Abstract
Soil enzyme activities serve as the key indicators of microbial nutrient limitations. Vegetation types after farmland is returned modify both the biological and abiotic properties of the soil, thereby impacting the soil nutrient cycle and the stability of forest ecosystems. However, soil enzyme activities and microbial nutrient limitations in degraded karst forests under different vegetation types after farmland return remain unclear. Therefore, this study investigated the soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities, and microbial resource limitations in different vegetation types (grasslands (G), transitional grass–shrub (SG), shrubland (S), and secondary forest (F)) after returning farmland on dip and anti-dip slopes in a karst trough valley. The relationships among the factors influencing soil enzyme activities were analyzed to identify the drivers of microbial nutrient limitation. The results revealed that soil enzyme activities and physicochemical properties were significantly greater on anti-dip slopes than on dip slopes. Total nitrogen (27.4%) and bulk density (24.4%) influenced mainly soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometric ratio, whereas carbon and phosphorus limitations impacted soil microorganisms on the dip slopes of the F and G vegetation types. The soil physicochemical properties and enzyme characteristics accounted for 85.5% and 75.6%, respectively, of the observed influence. Notably, the total phosphorus content (36.8%) on the anti-dip erosion slope was significantly greater than that on the other slopes. These factors, especially bedrock strata dip and vegetation type, significantly affect soil enzyme activity. This study confirms that vegetation type enhances soil enzyme activities on anti-dip erosion slopes, providing a scientific basis for karst ecosystem restoration.
1. Introduction
As one of the most essential components in the forest soil ecosystem, soil enzymes produced by microorganisms and plant root exudates play crucial roles in the microbial decomposition of complex organic matter and the transformation of soil nutrients [1,2]. They effectively regulate nutrient and energy cycling within forest ecosystems [3]. Studies have demonstrated that alkaline phosphatase (AKP) increases the rate of phosphorus removal and indicates the morphological transformation of phosphorus in soil. Additionally, enzymes such as β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), β-D-cellobiosidase (BDC), β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (BNA), and L-leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) play significant roles in reflecting the biogeochemical cycling characteristics of soil carbon and nitrogen, which are crucial for soil fertility. Specifically, BG and BDC influence the decomposition of soil organic matter, whereas LAP collaborates with microorganisms to release essential elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus from the soil matrix. This collaboration improves the degradation rate of organic matter and promotes the cycling of nitrogen and phosphorus [4,5]. In the presence of limited resources, soil enzymes are sensitive to microbial nutrient limitations, and their functioning is influenced by various factors, including soil physical and chemical properties, vegetation type, and topography [5,6,7]. For example, grassland establishment enhances the levels of soil available phosphorus and potassium, and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, thereby increasing the activity of soil enzymes such as BG and AKP. This phenomenon is closely associated with the compatibility between fruit trees and herbaceous plants, reflecting the trade-off between complementarity and competition, as well as site-specific conditions, including climate, soil characteristics, and topography [8,9]. Moreover, in subtropical regions, limited phosphorus constrains the vegetation type, whereas in desert steppes, insufficient nitrogen is the limiting factor [10,11]. Therefore, accurately identifying specific limiting nutrients within soils forms an essential foundation for conducting comprehensive research on forest ecology.
Furthermore, soil enzyme stoichiometry indicates the relationship between soil nutrient availability and microbial nutrient needs, reflecting the balance between microbial biomass and soil stoichiometry [12]. When microorganisms are limited by nutrients, they can acquire restricted nutrients through extracellular enzyme production, and the ecological stoichiometry of soil enzymes reflects the constraints on microbial metabolism [13,14,15]. For example, through the utilization of soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) as indicators for deriving enzymatic metrological characteristics, Sinsabaugh et al. (2008) [15,16] integrated enzymatic metrological data obtained from both aquatic and terrestrial environments. These findings revealed a logarithmic ratio of 1:1:1 for soil enzymes within ecosystems, which implies a prevalent microbial requirement for C, N, and P in soils. Nevertheless, it is important to acknowledge that climate conditions, vegetation types, and soil properties can potentially influence both soil enzyme activity and stoichiometric ratios [8,17]. The investigation of soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometric ratio can serve as indicators of the intricate interplay between soil nutrients and microbial nutrient demands, thereby enhancing our understanding of biogeochemical cycling [18]. Current research on soil enzymes and their stoichiometry has focused primarily on geographical variations and responses to global changes, revealing nutrient limitations for soil microorganisms and overall decomposition of soil organic matter [19,20]. Notably, the sensitivity of soil enzyme activity and stoichiometric ratios to nutrient status varies regionally, with most studies conducted in temperate regions.
The environmental plasticity of soil enzymes is an adaptive mechanism used by microorganisms to cope with changes in soil conditions [21]. Factors such as geographical region; soil pH; and the levels of C, N, and P influence enzyme activity [21,22]. Variations in plant communities and soil environments across regions lead to changes in soil C, N, and P contents and stoichiometric characteristics [7,21,23]. Additionally, the stoichiometric ratio of soil enzymes can serve as an indicator for assessing the relative constraints on microbial metabolism. On the one hand, the enzyme stoichiometric ratio serves as an indicator of the dynamic interaction between microbial nutrient demand and soil nutrient supply [24]. For example, the lower BG:AP ratio observed in tropical forests signifies phosphorus limitation within these ecosystems. Moreover, employing vector analysis on the basis of enzyme stoichiometry can offer insights into the transition of microbial community metabolism from energy (C) to nutrient restriction (N and P) [7,25]. In vector analysis, the ratio of enzyme activity is determined by comparing the C:N and C:P ratios. The vector of enzyme activity is subsequently calculated as both the distance (length) and angle from the origin [26]. Finally, quantification is performed to assess the relative C and nutrient acquisition, as well as the relative P and N acquisition. Drawing upon stoichiometric and metabolic theories of ecosystems, an increase in vector length signifies a relative increase in C restriction, whereas an increase in vector angle indicates a relative increase in P and N constraints [7,10,21]. Although some studies have examined soil microbial activity and nutrient limitations in forested areas, it is unclear how geological background and vegetation type affect soil enzyme characteristics and microbial nutrient limitations, especially in karst forests in Southwest China.
Karst regions are recognized globally as ecologically vulnerable because of slow soil formation, shallow soil layers, and limited land capacity. In China, karst areas cover 3.443 million square kilometers, with 550,000 square kilometers concentrated in the southwest [27]. Among the three major global karst regions, southwestern China has the largest expansion of contiguous bare carbonate rock and the most robust karst development. “Karst forest” refers to a specialized forest ecosystem on karst landforms that primarily thrives on limestone, dolomite, and carbonate rocks [28]. Rocky desertification, a significant form of land degradation in southwestern China’s karst regions, reduces land productivity and ecological health, hindering regional economic development. Owing to their distinctive geological characteristics, karst regions exhibit heightened susceptibility to environmental disturbances, rendering soil quality evaluation and ecosystem restoration paramount research priorities [29]. Human cultivation, especially the reclamation of steep slopes, is the principal driver of soil erosion and land degradation in karst regions. Such activities not only lead to a thinning of the soil layer and surface conditions analogous to desertification but also intensify the acute human–land conflict [30,31,32]. To address these challenges, China launched the Grain-for-Green Project, which has not only effectively mitigated the rapid expansion of rocky desertification in karst regions, but also provided significant support for local economic development [7,8]. Crews et al. (2000) [33] reported in their study on the evolution of restored forest areas over the past five decades that following the abandonment and reversion of farmland, the above-ground plant community has progressed from an herbaceous stage, through a shrub community stage, to an early forest community stage, ultimately reaching a late forest community stage [34]. Currently, the assessment of the ecological impacts resulting from the conversion of farmland to forest primarily focuses on evaluating the vegetation restoration status, changes in vegetation patterns, and improvements in the soil properties of the converted areas [19,20,21]. The alteration patterns of enzyme activity following the conversion of farmland to forests vary across different karst environments because of the influence of diverse geomorphic types and intricate habitats [35,36]. In karst plateau areas, the activities of sucrase, urease, and phosphatase are ranked as follows: tree forest > shrub forest (1–4 years old) > shrub forest > grassland > bare land [8]. Additionally, studies in karst peak depressions have shown that shrubs and shrublands exhibit enzyme activity levels that are either higher than or comparable to those found in forested areas [26,32]. This is attributed to favorable conditions in low-lying terrains that enhance nutrient preservation, leading to dense vegetation, diverse species, increased organic matter transport, and increased soil biological activity, which provide abundant reaction substrates. However, the influence of vegetation type on soil enzyme activity and nutrient limitations after farmland conversion in karst areas remains poorly understood.
