Abstract
The emerald ash borer (EAB; Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) is a deadly pest of ash trees (Fraxinus spp.) in North America. Chemical and biological control methods are already in use against EAB, but additional integrated pest management (IPM) strategies are needed to reduce EAB populations in remote, northerly forests on the edge of the infestation front, such as those in northern Minnesota, USA. One entomopathogenic fungus (EPF) isolate, Beauveria bassiana (Bals.-Criv) Vuill. CFL-A, deployed in autodissemination devices (ADDs) has previously shown promise in reducing EAB population growth. Additionally, EPF has been found to be associated with EAB in Minnesota. This study assessed the suitability of ten Minnesota-indigenous, and one commercial, EPF strains for potential use in ADDs targeting EAB adults. Fungal isolates spanned five genera, including Beauveria, Purpureocillium, Metarhizium, Clonostachys, and Samsoniella. Of those tested, Beauveria pseudobassiana S.A. Rehner and Humber EAB 16.8, Beauveria bassiana GHA, Metarhizium sp. Meta, and Purpureocillium sp. EAB 59-16-2 consistently reduced the mean survival time (MST) and probability of survival over time for EAB adults dropped into an EPF-containing ADD in the laboratory. Furthermore, these fungi were readily recovered from surface-sterilized EAB cadavers. Future ADD field trials using these isolates are warranted to validate their ability to reduce EAB population growth.
Keywords:
EAB; biocontrol; forest ecology; Beauveria; Purpureocillium; Metarhizium; Clonostachys; Samsoniella 1. Introduction
The emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) (EAB) is a destructive wood-boring insect which was inadvertently introduced to North America in the 1990s, likely through the importation of infested wood shipping materials [1]. EAB was first detected in southeast Michigan in 2002 when it was determined to be the cause of a wave of ash tree (Fraxinus spp. (L.)) deaths [2]. The beetle has since spread to 37 states and 6 Canadian provinces [3] killing hundreds of millions of mature ash trees and becoming one of the most destructive introduced forest pests in North America to date [1,4,5]. Larvae of the beetle feed on ash tree phloem, tunneling in a characteristic serpentine shape, severing the vascular transport pathways which sustain the tree. As infestation builds over 3–5 years, the tree will eventually completely succumb [6]. Although some Asian Fraxinus species are resistant to the feeding of EAB, North American ash trees largely lack substantial resistance, and the beetle can cause up to 99% mortality in highly infested stands [7]. EAB spreads locally through the flight of adult beetles, and it has spread to new distant locations via the transportation of infested firewood and nursery stock [5].
Management of EAB has historically involved a multifaceted integrated pest management approach: sanitary measures like removal of infested trees and preemptive removal of ash; regulatory measures such as quarantines and restriction of movement of ash materials; chemical insecticide applications; and importation of biological control agents [1]. Systemic insecticides like emamectin benzoate have been of critical importance for preserving higher value trees in mostly urban and suburban areas [1,5]. Several Asian parasitoid wasps have been released throughout infested areas of the United States, and alongside woodpecker foraging they have been contributing to the mortality of EAB in natural forest settings [8,9].
Although the imported biological control agents have proven to be successful at providing some level of EAB control in natural settings, they are not without limitations. One of the wasps—Tetrastichus planipennisi Yang—for example, has a relatively short ovipositor and therefore seems to only be effective at parasitizing EAB larvae in trees with thin bark. It is therefore regarded as more useful in managing EAB in younger stands of ash < 16 cm diameter [9]. Yet another parasitoid, Spathius agrili Ashmead, seems unable to persist in northern regions of North America due to climatic incompatibility [9]. Therefore, a need remains for additional management tactics which can slow the spread of EAB into natural mature ash stands across northern North America, where other forms of management may be less feasible.
The protection of ash trees in natural stands is especially important in the Great Lakes region, where black ash (F. nigra Marsh.) is a dominant overstory tree in marshy, hydrologically sensitive areas. Minnesota, for example, is home to expansive stands of black ash, most of which reside in the central and northern portions of the state where EAB is still building in numbers and expanding its range [10]. Due to the sheer number of ash trees at risk, and the relatively yet healthy status of those trees, Minnesota should be prioritized for the development and implementation of novel EAB management tools.
Biological control using entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) could be a useful alternative in managing EAB populations in these natural settings [1]. Early surveys of natural enemies of EAB in Michigan found that <2% of larvae and prepupae were infected with EPF Beauveria bassiana (Bals.-Criv) Vuill. and Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschn.) Sorokin [11]. Subsequent studies showed that isolates from several EPF genera associated with EAB in Michigan and Ontario are virulent against the adult beetles. Among these were Beauveria spp., Metarhizium spp., Cordyceps (form. Isaria) farinosa (Holmsk.) Kepler, B. Shrestha & Spatafora, and Purpureocillium lilacinum (Thom) Luangsa-ard, Houbraken, Hywel-Jones & Samson [12,13,14,15].
Autodissemination devices (ADDs) are a promising means for effectively deploying EPF in biological control settings and autodissemination systems have shown promise in controlling several insect pests, including EAB [16,17,18,19,20,21]. ADDs targeting EAB are green Lindgren funnels which are hung in the canopy of an infested ash tree. Baited with semiochemical lures, ADDs are attractive to adult EAB. The surfaces of the ADD are coated with a non-stick polymer, which prevents the beetles from successfully landing, causing them to fall through the series of funnels to a collection cup containing the EPF. Beetles must walk over a fungus colonized substrate to escape the ADD and exit through a hole. From there, the contaminated EAB may further spread EPF spores during mating [22]. A Canadian isolate B. bassiana CFL-A was found to be especially effective against EAB when deployed in ADDs in Quebec municipalities, causing rates of infection up to 40% and a significant decrease in EAB population growth rate over the course of a 3-year period [19].
Although these results are promising, there are important factors to consider for ADD-mediated fungal biocontrol, such as the origin of the fungal strain and the strain’s climatic compatibility with the target release area. It has been shown that EPF isolated from a given target pest are generally more virulent toward that pest than strains isolated elsewhere [23,24]. Furthermore, EPF strains indigenous to the target release area are considered more climatically competent than strains sourced from other geoclimatic regions [25,26,27].
