Applicability of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model for Evapotranspiration in Tropical Rubber Plantation and Its Response to Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
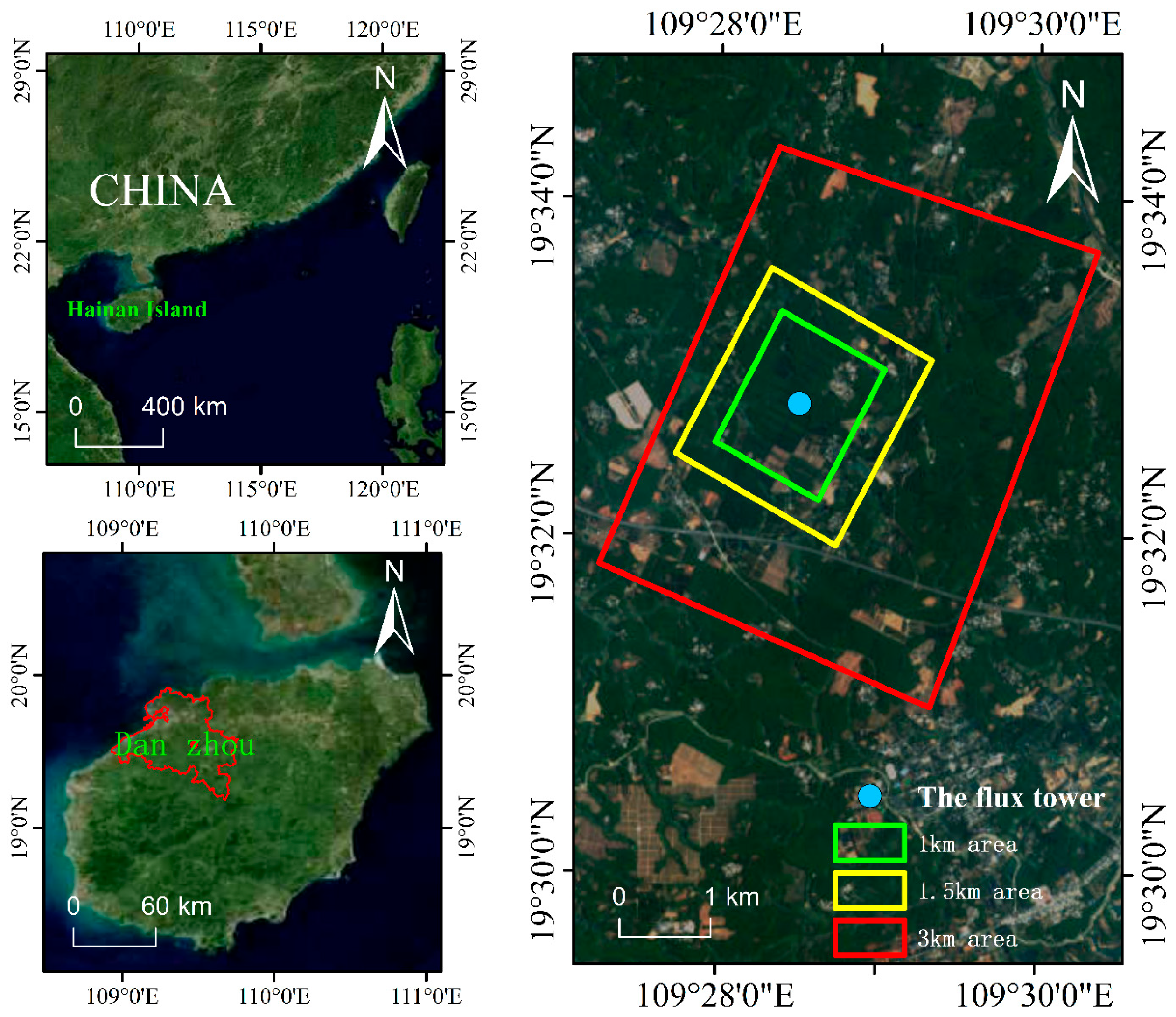
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Landsat-8 Remote Sensing Image Data
2.2.2. The Flux Tower Data
2.2.3. The Digital Elevation Data
2.3. SEBS Model Flux Calculation
2.4. Indicator Measurement
2.4.1. Measurement of Soil and Plant Analyzer Development (SPAD)
2.4.2. Determination of LAI
2.4.3. Measurement of Soil Water Content (SWC)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
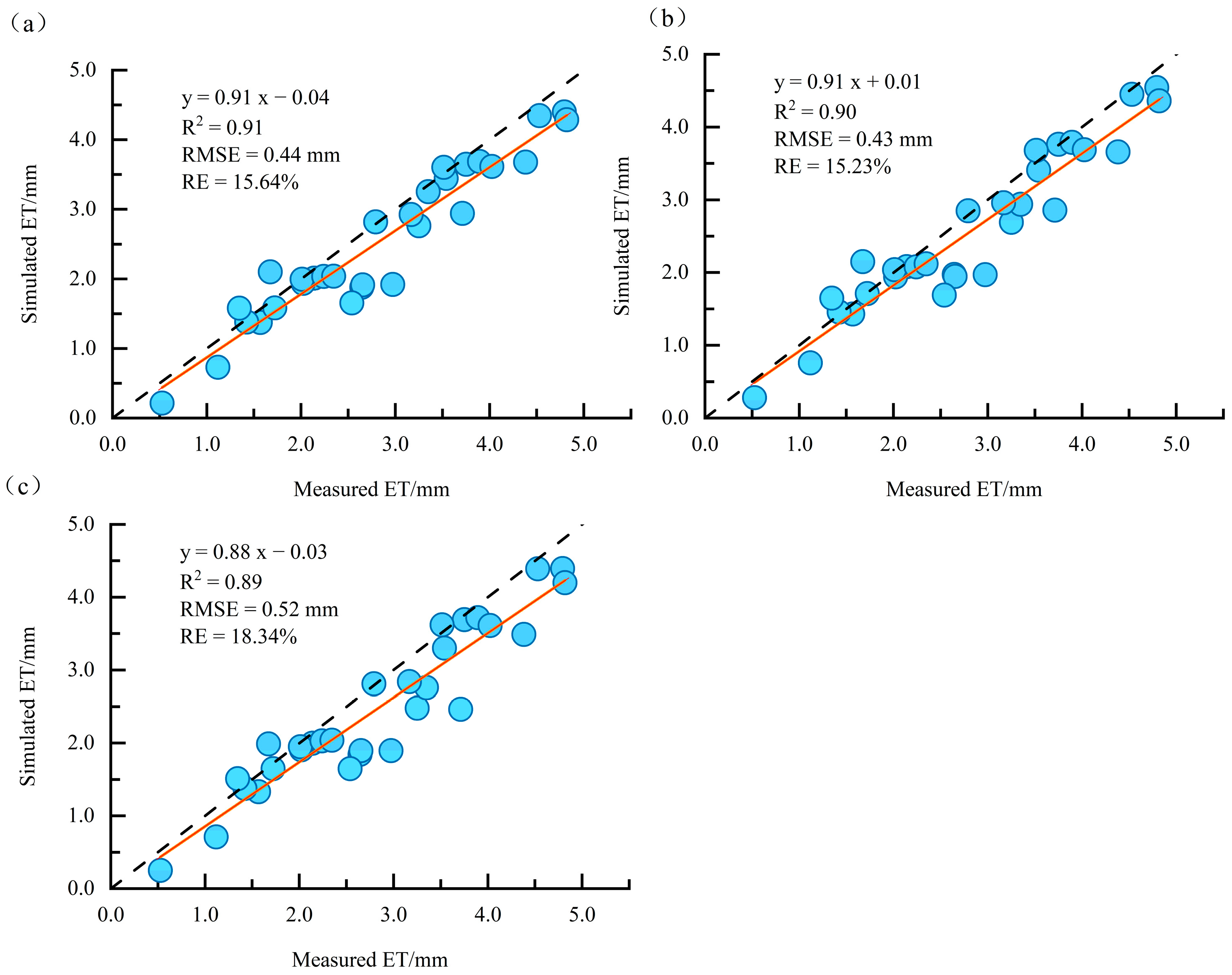
3.1. Inversion Results of Daily ET from Rubber Plantations in Different Source Areas
3.2. Variation Characteristics of ET in Rubber Plantation
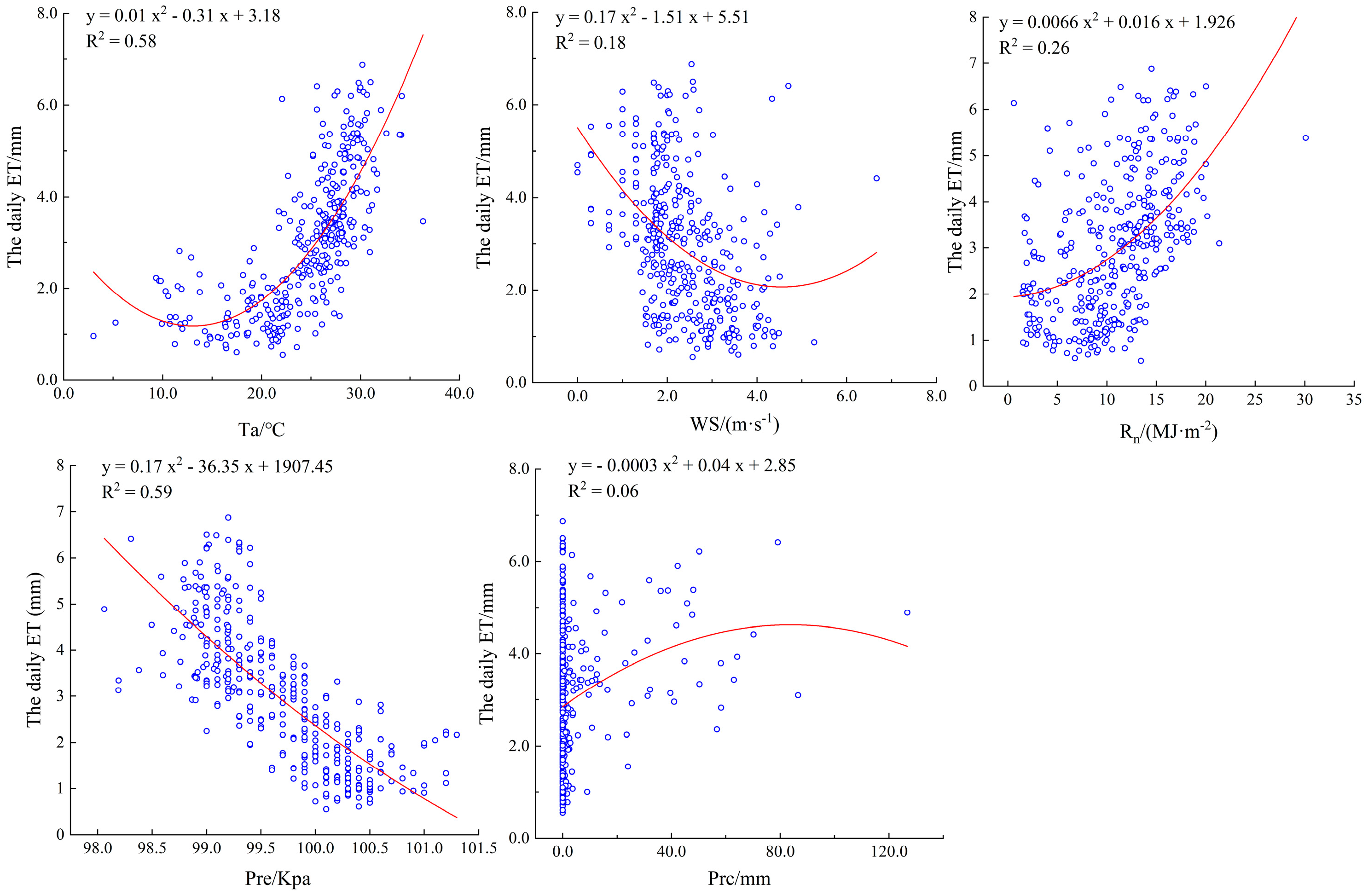
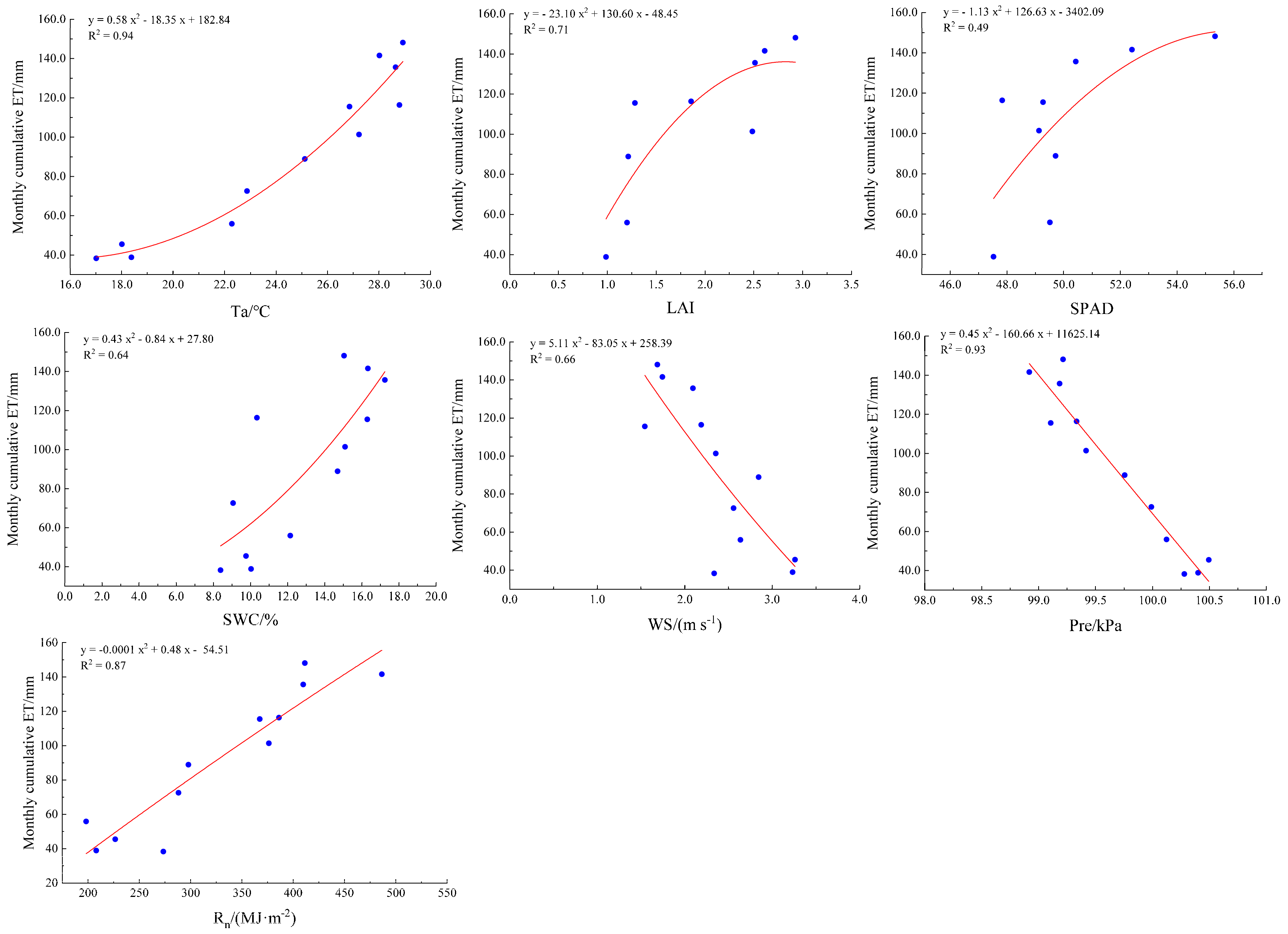
3.3. Factors Affecting ET in Rubber Plantation
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Accuracy of the SEBS Model for Inversion of ET in Rubber Plantations
4.2. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Changes in ET in Rubber Plantations
4.3. Main Driving Factors Affecting ET in Rubber Plantations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ET | Evapotranspiration |
| SEBS | Surface Energy Balance System |
| P–M | Penman–Monteith |
| P–T | Priestley–Taylor |
| PFT | Plant Functional Type |
| CLM5 | Community Land Model Version 5 |
| SVAT | Soil–Vegetation–Atmosphere Transfer |
| LUCIA | Land Use Change Impact Assessment |
| SEBAL | Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land |
| METRIC | Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration |
| S-SEBI | Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index |
| SSEBop | Operational Simplified Surface Energy Balance |
| DBH | Diameter at breast height |
| SPAD | Soil and plant analyzer development |
| LAI | Leaf area index |
| Ta | Air temperature |
| Pre | Atmospheric pressure |
| WS | Wind speed |
| Prc | Precipitation |
| Rn | Net radiation |
| SWC | Soil water content |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| USGS | United States Geological Survey |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| RE | Relative error |
References
- Oleinik, G.; Soares, L.C.; Benvegnú, D.M.; Lima, F.O.; Rodrigues, P.R.P.; Gallina, A.L. Rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) seed shell extracts as a promising green antioxidant alternative to increase biodiesel oxidation stability. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xiao, J.F.; Bai, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Gao, W.L.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Li, Q.F. Preseason sunshine duration determines the start of growing season of natural rubber forests. