Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings by LaCl3 Through Calcium Signaling Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Treatment Methods
2.2. Determination of the Growth Index of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
2.2.1. Biomass Determination of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
2.2.2. Determination of Photosynthetic Characteristics of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
2.2.3. Determination of Water Use Efficiency of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
2.2.4. Calcium Element Determinations in Each Quercus acutissima Organ
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. There Is an Optimal Calcium Concentration for the Growth of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
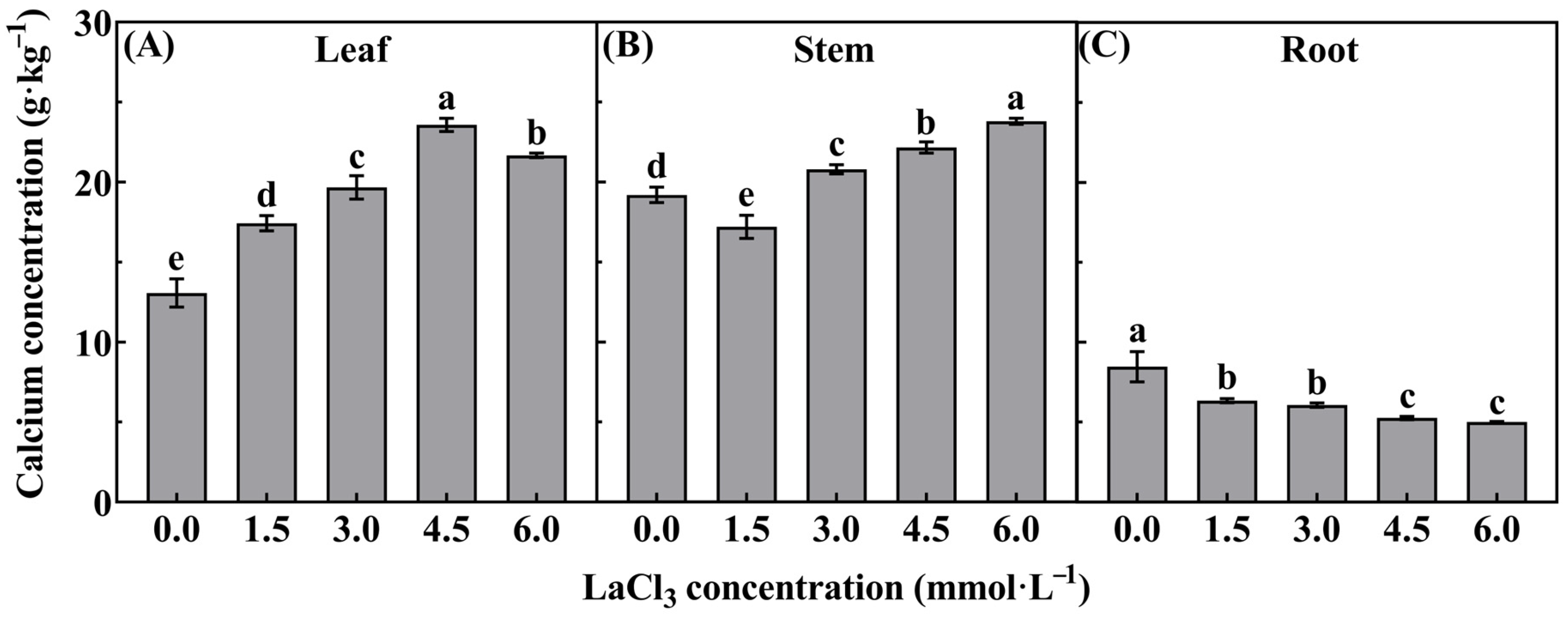
3.2. Effect of LaCl3 on the Calcium Concentration in Different Organs of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
3.3. Effect of LaCl3 on the Photosynthetic Characteristics of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
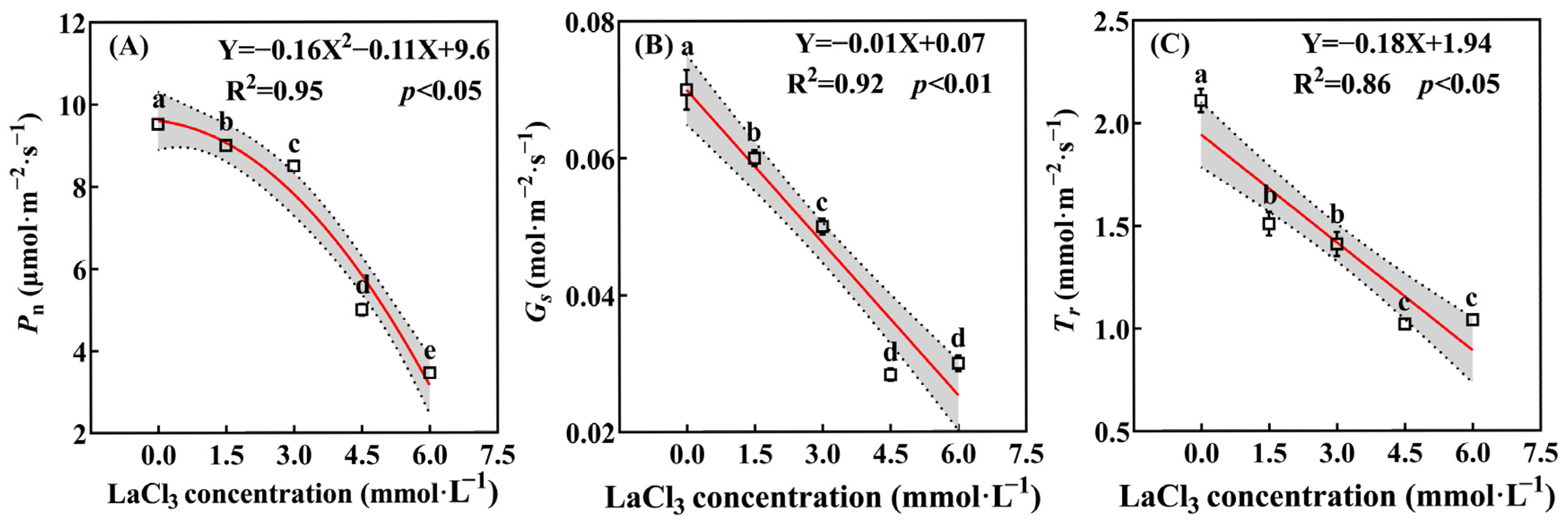
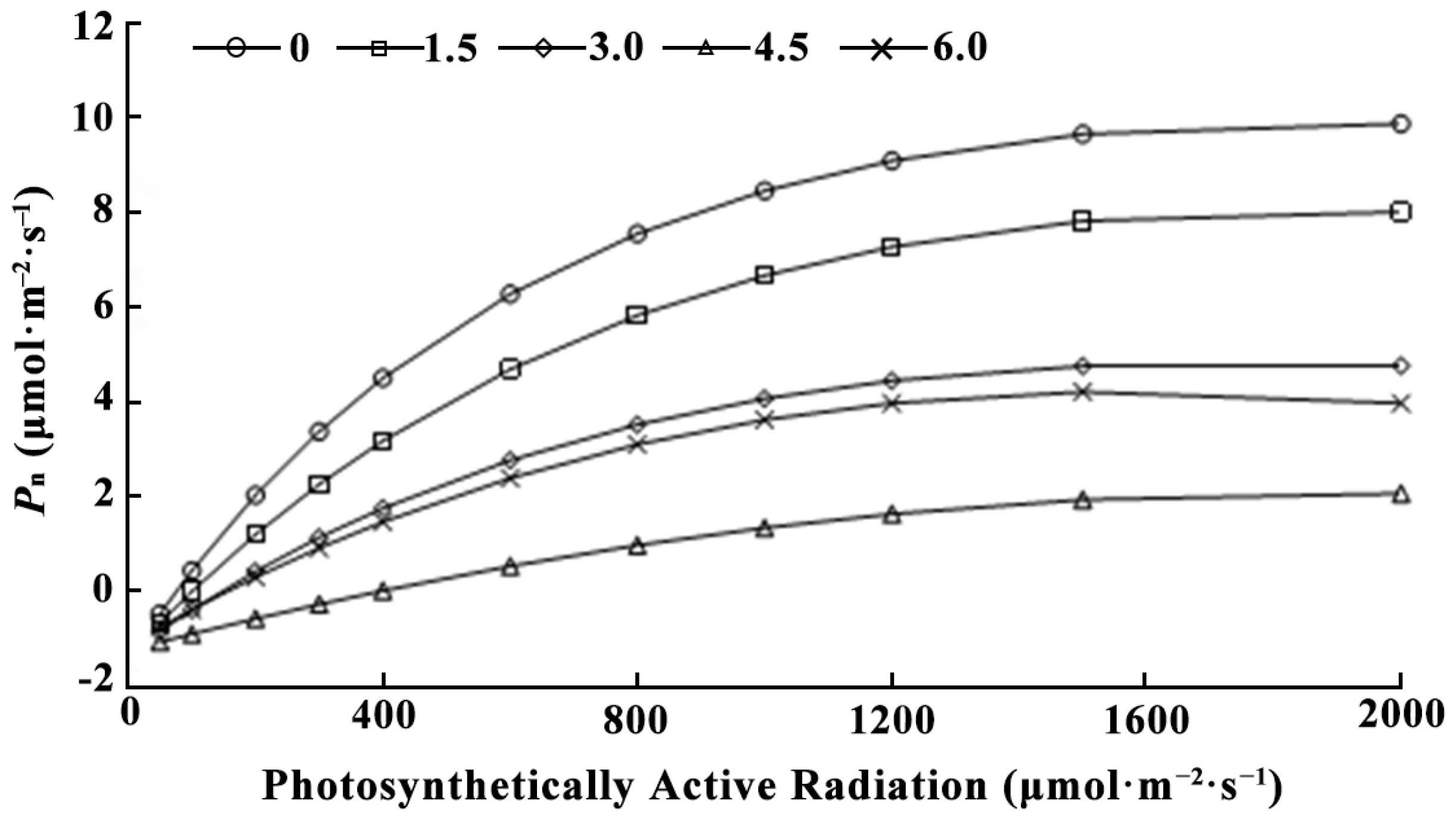
3.3.1. Effect of LaCl3 on the Photosynthetic Parameters of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
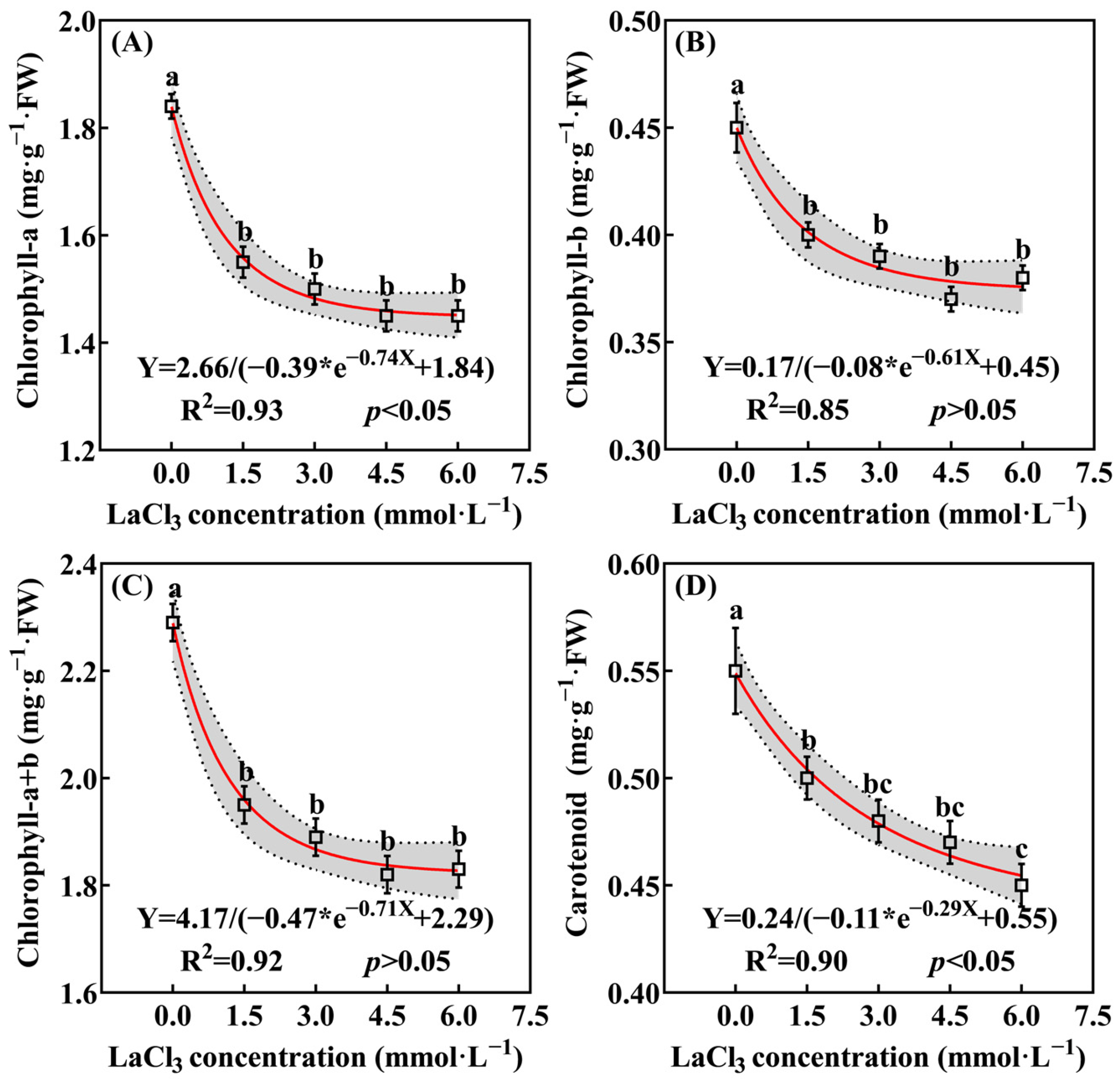
3.3.2. Effect of LaCl3 on the Photosynthetic Pigments’ Accumulation in Quercus acutissima Seedlings
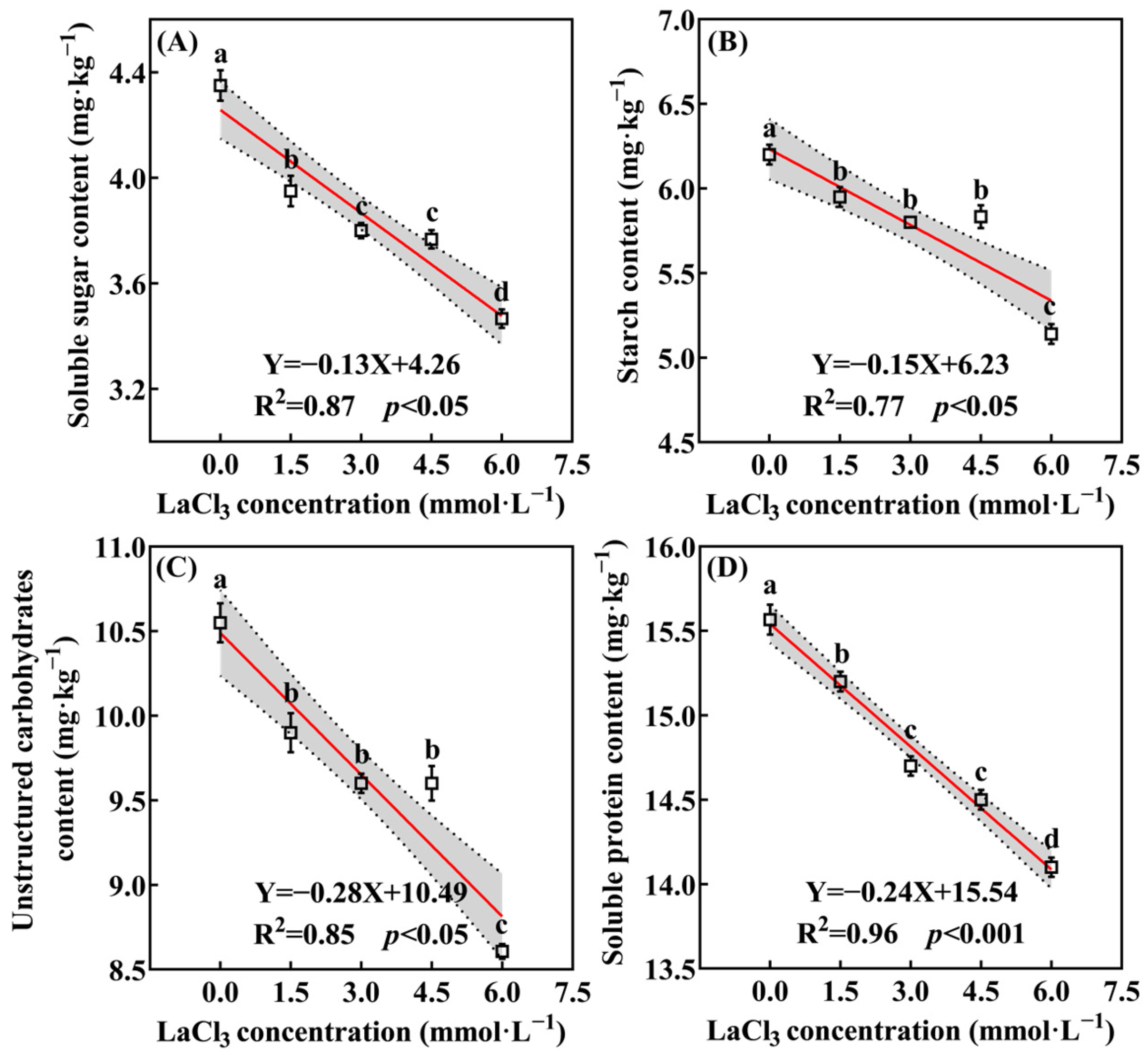
3.3.3. LaCl3 Inhibits the Accumulation of Photosynthate in the Leaves of Quercus acumosa Seedlings
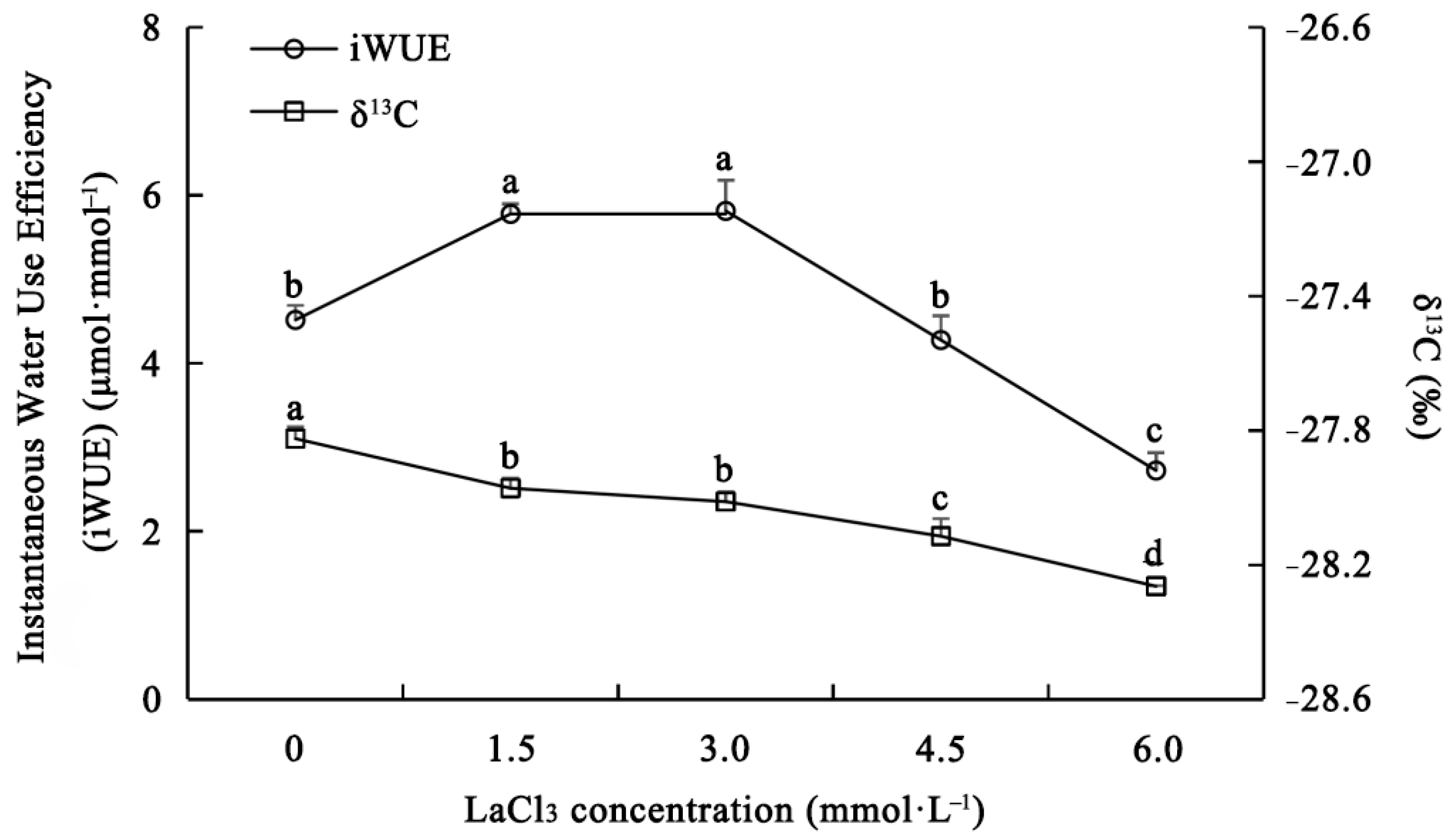
3.4. Effect of LaCl3 on the Water Use Efficiency of Quercus acutissima Seedlings
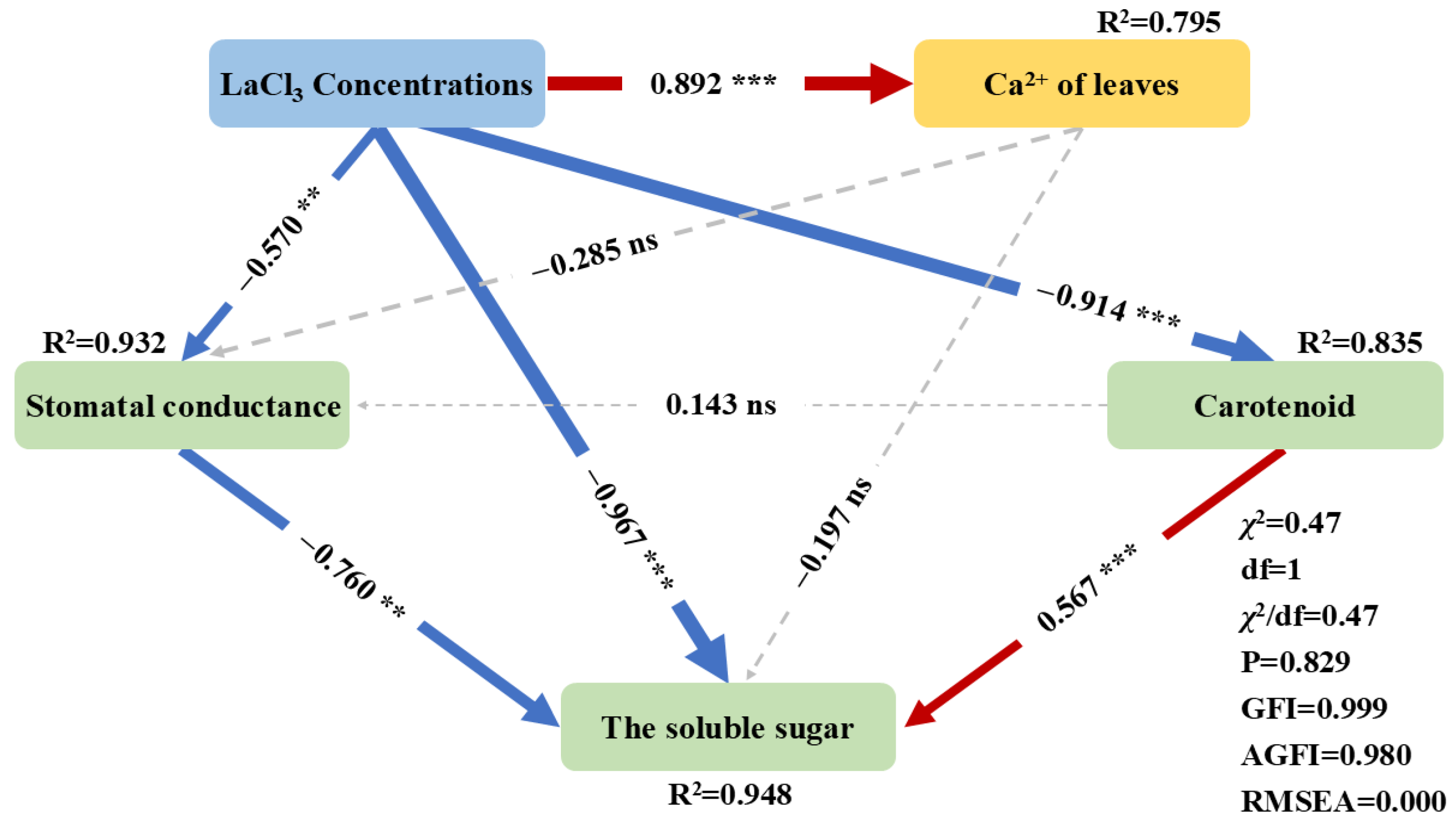
3.5. The Response Mechanism of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings to LaCl3
4. Discussion
4.1. LaCl3 Affects Calcium Ion Absorption and Distribution in Quercus acutissima Seedlings
4.2. The Inhibitory Effect of LaCl3 on Photosynthesis and Its Mechanism