A recent study isolated and identified 1126 fungal isolates associated with EAB larval galleries from across Minnesota [28]. Of those identified, 30% were categorized as canker pathogens, several of which have since been shown to cause significant cankers in ash trees [29]; 8% were decay fungi, with some implicated in the loss of structural integrity in infested ash trees [30]; and another 8% were entomopathogens. EPF identified in that study have since been assayed against EAB eggs, and some possess significant ovicidal activity [24]. Until now, however, this collection of Minnesotan EPF had not been used in studies against the adult stage of EAB.
The aim of the current study was to (i) screen several isolates of EAB-associated EPF for their biological control potential when used in ADDs targeting EAB adults; and (ii) carry out Koch’s postulates by incubating EAB cadavers to encourage mycosis and using microscopy to compare emerged fungi to pure cultures of the inoculated strains.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiment was first performed in June 2024 (Experiment 1) and was repeated in June 2025 (Experiment 2).
2.1. Insects
EAB adults were reared out of infested green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica Marshall) bolts. One infested tree was harvested in both the spring of 2024 and 2025 in the city parks of Minnetonka, Minnesota. Trees with obvious woodpecker damage along the main stem and little to no surviving foliage were selected. A draw blade was used to carefully strip the bark off an area on the lower bole to confirm the presence of EAB prepupae in each tree. Felled trees were segmented into logs (≤25 cm diameter, ≤53 cm length) and were stored at 4 °C before being moved to rearing tubes.
Rearing tubes were constructed, consisting of a building form tube (30 cm diameter, 60 cm length; Quikrete Holdings Inc., Atlanta, GA, USA) capped on either end with a 19 L bucket lid (United Solutions Inc., Leominster, MA, USA). One of the bucket lids for each rearing tube was modified with two cutouts: a semicircle hole covered with black felt mesh to allow for air circulation, and a circular one that allowed attachment of a metal mason jar lid. A clear plastic collection cup was screwed into each of the mason jar lids. An infested ash log was placed in each rearing tube, suspended above the bottom of the tube using Styrofoam™ (DuPont de Nemours Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA) blocks to allow clearance for emerging beetles. Rearing tubes were kept at 25 °C in a laboratory room with windows providing light.
Beetles emerged approximately 3–4 weeks after logs were first placed in the rearing tubes, and due to their affinity for sunlight, gathered in the clear collection cups. Mesh butterfly cages were then used to hold EAB en masse in a greenhouse for two days of maturation feeding on fresh ash leaves prior to being used in the experiments.
2.2. Entomopathogen Identification
Eleven isolates, spanning 5 genera, were used in the experiment (Table 1). Seven of the isolates were obtained from the investigation of Held et al., 2021 [28]: Clonostachys sp. EAB 8.8 (GenBank PX459604), Clonostachys sp. EAB 50-14 (GenBank PX459605), Beauveria pseudobassiana S.A. Rehner and Humber EAB 16.8 (GenBank PX459607), B. pseudobassiana EAB 53-5 (GenBank PX459610), Purpureocillium sp. EAB 50-11 (GenBank PX459608), Purpureocillium sp. EAB 50-15 (GenBank PX459609), and Samsoniella sp. 58-18 (GenBank PX459611). Two isolates were isolated from mycosed EAB larvae collected in the city of Minnetonka, Minnesota: Purpureocillium sp. EAB 59-16-2 (GenBank PX459612) and Purpureocillium sp. Hill 23-1 (GenBank PX459613). The isolate Metarhizium sp. Meta (GenBank PX459614) was donated from the collection of a Minnesota-based fungus cultivation business called Myco-Operative. Lastly, a commercially available strain of Beauveria bassiana GHA (GenBank PX459606) was obtained from the product BotaniGard® 22WP (LAM International Corporation Pte Ltd., Butte, MT, USA). Beauveria bassiana GHA was included as a positive control group, as this isolate has documented virulence against EAB adults [31,32,33].

Table 1.
Fungal isolates used in the autocontamination experiments. Initial identifications were made through Sanger sequencing of the ITS region of ribosomal rDNA and comparing to the NCBI BLASTn database. GenBank accession numbers are listed for sequences used.
The internal transcribed spacer region of rDNA (ITS) was sequenced for each of the fungal isolates using the universal primers ITS1F and ITS4. Sanger sequencing was performed, and consensus sequences were assembled with the MAFFT v7.490 alignment tool in Geneious v.11.1.5. The NCBI BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastn&BLAST_SPEC=GeoBlast&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch, accessed on 16 November 2025) algorithm was then used to compare the consensus sequences to those from known type material in GenBank. For isolates that couldn’t be identified to species level based off the ITS region genus level was used instead.
2.3. Inoculum Pouches
Fungal isolates were stored in slant tubes of potato dextrose agar at 4 °C. Each isolate was transferred to a bag of sterile barley grains which had been autoclaved in a nutrient broth (1000 mL water; 25 g dextrose—Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA; 25 g Bacto™ malt extract—Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). After one week, the colonized barley was assembled into inoculum pouches using sterile cheesecloth (Grade 10) sinched between a bamboo embroidery hoop (7.6 cm diameter). Assembled inoculum pouches were incubated for 1 week in darkness to allow for the fungus to completely cover the cheesecloth. Inoculum pouches were weighed prior to use in bioassays to ensure consistency of weights across treatments (59.46 ± 2.04 g). Additionally, a swab was taken using a sterile cotton tipped applicator (Puritan Medical Products Company LLC, Guilford, ME, USA) from each pouch prior to use, and those swabs were vortexed in microcentrifuge tubes containing 1 mL of a sterile solution of water and 0.02% Tween 20. A pipette was used to transfer 100 μL of the resulting spore suspension to a Petri dish of water agar (15 g agar—Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA; 1000 mL water), and a cell spreader was used to evenly coat the surface of the agar. Plates were incubated in the dark and evaluated under a light microscope (400×) 24 h post-inoculation for viability. Three hundred conidia were examined for each water agar plate, and a percent viability was calculated (% viable = number of viable conidia/300 conidia × 100). A conidium was considered viable if a germ tube was observed under the microscope. Only pouches with >75% viability were used in bioassays.