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kou, W.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yung, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal changes of rubber plantations in Hainan Island over the past 30 years. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2023, 47, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fu, R.; Cheng, S.; Qiao, D.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L. Effects of the conversion of natural tropical rainforest to monoculture rubber plantations on soil hydrological processes. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, P.; Gohet, E.; Nouvellon, Y.; Lacote, R.; Gay, F.; Do, F.C. Rubber tree ecophysiology and climate change. What do we know? In Proceedings of the Workshop on Natural Rubber Systems and Climate Change, CGIAR; CIFOR, Online, 23–25 June 2021; Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research. 2021. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-05177285v1 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Ling, Z.; Shi, Z.T.; Gu, S.X.; Peng, H.Y.; Feng, G.J.; Huo, H. Energy balance and evapotranspiration characteristics of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations in Xishuangbanna, Southwest of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, D.D.; Rosa, L.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P. The water-land-food nexus of natural rubber production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, W. Evaluation of the performance of three types of two-source evapotranspiration models in urban woodland areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Shi, Z.; Xia, T.; Gu, S.; Liang, J.; Xu, C.Y. Short-term evapotranspiration forecasting of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Shi, Z.; Gu, S.; He, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Gao, L. Estimation of applicability of soil model for rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations in xishuangbanna, southwest China. Water 2022, 14, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambelluca, T.W.; Mudd, R.G.; Liu, W.; Ziegler, A.D.; Kobayashi, N.; Kumagai, T.; Miyazawa, Y.; Lim, T.K.; Huang, M.; Fox, J.; et al. Evapotranspiration of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) cultivated at two plantation sites in Southeast Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 660–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola-Claramonte, M.; Troch, P.A.; Ziegler, A.D.; Giambelluca, T.W.; Durcik, M.; Vogler, J.B.; Nullet, M.A. Hydrologic effects of the expansion of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) in a tropical catchment. