The Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Aerial Applications of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on the Spruce Budworm and Its Parasitism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Selection and Experimental Design
2.2. Spruce Budworm Sampling and Defoliation Estimation
2.3. Spruce Budworm Pupal Mass and Parasitism
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effectiveness of Btk Sprays in Reducing Spruce Budworm Populations and Defoliation
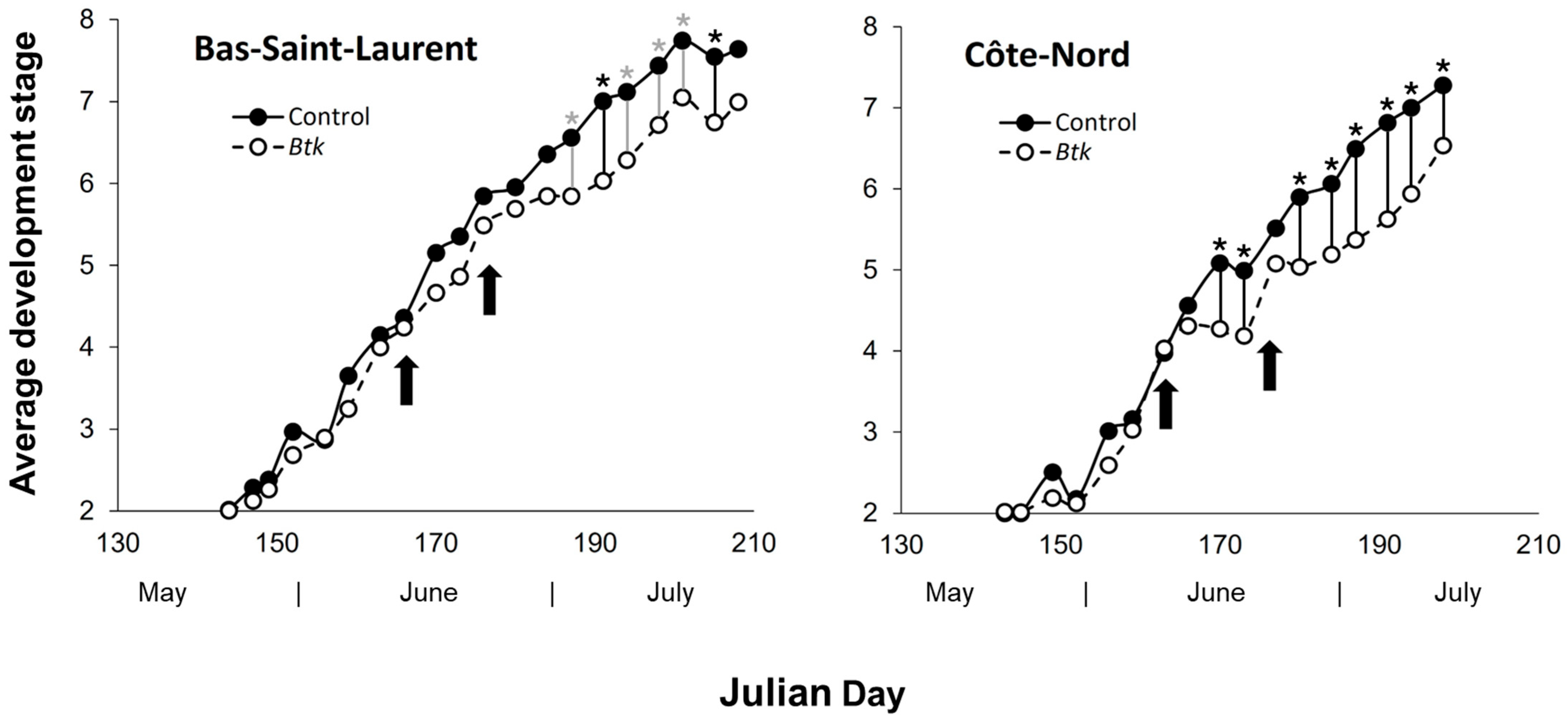
3.2. Sublethal Effects of Btk Sprays on the Spruce Budworm
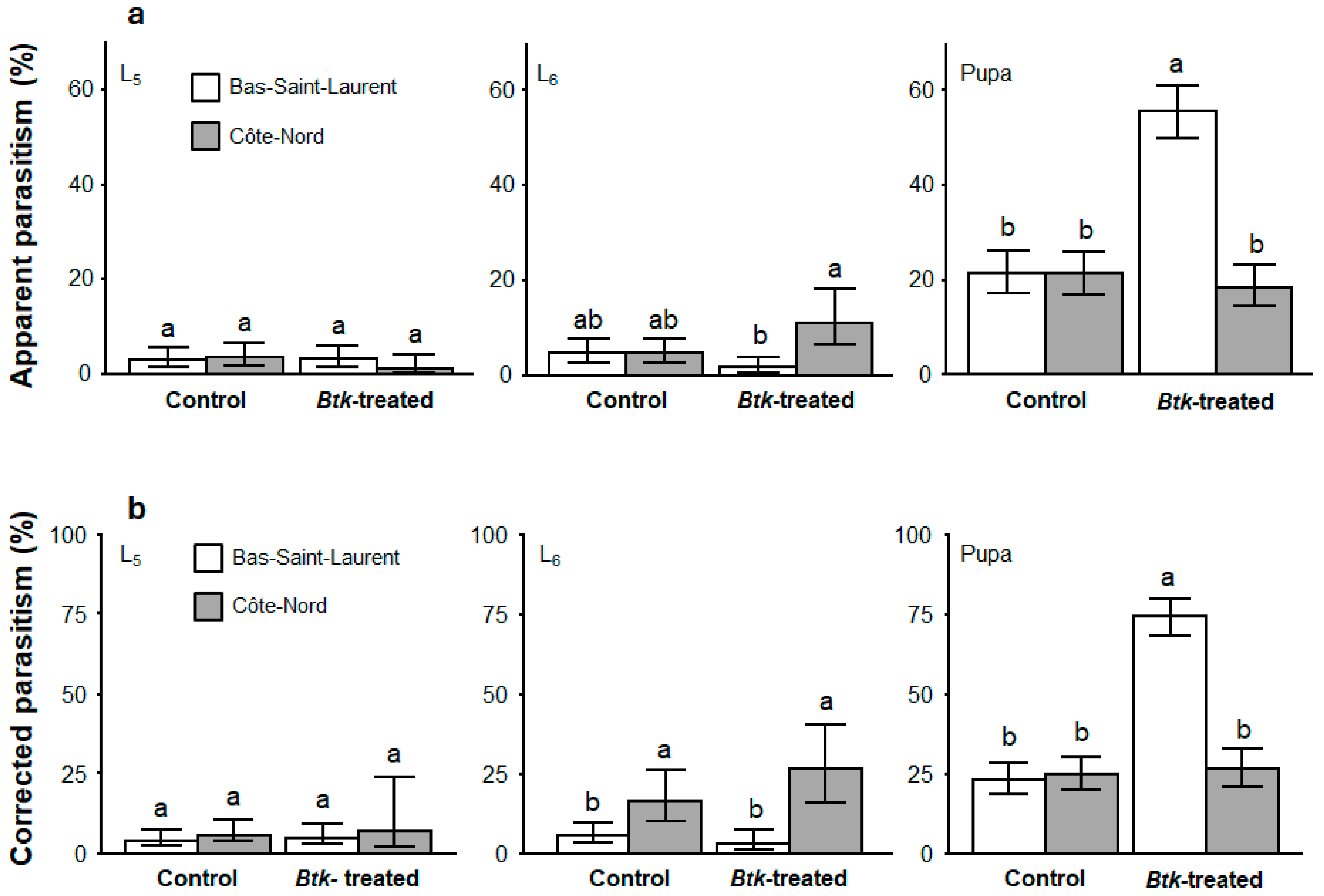
3.3. Spruce Budworm Parasitism and Development Failure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclean, D.A. Effects of spruce budworm outbreaks on the productivity and stability of balsam fir forests. For. Chron. 1984, 60, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, D.A. Impacts of insect outbreaks on tree mortality, productivity, and stand development. Can. Entomol. 2016, 148, S138–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, Y.; Arseneault, D. Spruce budworm outbreaks in eastern Quebec over the last 450 years. Can. J. For. Res. 2004, 34, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royama, T. Population dynamics of the spruce budworm Choristoneura fumiferana. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 429–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministère des Ressources Naturelles et de la Faune. Aires Infestées par la Tordeuse des Bourgeons de L’épinette, au Québec, en 1975; Direction de la Conservation des Forêts: Québec, QC, Canada, 2005; p. 7. Available online: http://www.mrnfp.gouv.qc.ca/forets/fimaq/insectes/fimaq-insectes-portrait-superficies.jsp (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Coulombe, G. Commission D’étude sur la Gestion de la Forêt Publique Québécoise. 2004, 307p. Available online: https://numerique.banq.qc.ca/patrimoine/details/52327/35677?docref=UeZamqRxtSqfsT10d57uPg&docsearchtext=2-550-43626-1 (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Hennigar, C.R.; Maclean, D.A.; Quiring, D.T.; Kershaw, J.A., Jr. Differences in spruce budworm defoliation among balsam fir and white, red, and black spruce. For. Sci. 2008, 54, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambaraju, K.S.; Shamoun, S.; Boulanger, Y.; Martel, V.; Desrochers, P.; Rioux, D.; Kulkarni, N.; Verma, R.K.; Pautasso, M.; Pureswaran, D.; et al. Forest ecosystem health and biotic disturbances: Perspectives on indicators and management approaches. In Ecological Forest Management Handbook; Larocque, G.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 434–478. [Google Scholar]
