Litter Quality and Soil Microorganisms Mediate Reduced Litter Decomposition Following Understory Vegetation Removal in Forest Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
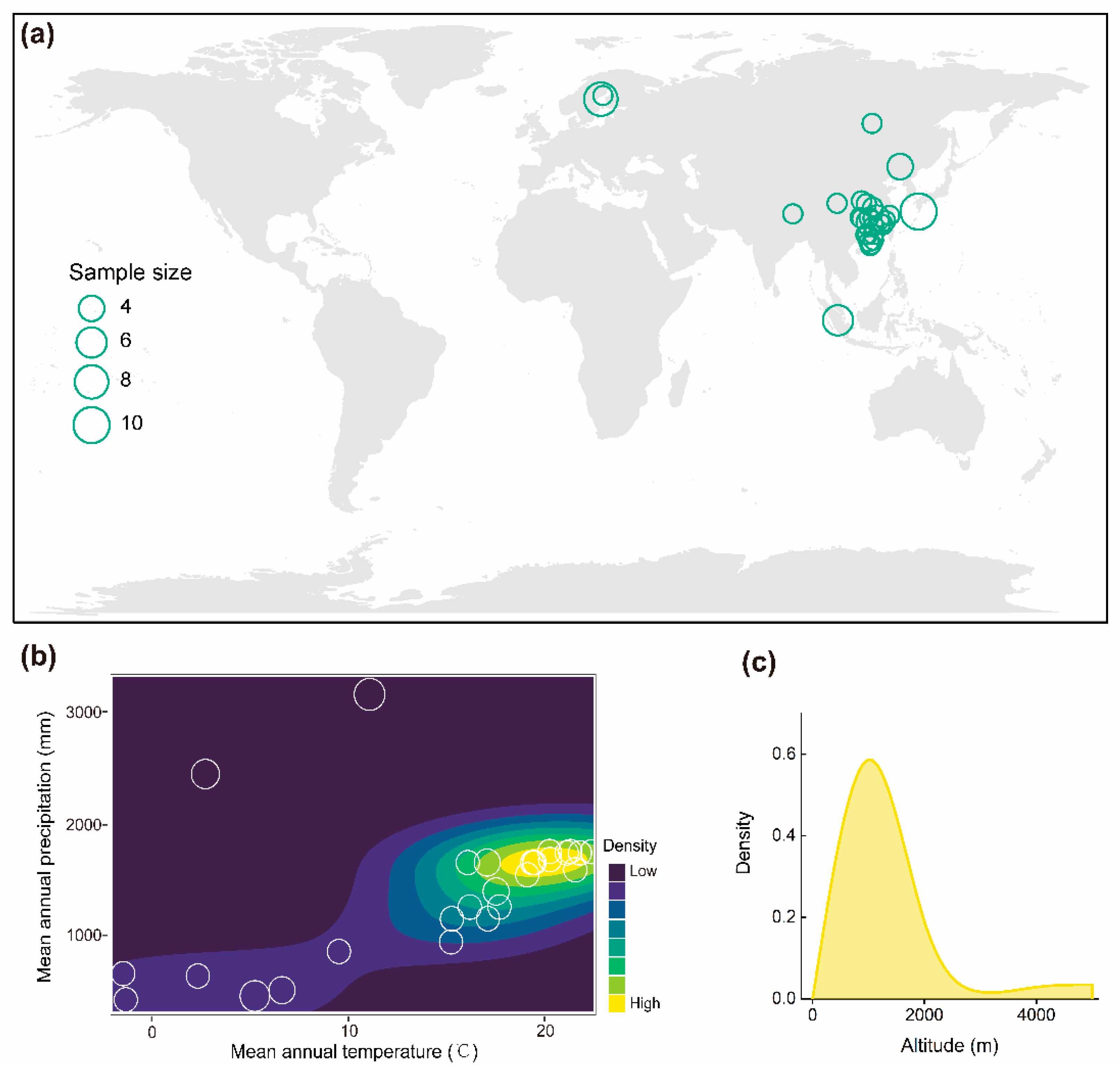
2.1. Data Compilation
| (“understory vegetation removal” OR “understory vegetation management” OR “vegetation removal” OR “understory thinning”) AND (decomposition OR decay OR breakdown OR processing) AND (litter OR leaf OR foliar OR needle) |
- (1)
- Only field experiments were included in this meta-analysis. Laboratory incubations and model-based predictions were excluded to ensure ecological relevance and comparability of the results.
