Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
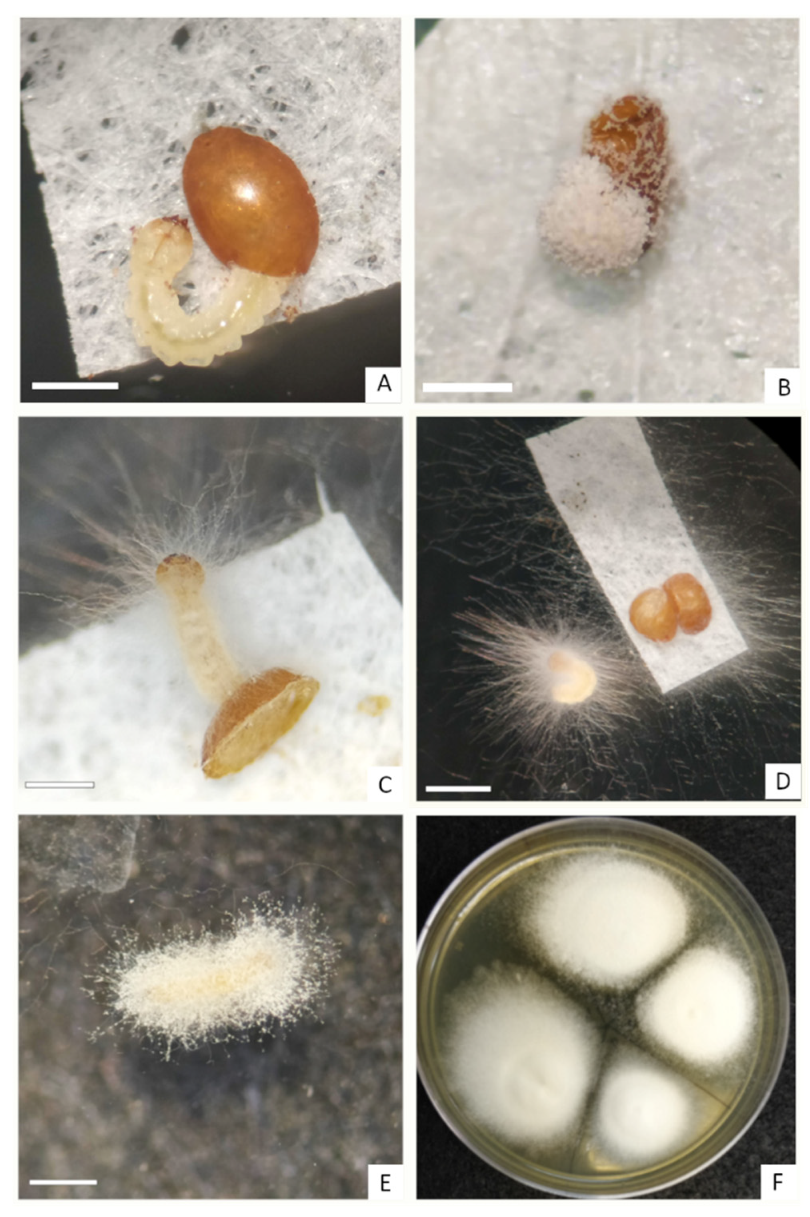
2.1. Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Experimental Setting and Egg Inoculation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
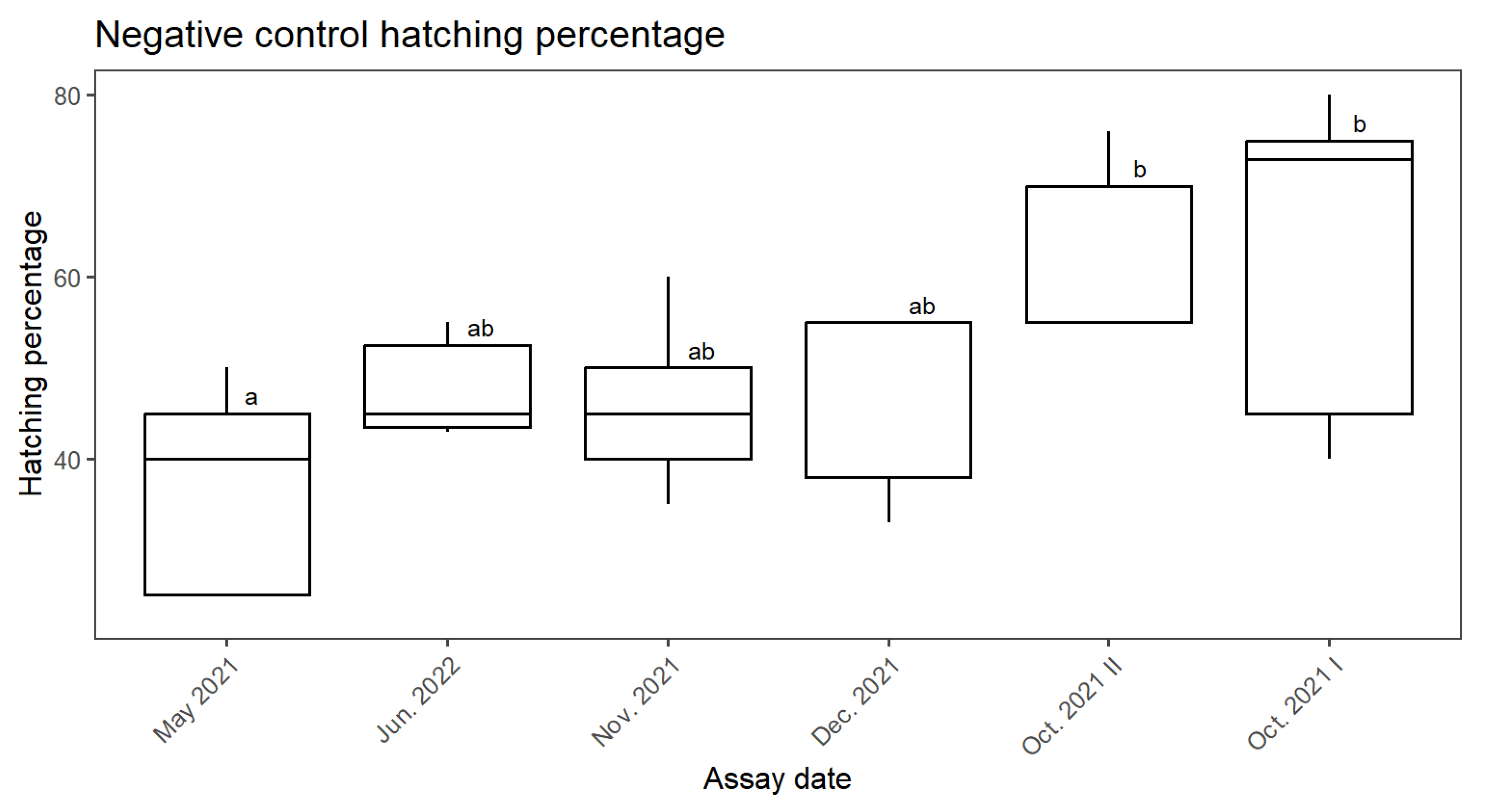
3.1. Negative and Positive Controls Comparison
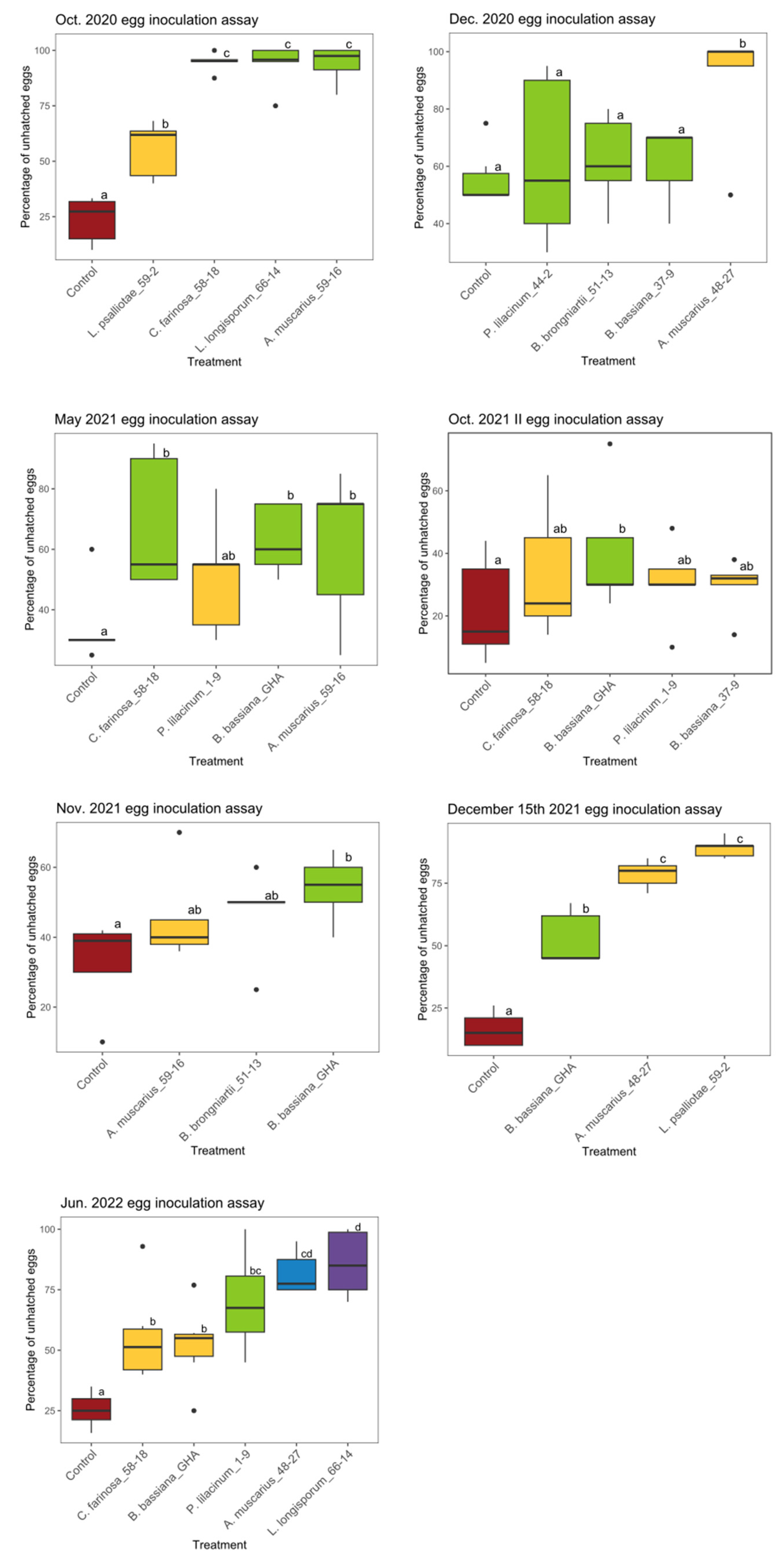
3.2. Ovicidal Effect Evaluation
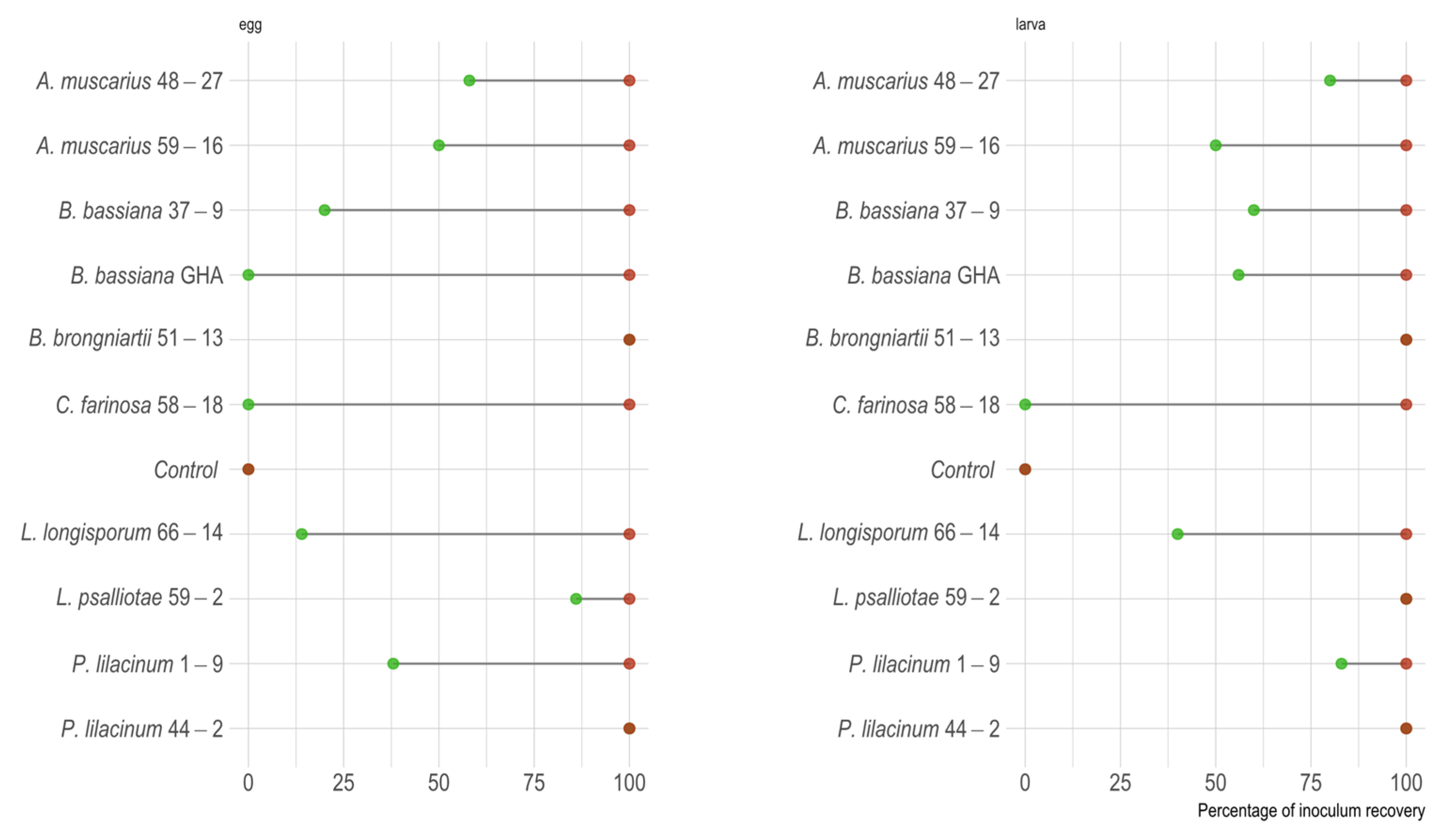
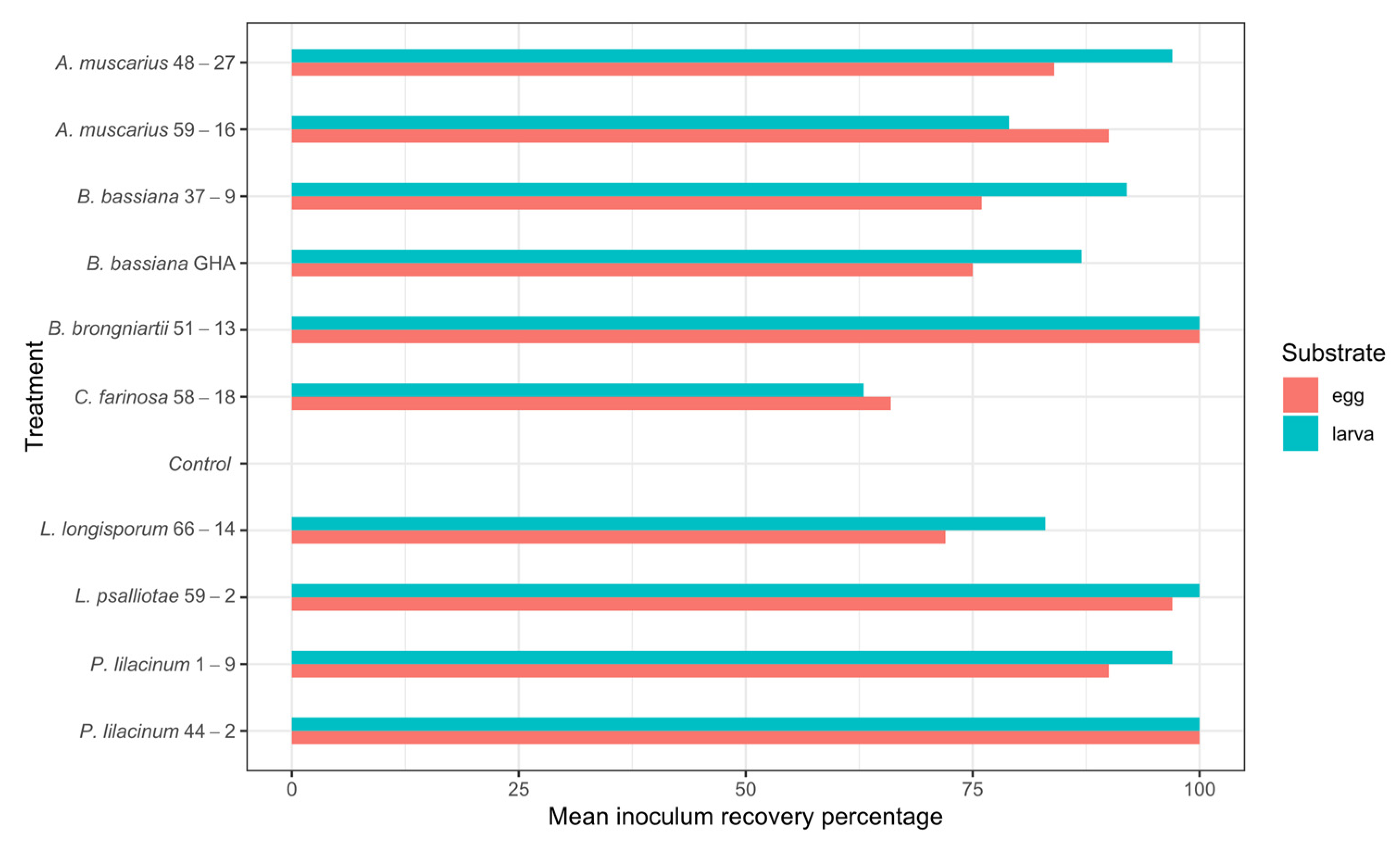
3.3. Inoculum Recovery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poland, T.M.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald Ash Borer: Invasion of the Urban Forest and the Threat to North America’s Ash Resource. J. For. 2006, 104, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, N.W.; McCullough, D.G.; Liebhold, A.M.; Telewski, F.W. Dendrochronological Reconstruction of the Epicentre and Early Spread of Emerald Ash Borer in North America. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald Ash Borer Invasion of North America: History, Biology, Ecology, Impacts, and Management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, D.G. Challenges, Tactics and Integrated Management of Emerald Ash Borer in North America. For. An. Int. J. For. Res. 2019, 93, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.S.; Liebhold, A.M.; Pugh, S.A.; Crocker, S.J. Regional Assessment of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis, Impacts in Forests of the Eastern United States. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, J.E.; Leung, B.; Kovacs, K.; Chivers, C.; Britton, K.O.; Englin, J.; Frankel, S.J.; Haight, R.G.; Holmes, T.P.; Liebhold, A.M.; et al. Economic Impacts of Non-Native Forest Insects in the Continental United States. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, K.J.K.; Herms, D.A. North American Arthropods at Risk Due to Widespread Fraxinus Mortality Caused by the Alien Emerald Ash Borer. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; Gandhi, K.J.; Smith, A.; Cardina, J.; Knight, K.S.; Herms, C.P.; Long, R.P.; McCullough, D.G. Ecological Impacts of Emerald Ash Borer in Forests of Southeast Michigan. In Proceedings of the 20th US Department of Agriculture Interagency Research Forum on Invasive Species 2009, Annapolis, MD, USA, 13–16 January 2009; McManus, K.A., Gottschalk, K.W., Eds.; Gen. Tech. Rep. NRS-P-51; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Klooster, W.S.; Gandhi, K.J.; Long, L.C.; Perry, K.I.; Rice, K.B.; Herms, D.A. Ecological Impacts of Emerald Ash Borer in Forests at the Epicenter of the Invasion in North America. Forests 2018, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolka, R.K.; D’Amato, A.W.; Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Slesak, R.A.; Pypker, T.G.; Youngquist, M.B.; Grinde, A.R.; Palik, B.J. Review of Ecosystem Level Impacts of Emerald Ash Borer on Black Ash Wetlands: What Does the Future Hold? Forests 2018, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, K.F.; Haight, R.G.; McCullough, D.G.; Mercader, R.J.; Siegert, N.W.; Liebhold, A.M. Cost of Potential Emerald Ash Borer Damage in U.S. Communities, 2009–2019. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.M. Forest Compositional Changes after a Decade of Emerald Ash Borer. Forests 2020, 11, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQuarrie, C.J.K.; Ryall, K.; Jones, G.; Martel, V.; Sweeney, J.; Gaudon, J.M.; Smith, S.M. Agrilus Planipennis Fairmaire, Emerald Ash Borer/Agrile Du Frêne (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). In Biological Control Programmes in Canada, 2013–2023; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2024; pp. 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.F.; Liebhold, A.M.; Morin, R.S.; Fei, S. Population Dynamics of Ash across the Eastern USA Following Invasion by Emerald Ash Borer. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 479, 118574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.F.; Fei, S.; Liebhold, A.M. Temporal Dynamics and Drivers of Landscape-Level Spread by Emerald Ash Borer. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinde, A.R.; Youngquist, M.B.; Slesak, R.A.; Kolbe, S.; Bednar, J.D.; Palik, J.B.; D’Amato, A.W. Potential Impacts of Emerald Ash Borer and Adaptation Strategies on Wildlife Communities in Black Ash Wetlands. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebek, E.J.; Herms, D.A.; Smitley, D.R. Interspecific Variation in Resistance to Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Among North American and Asian Ash (Fraxinus spp.). Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigsby, C.M.; Showalter, D.N.; Herms, D.A.; Koch, J.L.; Bonello, P.; Cipollini, D. Physiological Responses of Emerald Ash Borer Larvae to Feeding on Different Ash Species Reveal Putative Resistance Mechanisms and Insect Counter-Adaptations. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 78, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villari, C.; Herms, D.A.; Whitehill, J.G.A.; Cipollini, D.; Bonello, P. Progress and Gaps in Understanding Mechanisms of Ash Tree Resistance to Emerald Ash Borer, a Model for Wood-boring Insects That Kill Angiosperms. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.S.; Brown, J.P.; Long, R.P. Factors Affecting the Survival of Ash (Fraxinus spp.) Trees Infested by Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus Planipennis). Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.J.; Gould, J.R.; Quinn, N.F.; Petrice, T.R.; Slager, B.H.; Poland, T.M.; Bauer, L.S.; Rutledge, C.E.; Elkinton, J.S.; Van Driesche, R.G. Protection of North American Ash against Emerald Ash Borer with Biological Control: Ecological Premises and Progress toward Success. BioControl 2023, 68, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAO Invasive Forest Pests: Lessons Learned from Three Recent Infestations May Aid in Managing Future Efforts. Report of the United States Governmental Accounting Office. GAO-06-353. Available online: https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-06-353 (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Duan, J.J.; Van Driesche, R.G.; Schmude, J.; Crandall, R.; Rutlege, C.; Quinn, N.; Slager, B.H.; Gould, J.R.; Elkinton, J.S. Significant Suppression of Invasive Emerald Ash Borer by Introduced Parasitoids: Potential for North American Ash Recovery. J. Pest. Sci. 2022, 95, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G.; Smitley, D.R.; Sadof, C.S.; Miller, F.D.; Cranshaw, W. Insecticide Options for Protecting Ash Trees from Emerald Ash Borer. N. Cent. IPM Cent. Bull. 2009, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, M.; Parker, B.L.; Kim, J.S. Role of Entomopathogenic Fungi in Integrated Pest Management. In Integrated Pest Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 169–191. ISBN 978-0-12-398529-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wylie, F.R.; Speight, M. Integrated Pest Management (IPM). Insect Pests Trop. For. 2012, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilenberg, J.; Hajek, A.; Lomer, C. Suggestions for Unifying the Terminology in Biological Control. BioControl 2001, 46, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, A.E.; Bauer, L.S. Microbial Control of Wood-Boring Insects Attacking Forest and Shade Trees. In Field Manual of Techniques in Invertebrate Pathology; Lacey, L.A., Kaya, H.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 505–525. ISBN 978-1-4020-5931-5. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, P.A.; Pell, J.K. Entomopathogenic Fungi as Biological Control Agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, A.; Silini, A.