Short-Term Effects of N Deposition on Soil Respiration in Pine and Oak Monocultures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Measuring Soil Respiration (Rs)
2.4. Litterfall Collection
2.5. Fine Root Biomass Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
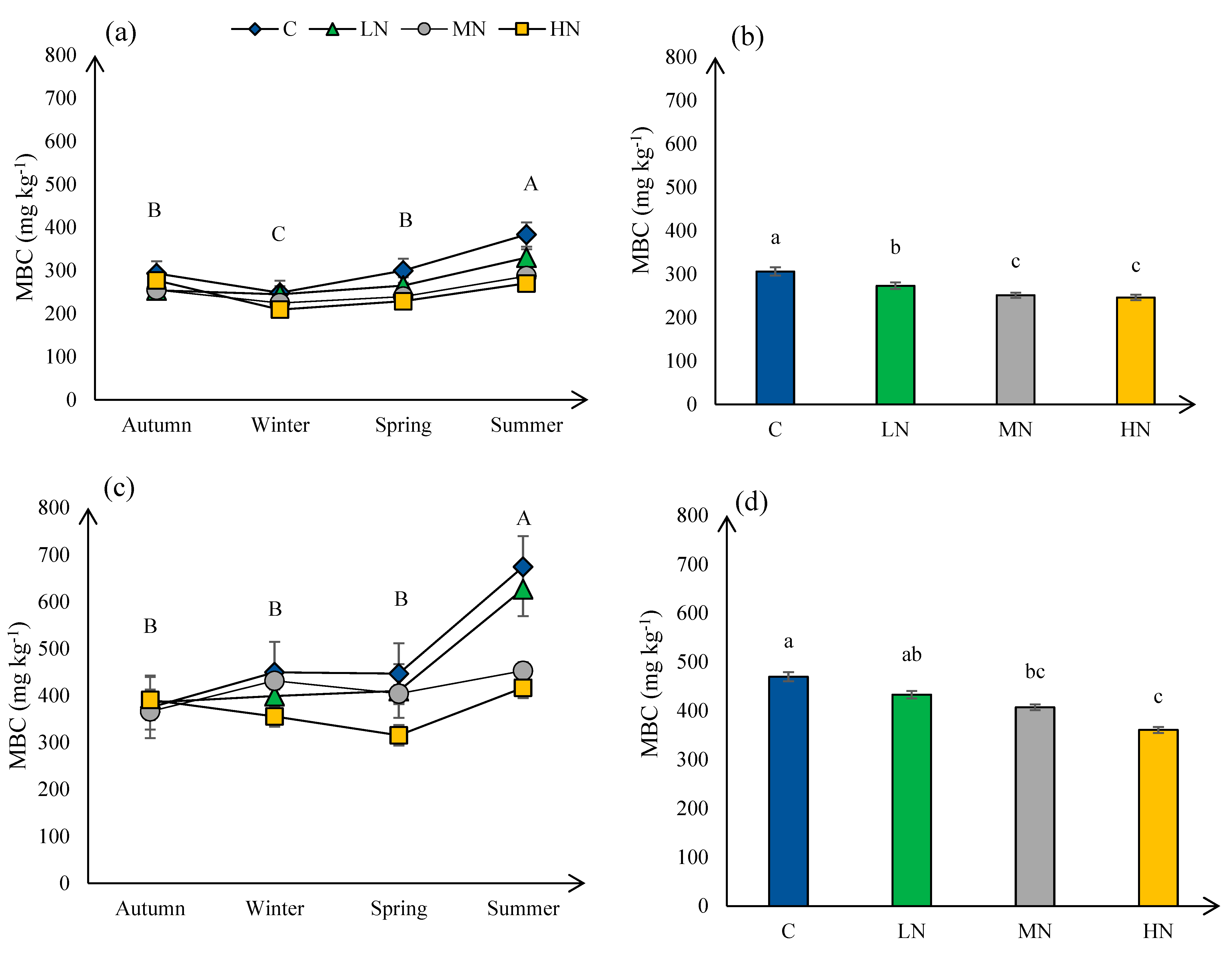
3.1. Microbial Biomass Carbon (MBC)
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
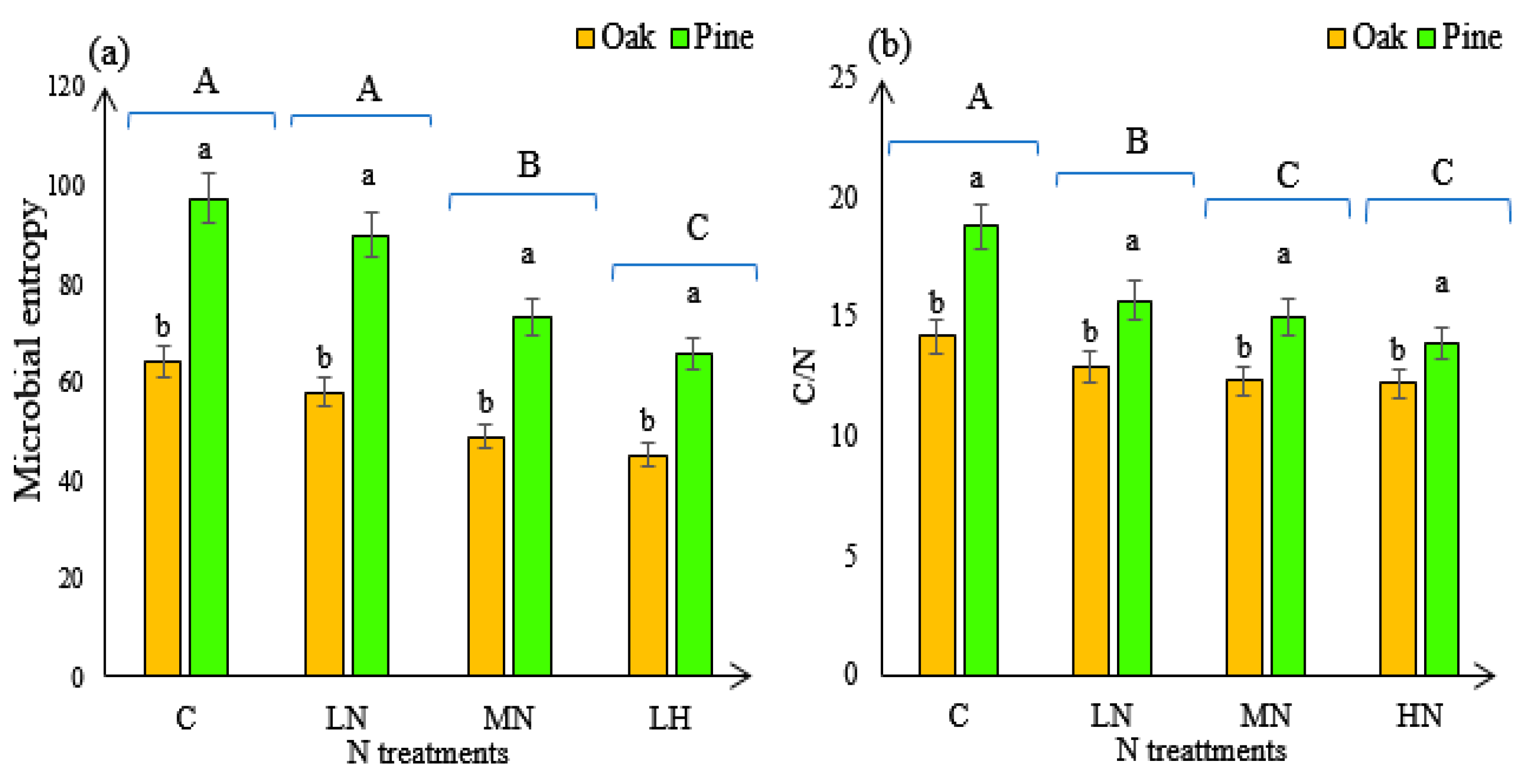
3.3. Soil Microbial Entropy and C/N Ratio
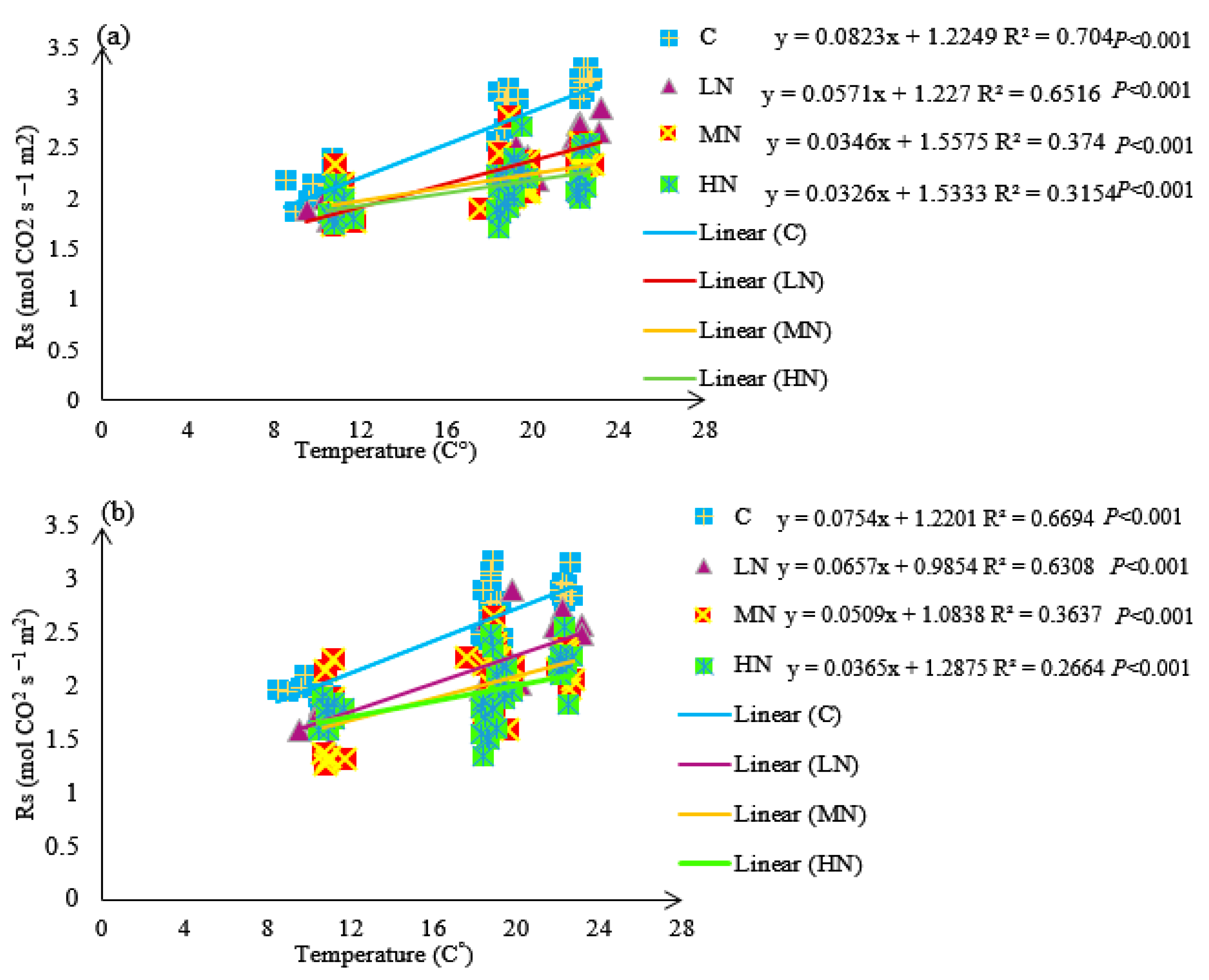
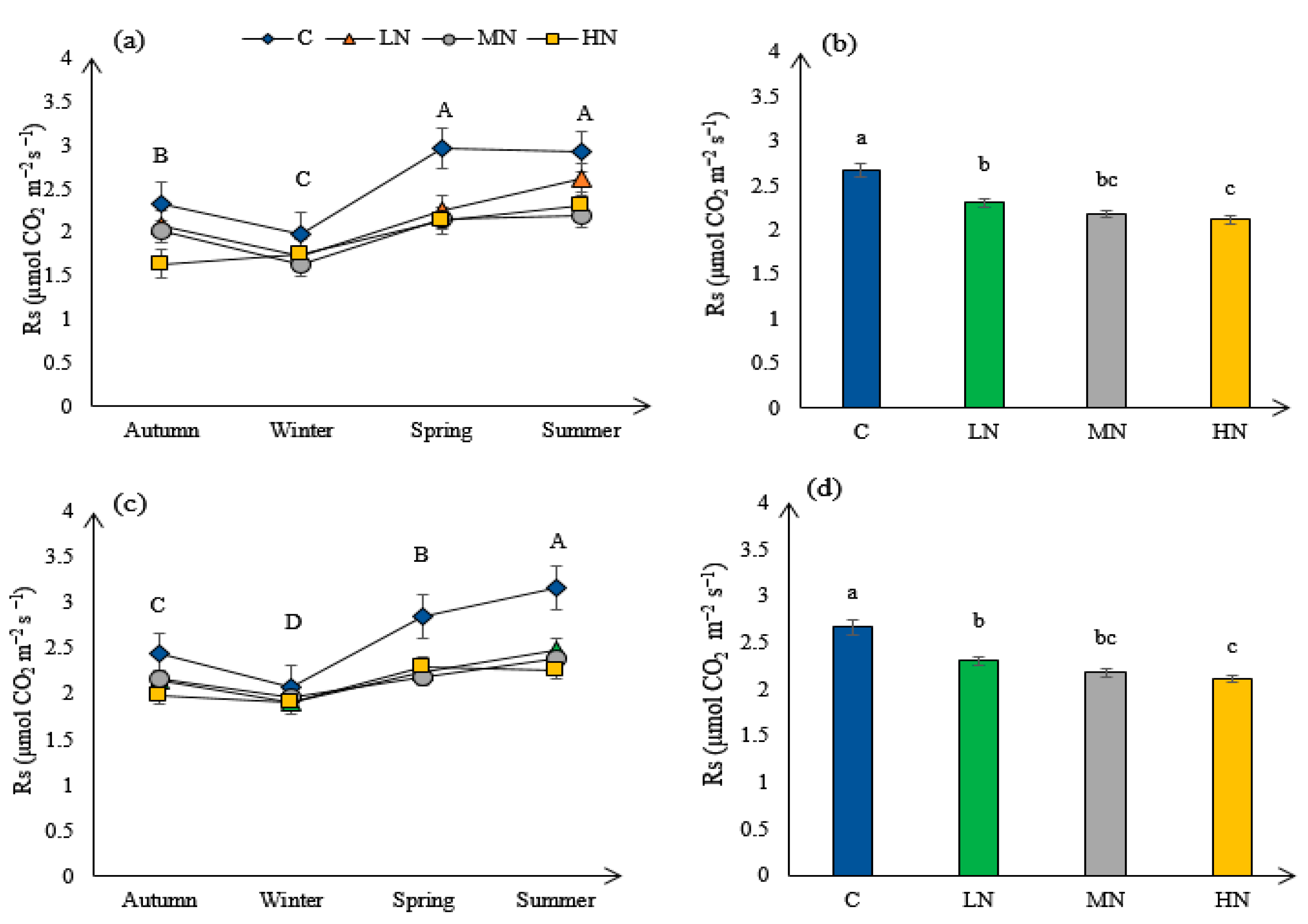
3.4. Soil Respiration (Rs)
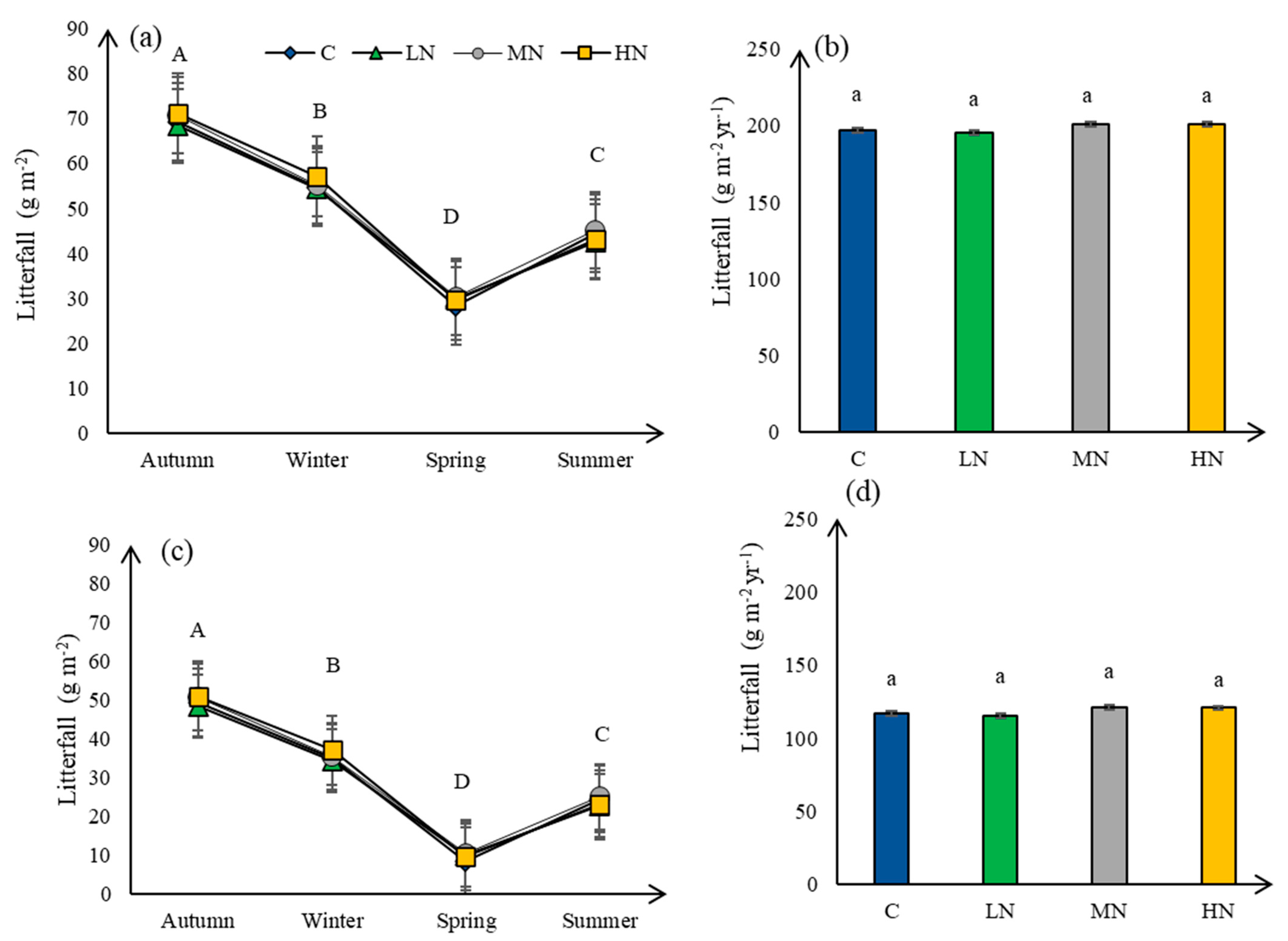
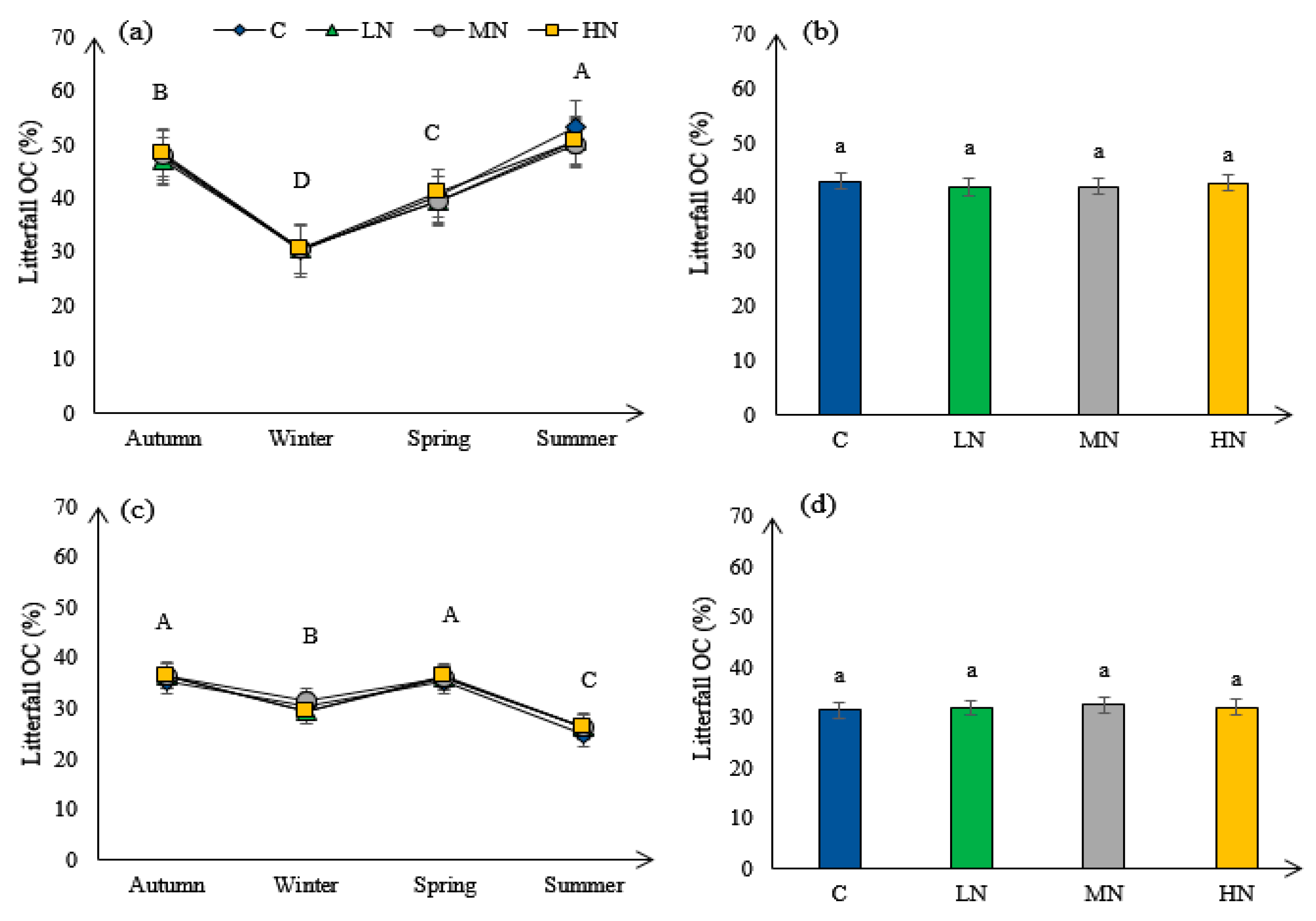
3.5. Litterfall
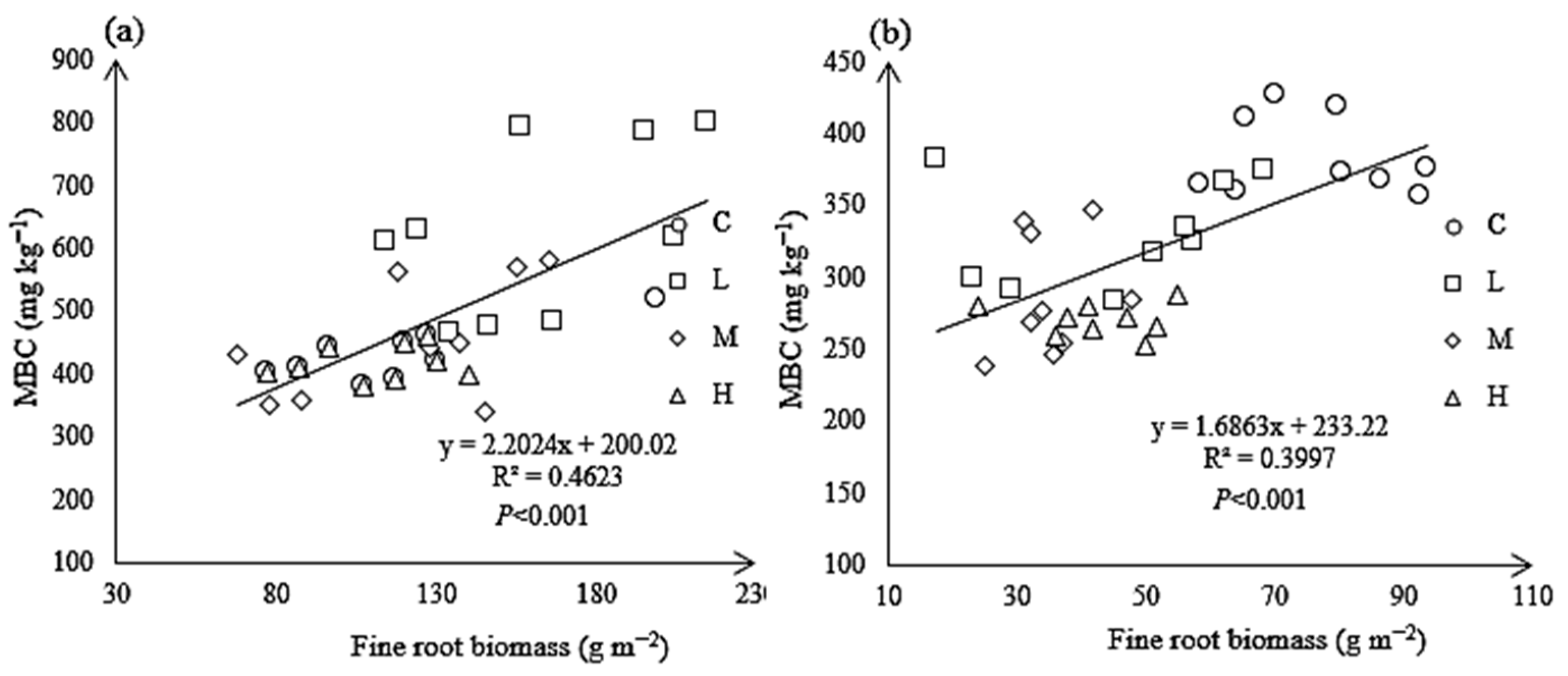
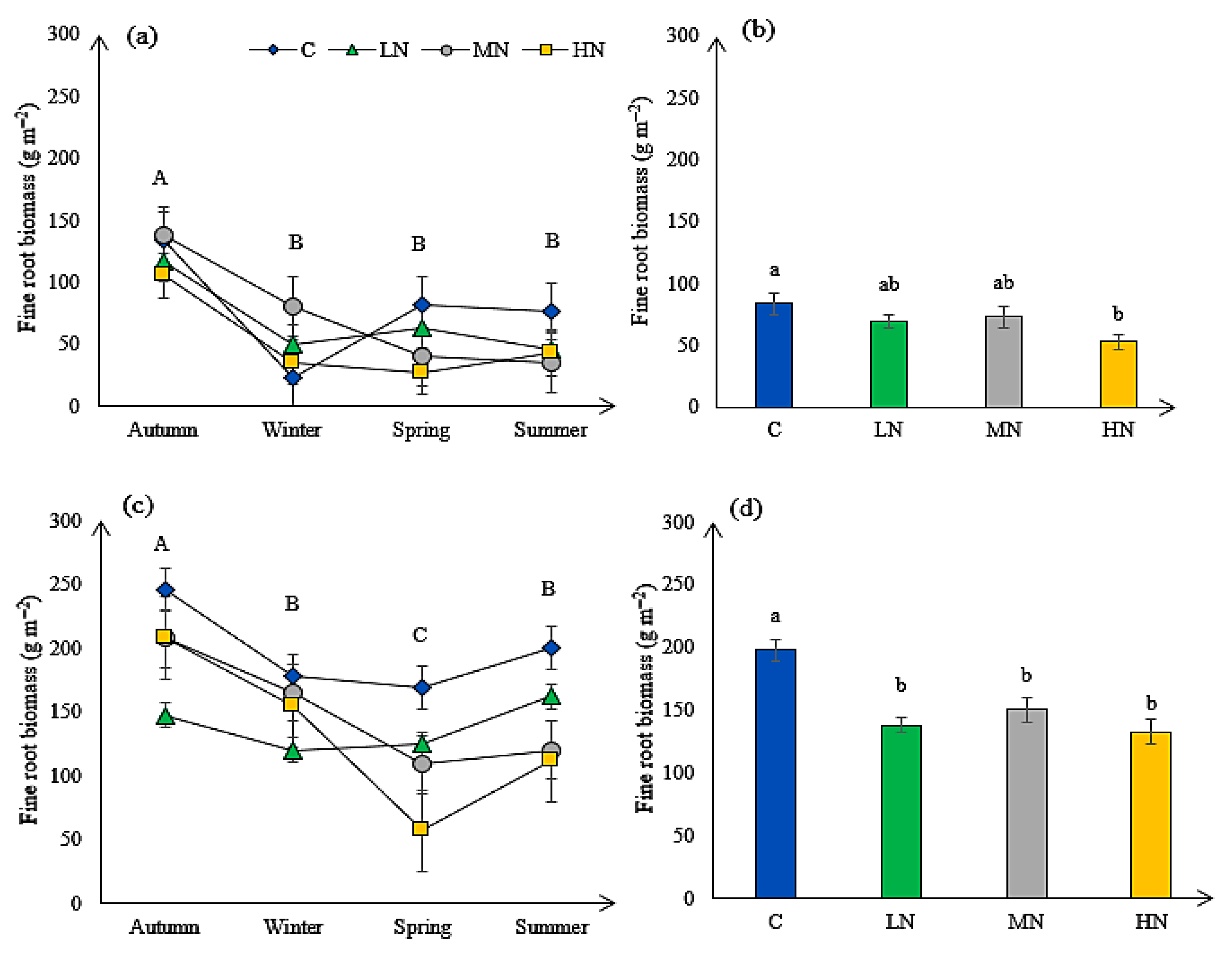
3.6. Fine Root Biomass
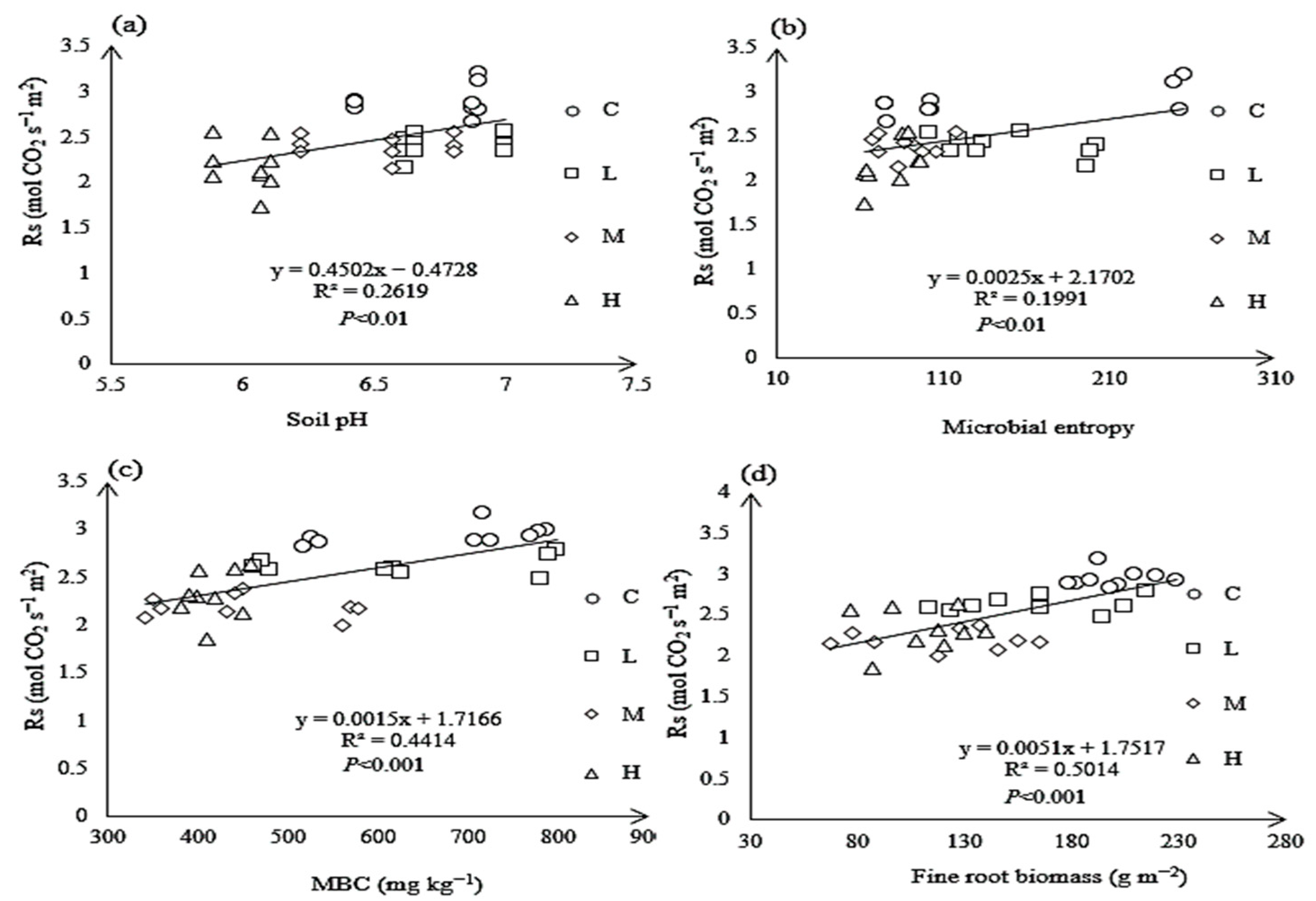
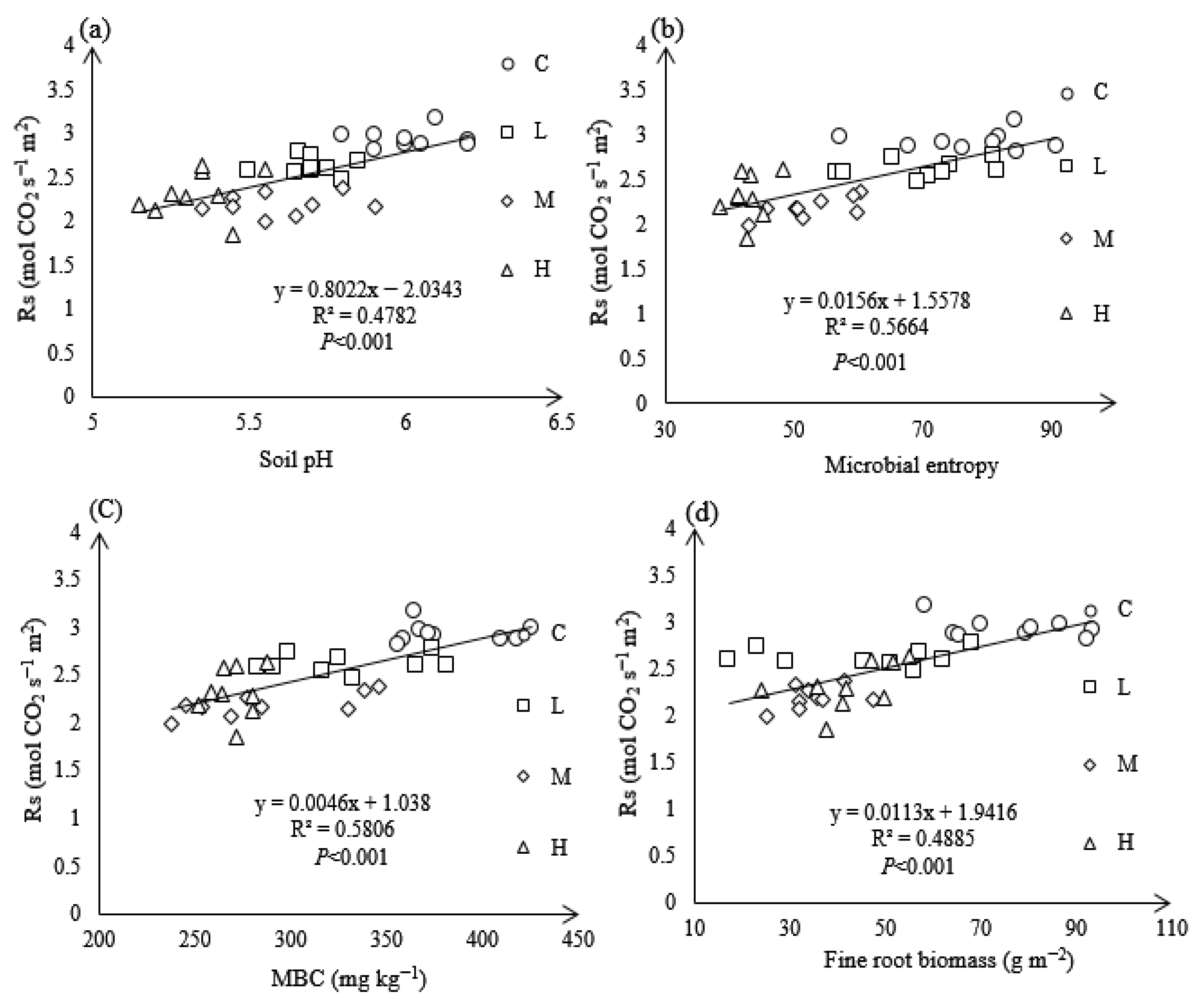
3.7. Relationship Between Rs and Soil Properties Under N Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, F.; Wang, G.G.; Mao, R.; Fang, X.; Wang, H.; Bu, W. Effects of experimental nitrogen addition on nutrients and nonstructural carbohydrates of dominant understory plants in a Chinese fir plantation. Forests 2018, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Song, S.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Chen, G.T.; Hu, H.L.; Xie, J.L.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Y.L.; Liu, L.; et al. Influences of nitrogen addition and aboveground litter-input manipulations on soil respiration and biochemical properties in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafazoli, M.; Hojjati, S.M.; Jalilvand, H.; Lamersdorf, N.; Tafazoli, M. Effect of nitrogen addition on soil CO2 efflux and fine root biomass in maple monocultures of the Hyrcanian region. Ann. For. Sci. 2021, 78, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mao, Q.; Gilliam, F.S.; Luo, Y.; Mo, J. Nitrogen deposition contributes to soil acidification in tropical ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3790–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafazoli, M.; Hojjati, S.M.; Jalilvand, H.; Lamersdorf, N. Simulated Nitrogen Deposition Reduces the Concentration of Soil Base Cations in Acer velutinum Bioss. Plantation, North of Iran. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraei, A.; Jalilvand, H.; Hojjati, S.M.; Schleppi, P.; Alavi, S.J. Effects of artificial nitrogen deposition on the forest floor and soil chemistry under chestnut-leaved oak (Quercus castaneifolia C. A. Mey) plantation in the north of Iran. Can. J. For. Res. 2022, 52, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xiang, Y.; Tie, L.; Han, B.; Huang, C. Simulated nitrogen deposition significantly reduces soil respiration in an evergreen broadleaf forest in western China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, L.H.; Hu, T.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.W.; Hu, H.L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.L. Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, R.; Ågren, G.I.; Linder, S.; Persson, T.