Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Association in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in East China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomic and Ecological Characteristics and Distribution Plot of Dominant Species
3.2. Distribution Patterns
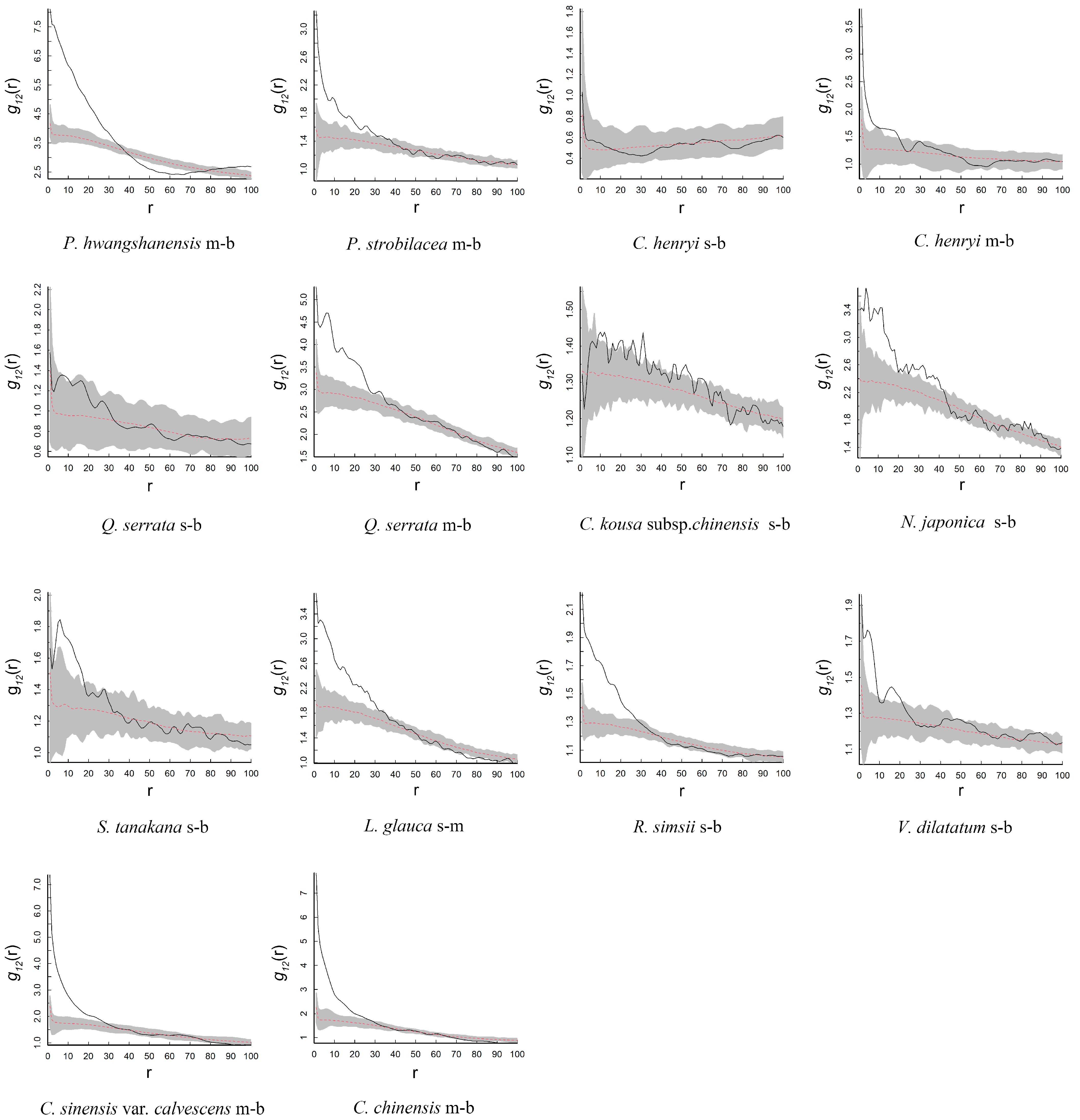
3.3. Intra-Specific and Inter-Specific Association
3.4. Environment Factors and Species Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. The Processes Shaping Species Distribution Patterns
4.2. Interpreting the Patterns of Intra- and Inter-Specific Associations
4.3. Drivers of Species Distribution: An Environmental Perspective
4.4. Management Implications in Deciduous Forests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | CSR | HP |
|---|---|---|
| P. hwangshanensis | + at all scales | + before 40 m, − at 40–80 m, after that, r |
| P. strobilacea | + at all scales, + decrease with the scale increase | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| C. henryi | + at all scales, 60–80 m, r | + before 20 m, after that, r |
| Q. serrata | + at all scales, + decrease with the scale increase | + before 40 m, after that, r |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis | + at all scales | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| N.japonica | + at all scales | + before 40 m, − at 40–80 m, after that, r |
| S. tanakana | + at all scales, + decrease with the scale increase | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| L. glauca | + at all scales | + before 40 m, after that, r |
| R. simsii | + at all scales | + before 35 m, − between 40 and 80 m, after that, r |
| V. dilatatum | + at all scales | + before 50 m, after that, r |
| C. sinensis var. calvescens | + at all scales, r after 90 m | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| C. chinensis | + before 70 m, after that, − | + before 40 m, r between 40 and 70 m, after that, − |
| Species | CSR | AC |
|---|---|---|
| P. hwangshanensis (b-m) | + at all scales | + before 35 m, − between 35 and 80 m, after that, r |
| P. strobilacea (b-m) | + at all scales | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| C. henryi (b-s) | r before 5 m, after that, − | + at all scales |
| C. henryi (b-m) | + before 52 m, after that, r | + before 20 m, after that, r |
| Q. serrata (b-s) | + before 20 m, 20–30 m, r, after that, − | + at all scales |
| Q. serrata (b-m) | + at all scales | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis (b-s) | + at all scales | + at all scales |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis (b-m) | + at all scales | + before 40 m, after that, r |
| N. japonica (b-s) | + at all scales | + before 42 m, after that, r |
| N. japonica (b-m) | + at all scales | + before 40 m, − between 40 and 80 m, after that, r |
| S. tanakana (b-s) | + at all scales | + before 20 m, after that, r |
| S. tanakana (b-m) | + before 85 m, after that, r | + before 25 m, r between 25 and 80 m, after that, − |
