Analyses of Sulfur and Iron in Waterlogged Archaeological Wood: The Case of Polyethylene-Glycol-Treated Yenikapı 12 Shipwreck
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
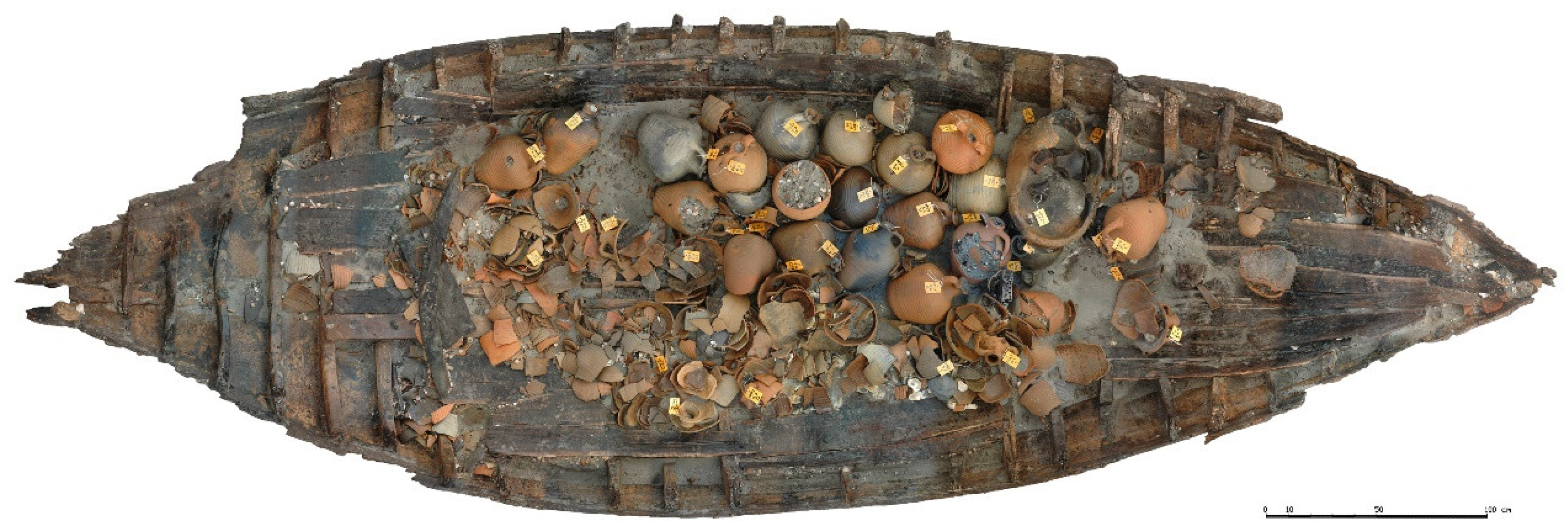
2.1. Sampling
2.2. FTIR Analyses
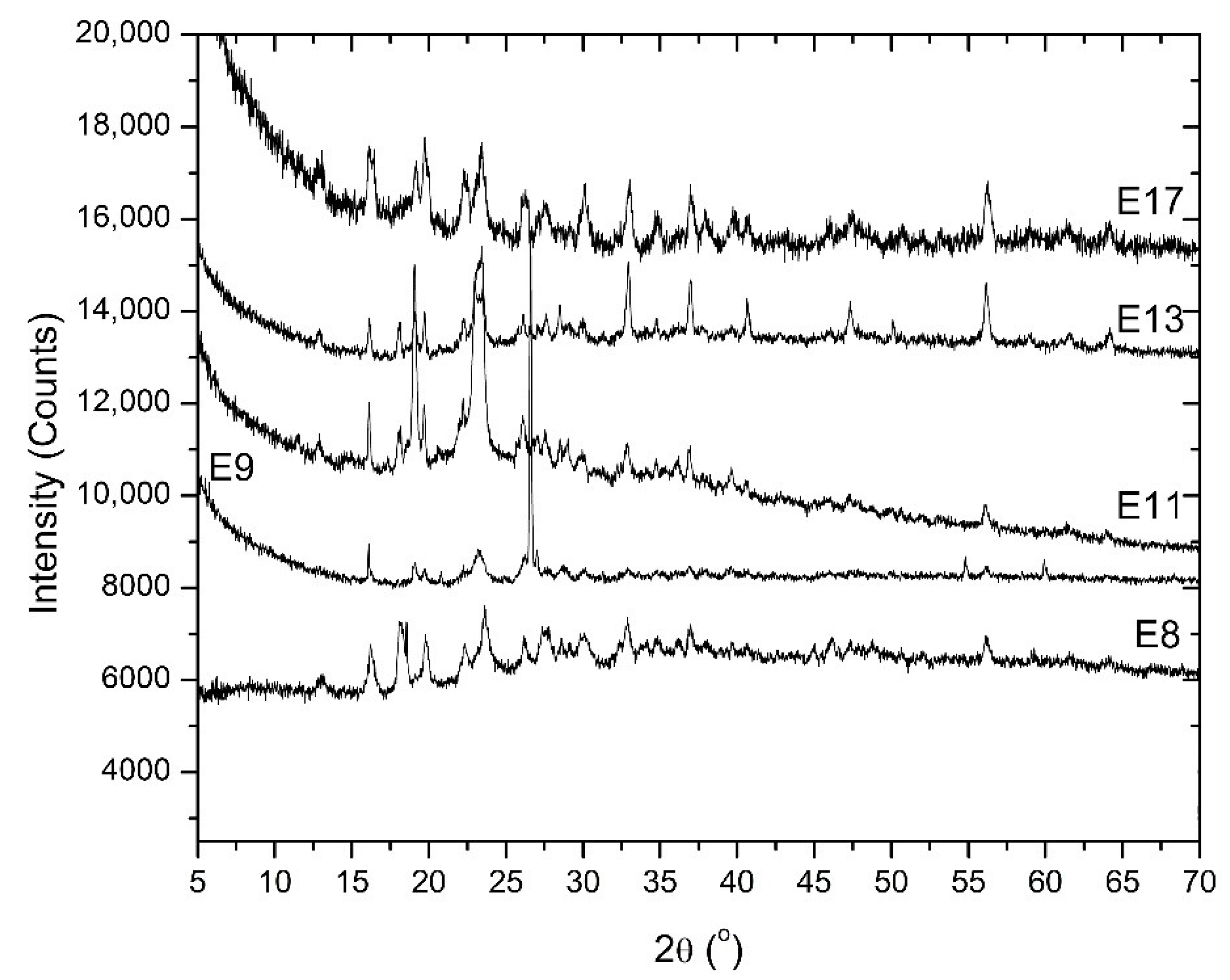
2.3. XRD Analyses
2.4. pH Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braovac, S.; Kutzke, H. The Presence of Sulfuric Acid in Alum-Conserved Wood–Origin and Consequences. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, S203–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.; Yelle, D.J. Reactivity of Waterlogged Archeological Elm Wood with Organosilicon Compounds Applied as Wood Consolidants: 2D 1H–13C Solution-State NMR Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, P.D. Archaeological Watercraft: A Review and Critical Analysis of the Practice. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Elding, L.I. Ten years of Vasa research-review and outlook. In Proceedings of the International Conference Shipwrecks 2011, Stockholm, Sweden, 18–21 October 2011; pp. 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, I.M.; Richards, V.; Cha, M. The post-treatment deterioration of marine archaeological wood–where to now? In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Regional Conference on Underwater Cultural Heritage, Manila, Philippines, 8–12 November 2011; pp. 697–713. [Google Scholar]
- Fors, Y. Sulfur-Related Conservation Concerns in Marine Archaeological Wood: The Origin, Speciation and Distribution of Accumulated Sulfur with Some Remedies for the Vasa. Ph.D. Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Håfors, B. Conservation of the Wood of the Swedish Warship Vasa of AD 1628. Evaluation of Polyethylene Glycol Conservation Programmes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Broda, M.; Hill, C.A. Conservation of waterlogged wood—Past, present and future perspectives. Forests 2021, 12, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monachon, M.; Albelda-Berenguer, M.; Pele, C.; Cornet, E.; Guilminot, E.; Remazeilles, C.; Joseph, E. Characterization of Model Samples Simulating Degradation Processes Induced by Iron and Sulfur Species on Waterlogged Wood. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, M.; Jaliehvand, F.; Damian, E.; Fors, Y.; Gelius, U.; Jones, M.; Salome, M. Sulfur accumulation in the timbers of King Henry Ⅷ’s warship Mary Rose: A pathway in the sulfur cycle of conservation concern. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14165–14170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almkvist, G.; Persson, I. Fenton-induced degradation of polyethylene glycol and oak holocellulose. A model experiment in comparison to changes observed in conserved waterlogged wood. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, Y.; Nilsson, T.; Risberg, E.D.; Sandström, M.; Torssander, P. Sulfur Accumulation in Pinewood (Pinus Sylvestris) Induced by Bacteria in a Simulated Seabed Environment: Implications for Marine Archaeological Wood and Fossil Fuels. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 62, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, A.G. Sulphur and Iron Analysis Together with Their Distribution in Woods and Their Removal from the Woods of Yenikapı Shipwrecks. Ph.D. Thesis, İstanbul University, Istanbul, Turkish, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rémazeilles, C.; Saheb, M.; Neff, D.; Guilminot, E.; Tran, K.; Bourdoiseau, J.A.; Refait, P. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of archaeological artefacts: Characterisation of iron (II) sulfides by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, N.; Kılıç, A.G. Analysis of Waterlogged Woods: Example of Yenikapı Shipwreck. Art-Sanat 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Remazeilles, C.; Leveque, F.; Minjacq, M.; Refait, P.; Sanchez, C.; Jézégou, M.P. Characterisation of iron (II) sulfides in wet archaeological woods: The wreck of Mandirac (IV) th century, antique ports of Narbonne, France. In Proceedings of the 13th ICOM-CC Group on Wet Organic Archaeol. Materials Conference, Florence, Italy, 16–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kılıç, A.G.; Kılıç, N.; Akgün, C. The Importance of Using Multiple Analyses Techniques to Determine the Physical Condition of the Waterlogged Wood. Wood Res. 2021, 66, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remazeilles, C.; Leveque, F.; Conforto, E.; Meunier, L.; Refait, P. Contribution of magnetic measurement methods to the analysis of iron sulfides in archaeological waterlogged wood iron assemblies. J. Microchem. 2019, 148, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almkvist, G.; Persson, I. Distribution of iron and sulfur and their speciation in relation to degradation processes in wood from the Swedish warship Vasa. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Jones, M.; Berko, A.; Chadwick, A.V.; Newport, R.J.; Skinner, T.; Salomé, M.; Frederick, J.; Mosselmans, W. An investigation of the Sulfur–Iron chemistry in timbers of the sixteenth century warship, the Mary Rose, by Synchrotron micro-X-ray spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium Archaeometry, Siena, Italy, 13–16 May 2008; Turbanti-Memmi, I., Ed.; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, A.G. Sulfur Problem in the Conservation of Waterlogged Wood. TINA 2020, 13, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, I.D. Conservation of waterlogged timbers from the Batavia 1629. Bull. Aust. Inst. Marit. Archaeol. 