The karst trough valley, a major karst type in China, displays its original geomorphic structure through ridges on both sides. The valley’s longitudinal extension forms a trough shape, creating the geologically significant “one mountain, two mountains, and one trough” phenomenon [28,35]. This valley represents a dual-layered geological structure shaped by surface and underground processes, as well as tightly curved dip and anti-dip slope formations [30]. The slope direction of the dip slope has been found to be consistent with the inclination of the bedrock strata dip in several studies, which only slightly hinders soil loss through runoff and consequently results in a high rate of exposed bare bedrock [28]. The anti-dip slope has a bedrock strata dip inclination opposite the slope direction, thereby effectively impeding soil loss and resulting in relatively minimal soil erosion and a low degree of bedrock exposure. There are significant disparities in the exposure of bare bedrock and the soil environment between dip slopes and anti-dip slopes, resulting in spatiotemporal variations in soil moisture between these two slopes [31]. Consequently, the distinctive geological structure of karst trough valleys, characterized by dip and anti-dip slopes, results in notable variations in soil enzyme activity compared with those in other karst regions [35]. This complexity contributes to a more intricate ecological restoration process following farmland reversion. Therefore, it is imperative to account for the inclination of bedrock strata when examining soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometry during the conversion of farmland to forests within karst trough valleys.
In general, karst forest ecosystems are influenced by dynamic mountain environments, causing significant geographical and temporal variations [37,38,39]. These variations lead to differences in microbial resource limitations and soil enzyme activity drivers in the conversion of farmland to forests within rocky desertification ecosystems in Southwest China. Therefore, this study selected four naturally evolved vegetation types from abandoned farmland (grasslands (G), transitional grass–shrub (SG), shrubland (S), and secondary forest (F)) following the Conversion of Farmland to Forests policy, which are located on both the dip and anti-dip slopes of a karst trough valley, as the sampling sites. The objectives of this study were to investigate the physical and chemical properties of the soil and the extracellular enzymes associated with carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycling, and to calculate enzyme stoichiometric ratios, vector lengths, and angles. The following scientific aspects are addressed: (1) analyzing the combined effects of vegetation type and bedrock strata dip on various soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry; (2) exploring the relationships between soil enzyme activities, enzymatic stoichiometry, and physicochemical properties; and (3) determining microbial resource limitations on both dip and anti-dip erosion slopes. This study aimed to investigate the adaptive strategies and regulatory mechanisms of forest soil enzymes and microbial metabolic constraints in degraded karst trough valleys after farmland was returned under different vegetation types and bedrock strata dips. This research offers a theoretical basis and data support for understanding nutrient limitations imposed by soil microbes in karst forest ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Soil Sampling
The experimental site was located in a degraded karst forest in the Qingmuguan karst trough valley, located at Chonging Municipality in Southwest China (106°15′30″–106°17′30″ E, 29°36′55″–29°39′10″ N). This study area has a subtropical humid monsoon climate, with an average annual precipitation of 1087.4 mm and a temperature of 17.9 °C [30]. The Qingmuguan karst trough valley displays typical bedrock formations on both sides of the aqueduct, with a consistent dip inclination but opposing slopes. This results in a consistent dip erosion slope on the northern side of the Qingmuguan Trough, with angles ranging from 12.3° to 35.7°, whereas an inconsistent anti-dip erosion slope, with angles varying from 15.9° to 40.8°, is observed on the southern side. The predominant soil types are yellow clay and lime clay [35]. Since the 1990s, with the promotion of ecological restoration policies in China, natural vegetation has occurred in many abandoned agricultural lands. In this study, historical remote sensing images were analyzed via 91 satellite maps in conjunction with geological time maps spanning different periods (3–5 years, 8–15 years, 15–20 years, and over 30 years). On the basis of the coordinates of the field measurement points, twelve representative field measurement points were subsequently selected for the slope farmland prior to its conversion through a combination of field visits and household survey data (Figure 1).
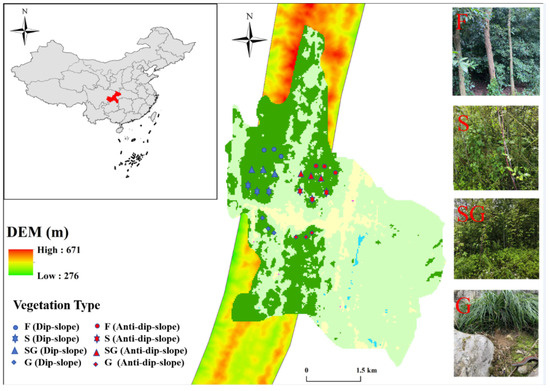
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
In general, the natural vegetation type after returning farmland in karst areas, which can be categorized into four stages: grasslands (G), transitional grass–shrub stages (SG), shrublands stage (S), and secondary forest stage (F). In the Qingmuguan karst trough valley, different habitats are observed in different vegetation types. The natural restoration period for grasslands (G) typically ranges from 3–5 years after farmland is returned. During the initial stages of restoration and succession, heliophilous herbs dominate the vegetation communities due to the intense light environment in the abandoned farmlands. The dominant species in these grasslands include Zebrinus (Miscanthus, ID: 24389785), Pennisetum flaccidum Griseb (grass wolftail), and various types of moss (Fissidens bryoides, Fissidens nobilis, etc.). The plants in the transitional grass–shrub stage (SG) regenerated naturally after a cultivation period of 8–15 years. In habitats with poor soil quality, shallow soil depth, limited water retention capacity, and susceptibility to droughts, herbaceous communities gradually transition into shrub or low-soil-demanding shrub communities with increased drought tolerance over time. The dominant species include Viburnum dilatatum Thunb (viburnum Linn), Yracantha fortuneana (Maxim.), and Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim (Rutaceae, ID: 341171481). The shrubland stage (S) transitions gradually into a state where broad-leaved tree seedlings dominate the shrub layer, which typically occurs 15–20 years after farmland is retracted. This resulting community results in improved soil conditions, including deeper layers, increased humus accumulation, and enhanced soil water retention capacity. Notably, the dominant species is white oak (Quercus fabri, ID: VCG211329143756). The secondary forest stage (F), which has undergone natural restoration after farmland has been retured for over 30 years, is characterized by the gradual establishment of cypress (Cupressaceae) and Pinus massoniana Lamb (Pinus) within the community.