2.4. Autodissemination Device-Mediated Inoculation of Beetles
For each treatment, an inoculum pouch was seated inside the collection cup of a green plastic (540 nm, 57% reflectance) 12-piece multifunnel trap (courtesy of Joe Francese, USDA APHIS, Riverdale, MA, USA). The multifunnels were coated in a dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, 30% w/w) which makes the trap surfaces slippery and beetles fall to the collection cup [34]. Multifunnels equipped with their respective inoculum pouches were hung in a greenhouse for the experiment. A multifunnel with an empty collection cup was used for the negative control group.
Experimental procedure was adapted from Lyons et al., 2012 [16]. For each treatment, 15 EAB (n = 180) were dropped from the highest funnel of a multifunnel trap into the collection cup. Beetles were held within the collection cup for 3 min prior to transferring them to incubation containers with sterile forceps. Incubation containers consisted of black plastic rectangular containers (22.5 cm × 15.5 cm × 5.5 cm) modified with two circular openings (2 cm diameter) in the lid covered with cheesecloth to allow airflow. A small hole was made in the short wall of each container to allow the insertion of an ash petiole. Fifteen beetles of the same treatment were kept within one incubation container, and all incubation containers were placed within an environmental growth chamber maintained at 25 °C, 75% RH, and 16:8 photoperiod. Each incubation container was provided with a fresh white ash (F. americana (L.)) leaf as needed, inserted through the hole in the container wall. Leaves were kept fresh for an extended period by inserting the protruding petiole into a falcon tube of water (Figure S1).
2.5. Recovery of Inoculum from Infected Beetle Cadavers
Incubation containers were checked daily for dead beetles. Cadavers were collected into sterile microcentrifuge tubes and stored in a freezer (−18 °C) until processing. Occasionally, when checking the containers, a beetle would be inadvertently crushed when resecuring the lid. Crushed individuals were removed from the experiment and not used in downstream analysis.
Cadavers were surface sterilized following the protocol outlined in Crippen & Sheffield, 2006 [35]. Briefly, each cadaver was transferred to a microcentrifuge tube containing 1 mL of 20% hydrogen peroxide with constant agitation for 2 min. Next, the cadavers were transferred to a microcentrifuge tube of sterile 0.02% Tween 20 solution and dipped three times. Cadavers were then placed on sterile Grade 1 Whatman® filter paper (Danaher Corporation, Washington, DC, USA) to remove any excess moisture before being transferred to an incubation container.
For Experiment 1, surface-sterilized cadavers were incubated inside microcentrifuge tubes and kept in darkness at room temperature for 2 weeks. Due to relatively low levels of fungal recovery from positive controls, an alteration was made in Experiment 2 so that sterilized cadavers were incubated on a plate of water agar covered with Parafilm and kept in darkness at room temperature for 2 weeks. After 2 weeks, cadavers were inspected under a stereoscope for fungal presence. Fungi were identified to genus level based on macro- and microscopic morphological characteristics for each of the fungal genera [36,37,38,39,40] and compared to reference cultures of the inoculated fungi grown on PDA. Cadavers were considered positive for fungal presence if conidiophores and conidia consistent with those of their respective inoculated fungus were observed on the insect integument.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed in RStudio v3.6.0. Each experimental year was analyzed separately. The mean survival time (MST) of all treatment groups were compared using one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05). If differences were detected between MST of treatment groups, a post hoc multiple comparison was performed using Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test. Significance letters were assigned to treatment groups using the “multcompView” package (RStudio v3.6.0). Log-rank tests were performed, using the “survival” package (RStudio v3.6.0), comparing each treatment group to the negative control and GHA treatment groups for that respective experimental year. Additionally, the negative control groups for each experimental year were compared using a log-rank test. The alpha level for all log-rank tests was adjusted for multiplicity to avoid Type I error using the Bonferroni correction (α/m = 0.05/24 = 0.00208). Survival curves were constructed using the “ggplot2”, “survminer”, and “survival” packages (RStudio v3.6.0). Rate of fungal recovery was calculated for each treatment group as the percentage of beetles positive for their inoculated fungus within a treatment group.
3. Results
An initial log-rank test indicated a significant difference in survival over time between the negative control groups of each experimental year (X2(1) = 19.6, p = 9 × 10−6); therefore, Experiment 1 and Experiment 2 were treated separately for analysis.
3.1. Experiment 1
The MST results for each of the Experiment 1 treatment groups are summarized in Figure 1. Treatments ranged from 13.73 ± 3.65 days for the control to 4.57 ± 0.65 days for GHA. Other treatments varied; EAB 16.8 (4.92 ± 1.12 days); Meta (5.43 ± 1.40 days); EAB 59-16-2 (7.56 ± 1.15 days); EAB 50-11 (11.13 ± 2.33 days); Hill 23-1 (11.86 ± 2.96 days); EAB 8.8 (15.50 ± 2.58 days); EAB 58-18 (10.27 ± 4.70 days); EAB 53-5 (9.80 ± 5.88 days); EAB 50-15 (10.64 ± 3.79 days); EAB 50-14 (17.93 ± 2.50 days). One-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) indicated that there were significant differences in MST between treatment groups (F(11,162) = 24.89, p < 2 × 10−16). Tukey’s HSD (α = 0.05) revealed that MST significantly differed from that of the negative controls for treatment groups GHA (p < 1 × 10−7), EAB 16.8 (p < 1 × 10−7), Meta (p < 1 × 10−7), EAB 59-16-2 (p = 1.16 × 10−5), EAB 53-5 (p = 0.036), and EAB 50-14 (p = 0.021); however MST was not significantly different from the negative controls for treatments EAB 50-11 (p = 0.50), Hill 23-1 (p = 0.90), EAB 8.8 (p = 0.95), EAB 58-18 (p = 0.11), and EAB 50-15 (p = 0.26). Additionally, MST did not significantly differ between the GHA group and treatments EAB 16.8 (p = 1.0) and Meta (p = 1.0).
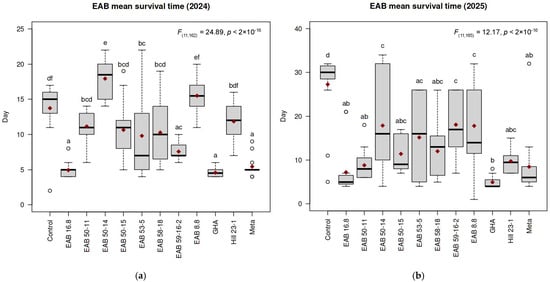
Figure 1.