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Chenari Bouket, A.; Moser, W.K.; Nowakowska, J.A.; Oszako, T.; Benia, F.; Belbahri, L. The Threat of Pests and Pathogens and the Potential for Biological Control in Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2021, 12, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M.S. Insect Pathogens as Biological Control Agents: Back to the Future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, M.C.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Davyt-Colo, B.; Pedrini, N. Is the Insect Cuticle the Only Entry Gate for Fungal Infection? Insights into Alternative Modes of Action of Entomopathogenic Fungi. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Luo, J.; Li, C.; Eleftherianos, I.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L. A Life-and-Death Struggle: Interaction of Insects with Entomopathogenic Fungi across Various Infection Stages. Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1329843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, S.K.; Montalva, C.; Barta, M. Microbial Control of Invasive Forest Pests with Entomopathogenic Fungi: A Review of the Current Situation. Insects 2019, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.S.; Mann, A.J.; Malesky, D.; Jankowski, E.; Bradley, C. Laboratory and Field Evaluation of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) for Population Management of Spruce Beetle, Dendroctonus Rufipennis (Coleoptera: Scolytinae), in Felled Trees and Factors Limiting Pathogen Success. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganova, S.A.; Doychev, D.D.; Pilarska, D.K.; Takov, D.I. Bioassays of Entomopathogenic Fungi against Xylophagous Insects in Bulgaria: Laboratory and Field Experiments. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2017, 69, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Fora, C.G.; Boja, N.; Moatăr, M.; Tóth, F.; Balog, A. Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi, Beauveria Bassiana (Cordycipitaceae), on the Bark Beetle, Ips Typographus (L.), under Field Conditions. Insects 2022, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajek, A.E.; van Frankenhuyzen, K. Use of Entomopathogens Against Forest Pests. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 313–330. ISBN 978-0-12-803527-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kreutz, J.; Vaupel, O.; Kolb, M.; Zimmermann, G. Effect of Mineral Dusts Alone and in Combination with the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. against the Bark Beetle Ips Typographus L. (Col., Scolytidae) in the Laboratory and under Field Conditions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 515, 120225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.J.; Davis, T.S. Entomopathogenic Fungi to Control Bark Beetles: A Review of Ecological Recommendations. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3841–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatinwo, R.; Walters, S.; Strom, B. Impact of Beauveria Bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) on the Small Southern Pine Engraver (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in a Loblolly Pine Bolt Assay1. J. Entomol. Sci. 2018, 53, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.S.; Liu, H.P.; Haack, R.A.; Gao, R.; Zhao, T.; Miller, D.L.; Petrice, T.R. Emerald Ash Borer Natural Enemy Surveys in Michigan and China. In Gottschalk. Proceedings of the XV US Department of Agriculture Interagency Research Forum on Gypsy Moth and Other Invasive Species 2004, Annapolis, MD, USA, 13–16 January 2004; Kurt, W., Ed.; General Technical Report NE-332; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northeastern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA; Romulus, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Bauer, L.S.; Liu, H.; Griggs, M.H.; Vandenberg, J.D. Characterization of Beauveria Bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Isolates Associated with Agrilus Planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Populations in Michigan. Biol. Control 2010, 54, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, B.W.; Simeto, S.; Rajtar, N.N.; Cotton, A.J.; Showalter, D.N.; Bushley, K.E.; Blanchette, R.A. Fungi Associated with Galleries of the Emerald Ash Borer. Fungal Biol. 2021, 125, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, S.