An Assessment Framework for Mapping the Air Purification Service of Vegetation at the Regional Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Data Sources and Processing
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Simulating PM2.5 Removal
2.4.2. Simulating of PM2.5 Removal Rate
2.4.3. Identification of Coldspots and Hotspots
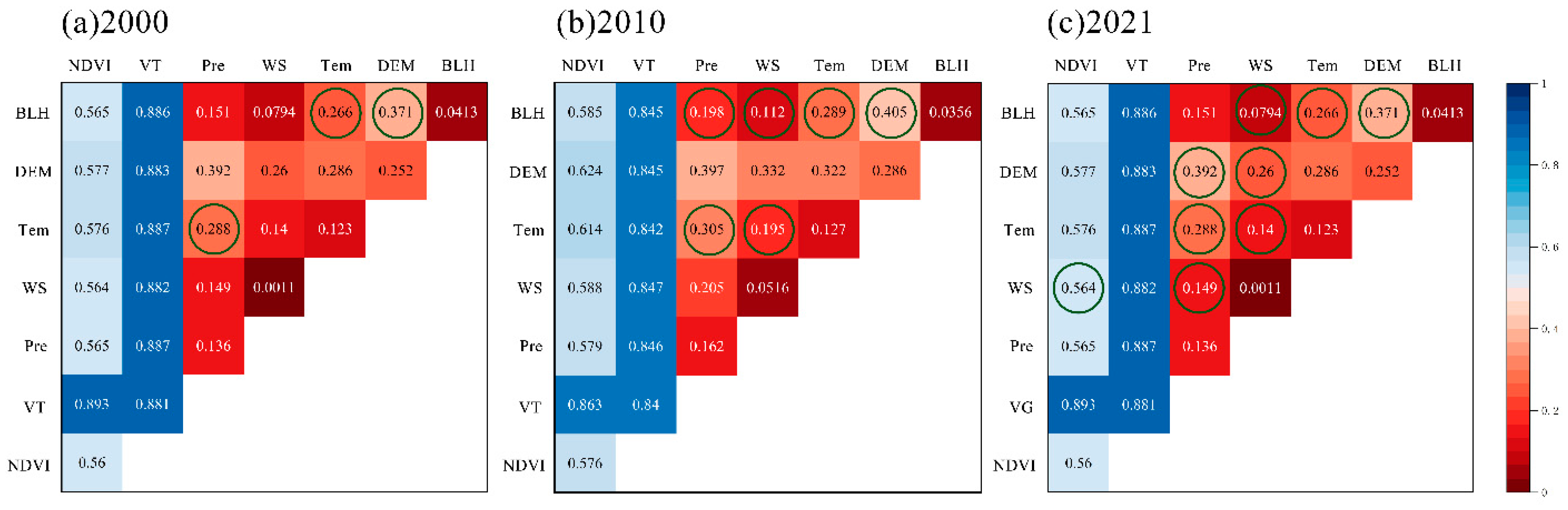
2.4.4. GeoDetector
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of PM2.5 Removal and Identification of Risk Areas
3.1.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of PM2.5 Concentration and Removal
3.1.2. Effect of Different Vegetation Types on PM2.5 Removal
3.1.3. Comparison of PM2.5 Removal Effect in Different Cities
3.1.4. Identification of Risk Areas
3.2. Influencing Factors of PM2.5 Removal Services in the Fenwei Plain
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect Analysis of Vegetation PM2.5 Purification Services
4.2. Policy Recommendations
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDuffie, E.E.; Martin, R.V.; Spadaro, J.V.; Burnett, R.; Smith, S.J.; O’Rourke, P.; Hammer, M.S.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Bindle, L.; Shah, V.; et al. Source Sector and Fuel Contributions to Ambient PM2.5 and Attributable Mortality across Multiple Spatial Scales. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chiueh, P.-T. Nexus of Ecosystem Service-Human Health-Natural Resources: The Nature-Based Solutions for Urban PM2.5 Pollution. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweileh, W.M. Bibliometric Analysis of Scientific Publications on “Sustainable Development Goals” with Emphasis on “Good Health and Well-Being” Goal (2015–2019). Glob. Health 2020, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.; Ramacher, M.O.P.; Speyer, O.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Karl, M.; Gerasopoulos, E. Localizing SDG 11.6.2 via Earth Observation, Modelling Applications, and Harmonised City Definitions: Policy Implications on Addressing Air Pollution. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junwu, D.; Yanhui, W.; Lili, W.; Wenji, Z.; Chong, H. Assessment of PM2.5 Exposure Risk towards SDG Indicator 11.6.2—A Case Study in Beijing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103864. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Managi, S. Spatial Variability of the Relationship between Air Pollution and Well-Being. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, X. Long-Term Trends and Spatial Patterns of Satellite-Retrieved PM2.5 Concentrations in South and Southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-Y.; Lane, K.J.; Miranda, M.L.; Bell, M.L. Health Disparities Attributable to Air Pollutant Exposure in North Carolina: Influence of Residential Environmental and Social Factors. Health Place 2020, 62, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lin, H.; Yang, X.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, P. Analyzing Synergies and Efficiency of Reducing CO2 and Air Pollutants in the Case of China’s Three-Year Action Plan to Fight Air Pollution. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 114028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. The Impact of the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” on PM2.5 Concentrations in Jing-Jin-Ji Region during 2012–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, X.; Seyler, B.C.; Tang, Y. Air Pollution Reduction in China: Recent Success but Great Challenge for the Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. Assessment on the reduction of atmospheric PM2.5 by urban forest and its ratio to the total PM2.5 pollutant in the Chinese major cities. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Ziv, G.; Hirabayashi, S.; Bakshi, B.R. Nature-Based Solutions Can Compete with Technology for Mitigating Air Emissions Across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13228–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, M.G.; Russo, F.; Adani, M.; Piersanti, A.; Vitali, L.; Tinarelli, G.; Ciancarella, L.; Zanini, G.; Donateo, A.; Rinaldi, M.; et al. Evaluating the Impact of a Wall-Type Green Infrastructure on PM10 and NOx Concentrations in an Urban Street Environment. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riondato, E.; Pilla, F.; Sarkar Basu, A.; Basu, B. Investigating the Effect of Trees on Urban Quality in Dublin by Combining Air Monitoring with I-Tree Eco Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tan, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. Better Urban Vegetation Planning for Maximum Utility in Air Pollutant Reduction: A Theoretical Perspective and Preliminary Analysis in Chinese Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Jin, J.; Yang, J. Simulating PM2.5 Removal in an Urban Ecosystem Based on the Social-Ecological Model Framework. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 47, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, F.; Marando, F.; Capotorti, G.; Blasi, C.; Salvatori, E.; Fusaro, L.; Ciancarella, L.; Mircea, M.; Marchetti, M.; Chirici, G.; et al. Regulating Ecosystem Services of Forests in Ten Italian Metropolitan Cities: Air Quality Improvement by PM10 and O3 Removal. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, C. Can National Forest City Construction Mitigate Air Pollution in China? Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment. Env. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 3003–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, K. New Prospects to Systematically Improve the Particulate Matter Removal Efficiency of Urban Green Spaces at Multi-Scales. Forests 2023, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, H. Mitigation Impact of Roadside Trees on Fine Particle Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.; Matos, P.; Mexia, T.; Silva, P.; Lopes, N.; Freitas, C.; Correia, O.; Santos-Reis, M.; Branquinho, C.; Pinho, P. Green Spaces Are Not All the Same for the Provision of Air Purification and Climate Regulation Services: The Case of Urban Parks. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Nowak, D.J. Spatial Heterogeneity and Air Pollution Removal by an Urban Forest. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Hirabayashi, S.; Bodine, A.; Hoehn, R. Modeled PM2.5 Removal by Trees in Ten U.S. Cities and Associated Health Effects. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, W.; Weber, C.; Rivière, E.; Blond, N.; Mehdi, L.; Nowak, D. Air Pollution Removal by Trees in Public Green Spaces in Strasbourg City, France. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 17, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Cui, L. Current Status, Characteristics and Causes of Particulate Air Pollution in the Fenwei Plain, China: A Review. JGR Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Xu, Y.; Lv, D.; Xie, X.; Kleeman, M.; Xing, J.; Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Source Contributions to Primary and Secondary Inorganic Particulate Matter during a Severe Wintertime PM2.5 Pollution Episode in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, T.; Cai, S. The Episodic Geomorphological-Sedimentary Evolution of Different Basins in the Fenwei Graben and Its Tectonic Implication. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 Km Resolution PM2.5 Estimates across China Using Enhanced Space–Time Extremely Randomized Trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-Km-Resolution High-Quality PM2.5 Data Records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Policy Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air Pollution Removal by Urban Trees and Shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, B. PM2.5 removal service of green spaces in Shanghai based on the dust retention simulation on urban vegetation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chiueh, P.