| L. glauca (m-s) | + before 85 m, after that, r | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| R. simsii (b-s) | + at all scales | − before 35 m, after that, r |
| R. simsii (m-s) | + at all scales | − before 35 m, after that, r |
| V. dilatatum (b-s) | + at all scales | + before 22 m, after that, r |
| V. dilatatum (m-s) | + at all scales | + before 22 m, after that, r |
| C. sinensis var. calvescens (b-m) | + before 80 m, after that, r | + before 35 m, r between 35 and 75 m, after that, − |
| C. chinensis (b-m) | + before 70 m, after that, − | + before 30 m, after that, r |
| Standard Deviation | Proportion of Variance | Cumulative Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 1.9849 | 0.3031 | 0.3031 |
| PC2 | 1.5781 | 0.1916 | 0.4946 |
| PC3 | 1.1135 | 0.0954 | 0.5900 |
| PC4 | 1.0187 | 0.0798 | 0.6698 |
| PC5 | 0.9860 | 0.0748 | 0.7446 |
| PC6 | 0.9008 | 0.0624 | 0.8070 |
| Soil Factors | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH value | 2.24 | 2.18 | 45.88 | 0.94 | 11.12 | 5.46 |
| Total Nitrogen | 20.18 | 1.59 | 2.27 | 0.01 | 2.17 | 0.92 |
| Total Carbon | 16.17 | 3.22 | 11.05 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.09 |
| Total Phosphorus | 8.68 | 1.33 | 2.96 | 1.96 | 0.07 | 15.32 |
| Total Potassium | 2.33 | 1.85 | 8.79 | 18.57 | 27.73 | 24.48 |
| Alkaline Hydrolyzable Nitrogen | 10.33 | 3.09 | 7.92 | 2.00 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| Available Phosphorus | 12.85 | 0.05 | 0.80 | 0.05 | 2.32 | 8.89 |
| Available Potassium | 14.29 | 0.88 | 6.61 | 1.62 | 0.46 | 0.02 |
| Soil Moisture Content | 1.12 | 20.83 | 4.24 | 10.21 | 0.66 | 0.58 |
| Bulk Density | 1.07 | 5.48 | 1.14 | 62.22 | 0.36 | 6.48 |
| Gravel Content | 5.13 | 27.06 | 2.95 | 0.02 | 4.25 | 0.04 |
| Root Content | 0.38 | 5.71 | 2.55 | 2.37 | 45.71 | 37.72 |
| Soil Content | 5.22 | 26.73 | 2.86 | 0.02 | 4.83 | 0.01 |
References
- Lu, F.; Wang, B.; Li, J.X.; Li, D.X.; Liu, S.Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Huang, F.Z.; Xiang, W.S.; Li, X.K. Both Biotic and Abiotic Factors Shape the Spatial Distribution of Aboveground Biomass in a Tropical Karst Seasonal Rainforest in South China. Forests 2004, 15, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.X.; Yang, L.S.; Jiang, Z.G.; Yao, H.; Yu, H.L.; Luo, F.L.; Qiao, X.J.; Xu, Y.Z.; Jiang, M.X. Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Associations of Dominant Tree Species in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in Shennongjia, China. Diversity 2025, 17, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Dong, L.B.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.G. Spatial patterns and interspecific associations during natural regeneration in three types of secondary forest in the central part of the Greater Khingan Mountains, Heilongjiang Province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, T.; Wang, X.G.; Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Bourg, N.A.; Cao, M.; Ci, X.Q.; Davies, S.J.; Hao, Z.Q.; Howe, R.W.; Kress, W.J.; et al. Consequences of spatial patterns for coexistence in species-rich plant communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Yan, H.B.; Li, B.H.; Han, Y.Z.; Song, B. Spatial distribution patterns of Symplocos congeners in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaf forest of southern China. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Lu, J.M.; Franklin, S.B.; Wang, Q.G.; Xu, Y.Z.; Zhang, K.H.; Bao, D.C.; Qiao, X.J.; Huang, H.D.; Lu, Z.J.; et al. Spatial distribution of tree species in a species-rich subtropical mountain forest in central China. Can. J. For. Res. 2013, 43, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.J.; Mi, X.C.; Nadrowski, K.; Ren, H.B.; Zhang, J.T.; Ma, K.P. Separating the effect of mechanisms shaping species abundance distributions at multiple scales in a subtropical forest. Oikos 2013, 121, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeck, C.A.; Harms, K.E.; Yavitt, J.B.; John, R.; Turner, B.L.; Valencia, R.; Navarrete, H.; Bunyavejchewin, S.; Kiratiprayoon, S.; Yaacob, A.; et al. Habitat filtering across tree life stages in tropical forest communities. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20130548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Gazol, A.; Wang, X.G.; Xing, D.L.; Lin, F.; Bai, X.J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, B.H.; Hao, Z.Q. What happens below the canopy? Direct and indirect influences of the dominant species on forest vertical layers. Oikos 2012, 121, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Li, J.M.; Chang, S.L.; Li, X.; Lu, J.J. Spatial distribution pattern of Picea schrenkiana population in the Middle Tianshan Mountains and the relationship with topographic attributes. J. Arid Land 2012, 4, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Cao, M.; Zhu, H. Topography related spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a tropical seasonal rain forest in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, G.; Ni, J. Effects of topographical and edaphic factors on the distribution of plant communities in two subtropical karst forests, southwestern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.; Song, B.; Ye, J.; Li, B.H. Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old-growth temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 252, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Sha, L.Q.; Blanchet, F.G.; Zhang, J.L.; Tang, Y.; Lan, G.Y.; Cao, M. Dominant species and dispersal limitation regulate tree species distributions in a 20-ha plot in Xishuangbanna, southwest China. Oikos 2012, 121, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mi, X.C.; Ren, H.B.; Ma, K.P. Density dependence is prevalent in a heterogeneous subtropical forest. Oikos 2010, 119, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.J.; Wu, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Z.G.; Yuan, W.G.; Zhu, J.R.; Li, T.T.; Yang, S.Z.; Yan, L.J. Negative density restricts the coexistence and spatial distribution of dominant species in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests in China. Forests 2022, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mi, X.C.; Ma, K.P. A mechanism of plant species coexistence: The negative density-dependent hypothesis. Biodivers. Sci. 2009, 17, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benot, M.L.; Bittebiere, A.K.; Ernoult, A.; Clement, B.; Mony, C. Fine-scale spatial patterns in grassland communities depend on species clonal dispersal ability and interactions with neighbours. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyns, R.; Bauman, D.; Drouet, T. Fine-scale tree spatial patterns are shaped by dispersal limitation which correlates with functional traits in a natural temperate forest. J. Veg. Sci. 2021, 32, e13070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A. Fifty year record of change in tree spatial patterns within a mixed deciduous forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 215, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.K.; Raghubanshi, A.S.; Singh, J.S. Plant functional traits with particular reference to tropical deciduous forests: A review. J. Biosci. 2011, 36, 963–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Umer, M.; Guo, Y.; Tian, Q.Y.; Kang, L.L.; Fang, Z.Y.; Shen, K.P.; Xia, T.T.; Wu, P.; et al. Strategic differentiation of subcommunities composed of evergreen and deciduous woody species associated with leaf functional traits in the subtropical mixed forest. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K.; Zhu, H.Z.; He, P.A.; Chen, C.Z.; Chen, H.M.; Zhou, J.M.; Su, D.C.; Xu, J.M.; Qin, H.Y.; Bao, S.D.; et al. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agro-Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.M.; Jia, S.H.; Luo, Y.; Hao, Z.Q.; Yin, Q.L. Spatial distribution and species association of dominant tree species in Huangguan Plot of Qinling Mountains, China. Forests 2022, 13, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Said, M. Spatial point-pattern analysis as a powerful tool in identifying pattern-process relationships in plant ecology: An updated review. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, T.; Moloney, K.A. Rings, circles, and null models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos 2004, 104, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, M.; Castagneri, D.; Popa, I.; Pividori, M.; Lingua, E. Tree spatial patterns and stand attributes in temperate forests: The importance of plot size, sampling design, and null model. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 407, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A.; Rubak, E.; Turner, R. Spatial Point Patterns: Methodology and Applications with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, M. Testing for spatial association between a point process and another stochastic process. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1986, 5, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A.; Turner, R. Spatstat: An R package for analyzing spatial point patterns. J. Stat. Softw. 