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnood, S.; Lotfata, A.; Mombeni, M.; Daneshi, A.; Verrelst, J.; Ghorbani, K. A spatial and temporal correlation between remotely sensing evapotranspiration with land use and land cover. Water 2023, 15, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Ito, K.; Takimoto, H. Abnormal data rejection range in the Bowen ratio and inverse analysis methods for estimating evapotranspiration. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 269, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lakshmi, V.; Wang, D.; Lin, P.; Pan, M.; Cai, X.; Wood, E.F.; Zeng, Z. The reliability of global remote sensing evapotranspiration products over amazon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Howell, T.A.; Jensen, M.E. Evapotranspiration information reporting: I. Factors governing measurement accuracy. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Lin, G.; Lin, L. Comparison of physical-based, data-driven and hybrid modeling approaches for evapotranspiration estimation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Fan, Y.; Corre, M.D.; Kotowska, M.M.; Preuss-Hassler, E.; Cahyo, A.N.; Moyano, F.E.; Stiegler, C.; Röll, A.; Meijide, A.; et al. Implementing a New Rubber Plant Functional Type in the Community Land Model (CLM5) Improves Accuracy of Carbon and Water Flux Estimation. Land 2022, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, T.; Mudd, R.G.; Miyazawa, Y.; Liu, W.; Giambelluca, T.W.; Kobayashi, N.; Lim, T.K.; Jomura, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Huang, M.; et al. Simulation of canopy CO2/H2O fluxes for a rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantation in central Cambodia: The effect of the regular spacing of planted trees. Ecol. Model 2013, 265, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Blagodatsky, S.; Marohn, C.; Liu, H.; Golbon, R.; Xu, J.; Cadisch, G. Climbing the mountain fast but smart: Modelling rubber tree growth and latex yield under climate change. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 439, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Liu, J. Evolution of evapotranspiration models using thermal and shortwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Losgedaragh, S.; Rahimzadegan, M. Evaluation of SEBS, SEBAL, and METRIC models in estimation of the evaporation from the freshwater lakes (Case study. Amirkabir dam, Iran). J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Shaw, S.B.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Im, J.; Niraula, R. Evaluating five remote sensing based single-source surface energy balance models for estimating daily evapotranspiration in a humid subtropical climate. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 49, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoratipour, E.; Mohammadi, A.S.; Zoratipour, A. Evaluation of SEBS and SEBAL algorithms for estimating wheat evapotranspiration (case study: Central areas of Khuzestan province). Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, T.F.; Pavek, M.J.; Holden, Z.J.; Garza, R. Evaluating potato evapotranspiration and crop coefficients in the Columbia Basin of Washington state. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 286, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P. Comparison of remote sensing evapotranspiration models: Consistency, merits, and pitfalls. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.; Liaqat, U.W.; Choi, M. Dual-model approaches for evapotranspiration analyses over homo-and heterogeneous land surface conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Li, C. Impacts of vegetation changes on global evapotranspiration in the period 2003–2017. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J.; Orgaz, F. Evapotranspiration of a young irrigated olive orchard in southern Spain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Fao Rome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Chaplot, B.; Omar, P.J.; Mishra, S.; Md. Azamathulla, H. Experimental study on infiltration pattern: Opportunities for sustainable management in the Northern region of India. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 2675–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Milroy, S.P. Soil-water thresholds for the responses of leaf expansion and gas exchange: A review. Field Crops Res. 1996, 47, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, Z.B. Changes in reference evapotranspiration and its driving factors in peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Xiong, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nie, T.; Wu, L.; Sun, Z. A Study on the Vulnerability of the Gross Primary Production of Rubber Plantations to Regional Short-Term Flash Drought over Hainan Island. Forests 2022, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Song, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Lan, G.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J. Responses of carbon exchange characteristics to meteorological factors, phenology, and extreme events in a rubber plantation of Danzhou, Hainan: Evidence based on multi-year data. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1194147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, M.Y.; Foken, T. Footprints in Micrometeorology and Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Estimating the actual evapotranspiration using remote sensing and SEBAL model in an arid environment of Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevin, W.R.; Brown, W.J. A precise measurement of the Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Metrologia 1971, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D. Evapotranspiration estimation based on MODIS products and surface energy balance algorithms for land (SEBAL) model in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.H. Water content. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; Volume 5, pp. 493–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baboli, N.; Ghamarnia, H.; Hafezparast Mavaddat, M. Estimating wheat evapotranspiration through remote sensing utilizing GeeSEBAL and comparing with lysimetric data. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J.; Yang, Y. Estimation of evapotranspiration and its relationship with environmental factors in Jinghe River Basin. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 034518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, H. Estimation and validation of high-resolution evapotranspiration products for an arid river basin using multi-source remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.Z.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Bernhofer, C. Exploring eddy-covariance measurements using a spatial approach: The eddy matrix. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2016, 161, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Che, T.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Liu, Q.; Jin, R.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; et al. The Heihe Integrated Observatory Network: A basin-scale land surface processes observatory in China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Estimation of the soil heat flux/net radiation ratio from spectral data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1990, 49, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Zhan, W.; Wang, C.; Ma, W.; Yao, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, K.; Sun, R. Enhanced observations from an optimized soil-canopy-photosynthesis and energy flux model revealed evapotranspiration-shading cooling dynamics of urban vegetation during extreme heat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecikalski, J.R.; Diak, G.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M. Estimating fluxes on continental scales using remotely sensed data in an atmospheric-land exchange model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 1352–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Aspects of bulk atmospheric boundary layer similarity under free-convective conditions. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T. 50 years of the Monin-Obukhov similarity theory. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Whittaker, R.J.; Malhi, Y. ET come home: Potential evapotranspiration in geographical ecology. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, W. Satellite-based actual evapotranspiration estimation in the middle reach of the Heihe River Basin using the SEBAL method. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Dong, Y.; Fei, X.; Song, Q.; Sha, L.; Wang, S.; Grace, J. Pattern and driving factor of intense defoliation of rubber plantations in SW China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.K.V. The water relations of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis): A review. Exp. Agric. 2012, 48, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Zou, Z.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Rookes, J.; Lin, W.; Cahill, D.; Kong, L. Regulation of HbPIP2; 3, a latex-abundant water transporter, is associated with latex dilution and yield in the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshan, P.M. Breeding hevea rubber: Formal and molecular genetics. Adv. Genet. 2004, 52, 51–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jia, Q.; Ping, X. Direct and indirect effects of environmental factors on daily CO2 exchange in a rainfed maize cropland-a SEM analysis with 10 year observations. Field Crops Res. 2019, 242, 107591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, S.; Bayzidi, Y.; Trachte, K. Spatio-temporal patterns of evapotranspiration in the temperate Eastern German lowlands and its response to climate and land use change. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, A.; Renner, M.; Kleidon, A. Imprints of evaporation and vegetation type in diurnal temperature variations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 4923–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and contributing climatic factors in China during 1961–2013. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y. Analysis of dynamic spatiotemporal changes in actual evapotranspiration and its associated factors in the Pearl River Basin based on MOD16. Water 2017, 9, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Shi, Z.; Gu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Feng, G. Impact of climate change and rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantation expansion on reference evapotranspiration in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 830519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J. Spatial and temporal characteristics of actual evapotranspiration and its influencing factors in Selin Co Basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 6195–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, D.; Dinpashoh, Y.; Kahya, E.; Singh, V.P.; Fakheri-Fard, A. Trends in reference evapotranspiration in the humid region of northeast India. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-X.; Thomas, A. Spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and its contributing climatic factors in Yunnan Province, SW China, 1961–2004. Clim. Change 2013, 116, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, D. Spatiotemporal variations of actual evapotranspiration over the Lake Selin Co and surrounding small lakes (Tibetan Plateau) during 2003–2012. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, D.; Singh, V.P. Spatial and temporal characteristics of actual evapotranspiration over Haihe River basin in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2012, 26, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J. Estimating spatiotemporal dynamics of ET and assessing the cause for its increase in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 333, 109394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringgaard, R.; Herbst, M.; Friborg, T. Partitioning forest evapotranspiration: Interception evaporation and the impact of canopy structure, local and regional advection. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Kang, S.; Yao, L.; Zhang, L. Estimation of evapotranspiration and its components from an apple orchard in northwest China using sap flow and water balance methods. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.G. Tamm review: Leaf Area Index (LAI) is both a determinant and a consequence of important processes in vegetation canopies. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 477, 118496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Paredes, P.; Melton, F.; Johnson, L.; Mota, M.; Wang, T. Prediction of crop coefficients from fraction of ground cover and height. background and validation using ground and remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 | 28 January | 7 January | 18 January |
| / | 8 February | 11 February | |
| 9 March | 20 March | 6 March | |
| 10 April | 5 April | 7 April | |
| 28 May | 31 May | / | |
| 29 June | / | 10 June | |
| 31 July | 26 July | 12 July | |
| / | 27 August | 5 August | |
| 1 September | / | 14 September | |
| 11 October | / | 24 October | |
| 28 November | 23 November | 1 November | |
| 22 December | 9 December | 19 December |
| Time | ET/mm | RMSE/mm | RE/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eddy Covariance Method | SEBS Model | ||||
| 2022 | 28 January | 1.57 | 1.43 | 0.14 | 8.81 |
| 9 March | 1.42 | 1.46 | 0.04 | 2.49 | |
| 10 April | 2.14 | 2.08 | 0.06 | 2.69 | |
| 28 May | 3.75 | 3.76 | 0.01 | 0.32 | |
| 29 June | 3.71 | 2.86 | 0.85 | 23.03 | |
| 31 July | 4.79 | 4.54 | 0.25 | 5.20 | |
| 1 September | 3.54 | 3.41 | 0.13 | 3.69 | |
| 11 October | 2.64 | 1.98 | 0.67 | 25.28 | |
| 28 November | 2.97 | 1.97 | 1.00 | 33.74 | |
| 22 December | 2.65 | 1.95 | 0.71 | 26.63 | |
