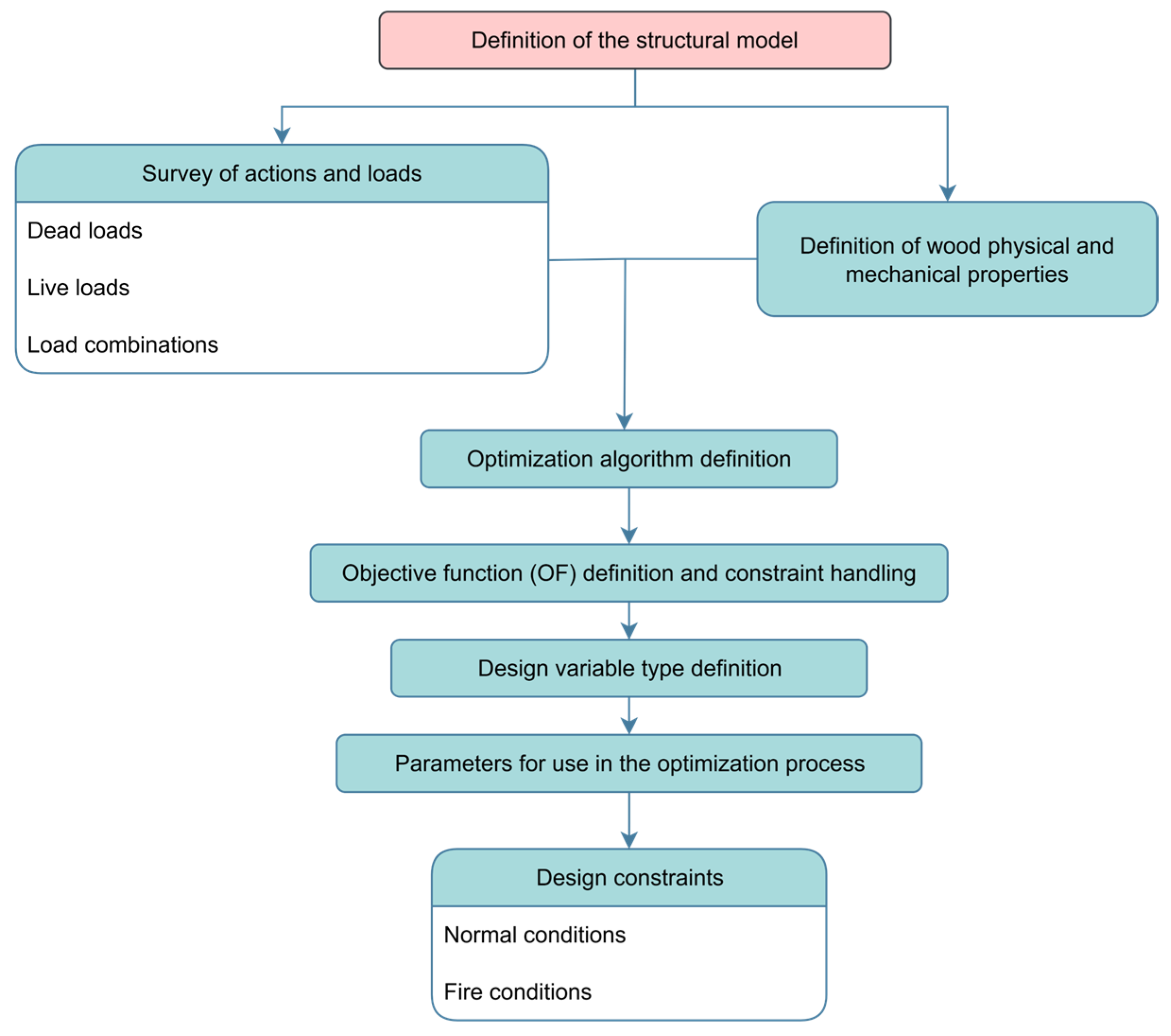
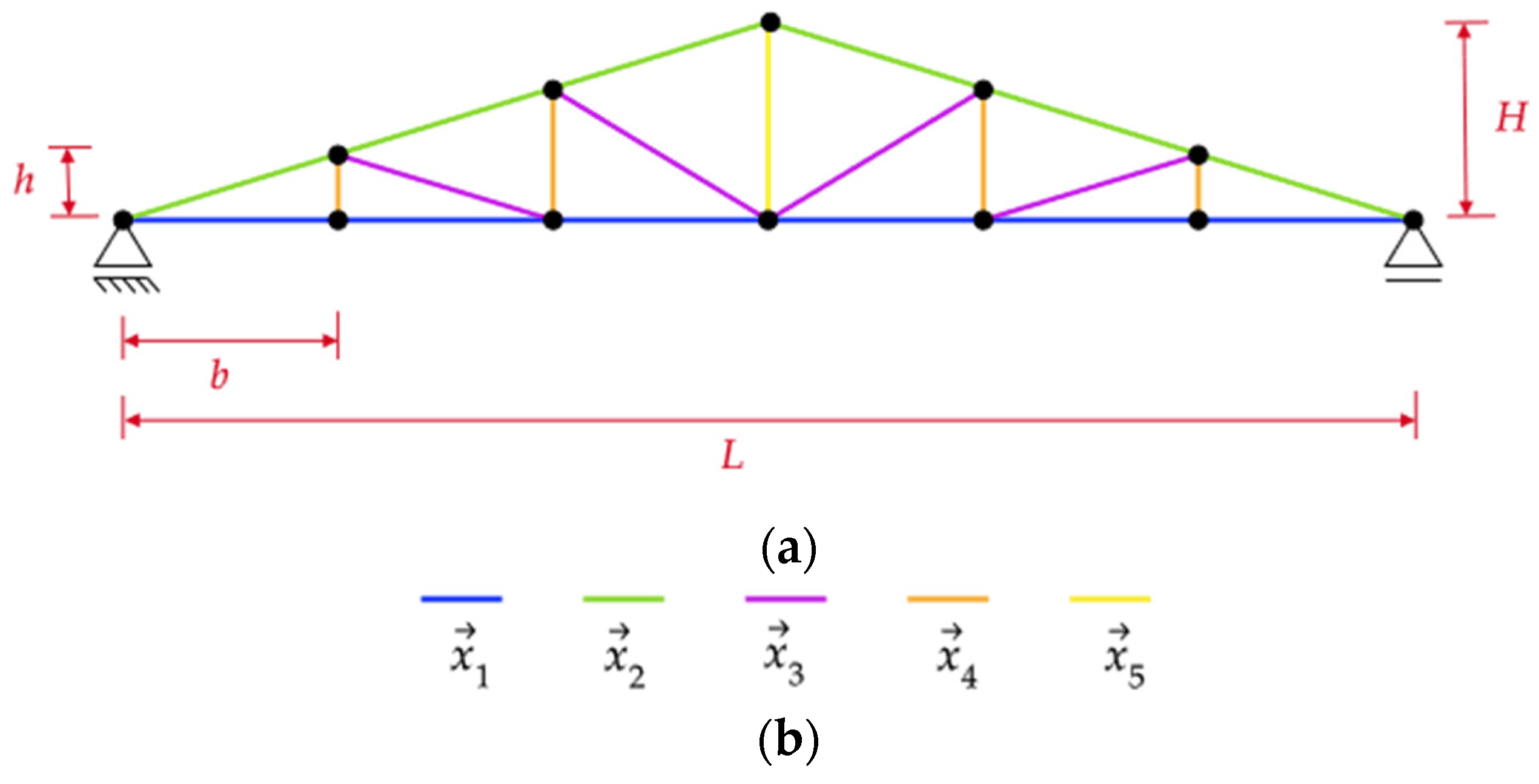
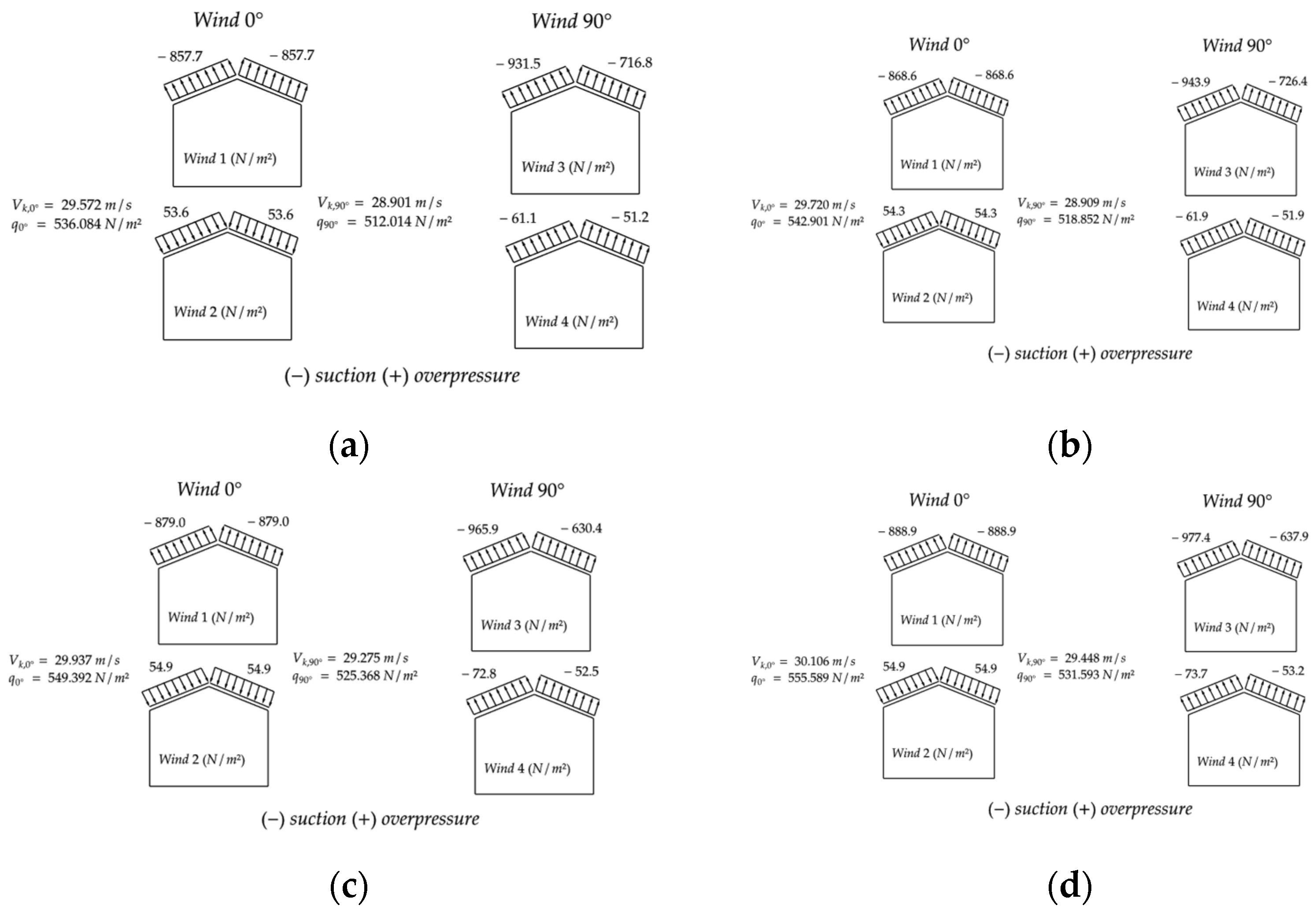
In this section, the results obtained in the optimization process for the evaluated trusses are discussed. For the representation of results, an identification of the type H-x-y-z will be adopted for the trusses, where x, y, and z indicate the truss span, species ID, and exposure time, respectively.
3.1. Optimization Under Normal Conditions
Table 9 presents the general results of 30 executions of the optimization algorithm for the different types of trusses considered, specifically for the Howe trusses evaluated under normal conditions (no fire). The values recorded in the table include the maximum (
) and minimum (
) of the penalized objective function, as well as the amplitude (
), median (
), mean (
), standard deviation (
), and feasibility rate (FR). It is worth noting that the feasibility rate represents the ratio between the total number of tests in which all constraints were met and the total number of tests performed (30 in this case). The gross mass increase represents the percentage increase over the gross mass under normal conditions. The observed oscillations between minimum and maximum values are associated with the discrete definition of cross-sections and the stochastic exploration of the Firefly Algorithm. These variations are inherent to population-based methods but do not compromise the feasibility or robustness of the optimized solutions.
In all cases, the feasibility rate (FR) was equal to 100%, and all optimal solutions strictly satisfied the imposed design constraints. No violations were observed, indicating that the optimized trusses were consistently robust with respect to the feasibility margins.
The distribution of results can be visualized through a boxplot, shown in