4.3. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hepler, P.K. Calcium: A Central Regulator of Plant Growth and Development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarty, M.; Morvan, C.; Thellier, M. Calcium and the Cell Wall. Plant Cell Environ. 1984, 7, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.N.; Reddy, V.S. Calcium as a Messenger in Stress Signal Transduction. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, P.; Sun, X. Exogenous Calcium: Its Mechanisms and Research Advances Involved in Plant Stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1143963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.; Li, H.; Ren, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. Calcium Regulates Growth and Nutrient Absorption in Poplar Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 887098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zou, X. Linking Tree Water Use Efficiency with Calcium and Precipitation. Tree Physiol. 2022, 42, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Weng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pei, J. The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus Tabuliformis, Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica, Populus, and Morus Alba as Examples. Forests 2023, 14, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.C.; Rebelo, M.C.; Santos, M.E.; Antunes, M.L.; Nunes, M.A. Effects of Calcium Deficiency on Coffea Arabica. Nutrient Changes and Correlation of Calcium Levels with Some Photosynthetic Parameters. Plant Soil 1995, 172, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Long, S.; Zhao, L. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Seed Germination and Physiological Traits of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Ju, C.; Wang, C. Calcium Signaling in Plant Mineral Nutrition: From Uptake to Transport. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N.; Mahajan, S. Calcium Signaling Network in Plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistič, O.; Kudla, J. Analysis of Calcium Signaling Pathways in Plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X. Calcium Signaling and the Response to Heat Shock in Crop Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidchik, V.; Shabala, S.; Isayenkov, S.; Cuin, T.A.; Pottosin, I. Calcium Transport across Plant Membranes: Mechanisms and Functions. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Ramírez-Martínez, M.; Castillo-González, A.M.; Trejo-Téllez, L.I. Lanthanum Prolongs Vase Life of Cut Tulip Flowers by Increasing Water Consumption and Concentrations of Sugars, Proteins and Chlorophylls. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentel, M.C.; Knight, M.R. Oxidative Stress-Induced Calcium Signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Mei, W.; Feng, N.; Zheng, D. Photosynthetic Performance Index (PIabs) and Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content Determine Rice Biomass under Combined Salt Stress and Prohexadione-Calcium Treatment. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, W.; Han, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; He, W.; Nie, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Bai, W.; et al. Diel Dynamics of Multi-Omics in Elkhorn Fern Provide New Insights into Weak CAM Photosynthesis. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.G.; Seixas, D.P.; Barzotto, G.R.; Jorge, L.G.; Ducatti, K.R.; Ferreira, G.; Rodrigues, T.M.; da Silva, E.A.A.; Boaro, C.S.F. Roles of Calcium Signaling in Gene Expression and Photosynthetic Acclimatization of Solanum lycopersicum Micro-Tom (MT) after Mechanical Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yuan, H.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M. Effects of Provenance and Initial Planting Density on Growth and Wood Properties in Young Sawtooth Oak (Quercus acutissima) Plantations. Eur. J. For. Res. 2020, 139, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Z. Quercus acutissima Exhibits More Adaptable Water Uptake Patterns in Response to Seasonal Changes Compared to Pinus massoniana. For. Ecosyst. 