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
Soil sampling was carried out on four vegetation types on both dip and anti-dip erosion slopes between 21 and 30 August 2023. There had been no rainfall for two weeks before the sampling date. Field investigations revealed significant bedrock exposure in the study area, characterized by a predominantly shallow soil layer that typically does not exceed a thickness of 30 cm. The experimental design included three independent replicate plots measuring 20 m × 20 m each for every vegetation type [8]. These plots were carefully selected to have similar slope aspects, elevations, soil parent material, and other relevant factors. At each sampling site, five soil samples were collected at depths of 0–10 cm in an “S” shape [31]. To ensure the spatial independence of the soil nutrients and microbial variables, the distance between replicate plots within the same vegetation type was maintained at approximately 100 m. A total of 240 soil samples were collected in this study (5 replicate samples × 4 vegetation types × 2 bedrock strata dips × 3 replicate samples). All the soil samples were analyzed for their physical and chemical properties as well as their soil enzymatic activity.
In each subplot, undisturbed soil columns were measured for soil bulk density (BD), soil water content (SWC), and total soil porosity (TSP). The visible roots and gravel were removed from the fresh soil samples, which were thoroughly mixed and passed through a 2 mm steel sieve in two separate portions [29]. In the laboratory, the soil samples were divided into two parts: one part was air-dried for physicochemical analysis, while the remaining part was stored at 4 °C for enzyme activity assessment.
Additionally, BD, SWC and TSP were determined via the drying method, where the soil samples were dried at 107 °C for 24 h [32]. The soil pH was determined with a pH meter (PHSJ-5, REX Company, Shanghai, China) in a 1:2.5 (w/v) soil-to-water suspension [35]. The soil organic carbon (OC) content was measured via the potassium dichromate oxidation method. The total nitrogen (TN) content was determined via the Kjeldahl digestion method [1,4]. The total phosphorous (TP) content was assessed through the sulfuric acid-perchloric acid digestion method.
Five soil enzyme activities related to C (β-1,4-glucosidase (BG) and β-D-cellobiosidase (BDC)), N (β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (BNA), L-leucine aminopeptidase acid (LAP)), and P (phosphatase (AKP)) cycling were analyzed [18]. The soil enzyme activities were measured via a soil enzyme assay kit provided by SinoBestBio in Shanghai, China. BG and BDC activities were determined with 4-MUB-β-D-glucoside and 4-MUB-β-D-cellobioside as substrates, respectively. BNA and LAP activities were determined with 4-MUB-N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide and L-I eucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrochloride as substrates, respectively. AKP activity was determined with 4-MUB-phosphate as the substrate [12]. The ratios of the soil enzymes C:N, C:P and N:P were calculated as (BG + BDC): (BNA + LAP), (BG + BDC):AKP and (BNA + LAP): AKP, respectively [10].
2.3. Calculation of Microbial Nutrient Limitation
Enzyme stoichiometric vector length (VL) and vector angle (VA) were used to calculate the energy and nutrient limitations of soil microorganisms, respectively [40].
where VL is the vector length and VA is the vector angle. The longer the VL is, the greater the limitation of C. When the VA is less than 45°, a smaller value corresponds to a higher N limitation, and when the VA exceeds 45°, a higher value indicates a stronger P limitation. Another approach is based on enzyme activity ratios. The microbiota encounters nitrogen limitation when the ratio of (BNA + LAP)/AKP exceeds 1, whereas microbial phosphorus limitation arises when this ratio falls below 1. The presence of microbial carbon and nitrogen limitations, as well as carbon and phosphorus limitations, is observed when the ratio of (BG + BDC)/(BNA + LAP) soil enzymes exceeds 1 [11].
VA = Degrees (ATAN2((ln(BG + BDC)/ln AKP), (ln(BG + BDC)/ln(BNA + LAP)))
2.4. Data Analysis
The normality of variables was assessed via the Shapiro–Wilk test. The effects of the soil physicochemical properties, soil enzyme activities, and environmental variables were examined via two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to explore the relationships between the soil enzymeometric ratio and the soil physicochemical properties. Multiple comparisons between treatments were conducted via the least significant difference (LSD) method when p < 0.05. The data presented in the figure represent the measured original values [30]. All the statistical analyses were conducted via the SPSS 22.0 software package (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Graphical representations were generated with Sigmaplot 13.0 (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) and the R programming environment (version 3.5.2).
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties with Vegetation Type
The soil physicochemical properties significantly varied throughout the different stages of the vegetation type. The levels of OC, TN, and TP in F were significantly greater than those observed in the three vegetation types, namely, SG, S, and G (Figure 2). However, F presented the lowest SWC and BD. Among the three successions, the SG had the highest SWC values, which were 1.16, 2.23, and 2.49 times greater than those of G, S, and F, respectively, while G had significantly higher BD values than those of SG, S, and F; conversely, there was no significant effect of vegetation type on pH. In addition, the mean values of SWC, TSP, OC, and TN on anti-dip erosion slopes were significantly greater than those on dip erosion slopes (p < 0.05). Conversely, the mean values of BD, pH, and TP on anti-dip erosion slopes were lower than those observed on dip erosion slopes. Moreover, the TSP and pH values in the SG and G of dip erosion slopes were significantly lower than those recorded in the corresponding areas of the anti-dip erosion slope.
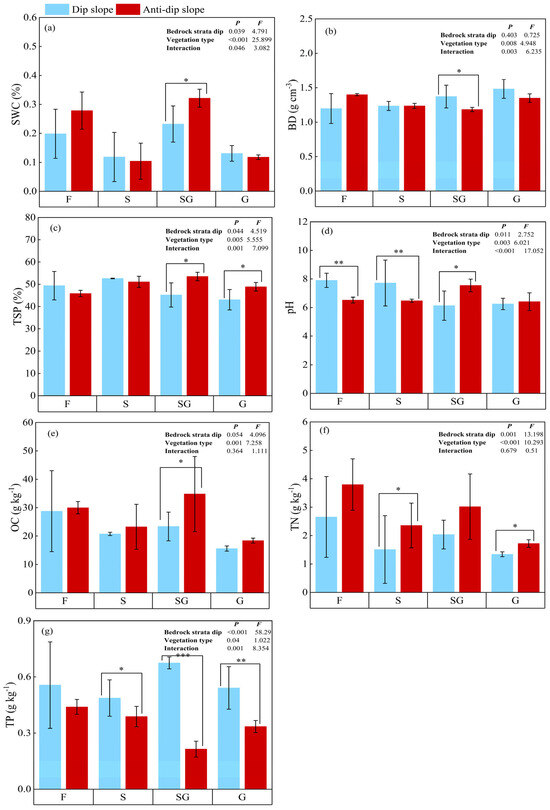
Figure 2.
The influence of vegetation type on the physicochemical properties of soil in dip/anti-dip erosion slopes. Note: (a) SWC: soil water content; (b) BD: soil bulk density; (c) TSP: total soil porosity; (d) PH: pH; (e) OC: organic carbon; (f) TN: total nitrogen content; (g) TP: total phosphorus; G: four stages: grasslands; SG: transitional grass–shrub; S: shrubland; F: secondary forest. Significant differences between treatments, denoted by different asterisk number, “*” is statistically significant at the p < 0.05 level; and the “**” is statistically significant at the p < 0.01 level; “***” is statistically significant at the p < 0.001 level. The graph also presents the standard deviation.