Figure 11. For each analyzed span, a boxplot was generated. In this type of graph, the central line represents the median, the diamond-shaped point represents the mean, and the box represents the interquartile range (IQR), bounded by the lower quartile (Q1) and the upper quartile (Q3). The whiskers extend from the box up to 1.5 times the IQR, indicating the minimum and maximum values within this range, while values beyond the whiskers are plotted as asterisk-shaped points, representing outliers. In addition, the results correspond to
n = 30 independent optimization runs, which ensures statistical robustness of the comparisons.
From
Figure 11, it can be observed that the minimum values of the penalized objective function, considering the same optimization process, ranged between 100.71 kg and 126.28 kg for spans of 6 m, and between 149.74 kg and 208.60 kg for spans of 9 m. For 12 m trusses, the minimum values ranged between 288.45 kg and 343.12 kg, and for 15 m trusses, between 407.28 kg and 513.22 kg.
The analysis of the results indicates that species ID 03 (Angelim-pedra) and ID 04 (Garapa) showed the best performances regarding the minimization of the objective function. Although tensile strength parallel to the grain is a relevant parameter in selecting the species for trussed structures, density and longitudinal modulus of elasticity were also determining factors in obtaining lighter and structurally efficient trusses.
It is emphasized that for timber structures, it is essential to consider a multidimensional approach in selecting the species and the geometric configuration of the truss. The results reinforce the effectiveness of the optimization algorithm used (FA), which enabled design solutions compliant with normative constraints while promoting material savings.
Additionally, the optimization process showed a feasibility rate of 100%, indicating that all viable solutions obtained fully met the geometric and structural constraints imposed in the design problem.
Table 10 summarizes the design variables obtained for the Howe truss, indicating that the dimension and minimum area constraints were respected.