- Piene, H. Spruce budworm defoliation and growth loss in young balsam fir: Recovery of growth in spaced stands. Can. J. For. Res. 1989, 19, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauce, É.; Dupont, A.; Hébert, C.; Berthiaume, R.; Quezada-García, R.; Fuentealba, A. Biennial aerial application of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner var. kurstaki is the most cost-effective approach of protection against spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana [Clemens]). Ann. For. Sci. 2024, 81, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, J.R. The vulnerability of balsam fir to spruce budworm attack in northwestern Ontario with special reference to the physiological age of the tree. For. Chron. 1958, 34, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, D.A. Vulnerability of fir-spruce stands during uncontrolled spruce budworm outbreaks: A review and discussion. For. Chron. 1980, 56, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, D.A.; Ostaff, D.P. Patterns of balsam fir mortality caused by an uncontrolled spruce budworm outbreak. Can. J. For. Res. 1989, 19, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, J.R. Mortality of balsam fir and white spruce following a spruce budworm outbreak in the Ottawa river watershed in Quebec. Can. J. For. Res. 1981, 11, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorais, L.; Auger, M.; Pelletier, M.C.; Bordeleau, C.; Cabana, J. Insect control in Quebec, 1974–1987. In Forest Insect Pests in Canada; Armstrong, J.A., Ives, W.G.H., Eds.; Canadian Forest Service, Science and Sustainable Development Directorate: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1995; pp. 667–678. [Google Scholar]
- Jallouli, W.; Driss, F.; Fillaudeau, L.; Rouis, S. Review on biopesticide production by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki since 1990: Focus on bioprocess parameters. Process Biochem. 2020, 98, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.; Dedes, J.; Gauthier, D.; Van Frankenhuyzen, K. Sublethal effects of Bacillus thuringiensis on the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 83, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Payne, N.J. Theoretical optimization of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner for control of the eastern spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clem. (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): Estimates of lethal and sublethal dose requirements, product potency, and effective droplet sizes. Can. Entomol. 1993, 125, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, B.M. Global insights on insecticide use in forest systems: Current use, impacts and perspectives in a changing world. Curr. For. Rep. 2025, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, D.K.; Krishnappa, C.; Bhoi, T.K. Microbial control of forest insect pests over 60 years (1964–2024): Network analysis and bibliometric mapping. J. Nat. Pestic. Res. 2025, 12, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyouki, F.F.R.; Fuxa, J.R.; Richter, A.R. Spore-toxin interactions and sublethal effects of Bacillus thuringiensis in Spodoptera frugiperda and Pseudoplusia includens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 1996, 31, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.C.Q. Sublethal Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner in Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista—Campus Jaboticabal Faculty of Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences, Jaboticabal, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Nystrom, C.W. Effect of temperature on mortality and recovery of spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) exposed to Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Can. Entomol. 1987, 119, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Esposito, M.-P.; Babin, A.; Pasco, M.; Poirié, M.; Gatti, J.-L.; Gallet, A. Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticides induce developmental defects in non-target Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Insects 2020, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartling, M.-T.; Brandt, A.; Hollert, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Current insights into sublethal effects of pesticides on insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Raffa, K.F.; Miller, M.J.; Ellis, D.D.; McCown, B.H. Behavioral responses and sublethal effects of spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) and Fall webworm (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae) larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis cry1a(a) toxin in diet. Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, G.; Bauce, É. Lethal and sublethal effects of single and double applications of Bacillus thuringiensis variety kurstaki on spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) larvae. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemele, M.A. Impact of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner var. kurstaki application on population densities of Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), and its dominant parasitoid, Cotesia vestalis Haliday (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and the implications on cabbage yield. Afr. Entomol. 2016, 24, 398–406. [Google Scholar]
- Stemele, M.A. Comparative effects of a selective insecticide, Bacillus thuringiensis var kurstaki and the broad-spectrum insecticide cypermethrin on diamondback moth and its parasitoid Cotesia vestalis (Hymenoptera; Braconidae). Crop Prot. 2017, 101, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, A.; Zappala, L.; Stark, J.D.; Desneux, N. Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedatarian, A.; Fathipour, Y.; Talaei-Hassanloui, R. Deleterious effects of Bacillus thuringiensis on biological parameters of Habrobracon hebetor parasitizing Helicoverpa armigera. BioControl 2014, 59, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, B.H.; Portilla, M.; Allen, K.C.; Little, N.S.; Mullen, R.M.; Paulk, R.T.; Read, Q.D. Sublethal effects of a commercial Bt product and Bt cotton flowers on the bollworm (Helicoverpa zea) with impacts to predation from a lady beetle (Hippodamia convergens). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.S.; Scriber, J.M.; Nitao, J.K.; Smitley, D.R. Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki to three nontarget Lepidoptera in field studies. Environ. Entomol. 1995, 24, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriber, J.M. Bt or not Bt: Is that the question? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12328–12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccino, N.; Lavertu, D.; Bergeron, Y.; Régnière, J. Spruce budworm impact, abundance and parasitism rate in a patchy landscape. Oecologia 1998, 114, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveleigh, E.S.; Mccann, K.S.; Mccarthy, P.C.; Pollock, S.J.; Lucarotti, C.J.; Morin, B.; Mcdougall, G.A.; Strongman, D.B.; Huber, J.T.; Umbanhowar, J.; et al. Fluctuations in density of an outbreak species drive diversity cascades in food webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16976–16981. [Google Scholar]
- Maltais, J.; Régnière, J.; Cloutier, C.; Hébert, C.; Perry, D.F. Seasonal biology of Meteorus trachynotus Vier. (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and of its overwintering host Choristoneura rosaceana (Harr.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Can. Entomol. 1989, 121, 745–756. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, M.; Martel, V.; Régnière, J.; Therrien, P.; Correia, D.L.P. Do natural enemies explain fluctuations in low-density spruce budworm populations? Ecology 2018, 99, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royama, T.; Eveleigh, E.S.; Morin, J.R.B.; Pollock, S.J.; Mccarthy, P.C.; Mcdougall, G.A.; Lucarotti, C.J. Mechanisms underlying spruce budworm outbreak processes as elucidated by a 14-year study in New Brunswick, Canada. Ecol. Monogr. 2017, 87, 600–631. [Google Scholar]
- Glaus, V.; Nisole, A.; Edwards, S.; Bélanger, S.; Johns, R.C.; Djoumad, A.; Cusson, M.; Fournier, V.; Martel, V. Nontarget impacts of insecticide-based population control of eastern spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) on nontarget caterpillar communities and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 2023, 155, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisole, A.; Stewart, D.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Nadeau, M.; Trudeau, S.; Huron, P.; Djoumad, A.; Kamenova, S.; Smith, M.A.; Eveleigh, E.; et al. Identification of spruce budworm natural enemies using a qPCR-based molecular sorting approach. Forests 2020, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauce, É.; Carisey, N.; Dupont, A.; Van Frankenhuyzen, K. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki aerial spray prescriptions for balsam fir stand protection against spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuentealba, A.; Dupont, A.; Hébert, C.; Berthiaume, R.; Quezada-García, R.; Bauce, É. Comparing the efficacy of various aerial spraying scenarios using Bacillus thuringiensis to protect trees from spruce budworm defoliation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 432, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A.; Kettela, E.G.; Mcdougall, G.A. A sampling technique for overwintering spruce budworm and its applicability to population surveys. In Information Report M-X-25; Canadian Forestry Service, Department of Fisheries and Forestry: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Fettes, J.J.F.P. Investigations of Sampling Techniques for Population Studies of the Spruce Budworm on Balsam Fir in Ontario; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Tilles, D.A.; Woodley, N.E. Spruce budworm parasites in Maine: A reference manual for collection and identification of common cpecies. In Agriculture Handbook No. 616; USDA Forest Service: Lakewood, CO, USA, 1984; 35p. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, J.T.; Eveleigh, E.; Pollock, S.; McCarthy, P. The Chalcidoid parasitoids and hyperparasitoids (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) of Choristoneura species (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in America North of Mexico. Can. Entomol. 1996, 128, 1167–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.M.R. Review and identification keys to the Ichneumonid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) of Nearctic Choristoneura species (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Can. Entomol. 2008, 140, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, J.E. A review of the Tachinid parasitoids (Diptera: Tachinidae) of Nearctic Choristoneura species (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), with keys to adults and puparia. Zootaxa 2005, 938, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.A. A technique for assessing spruce budworm larval mortality caused by parasites. Can. J. Zool. 1955, 33, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Narvaez, E.; Castro-Webb, N.A. Simple method to estimate percentage parasitism when the host and parasitoid phenologies are unknown: A statistical approach. BioControl 2003, 48, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leius, K. Influence of food on fecundity and longevity of adults of Itoplectis conquisitor (Say) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Can. Entomol. 1961, 93, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T. Host-feeding and acceptance by a parasitic wasp (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) as influenced by egg load and experience in a patch. Evol. Ecol. 1999, 13, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.W. Some Ichneumonid-Sarcophagid interactions in the Gypsy Moth Porthetria dispar (L.) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Can. Entomol. 1963, 95, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Nystrom, C.; Dedes, J.; Seligy, V. Mortality, feeding inhibition, and recovery of spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) larvae following aerial application of a high-potency formulation of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Can. Entomol. 