2005, 12, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. Analysing spatial point patterns in R[C]//Workshop Notes. 2008. Available online: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/52438478/baddeley2010-spatial_point_pattern_analysis-libre.pdf?1491178707=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DAnalysing_spatial_point_patterns_in_R.pdf&Expires=1758550582&Signature=gfOuzE-qYmM5AulBDe~OwnMKLED9QaUZK~5MR8tZzkfroLvAdvDuT2Q~PRJtduh2fcSvktskYDyRaDHnGCYTOqWFKkfUPuDFd-gCUIhznWM~24BvoSgaZnAVEexRIfly8p4TNj41aYG6eui-auNCm5g7oai9fUgXO5y2EoUfHgdj5ZXelbmg6WIClMoMcdRmGEqZVR1DS2udAkNzUpiDMpwHIsaKusvtbN7w8I-TU7TSZGqHCgXCXLpw2J16RfDBzMjVr2DhWRmppS1Pnbqg6R86tbadiVOMkM9cCq~QQ0S-D97Z9-GHFKLPSJGOFv9cXaeoBMNBMuYd8TPiygWvKA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Pijl, L.V.D. Principles of Dispersal in Higher Plants. Q. Rev. Biol. 1970, 72, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Raven, P.H.; Hong, D.Y.; Li, D.Z.; Boufford, D.E.; Peter, H.; Brach, A.R.; Stuessy, T.F.; Lang, K.Y.; Gilbert, M.G.; et al. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Perea, A.J.; Wiegand, T.; Garrido, J.L.; Rey, P.J.; Alcántara, J.M. Legacy effects of seed dispersal mechanisms shape the spatial interaction network of plant species in Mediterranean forests. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3670–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, G.; Zhu, J.D.; Ni, J. Aggregated spatial distributions of species in a subtropical karst forest, southwestern China. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 6, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzin, S.; Wiegand, T.; Wiegand, K.; He, F.L. Heterogeneity influences spatial patterns and demographics in forest stands. J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.C.; He, F.L.; Waagepetersen, R.; Sun, I.F.; Hao, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.S.; Yu, M.J. Quantifying effects of habitat heterogeneity and other clustering processes on spatial distributions of tree species. Ecology 2013, 94, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Zhao, R.; Wang, N.J.; Xie, L.; Feng, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, H.; Fang, Y.M. Spatial distributions of intra-community tree species under topographically variable conditions. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.Z.; Yu, J.H.; Yin, G.J.; Song, Z.M.; Wei, D.X.; Wang, C.J. Effects of soil properties on the spatial distribution of forest vegetation across China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 18, e00635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.R.; Fan, W.; Song, G.H. The relationship between secondary forest and environmental factors in the southern Taihang Mountains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.Q.; Song, B.; Li, B.H.; Wang, X.G.; Ye, J. Fine-scale species co-occurrence patterns in an old-growth temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.H.; Mi, X.C.; Liu, C.R.; Ma, K.P. Spatial patterns and associations in a Quercus-Betula forest in northern China. J. Veg. Sci. 2004, 15, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, H.A. Neighbour-regulated mortality: The influence of positive and negative density dependence on tree populations in species-rich tropical forests. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 6, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shi, H.; Shu, X.; Xie, F.L.; Zhang, K.R.; Zhang, Q.F.; Dang, H.S. Spatial distribution and interspecific associations in a deciduous broad-leaved forest in north-central China. J. Veg. Sci. 2019, 30, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.R.; Yu, M.J.; Chen, D.L.; Wu, Y.G.; Ding, B.Y. Spatial associations of tree species in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 5, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Peng, W.X.; Song, T.Q.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Song, M.; Zhang, H. Spatial pattern of woody plants and their environmental interpretation in the karst forest of southwest China. Plant Biosyst. 2015, 149, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelko, A.; Ukhvatkina, O.; Zhmerenetsky, A.; Sibirina, L.; Petrenko, T.; Bobrovsky, M. From young to adult trees: How spatial patterns of plants with different life strategies change during age development in an old-growth Korean pine-broadleaved forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 411, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
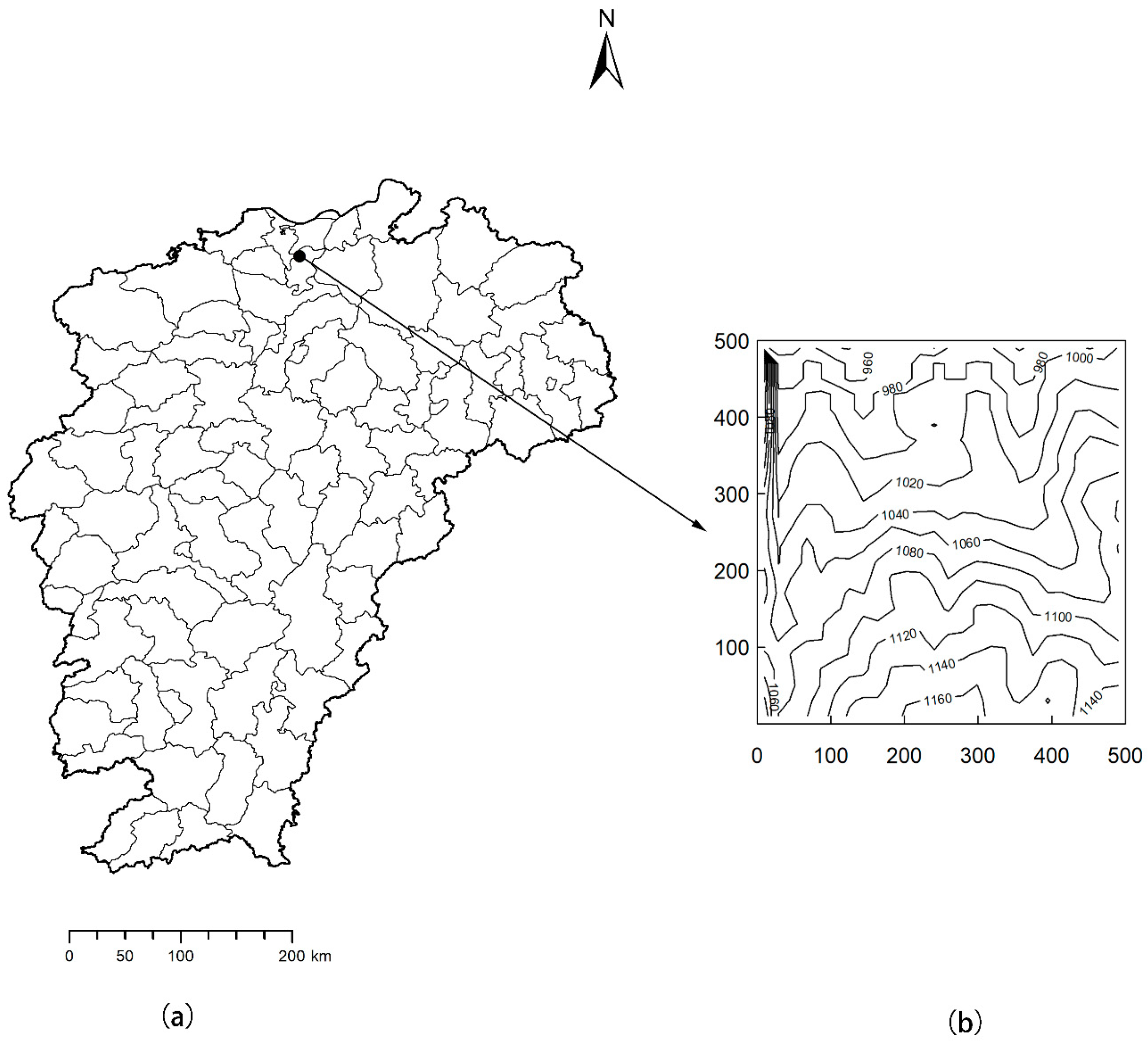
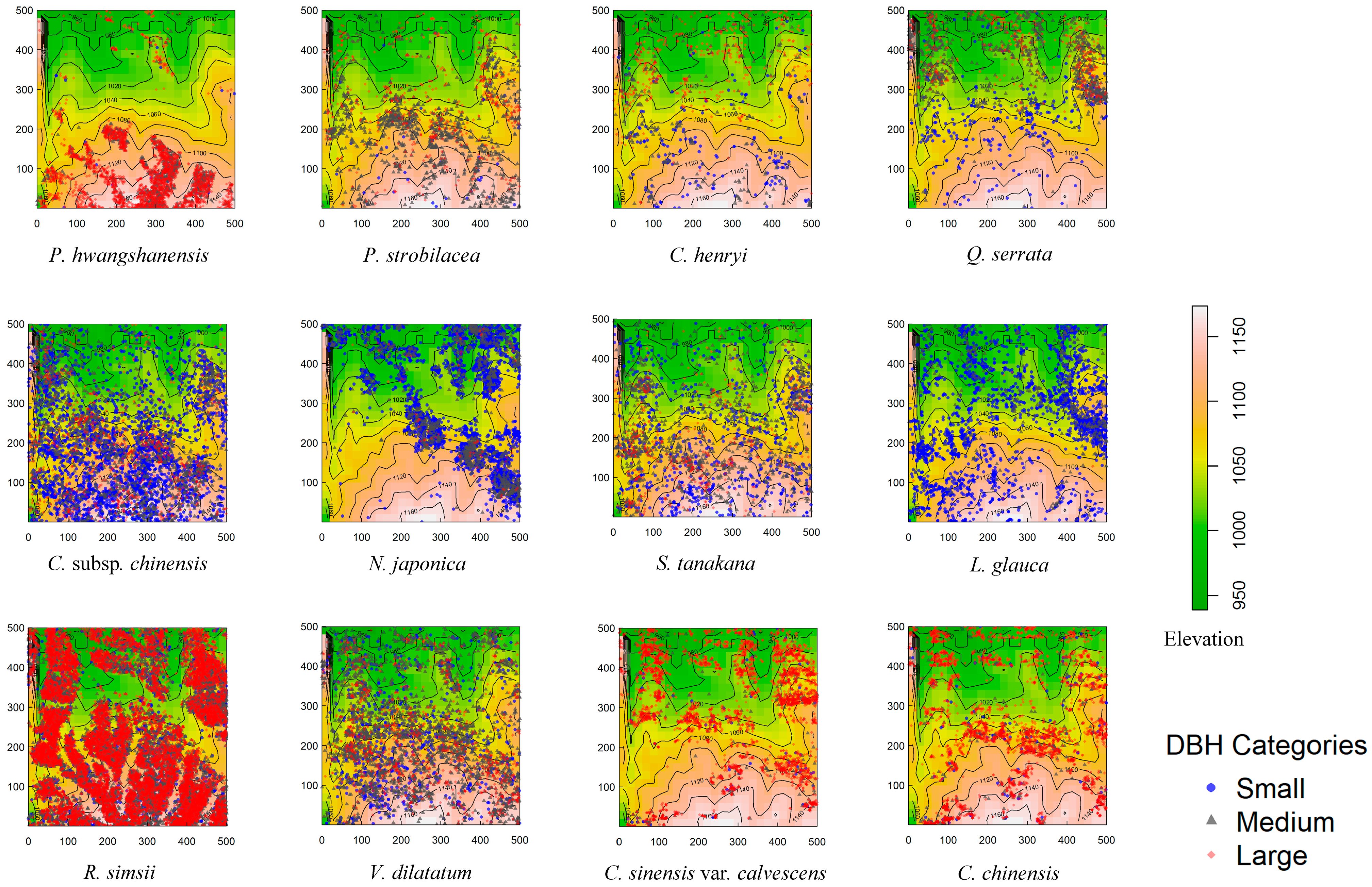

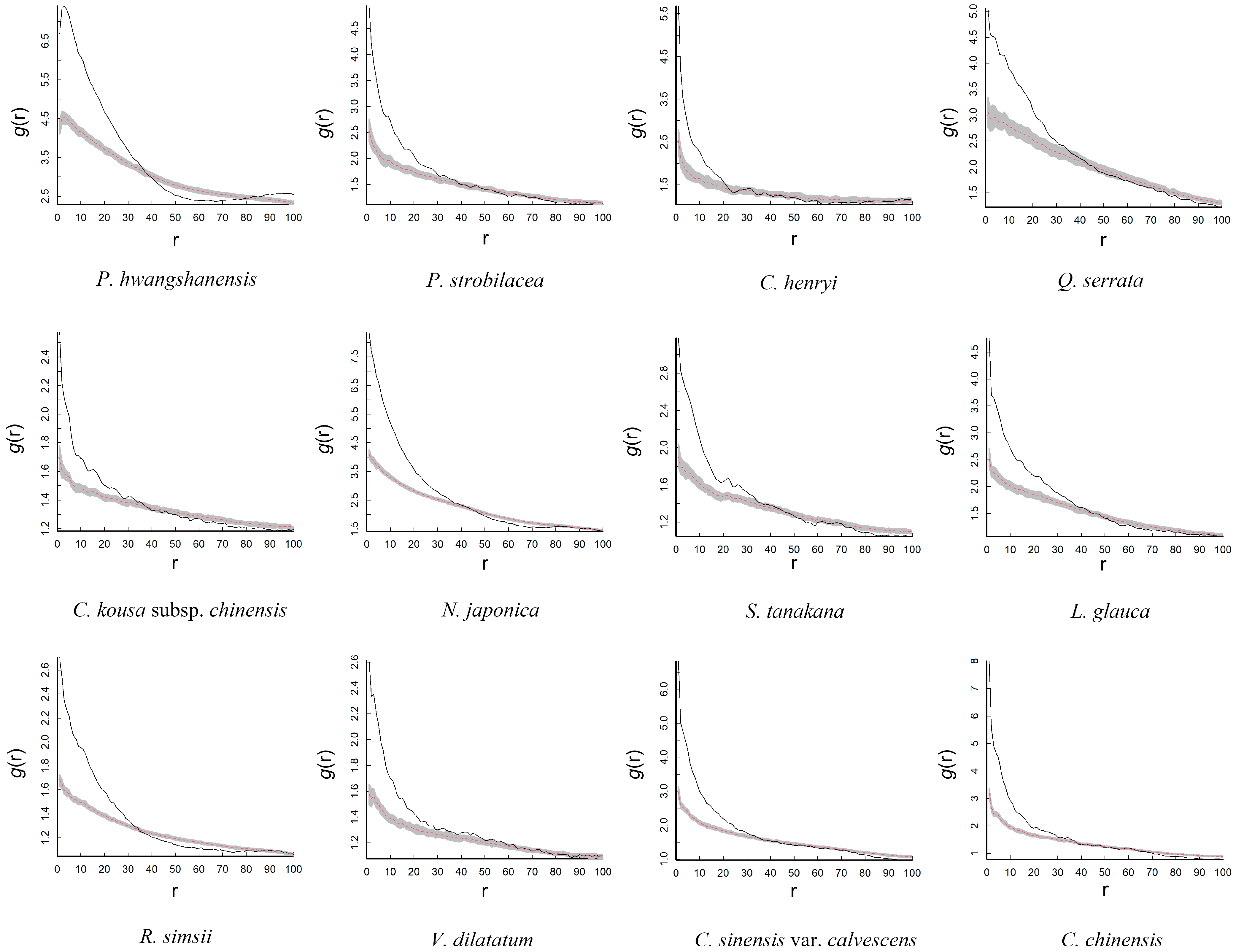
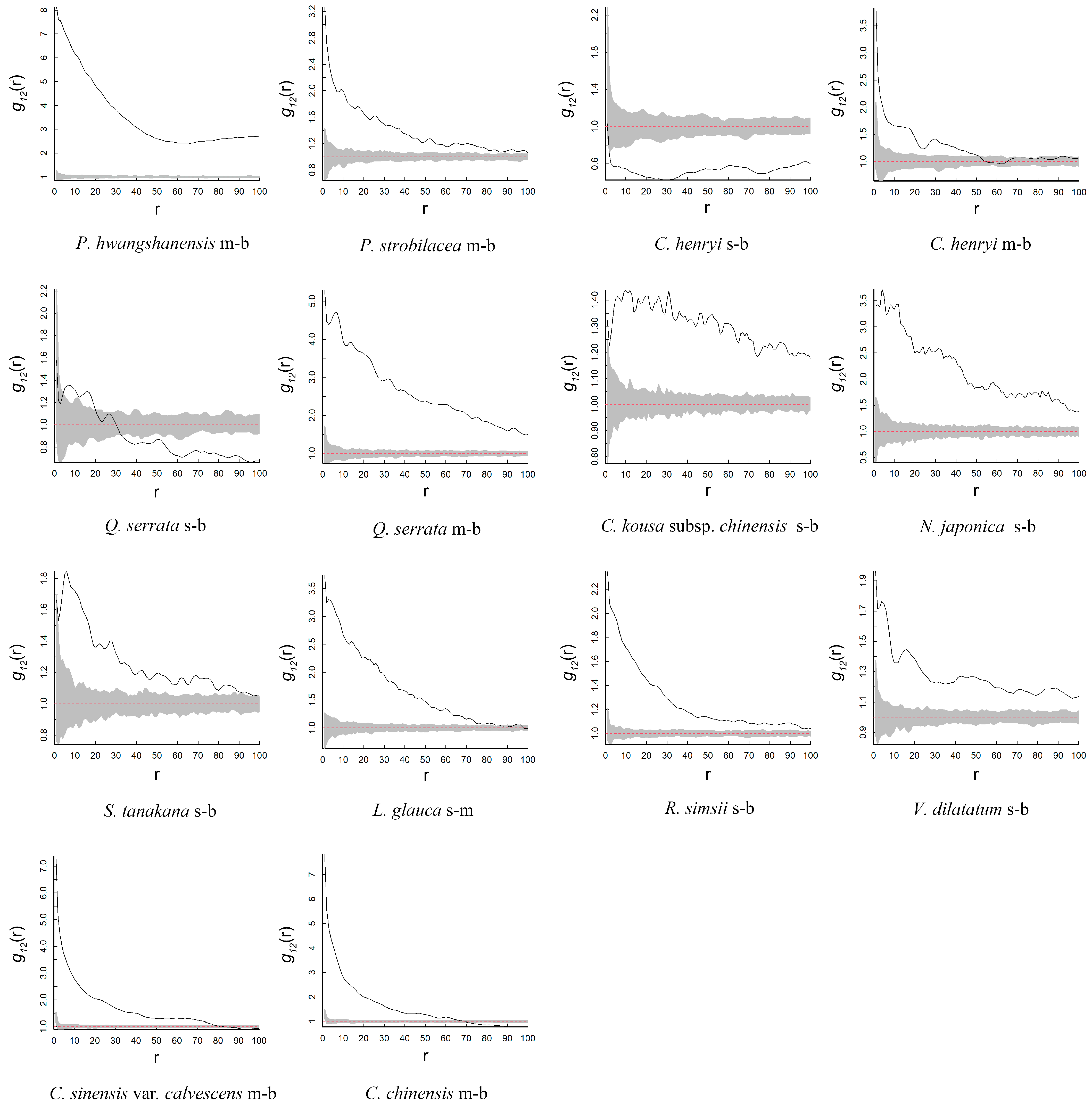
| Species | Family | Abundance | Fruit Type | Dispersal Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinus hwangshanensis W. Y. Hsia | Pinaceae | 3099 | Nut | Gravity; animal |
| Platycarya strobilacea Siebold & Zucc. | Juglandaceae | 1676 | Samara | Wind |
| Castanea henryi (Skan) Rehder & E. H. Wilson | Fagaceae | 849 | Nut | Gravity; animal |
| Quercus serrata Thunb. | Fagaceae | 1480 | Nut | Gravity; animal |
| Cornus kousa subsp. chinensis (Osborn) Q. Y. Xiang | Cornaceae | 5434 | Aggregate | Gravity; animal |
| Neoshirakia japonica (Siebold & Zucc.) Esser | Euphorbiaceae | 4828 | Capsule | Animal |
| Symplocos tanakana Nakai | Symplocaceae | 2158 | Drupe | Gravity; animal |
| Lindera glauca (Siebold & Zucc.) Blume | Lauraceae | 2492 | Drupe | Gravity; animal |
| Rhododendron simsii Planch. | Ericaceae | 28,433 | Capsule | Wind; animal |
| Viburnum dilatatum Thunb. | Viburnaceae | 4126 | Drupe | Gravity; animal |
| Corylopsis sinensis var. calvescens Rehder & E. H. Wilson | Hamamelidaceae | 3501 | Capsule | Gravity; animal |
| Corylopsis sinensis Hemsl. | Hamamelidaceae | 3256 | Capsule | Gravity; animal |
| Species | Layer | Small Trees Proportion (%) | Medium Trees Proportion (%) | Big Trees Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. hwangshanensis | Tree | 1.16 | 31.69 | 67.15 |
| P. strobilacea | Tree | 2.57 | 68.44 | 29.00 |
| C. henryi | Tree | 19.79 | 31.68 | 48.53 |