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Soil Enzyme Activity and Its Stoichiometry Across Vegetation Types
Both the vegetation type and the dip of the bedrock strata significantly influenced the soil enzyme activity (p < 0.01). Compared with the other three vegetation types, the SG vegetation type presented significantly greater mean values for AKP, BNA, LAP, and EN:P, indicating that SG had the highest overall soil enzyme activities among the vegetation types. Conversely, SG presented the lowest levels of EC:N and EC:P. In contrast, S presented the lowest mean values for AKP, BNA, and LAP. Furthermore, F presented the highest BG, BDC, EC:N, and EC:P activities, whereas G presented the lowest BG and BDC activities. S clearly presented the highest C-related soil enzyme activities. Additionally, anti-dip erosion slopes presented significantly greater mean BG, BDC, BNA, LAP, EC:P, and EN:P activities than dip erosion slopes did, indicating that anti-dip erosion slopes presented higher C- and N-related soil enzyme activities. However, AKP activity on dip erosion slopes ranged from 75.51 to 149.61 nmol·g−1·h−1, which was slightly higher than the range observed on anti-dip erosion slopes (56.19–135.6 nmol·g−1·h−1). Moreover, BG, LAP, and EC:N activities were significantly greater on the G of the dip erosion slope than on the anti-dip erosion slope, suggesting that the G of the dip erosion slope had higher C-related soil enzyme activities (Figure 3).
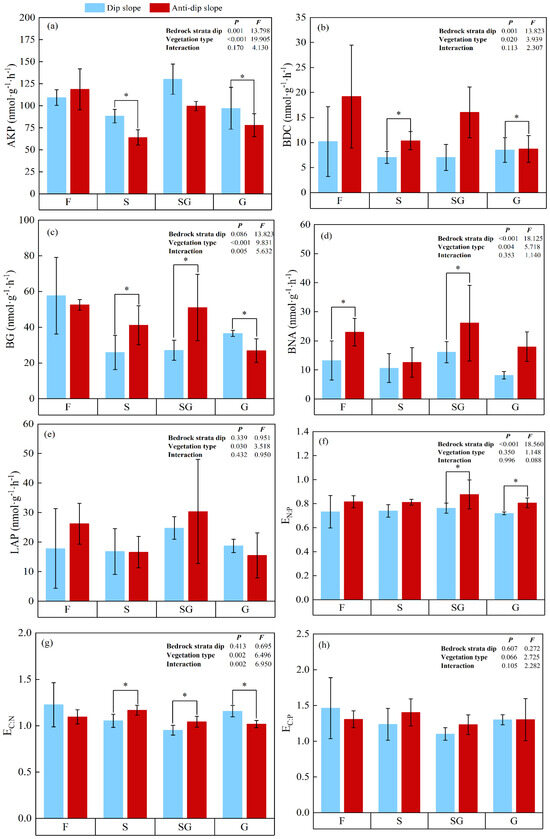
Figure 3.
Soil enzyme activities and its stoichiometry under different vegetation type on dip/anti-dip erosion slope. Note: Samples from different vegetation types at dip/anti-dip slopes, respectively. (a) AKP: acid phosphatase; (b) BDC: β-D-cellobiosidase; (c) BG: β-1,4-glucosidase; (d) BNA: β-1,4- N-acetylglucosaminidase; (e) LAP: L-leucine aminopeptidase; (f) EN:P: the ratio of (BNA + LAP) and AKP; (g) EC:N: the ratio of (BG + BDC): (BNA + LAP); (h) EC:P: the ratio of (BG + BDC):AKP; G: four stages: grasslands; SG: transitional grass–shrub stages; S: shrubland stage; F: secondary forest stage; Significant differences between treatments, denoted by different asterisk number, “*” is statistically significant at the p < 0.05 level. The graph also presents the standard deviation.
3.3. Analysis of Soil Enzymes and Soil Physicochemical Properties
A correlation heatmap was generated to further investigate the extent of the relationship between soil physicochemical properties and soil enzyme activities on slopes affected by dip and anti-dip erosion. This relationship is visually depicted in Figure 4a,b. For the dip erosion slope, BD exhibited a significant negative correlation with AKP, TSP, TN, OC, and BG. Furthermore, LAP was negatively correlated with EC:N and EC:P but positively correlated with BDC and EN:P, demonstrating substantial differences in their respective correlation coefficients. For the anti-dip erosion slope, the concentrations of BG and AKP exhibited a significant negative correlation with TP, with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.4. Additionally, BNA was positively associated with LAP, EN:P, BG, and AKP but negatively related to EC:N.
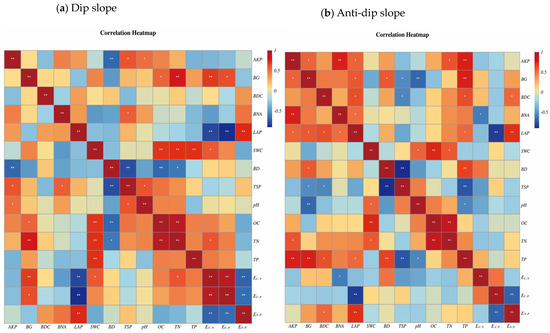
Figure 4.
Correlation heatmap of soil physicochemical properties and soil enzyme activities under different vegetation types on dip and anti-dip slopes. Note: All abbreviations in this figure are consistent with those in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Significant differences between treatments, denoted by different asterisk number, “*” is statis-tically significant at the p < 0.05 level; and the “**” is statistically significant at the p < 0.01 level.
3.4. Redundancy Analysis of Soil Enzyme and Soil Physicochemical Properties
The relationships between soil physicochemical properties and soil enzyme characteristics were examined by analyzing soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry via redundancy analysis (RDA). The constrained axes of the RDA for soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry explained 81.9% and 69.9% of the variation in dip and anti-dip slopes, respectively. Specifically, for the dip slope, the first and second axes accounted for 49.5% and 32.4%, respectively, of the variation, whereas for the anti-dip slope, the first and second axes accounted for 60.5% and 9.4%, respectively, of the variation (Figure 5). The first and second axes clearly accounted for the highest percentage of explained variance, collectively representing approximately half of the total variation in both dip and anti-dip slopes. For the dip slope, the TN (27.4%) and BD (24.4%) concentrations were significantly greater than the TP (14.1%), OC (8.6%), pH (6.9%), TSP (2.3%), and SWC (1.9%) concentrations were. These findings indicate that TN and BD are significant factors influencing soil enzyme activity on dip erosion slopes in decreasing order of effect. Furthermore, TN was significantly positively correlated with BG, EC:P, and EC:N but negatively correlated with BNA, LAP, and EN:P. In contrast, BD was significantly positively correlated with BDC and EN:P but negatively correlated with AKP, BG, EC:P, and EC:N. In addition, for the anti-dip slope, TP (36.8%) was significantly greater than the other soil physicochemical properties; thus, it can be concluded that TP was the most significant factor affecting soil enzyme activity on the anti-dip erosion slope (Table 1). Moreover, TP was significantly positively correlated with BG, BDC, LAP, AKP, and EN:P, whereas it was negatively correlated with EC:N and EC:P.