2000, 132, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awmack, C.S.; Leather, S.R. Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 817–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A. A technique for estimating the fecundity of natural populations of the spruce budworm. Can. J. Zool. 1957, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, R.C.; Bowden, J.J.; Carleton, D.R.; Cooke, B.J.; Edwards, S.; Emilson, E.J.S.; James, P.M.A.; Kneeshaw, D.; Maclean, D.A.; Martel, V.; et al. A conceptual framework for the spruce budworm early intervention strategy: Can outbreaks be stopped? Forests 2019, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauce, E.; Hardy, Y. Effects of drainage and severe defoliation on the rawfiber content of balsam fir needles and growth of the spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, H.M. The effect of a microsporidian parasite on the development, reproduction, and mortality of the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Clem.). Can. J. Zool. 1958, 36, 499–511. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, H.M. Some aspects of the epidemiology of a microsporidian parasite of the spruce budwo.rm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Clem.). Can. J. Zool. 1958, 36, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, H.M. The possible control of a budworm infestation by a microsporidian disease. Bi-Mon. Prog. Rep. 1960, 16, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst, M.; Fusco, R.A.; Blumenthal, E.M. Effects of reduced rates of Dipel 4L, Dylox 1.5 Oil, and Dimilin W-25 on Lymantria dispar (L.) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) parasitism and defoliation. Environ. Entomol. 1982, 11, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stireman, J.O., III. Host location and selection cues in a generalist Tachinid parasitoid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 103, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Weseloh, R.M. Host recognition behavior of the Tachinid parasitoid, Compsilura concinnata. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1980, 73, 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, C.; Cloutier, C. Host instar as a determinant of preference and suitability for two parasitoids attacking late instars of the spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1990, 83, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, C.; Cloutier, C.; Régnière, J.; Perry, D.F. Seasonal biology of Winthemia fumiferanae Toth. (Diptera: Tachinidae), a larval–pupal parasitoid of the spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Can. J. Zool. 1989, 67, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar, D.M.; Kaya, H.K.; Doane, C.C.; Anderson, J.F.; Weseloh, R.M. Aerial application of Bacilllus thuringiensis against larvae of the Elm Spanworm and Gypsy Moth and effects on parasitoids of the Gypsy Moth. In Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin No. 735; Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station: New Haven, CT, USA, 1973; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, J.R. Spruce budworm parasite investigations in the lower St. Lawrence and Gaspé regions of Quebec. Can. Entomol. 