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Gauthier, D.; van Frankenhuyzen, K. Isolation and Characterisation of Isaria Farinosa and Purpureocillium Lilacinum Associated with Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis in Canada. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, S.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Gauthier, D.; van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Krell, P.J. Characterization and Virulence of Beauveria Spp. Recovered from Emerald Ash Borer in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Griggs, M.H.; Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S.; Vandenberg, J.D. Assessing Deposition and Persistence of Beauveria Bassiana GHA (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) Applied for Control of the Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in a Commercial Tree Nursery. Biol. Control 2010, 54, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S. Microbial Control of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) with Beauveria Bassiana Strain GHA: Greenhouse and Field Trials. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, D.B.; Lavallée, R.; Kyei-Poku, G.; Van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Johny, S.; Guertin, C.; Francese, J.A.; Jones, G.C.; Blais, M. Towards the Development of an Autocontamination Trap System to Manage Populations of Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) with the Native Entomopathogenic Fungus, Beauveria Bassiana. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srei, N.; Guertin, C.; Lavallée, R.; Lajoie, M.-È.; Brousseau, C.; Bergevin, R.; Miller, F.; McMillin, K.; Trudel, R. Microbial Control of the Emerald Ash Borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Using Beauveria Bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) by the Means of an Autodissemination Device. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akutse, K.S.; Kimemia, J.W.; Ekesi, S.; Khamis, F.M.; Ombura, O.L.; Subramanian, S. Ovicidal Effects of Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates on the Invasive Fall Armyworm Spodoptera Frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S.; Adamu, R.S.; Maniania, N.K. Ovicidal Activity of Entomopathogenic Hyphomycetes to the Legume Pod Borer, Maruca Vitrata and the Pod Sucking Bug, Clavigralla Tomentosicollis. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Kirk, A.A.; Millar, L.; Mercadier, G.; Vidal, C. Ovicidal and Larvicidal Activity of Conidia and Blastospores of Paecilomyces Fumosoroseus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) Against Bemisia Argentifolii (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) with a Description of a Bioassay System Allowing Prolonged Survival of Control Insects. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1999, 9, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, C.; Tai, M.H.H.; Santos, A.H.; Rocha, L.F.N.; Albernaz, D.A.S.; Silva, H.H.G. Ovicidal Activity of Entomopathogenic Hyphomycetes on Aedes Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Under Laboratory Conditions. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marannino, P.; Santiago-Álvarez, C.; de Lillo, E.; Quesada-Moraga, E. A New Bioassay Method Reveals Pathogenicity of Metarhizium Anisopliae and Beauveria Bassiana against Early Stages of Capnodis Tenebrionis (Coleoptera; Buprestidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006, 93, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochi, D.A.; Monteiro, A.C.; Machado, A.C.R.; Yoshida, L. Efficiency of Entomopathogenic Fungi in the Control of Eggs and Larvae of the Horn Fly Haematobia Irritans (Diptera: Muscidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, R.I.; Coracini, D.L.A.; Martins dos Santos, C.A.; Gava, C.A.T. Infection of Blissus Antillus (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae) Eggs by the Entomopathogenic Fungi Metarhizium Anisopliae and Beauveria Bassiana. Biol. Control 2002, 23, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, V.W.; Knapp, M.; Maniania, N.K.; Boga, H.I. Effects of Beauveria Bassiana and Metarhizium Anisopliae on Mortality, Fecundity and Egg Fertility of Tetranychus Evansi. J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappaert, D.; McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M.; Siegert, N.W. Emerald Ash Borer in North America: A Research and Regulatory Challenge. Am. Entomol. 2005, 51, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, D.E.; Taylor, P.B.; Duan, J.J. The Mating and Oviposition Behavior of the Invasive Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus Planipennis), with Reference to the Influence of Host Tree Condition. J. Pest. Sci. 2014, 87, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, D.; Jones, G.; Wainio-Keizer, K. Biology and Phenology of the Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis. In Gottschalk. Proceedings of the XV U.S. Department of Agriculture Interagency Research Forum on Gypsy Moth and Other Invasive Species 2004, Annapolis, MD, USA, 13–16 January 2004; Kurt, W., Ed.; General Technical Report NE-332; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northeastern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, L.; Haack, R.A.; Miller, D.L.; Petrice, T.R. Emerald Ash Borer Life Cycle. In Mastro, Victor; Reardon, Richard, comps. Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer Research and Technology Development Meeting, Port Huron, MI, USA, September 30–October 1 2003; FHTET 2004-02; U.S. Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Alfiky, A. Screening and Identification of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates from Agricultural Farmland Soils in Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Akutse, K.S.; Ramos Aguila, L.C.; Xu, Y. General Limitations to Endophytic Entomopathogenic Fungi Use as Plant Growth Promoters, Pests and Pathogens Biocontrol Agents. Plants 2021, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla-Carrera, L.; Morton, A.; Santamaria, S.; García-del-Pino, F. Isolation and Virulence of Entomopathogenic Fungi against Larvae of Hazelnut Weevil Curculio Nucum (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) and the Effects of Combining Metarhizium Anisopliae with Entomopathogenic Nematodes in the Laboratory. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.N.; Chowdhury, M.Z.H.; Mim, M.F.; Momtaz, M.B.; Islam, T. Biocontrol Potential of Native Isolates of Beauveria Bassiana against Cotton Leafworm Spodoptera Litura (Fabricius). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.-R.; Ibrahim, R.A. Assessment of the Virulence and Proteolytic Activity of Three Native Entomopathogenic Fungi against the Larvae of Oryctes Agamemnon (Burmeister) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2019, 29, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.B.; Martins, I.; Souza, D.A.; Faria, M. Influence of Some Parameters on the Germination Assessment of Mycopesticides. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 112, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A. Host Range and Host Resistance. In Biology and Control of Emerald Ash Borer—Technical Bulletin FHTET 2014–09.; Van Driesche, R.G., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2015; pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Gould, J.R.