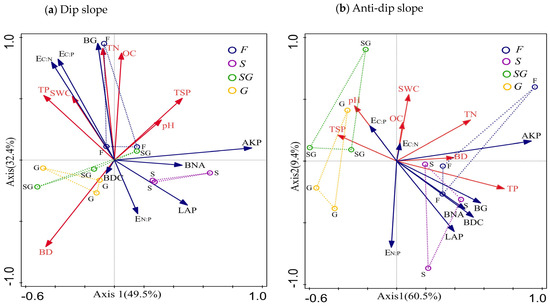

Table 1.
The contribution of main soil properties on soil enzyme activities.
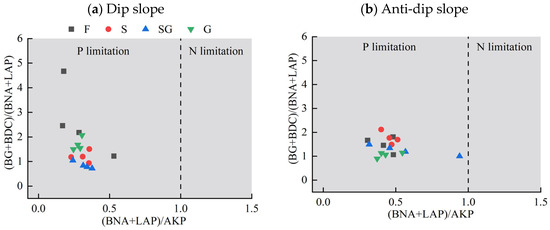
3.5. Microbial Nutrient Limitation with Vegetation Type
The analysis of ecological enzyme stoichiometric ratios revealed significant phosphorus (P) limitation without nitrogen (N) limitation in the vegetation types employed on both dip slopes and anti-dip slopes, as indicated by all ratios of (BNA + LAP)/AKP exceeding 1 (Figure 6). Additionally, the mean ratio of (BG + BDC)/(BNA + LAP) in the SG of the dip slope was found to be less than 1, whereas it exceeded 1 for the other vegetation types. The presence of SGs on dip slopes contributes to microbial C and P limitations. Specifically, the vegetation type on the anti-dip slope is predominantly constrained by C and P.
Furthermore, the C and P limitations were quantified by calculating the vector length and angle on the basis of the relative proportion of enzyme stoichiometric activity (Figure 7). The length and angle of the vector were changed from 1.16 to 1.80 and 45.39 to 57.84, respectively. The longer the vector length is, the greater the degree of C limitation associated with vegetation types under conversion from cropland into forest. Moreover, all vector angles were found to exceed 45°, indicating that this is also a P limitation in these types of slopes. Moreover, throughout all the vegetation types, there was a significant increase in microbial P limitations with increasing vegetation type; however, N limitations were not clearly evident. Additionally, the F and S stages presented the highest values of vector length and angle, indicating that these stages represent the upper limits for microbial C and P.
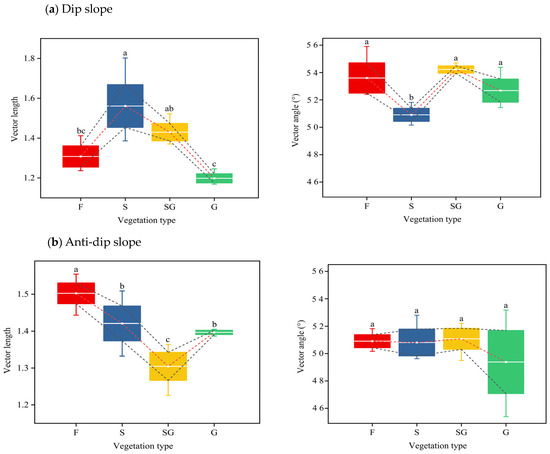
Figure 7.
Variation of vector length and angle under different vegetation types on dip and anti-dip slopes. Note: all abbreviations in this figure are consistent with those in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Significant differences between treatments, denoted by different lowercase letters (e.g., a, b), are statistically significant at the p < 0.05 level. The graph also displays the standard deviation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity to Vegetation Type on Dip and Anti-Dip Erosion Slopes
Variation in vegetation type and topographic factors influences soil physicochemical properties as well as soil enzyme activity, thereby impacting soil quality. Compared with those in other regions, the unique soil conditions in karst mountain forests, including elevated pH levels, increased calcium content and buffer capacity, as well as distinct hydrological characteristics, result in distinctive responses of ecosystem processes to global change. The mean carbon (C) content (24.36 mg/g) and total nitrogen (TN) content (2.30 mg/g) of surface soil (0–10 cm) in different vegetation types in this study were significantly greater than those of the Loess Plateau soil layer (0–10 cm) under the same drought conditions, with a C content of 3.0 mg/g and an N content of 0.3 mg/g [31]. In contrast to the temperate arid conditions found on the Loess Plateau, subtropical karst areas present higher levels of surface soil organic matter and nitrogen content. Furthermore, previous research has demonstrated that the geological environment of dip and anti-dip slopes in unique karst trough valleys significantly influences the soil element content [30,35]. Our results revealed that most of the soil physicochemical properties (such as SWC, TSP, OC, and TN) and the activities of enzymes involved in the soil C and N cycles on anti-dip slopes were greater than those on dip slopes. These findings indicate that the soil quality and soil enzyme activity of the anti-dip erosion slope were significantly greater than those of the dip erosion slope. In our previous study, the bedrock strata dip of the dip erosion slope, which acts as a barrier to runoff and soil erosion, has a substantial blocking effect on the inclination slope opposite the mountainside [32,41]. A thicker soil layer, greater soil moisture and nutrient content, and improved temperature retention on anti-dip erosion slopes significantly enhance the soil carbon and nitrogen cycles. Additionally, these conditions provide ample substrates for enzymatic reactions in the soil, thereby increasing soil enzyme activity. Moreover, it can be found that the dip-slope faces south whereas the “anti-dip” slopes face north. The annual potential for direct solar radiation is maximized on the south-facing dip slope and minimized on the north-facing anti-dip slope. McCune and Keon [42] also reported that the potential annual direct incident radiation on a south-facing dip slope is 93% greater than that on a north-facing slope. This increased radiation intensity leads to higher soil temperatures and decreased soil moisture levels on south-facing slopes. Coupled with limited vegetation cover, these conditions diminish the moisture retention capacity of the soil, leading to reduced soil enzyme activity. Furthermore, the direct impact of rainfall exacerbates soil structure degradation, ultimately contributing to the loss of organic carbon (OC). In contrast, the north-facing anti-slope area receives less solar radiation, leading to decreased soil evaporation and lower soil temperatures. These conditions preserve relatively high soil moisture levels and suppress microbial decomposition of organic matter, thereby facilitating the accumulation of C, N, and P. Moreover, the relatively dense vegetation on this slope contributes to a relatively high influx of organic carbon into the soil. As a result, under the combined influence of bedrock strata dip and slope orientation, anti-dip erosion slopes demonstrate markedly greater soil enzyme activity than dip erosion slopes do [27,30]. Moreover, the average soil phosphorus (P) content within the study area was 0.34 mg/g, which is lower than the global average of 2.80 mg/g. This finding is consistent with observations of phosphorus deficiency in other karst regions.