- (2)
- Studies should be designed to incorporate a control retaining understory vegetation and a treatment from which it is removed, with all abiotic and biotic conditions held constant between the groups throughout the experimental period. For experiments involving multiple drivers with shared control, we extracted data only from the understory presence and absence treatments to avoid potential confounding effects.
- (3)
- Only studies that used the litterbag method were included to minimize methodological bias. The initial litter mass and litter type are reported.
- (4)
- At least one decomposition metric, for example, litter mass loss, decomposition rate, residual C, N, P, or lignin, must be reported for a defined period. The decomposition rate coefficient is generally calculated using the single exponential model [38]:where is decomposition time. According to this model, litter mass loss could be used as a proxy for decomposition rate in subsequent analyses.
- (5)
- For each variable, mean values, variability estimates (standard deviation or error), and sample sizes were necessary, and these could be directly reported or extracted from published figures, tables, or supplementary data. When data were presented graphically, Web Plot Digitizer 4.6 (https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer, accessed on 1 August 2025) was used to extract the values.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
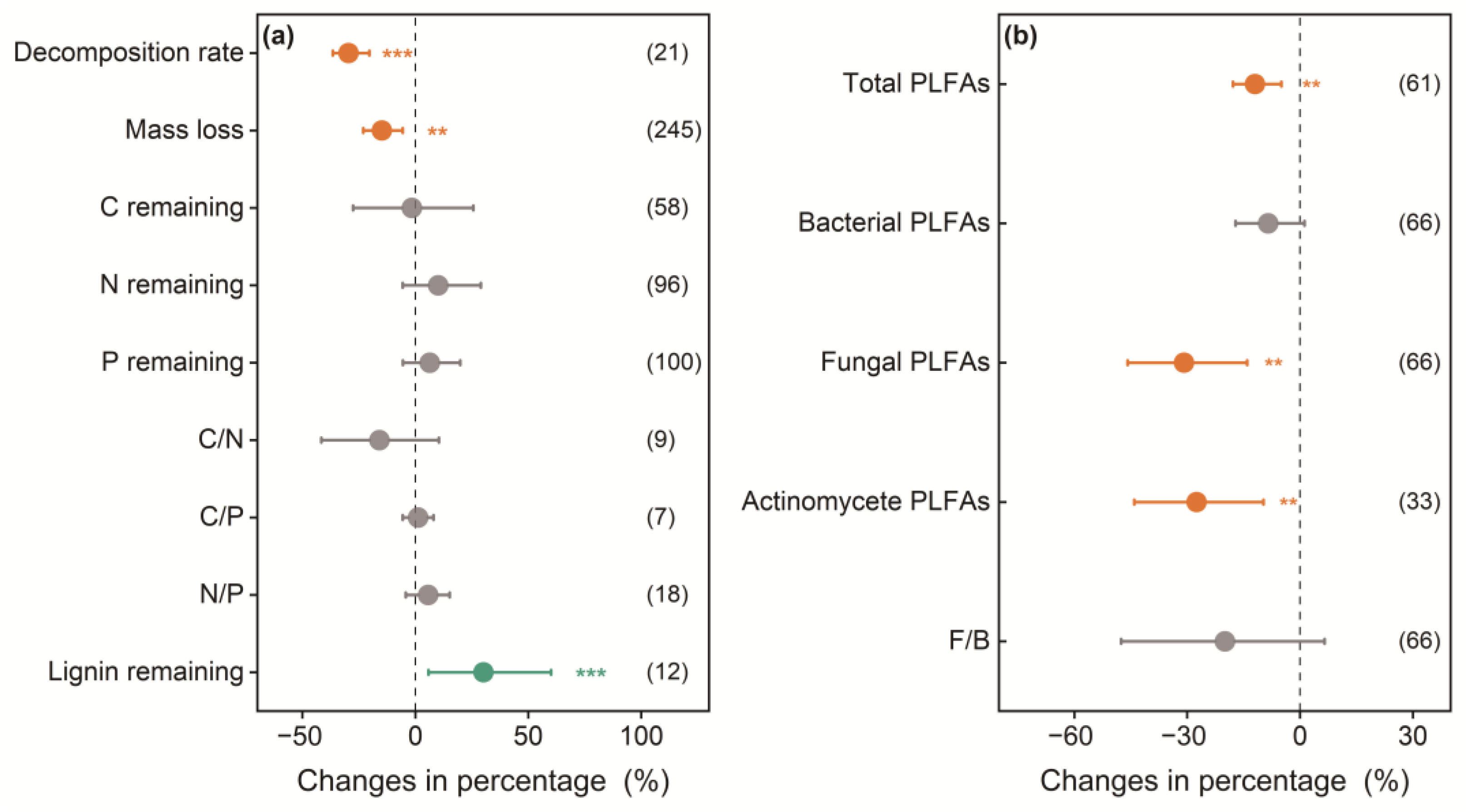
3.1. Overall Effects of Understory Removal
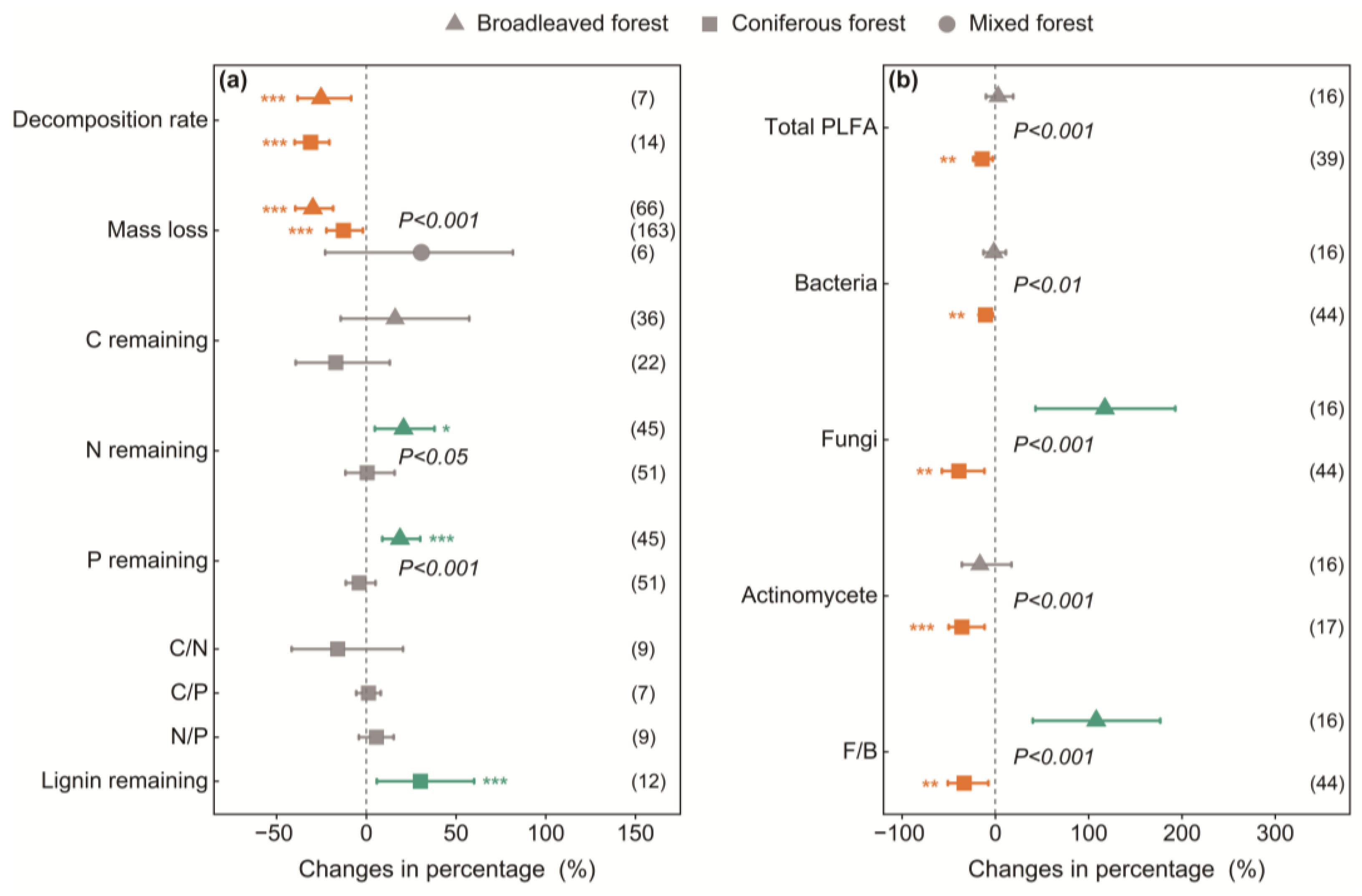
3.2. Variations Among Canopy Types
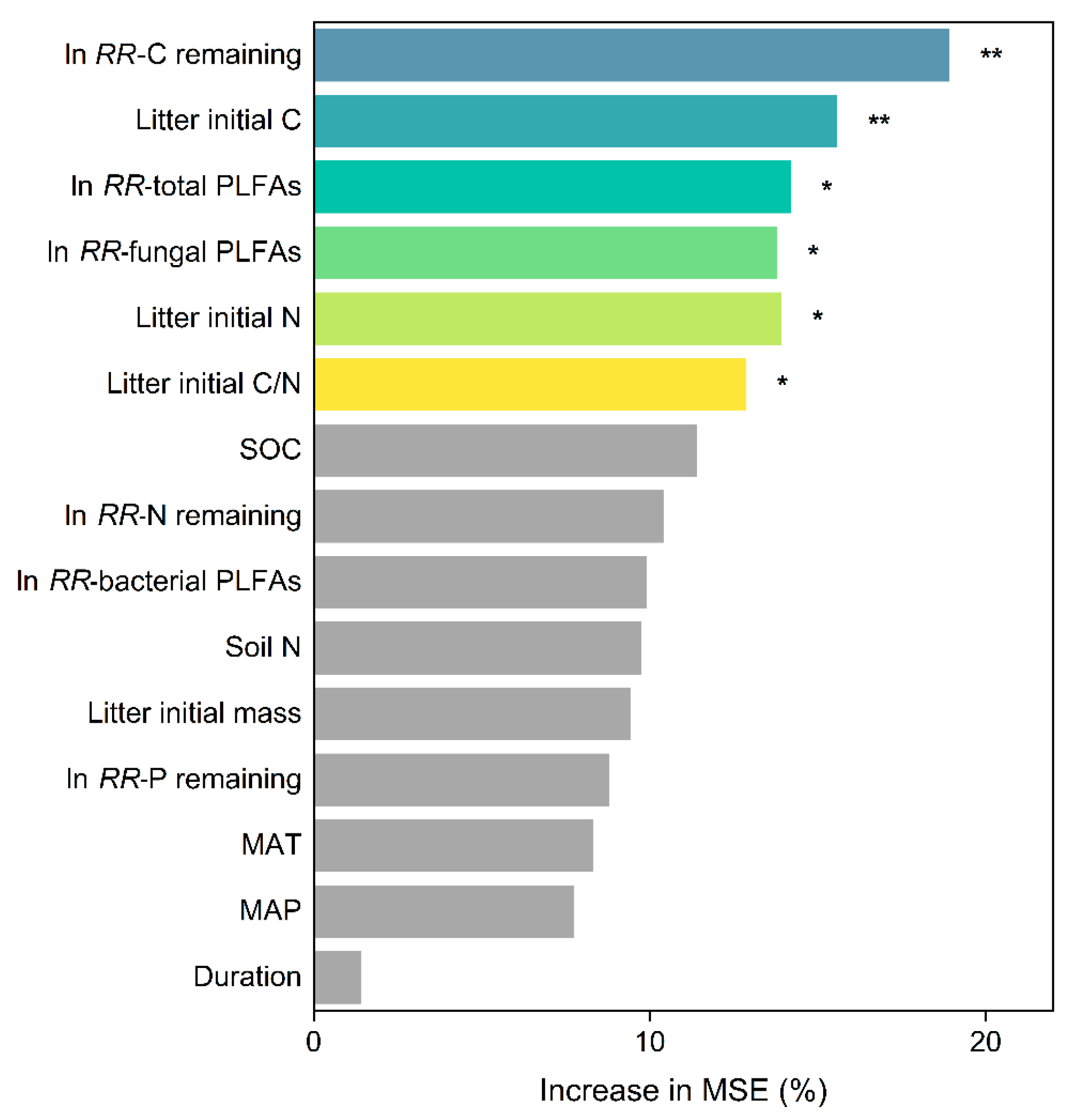
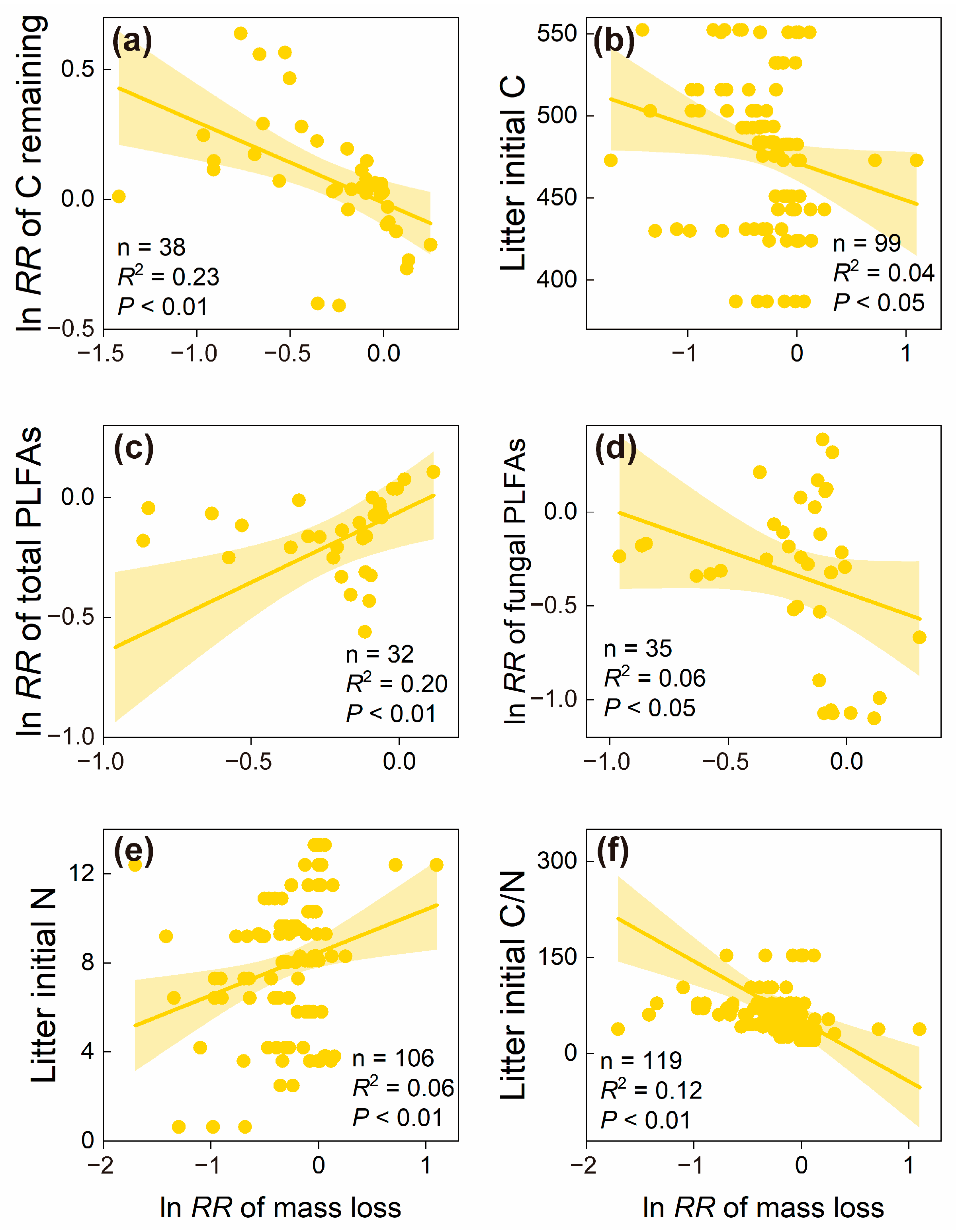
3.3. Factors Driving the Responses of Litter Decomposition to Understory Removal
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Understory Removal on Litter Decomposition and Soil Microorganisms
4.2. Canopy Types Regulate the Effects of Understory Removal
4.3. Mechanisms Related to the Effects of Soil Microorganisms on Litter Decomposition
4.4. Study Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C | Carbon |
| N | Nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| SOC | Soil carbon content |
| PLFAs | Phospholipid fatty acids |
| MAT | Mean annual temperature |
| MAP | Mean annual precipitation |
References
- Nilsson, M.-C.; Wardle, D.A. Understory Vegetation as a Forest Ecosystem Driver: Evidence from the Northern Swedish Boreal Forest. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.; Fu, S. Effects of Understory Removal and Tree Girdling on Soil Microbial Community Composition and Litter Decomposition in Two Eucalyptus Plantations in South China: Understory Removal and Tree-Girdling Effects on Soil Microbial Communities. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.A.; Hunter, M.D.; Kominoski, J.S.; Swan, C.M.; Bradford, M.A. Consequences of Non-random Species Loss for Decomposition Dynamics: Experimental Evidence for Additive and Non-additive Effects. J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, D.; Yang, W.; Tan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q. The Effects of Forest Gaps on Cellulose Degradation in the Foliar Litter of Two Shrub Species in an Alpine Fir Forest. Plant Soil 2015, 393, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, E.E.; Skinner, C.N.; North, M.P.; Estes, B.L. Long-Term Overstory and Understory Change Following Logging and Fire Exclusion in a Sierra Nevada Mixed-Conifer Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Chen, F.; Wan, S.; Sun, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, J. Understory Vegetation Plays the Key Role in Sustaining Soil Microbial Biomass and Extracellular Enzyme Activities. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 4481–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-H.; Shi, F.-X.; Mao, R. Effect of Shrub Encroachment on Leaf Nutrient Resorption in Temperate Wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain of Northeast China. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, D.; De Lombaerde, E.; Perring, M.P.; Hertzog, L.R.; Ampoorter, E.; Maes, S.L.; De Frenne, P.; Ma, S.; Proesmans, W.; Blondeel, H.; et al. The Functional Role of Temperate Forest Understorey Vegetation in a Changing World. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3625–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Yuan, C.; Wu, Q.; Fornara, D.A.; Heděnec, P.; Chen, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, F.; Yue, K. Understory Vegetation Removal Significantly Affected Soil Biogeochemical Properties in Forest Ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. A Meta-Analysis of Understory Plant Removal Impacts on Soil Properties in Forest Ecosystems. Geoderma 2022, 426, 116116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Xu, G.; Fu, S. Effects of Vegetation Removal on Soil Properties and Decomposer Organisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.A.; Liu, W.; Ullah, S.; Duan, H.; Shen, F.; Liao, Y.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Linkages among Leaf Nutrient Concentration, Resorption Efficiency, Litter Decomposition and Their Stoichiometry to Canopy Nitrogen Addition and Understory Removal in Subtropical Plantation. Ecol. Process. 2024, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Fu, S.; Wang, J.; Lambers, H.; Liu, Z. Divergent Responses of Fine Root Decomposition to Removal of Understory Plants and Overstory Trees in Subtropical Eucalyptus urophylla Plantations. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Ten, M.; Yan, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, P. Understory Vegetation Removal Reduces the Incidence of Non-Additive Mass Loss during Leaf Litter Decomposition in a Subtropical Pinus massoniana Plantation. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, N.C.; Stark, J.M.; Newman, G.S.; Hart, S.C. Carbon Control on Terrestrial Ecosystem Function across Contrasting Site Productivities: The Carbon Connection Revisited. Ecology 2019, 100, e02695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppert, K.N.; Niklaus, P.A.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M. Does Species Richness of Subtropical Tree Leaf Litter Affect Decomposition, Nutrient Release, Transfer and Subsequent Uptake by Plants? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasota, J.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Błońska, E. Understory Shrub Root Systems and Their Exudates Improve Soil Biochemistry in Pine Stands in Temperate Climate. Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zou, B.; Li, H.; Li, Z. The Effect of Understory Removal on Microclimate and Soil Properties in Two Subtropical Lumber Plantations. J. For. Res. 2014, 19, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wan, S.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Liang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X. Effects of Understory Removal and Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Microbial Communities in Eucalyptus Plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, A.D.; Knoepp, J.D.; Bradford, M.A. Microbial Communities may Modify How Litter Quality Affects Potential Decomposition Rates as Tree Species Migrate. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Fu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R. Effects of Understory Removal and Litter Addition on Leaf and Twig Decomposition in a Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5004–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Keyhani, A.B.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Teng, M.; Yan, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, P. Leaf Litter Lignin Degradation in Response to Understory Vegetation Removal in a Masson Pine Plantation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1632–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Long, J.R.; Dorrepaal, E.; Kardol, P.; Nilsson, M.-C.; Teuber, L.M.; Wardle, D.A. Understory Plant Functional Groups and Litter Species Identity Are Stronger Drivers of Litter Decomposition than Warming along a Boreal Forest Post-Fire Successional Gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.-L.; Lin, G.-G.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.-T.; Zeng, D.