Genetic Diversity of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an Endemic and Critically Endangered Species in China, Based on ITS Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Research Materials
2.2. Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Analysis of Genetic Diversity
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity and Ribotype Variation
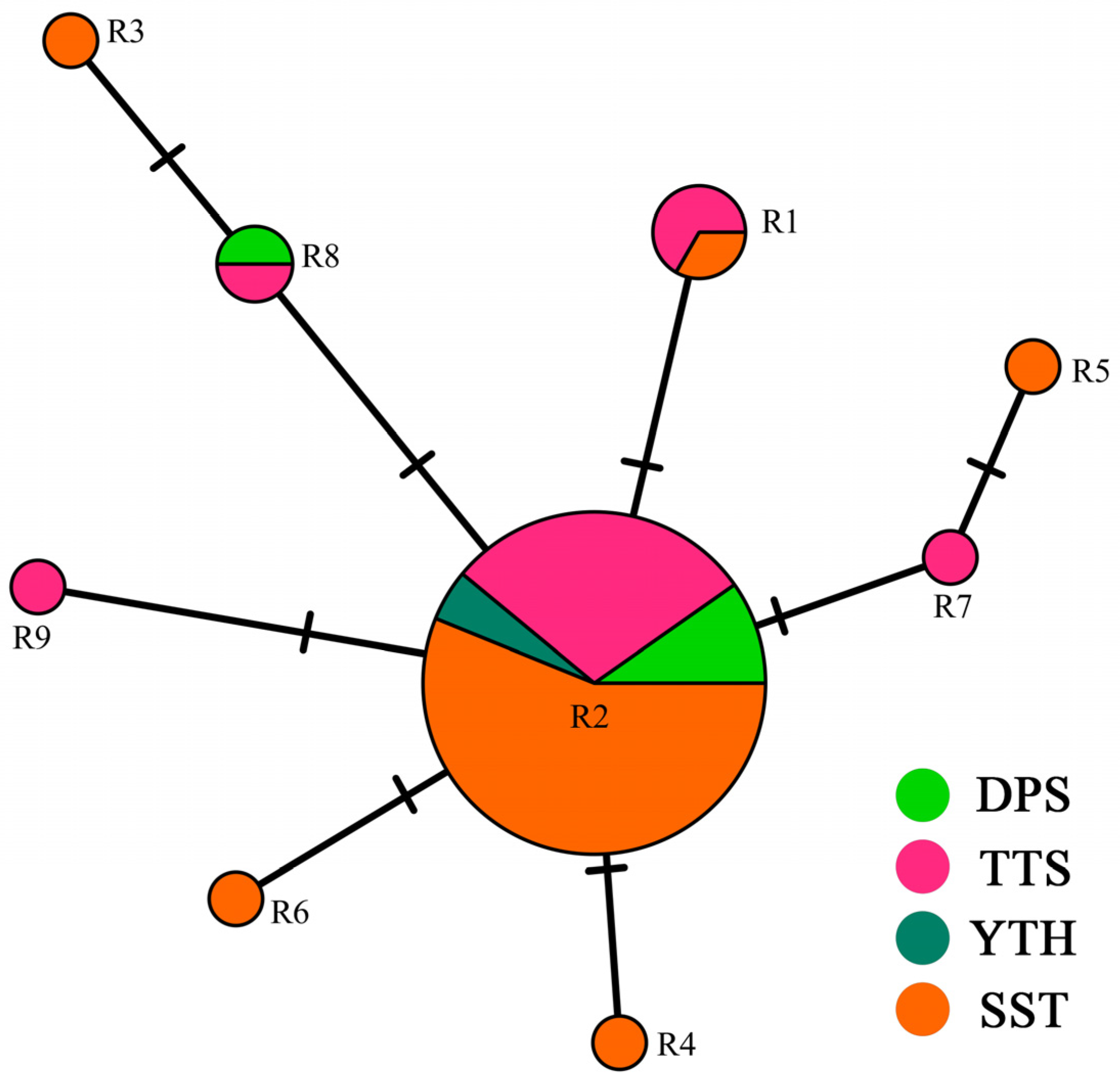
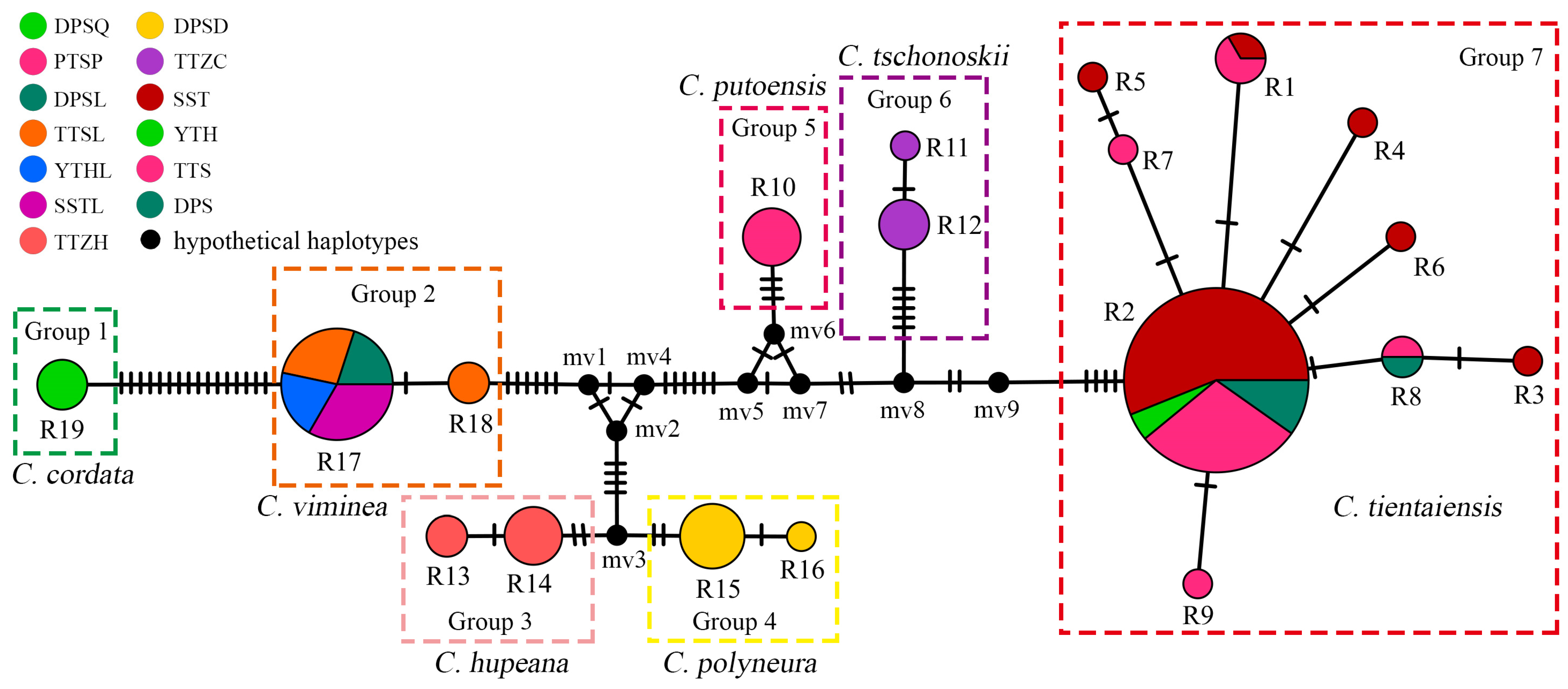
3.2. Ribotype Distribution and Network Structure
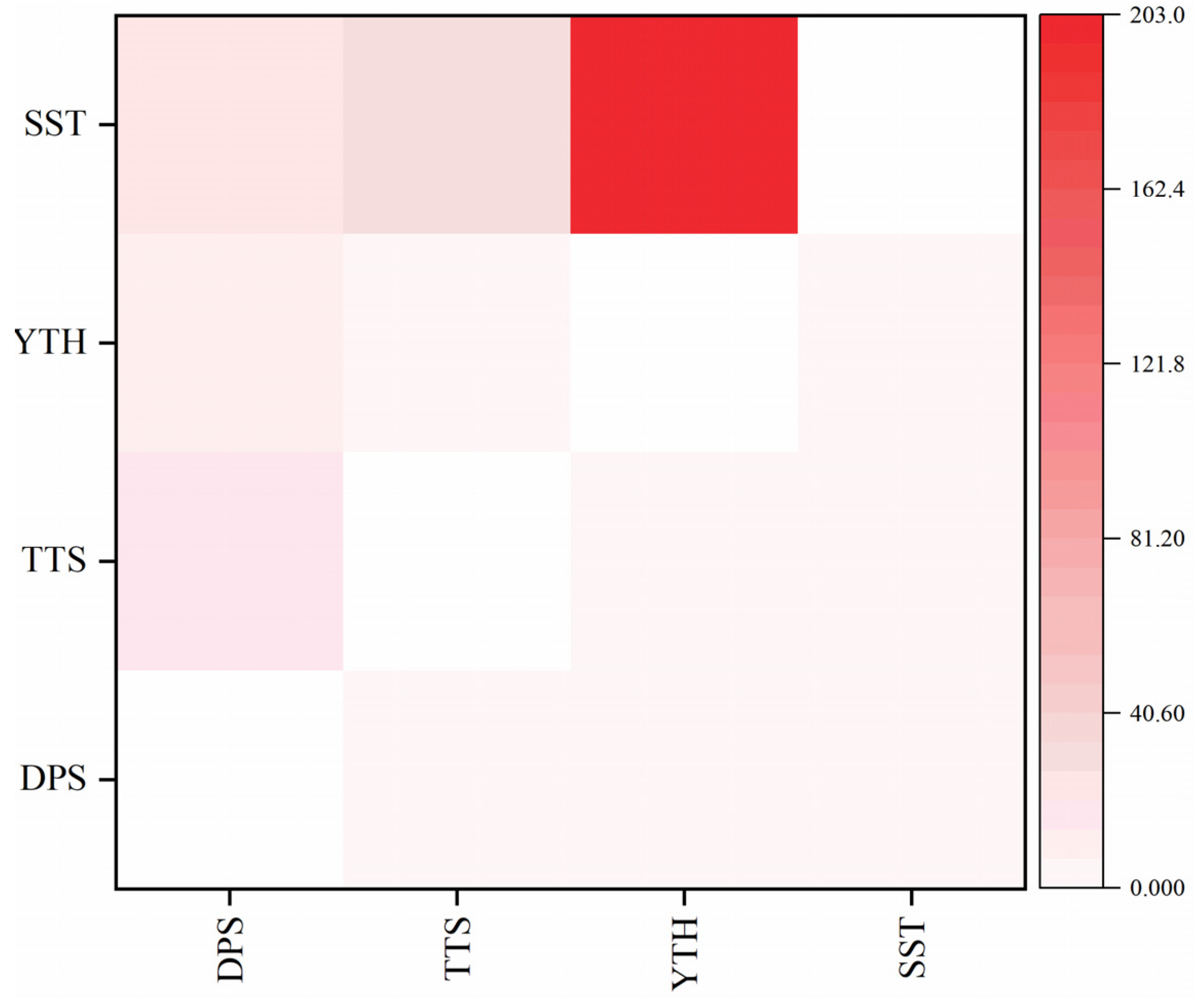
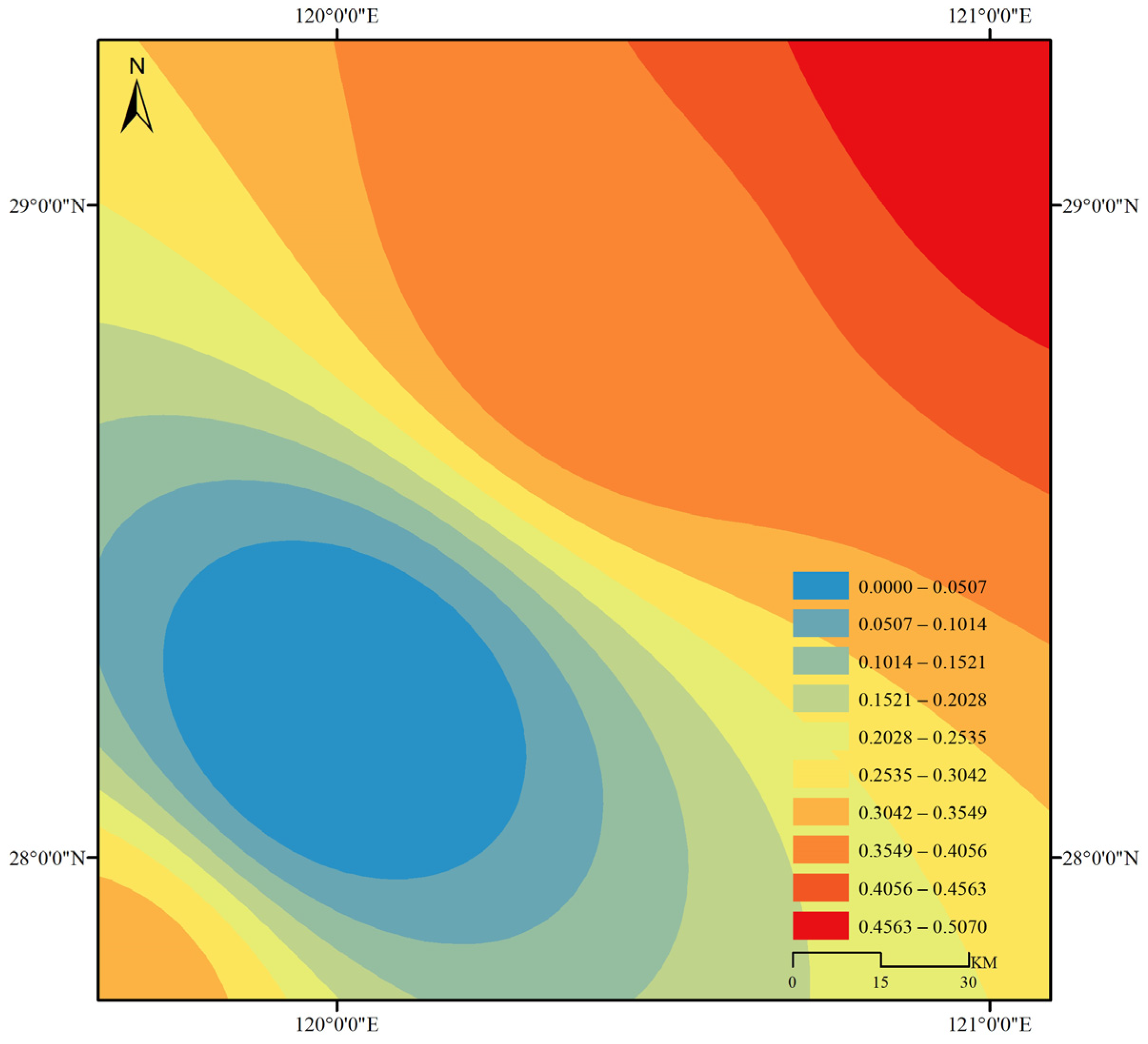
3.3. Gene Flow and Genetic Structure
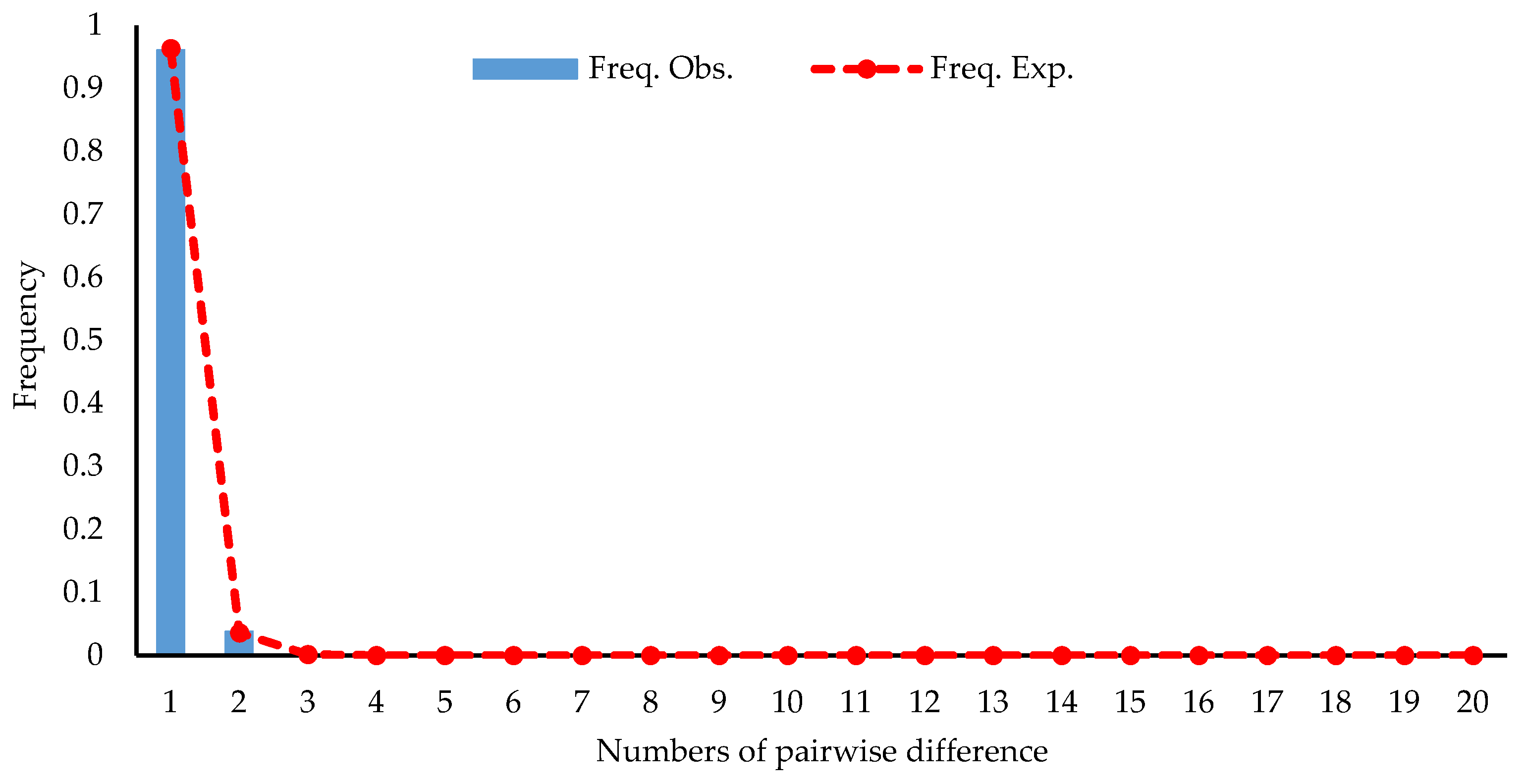
3.4. Population Historical Dynamics
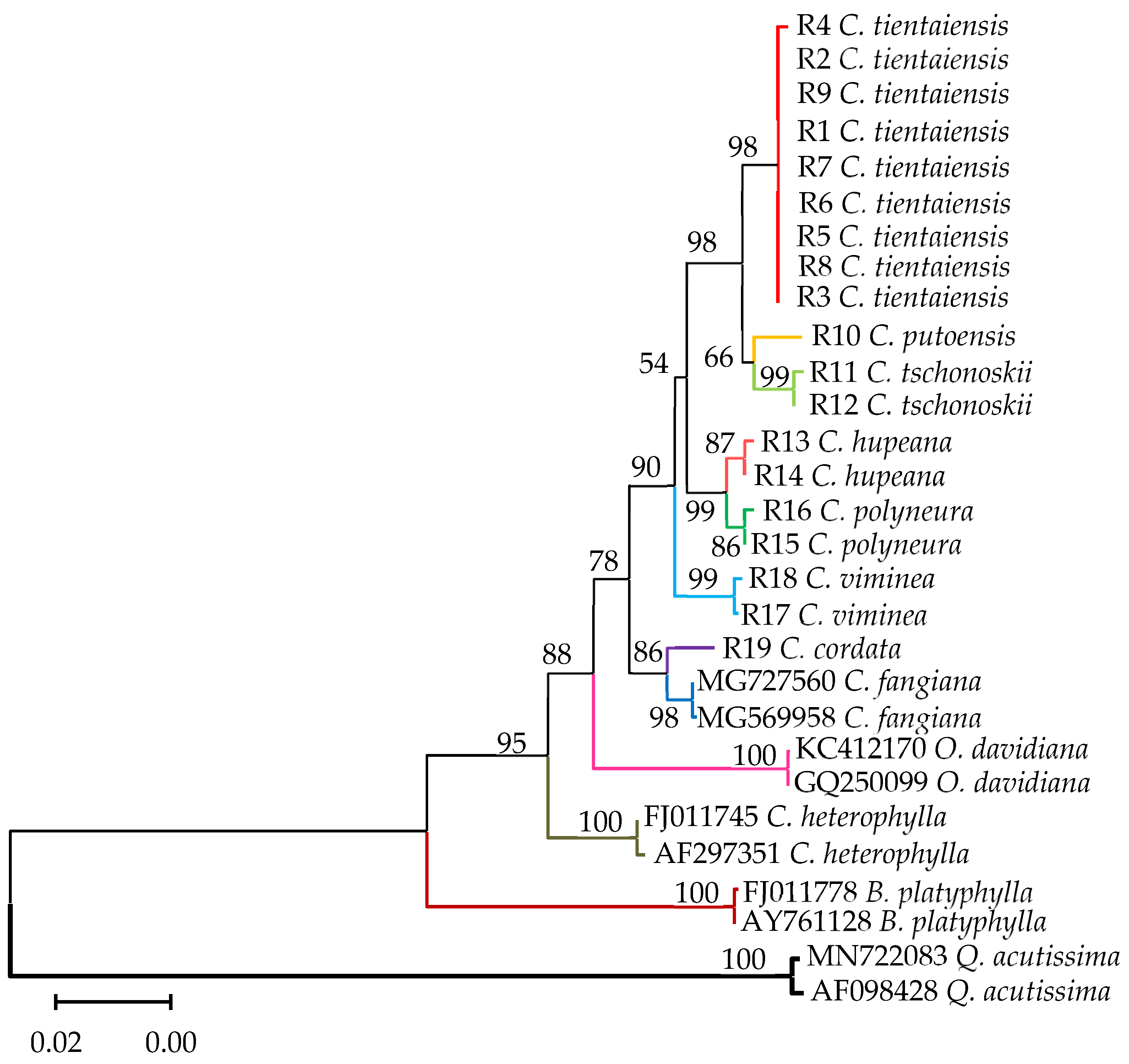
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanatha Rao, V.; Hodgkin, T. Genetic diversity and conservation and utilization of plant genetic resources. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2002, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Toro, M.A. Analysis of genetic diversity for the management of conserved subdivided populations. Conserv. Genet. 2002, 3, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWoody, J.A.; Harder, A.M.; Mathur, S.; Willoughby, J.R. The long-standing significance of genetic diversity in conservation. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 4147–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.V.; Gómez-Silva, V.; Ramírez, M.J.; Fontúrbel, F.E. Meta-analysis of the differential effects of habitat fragmentation and degradation on plant genetic diversity. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holderegger, R.; Kamm, U.; Gugerli, F. Adaptive vs. neutral genetic diversity: Implications for landscape genetics. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Jiang, X.H. Progress in studies of genetic diversity and conservation biology of endangered plant species. Biodivers. Sci. 1999, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xiao, P.N.; Li, T.T.; Wang, Z.X. Research Progress on endangered plants: A bibliometric analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2022, 31, 1125–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; Wendel, J.F. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Plant BOL Group; Li, D.Z.; Gao, L.M.; Li, H.T.; Wang, H.; Ge, X.J.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, Z.D.; Zhou, S.L.; Chen, S.L.; Yang, J.B.; et al. Comparative analysis of a large dataset indicates that internal transcribed spacer (ITS) should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19641. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, K.; Tsou, C.H. DNA barcoding in plants: Taxonomy in a new perspective. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Yi, X.G.; Li, Y.F.; Zhu, S.X.; Li, M.; Duan, Y.F.; Wang, X.R. Phylogeography and population genetic structure of flowering cherry species Cerasus dielsiana in subtropical China. Syst. Biodivers. 2019, 17, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J. Plant DNA barcodes: Applications today and in the future. J. Sytematics Evol. 2017, 55, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.C. Plantae novae Chekiangenses. Contrib. Biol. Lab. Sci. Soc. China Bot. Ser. 1932, 8, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Q.; Zheng, S.X. Betulaceae. In Flora Republicae Popularis Sinica 21; Kuang, K.R., Li, P.Q., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.Q.; Skvortsov, A.K. Betulaceae. In Flora of China 4; Wu, C.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, K.; Roy, S.; Wilson, B. Carpinus tientaiensis. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014, e.T194617A2353175. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/194617/2353175 (accessed on 17 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantity of fresh leaf material. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 119, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Garfield, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, American, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Bao, Y.X.; Chen, L.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ge, B.M. Effects of habitat fragmentation on gene flow of the black muntjac (Muntiacus crinifrons). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartier, P.M.; Keller, C.P. Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW). Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, O.; Petit, R.J. Measwring and Testing Genetic Differentiation with Ordered Versus Unordered Alleles. Genetics 1996, 144, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.J.; Duminil, J.; Fineschi, S.; Hampe, A.; Salvini, D.; Vendramin, G.G. INVITED REVIEW: Comparative organization of chloroplast, mitochondrial and nuclear diversity in plant populations. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.N.; Xiao, J.H.; Ci, X.Q.; Conran, J.G.; Li, J. Genetic diversity of Horsfieldia tetratepala (Myristicaceae), an endangered Plant Species with Extremely Small Populations to China: Implications for its conservation. Plant Syst. Evol. 2021, 307, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zang, F.Q.; Wu, Q.C.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Zang, D.K. Genetic diversity and population structure of the endangered plant Salix taishanensis based on CDDP markers. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Chen, W.C.; Luo, J.; Yao, Z.X.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, S.Z.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, M.R.; Shen, Y.M. Development of EST-SSR markers and their application in an analysis of the genetic diversity of the endangered species Magnolia Sinostellata. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.C.; Zang, F.Q.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Zang, D.K. Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure in endangered Populus wulianensis based on 18 newly developed EST-SSR markers. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Goossens, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Bruford, M.W.; Wei, F. Genetic Viability and Population History of the Giant Panda, Putting an End to the “Evolutionary Dead End”? Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, M.N.; Duy, D.V.; Duc, M.N.; Hien, P.D.; Long, K.P.; Phuong, X.B. Microsatellite analysis reveals genetic diversity of the endangered species Dipterocarpus dyeri. J. For. Res. 2020, 25, 198–201. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Godt, M.J.W. Effects of life history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, B.; Martín, J.P.; Mohanty, A. Differences in population genetic structure of two ethnomedicinal herbs of the genus Phyllanthus from India: A consequence of anthropogenic intervention? Plant Syst. Evol. 2015, 301, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaisberger, H.; Legay, S.; Andre, C.; Loo, J.; Azimov, R.; Aaliev, S.; Bobokalonov, F.; Mukhsimov, N.; Kettle, C.; Vinceti, B. Diversity under Threat: Connecting Genetic Diversity and Threat Mapping to Set Conservation Priorities for Juglans regia L. Populations in Central Asia. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Mu, K.; Ni, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Analysis of genetic diversity of ancient Ginkgo populations using SSR markers. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 145, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, L.P.; Shan, H.Y.; Ma, H. Highly conserved low-copy nuclear genes as effective markers for phylogenetic analyses in angiosperms. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.J.; Hegarty, M.J.; Hiscock, S.J.; Brennan, A.C. Homoploid hybrid speciation in action. Taxon 2010, 59, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Bi, H.; Lu, Z.Q.; Ma, Y.Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, N.N.; Tian, B.; Liu, B.B.; Mao, X.X.; et al. Hybrid speciation via inheritance of alternate alleles of parental isolating genes. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Kang, M.H.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Liu, J.Q. Genomic evidence for homoploid hybrid speciation between ancestors of two different genera. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Yu, L.; Du, X.; Ren, G.P. Plastomes of nine hornbeams and phylogenetic implications. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 8770–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Luo, W.C.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, J.Q.; Ren, G.P. Plastomes of Betulaceae and phylogenetic implications. J. Syst. Evol. 2019, 57, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Ke, S.X.; Jin, Z.X.; Li, J.M.; Chen, Z. Conservation Biology of Carpinus Tientaiensis; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. Popul. Fr. Ed. 1970, 26, 1176. [Google Scholar]
- Mayrose, I.; Zhan, S.H.; Rothfels, C.J.; Magnuson-Ford, K.; Barker, M.S.; Rieseberg, L.H.; Otto, S.P. Recently Formed Polyploid Plants Diversify at Lower Rates. Science 2011, 333, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.; Zhang, H.; Henry, C.E.; Franklin, F.C.H.; Bomblies, K. Derived alleles of two axis proteins affect meiotic traits in autotetraploid Arabidopsis arenosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8980–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhu, K.X.; Han, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, X.Y. Genetic variation and phylogeographic structure of Laodelphax striatellus in China based on microsatellite markers. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, L.; Vanoverbeke, J.; Swillen, I.; Mergeay, J.; De Meester, L. Drivers of population genetic differentiation in the wild: Isolation by dispersal limitation, isolation by adaptation and isolation by colonization. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5983–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeland, J.R.; Kirk, H.; Petersen, S.D. Chapter 6: Phylogeography. In Molecular Ecology, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 225–269. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, G. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 2000, 405, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.D. Phylogeny and Phytogeography of the Betulaceae (Cont.). Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1994, 32, 101–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.M. Cytological studies on some plants of woody flora in Huangshan, Anhui province. Plant Sci. J. 1995, 13, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, K.O.; Wen, J. Phylogeny and biogeography of Carpinus and subfamily Coryloideae (Betulaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 2002, 163, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.O.; Wen, J. Phylogeny of Carpinus and subfamily Coryloideae (Betulaceae) based on chloroplast and nuclear ribosomal sequence data. Plant Syst. Evol. 2007, 267, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahee, A.; Assadi, M.; Zare, H.; Mehregan, I. Systematics of Carpinus: Molecular Phylogeny and Morphology. J. Genet. Resour. 2022, 8, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.C.; Lu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, M.J. Delimiting 33 Carpinus (Betulaceae) species with a further phylogenetic inference. AoB Plants 2022, 14, plac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Identifier | Populations | Geographic Location | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude | Number | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1–1-5 | DPS | Dapanshan National Nature Reserve, Pan’an, Zhejiang | 120.5218 | 28.9708 | 1138 | 5 | C. tientaiensis |