Mean survival time (MST) values of emerald ash borer (EAB; Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) adults post-exposure to entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) via an autodissemination device (ADD) varied depending on the fungal isolate: (a) Experiment 1 in 2024; (b) Experiment 2 in 2025. For both panels, fungal strain names are listed along the x-axes. Y-values indicate the day post-exposure to the ADD. Red diamonds indicate MST for each treatment. Bold black lines represent median survival times. Circles represent outliers. The listed p-values were obtained from ANOVA of MST values across all treatment groups. Significance letters correspond to Tukey’s HSD test comparing MST values across treatments and are listed directly above their respective boxes.
Results from the log-rank tests (α = 0.00208) for Experiment 1 are as follows: six of the treatments significantly differed in probability of survival over time from the negative control group, including GHA (X2(1) = 23.6, p = 1 × 10−6), EAB 16.8 (X2(1) = 23.7, p = 1 × 10−6), Meta (X2(1) = 24.9, p = 6 × 10−7), EAB 59-16-2 (X2(1) = 26.4, p = 3 × 10−7), EAB 50-11 (X2(1) = 12.8, p = 3 × 10−4), and EAB 50-14 (X2(1) = 13.4, p = 3 × 10−4); whereas five of the treatment groups did not significantly differ from the negative control group, including EAB 50-15 (X2(1) = 2.9, p = 0.09), EAB 53-5 (X2(1) = 1.2, p = 0.3), EAB 58-18 (X2(1) = 1.4, p = 0.2), EAB 8.8 (X2(1) = 3.5, p = 0.06), and Hill 23-1 (X2(1) = 5, p = 0.03). Kaplan–Meier survival curves for Experiment 1 are depicted in Figure 2.
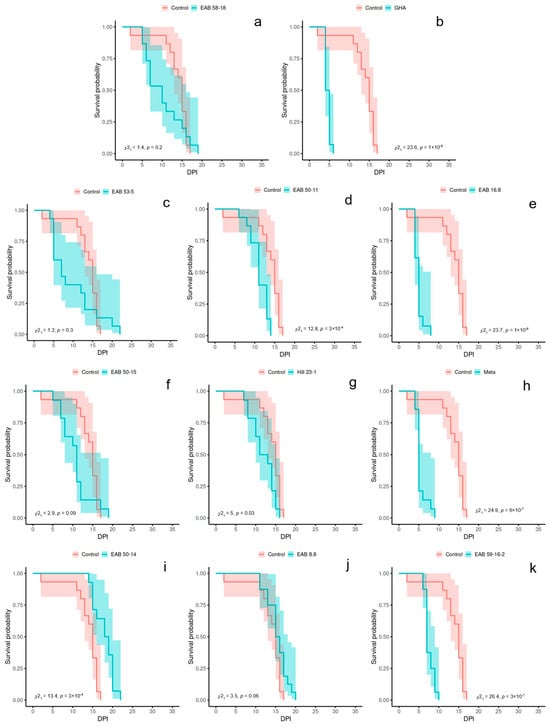
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for Experiment 1 (2024 year) represent the survival probability over time for emerald ash borer adults exposed to entomopathogenic fungus via an autodissemination device. X-values are days post inoculation (DPI). Each panel depicts the negative control group as a red line and a fungal treatment as the blue line: (a) EAB 58-18, (b) GHA, (c) EAB 53-5, (d) EAB 50-11, (e) EAB 16.8, (f) EAB 50-15, (g) Hill 23-1, (h) Meta, (i) EAB 50-14, (j) EAB 8.8, (k) EAB 59-16-2. Listed p values correspond to the log-rank test (α = 0.00208) comparing each fungal isolate to the negative control group. 95% confidence intervals are represented as shading around each survival line.
The inoculated fungus was successfully recovered from all treatment groups in Experiment 1, with the highest rate of recovery from the EAB 59-16-2 group at 62.5% of beetles positive for Purpureocillium (Table 2). None of the inoculated fungi were recovered from negative control beetles, although presumably saprophytic fungi in the genera Aspergillus Micheli ex Haller and Penicillium Link were observed.

Table 2.
Mean survival time (MST), log-rank p-value, and rate of fungal recovery for emerald ash borer (EAB) adults in each fungal treatment post-exposure via an autodissemination device across two experimental years. Significant log-rank p values (α = 0.00208) are indicated by a (**) next to the value.
3.2. Experiment 2
The MST for each treatment group in Experiment 2 is presented in Figure 1. Maximum MST for 2025 was 27.27 ± 8.08 days for the negative control group, and the minimum MST observed was 4.93 ± 1.28 days for the GHA group. Other treatments included EAB 16.8 (7.2 ± 5.68 days); Meta (8.47 ± 7 days); EAB 59-16-2 (18.07 ± 6.83 days); EAB 50-11 (8.8 ± 3.45 days); Hill 23-1 (9.71 ± 2.67 days); EAB 8.8 (17.8 ± 9.43 days); EAB 58-18 (12 ± 5.89 days); EAB 53-5 (15.15 ± 9.74 days); EAB 50-15 (11.4 ± 4.15 days); EAB 50-14 (17.87 ± 11.45 days). Results of the one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) indicated differences in MST between treatment groups (F(11,165) = 12.17, p < 2 × 10−16). Tukey’s HSD (α = 0.05) showed that the MST for all fungal treatment differed from that of the negative controls: GHA (p < 1 × 10−7), EAB 16.8 (p < 1 × 10−7), Meta (p < 1 × 10−7), EAB 59-16-2 (p = 0.018), EAB 50-11 (p < 1 × 10−7), Hill 23-1 (p < 1 × 10−7), EAB 8.8 (p = 0.013), EAB 58-18 (p = 7 × 10−6), EAB 53-5 (p = 4.93 × 10−4), EAB 50-15 (p = 2 × 10−6), EAB 50-14 (p = 0.014). In addition, the MST did not differ from GHA for treatment groups EAB 16.8 (p = 0.99), Meta (p = 0.96), EAB 50-11 (p = 0.93), Hill 23-1 (p = 0.78), EAB 58-18 (p = 0.19), and EAB 50-15 (p = 0.31).