Furthermore, we also observed significant variations in the soil nutrient contents among the SI, G, S, and SG treatments. Specifically, there was a gradual decrease in OC, TN, TP, BG, and BDC levels, as did most soil enzyme activities, as the vegetation type transitioned from SI to G to S to SG during the conversion from cropland to forest. This may be attributed tto the high soil nutrient content in the F vegetation type of karst forest, combined with loose soil, good ventilation, and hydrothermal conditions in the habitat, creating an optimal environment for the proliferation and growth of soil microorganisms. This consequently enhances soil enzyme activity [43]. However, as farmland transitions into grassland within karst trough valleys, there is increased exposure of rocks and a significant decline in soil biomass [44]. Consequently, this leads to a reduction in the availability of organic matter within the soil. Moreover, as the habitat progresses toward early growth stages, there is a decrease or complete disruption in nutrient transport from vegetation to the soil, resulting in the loss of dead branches and leaves on the soil surface due to destruction of the vegetation [23,45]. Consequently, valuable organic matter and essential nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus in the topsoil are also depleted. In contrast, deforestation has led to a significant decline in both organism diversity and abundance, resulting in a continuous weakening of biological enrichment [24]. Additionally, mineralization processes within the parent rock have decelerated, and soil enzyme activity has significantly declined, resulting in diminished soil nutrient content [20]
4.2. Driving Factors of Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Resource Limitation Under Different Vegetation Type on Dip and Anti-Dip Erosion Slopes
Soil physicochemical properties play crucial roles in mediating both soil enzyme activity and stoichiometric ratios in karst forest ecosystems, resulting in significant variations across different geological backgrounds [7]. In this study, correlation and redundancy analysis were employed to investigate the relationships between soil physicochemical factors and soil enzyme activity. The results showed that TN and BD primarily regulated soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometric ratio on karst forest dip slopes, followed by other soil physicochemical properties. These findings align with those of Peng et al.’s (2024) study on niches in karst areas [46]. The soil enzyme activities on dip slopes are controlled by TN and BD, which significantly differ from those in nonkarst forests, where soil nutrient levels have a greater influence on soil enzyme activities than physical properties. This discrepancy arises from the relatively low content of OC in dip slope soils, with C and N being the primary constituents of the microbial composition [21]. Consequently, the diminished role of OC may amplify the regulatory effect of N on soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometric ratio. However, in anti-dip slopes, TP is an important regulatory factor for soil enzyme activity, which is also similar to the results of most researchers in determining the key factors of soil enzymes in karst areas [32]. The reason may be attributed to the relatively high OC and TN contents in anti-dip slopes, and the low TP content can directly affect the metabolism of microorganisms and mediate the secretion of soil enzymes. In addition, BD in this study was significantly negatively correlated with the activities of five extracellular enzymes, which was consistent with the results of different grazing intensities in desert steppe ecosystems [11,44,47]. This occurred because the shallow soil in karst forests leads to an increase in the soil BD, which subsequently reduces the soil porosity and water content. This, in turn, intensifies the inhibitory effect of BD on plant growth by impeding root development and diminishing the metabolic enzyme production capacity of soil microorganisms.
Moreover, the soil enzyme stoichiometry ratio reflects the relative allocation of microbial resources. In the presence of resource demands, microorganisms secrete corresponding enzymes to meet their own requirements, thereby leading to a modification in the soil enzyme stoichiometry ratio [31,45]. In essence, soil microorganisms strategically allocate energy and secrete extracellular enzymes to acquire limited resources, thereby modulating soil enzyme production on the basis of resource availability [15,45]. In this study, the mean values of EC:P (1.33) and EN:P (0.78) were significantly greater than the global mean values of EC:P (0.62) and EN:P (0.44) values, whereas the mean value of EC:N (1.09) was significantly lower than the global mean value of EC:N (1.41) for both dip and anti-dip slopes. The soil AKP activity in the karst trough region was relatively low, indicating a potentially high contribution from microorganisms to obtaining phosphorus through enzymes. This finding also indicates a relative deficiency of P in the soil of this region, which is consistent with the findings of Wang et al. (2022) [3]. Moreover, a (BG + BDC):(BNA + LAP) ratio exceeding 1 and a (BNA + LAP):AKP ratio below 1 indicate a preference of soil microorganisms in the vegetation type of karst trough valleys to produce elevated levels of (BG + BDC) and AKP enzymes, with the aim of increasing nutrient availability. This result also confirms the resource allocation theory, indicating that higher levels of C, N, and P acquisition enzymes are associated with increased carbon energy limitations and phosphorus nutrient limitations [7,21]. In particular, this study further revealed that the SG of the anti-dip slope had the highest (BNA + LAP):AKP, and the SG of the dip slope had the lowest (BG + BDC):(BNA + LAP). These findings suggest that the soil microorganisms on the anti-dip slope secrete a significant amount of N-related enzymes, indicating that their growth is somewhat limited by nitrogen availability. These findings are consistent with those reported by Pan et al. (2018) [25]. The limited vegetation and litter return on the SG of anti-dip erosion slopes can potentially be ascribed to insufficient soil nitrogen content, which fails to provide an adequate substrate for N-related enzymes. Consequently, this leads to reduced enzyme activity in the soil and restricts microorganisms due to nitrogen limitation [23,38]. For both dip and anti-dip erosion slopes, (BNA + LAP):AKP was the highest on the SG and the lowest on the G, whereas (BG + BDC):(BNA + LAP) was the highest on the S and the lowest on the SG. This observation suggests that the growth of soil microorganisms was somewhat constrained at S.
Furthermore, Moorhead et al. (2016) introduced the concepts of vector length and vector angle on the basis of extracellular activity, providing a perspective on the response of microorganisms to carbon limitation (vector length) and nitrogen/phosphorus limitation (vector angle) [48]. In this study, the VL and VA values were greater in the F and G of the dip slope than in those of the anti-dip slope, suggesting that the soil microorganisms on the F and G of the dip slope experienced a certain level of C and P limitation. This observation is consistent with that of Liu et al. (2023), who reported a significant positive correlation between soil enzyme activity and soil water content on south-facing dip slopes characterized by low soil moisture and temperature conditions [2]. The limited availability of water restricts the production of extracellular hydrolases. The vegetation coverage of F on dip erosion slopes is relatively low, resulting in a higher rate of bedrock exposure than that on anti-dip slopes [31]. Consequently, this results in a reduction in soil organic input and hinders the availability of carbon for microorganisms. As a result, an increased number of microorganisms are stimulated to allocate resources toward producing carbon-degrading enzymes, as they actively seek additional sources of carbon from the soil to support their own growth and metabolism. Moreover, P is an essential nutrient for plant growth and metabolism. The findings of our study indicate a gradual increase in the limitation of P with the progression of grain for green projects, specifically from G to S and F. This result is consistent with the research of Liu et al. (2023) but inconsistent with the results of Xiao et al. (2021), which suggest that nitrogen is the primary limiting factor for soil nutrient availability in karst regions [2,44]. These discrepancies may be attributed to various factors, such as differences in research locations, sampling depths, and seasonal variations [24,38,41]. Thus, it can be inferred that the intricate regulatory mechanisms governing soil nutrients in karst rocky desertification areas of Southwest China are further elucidated. In primary forests with undisturbed karst ecosystems, the presence of greater soil microbial biomass can alleviate P limitation by releasing hydrolases to catalyze organic matter decomposition and enhance nutrient cycling [23,24]. Conversely, root secretions, including organic acids, are more abundant in forests than in bushes, thereby increasing the forest’s capacity to acquire P bound to calcium minerals and soil organic matter [25,47,49]. Additionally, a significant amount of soil water is generated during the concentrated rainy season in southwestern karst regions, and changes in soil water content significantly affect the turnover of SOM as well as the microbially mediated release of carbon dioxide from the soil [49,50]. The excessive growth and proliferation of specific vegetation species deplete both water and nutrient resources within the soil, thereby constraining vegetation growth due to the limited availability of soil nutrients, particularly P [39]. Furthermore, we found that all the vegetation types experienced P limitation without N limitation. This phenomenon can be attributed to the restoration of farmland, which has facilitated vegetation recovery. The rapid growth of aboveground biomass significantly promotes the transfer of N and P from the soil to plants. P in the soil is predominantly a sedimentary element, primarily derived from the slow weathering of minerals and rocks, whereas nitrogen mainly originates from the microbial decomposition of organic matter. In addition, some researchers have confirmed this view. These studies, which are grounded in the stoichiometric characteristics of soil primary N conversion rates and extracellular enzyme activities, indicate that karst forests exhibit pronounced N saturation features. This results in the response and adaptability of the soil N cycle to N deposition differing from those of other regions and forest types. In contrast, neighboring subtropical non-karst forests are typically nitrogen limited. Consequently, the replenishment of phosphorus in soil poses a greater challenge than that of nitrogen. As a result, plant nutrient uptake is more likely to deplete soil phosphorus levels, thereby exacerbating phosphorus limitation in karst trough valleys. Therefore, it is crucial to further investigate the significant impact of low phosphorus availability on various vegetation types in future research.