| 2-1–2-17 | TTS | Tiantai Mountain, Tiantai County, Zhejiang | 121.0917 | 29.2568 | 901 | 17 | C. tientaiensis |
| 3-1–3-2 | YTH | Yangtianhe, Qingtian, Zhejiang | 119.9907 | 28.2084 | 1249 | 2 | C. tientaiensis |
| 4-1–4-28 | SST | Shangshantou, Jingning She Autonomous County, Zhejiang | 119.6320 | 27.7823 | 1506 | 28 | C. tientaiensis |
| P1-1 | PTSP | Mount Putuo, Zhoushan, Zhejiang | 122.3977 | 30.0177 | 292 | 1 | C. putoensis |
| P1-2–P1-4 | PTSP | Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, Jiangsu (introduced from Mount Putuo) | 118.8276 | 32.0852 | 24 | 3 | C. putoensis |
| L1-1–L1-3 | DPSL | Dapanshan National Nature Reserve, Pan’an, Zhejiang | 120.5229 | 28.9747 | 1136 | 3 | C. viminea |
| L2-1–L2-6 | TTSL | Tiantai Mountain, Tiantai County, Zhejiang | 121.0908 | 29.2525 | 926 | 6 | C. viminea |
| L3-1–L3-3 | YTHL | Yangtianhe, Qingtian, Zhejiang | 119.9907 | 28.2084 | 1249 | 3 | C. viminea |
| L4-1–L4-5 | SSTL | Shangshantou, Jingning She Autonomous County, Zhejiang | 119.6309 | 27.7840 | 1518 | 5 | C. viminea |
| H1-1–H1-6 | TTZH | Tiantangzhai Scenic Spot, Lu’an, Anhui | 115.7625 | 31.1567 | 760 | 6 | C. hupeana |
| D1-1–D1-6 | DPSD | Dapanshan National Nature Reserve, Pan’an, Zhejiang | 120.5226 | 28.9732 | 1086 | 6 | C. polyneura |
| C1-1–C1-4 | TTZC | Tiantangzhai Scenic Spot, Lu’an, Anhui | 115.7767 | 31.1294 | 1040 | 4 | C. tschonoskii |
| Q1-1–Q1-3 | DPSQ | Dapanshan National Nature Reserve, Pan’an, Zhejiang | 120.5216 | 28.9710 | 1131 | 3 | C. cordata |
| Species | GenBank ID | |
|---|---|---|
| C. fangiana | MG569958 | MG727560 |
| Ostryopsis davidiana | GQ250099 | KC412170 |
| Corylus heterophylla | AF297351 | FJ011745 |
| Betula platyphylla | AY761128 | FJ011778 |
| Quercus acutissima | AF098428 | MN722083 |
| Ribotypes | Variable Sites/bp | Number | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 26 | 78 | 605 | 612 | 614 | 619 | 641 | ||
| R1 | T | - | - | - | T | - | - | A | 3 |
| R2 | T | A | - | - | T | - | - | A | 41 |