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Liu, G.-J.; Liu, E. The Biology and Ecology of the Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus Planipennis, in China. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwaneen, W.S.; Wakil, W.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Qayyum, M.A.; Tahir, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Husain, M.; Aldawood, A.S.; Shapiro-Ilan, D. Efficacy and Persistence of Entomopathogenic Fungi against Rhynchophorus Ferrugineus on Date Palm: Host to Host Transmission. Agronomy 2024, 14, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrucci, N.; Velazquez, M.-S.; Russo, M.-L.; Vianna, M.-F.; Abarca, C.; Scorsetti, A.-C.; Allegrucci, N.; Velazquez, M.-S.; Russo, M.-L.; Vianna, M.-F.; et al. Establishment of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana as an Endophyte in Capsicum Annuum and Its Effects on the Aphid Pest Myzus Persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Rev. De Biol. Trop. 2020, 68, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2024. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means 2024. R Package Version 1.10.5. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. Dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation; 2023. R Package Version 1.1.4. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, S.; Piepho, H.-P.; Dorai-Raj, L.S. With Help from S. multcompView: Visualizations of Paired Comparisons; 2019. R package version 0.1-10. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=multcompView (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Zhang, W.; Tettamanti, G.; Daley, L.; Mohamed, A.; Stanley, D. Nutrition Influences Immunity: Diet and Host-Parasite Interactions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 175, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Tiwary, B.N. Pathogenicity of Entomopathogenic Fungi to Eggs and Larvae of Spodoptera Litura, the Common Cutworm. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khoury, C.; Nemer, N.; Bernigaud, C.; Fischer, K.; Guillot, J. First Evidence of the Activity of an Entomopathogenic Fungus against the Eggs of Sarcoptes Scabiei. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 298, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.-B.; Feng, M.-G. Lethal Effect of Beauveria Bassiana, Metarhizium Anisopliae, and Paecilomyces Fumosoroseus on the Eggs of Tetranychus Cinnabarinus (Acari: Tetranychidae) with a Description of a Mite Egg Bioassay System. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, W.-B.; Feng, M.-G. Histopathological and Molecular Insights into the Ovicidal Activities of Two Entomopathogenic Fungi against Two-Spotted Spider Mite. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 117, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, C.; Fargues, J. Dependence of the Entomopathogenic Fungus, Beauveria Bassiana, on High Humidity for Infection of Rhodnius Prolixus. Mycopathologia 1999, 146, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari, M.; Zibaee, A.; Khodaparast, S.A.; Fazeli-Dinan, M. Screening and Virulence of the Entomopathogenic Fungi Associated with Chilo Suppressalis Walker. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, G.D.; Goettel, M.S.; Butt, T.M.; Strasser, H. Use of Hyphomycetous Fungi for Managing Insect Pests. In Fungi as Biocontrol Agents: Progress, Problems and Potential; Butt, T.M., Jackson, C., Magan, N., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 23–69. ISBN 978-0-85199-356-0. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; González-Mas, N.; Yousef-Yousef, M.