-H. Mixing Effects of Understory Plant Litter on Decomposition and Nutrient Release of Tree Litter in Two Plantations in Northeast China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, M.; Chang, S.X. Effects of Understory Removal, N Fertilization, and Litter Layer Removal on Soil N Cycling in a 13-Year-Old White Spruce Plantation Infested with Canada Bluejoint Grass. Plant Soil 2007, 292, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.; Bowman, W.; Kaufmann, R.; Schmidt, S. A Temporal Approach to Linking Aboveground and Belowground Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, M.; Jing, S. Effects of Different Carbon Inputs on Soil Nematode Abundance and Community Composition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Beggi, F.; Kumar, S. Belowground Carbon Allocation by Trees, Understory Vegetation and Soil Type Alter Microbial Community Composition and Nutrient Cycling in Tropical Eucalyptus Plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ru, J.; Song, J.; Wan, S. Litter Removal Exerts Greater Effects on Soil Microbial Community than Understory Removal in a Subtropical-Warm Temperate Climate Transitional Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, J. Canopy Nitrogen Addition and Understory Removal Destabilize the Microbial Community in a Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Xia, H.; Li, Z.; Cai, X.; Fu, S. Impacts of Litter and Understory Removal on Soil Properties in a Subtropical Acacia Mangium Plantation in China. Plant Soil 2008, 304, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Strickland, M.S.; Liptzin, D.; Bradford, M.A.; Cleveland, C.C. Global Patterns in Belowground Communities. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, L.; Zou, X.; Fu, S. Fungi to Bacteria Ratio: Historical Misinterpretations and Potential Implications. Acta Oecol. 2019, 95, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Reed, S.C.; Keller, A.B.; Nemergut, D.R.; O’Neill, S.P.; Ostertag, R.; Vitousek, P.M. Litter Quality versus Soil Microbial Community Controls over Decomposition: A Quantitative Analysis. Oecologia 2014, 174, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Weedon, J.T.; Aerts, R.; Van Hal, J.R.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Interspecific Differences in Wood Decay Rates: Insights from a New Short-term Method to Study Long-term Wood Decomposition. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Wan, S. Understory Removal Accelerates Nucleic Phosphorus Release but Retards Residual Phosphorus Release in Decomposing Litter of Phyllostachys Edulis in Subtropical China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, Q.; Liu, J. Effects of Lime Application and Understory Removal on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Eucalyptus L’Hér. Plantations. Forests 