1990, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Q. Characterization of degradation and iron deposits of the wood of Nanhai I shipwreck. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémazeilles, C.; Meunier, L.; Lévêque, F.; Plasson, N.; Conforto, E.; Crouzet, M.; Refait, P.; Caillat, L. Post-treatment study of Iron/Sulfur-containing compounds in the wreck of Lyon Saint-Georges 4 (Second Century ACE). Stud. Conserv. 2019, 65, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, M.; Jalilehvand, F.; Persson, I.; Gelius, U.; Frank, P.; Hall-Roth, I. Deterioration of the seventeenth-century warship Vasa by internal formation of sulphuric acid. Nature 2002, 415, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.Y.; Godfrey, I.; Richards, V.; Kasi, K.; Byrne, L. Analysis and Deacidification of Acid-Affected PEG Treated Timbers From the Korean Shinan Ship. In Proceedings of the 12th ICOM-CC Wet Organic Archaeolgical Materials Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–17 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Seojin, K.; Eung-ho, K.; Yu-na, L. Effect of the Acid Degradation of the Shinan Shipwreck on Indoor Air Quality in the Korean National Maritime Museum. Stud. Conser. 2021, 66, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, A.G. Monitoring of the Conserved YK1 Shipwreck During Storage. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Restoration and Conservation of Traditional Timber Structures 7, Istanbul, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fors, Y. What Happens in the Museum Environment? Post-Conservation Challenges in the Vasa and the Mary Rose. In Conserving Wrecks for Future Generations, Antarctica Symposium and Workshop; Hasselt University: Hasselt, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fors, Y.; Grudd, H.; Rindby, A.; Jalilehvand, F.; Sandström, M.; Cato, I.; Bornmalm, L. Sulfur and iron accumulation in three marine-archaeological shipwrecks in the Baltic Sea: The Ghost, the Crown and the Sword. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, W.J. Characteristics of Emission Substances by Acid degradation of Shinan Wreck, Republic of Korea. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 11, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kocabaş, U. The Yenikapı Byzantine-Era Shipwrecks, Istanbul, Turkey: A preliminary report and inventory of the 27 wrecks studied by Istanbul University. Int. J. Nautical Archaeol. 2015, 44, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsait-Kocabaş, I. The Yenikap 12 Shipwreck, a 9th-Century Merchantman from the Theodosian Harbour in Istanbul, Turkey: Construction and reconstruction. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2018, 47, 357–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsait-Kocabaş, I. Yenikapı 12 An Early Medieval Merchantman; Ege Publishing: Istanbul, Turkey, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kılıç, N. Assessment of Pre-Impregnation with Polyethylene Glycol and Vacuum Freeze Drying Method for the Conservation of Yenikapı Shipwrecks. Ph.D. Thesis, İstanbul University, Istanbul, Turkish, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Łucejko, J.J.; McQueen, C.M.A.; Sahlstedt, M.; Modugno, F.; Colombini, M.P.; Braovac, S. Comparative chemical investigations of alum treated archaeological wood from various museum collections. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K. Various Physical and Analytical Methods to Control the Impregnation Efficiency of Archaeological Artefacts by Different Consolidating Resins. In Proceedings of the Wood Science for Conservation of Cultural Heritage, Florence, Italy, 8–10 November 2007; Uzielli, L., Ed.; pp. 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, N.M. Stabilization of Polyethylene Glycol in Archaeological Wood. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fors, Y.; Jalilehvand, F.; Sandström, M. Analytical aspects of waterlogged wood in historical shipwrecks. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubovský, I.; Kačíková, D.; Kačík, F. Structural changes of oak wood main components caused by thermal modification. Polymers 2020, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zborowska, M.; Stachowiak-Wencek, A.; Waliszewska, B.; Prądzyński, W. Colourimetric and FT-IR ATR spectroscopy studies of degradative effects of ultraviolet light on the surface of exotic ipe (Tabebuia sp.) wood. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2016, 50, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Yi, J.; Li, J.; He, T.; Hu, C. Promoting effect of sodium chloride on the solubilization and depolymerization of cellulose from raw biomass materials in water. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémazeilles, C.; Tran, K.; Guilminot, E.; Conforto, E.; Refait, P. Study of Fe (II) sulphides in waterlogged archaeological wood. Stud. Conser. 2013, 58, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, M.; Fors, Y.; Jalilehvand, F.; Damian, E.; Gelius, U. Analyses of sulfur and iron in marine-archaeological wood. In Proceedings of the Ninth ICOM Group on Wet Organic Archaeological Materials Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 June 2004; pp. 181–199. [Google Scholar]
- Almkvist, G.; Persson, I. Extraction of iron compounds from wood from the Vasa. Holzforschung 2006, 60, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.L. Methods of Conserving Archaeological Material from Underwater Sites, Conservation of Cultural Resources I 1999, Nautical Archaeology Program, Texas A&M University. 1999. Available online: http://nautarch.tamu.edu/class/ANTH605 (accessed on 27 January 2023).