-T. High-Resolution Spatial Analysis for the Air Quality Regulation Service from Urban Vegetation: A Case Study of Taipei City. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 83, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Modeled Particulate Matters Removal by Urban Green Lands in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, H. Derivation and validation of leaf area index maps using NDVI data of different resolution satellite imageries. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 11, 3826–3834. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhai, T.; Wang, J. Effects of Land-Use Patterns on PM2.5 in China’s Developed Coastal Region: Exploration and Solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. In Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis; Anselin, L., Rey, S.J., Eds.; Advances in Spatial Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 127–145. ISBN 978-3-642-01976-0. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, N.; Cheng, W.; Fu, B. Mapping the hotspots and coldspots of ecosystem services in conservation priority setting. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Nie, D.; Zhang, S.; Yu, W.; Ge, X.; Song, N. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Air Pollutants and Their Health Effects in China during 2019–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, N.; Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C. Atmospheric PM2.5 removal by green spaces in Beijing. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.A. Mountain Pine Beetle Impacts on Health through Lost Forest Air Pollutant Sinks. Forests 2021, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giess, P.; Goddard, A.J.H.; Shaw, G. Factors Affecting Particle Resuspension from Grass Swards. J. Aerosol Sci. 1997, 28, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, D.; Gao, B.; He, B.; Cheng, N.; Xu, B. Understanding Meteorological Influences on PM2.5 Concentrations across China: A Temporal and Spatial Perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5343–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R.; Liu, M. Influence and Prediction of PM2.5 through Multiple Environmental Variables in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Jiao, L.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, C. Influences of Wind and Precipitation on Different-Sized Particulate Matter Concentrations (PM2.5, PM10, PM2.5–10). Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z. Uncertainties in Research between Urban Landscape and Air Quality: Summary, Demonstration, and Expectation. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, C.; Lu, D.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.; Bai, L. Quantifying the Influence of Natural and Socioeconomic Factors and Their Interactive Impact on PM2.5 Pollution in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z. The Impact of Greenspace on Air Pollution: Empirical Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H. Shade Trees Reduce Building Energy Use and CO2 Emissions from Power Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, S119–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baró, F.; Chaparro, L.