4.3. Implications
In this study, the bedrock strata dip and vegetation type influenced microbial activity by affecting the nutrient retention capabilities of karst trough valleys, ultimately impacting the soil nutrient content and enzyme activity. Furthermore, the Fof dip slope presented a relatively high EC:P value, suggesting that the P availability on the dip slope was lower than that on the anti-dip slope. As vegetation continues to succeed in carbon sink forests, phosphorus may emerge as the primary limiting factor for carbon sequestration. This finding is also consistent with the results of Kong et al. (2023) [13]; that is, the availability of P in soil decreases during grassland succession to forestland. Moreover, recently, nitrogen deposition has steadily increased, resulting in an imbalance in the nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio. Consequently, phosphorus has become a crucial limiting factor for vegetation types following the implementation of the policy to convert farmland back to forests. When considering the future growth of carbon sink functions in the later stages of reforestation, accounting for phosphorus nutrient restrictions remains crucial for harnessing the significant potential for carbon sequestration. Additionally, soil phosphorus supplementation plays a particularly important role in the care and management of dip slopes in karst trough valley carbon sink forests. With the frequent occurrence of extreme weather events, the complexity and variability of soil enzymes and nutrient limitations in karst trough valleys have become more pronounced. Therefore, it is imperative to further investigate the relationships among vegetation litter, soil microorganisms, and microbial enzyme stoichiometry under various vegetation types and bedrock strata under extreme climatic conditions. This exploration could facilitate a deeper comprehension of the response of plant–soil–microbiota interactions to climate change.
5. Conclusions
This study examines the effects of natural vegetation type on soil enzyme activity and microbial nutrient limitations following farmland abandonment, with a specific focus on the different bedrock strata dips (dip and anti-dip slopes) of a karst trough valley. Our results indicate that the majority of soil physicochemical properties, including SWC, TSP, OC, and TN, as well as the soil enzyme activities involved in the soil C and N cycles, were significantly greater on the anti-dip slope than on the dip slope. Compared with those of G, F, and S, the SGs presented significantly greater mean values for AKP, BNA, LAP, and EN:P. Specifically, the increases ranged from 0.83% to 33.74% for AKP, 14.10% to 45.06% for BNA, 20.08% to 39.40% for LAP, and 5.53% to 6.95% for EN:P. Correlation and redundancy analyses revealed that TN and BD primarily regulated soil enzyme activity and its stoichiometric ratio. Furthermore, the mean values of EC:P (1.33) and EN:P (0.78) were significantly greater than the global averages, whereas the mean value of EC:N (1.09) was lower than the global average value for both dip and anti-dip slopes. Additionally, the VL and VA values were greater for the F and G slopes than for the anti-dip slope, indicating that the soil microorganisms on the F and G slopes experienced C and P limitations. These findings suggest that the vegetation type following the conversion of farmland to forests, influenced by bedrock strata dip and ecological restoration initiatives, significantly enhances soil enzyme activity and alleviates phosphorus limitation in karst trough valleys. This study deepens our understanding of the mechanisms governing soil enzyme activity and provides clearer insight into microbial nutrient limitations in these regions. Furthermore, the results enhance our ability to regulate and manage carbon cycles in karst areas, thereby promoting carbon sequestration, maintaining soil fertility, and providing a theoretical foundation for major ecological projects such as “returning farmland to forest and grassland” in karst valleys. Additionally, supplementary fertilizers should be incorporated during this process, along with measures to prevent erosion and introduce new plant species to the existing vegetation, which will further increase soil enzyme activity and address microbial nutrient limitations after the conversion of farmland to forests in karst trough valleys.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.G., H.S., X.T., W.L., Y.Y. and Y.F.; Methodology, F.G., L.J., Y.X., J.P. and Q.D.; Software, F.G.; Validation, F.G.; Formal analysis, F.G.; Investigation, F.G.; Resources, F.G.; Writing—original draft, F.G.; Writing—review & editing, F.G.; Visualization, F.G.; Project administration, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Science Foundation (W2412149, 42467045, 42107355, 42167044, 42007045), Guizhou University Cultivation Project (Guizhou University Cultivation [2019] No. 10), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023MD744195), the Scientific research project of Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1053), and the Science and technology project of Chongqing Education Commission (KJQN202400504).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ananbeh, H.; Stojanović, M.; Pompeiano, A.; Voběrková, S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Use of soil enzyme activities to assess the recovery of soil functions in abandoned coppice forest systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.C.; Wang, H.; Yan, G.Y.; Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, X.C.; Xue, J.S.; Xu, M.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Q. Soil enzyme activities and microbial nutrient limitation during the secondary succession of boreal forests. Catena 2023, 230, 107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Fan, B.; Mao, X.H.; Luo, H.; Jiang, F.Y.; Liang, C.F.; Chen, J.H.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q.F.; et al. Litter Inputs Control the Pattern of Soil Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon and Enzyme Activities in Three Typical Subtropical Forests. Forests 2022, 13, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, H.; Meli, P.; Butler, B.; Jorge, P.; Matus, F.; Merino, C.; Cornejo, P.; Kuzyakov, Y. Meta-Analysis of heavy metal effects on soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.J.; A, D.M.; An, S.S.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, H.X.; Sebastian, L. Extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry: The effect of soil microbial element limitation during leaf litter decomposition. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-López, M.; Siles, J.A.; Ros, C.; Bastida, F.; Nicolás, E. The effects of ozone treatments on the agro-physiological parameters of tomato plants and the soil microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, Y.Y.; Dong, X.F.; Wang, X.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhao, G.Y.; Zang, S.Y. Soil Enzyme Activities and Their Relationships with Soil C, N, and P in Peatlands From Different Types of Permafrost Regions, Northeast China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 670769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.L.; Ou, Y.S.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.F.; Li, J.; Xiao, J.J.; Hao, Z.G.; Wang, K.C. Response of Soil Enzyme Activities to Natural Vegetation Restorations and Plantation Schemes in a Landslide-Prone Region. Forests 2022, 13, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F.; Cheng, S.L.; Fang, H.J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.N.; Zhou, Y. Responses of soil fungal taxonomic attributes and enzyme activities to copper and cadmium co-contamination in paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.H.; Wade, J.; Li, C.Y.; Daughtridge, R.C.; Margenot, A.J. Quantifying the relative importance of controls and assay conditions for reliable measurement of soil enzyme activities with para-nitrophenol substrates. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.K.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity, and compositions to altitudinal gradients depend on plant and soil characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Ju, W.L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Cui, Y.X.; Beiyuan, J.Z.; Fan, Q.H.; Wei, S.Y.; Li, S.Q.; et al. Microbial metabolic limitation of rhizosphere under heavy metal stress: Evidence from soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.H.; Qu, A.R.; Feng, E.; Chen, R.; Yang, X.T.; Lai, Y. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Enzymatic Activity under Different Land-Use Types in Rocky Mountainous Region of North China. Forests 2023, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Gunina, A.; Zamanian, K.; Tian, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Yudina, A.; Aponte, H.; Alharbi, H.; Ovsepyan, L.; et al. New approaches for evaluation of soil health, sensitivity and resistance to degradation. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, X.Z.; Kim, Y.; Lv, J.H.; Li, Y.F.; Wu, J.S.; Qin, H. Biochar mitigates the effect of nitrogen deposition on soil bacterial community composition and enzyme activities in a Torreya grandis orchard. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 457, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh Robert, L.; Lauber Christian, L.; Weintraub Michael, N.; Bony, A.; Allison Steven, D.; Chelsea, C.; Zeglin Lydia, H. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, M.I.; Ali, A.; Atif, M.J.; Pathan, S.I.; Pietramellara, G.; Ali, M.; Amin, B.; Cheng, Z.H. Diversified crop rotation improves continuous monocropping eggplant production by altering the soil microbial community and biochemical properties. Plant Soil 2022, 480, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvena, B.; Anelia, K.; Michaella, P.; Stela, G.; Christo, C.; Galina, R. Soil enzyme activities after application of fungicide QuadrisR at increasing concentration rates. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Curtright, A.J.; Tiemann, L.K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Gujre, N.; Gupta, D.; Agnihotri, R.; Mitra, S. Application of enzymes as a diagnostic tool for soils as affected by municipal solid wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; He, X.X.; Ye, S.M.; Wang, S.Q. Soil Aggregate-Associated Carbon-Cycle and Nitrogen-Cycle Enzyme Activities as Affected by Stand Age in Chinese Fir Plantations. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4361–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, H. Grass cultivation alters soil organic carbon fractions in a subtropical orchard of southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 181, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Nong, Z.; Ye, S.; Deng, Q. Introduction of Dalbergia odorifera enhances nitrogen absorption on Eucalyptus through stimulating microbially mediated soil nitrogen-cycling. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, S.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Cerdà, A.; Heydarpoor, G. Functionalization of ultrasound enhanced sewage sludge-derived biochar: Physicochemical improvement and its effects on soil enzyme activities and heavy metals availability. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, K. Increased associated effects of topography and litter and soil nutrients on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass along vegetation sucessions in karst ecosystem, southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16979–16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Aoyagi, R.; Kitayama, K.; Mo, J.M. Does the ratio of β-1,4-glucosidase to β-1,4 N acetylglucosaminidase indicate the relative resource allocation of soil microbes to C and N acquisition? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; He, B.H.; Qin, Z.Y.; Li, W.B. Role of rock dip angle in runoff and soil erosion processes on dip/anti-dip slopes in a karst trough valley. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; He, B.H.; Qin, Z.Y. Hydrological response and soil detachment rate from dip/anti-dip slopes as a function of rock strata dip in karst valley revealed by rainfall simulations. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; He, B.H.; Qin, Z.Y.; Li, W.B. Contribution of bedrock dip angle impact to nitrogen and phosphorus leakage loss under artificial rainfall simulations on slopes parallel to and perpendicular to the bedrock dip in a karst trough valley. Catena 2021, 196, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; Shi, H.L.; Gou, J.F.; Zhang, L.X.; Dai, Q.H.; Yan, Y.J. Responses of soil aggregate stability and soil erosion resistance to different bedrock strata dip and land use types in the karst trough valley of Southwest China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; Shi, H.L.; Gou, J.F.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, C.H. Effects of bedrock strata dip on soil infiltration capacity under different land use types in a karst trough valley of Southwest China. Catena 2023, 230, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.D.; Dai, Q.H. Drivers of soil erosion and subsurface loss by soil leakage during karst rocky desertification in SW China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, T.E.; Farrington, H.; Vitousek, P.M. Changes in Asymbiotic, Changes in Asymbiotic, Heterotrophic Nitrogen Fixation on Leaf Litter of Metrosideros polymorpha with Long-Term Ecosystem Development in Hawaii. Ecosystems 2000, 3, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.R.; Ali, A.; Haider, G.; Asad, M.; Munsif, F. Microplastics alter soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure without negatively affecting plant growth in an agroecosystem. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.L.; Shi, H.L.; Yan, Y.J.; Pu, J.B.; Dai, Q.H.; Gou, J.F.; Fan, Y.C. Soil quality assessment of karst trough valley under different bedrock strata dip and land-use types, based on a minimum data set. Catena 2024, 241, 108048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Mao, D.H.; Song, K.S.; Xiang, H.X.; Li, S.J.; Wang, Z.M. Effects of landscape changes on water quality: A global meta-analysis. Water Res. 2024, 260, 121946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ren, C.J.; Feng, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Doughty, R.; Zhao, F.Z. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition due to shifts in soil extracellular enzymes after afforestation. Geoderma 2020, 374, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; An, N.; Jiang, D.; Cao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, Y.W.; Ming, C.S.; Meng, Q.J.; Han, W. Short-term response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities in black soil to a herbicide mixture: Atrazine and Acetochlor. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Kang, D.; Wu, J.P.; Zhao, F.Z.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Temporal variation in soil enzyme activities after afforestation in the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2016, 282, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.X.; Ge, J.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Lei, X.H.; Wang, J.L.; Wan, C.X.; Wang, P.K.; Gao, X.L.; Gao, J.F. Soil enzyme activities, physiological indicators, agronomic traits and yield of common buckwheat under herbicide combined with safeners. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouni, F.; Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Brouchoud, C.; Capowiez, Y.; Rault, M. Role of soil texture and earthworm casts on the restoration of soil enzyme activities after exposure to an organophosphorus insecticide. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 187, 104840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Keon, D. Equations for potential annual direct incident radiation and heat load. J. Veg. Sci. 2002, 13, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y. Effects of conservation tillage on soil enzyme activities of global cultivated land: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, G.B.; Li, P.; Xue, S. Dynamics of soil specific enzyme activities and temperature sensitivities during grassland succession after farmland abandonment. Catena 2021, 199, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.B.; Zhang, Y.E.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Zheng, P.F.; Li, Z.D. Effects of forest cover type and ratio changes on runoff and its components. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.D.; Li, C.L.; Dai, Q.H.; Xu, S.B.; Zang, J. Morphological development of drying shrinkage cracks at the rock-soil—Soil interface in a karst rocky desertification area. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 54, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; Yang, H.S.; Wang, W.E.; Wang, C.X.; Pang, Y.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Hu, X.T. Effects of Living Grass Mulch on Soil Properties and Assessment of Soil Quality in Chinese Apple Orchards: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.T.; Chen, H.M.; Qu, P.; Lin, R.; He, S.M.; Li, W.F.; Zhang, C.L.; Shi, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Du, H.B.; et al. Effect of Different Cultivation Patterns on Amomum villosum Yield and Quality Parameters, Rhizosphere Soil Properties, and Rhizosphere Soil Microbes. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.Q.; He, B.P.; Wang, S. Effect of the Different Fertilization Treatments Application on Paddy Soil Enzyme Activities and Bacterial Community Composition. Agronomy 2023, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).