The log-rank test (α = 0.00208) results for Experiment 2 are as follows: the probability of survival over time differed from that of the negative controls for nine fungal treatments, including GHA (X2(1) = 30, p = 4 × 10−8), EAB 16.8 (X2(1) = 26.3, p = 3 × 10−7), Meta (X2(1) = 14.2, p = 2 × 10−4), EAB 59-16-2 (X2(1) = 17, p = 4 × 10−5), EAB 50-11 (X2(1) = 24.2, p = 9 × 10−7), Hill 23-1 (X2(1) = 22.6, p = 2 × 10−6), EAB 58-18 (X2(1) = 21.6, p = 3 × 10−6), EAB 53-5 (X2(1) = 17.3, p = 3 × 10−5), and EAB 50-15 (X2(1) = 21.3, p = 4 × 10−6); however, two of the fungal treatments did not differ from the negative controls, including EAB 8.8 (X2(1) = 5.6, p = 0.02) and EAB 50-14 (X2(1) = 0.3, p = 0.6). Kaplan–Meier curves for Experiment 2 are represented in Figure 3.
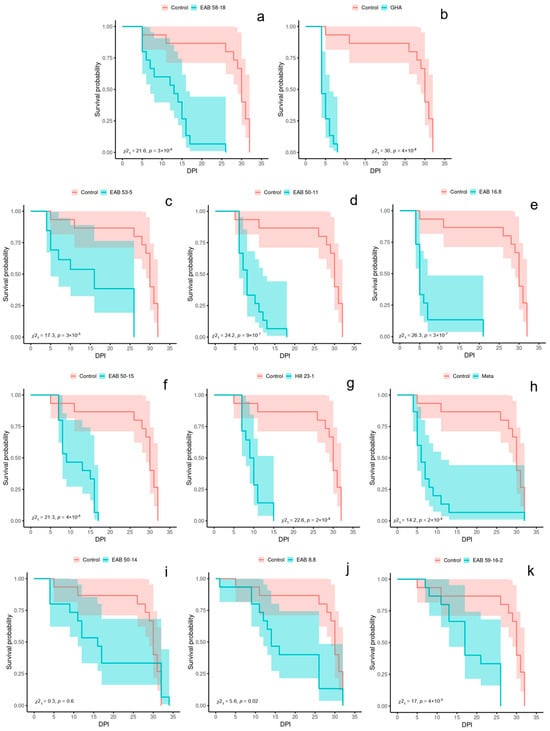
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for Experiment 2 (2025 year) represent the survival probability over time for emerald ash borer adults exposed to entomopathogenic fungus via an autodissemination device. X-values are days post inoculation (DPI). Each panel depicts the negative control group as a red line and a fungal treatment as the blue line: (a) EAB 58-18, (b) GHA, (c) EAB 53-5, (d) EAB 50-11, (e) EAB 16.8, (f) EAB 50-15, (g) Hill 23-1, (h) Meta, (i) EAB 50-14, (j) EAB 8.8, (k) EAB 59-16-2. Listed p values correspond to the log-rank test (α = 0.00208) comparing each fungal isolate to the negative control group. 95% confidence intervals are represented as shading around each survival line.
The inoculated fungi were recovered from cadavers in all the fungal treatment groups, with 100% rate of recovery for treatment groups EAB 50-15, EAB 50-11, Hill 23-1, EAB 58-18, and EAB 8.8 (Table 2). None of the inoculated fungi were observed on negative control cadavers.
4. Discussion
Emerald ash borer adults exposed in the lab to one of 11 strains of Minnesota-sourced EPF via an ADD containing a myceliated barley grain inoculum pouch varied in MST and probability of survival over time. When compared to the negative control group, five of the fungal isolates significantly decreased the MST of EAB adults post-exposure across both experimental years: B. bassiana GHA, B. pseudobassiana EAB 16.8, Metarhizium sp. Meta, Purpureocillium sp. EAB 59-16-2, and B. pseudobassiana EAB 53-5 (Figure 1). The positive control strain B. bassiana GHA resulted in the lowest MST for experiments: 4.57 and 4.93 days for Experiment 1 and Experiment 2, respectively. While former studies demonstrating the virulence of B. bassiana GHA against EAB adults have used a dip inoculation method, our study used an ADD-mediated inoculation. Therefore, a direct comparison of MST values is not feasible; however, the observed MST values for the B. bassiana GHA group in this study are similar to those of previous studies reporting MST of 4.6, 4.2, and 6.93 days for EAB adults exposed to GHA at concentrations of 106, 107, and 2 × 107 conidida/mL, respectively [12,14]. The highest MST value was observed for the negative control group in Experiment 2 at 27.27 days; however, it is interesting that in Experiment 1 the highest MST was for the Clonostachys sp. EAB 50-14 group at 17.93 days.
Four fungi significantly decreased the probability of EAB survival over time across both experiments according to the log-rank tests comparing fungal groups to the negative control: B. bassiana GHA, B. pseudobassiana EAB 16.8, Metarhizium sp. Meta, and Purpureocillium sp. EAB 59-16-2 (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Although all fungi significantly decreased the probability of EAB survival in Experiment 2, only four fungi did so in Experiment 1, presumably due to the relatively short lifespan of control beetles in Experiment 1 masking some of the effects of the slower-acting fungi. These four successful fungi also significantly decreased the MST of EAB adults across both experiments, implicating them as the most promising isolates tested in this study.
There was a significant difference in probability of survival between the negative control groups of each experiment, with the MST of the Experiment 2 control group (27.27 ± 8.08 days) being more than twice that of the Experiment 1 controls (13.73 ± 3.65 days). The authors can only speculate as to the reason for this difference in negative control survival between experiments, since many external factors could have influenced EAB adult lifespan. For Experiment 1, logs were harvested on March 8 and stored for 77 days; however, for Experiment 2, logs were harvested on April 16 and stored for only 29 prior to use. We recognize the possibility that a longer duration of cold storage in Experiment 1 may have some detrimental effects on the lifespan of EAB adults which emerged from those logs, as this has been shown in other insect systems [41,42]. However, it has been reported that while a longer period of cold storage results in lower numbers of EAB adults emerging from logs, it does not affect the fat and water content in those resulting adults, indicating that increased duration of cold storage may not actually decrease fitness of emerging EAB adults [43]. Furthermore, adult Buprestids have been found to emerge from wood construction materials several years after installation, suggesting that some Buprestids can withstand extended periods of delayed emergence [43,44].