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Langemeyer, J.; Nowak, D.J.; Terradas, J. Contribution of Ecosystem Services to Air Quality and Climate Change Mitigation Policies: The Case of Urban Forests in Barcelona, Spain. AMBIO 2014, 43, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Estimation of the PM2.5 Removal Capacity and Influencing Factors of Urban Green Infrastructure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, D.H.; Likongwe, P.J.; Chiotha, S.S.; Nduwayezu, G.; Mallick, D.; Uddin, M.d.N.; Rahman, A.; Golovátina-Mora, P.; Lotero, L.; Bricker, S.; et al. Using Demand Mapping to Assess the Benefits of Urban Green and Blue Space in Cities from Four Continents. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babí Almenar, J.; Petucco, C.; Sonnemann, G.; Geneletti, D.; Elliot, T.; Rugani, B. Modelling the Net Environmental and Economic Impacts of Urban Nature-Based Solutions by Combining Ecosystem Services, System Dynamics and Life Cycle Thinking: An Application to Urban Forests. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 60, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
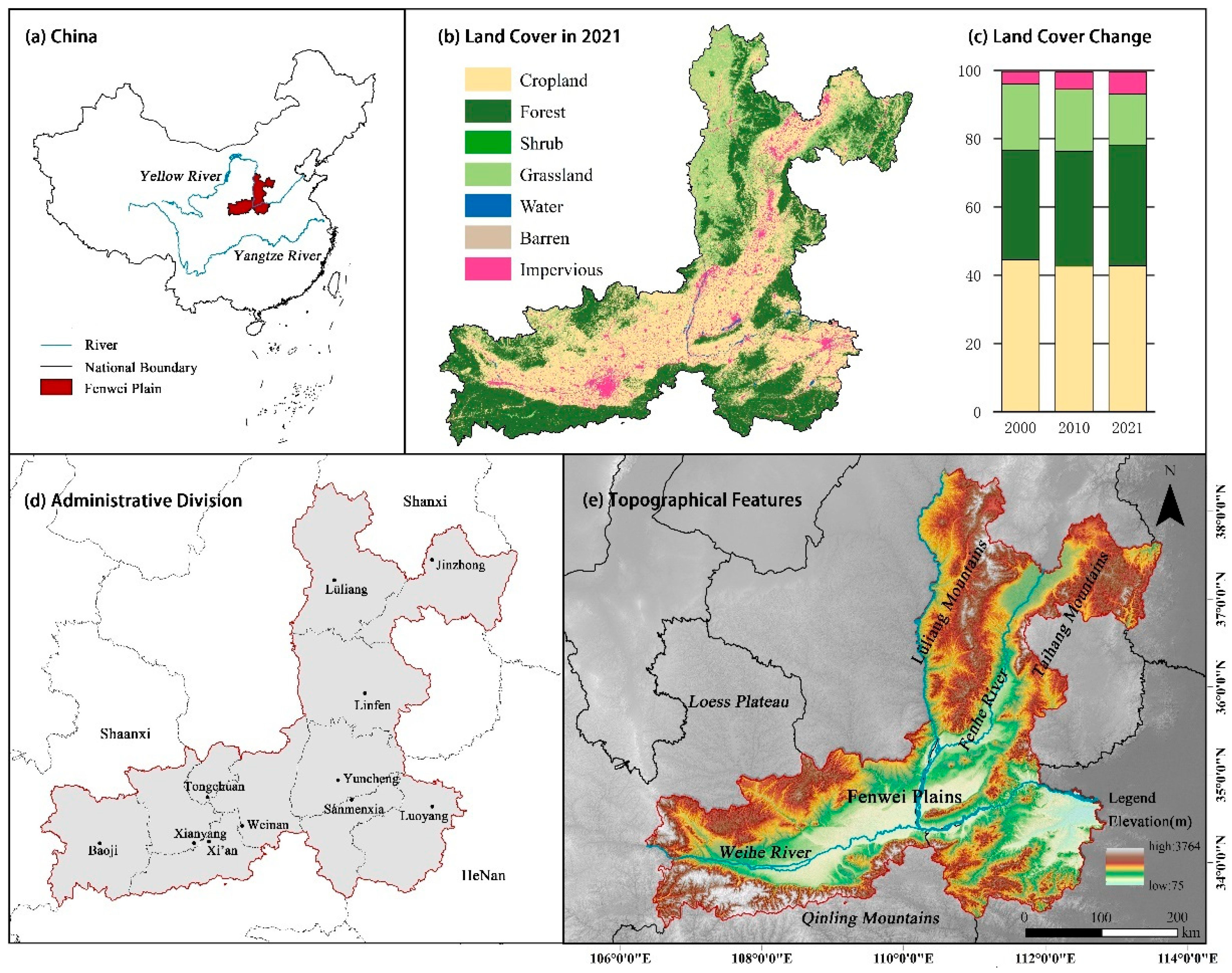





| Data Classification | Data Name | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| CLCD | 2000, 2010, 2021 Land use data | 30 m |
| Vegetation data | 2000, 2010, 2021 NDVI | 30 m |
| PM2.5 data | 2000, 2010, 2021 Annual average concentration of PM2.5 | 1000 m |
| Meteorological data | Average annual wind speed | - |
| Average daily precipitation | - | |
| Average annual temperature | - | |
| Atmospheric boundary layer height | 0.1° | |
| Terrain data | DEM data (ASTER DEM v3) | 30 m |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation Types | |||||||||
| Mixed Forest | 0.02 | 0.285 | 0.545 | 0.64 | 0.735 | 0.83 | 0.925 | 1.02 | |
| Shrub | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.96 | |
| Grassland | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.056 | 0.082 | |
| Cropland | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.056 | 0.082 | |
| Resuspension rate | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.032 | 0.036 | 0.039 | 0.059 | 0.079 | 0.099 | |
| Vegetation Types | Regression Equation |
|---|---|
| Forest | LAI = 4.689NDVI/(1.818 − NDVI) |
| Shrub | LAI = 6.211NDVI − 1.088 |
| Grassland | LAI = 3.227NDVI/NDVIavg |
| Cropland | LAI = 8.547NDVI − 0.932 |
| Year | 2000 | 2010 | 2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation Type | Removal (t) | Removal Rate (%) | Removal (t) | Removal Rate (%) | Removal (t) | Removal Rate (%) | |
| Cropland | 1375.80 | 0.004 | 1731.02 | 0.004 | 1763.43 | 0.007 | |
| Forest | 68,287.13 | 0.179 | 93,504.70 | 0.236 | 106,175.11 | 0.424 | |
| Shrub | 846.92 | 0.002 | 617.02 | 0.002 | 421.54 | 0.002 | |
| Grassland | 677.17 | 0.002 | 718.15 | 0.002 | 613.40 | 0.002 | |
| Sum | 71,187.01 | 0.186 | 96,570.89 | 0.243 | 108,973.47 | 0.435 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, H. An Assessment Framework for Mapping the Air Purification Service of Vegetation at the Regional Scale. Forests 2024, 15, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020391
Liu Y, Zhao W, Zhang L, Li X, Peng L, Wang Z, Song Y, Jiao L, Wang H. An Assessment Framework for Mapping the Air Purification Service of Vegetation at the Regional Scale. Forests. 2024; 15(2):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020391
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu, Wudong Zhao, Liwei Zhang, Xupu Li, Lixian Peng, Zhuangzhuang Wang, Yongyong Song, Lei Jiao, and Hao Wang. 2024. "An Assessment Framework for Mapping the Air Purification Service of Vegetation at the Regional Scale" Forests 15, no. 2: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020391
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhao, W., Zhang, L., Li, X., Peng, L., Wang, Z., Song, Y., Jiao, L., & Wang, H. (2024). An Assessment Framework for Mapping the Air Purification Service of Vegetation at the Regional Scale. Forests, 15(2), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020391