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S. Energy Storage and the Balance of Producers and Decomposers in Ecological Systems. Ecology 1963, 44, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.; Gee, A.; Liang, G.; Adkins, S. A Quantitative Analysis of Microbial Community Structure-Function Relationships in Plant Litter Decay. iScience 2022, 25, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The Meta-Analysis of Response Ratios in Experimental Ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensgens, G.; Laudon, H.; Peichl, M.; Gil, I.A.; Zhou, Q.; Berggren, M. The Role of the Understory in Litter DOC and Nutrient Leaching in Boreal Forests. Biogeochemistry 2020, 149, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascault, N.; Ranjard, L.; Kaisermann, A.; Bachar, D.; Christen, R.; Terrat, S.; Mathieu, O.; Lévêque, J.; Mougel, C.; Henault, C.; et al. Stimulation of Different Functional Groups of Bacteria by Various Plant Residues as a Driver of Soil Priming Effect. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.G. Litter Decomposition and Nutrient Release from Monospecific and Mixed Litters: Comparisons of Litter Quality, Fauna and Decomposition Site Effects. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chi, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, M.; Guan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. The Response of Soil Respiration to Thinning Was Not Affected by Understory Removal in a Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Plantation. Geoderma 2019, 353, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Wang, X.; Guo, T.; Chai, B. Litter Decomposition of Imperata cylindrica in a Copper Tailing Areas With Different Restoration History: Fungal Community Dynamics and Driving Factors. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 780015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ramos, J.C.; Cale, J.A.; Cahill, J.F.; Simard, S.W.; Karst, J.; Erbilgin, N. Changes in Soil Fungal Community Composition Depend on Functional Group and Forest Disturbance Type. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.L. Lignocellulose Decomposition by Selected Streptomyces Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, B.A.T.D.; Parkinson, D. Actinomycetes as Antagonists of Litter Decomposer Fungi. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, M.; Classen, A.T.; Castro, H.F.; Schadt, C.W. Labile Soil Carbon Inputs Mediate the Soil Microbial Community Composition and Plant Residue Decomposition Rates. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, S. Fast Bacterial Succession Associated with the Decomposition of Quercus Wutaishanica Litter on the Loess Plateau. Biogeochemistry 2019, 144, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Schmidt, I.K.; Zheng, H.; Heděnec, P.; Bachega, L.R.; Yue, K.; Wu, F.; Vesterdal, L. Tree Species Effects on Topsoil Carbon Stock and Concentration Are Mediated by Tree Species Type, Mycorrhizal Association, and N-Fixing Ability at the Global Scale. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 478, 118510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B. Decomposition Patterns for Foliar Litter–A Theory for Influencing Factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.E. Litter Decomposition: What Controls It and How Can We Alter It to Sequester More Carbon in Forest Soils? Biogeochemistry 2010, 101, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Duan, C.; Chen, Q.; Song, X.; Tian, X. Enlarging Interface Reverses the Dominance of Fungi over Bacteria in Litter Decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Gómez, J.; Elosegi, A.; Duarte, S.; Cássio, F.; Pascoal, C.; Romaní, A.M. Differences in the Sensitivity of Fungi and Bacteria to Season and Invertebrates Affect Leaf Litter Decomposition in a Mediterranean Stream. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Lu, Y.; Lyu, M.; Deng, C.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J. Chemical Composition of Soil Carbon Is Governed by Microbial Diversity during Understory Fern Removal in Subtropical Pine Forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüblová, L.; Frouz, J. Contrasting Effect of Coniferous and Broadleaf Trees on Soil Carbon Storage during Reforestation of Forest Soils and Afforestation of Agricultural and Post-Mining Soils. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 290, 112567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, K.; Lyu, Z.; Zhu, J. Microbial Groups and Their Functions Control the Decomposition of Coniferous Litter: A Comparison with Broadleaved Tree Litters. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, L.M.; Hättenschwiler, S.; Milcu, A.; Wambsganss, J.; Shihan, A.; Fromin, N. Tree Species Mixing Affects Soil Microbial Functioning Indirectly via Root and Litter Traits and Soil Parameters in European Forests. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 2190–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Fan, X.; Song, R. Review of Mixed Forest Litter Decomposition Researches. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Berg, B.; Maynard, D.S.; Wieder, W.R.; Wood, S.A. Future Directions: Understanding the Dominant Controls on Litter Decomposition. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palacios, P.; McKie, B.G.; Handa, I.T.; Frainer, A.; Hättenschwiler, S. The Importance of Litter Traits and Decomposers for Litter Decomposition: A Comparison of Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems within and across Biomes. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, P.A.; Jayashankar, M. A Review on Litter Decomposition by Soil Fungal Community. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2016, 11, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osono, T. Functional Diversity of Ligninolytic Fungi Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition. Ecol. Res. 2020, 35, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, D.A.; Bonner, K.I.; Barker, G.M. Linkages between Plant Litter Decomposition, Litter Quality, and Vegetation Responses to Herbivores. Funct. Ecol. 2002, 16, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santschi, F.; Gounand, I.; Harvey, E.; Altermatt, F. Leaf Litter Diversity and Structure of Microbial Decomposer Communities Modulate Litter Decomposition in Aquatic Systems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Schmid, E.; Sterflinger-Gleixner, K.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Roschitzki, B.; Richter, A.; Eberl, L.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Riedel, K. Who Is Who in Litter Decomposition? Metaproteomics Reveals Major Microbial Players and Their Biogeochemical Functions. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Pieristè, M.; Liu, C.; Kenta, T.; Robson, T.M.; Kurokawa, H. The Contribution of Photodegradation to Litter Decomposition in a Temperate Forest Gap and Understorey. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giweta, M. Role of Litter Production and Its Decomposition, and Factors Affecting the Processes in a Tropical Forest Ecosystem: A Review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Xiao, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Nong, X. Litter Quality and Soil Microorganisms Mediate Reduced Litter Decomposition Following Understory Vegetation Removal in Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2025, 16, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121783
Wei X, Xiao J, Hu Y, Liu W, Nong X. Litter Quality and Soil Microorganisms Mediate Reduced Litter Decomposition Following Understory Vegetation Removal in Forest Ecosystems. Forests. 2025; 16(12):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121783
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xinyu, Jie Xiao, Ye Hu, Wei Liu, and Xiang Nong. 2025. "Litter Quality and Soil Microorganisms Mediate Reduced Litter Decomposition Following Understory Vegetation Removal in Forest Ecosystems" Forests 16, no. 12: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121783
APA StyleWei, X., Xiao, J., Hu, Y., Liu, W., & Nong, X. (2025). Litter Quality and Soil Microorganisms Mediate Reduced Litter Decomposition Following Understory Vegetation Removal in Forest Ecosystems. Forests, 16(12), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16121783