According to the data presented in
Table 10, the minimum dimension requirement was also met for different elements. Trusses H-6-1-0, H-6-2-0, H-6-3-0, H-6-4-0, H-6-5-0, H-9-3-0, H-9-4-0, H-9-5-0, H-12-3-0, H-12-4-0, H-12-5-0, H-15-4-0, and H-15-5-0 met the minimum dimension for the lower chords (index 1). For the upper chords (index 2), trusses H-6-1-0, H-6-3-0, H-6-5-0, H-9-3-0, H-9-4-0, and H-9-5-0 reached the 50 mm minimum. In the diagonals (index 3), this minimum value was observed in trusses H-6-1-0, H-6-2-0, H-6-4-0, H-9-1-0, H-9-2-0, H-9-3-0, H-9-4-0, and H-9-5-0. For the secondary verticals (index 4), notable cases include trusses H-6-2-0, H-9-1-0, H-9-3-0, H-9-4-0, H-9-5-0, H-12-5-0, and H-15-3-0. Finally, for the main vertical (index 5), trusses H-6-1-0, H-9-1-0, and H-9-4-0 reached the minimum allowable dimensions.
These results reinforce that the optimization effectively distributed section sizes, allocating minimum dimensions to less stressed regions, resulting in lighter structures while complying with normative requirements.
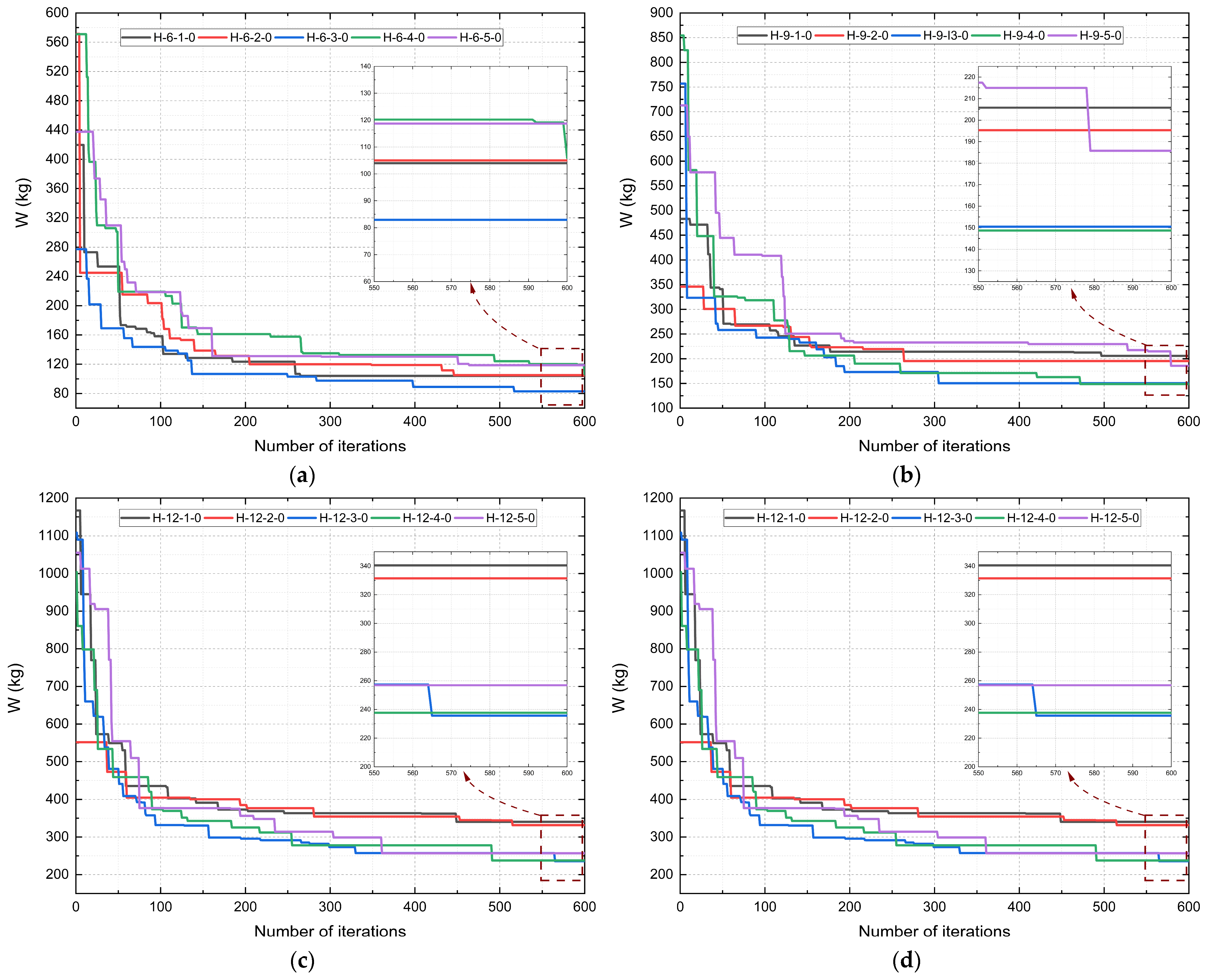
Figure 12 shows the convergence curves for the Howe typology, considering a tolerance rate of 10
−2. Convergence occurred at iterations 264, 445, 516, 599, and 496 for trusses H-6-1-0, H-6-2-0, H-6-3-0, H-6-4-0, and H-6-5-0, respectively. For trusses with a 9 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 496, 263, 304, 471, and 578 for trusses H-9-1-0, H-9-2-0, H-9-3-0, H-9-4-0, and H-9-5-0, respectively. For trusses with a 12 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 448, 514, 564, 490, and 360 for trusses H-12-1-0, H-12-2-0, H-12-3-0, H-12-4-0, and H-12-5-0, respectively. Finally, for trusses with a 15 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 417, 376, 561, 278, and 403 for trusses H-15-1-0, H-15-2-0, H-15-3-0, H-15-4-0, and H-15-5-0, respectively.
The optimization approach proved effective for obtaining efficient and economical truss designs. Nonetheless, the results remain sensitive to input parameters and constraints, which highlights the need for complementary analyses and additional performance metrics before final design decisions are made.
3.1.1. Constraints Under Normal Conditions
As discussed in the previous chapter, the constraints include checks for minimum dimension and area, slenderness limits, geometric limits, design at the Ultimate Limit State (ULS) considering normal stresses in the bars, and design at the Serviceability Limit State (SLS) considering immediate and long-term deflection.
