Beiru River exhibiting better conditions than the northern side, primarily due to higher vegetation coverage in the south. To enhance ecological restoration behind the dam, priority should be given to the northern part of the Beiru River. The southwestern and low-altitude mountainous forest areas, characterized by complex terrain, high vegetation coverage, and limited human activity, demonstrated better ecological conditions. This suggests that the EEQ of forested areas surpasses that of cultivated land, grassland, and bare land. From 2000 to 2020, the overall EEQ in the study area significantly improved, consistent with previous research findings [44]. The fluctuations in EEQ within the reservoir area were primarily attributed to severe ecological damage during the reservoir’s construction. Nonetheless, the EEQ has steadily increased before and after construction, benefiting from the implementation of soil and water conservation and ecological restoration techniques at Qianping Reservoir.
This study found that the ecological restoration behind the reservoir dam has produced positive results, transforming the original fragmented landscape pattern. Specifically, it has evolved from various fragmented patches into several large, continuous areas (Figure 7e). Between 2015 and 2020, the annual stable area accounted for 27.1%, indicating that stability has predominated behind the reservoir dam and the overall quality of the ecological environment has stabilized. This suggests that the environmental management measures implemented have achieved notable success (Figure 7d). The significantly improved areas are primarily located in areas with minimum human interference and fragile natural substrates. These areas have undergone considerable change due to natural ecological restoration and policies aimed at returning farmland to forests. Conversely, the significantly deteriorated areas are mainly found in urban locations with complex human activities. However, some studies have indicated that urbanization, when it reaches a certain stage, can maintain or even improve ecological quality [49]. As the noticeable deterioration around the reservoir expands to the surrounding slopes, it is crucial to focus on the ecological restoration of these slopes in the future.
In contrast to previous ecological quality assessments that primarily utilized five-year intervals, this study’s annual RSEI, including data from the initial phase of Qianping Reservoir construction in 2015, is better suited to tracking both short-term changes and long-term trends in ecological quality. The RSEI image for Qianping Reservoir in 2015 effectively captured this degradation. Other studies have also noted that environmental changes are not merely comparisons between two time points; rather, they represent a continuous process [50]. When examining long-term trends, integrating the annual RSEI with trend analysis helps mitigate the impact of data fluctuations across multiple years and the selection of reference years on changes in EEQ. This study found that land use changes have impacted ecological quality in certain areas; however, the RSEI alone cannot adequately reveal this degradation.
4.3. Trends and Influencing Factors in EEQ
In the Qianping Reservoir, notable improvements in the RSEI are primarily observed in mountainous forested regions, where significant terrain variations and minimal human disturbance foster ecological resilience. These areas benefit from natural vegetation recovery and stable hydrological conditions, as evidenced by the sustained NDVI values (>0.6) and low surface temperature anomalies. Notably, water quality monitoring data (e.g., dissolved oxygen: 6.8–8.2 mg/L; turbidity: 1–5 NTU) in upstream forested catchments further corroborate the stability of aquatic ecosystems in these zones. Conversely, the degraded areas are primarily located along both banks of the Beiru River, primarily due to the relatively flat terrain, frequent human activity, and substantial impacts from reservoir construction. Between 2015 and 2020, the study area surrounding the reservoir witnessed a considerable expansion in the regions where EEQ has recovered and improved, surpassing the areas experiencing degradation. This suggests variations in ecological damage resulting from engineering activities [13]. The regions adjacent to water bodies mainly consist of valleys, where ecological vulnerability is more pronounced. Conversely, urban built-up areas in the northeast exhibit fewer impacts from reservoir construction. In the transitional zone between the western mountainous regions and urban developments, human interference is comparatively lower. Consequently, a prevalent trend of EEQ recovery and improvement persists across most areas of the study zone.
To a certain extent, the quality of the ecological environment is directly proportional to the elevation and slope. Excluding the interference of human factors, the quality of the ecological environment has been reduced in valley areas with large elevations and steep slopes. High altitudes and high slopes make ecological restoration more difficult and should be used as a key area for ecological restoration and protection.