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Ekblad, A.; Freeman, M.; Grelle, A.; Janssens, I.A.; Jarvis, P.G.; et al. The likely impact of elevated CO2, nitrogen deposition, increased temperature and management on carbon sequestration in temperate and boreal forest ecosystems: A literature review. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J.; King, J.S.; Zak, D.R. Soil respiration, root biomass, and root turnover following long-term exposure of northern forests to elevated atmospheric CO2 and tropospheric O3. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yan, W.; Shangguan, Z. Soil carbon and nitrogen fractions in the soil profile and their response to long-term nitrogen fertilization in a wheat field. Catena 2015, 135, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Geng, Y.; Cao, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, X. Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China. Forests 2018, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Peng, M.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil respiration: Evidence from a three-year field study of the Abies georgei (Orr) forest in the Jiaozi Snow Mountains National Nature Reserve, Southwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 542, 121098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, S.; Huang, E.; Zhang, D.; Chen, G.; Zhu, J.; Ji, C.; Zhu, B.; Liu, L.; Fang, J. Nitrogen addition promotes soil carbon accumulation globally. Sci. China Life Sci. 2025, 68, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, C.A.; Filley, T.R.; Boutton, T.W.; Oleynik, S.; Kantola, I.B. Controls on soil carbon accumulation during woody plant encroachment: Evidence from physical fractionation, soil respiration, and δ13C of respired CO2. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S.E.G. Increased carbon transport in the Hudson River: Unexpected consequence of nitrogen deposition. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, D.S. Terrestrial ecosystems and the carbon cycle. Glob. Change Biol. 1995, 1, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Shao, J.; Nie, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Z.; Bai, S.H. Interactive effects of global change factors on soil respiration and its components: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang Biol. 2016, 22, 3157–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Ito, A.; Yonemura, S.; Takeuchi, W. Estimation of global soil respiration by accounting for land-use changes derived from remote sensing data. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Wang, S.P.; Yue, C.; Shen, H.H. Global warming, human-induced carbon emissions, and their uncertainties. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mao, Q.; Gilliam, F.S.; Luo, Y.; Turner, B.L.; Zhou, G.; Mo, J. Nitrogen deposition accelerates soil carbon sequestration in tropical forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024460118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, G.; Wang, H.; Xing, Y. Natural δ13C and δ15N abundance of plants and soils under long-term N addition in a temperate secondary forest. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3491–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, N.I.; Nordin, A.; Hasselquist, N.J.; Bach, L.H.; Palmqvist, K.; Gundale, M.J. Anthropogenic nitrogen deposition enhances carbon sequestration in boreal soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3169–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y. Inorganic Nitrogen Addition Affects Soil Respiration and Belowground Organic Carbon Fraction for a Pinus tabuliformis Forest. Forests 2019, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, X.; Chang, S.X.; Peng, C.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. Nitrogen depositions increase soil respiration and decrease temperature sensitivity in a Moso bamboo forest. Agri. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Davidson, E.; Savage, K.; Arabia, C.; Steudler, P. Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.J.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Reuss, R.W.; Hendrick, R.L.; Allen, M.F. Root respiration in North American forests: Effects of nitrogen concentration and temperature across biomes. Oecologia 2002, 131, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Giardina, C.P.; Xiong, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; et al. Will nitrogen deposition mitigate warming-increased soil respiration in a young subtropical plantation? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 246, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.E.; Davidson, E.A. Interannual variation of soil respiration in two New England forests. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, N.; Kosugi, Y.; Sakabe, A.; Kanazawa, A.; Ohkubo, S.; Tani, M. Seasonal and diurnal patterns of soil respiration in an evergreen coniferous forest: Evidence from six years of observation with automatic chambers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Zhou, J.; Yan, G.; Liu, G.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition and precipitation reduction on the fine root dynamics and morphology in a temperate forest. Eur. J. For. Res. 2022, 141, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, M.C.; Fahey, T.J. Microbial biomass and nitrogen cycling responses to fertilization and litter removal in young northern hardwood forests. Biogeochemistry 2001, 53, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.-A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, D.; Hall, S.J.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Fu, H.; Wan, C.; Elser, J.J. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components and their temperature sensitivities in a semiarid grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wan, S. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsmark, B.; Nordin, A.; Maaroufi, N.I.; Lundmark, T.; Gundale, M.J. Low and High Nitrogen Deposition Rates in Northern Coniferous Forests Have Different Impacts on Aboveground Litter Production, Soil Respiration, and Soil Carbon Stocks. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-T.; Liu, Y.-N.; Zhong, H.-X.; Chen, X.-W.; Xin, S. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on the soil microbial community diversity of a Deyeuxia angustifolia wetland in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Gallo, M.E.; Lauber, C.; Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R. Extracellular enzyme activities and soil organic matter dynamics for northern hardwood forests receiving simulated nitrogen deposition. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Lv, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, L. Ecological effects of atmospheric nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activity. J. For. Res. 2013, 24, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, P.; Qiu, J.; Shang, S. Impacts of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activity in a northern temperate forest ecosystem depend on the form and level of added nitrogen. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 103, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagheb-Talebi, K.; Sajedi, T.; Pourhashemi, M. Forests of Iran, A Treasure from the Past, a Hope for the Future. Springer 2014, 1007, 978–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M. Outstanding universal values of Hyrcanian Forest, the newest Iranian property, inscribed in the UNESCO’s World Heritage List. Tourism Res. 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Asadian, M.; Hojjati, S.M.; Pourmajidian, M.R.; Fallah, A. Impact of land-use management on nitrogen transformation in a mountain forest ecosystem in the north of Iran. J. For. Res. 2013, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvi-Mohajer, M.R. Silviculture and Forest Tending; University of Tehran Press: Tehran, Iran, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Lu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hartley, I.P.; Zhang, W.; Mo, J.; Yu, G.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Long-term nitrogen addition modifies microbial composition and functions for slow carbon cycling and increased sequestration in tropical forest soil. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3267–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Kang, F.; Cheng, X.; Han, H. Response of soil organic carbon and nitrogen to nitrogen deposition in a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Gruber, F.; Geranfar, S.; Moniri, V.R. Investigation on nitrogen deposition in the greater Tehran metropolitan area and Caspian Sea lowland areas of Iran, up to altitude of 2200 meters. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 4, 426–431. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, L.E. Organic carbon. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, AL, USA, 1975; p. 1367. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, L.A. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate USDA Circular 030; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Sparling, G.P.; Feltham, C.W.; Reynolds, J.; West, A.W.; Singleton, P. Estimation of soil microbial C by a fumigation-extraction method: Use on soils of high organic matter content, and a reassessment of the EC-factor. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in the soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Domsch, K.H. Relationship between soil organic carbon and microbial biomass on chronosequences of reclamation sites. Microb. Ecol. 1988, 15, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, S.M.; Lamersdorf, N.P. Effect of canopy composition on soil CO2 emission in a mixed spruce beech forest at Solling, Central Germany. J. For. Res. 2010, 21, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, S.M.; Hagen-Thorn, A.; Lamersdorf, N.P. Canopy composition as a measure to identify patterns of nutrient input in a mixed European beech and Norway spruce forest in central Europe. Eur. J. For. Res. 2009, 128, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.T.S.; Miranda, I.S.; Vasconcelos, S.S. Effects of water and nutrient availability on fine root growth in eastern Amazonian forest regrowth, Brazil. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhelm, A.F.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J. No evidence that chronic nitrogen additions increase photosynthesis in mature sugar maple forests. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Fu, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, X. Short-term effects of nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components in two alpine coniferous forests, southeastern Tibetan plateau. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, A.H.; Aber, J.D.; Currie, W.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Martin, M.E.; McDowell, W.H.; Melillo, J.M.; Steudler, P. Ecosystem response to 15 years of chronic nitrogen additions at the Harvard Forest LTER, Massachusetts, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, G.; Li, S.; Peng, T.; Qiu, X.; Luo, J.; Yang, S.; Hu, T.; Hu, H.; et al. Soil biochemical responses to nitrogen addition in a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.D.; Evans, C.D.; Dise, N.B.; Hall, J.R.; Caporn, S.J. Long-term nitrogen deposition increases heathland carbon sequestration. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 15, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Wang, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. N fertilization decreases soil organic matter decomposition in the rhizosphere. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Ollinger, S.; Nadelhoffer, K.E.; Bowden, R.; Brzostek, E.; Burton, A.; Caldwell, B.A.; Crow, S.; Goodale, C.L.; Grandy, A.S.; et al. Chronic nitrogen additions suppress decomposition and sequester soil carbon in temperate forests. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, K.G. CO2 efflux from coniferous forest soils: Comparison of measurement methods and effects of added nitrogen. In Advances in Soil Science: Soils and Global Change; Lal, R., Kimnble, J., Levine, E., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 329–342. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, C.A.; Kress, L.W. Soil CO2 evolution and root respiration in 11-year-old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) plantations as affected by moisture and nutrient availability. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.-X. Major factors controlling nitrous oxide emission and methane uptake from forest soil. J. For. Res. 2001, 12, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Xing, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; et al. Sequestration of atmospheric CO2 in boreal forest carbon pools in northeastern China: Effects of nitrogen deposition. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 248, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Nitrogen addition alleviates microbial nitrogen limitations and promotes soil respiration in a subalpine coniferous forest. Forests 2019, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 2332–2343. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/13652486 (accessed on 29 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.S.; Rovira, A.D. Oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide evolution of heat-sterilized soil. Nature 1954, 173, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, S.M.; Tafazoli, M.; Asadian, M.; Baluee, A. Soil respiration and carbon stock responses to land use changes in the temperate forest of northern Iran. Env. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jose, S. Soil respiration, fine root production, and microbial biomass in cottonwood and loblolly pine plantations along a nitrogen fertilization gradient. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 185, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T.; Chen, L.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F. N and P fertilization reduced soil autotrophic and heterotrophic respiration in a young Cunninghamia lanceolata forest. Agri. For. Meteo. 2017, 232, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxman, A.W.; Blanck, K.; Brandrud, T.E.; Emmett, B.A.; Gundersen, P.; Hogervorst, R.F.; Kjønaas, O.J.; Persson, H.; Timmermann, V. Vegetation and soil biota response to experimentally-changed nitrogen inputs in coniferous forest ecosystems of the NITREX project. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 101, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Greaver, T.L. A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baath, E.; Berg, B.; Lohm, U.; Lundgren, B.; Lundkvist, H.; Rosswall, T.; Soderstrom, B.; Wirén, A. Effects of experimental acidification and liming on soil organisms and decomposition in a Scots pine forest. Pedobiologia 1980, 20, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Smolander, A.; Kurka, A.; Kitunen, V. Microbial biomass C and N and respiratory activity in soil of repeatedly limed and N and P fertilized Norway spruce plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Downing, A. Non-linear response of microbial activity across a gradient of nitrogen addition to the soil from the Gurbantunggut Desert, northwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 47, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Song, X. Interaction of Biochar Amendment and Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Enzyme Activity in a Torreya Grandis Orchard. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3605–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Talley, M.; Luo, Y. Biomass, litter, and soil respiration along a precipitation gradient in Southern Great Plains, USA. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, S.; Uchida, M.; Koizumi, H.; Nakatsubo, T. Carbon and nitrogen limitation of soil microbial respiration in a High Arctic successional glacier foreland near Ny-Alesund, Svalbard. Polar Res. 2007, 26, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.; Feng, M.; Lin, S.; Malghani, S.; Ali, I.M. Microbial biomass, and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses: A case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, S.M.; Tafazoli, M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Tafazoli, M. The study of litter decomposition process of Caucasian oak and Red pine using litter bag technique. J. Plant Res. 2016, 28, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.L.; Zhao, J.; You, Y.M. Soil microbial responses to forest floor litter manipulation and nitrogen addition in a mixed-wood forest of northern China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Woo, C.H. Decomposition of Pine and Oak litters as affected by their lignin and mineral concentrations. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2018, 51, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Taylor, J.A. On the temperature dependence of soil respiration. Funct. Ecol. 1994, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Song, H.; Wang, Z.; Teramoto, M.; Wang, J.; Liang, N.; Ma, C.; Sun, Z.; Xi, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Temperature sensitivity of respiration across multiple time scales in a temperate plantation forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 688, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A.; Luo, Y. On the variability of respiration in terrestrial ecosystems: Moving beyond Q10. Glob. Change Biol. 2006, 12, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, P.; Christiansen, J.R.; Alberti, G.; Brüggemann, N.; Castaldi, S.; Gasche, R. The response of methane and nitrous oxide fluxes to forest change in Europe. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3999–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ruan, Y.; Jia, Z. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Microbial Biomass: A Meta-Analysis. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, L.E.; Vance, E.D.; Swanston, C.W.; Curtis, P.S. Impacts of elevated N inputs on north temperate forest soil C storage, C/N, and net N-mineralization. Geoderma 2009, 153, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Vosátka, M.; Cai, B.; Ding, J.; Lu, C.; Xu, J.; Yan, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. The role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in nitrogen uptake by Plantago lanceolata in two soils with different levels of available nitrogen. Plant Soil 2012, 351, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhang, D. Effects of elevated CO2 and nitrogen addition on soil organic carbon fractions in a subtropical forest. Plant Soil 2012, 357, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Plantation | Soil Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Pinus radiata D. Don | Moisture (%) | 18.58 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.6 | |
| Lime (%) | 2.82 | |
| pH (1:2.5 H2O) | 6.6 | |
| EC (dS/m2) | 0.4 | |
| C (%) | 5.9 | |
| Quercus castanifolia | Moisture (%) | 29.5 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.35 | |
| Lime (%) | 2.85 | |
| pH (1:2.5 H2O) | 6.1 | |
| EC (dS/m2) | 0.49 | |
| C (%) | 4.8 |
| Nutrient Concentrations in Soil | Species | Different Seasons | Nitrogen Treatments | Different Seasons × Nitrogen Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | ||
| Rs (mol CO2 s−1 m2) | oak | 95.658 | <0.01 | 50.537 | <0.01 | 5.336 | <0.01 |
| pine | 121.007 | <0.01 | 61.115 | <0.01 | 11.359 | <0.01 | |
| MBC (mg kg−1) | oak | 64.796 | <0.01 | 23.536 | <0.01 | 5.340 | <0.01 |
| pine | 38.509 | <0.01 | 16.586 | <0.01 | 6.092 | <0.01 | |
| Soil OC (%) | oak | 30.039 | <0.01 | 40.529 | <0.01 | 7.754 | <0.01 |
| pine | 92.706 | <0.01 | 4.987 | <0.01 | 3.680 | <0.01 | |
| Litterfall OC (%) | oak | 262.287 | <0.01 | 0.485 | 0.714 | 0.560 | <0.01 |
| pine | 25.048 | <0.01 | 0.436 | 0.728 | 0.120 | 0.999 | |
| Litterfall mass (g m−2) | oak | 2866.858 | <0.01 | 2.208 | 0.106 | 2.253 | 0.025 |
| pine | 2891.092 | <0.01 | 1095 | 0.365 | 1.553 | 0.220 | |
| Fine root biomass (g m−2) | oak | 87.670 | <0.01 | 11.579 | <0.01 | 6.790 | <0.01 |
| pine | 39.356 | <0.01 | 17.920 | <0.01 | 6.450 | <0.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouraei, A.; Hojjati, S.M.; Jalilvand, H.; Schleppi, P.; Alavi, S.J. Short-Term Effects of N Deposition on Soil Respiration in Pine and Oak Monocultures. Forests 2025, 16, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101570
Nouraei A, Hojjati SM, Jalilvand H, Schleppi P, Alavi SJ. Short-Term Effects of N Deposition on Soil Respiration in Pine and Oak Monocultures. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101570
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouraei, Azam, Seyed Mohammad Hojjati, Hamid Jalilvand, Patrick Schleppi, and Seyed Jalil Alavi. 2025. "Short-Term Effects of N Deposition on Soil Respiration in Pine and Oak Monocultures" Forests 16, no. 10: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101570
APA StyleNouraei, A., Hojjati, S. M., Jalilvand, H., Schleppi, P., & Alavi, S. J. (2025). Short-Term Effects of N Deposition on Soil Respiration in Pine and Oak Monocultures. Forests, 16(10), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101570