Another possible factor which could have driven the difference in survival between the negative control groups is the nutrient quality of ash leaves provided during incubation. Although the leaves provided to beetles were picked from the same stand of ash trees each experimental year, the authors noted that in 2024 the leaves for Experiment 1 were generally lower quality (i.e., lighter green color and slightly robust texture). It is known that food nutrient quality, or the ratio of proteins to carbohydrates, can affect the expected lifespan of insects [45,46]. Furthermore, it is known that readsorption of nitrogen can occur throughout the lifespan of a leaf, particularly when that leaf is shaded [47,48]. Ash leaves fed to beetles for the current study were harvested at 784 growing degree days (GDD) in 2024 for Experiment 1, whereas for Experiment 2 they were harvested at 562 GDD in 2025. Both the difference in physiological maturity of leaves between years, as well as the physical location of harvested leaves within the canopy (i.e., full sun vs. shaded) therefore could have affected the nutrient composition of food for the EAB, driving differences in negative control longevity. Additionally, differences in factors such as EAB microbiome composition could have affected the immune responses between individuals, as this has been observed to play a role in entomopathogen success in other systems [49,50].
The authors additionally recognize that EAB used in each experimental year were sourced from different ash trees. Differences in the survival of negative control beetles could have occurred due to variation between trees in factors affecting larval development and/or overwintering success of EAB. Some of these factors include intraspecific competition, exposure to extreme cold, and extent of tree defense response [8]. These factors are difficult to control, and the authors of this study chose rather to analyze each experimental year separately.
All inoculated fungi were successfully recovered from surface-sterilized cadavers across both years, indicating that these fungi can infect EAB adults (Table 2, Figure 4). None of the inoculated fungal genera were observed on any of the negative control cadavers. In each experimental year, surface-sterilized EAB cadavers were incubated to encourage mycosis; however, the incubation container was different between years. In Experiment 1 cadavers were incubated in a sterile microcentrifuge tube, while in Experiment 2 cadavers were incubated on a plate of water agar. While there were some cadavers which mycosed in Experiment 1, there was a notable increase in the successful recovery of the inoculated fungi by using the water agar incubation method, presumably due to the higher relative humidity and availability of water [51]. The water agar method of fungal recovery from surface-sterilized insect cadavers is therefore recommended.
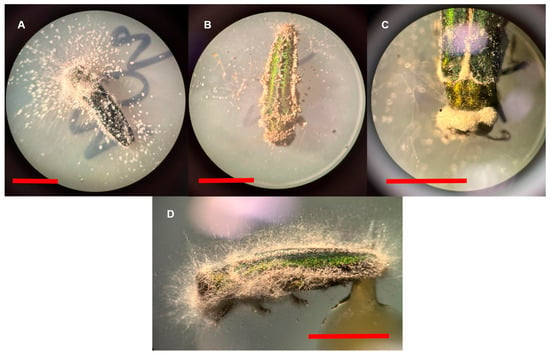
Figure 4.
Emerald ash borer cadavers showing signs of infection from several entomopathogenic fungi: (A) Clonostachys sp. EAB 8.8; (B) Metarhizium sp. Meta; (C) Beauveria bassiana GHA; (D) Purpureocillium sp. EAB 50-11. Red scale bars represent 5 mm.
This study supports previous findings showing that entomopathogenic fungal genera such as Beauveria, Metarhizium, and Purpureocillium are virulent against EAB adults [12,13,14,15]. For example, EAB adults dipped in conidial suspensions of B. bassiana isolates have shown MST values varying from 4.2–9.09 days, depending on the isolate and spore concentration used [12,14]. Additionally, EAB adults exposed to B. bassiana CFL-A via an ADD resulted in MST of 7.4 days in one study [16]. Our results show that B. bassiana GHA used in an ADD context produces MST values comparable to those observed via the dipping inoculation method used in previous studies, and seems to decrease EAB MST even more than CFL-A. Previous reports exposing EAB adults to isolates of B. pseudobassiana via dipping showed MST values of 7.64–8.07 days [14], comparable to the 4.92–15.15 days observed for B. pseudobassiana isolates in the current study. The observed 5.43–8.47 days MST values for Metarhizium sp. Meta reported here are also similar to a previous study exposing EAB adults to Metarhizium isolates via dipping, resulting in MST values of 4.8–5.4 days [12,15]. The isolates of Purpureocillium spp. used in this study produced EAB MST values (7.56–18.07 days) comparable to a previous study finding a range of 10.96–13.4 days via dipping [15].
We add data for an isolate in the genus Samsoniella, which was successful in decreasing EAB MST and survival probability over time in Experiment 2, while also being recovered from 100% of cadavers. This isolate, however, did not significantly decrease the survival-related values in Experiment 1. The current study additionally looked at two fungi in the genus Clonostachys, finding they were successful at infecting EAB adults, as evidenced by consistent recovery from cadavers, although they did not significantly reduce EAB MST or probability of survival over time in either experiment. In Experiment 1, Clonostachys sp. EAB 50-14 even increased the MST of EAB adults. Isolates in the genus Clonostachys have been previously reported to be either strong entomopathogens or relatively weak entomopathogens, depending on the insect system being examined [52,53]. Therefore, the isolates of Clonostachys spp. in the current study appear to be only weak pathogens of EAB in an autocontamination context and may therefore not provide effective ADD-mediated control of EAB populations.
This study additionally supports the potential utility of an auto-contamination-dissemination format for delivering entomopathogenic fungi to EAB adults through ADDs, as previously described [16,19]. To our knowledge, however, this is the first study to investigate the pathogenicity of Minnesota-indigenous isolates of entomopathogenic fungi against EAB adults, as well as the first study to assay fungi in the genera Clonostachys and Samsoniella against EAB adults.