The main human factors affecting the ecological environmental quality of the reservoir are engineering construction and land use changes. Land use changes directly affect the ecological quality. Their changes are not only driven by natural interference but also affected by policy adjustments. The impact of land use in the study area on the ecological environment is mainly reflected in the transformation of cultivated land into water areas and construction land, which weakens the quality of the ecological environment. From 2000 to 2010, the loss of cultivated land was concentrated in the waters and construction land in the eastern part of the reservoir area. The spatial distribution is relatively concentrated, while the conversion of cultivated land to grassland and woodland is relatively scattered; the change in the RSEI in the study area is highly negatively correlated with the conversion of cultivated land to construction land and water bodies and positively correlated with the conversion of cultivated land to woodland and grassland.
4.4. Limitations
This study examined the impact of land use change on the EEQ of the reservoir area using land use data spanning the past 20 years. However, it lacked consideration and quantitative analysis of natural and other anthropogenic factors. The study relied on satellite imagery with a resolution of 10 m, which limited the depth of analysis. Given the strong correlation between the RSEI and the NDVI, water areas with low vegetation coverage received lower EEQ grades in this study, highlighting a limitation of the RSEI in assessing the ecological quality of water bodies. While the CA-Markov model demonstrated a high degree of consistency in the simulation results, as indicated by the Kappa coefficient, a margin of error remains. Future research will focus on refining the constituent indicators used in constructing the RSEI, specifically tailoring them to the unique characteristics of the reservoir area. Additionally, efforts will be made to explore the integration of additional metrics, such as carbon emissions, to enhance the accuracy of the index in reflecting the EEQ of the study area [51].
5. Recommendations
This study proposes a targeted ecological restoration framework for reservoir areas, prioritizing four intervention zones with evidence-based strategies:
- Implement strict cultivated land protection policies to counter progressive farmland loss (279.97 hm2 net reduction since 2000), coupled with precision agriculture technologies to enhance land productivity while balancing urban–rural development needs.
- Reconstruct multi-layered vegetation communities (tree–shrub–herb mosaics) in dam-adjacent areas using native flood/drought-resilient species, addressing acute vegetation degradation post-construction.
- Stabilize hydrologically sensitive slopes through root-intensive shrubs and pollutant-filtering herbaceous covers to mitigate water level fluctuation impacts.
- Apply soil-bioengineering techniques (e.g., rain-harvesting terraces, geotextile-reinforced planting) on bare slopes to rebuild erosion-resistant plant communities.
These measures synergistically address the spatial heterogeneity of reservoir-induced ecological damage, with cross-sectoral monitoring recommended to evaluate long-term restoration efficacy.
6. Conclusions
This study employed RS imagery alongside the CA-Markov and LUCER models to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamics of EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir. The results indicate that from 2000 to 2020 the RSEI of the Qianping Reservoir increased from 0.412 to 0.820, with an average annual change rate of 0.0204. The RSEI shows an overall fluctuating upward trend, with notable variations during the reservoir construction period. Due to the relatively complex terrain, high vegetation coverage, and limited human activity surrounding the reservoir, the changes in EEQ were minimal. Regions with enhanced EEQ consistently expanded toward the northeast. Projections suggest that, by 2030, the RSEI will continue to show a slight upward trend, with an increase in the proportion areas rated as excellent. Areas classified as fair, moderate, and good are expected to transition into higher EEQ categories. The surrounding mountains will likely contribute to maintaining ecological quality in the study area. This study also found a strong negative correlation between changes in the RSEI and the conversion of cultivated land to construction land and water bodies. The loss of cultivated land was mainly concentrated in the eastern areas near water bodies and construction sites within the reservoir area. Future development should aim to minimize human encroachment on cultivated land and prioritize ecological restoration efforts behind the reservoir dam. By employing the RSEI, this study explored spatiotemporal changes in EEQ in the Qianping Reservoir and provided practical insights, theoretical support, and valuable recommendations for the ecological restoration and improvement in areas behind the dam.