| R3 | T | A | C | G | T | - | - | A | 1 |
| R4 | T | A | - | - | G | - | - | A | 1 |
| R5 | - | A | - | - | T | G | - | A | 1 |
| R6 | T | A | - | - | T | - | - | - | 1 |
| R7 | - | A | - | - | T | - | - | A | 1 |
| R8 | T | A | - | G | T | - | - | A | 2 |
| R9 | T | A | - | - | T | - | C | A | 1 |
| Populations | Ribotype Diversity (Hd) | Nucleotide Diversity (π × 10−3) | Ribotype Number | Ribotype Composition and Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | 0.331 ± 0.114 | 0.730 | 6 | R1 (1), R2 (23), R3 (1), R4 (1), R5 (1), R6 (1) |
| YTH | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | R2 (2) |
| TTS | 0.507 ± 0.140 | 0.840 | 5 | R1 (2), R2 (12), R7 (1), R8 (1), R9 (1) |
| DPS | 0.400 ± 0.237 | 0.590 | 2 | R2 (4), R8 (1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; He, Q.; Chu, X.; He, A.; Zhu, Z. Genetic Diversity of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an Endemic and Critically Endangered Species in China, Based on ITS Sequences. Forests 2023, 14, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081600
Zhao R, He Q, Chu X, He A, Zhu Z. Genetic Diversity of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an Endemic and Critically Endangered Species in China, Based on ITS Sequences. Forests. 2023; 14(8):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081600
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Runan, Qianqian He, Xiaojie Chu, Anguo He, and Zunling Zhu. 2023. "Genetic Diversity of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an Endemic and Critically Endangered Species in China, Based on ITS Sequences" Forests 14, no. 8: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081600
APA StyleZhao, R., He, Q., Chu, X., He, A., & Zhu, Z. (2023). Genetic Diversity of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an Endemic and Critically Endangered Species in China, Based on ITS Sequences. Forests, 14(8), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081600