| Q. serrata | Tree | 19.12 | 57.57 | 23.31 |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis | Sub-arbor | 59.66 | 26.63 | 13.71 |
| N. japonica | Sub-arbor | 77.59 | 20.73 | 1.68 |
| S. tanakana | Sub-arbor | 32.62 | 47.64 | 19.74 |
| L. glauca | Sub-arbor | 84.83 | 14.93 | 0.24 |
| R. simsii | Shrub | 8.62 | 45.80 | 45.59 |
| V. dilatatum | Shrub | 15.85 | 61.51 | 22.64 |
| C. sinensis var. calvescens | Shrub | 1.66 | 10.37 | 87.97 |
| C. chinensis | Shrub | 2.92 | 12.87 | 84.21 |
| Species | CSR | AC |
|---|---|---|
| P. hwangshanensis–C. kousa subsp. chinensis | + at all scales | + before 28 m, after that, r |
| P. hwangshanensis–N. japonica | − at all scales | + before 45 m, after that, r |
| P. hwangshanensis–S. tanakana | + at all scales | r at all scales |
| P. hwangshanensis–L. glauca | − at all scales | r at all scales |
| P. hwangshanensis–R. simsii | + at all scales | + before 30 m and 80–100 m, r between 30 and 38 m and 70–80 m, − between 38 and 70 m |
| P. hwangshanensis–V. dilatatum | − before 38 m, r between 38 and 40 m, after that, + | − before 30 m, after that, r |
| P. hwangshanensis–C. sinensis var. calvescens | − at all scales | − between 7 and 17 m, r at other scales |
| P. strobilacea–C. kousa subsp. chinensis | + before 55 m, after that, r | r at all scales |
| P. strobilacea–N. japonica | + at all scales | + before 40 m, after that, r |
| P. strobilacea–S. tanakana | r at all scales | r at all scales |
| P. strobilacea–L. glauca | + before 55 m, after that, r | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| P. strobilacea–R. simsii | + between 30 and 62 m, r between 0 and 30 m and 62–72 m, after 72 m, − | r at all scales |
| P. strobilacea–V. dilatatum | r before 52 m, after that, + | r at all scales |
| P. strobilacea–C. sinensis var. calvescens | + at all scales | + between 25 and 30 m, r at other scales |
| C. henryi–C. kousa subsp. chinensis | − at all scales | r at all scales |
| C. henryi–N. japonica | + between 25 and 50 m and after 75 m, r at other scales | + between 85 and 95 m, r at other scales |
| C. henryi–S. tanakana | r before 13 m, after that, − | r at all scales |
| C. henryi–L. glauca | − before 72 m, r between 72 and 94 m, after that, − | r at all scales |
| C. henryi–R. simsii | r before 20 m, after that, − | + before 20 m, r between 20 and 80 m, after that, − |
| C. henryi–V. dilatatum | + before 17 m, r at 17–28 m, after that, − | + before 20 m, after that, r |
| C. henryi–C. sinensis var. calvescens | + at all scales | + before 35 m, after that, r |
| Species | Elevation | Slope | Aspect | Convex | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | p | Z1 | p | Z1 | p | Z1 | p | |
| P. hwangshanensis | 3.399 | <0.001 | −1.280 | 0.201 | −1.296 | 0.195 | −2.860 | 0.004 |
| P. strobilacea | 0.562 | 0.574 | 1.253 | 0.210 | −0.235 | 0.814 | −1.673 | 0.094 |
| C. henryi | −0.313 | 0.754 | −0.414 | 0.679 | 0.340 | 0.734 | −1.012 | 0.312 |
| Q. serrata | −0.829 | 0.407 | −0.988 | 0.323 | 2.181 | 0.029 | −1.087 | 0.277 |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis | 1.723 | 0.085 | 1.078 | 0.281 | −0.200 | 0.842 | −1.150 | 0.250 |