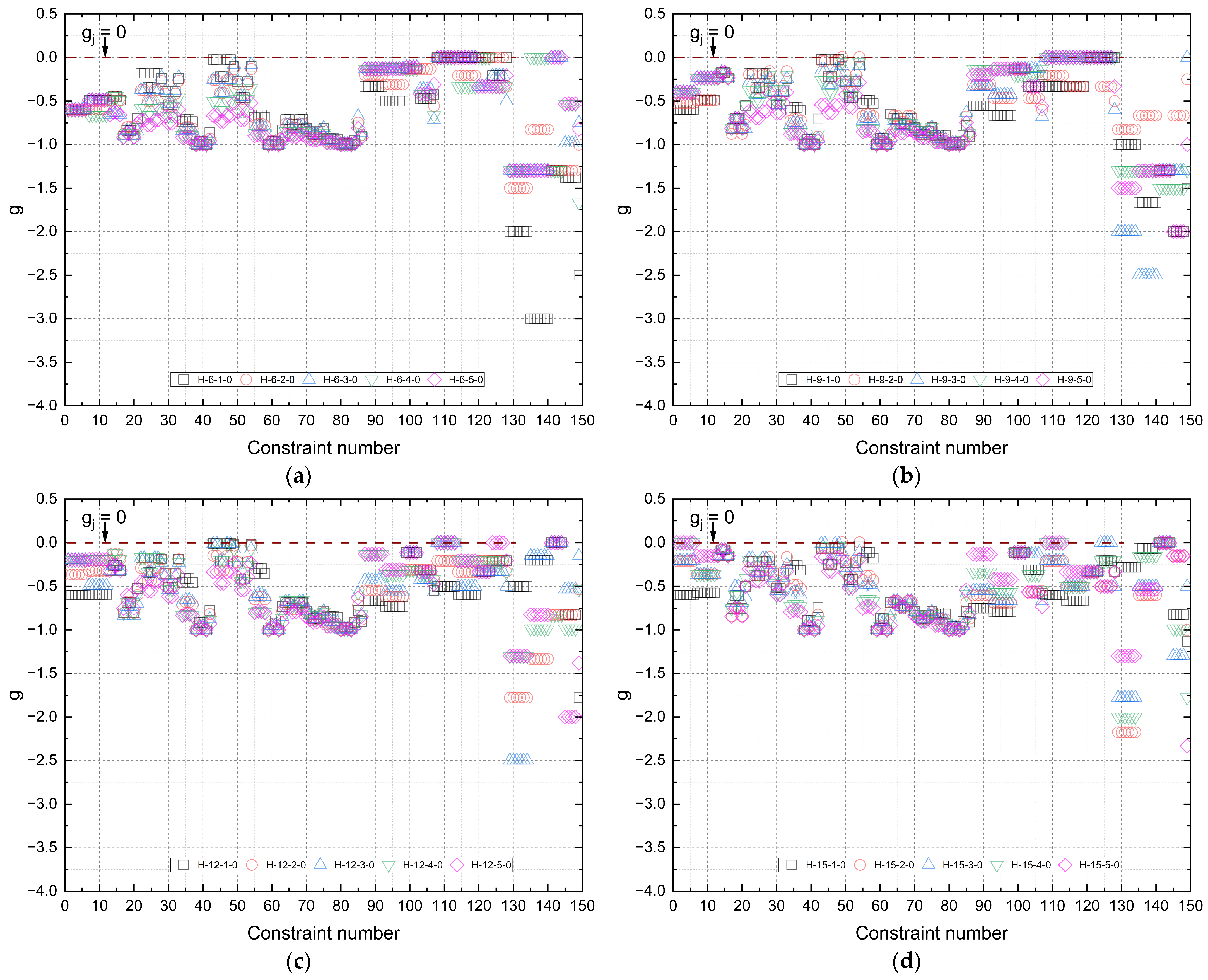
Figure 13 presents the design constraints obtained from the best simulations.
Based on the optimization results, all trusses satisfied the imposed constraints, confirming that the designs are viable in terms of safety and performance (slenderness, ULS, minimum dimensions, and geometric limits). Some members, particularly in lower and upper chords of shorter spans, reached the minimum dimensional limits, while in other cases slenderness and ULS checks governed the design.
These findings highlight that constraint sensitivity varies with the structural role of each member and the wood species adopted. Consequently, the selection of species and the definition of constraints for each application must be made carefully to ensure efficiency and safety.
In summary, the optimization process demonstrated that the imposed constraints provided feasible, safe, and efficient timber truss designs.
3.1.2. ULS Constraints Under Normal Conditions
To evaluate the capacity for distributing normal forces in the truss under normal conditions, analyses of the normal stress constraints were carried out. These analyses were conducted considering combinations 1, 2, and 3 for the loaded bars. The results were summarized (
Table 11) considering the mean (
), standard deviation (
), and the 95% confidence interval (CI).
Analyzing the ULS constraints is essential for understanding the stress level in the truss bars relative to the allowable stress limit. Observing the results in
Table 11, it can be noted that trusses composed of species ID 01 (
Cambará-rosa), ID 02 (
Cupiúba), ID 03 (
Angelim-pedra), and ID 04 (
Garapa) presented mean constraint values closer to zero, suggesting greater bar stress in these configurations. On the other hand, the
Jatobá species (ID 05), which has the highest strength, showed mean constraint values further from zero, indicating lower stress levels.
This behavior reinforces the correlation between the magnitude of acting normal stresses and the mechanical properties of the wood species, especially the characteristic tensile and compressive strengths parallel to the grain ( and ). In other words, species with lower strength resulted in more stressed bars, while stronger species allowed greater relief of internal stresses.
3.2. Optimization Under Fire Conditions
Table 12 presents the overall results from 30 runs of the optimization algorithm for the different Howe truss configurations, considering fire exposure times of 10, 20, and 30 min. The values reported in the tables include the maximum value (
) and the minimum value (
) of the penalized objective function (FO), as well as the amplitude (
), median (
), mean (
), standard deviation (
), feasibility rate (FR), and gross mass increase (GMI).
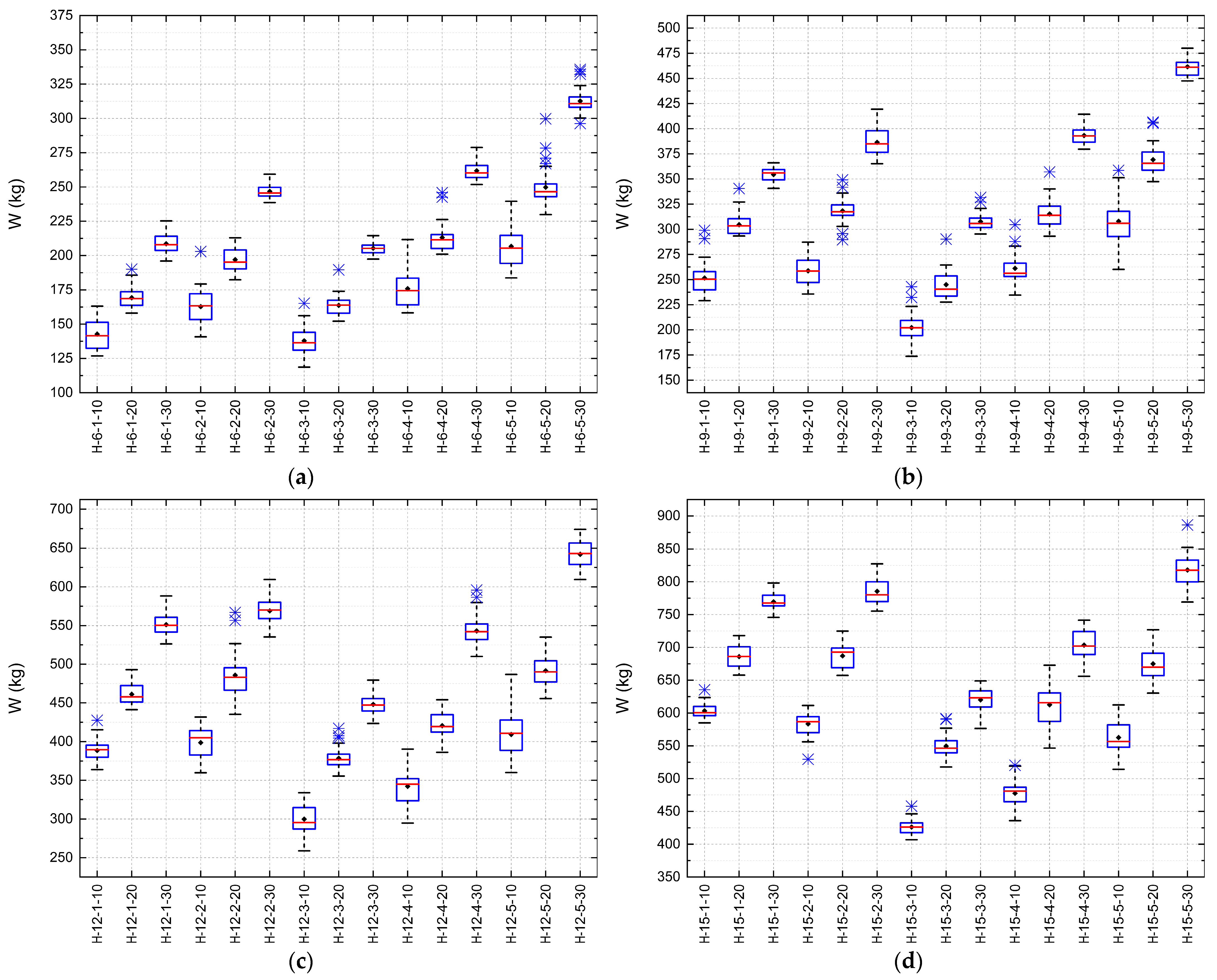
Figure 14 presents the boxplots of the penalized objective function (W) for the Howe-type trusses under fire conditions, considering exposure times of 10, 20, and 30 min for spans of 6 m, 9 m, 12 m, and 15 m. For each analyzed truss configuration, a boxplot was generated. In this type of graph, the central line represents the median, the diamond-shaped point represents the mean, and the box represents the interquartile range (IQR), bounded by the lower quartile (Q1) and the upper quartile (Q3). The whiskers extend from the box up to 1.5 times the IQR, indicating the minimum and maximum values within this range, while values beyond the whiskers are plotted as asterisk-shaped points, representing outliers. In addition, the results correspond to
n = 30 independent optimization runs, which ensures statistical robustness of the comparisons. The data reveal a progressive increase in structural weight, consistent with the progression of charring and the constraints imposed under fire conditions, as modeled according to the guidelines of Eurocode 5 [
6].