Author Contributions
E.X.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Software. G.Z.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Software. H.W.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. M.Y.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources. H.T.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources. M.Z.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources. N.D.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing—review and editing. C.L.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources. Y.H.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing. G.T.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing. Y.L.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources. Q.C.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources. D.W.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by The Key Research and Development and Promotion Project of Henan Province (222102320465, 232102320323, 232102521015), Urban-Rural Green Space Resources Control and Landscape Ecological Design Disciplinary Innovation and Talents Introduction Center Program of Henan, China (GXJD006), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470029), Water Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (GG202069), National Key Wildlife Protection Project of Central Finance (30602609), and Research and Practice Project on Research based Teaching Reform in Undergraduate Universities in Henan Province in 2022: Innovation and Practice of Research based Teaching in the Discipline of Human Settlements and Environment from an International Perspective (2022SYJXLX019). General Project of Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province: Study on the Coupling Relationship between Vegetation Health and Soil Quality in the Process of Vegetation Succession on Highway Slope—A Case Study of Henan Province (252300420194).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Marinello, F. Exploration of Eco-Environment and Urbanization Changes in Coastal Zones: A Case Study in China over the Past 20 Years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.I.; Costa, F.L. Land Cover Changes and Landscape Pattern Dynamics in Senegal and Guinea Bissau Borderland. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Watson, A.E.; He, H.; Ye, H.; Ouyang, X.; Li, Y. Pixel-Scale Historical-Baseline-Based Ecological Quality: Measuring Impacts from Climate Change and Human Activities from 2000 to 2018 in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Advances in Separating Effects of Climate Variability and Human Activity on Stream Discharge: An Overview. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 71, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudennec, C.; Leduc, C.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Dryland Hydrology in Mediterranean Regions—A Review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.D.; Lake, P.S.; Sabater, S.; Melack, J.M.; Sabo, J.L. The Effects of Land Use Changes on Streams and Rivers in Mediterranean Climates. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 383–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmar, O.; Velasco, J.; Martinez-Capel, F.; Marín, A.A.; Martínez-Capel, F. Natural Flow Regime, Degree of Alteration and Environmental Ows in the Mula Stream (Segura River Basin, SE Spain). Limnetica 2010, 29, 0353–0368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H. Mapping the World’s Free-Flowing Rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Huo, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Zhu, H.-L.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.-L. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Vegetation Coverage in the Middle Section of Yellow River Basin Based on Terrain Gradient: Taking Yan’an City as an Example. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao (J. Appl. Ecol.) 2021, 32, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Kumar, P.; Pathan, S.K.; Sharma, K.P. Urban Neighborhood Green Index—A Measure of Green Spaces in Urban Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.O.; Han, C. Bi-Temporal Characterization of Land Surface Temperature in Relation to Impervious Surface Area, NDVI and NDBI, Using a Sub-Pixel Image Analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A New Index for Delineating Built-up Land Features in Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Kasimu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, B.; Chai, J.; Ruzi, T.; Zhao, H. Evaluation of the Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ecological Quality in the Hami Oasis Based on RSEI. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.; Meng, H.; Li, M.; Peng, C. RSEI-Based Dynamic Monitoring of Ecological Quality of the Soil and Water Conservation Functional Area in the Chongqing Section of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Wang, H.; Ning, X.; Zhang, H. Extraction of Zhalong Wetlands Information Based on Images of Sentinel-2 Red-Edge Bands and Sentinel-1 Radar Bands. Wetl. Sci. 2020, 18, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y. Dynamic Monitoring of Ecology and Environment in the Agro-Pastral Ecotone Based on Remote Sensing: A Case of Yanchi County in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Arid Land Geogr. 2017, 40, 1070. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q.; Shi, T.T.; Wang, M.Y.; Lin, Z.L. Land Cover Changes in the Xiong’an New Area and a Prediction of Ecological Response to Forthcoming Regional Planning. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6289–6301. [Google Scholar]
- Nong, L.; Wang, J. Dynamic Monitoring of Ecological Environment Quality in Kunming Based on RSEI Model. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2042. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, W. Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Lin, J.H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Qi, X. Ecological Vulnerability Assessment of Key Villages of Tourism Poverty Alleviation in Fujian Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7093–7101. [Google Scholar]