| 2023 | 7 January | 0.53 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 46.84 |
| 8 February | 1.35 | 1.65 | 0.30 | 22.67 | |
| 20 March | 1.67 | 2.15 | 0.48 | 28.54 | |
| 5 April | 3.25 | 2.69 | 0.56 | 17.23 | |
| 31 May | 4.38 | 3.66 | 0.72 | 16.48 | |
| 26 July | 3.35 | 2.94 | 0.41 | 12.24 | |
| 27 August | 3.17 | 2.96 | 0.21 | 6.57 | |
| 23 November | 2.02 | 1.94 | 0.08 | 4.02 | |
| 9 December | 2.54 | 1.69 | 0.85 | 33.40 | |
| 2024 | 18 January | 2.01 | 2.04 | 0.03 | 1.39 |
| 11 February | 1.12 | 0.76 | 0.36 | 31.97 | |
| 6 March | 2.79 | 2.85 | 0.06 | 2.09 | |
| 7 April | 3.52 | 3.68 | 0.16 | 4.69 | |
| 10 June | 3.89 | 3.79 | 0.10 | 2.64 | |
| 12 July | 4.53 | 4.45 | 0.08 | 1.74 | |
| 5 August | 4.02 | 3.69 | 0.33 | 8.30 | |
| 14 September | 4.82 | 4.36 | 0.46 | 9.51 | |
| 24 October | 2.24 | 2.08 | 0.16 | 7.20 | |
| 1 November | 2.35 | 2.12 | 0.23 | 9.66 | |
| 19 December | 1.72 | 1.71 | 0.01 | 0.66 | |
| Impact Factor | r | Impact Factor | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ta | 0.69 ** | Pre | −0.77 ** |
| Prc | 0.24 ** | WS | −0.40 ** |
| Rn | 0.50 ** |
| Impact Factor | r | Impact Factor | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ta | 0.95 ** | SWC | 0.80 ** |
| Prc | 0.64 * | SPAD | 0.68 ** |
| Pre | −0.96 ** | LAI | 0.82 ** |
| WS | −0.81 ** | Rn | 0.93 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Lin, W.; Cheng, Q.; Ye, H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Wu, B. Applicability of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model for Evapotranspiration in Tropical Rubber Plantation and Its Response to Influencing Factors. Forests 2025, 16, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121820
Wang J, Lin W, Cheng Q, Ye H, Zhu J, Wu Z, Yang C, Wu B. Applicability of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model for Evapotranspiration in Tropical Rubber Plantation and Its Response to Influencing Factors. Forests. 2025; 16(12):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121820
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingjing, Weiqing Lin, Qiwen Cheng, Huichun Ye, Jinlong Zhu, Zhixiang Wu, Chuan Yang, and Bingsun Wu. 2025. "Applicability of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model for Evapotranspiration in Tropical Rubber Plantation and Its Response to Influencing Factors" Forests 16, no. 12: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121820
APA StyleWang, J., Lin, W., Cheng, Q., Ye, H., Zhu, J., Wu, Z., Yang, C., & Wu, B. (2025). Applicability of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model for Evapotranspiration in Tropical Rubber Plantation and Its Response to Influencing Factors. Forests, 16(12), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121820