Taking the results of truss H-6-1 as an example, the GMI increased from 21.94% (10 min) to 51.91% (20 min), reaching 88.51% (30 min). This evolution reflects the need for larger cross-sectional dimensions to compensate for the reduction in the load-bearing section and the degradation of mechanical properties under thermal exposure. Even more strikingly, the H-15-5 truss, with the largest span and simulated using the Jatobá species (ID 05), shows an GMI rising from 35.80% at 10 min to 103.17% at 30 min, demonstrating that fire exposure time imposes substantial penalties on the structural design.
The increasing GMI trend reinforces the nonlinear relationship between exposure time and final structural mass. As the charring depth increases over time, the algorithm must compensate with larger cross-sections not only to ensure load-bearing capacity but also to keep slenderness ratios within acceptable limits. The sharp rise in GMI between 20 and 30 min suggests the existence of a thermal critical point beyond which structural losses become exponential.
It is also observed that dispersion values, represented by the interquartile range and standard deviation, tend to decrease with increasing exposure time, indicating greater convergence of optimized solutions under more severe conditions. This behavior reflects the reduced feasible search space imposed by thermal and geometric constraints.
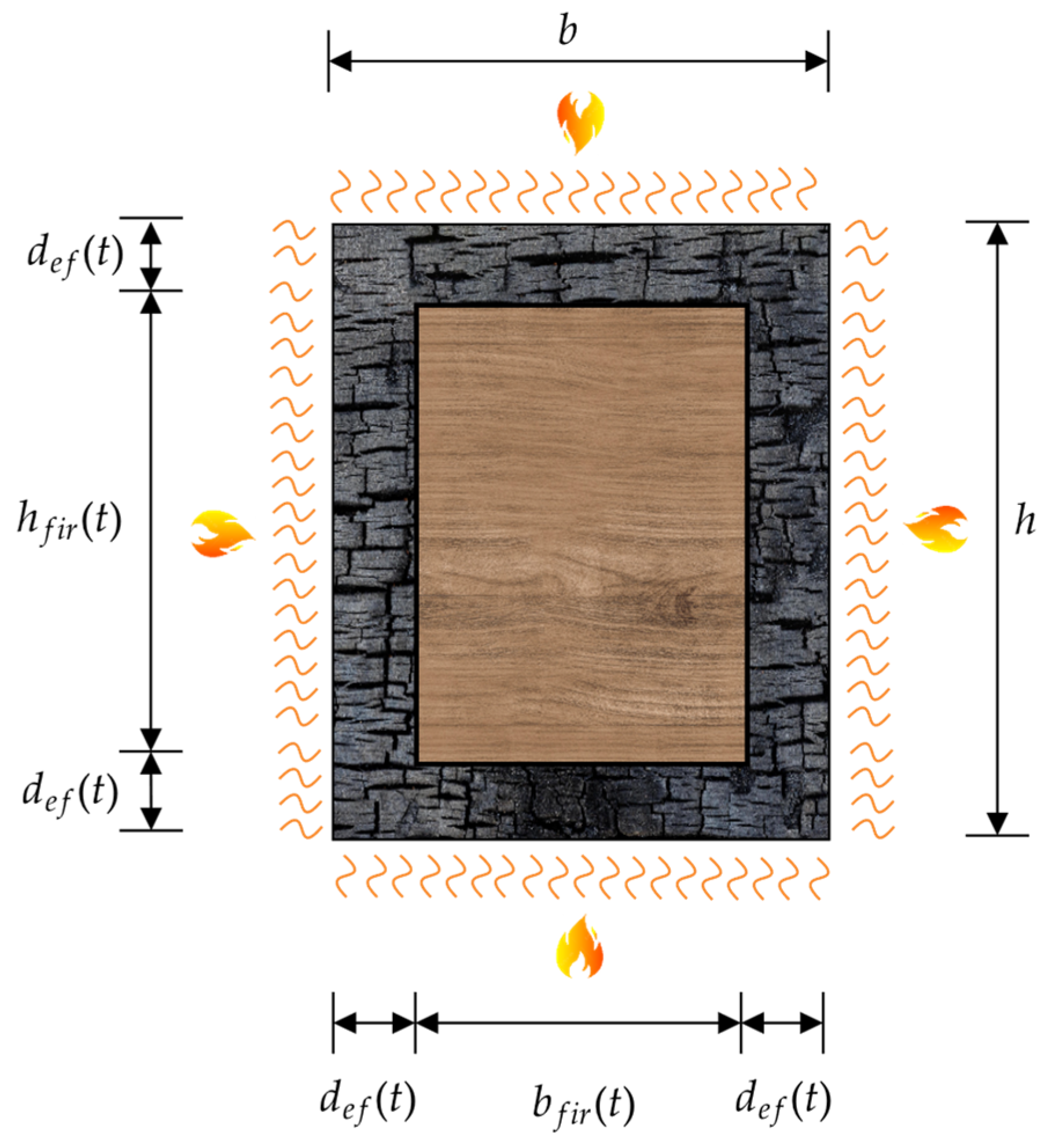
Table 13 presents the final dimensions of the design variables obtained from the optimization process for trusses subjected to fire exposure times of 10, 20, and 30 min. The variables are organized according to the five main groups of structural elements: lower chord (h
1, b
1), upper chord (h
2, b
2), diagonals (h
3, b
3), secondary verticals (h
4, b
4), and main vertical (h
5, b
5), following the nomenclature adopted in this study.