2025, 12, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, N.; Fan, P.; You, C.; Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Wang, H. Dynamics of the Distribution of Invasive Alien Plants (Asteraceae) in China under Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.B.; Han, S.H.; Hernandez, J.O.; An, J.Y.; Youn, W.B.; Choi, H.-S.; Jung, S. Leaf Litter Decomposition of Deciduous Quercus acutissima Carruth. and Evergreen Quercus glauca Thunb. in an Inter-Site Experiment in Three Contrasting Temperate Forest Stands in South Korea. Ann. For. Sci. 2021, 78, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delian, E.; Chira, A.; Badulescu, L.; Chira, L. Calcium Alleviates Stress in Plants: Insight into Regulatory Mechanisms. AgroLife Sci. J. 2014, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Parvin, K.; Nahar, K.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Fujita, M. Calcium-Mediated Growth Regulation and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. In Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance: Agronomic, Molecular and Biotechnological Approaches; Hasanuzzaman, M., Hakeem, K.R., Nahar, K., Alharby, H.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 291–331. ISBN 978-3-030-06118-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Hussian, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, S.; Qi, G. Calcium Signaling-Mediated Transcriptional Reprogramming during Abiotic Stress Response in Plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. Soil and Plant Nutrition Experiments; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2014; ISBN 7-308-13552-7. [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo, P.; Zepeda, B.; Rojas, B.; Silva-Sanzana, C.; Delgado-Rioseco, J.; Fernández, K.; Balic, I.; Arriagada, C.; Moreno, A.A.; Defilippi, B.G.; et al. Cell Wall Calcium and Hemicellulose Have a Role in the Fruit Firmness during Storage of Blueberry (Vaccinium spp.). Plants 