- Aburas, M.M.; Abdullah, S.H.; Ramli, M.F.; Ash’aari, Z.H. Measuring Land Cover Change in Seremban, Malaysia Using NDVI Index. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.S.; Kawamukai, H. Prediction of NDVI Using the Holt-Winters Model in High and Low Vegetation Regions: A Case Study of East Africa. Sci. Afr. 2021, 14, e01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P. A TM Tasseled Cap Equivalent Transformation for Reflectance Factor Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yao, F.; Wu, P.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Research on the Contribution of Urban Land Surface Moisture to the Alleviation Effect of Urban Land Surface Heat Based on Landsat 8 Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10737–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, A.; Liang, S.; Zhou, W. Eco-Environmental Vulnerability Evaluation in Mountainous Region Using Remote Sensing and GIS—A Case Study in the Upper Reaches of Minjiang River, China. Ecol. Model. 2006, 192, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J. Remote Sensing of Urban Heat Islands by Day and Night. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Engel, B.; Mercado, J.A.V.; Zhang, Z. Analysis on Net Primary Productivity Change of Forests and Its Multi–Level Driving Mechanism–A Case Study in Changbai Mountains in Northeast China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 153, 119939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Gao, Q.; Wang, R.; Yang, P.; Peng, Q.; Liu, C. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality in Shijiazhuang Based on RSEI Model. Prog. Geophys. 2021, 36, 968–976. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.-H.; Su, Z.L.-T.; Lu, E.H.-C. Spatial Perspectives toward the Recommendation of Remote Sensing Images Using the INDEX Indicator, Based on Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.J.; Zhao, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Comprehensive Evaluation and Spatial-Temporal Changes of Eco-Environmental Quality Based on MODIS in Tibet during 2006–2016. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G.; Gibbons, J.D. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Gu, H.-H.; Song, W.; Li, F.-P.; Cheng, S.-P.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Ai, Y.-J. Environmental Assessments in Dense Mining Areas Using Remote Sensing Information over Qian’an and Qianxi Regions China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Gedam, S. Assessing the Impacts of Urbanization on Hydrological Processes in a Semi-Arid River Basin of Maharashtra, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.T.; Chen, J.J.; Yang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, G.Q.; You, H.T.; Han, X.W. Spatiotemporal Variations of Vegetation and Its Response to Topography and Climate in the Source Region of the Yellow River. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Zhu, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Quantifying Impacts of Climate and Human Activities on the Grassland in the Three-River Headwater Region after Two Phases of Ecological Project. Geogr. Sustain. 2022, 3, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, C. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Land Use and Habitat Quality in the Weihe River Basin Based on the PLUS and InVEST Models and Predictions. Arid Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Surabuddin Mondal, M.; Sharma, N.; Kappas, M.; Garg, P.K. Ca Markov Modeling of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics and Sensitivity Analysis to Identify Sensitive Parameter (S). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Marcinek, P.A. Fish Assemblage Responses to Water Withdrawals and Water Supply Reservoirs in Piedmont Streams. Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.C.; Kong, J.; Yang, Y. Monitoring and Prediction of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Yanhe River Basin Based on the Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 943–954. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Kazmi, J.H.; Tariq, A.; Zhao, N.; Guluzade, R.; Soufan, W.; Almutairi, K.F.; Sabagh, A.E.; Aslam, M. Modelling of Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Prediction Using CA-Markov and Random Forest. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2210532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.C.; Liu, G. Analysis and Forecast of Landscape Pattern in Xi’an from 2000 to 2011. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y.; Du, Y.Y. Monitoring and Assessment of the Eco-Environment Quality in the Sanjiangyuan Region Based on Google Earth Engine. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.-H.; Lin, Y.-M.; Nan, X.-X.; Hu, Z.-R. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Driving Force Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality in Typical Ecological Areas of the Yellow River Basin from 1990 to 2020. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2023, 44, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, W.T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.D. Monitoring and Evaluation of Ecological Environment Changes in Dongzhuang Reservoir Basin in Shaanxi Province Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.P.; Saito, Y.; Nguyen, V.L. Recent Evolution of the Mekong Delta and the Impacts of Dams. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 175, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shumba, A.; Gumindoga, W.; Togarepi, S.; Edward, T.P.M. A Remote Sensing and GIS Based Application for Monitoring Water Levels at Kariba Dam. In Proceedings of the ACRID 2017: EAI International Conference for Research, Innovation and Development for Africa, European Alliance for Innovation, Bratislava, Slovakia, 20 June 2017; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yi, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, F. A Novel Framework for Vegetation Change Characterization from Time Series Landsat Images. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, R.; Mei, Z. Analysis on the Influence of Urbanization and Greenland-Degradation on City Thermal Environment. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 19, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T.; Chang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, J. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Ecological Vulnerability in Jilin Province (China), 2000 to 2018. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Xie, P.; He, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Khanal, R. Local and Tele-Coupling Development between Carbon Emission and Ecologic Environment Quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 394, 136409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).