In general, there is a progressive increase in cross-sectional dimensions as exposure time increases. This behavior reflects the need to compensate for the loss of effective area caused by charring and the thermal degradation of wood properties, as modeled by the Eurocode 5 [
6] equations. At early exposure times (10 min), intermediate cross-sections (such as 75 × 115 mm or 100 × 115 mm) predominate, whereas at 30 min the algorithm frequently adopts maximum sections, such as 100 × 150 mm, 125 × 160 mm, and in some cases up to 150 × 200 mm, especially in compression members.
For shorter spans (6 m and 9 m), the optimization resulted in smaller cross-sections, reflecting lower structural demands, while still complying with multiple charring constraints. For longer spans (12 m and 15 m), there is a tendency toward systematically using larger sections across all groups of members, showing that thermal conditions combined with structural instability (such as critical slenderness in long members) require greater stiffness and strength. Elements such as the main vertical (h5, b5) and the diagonals (h3, b3) are particularly affected, given their central role in compression resistance and load redistribution.
These results reinforce the importance of considering fire exposure time as a design parameter, directly influencing the final geometry of the structure.
Table 13 confirms that the optimization algorithm used was able to precisely adjust the dimensions of the structural elements of the Howe typology to meet code requirements in different fire scenarios, ensuring both safety and technical feasibility of the solutions obtained.
3.2.1. Results of the Gross Area Correction Index (GACI)
Table 14 presents the optimized gross area values for the five main bar groups of the Howe trusses (bottom chord, top chord, diagonals, secondary verticals, and main vertical) considering the variation in fire exposure time and truss span. For each group and for each evaluated instance, the respective GACI value is indicated. These data make it possible to identify patterns of fire sensitivity by category or bar group and provide important information for the development of predictive models.
Based on these results, it is observed that GACI values vary significantly among bar groups and among different design instances. While some cases present indices close to unity, indicating a low need for correction, others require doubling or even tripling the original gross area to meet structural criteria under thermal effects, as in truss H-12-2-10. In the Main Vertical group (A5), the gross area correction index GACI5 is equal to 3.48, which represents an increase in more than 248% in relation to the original area. This variability reinforces the need for predictive tools that simultaneously consider multiple variables involved in truss design.
With the objective of estimating the Gross Area Correction Index (GACI) analytically, symbolic regression techniques were applied to generate predictive equations associated with each bar group of Howe-type trusses. This approach allows obtaining interpretable mathematical expressions capable of predicting GACI as a function of variables involved in the structural design, such as truss span, fire exposure time, and bar typology.
Initially, a general model was generated considering all bar groups or categories and design instances. Despite the structural simplicity of the equation, the model presented moderate performance, with a coefficient of determination R
2 of 46.60, mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 18.73%, and maximum absolute error of 119.78%. The regression corresponding to the general model is shown in Equation (33).
In order to improve accuracy in estimating GACI, equations specific to each bar group were subsequently adjusted.
For the bottom chord (Variable 1), the model showed excellent predictive performance, with R
2 of 85.17, MAPE of 8.35%, and maximum absolute error of 29.31. The obtained regression is presented in Equation (34).
The model corresponding to the top chord (Variable 2) also yielded good results, with R
2 of 69.83 and MAPE of 10.82%, although the maximum absolute error was 56.83, indicating some points with greater dispersion. The generated regression is shown in Equation (35).
For the diagonal group (Variable 3), high performance was again observed, with R
2 of 86.51, MAPE of 8.13%, and maximum absolute error of 32.13. The corresponding equation is presented in Equation (36).
In the case of secondary verticals (Variable 4), the adjustment also presented satisfactory results, with R
2 of 66.03, MAPE of 13.62%, and maximum absolute error of 62.02, as represented in Equation (37).
For the main vertical (Variable 5), the worst performance among the specific models was observed, with R
2 of only 27.70, MAPE of 23.17%, and maximum absolute error of 129.52. This result may be associated with the smaller amount of available data for this group and the high sensitivity of this component to geometric and thermal variation. The corresponding equation is presented in Equation (38).
The symbolic regression models adjusted for the Gross Area Correction Index (GACI) revealed notably superior performance in Variable 1 (bottom chord) and Variable 3 (diagonals), whose coefficients of determination reached, respectively, R2 = 85.17% and R2 = 86.51%, with mean absolute percentage errors around 8%.
This high predictive capability results, first of all, from the relatively simple structural function performed by these elements. The bottom chord works predominantly in tension, distributing forces almost uniformly along the span, while the diagonals form well-defined struts whose compression or tension regime depends basically on the fixed truss angle. This mechanical regularity results in GACI curves almost proportional to fire exposure time, a pattern readily captured by the square and cube operators included in PySR’s search space.
Furthermore, these groups exhibit low geometric variability: there are two bottom chords per truss, all with length equal to the span, and the diagonals maintain a constant angle defined by the L/H ratio. Since the parametric study covered four spans (6 m, 9 m, 12 m, and 15 m), five wood species, and four fire times (0, 10, 20, and 30 min), the largest observation base was formed precisely for Variable 1 and Variable 3. Larger samples reduce statistical error and increase goodness-of-fit, favoring high R2 values.
Another decisive factor is how the design constraints manifest themselves in these elements. For the bottom chord, slenderness and minimum area checks rarely become critical; thus, GACI increases smoothly, almost linearly, with fire time. In the diagonals, the constraints only worsen in the largest spans and at 30 min of exposure, remaining moderate in the rest of the analysis domain. The absence of abrupt changes in the constraint regime avoids inflection points in the response, allowing compact symbolic expressions to adequately represent GACI behavior.
In contrast, the top chord (Variable 2) and the secondary verticals (Variable 4) presented R2 between 66% and 70%, as they alternate between tension and compression depending on the combination of wind and dead load, introducing nonlinearities difficult to capture; the GACI estimate for the main vertical (Variable 5) resulted in a coefficient of determination close to 28%, impaired by the smaller data volume and the high geometric and thermal sensitivity of this component. Thus, the combination of unidirectional loading pattern, repetitive geometry, large data volume, and low interference of severe constraints explains the superior performance of the models for the bottom chord and the diagonals, making them reliable instruments for quick section increase estimates in preliminary design stages of timber trusses under fire.
The variables employed in Equations (35)–(38) were defined according to the ranges observed in the case studies. The fire exposure time (
) varied from 0 to 30 min, consistent with the parametric analyses summarized in
Table 5, covering both the initial condition (t = 0 min) and final condition (t = 30 min), with intermediate values of 10 and 20 min adopted to capture the progressive degradation trend. The ratio L/H was defined according to the span and height of each truss configuration analyzed. The mechanical properties (
,
and
) were defined based on the experimental characterization of the five Brazilian timber species, as reported in
Table 2. For these species, the tensile strengths were approximately between 50 MPa and 130 MPa, the compressive strengths were approximately between 35 MPa and 100 MPa, and the mean moduli of elasticity were approximately between 12,000 MPa and 22,000 MPa. By explicitly establishing these ranges, the dimensional consistency of the symbolic regression equations is guaranteed, and their application domain is clearly delimited.