2021, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Photosynthetic Properties and Potentials for Improvement of Photosynthesis in Pale Green Leaf Rice under High Light Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.P.; Bowden, W.B.; Flinn, M.B. The Effect of Acid Strength and Postacidification Reaction Time on the Determination of Chlorophyll a in Ethanol Extracts of Aquatic Periphyton. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2016, 14, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjorin, F.B.; Adejumo, S.A.; Agboola, L.; Samuel, Y.D. Proline, Soluble Sugar, Leaf Starch and Relative Water Contents of Four Maize Varieties in Response to Different Watering Regimes. Cercet. Agron. Mold. 2016, 49, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Coomassie Brilliant Blue-Binding: A Simple and Effective Method for the Determination of Water-Insoluble Protein Surface Hydrophobicity. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y. Increasing Leaf δ13C Values of Woody Plants in Response to Water Stress Induced by Tunnel Excavation in a Karst Trough Valley: Implication for Improving Water-Use Efficiency. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisergaeva, R.A.; Sirieva, Y.N. Determination of Calcium and Magnesium by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Flame Photometry. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1691, 12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Afzal, M.R.; Raza, M.A.; Pandey, S.; Qi, S.; Dai, Z.; Du, D. Calcium (Ca2+) Signaling in Plants: A Plant Stress Perspective. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 169, 464–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocca, G.N.; Baldi, E.; Toselli, M. Understanding the Role of Calcium in Kiwifruit: Ion Transport, Signaling, and Fruit Quality. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Tan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, G.; Jing, M.; et al. An Insect Salivary Sheath Protein Triggers Plant Resistance to Insects and Pathogens as a Conserved HAMP. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2415474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S.; Demidchik, V.; Shabala, L.; Cuin, T.-A.; Smith, S.-J.; Miller, A.-J.; Davies, J.-M.; Newman, I.-A. Extracellular Ca2+ ameliorates NaCl-induced K+ loss from Arabidopsis root and leaf cells by controlling plasma membrane K+-permeable channels. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Xie, W.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Jiao, W. Effect of exogenous lanthanum on accumulation and chemical forms of cadmium in different varieties of cucumber (Cucumis satiuus L.). Food Sci. 2015, 36, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.F.; Ruiz, M.-C.; Chemello, M.E.; Michelangeli, F. Characterization of a Membrane Calcium Pathway Induced by Rotavirus Infection in Cultured Cells. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.Y.; Díaz-Pérez, J.C. Calcium Route in the Plant and Blossom-End Rot Incidence. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Tang, Z.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, S.; Zhao, F.J. Mechanosensing Antagonizes Ethylene Signaling to Promote Root Gravitropism in Rice. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Gao, W.; Chen, G. Toxic effects of lanthanum(III) on photosynthetic performance of rice seedlings: Combined chlorophyll fluorescence, chloroplast structure and thylakoid membrane protein assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, M.; Kubalová, I.; Brun, A.; Cervela-Cardona, L.; Monte, E.; Strand, Å. Retrograde Signals Control Dynamic Changes to the Chromatin State at Photosynthesis-Associated Loci. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.; Zhang, D.; Chu, C. Interplay of Light and Nitrogen for Plant Growth and Development. Crop J. 2025, 13, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Cai, C.