1960, 92, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, J.R. Parasite studies in two residual spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana (Clem.)) outbreaks in Quebec. Can. Entomol. 1965, 97, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgugan, B.M.; Blais, J.R. Spruce budworm parasite studies in northwestern Ontario. Can. Entomol. 1959, 91, 758–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, G.A. Parasites of Forest Lepidoptera in Canada: Subfamilies Metopiinae and Pimplinae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumondiae), Part 1; Environment Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1974; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Morneau, C.; Couillard, P.-L.; Laflamme, J.; Major, M. Classification Écologique du Territoire Québécois; Direction des Inventaires Forestiers: Québec, QC, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
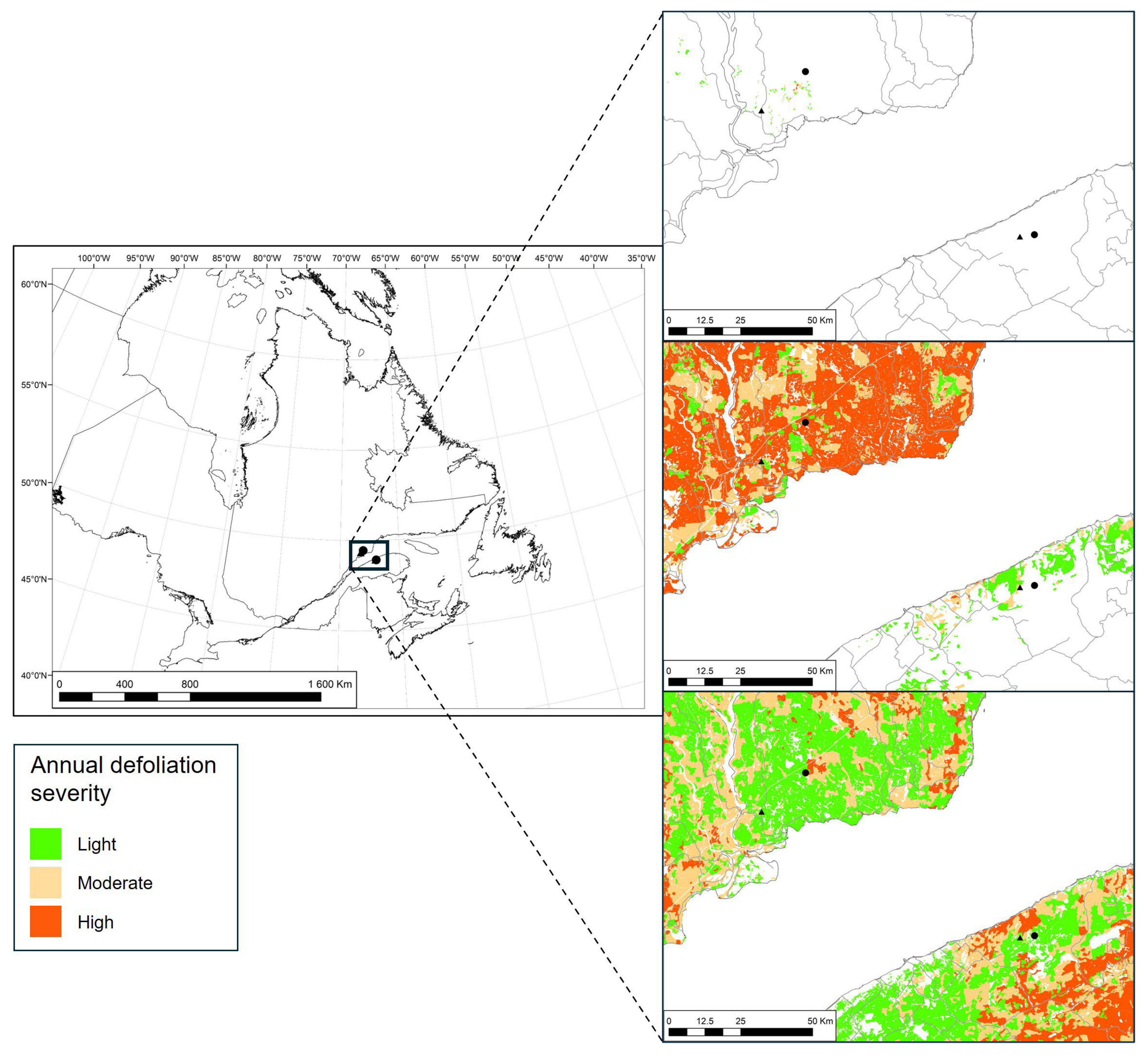


| Region | Treatment | Ecoforest map designation | Altitude | ||
| Composition a | Density/height b | Age | (m) | ||
| Bas-Saint-Laurent | Btk | SBSB | B3 | 50–70 | 467 |
| Control | SBSB | B3 | 50–70 | 388 | |
| Cote-Nord | Btk | SBSB | B3 | 70 | 333 |
| Control | SBSB | B3 | 70 | 220 | |
| Region | Treatment | Larvae/Branch 1 | Mortality 2 | Defoliation 3 | |
| Pre-treat. | Post-treat. | (%) | (%) | ||
| Bas-Saint-Laurent | Btk | 21.7 ± 4 a | 4.4 ± 1 b | 79.7 | 76.7 ± 9 ab |
| Control | 33.4 ± 4 a | 14.0 ± 3 a | 56.5 | 92.8 ± 9 a | |
| Côte-Nord | Btk | 23.2 ± 7 a | 1.8 ± 1 b | 92.2 | 56.1 ± 9 b |
| Control | 42.8 ± 13 a | 16.4 ± 4 a | 61.7 | 100.0 ± 9 a | |
| Treatments | Df | F | p > F |
|---|---|---|---|
| Btk application | 1 | 613.77 | <0.001 |
| Region | 1 | 67.98 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 1 | 286.57 | <0.001 |
| Btk application*Region | 1 | 112.47 | <0.001 |
| Btk application*Sex | 1 | 0.37 | 0.543 |
| Region*Sex | 1 | 0.43 | 0.509 |
| Btk application*Region*Sex | 1 | 1.43 | 0.233 |
| Bas-Saint-Laurent | Côte-Nord | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Order | Family | Species | Btk Sprays | Control | Btk Sprays | Control |
| L5 | Hymenoptera | Braconidae | Apanteles fumiferanae | 2 | |||
| Meteorus trachynotus | 1 | ||||||
| Ichneumonidae | Enytus montanus | 1 | |||||
| Glypta fumiferanae | 9 | 8 | 2 | 8 | |||
| Diptera | Tachinidae | Eumea caesar | 1 | ||||
| Number of SBW—L5 reared | 300 | 300 | 195 | 300 | |||
| L6 | Hymenoptera | Braconidae | Meteorus trachynotus | 3 | 1 | 4 | |
| Undetermined | 1 | ||||||
| Ichneumonidae | Dirophanes maculicornis | 2 * | |||||