These equations can be employed in preliminary design stages to estimate the required increase in the gross area of each bar group as a function of fire exposure time and the geometric characteristics of the truss, without the need to rerun optimization algorithms for each new instance. Therefore, they constitute a relevant auxiliary tool for the design of timber truss structures under different fire scenarios.
3.2.2. Convergence of Results Under Fire Conditions
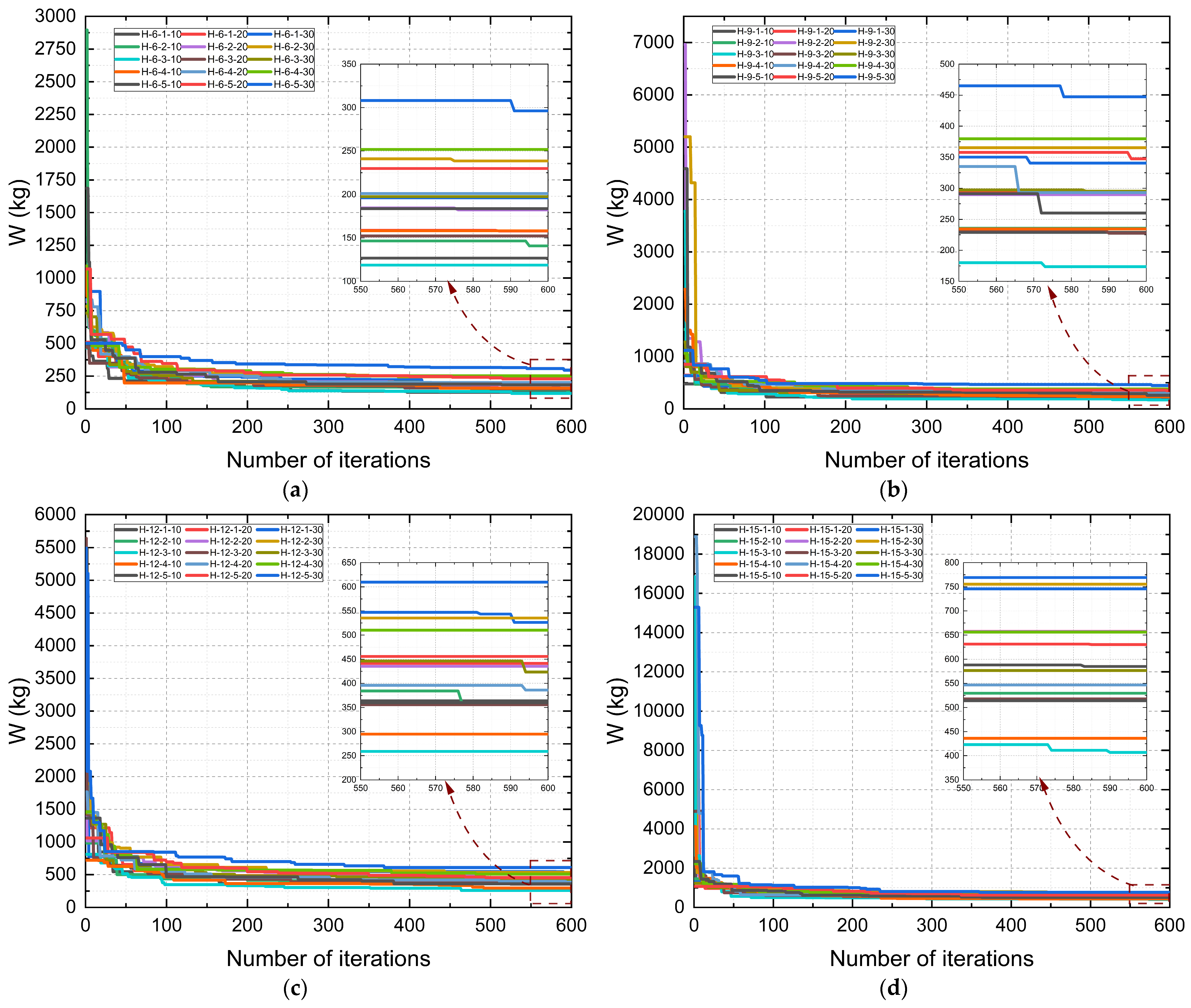
Figure 15 shows the convergence curves of the best responses obtained after 30 repetitions of the mass optimization process for Howe-type trusses with spans of 6 m, 9 m, 12 m, and 15 m, considering species ID 01, ID 02, ID 03, ID 04, and ID 05, for fire exposure times of 10, 20, and 30 min.
Considering a tolerance ratio of 10−2, convergence occurred at iterations 396, 586, 476, 594, 575, 574, 525, 547, 412, 437, 427, 321, 513, 514, and 590 for trusses H-6-1-10, H-6-1-20, H-6-1-30, H-6-2-10, H-6-2-20, H-6-2-30, H-6-3-10, H-6-3-20, H-6-3-30, H-6-4-10, H-6-4-20, H-6-4-30, H-6-5-10, H-6-5-20, and H-6-5-30, respectively.
For trusses with a 9 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 101, 348, 568, 305, 539, 240, 572, 589, 583, 485, 565, 329, 571, 595, and 577 for trusses H-9-1-10, H-9-1-20, H-9-1-30, H-9-2-10, H-9-2-20, H-9-2-30, H-9-3-10, H-9-3-20, H-9-3-30, H-9-4-10, H-9-4-20, H-9-4-30, H-9-5-10, H-9-5-20, and H-9-5-30, respectively.
For trusses with a 12 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 167, 549, 590, 576, 492, 443, 463, 524, 593, 491, 593, 481, 380, 493, and 368 for trusses H-12-1-10, H-12-1-20, H-12-1-30, H-12-2-10, H-12-2-20, H-12-2-30, H-12-3-10, H-12-3-20, H-12-3-30, H-12-4-10, H-12-4-20, H-12-4-30, H-12-5-10, H-12-5-20, and H-12-5-30, respectively.
Finally, for trusses with a 15 m span, convergence occurred at iterations 517, 564, 570, 353, and 546 for trusses H-15-1-10, H-15-1-20, H-15-1-30, H-15-2-10, H-15-2-20, H-15-2-30, H-15-3-10, H-15-3-20, H-15-3-30, H-15-4-10, H-15-4-20, H-15-4-30, H-15-5-10, H-15-5-20, and H-15-5-30, respectively.