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Fernández-Bravo, M. Key Role of Environmental Competence in Successful Use of Entomopathogenic Fungi in Microbial Pest Control. J. Pest. Sci. 2024, 97, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Lopes, R.B.; Souza, D.A.; Wraight, S.P. Conidial Vigor vs. Viability as Predictors of Virulence of Entomopathogenic Fungi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 125, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettel, M.S.; Eilenberg, J.; Glare, T. 6.11—Entomopathogenic Fungi and Their Role in Regulation of Insect Populations. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Gilbert, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 361–405. ISBN 978-0-444-51924-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, C.; dos Santos, P.L.; dos Santos Oliveira, L.R.; Domingues, M.M.; Gêa, B.C.C.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Mascarin, G.M.; Wilcken, C.F. Entomopathogenic Fungi as the Microbial Frontline against the Alien Eucalyptus Pest Gonipterus Platensis in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Hernández, R.A.; Toledo, J.; Valle-Mora, J.; Holguín-Meléndez, F.; Liedo, P.; Huerta-Palacios, G. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Purpureocillium Lilacinum (Hypocreales: Ophiocordycipitaceae) on Mexican Fruit Fly Adults. Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzoukas, S.; Lagogiannis, I.; Mpekiri, M.; Pettas, I.; Eliopoulos, P.A. Insecticidal Action of Several Isolates of Entomopathogenic Fungi against The Granary Weevil Sitophilus Granarius. Agriculture 2019, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd ElHafeez, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Leonardis, D.; Fusaro, M.; Tripepi, G.; Roumeliotis, S. Methods to Analyze Time-to-Event Data: The Cox Regression Analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, e1302811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietsch, R.; Jakobs-Schönwandt, D.; Grünberger, A.; Patel, A. Desiccation-Tolerant Fungal Blastospores: From Production to Application. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanicki, N.S.; de Oliveira Ferreira, B.; Mascarin, G.M.; Júnior, Í.D. Modified Adamek’s Medium Renders High Yields of Metarhizium Robertsii Blastospores That Are Desiccation Tolerant and Infective to Cattle-Tick Larvae. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarin, G.M.; Kobori, N.N.; Jackson, M.A.; Dunlap, C.A.; Delalibera, Í. Nitrogen Sources Affect Productivity, Desiccation Tolerance and Storage Stability of Beauveria Bassiana Blastospores. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.-L.; Fox, E.G.P.; Qin, C.-S.; Zhao, D.-Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.-Z. Microcapsuled Entomopathogenic Fungus against Fire Ants, Solenopsis Invicta. Biol. Control 2019, 134, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakov, N.; Ananth Mani, K.; Felfbaum, R.; Lahat, M.; Da Costa, N.; Belausov, E.; Ment, D.; Mechrez, G. Single Cell Encapsulation via Pickering Emulsion for Biopesticide Applications. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14294–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Fungal Species | Strain ID | GenBank |
|---|---|---|
| Akanthomyces muscarius (Petch) Spatafora, Kepler and B. Shrestha | EAB 48-27 | MT777299.1 |
| Akanthomyces muscarius (Petch) Spatafora, Kepler and B. Shrestha | EAB 59-16 | PQ578688 |
| Beauveria bassiana (Bals.-Criv.) Vuill. | EAB 37-9 | PQ578689 |
| Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch | EAB 51-13 | MT777312.1 |
| Beauveria bassiana (Bals.-Criv.) Vuill. | GHA | --- |
| Cordyceps farinosa (Holmsk.) Kepler, B. Shrestha and Spatafora | EAB 58-18 | MT777317.1 |
| Lecanicillium longisporum (Treschew) Zare and W. Gams | EAB 66-14 | MT777366.1 |
| Lecanicillium psalliotae (Treschew) Zare and W. Gams | EAB 59-2 | PQ578690 |
| Purpureocillium lilacinum (Thom) Luangsa-ard, Houbraken, Hywel-Jones and Samson | EAB 1-9 | PQ578691 |