| N. japonica | −0.752 | 0.452 | 2.620 | 0.009 | −0.674 | 0.500 | 3.560 | <0.001 |
| S. tanakana | 0.702 | 0.482 | 0.154 | 0.878 | 2.437 | 0.015 | −4.193 | <0.001 |
| L. glauca | −0.435 | 0.664 | −0.229 | 0.819 | 2.990 | <0.001 | −1.198 | 0.231 |
| R. simsii | 3.251 | 0.001 | 1.745 | 0.081 | −0.579 | 0.563 | −10.672 | <0.001 |
| V. dilatatum | 0.604 | 0.546 | 0.786 | 0.432 | −0.810 | 0.418 | −1.836 | 0.066 |
| C. sinensis var. calvescens | −0.641 | 0.522 | 0.199 | 0.842 | 0.228 | 0.820 | −2.751 | 0.006 |
| C. chinensis | 0.161 | 0.872 | −1.957 | 0.050 | −0.153 | 0.878 | −3.918 | <0.001 |
| Species | N | C | GO | PH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | p | Z1 | p | Z1 | p | Z1 | p | |
| P. hwangshanensis | −6.140 | <0.001 | 1.247 | 0.212 | −1.426 | 0.154 | −1.352 | 0.177 |
| P. strobilacea | −1.311 | 0.190 | −1.012 | 0.311 | −0.018 | 0.985 | −0.175 | 0.861 |
| C. henryi | −2.469 | 0.014 | −1.315 | 0.189 | −0.370 | 0.711 | −0.488 | 0.626 |
| Q. serrata | −6.023 | <0.001 | −4.465 | <0.001 | −0.644 | 0.520 | −0.184 | 0.854 |
| C. kousa subsp. chinensis | −1.586 | 0.113 | −0.149 | 0.882 | −4.311 | <0.001 | −0.616 | 0.538 |
| N. japonica | −1.710 | 0.087 | −2.551 | 0.011 | −1.328 | 0.184 | 0.133 | 0.895 |
| S. tanakana | 0.026 | 0.979 | 0.428 | 0.669 | −3.420 | <0.001 | −0.589 | 0.556 |
| L. glauca | 4.270 | <0.001 | 2.761 | 0.006 | 3.294 | <0.001 | 0.516 | 0.606 |
| R. simsii | −13.730 | <0.001 | −4.180 | <0.001 | −8.031 | <0.001 | −2.765 | 0.006 |
| V. dilatatum | −0.990 | 0.322 | −0.650 | 0.516 | −3.168 | 0.002 | −0.885 | 0.376 |
| C. sinensis var. calvescens | −6.878 | <0.001 | −5.223 | <0.001 | −3.852 | <0.001 | −0.548 | 0.584 |
| C. chinensis | −2.253 | 0.024 | −1.606 | 0.108 | −2.838 | 0.005 | −0.441 | 0.660 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Xi, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J. Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Association in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in East China. Forests 2025, 16, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101511
Wang J, Xiang Z, Xi D, Zhang Z, Zhou S, Zhang J. Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Association in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in East China. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101511
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jingxuan, Zeyu Xiang, Dan Xi, Zhaochen Zhang, Saixia Zhou, and Jiaxin Zhang. 2025. "Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Association in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in East China" Forests 16, no. 10: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101511
APA StyleWang, J., Xiang, Z., Xi, D., Zhang, Z., Zhou, S., & Zhang, J. (2025). Spatial Distribution and Intraspecific and Interspecific Association in a Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest in East China. Forests, 16(10), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101511