Therefore, we conclude that B. bassiana GHA, B. pseudobassiana EAB 16.8, Metarhizium sp. Meta, and Purpureocillium sp. EAB 59-16-2 are virulent against EAB adults and merit further investigation for potential as biological control agents of EAB in an ADD context. Future studies should evaluate the effectiveness of these fungi in ADD trials under field conditions. In many cases, environmental degradation of fungal inoculum is cited as a limiting factor in the effective use of entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents, with exposure to ultraviolet radiation often considered especially detrimental [54,55]. Past studies using ADDs containing B. bassiana additionally cited uneven growth of the fungus across the inoculum pouch as limiting the reliability of these inoculum pouches over time to deliver a sufficient load of conidia to each beetle [16]. Therefore, research is needed to optimize the type and/or formulation of inoculum used in ADDs to prolong fungal viability in the field.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f16111742/s1, Figure S1: Experimental procedure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.J.P., N.N.R., and R.A.B.; methodology, C.J.P. and N.N.R.; software, C.J.P. and N.N.R.; validation, C.J.P., N.N.R. and R.A.B.; formal analysis, C.J.P.; investigation, C.J.P. and N.N.R.; resources, R.A.B.; data curation, C.J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, C.J.P.; writing—review and editing, C.J.P., N.N.R. and R.A.B.; visualization, C.J.P.; supervision, R.A.B.; project administration, R.A.B.; funding acquisition, R.A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this project was provided by the Minnesota Invasive Terrestrial Plants and Pests Center, supported by the Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund as recommended by the Legislative-Citizen Commission on Minnesota Resources and USDA Hatch project MIN22-089.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the City of Minnetonka, Minnesota for assistance in selection and harvesting of infested ash trees, Sofia Simeto for discussions, Andrew Mann for advice regarding survival curves, Courtney Osborne of Myco-Operative for the donation of fungal isolate Metarhizium sp. Meta, Brian Aukema for providing rearing tubes and for his suggestions and discussions, and Tessa Kothlow, Ty Flanagan, Isaac Leppanen, and Benjamin Held for assistance in both the laboratory and field. We also thank Rob Venette and the Minnesota Invasive Terrestrial Plants and Pests Center at the University of Minnesota for their collaboration, discussions, and advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EAB | Emerald ash borer |
| EPF | Entomopathogenic fungi |
| ADD | Autodissemination device |
| IPM | Integrated pest management |
| MST | Mean survival time |
| GDD | Growing degree days |
| DPI | Days post-inoculation |
References
- Sun, J.; Koski, T.M.; Wickham, J.D.; Baranchikov, Y.N.; Bushley, K.E. Emerald Ash Borer Management and Research: Decades of Damage and Still Expanding. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2024, 69, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, R.A.; Jendak, E.; Houping, L.; Marchant, K.R.; Petrice, T.R.; Poland, T.M.; Ye, H. The emerald ash borer: A new exotic pest in North America. Newsl. Mich. Entomol. Soc. 2002, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- EAB Information Network. Available online: https://www.emeraldashborer.info/ (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Aukema, J.E.; Leung, B.; Kovacs, K.; Chivers, C.; Britton, K.O.; Englin, J.; Frankel, S.J.; Haight, R.G.; Holmes, T.P.; Liebhold, A.M.; et al. Economic impacts of non-native forest insects in the continental United States. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, D.G. Challenges, tactics and integrated management of emerald ash borer in North America. Forests 2019, 93, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, C.E.; Knight, K.S.; Rebbeck, J.; Gonzalez-Meler, M.A. The relationship between the emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) and ash (Fraxinus spp.) tree decline: Using visual canopy condition assessments and leaf isotope measurements to assess pest damage. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 303, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald Ash Borer Invasion of North America: History, Biology, Ecology, Impacts, and Management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, D.B. What’s killing the green menace: Mortality factors affecting the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in North America? Can. Entomol. 2015, 147, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.J.; Bauer, L.S.; van Driesche, R.G.; Gould, J.R. Progress and Challenges of Protecting North American Ash Trees from the Emerald Ash Borer Using Biological Control. Forests 2018, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnesota Department of Agriculture EAB Status Map. Available online: https://mnag.maps.arcgis.com/apps/webappviewer/index.html?id=63ebb977e2924d27b9ef0787ecedf6e9 (accessed on 29 October 2025).
- Bauer, L.S.; Liu, H.; Haack, R.A.; Petrice, T.R.; Miller, D.L. Natural enemies of emerald ash borer in southeastern Michigan. In Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer Research and Technology Development Meeting, Port Huron, MI, USA, 30 September–1 October 2003; U.S. Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S. Susceptibility of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) to Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Bauer, L.S.; Liu, H.; Griggs, M.H.; Vandenberg, J.D. Characterization of Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) isolates associated with Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) populations in Michigan. Biol. Control 2010, 54, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, S.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Gauthier, D.; van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Krell, P.J. Characterization and virulence of Beauveria spp. recovered from emerald ash borer in southwestern Ontario, Canada. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, S.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Gauthier, D.; van Frankenhuyzen, K. Isolation and characterization of Isaria farinosa and Purpureocillium lilacinum associated with emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis in Canada. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, D.B.; Lavallée, R.; Kyei-Poku, G.; van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Johny, S.; Guertin, C.; Francese, J.A.; Jones, G.C.; Blais, M. Towards the Development of an Autocontamination Trap System to Manage Populations of Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) With the Native Entomopathogenic Fungus, Beauveria bassiana. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, T.W.; Hough, G.; Arbona, C.; Roberts, H.; Bennison, J.; Buxton, J.; Prince, G.; Chandler, D. Investigating the potential of an autodissemination system for managing populations of vine weevil, Otiorhynchus sulcatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) with entomopathogenic fungi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 154, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuti, C.; Barzanti, G.P.; Marianelli, L.; Peverieri, G.S.; Paoli, F.; Bosio, G.; Venanzio, D.; Giacometto, E.; Roversi, P.F. A new device for auto-disseminating entomopathogenic fungi against Popillia japonica: A study case. Bull. Insectol. 2019, 72, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Srei, N.; Guertin, C.; Lavallée, R.; Lajoie, M.E.; Brousseau, C.; Bergevin, R.; Miller, F.; McMillin, K.; Trudel, R. Microbial Control of the Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Using Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) by the Means of an Autodissemination Device. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unlu, I.; Rochlin, I.; Suman, D.S.; Wang, Y.; Chandel, K.; Gaugler, R. Large-Scale Operational Pyriproxyfen Autodissemination Deployment to Suppress the Immature Asian Tiger Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) Populations. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, M.; Neuenschwander, H.; Hoesli, E.; Maurhofer, M.; Grabenweger, G. Autodissemination of Metarhizium brunneum: A strategy for biological control of adult Japanese beetles. J. Pest Sci. 2025, 98, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srei, N.; Lavallée, R.; Guertin, C. Horizontal Transmission of the Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolate INRS-242 of Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) in Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 113, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, A.J.; Abalo, P.; Hell, K. A laboratory assessment of the potential of different strains of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin and Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) to control Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in stored cowpea. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2005, 41, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeto, S.; Held, B.W.; Showalter, D.N.; Bushley, K.E.; Blanchette, R.A. Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs. Forests 2024, 15, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla-Carrera, L.; Morton, A.; Santamaria, S.; García-del-Pino, F. Isolation and virulence of entomopathogenic fungi against larvae of hazelnut weevil Curculio nucum (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) and the effects of combining Metarhizium anisopliae with entomopathogenic nematodes in the laboratory. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.N.; Chowdhury, Z.H.; Mim, M.F.; Momtaz, M.B.; Islam, T. Biocontrol potential of native isolates of Beauveria bassiana against cotton leafworm Spodoptera litura (Fabricius). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; González-Mas, N.; Yousef-Yousef, M.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Fernández-Bravo, M. Key role of environmental competence in successful use of entomopathogenic fungi in microbial pest control. J. Pest Sci. 2024, 97, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, B.W.; Simeto, S.; Rajtar, N.N.; Cotton, A.J.; Showalter, D.N.; Bushley, K.E.; Blanchette, R.A. Fungi associated with galleries of the emerald ash borer. Fungal Biol. 2021, 125, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajtar, N.N.; Held, B.W.; Blanchette, R.A. Fungi from Galleries of the Emerald Ash Borer Produce Cankers in Ash Trees. Forests 2021, 12, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeto, S.; Held, B.W.; Blanchette, R.A. Wood Decay Fungi Associated with Galleries of the Emerald Ash Borer. Forests 2023, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S. Microbial control of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) with Beauveria bassiana strain GHA: Field applications. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2008, 18, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S. Microbial control of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) with Beauveria bassiana strain GHA: Greenhouse and field trials. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Griggs, M.H.; Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S.; Vandenberg, J.D. Assessing deposition and persistence of Beauveria bassiana GHA (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) applied for control of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in a commercial tree nursery. Biol. Control 2010, 54, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francese, J.A.; Fraser, I.; Lance, D.R.; Mastro, V.C. Efficacy of Multifunnel Traps for Capturing Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae): Effect of Color, Glue, and Other Trap Coatings. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippen, T.L.; Sheffield, C. External Surface Disinfection of the Lesser Mealworm (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangsa-ard, J.; Houbraken, J.; van Doorn, T.; Hong, S.B.; Borman, A.M.; Hywel-Jones, N.L.; Samson, R.A. Purpureocillium, a new genus for the medically important Paecilomyces lilacinus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 321, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, D.E.; Oliva, M.; Leiva, S.; Mendoza, J.E.; Bobadilla, L.; Angulo, G.; Calderon, M.S. Phylogeny and species delimitations in the entomopathogenic genus Beauveria (Hypocreales, Ascomycota), including the description of B. peruviensis sp. nov. MycoKeys 2019, 58, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Thanarut, C.; Dao, V.M.; Wang, Y.B.; Yu, H. Phylogeny and species delimitations in the economically, medically, and ecologically important genus Samsoniella (Cordycipitaceae, Hypocreales). MycoKeys 2023, 99, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, D.X.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y.B.; Thanarut, C.; Dao, V.M.; Yu, H. Phylogeny and systematics of the genus Clonostachys. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, O. Phylogenetic classification and physiological and ecological traits of Metarhizium spp. Mycoscience 2024, 65, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, J.C.; Bueno, V.H.P.; Sidney, L.A.; Silva, D.B.; Sampaio, M.V.; Pereira, J.M.; Nomelini, Q.S.S.; van Lenteren, J.C. Cold storage affects mortality, body mass, lifespan, reproduction and flight capacity of Praon volucre (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, M. The Impact of Cold Storage on the Survival and Viability of Parasitoid Bee Pupae and Whole Insects. Int. J. Vet. Res. Allied Sci. 2024, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, W.E.; MacQuarrie, C.J.K. An artificial delay in emergence influences the number but not the fitness of adult emerald ash borer emerging from infested ash wood. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 166, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.N. Prolonged Larval Development in Buprestis aurulenta L. (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). A Review with New Cases. Can. Entomol. 1962, 94, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, K.A.; Behmer, S.T. Lifetime consequences of food protein-carbohydrate content for an insect herbivore. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissold, F.J.; Simpson, S.J. Temperature, food quality and life history traits of herbivorous insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerly, D.D.; Bazzaz, F.A. Leaf dynamics, self-shading and carbon gain in seedlings of a tropical pioneer tree. Oecologia 1995, 101, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, I.J.; Westoby, M. Nutrient concentration, resorption and lifespan: Leaf traits of Australian sclerophyll species. Funct. Ecol. 2003, 17, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, L.; Ma, L. Gut bacterial microbiota of Lymantria dispar asiatica and its involvement in Beauveria bassiana infection. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2023, 197, 107897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tu, C.; Han, R.; Luo, J.; Xu, L. Enhanced capacity of a leaf beetle to combat dual stress from entomopathogens and herbicides mediated by associated microbiota. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Bergamini, C.; Montalva, C.; Humber, R.A.; Luz, C. Simple method to detect and to isolate entomopathogenic fungi (Hypocreales) from mosquito larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 182, 107581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, A.V.; Virla, E.; Humber, R.A.; Paradell, S.L.; López Lastra, C.C. First record of Clonostachys rosea (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) as an entomopathogenic fungus of Oncometopia tucumana and Sonesimia grossa (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) in Argentina. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006, 92, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, F.M.; Bendebbah, R.; Benssaci, B.; Toudji, F.; Tafifet, L.; Krimi, Z. Entomopathogenic efficacy of the endophytic fungi: Clonostachys sp. and Beauveria bassiana on Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) larvae under laboratory and greenhouse conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Akutse, K.S.; Aguila, L.C.R.; Xu, Y. General Limitations to Endophytic Entomopathogenic Fungi Use as Plant Growth Promoters, Pests and Pathogens Biocontrol Agents. Plants 2021, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couceiro, J.C.; Fatoretto, M.B.; Demétrio, C.G.B.; Meyling, N.V.; Delalibera, I. UV-B Radiation Tolerance and Temperature-Dependent Activity Within the Entomopathogenic Fungal Genus Metarhizium in Brazil. Front. Fungal Biol. 2021, 2, 645737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).