| Purpureocillium lilacinum (Thom) Luangsa-ard, Houbraken, Hywel-Jones and Samson | EAB 44-2 | PQ578692 |
| Oct. 2020 | Dec. 2020 | May 2021 | Oct. 2021 I | Oct. 2021 II | Nov. 2021 | Dec. 2021 | Jun. 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. muscarius 48-27 | • | • | • | |||||
| A. muscarius 59-16 | • | • | • | |||||
| B. bassiana 37-9 | • | • | • | |||||
| B. bassiana GHA | • | • | • | • | • | • | ||
| B. brongniartii 51-13 | • | • | ||||||
| C. farinosa 58-18 | • | • | • | • | ||||
| L. longisporum 66-14 | • | • | • | |||||
| L. psalliotae 59-2 | • | • | ||||||
| P. lilacinum 1-9 | • | • | • | |||||
| P. lilacinum 44-2 | • | • |
| Fungal Treatment | Bioassay Date | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | |||||||
| Oct. 2020 | Dec. 2020 | May 2021 | Oct. 2021 II | Nov. 2021 | Dec. 2021 | Jun. 2022 | |
| A. muscarius 48-27 | 1.59 × 10−6 *** | 5.67 × 10−14 *** | 8.22 × 10−14 *** | ||||
| A. muscarius 59-16 | 6.3 × 10−13 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.188 | ||||
| B. bassiana 37-9 | 0.833 | 0.663 | |||||
| B. bassiana GHA | n/a | n/a | 0.001 *** | 0.029 * | 0.024 * | 5.82 × 10−7 *** | 7.45 × 10−4 *** |
| B. brongniartii 51-13 | 0.753 | 0.264 | |||||
| C. farinosa 58-18 | 4.7 × 10−14 *** | 3.86 × 10−5 *** | 0.322 | 1.21 × 10−4 *** | |||
| L. longisporum 66-14 | 4.85 × 10−14 *** | 5.42 × 10−14 *** | |||||
| L. psalliotae 59-2 | 3.76 × 10−5 *** | 2.9 × 10−14 *** | |||||
| P. lilacinum 1-9 | 0.146 | 0.565 | 7.57 × 10−10 *** | ||||
| P. lilacinum 44-2 | 0.753 | ||||||
| Treatment | Substrate | Min | Max | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. muscarius_48-27 | egg | 58 | 100 | 84 |
| A. muscarius_48-27 | larva | 80 | 100 | 97 |
| A. muscarius_59-16 | egg | 50 | 100 | 90 |
| A. muscarius_59-16 | larva | 50 | 100 | 79 |
| B. bassiana_37-9 | egg | 20 | 100 | 76 |
| B. bassiana_37-9 | larva | 60 | 100 | 92 |
| B. bassiana_GHA | egg | 0 | 100 | 75 |
| B. bassiana_GHA | larva | 56 | 100 | 87 |
| B. brongniartii_51-13 | egg | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| B. brongniartii_51-13 | larva | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| C. farinosa_58-18 | egg | 0 | 100 | 66 |
| C. farinosa_58-18 | larva | 0 | 100 | 63 |
| Control | egg | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | larva | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| L. longisporum_66-14 | egg | 14 | 100 | 72 |
| L. longisporum_66-14 | larva | 40 | 100 | 83 |
| L. psalliotae_59-2 | egg | 86 | 100 | 97 |
| L. psalliotae_59-2 | larva | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| P. lilacinum_1-9 | egg | 38 | 100 | 90 |
| P. lilacinum_1-9 | larva | 83 | 100 | 97 |
| P. lilacinum_44-2 | egg | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| P. lilacinum_44-2 | larva | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simeto, S.; Held, B.W.; Showalter, D.N.; Bushley, K.E.; Blanchette, R.A. Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs. Forests 2024, 15, 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122170
Simeto S, Held BW, Showalter DN, Bushley KE, Blanchette RA. Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs. Forests. 2024; 15(12):2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122170
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimeto, Sofía, Benjamin W. Held, David N. Showalter, Kathryn E. Bushley, and Robert A. Blanchette. 2024. "Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs" Forests 15, no. 12: 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122170
APA StyleSimeto, S., Held, B. W., Showalter, D. N., Bushley, K. E., & Blanchette, R. A. (2024). Ovicidal Effect of Entomopathogenic Fungi on Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, Eggs. Forests, 15(12), 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122170