| Glypta fumiferanae | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Undetermined | 1 | 2 | |||||
| Diptera | Tachinidae | Eumea caesar | 4 | 1 | |||
| Phryxe pecosensis | 3 | ||||||
| Smidtia fumiferanae | 1 | 5 | 1 | 9 | |||
| Undetermined | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Number of SBW—L6 reared | 300 | 300 | 118 | 300 | |||
| Pupa | Hymenoptera | Ichneumonidae | Apechthis ontario | 46 | 7 | ||
| Dirophanes maculicornis | 95 | 55 | 48 | 59 | |||
| Itoplectis conquisitor | 5 | ||||||
| Undetermined | 4 | 1 | |||||
| Pteromalidae | Mesopolobus tortricis | 2 | |||||
| Mesopolobus verditer | 6 | 1 | |||||
| Diptera | Tachinidae | Eumea caesar | 1 | ||||
| Phryxe pecosensis | 1 | ||||||
| Smidtia fumiferanae | 5 | 3 | 2 | ||||
| Undetermined | 3 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Number of SBW pupae reared | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | |||
| SBW Stage | Factors | Probability Metric | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitism | Developmental Failure | |||||||
| Df | Dev. | Pr > Chi | Df | Dev. | Pr > Chi | |||
| L5 | Btk treatment | 1 | 0.80 | 0.371 | 1 | 68.27 | <0.001 | |
| Region | 1 | 0.39 | 0.530 | 1 | 155.60 | <0.001 | ||
| Btk treatment*Region | 1 | 2.81 | 0.094 | 1 | 28.89 | <0.001 | ||
| L6 | Btk treatment | 1 | 0.07 | 0.785 | 1 | 2.52 | 0.112 | |
| Region | 1 | 6.07 | 0.014 | 1 | 150.94 | <0.001 | ||
| Btk treatment*Region | 1 | 9.65 | 0.002 | 1 | 47.21 | <0.001 | ||
| Pupa | Btk treatment | 1 | 36.10 | <0.001 | 1 | 57.91 | <0.001 | |
| Region | 1 | 53.09 | <0.001 | 1 | 7.10 | <0.001 | ||
| Btk treatment*Region | 1 | 38.28 | <0.001 | 1 | 1.75 | 0.186 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hébert, C.; Béland, J.-M.; Dupont, A.; Berthiaume, R. The Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Aerial Applications of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on the Spruce Budworm and Its Parasitism. Forests 2025, 16, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111666
Hébert C, Béland J-M, Dupont A, Berthiaume R. The Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Aerial Applications of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on the Spruce Budworm and Its Parasitism. Forests. 2025; 16(11):1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111666
Chicago/Turabian StyleHébert, Christian, Jean-Michel Béland, Alain Dupont, and Richard Berthiaume. 2025. "The Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Aerial Applications of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on the Spruce Budworm and Its Parasitism" Forests 16, no. 11: 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111666
APA StyleHébert, C., Béland, J.-M., Dupont, A., & Berthiaume, R. (2025). The Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Aerial Applications of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on the Spruce Budworm and Its Parasitism. Forests, 16(11), 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111666