3.2.3. Constraints Under Fire Conditions
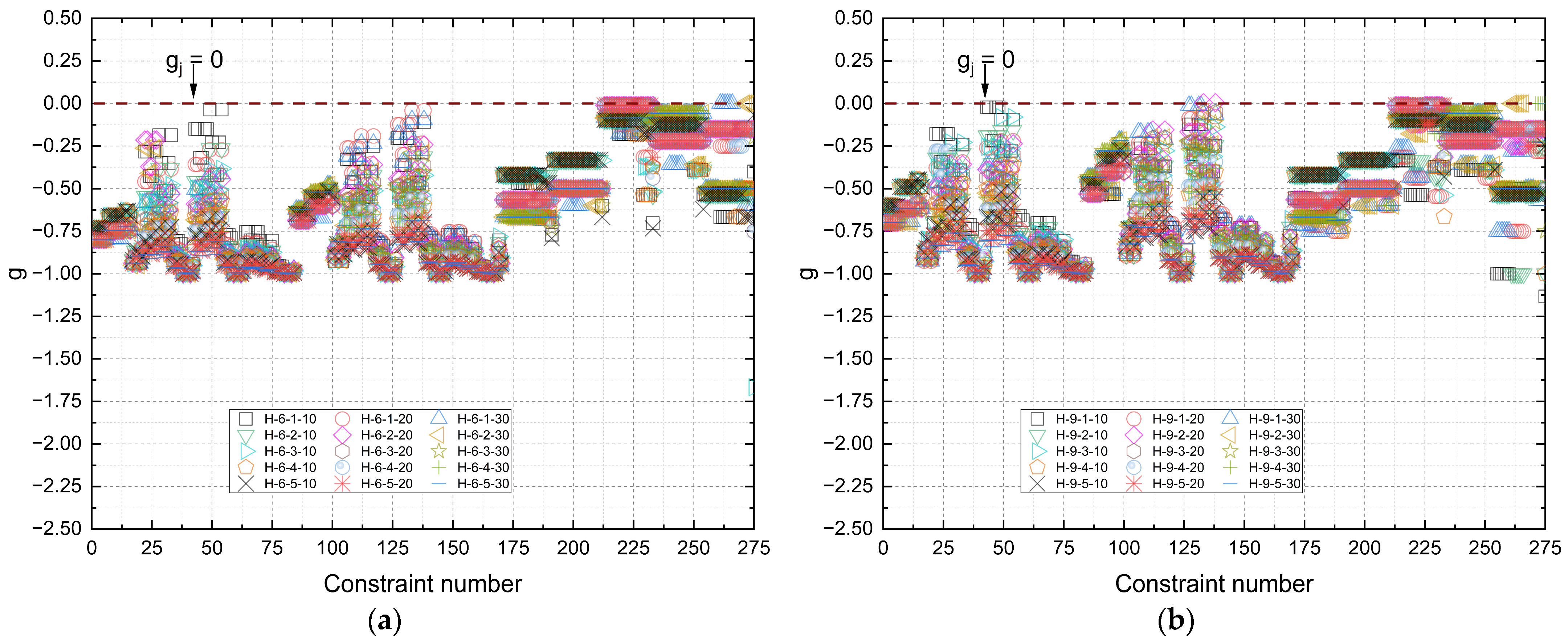
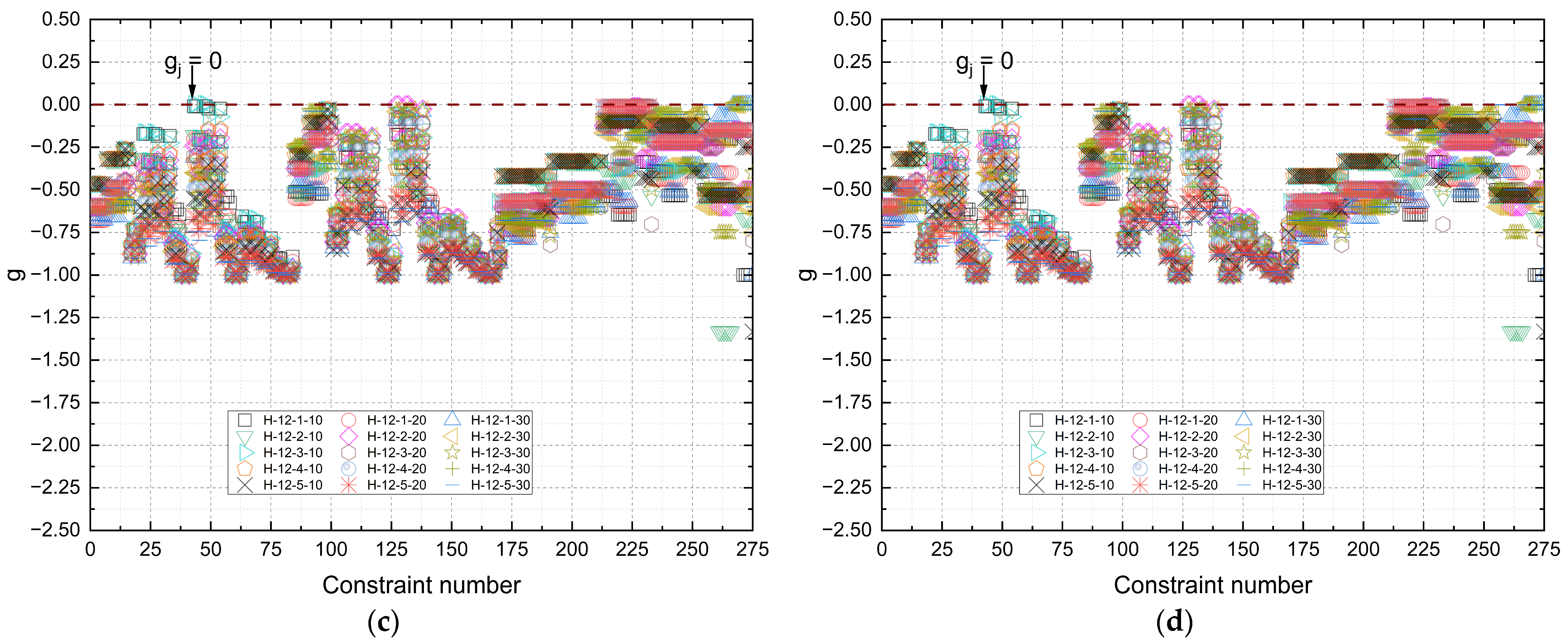
Figure 16 shows the distribution of design constraints (
g) for Howe-type trusses, considering the best results obtained by the optimization process under fire conditions for different exposure times (10, 20, and 30 min) and spans (6 m, 9 m, 12 m, and 15 m). The graphs illustrate the degree of stress in the structural members and the adherence of the solutions to the limits imposed by technical standards, adjusted to the scenario of thermal degradation of the timber.
The constraint values remained negative across all configurations, which confirms that the solutions fully met the regulatory requirements. The average g values predominantly range between −0.50 and −0.65.
It is also observed that as the fire exposure time increases, there is a tendency toward reduced dispersion of constraints, especially for the larger spans (12 m and 15 m). This effect indicates that the algorithm, when facing more critical thermal conditions, converges to a more restricted set of viable solutions, leading to the design of members with smaller safety margins relative to the regulatory limits. Furthermore, there is evidence of constraint activation (g ≈ 0) in long, compressed members, especially in the top chords and diagonals, in 30 min scenarios, which reinforces the structural criticality of these members under fire conditions.
Based on the results shown in
Figure 15, it is evident that the Howe typology exhibits robust and safe performance in meeting fire design requirements, with solutions that remain viable even under severe thermal degradation.
3.2.4. ULS Constraints Under Fire Conditions
Table 15 presents a summary of Ultimate Limit State (ULS) constraints for the Howe truss, considering different fire exposure times (10, 20, and 30 min) and spans of 6 m, 9 m, 12 m, and 15 m. The values were obtained from the best solutions of the optimization process and are expressed in terms of the mean, standard deviation, and confidence interval (CI).
In general, the constraint (g) values remain negative and predominantly range between −0.60 and −0.92, indicating that all members operate within the limits established by the standard but with different stress levels. In smaller spans (6 m and 9 m), the average g values tend to be less negative, with lower stress intensity, reflecting the reduced structural demand of these models. Conversely, in larger spans (12 m and 15 m), g values become more negative, especially in 30 min exposure scenarios, showing that the trusses are operating under more critical structural conditions and closer to the regulatory limit. This is due to the significant loss of load-bearing area in charred sections and the degradation of timber properties at elevated temperatures.