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X. Spatial and Temporal Calcium Signaling and Its Physiological Effects in Moso Bamboo under Drought Stress. Forests 2019, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yang, X.; Xuan, X.; Yu, Z. Glucomannan Accumulation Induced by Exogenous Lanthanum in Amorphophallus Konjac: Insights from a Comparative Transcriptome Analysis. Biology 2025, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y. The influence of LaCl3 to the growth and differentiation of mulberry tissue culture seedling. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2008, 14, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Yang, G.; Zhao, M.; Huang, L. Effects of LaCl3 on Photosynthesis and the Accumulation of Tanshinones and Salvianolic Acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza Seedlings. J. Rare Earths 2011, 29, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Vacek, S.; Marti, E.J. Integrating Lanthanide-Reclaimed Wastewater and Lanthanide Phosphate in Corn Cultivation: A Novel Approach for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, N.; Gao, Q.; Fan, P.; Du, N.; Wang, H.; et al. Effects of Drought Hardening on the Carbohydrate Dynamics of Quercus acutissima Seedlings under Successional Drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1184584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, A.M.; Woodward, F.I. The Role of Stomata in Sensing and Driving Environmental Change. Nature 2003, 424, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, T.A.; Robinson, W.D. Deciphering ecology from statistical artefacts: Competing influence of sample size, prevalence and habitat specialization on species distribution models and how small evaluation datasets can inflate metrics of performance. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ca2+ Concentration (mmol·L−1) | Underground Biomass (g) | Aboveground Biomass (g) | Total Biomass (g) | Root-Shoot Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.28 ± 0.054 c | 1.55 ± 0.048 bc | 2.83 ± 0.118 d | 31.50 ± 2.33 ab |
| 1.25 | 1.52 ± 0.074 b | 1.61 ± 0.07 bc | 3.13 ± 0.103 cd | 33.87 ± 0.57 a |
| 2.5 | 1.72 ± 0.202 a | 1.69 ± 0.050 b | 3.42 ± 0.075 bc | 32.39 ± 2.05 ab |
| 5 | 1.77 ± 0.176 a | 2.18 ± 0.114 a | 3.95 ± 0.218 a | 27.86 ± 1.35 b |
| 10 | 1.57 ± 0.054 b | 2.06 ± 0.095 a | 3.63 ± 0.075 ab | 27.41 ± 1.34 b |
| 15 | 1.54 ± 0.187 b | 1.76 ± 0.062 b | 3.30 ± 0.131 c | 29.49 ± 0.94 b |
| 20 | 1.47 ± 0.147 b | 1.41 ± 0.081 c | 2.87 ± 0.128 d | 32.62 ± 2.73 ab |
| LaCl3 (mmol·L−1) | Apparent Carboxylation Efficiency (mol·mol−1) | Maximum Net Photosynthetic Rate (μmol·m−2·s−1) | CO2 Saturation Point (μmol·mol−1) | CO2 Compensation Point (μmol·mol−1) | Dark Breathing Rate (μmol·m−2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0209 a | 9.88 a | 1903.39 a | 74.81 c | 1.46 a |
| 1.5 | 0.0147 b | 8.03 a | 1873.17 a | 99.29 c | 1.37 b |
| 3.0 | 0.0100 b | 4.83 b | 1746.44 ab | 145.14 b | 1.31 b |
| 4.5 | 0.0034 c | 1.87 c | 1741.46 ab | 364.63 a | 1.12 c |
| 6.0 | 0.0082 c | 4.22 b | 1586.63 b | 157.38 b | 1.19 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Yu, S.; Zheng, Y. Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings by LaCl3 Through Calcium Signaling Regulation. Forests 2025, 16, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101553
Weng X, Li H, Zhou Y, Wang H, Feng J, Yu S, Zheng Y. Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings by LaCl3 Through Calcium Signaling Regulation. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101553
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Xiaohang, Hui Li, Yongbin Zhou, Hongbo Wang, Jian Feng, Shihe Yu, and Ying Zheng. 2025. "Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings by LaCl3 Through Calcium Signaling Regulation" Forests 16, no. 10: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101553
APA StyleWeng, X., Li, H., Zhou, Y., Wang, H., Feng, J., Yu, S., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Quercus acutissima Seedlings by LaCl3 Through Calcium Signaling Regulation. Forests, 16(10), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101553