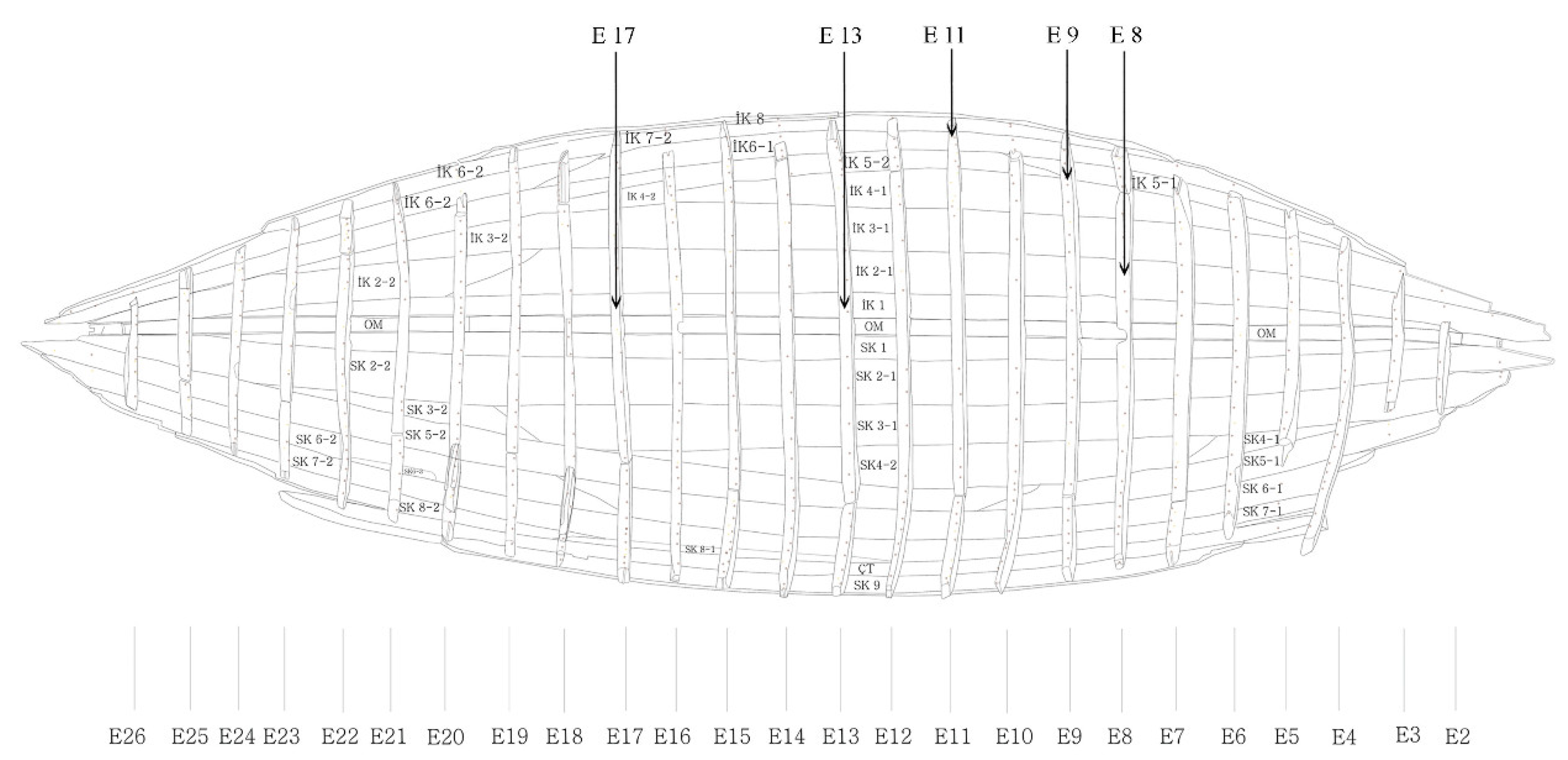

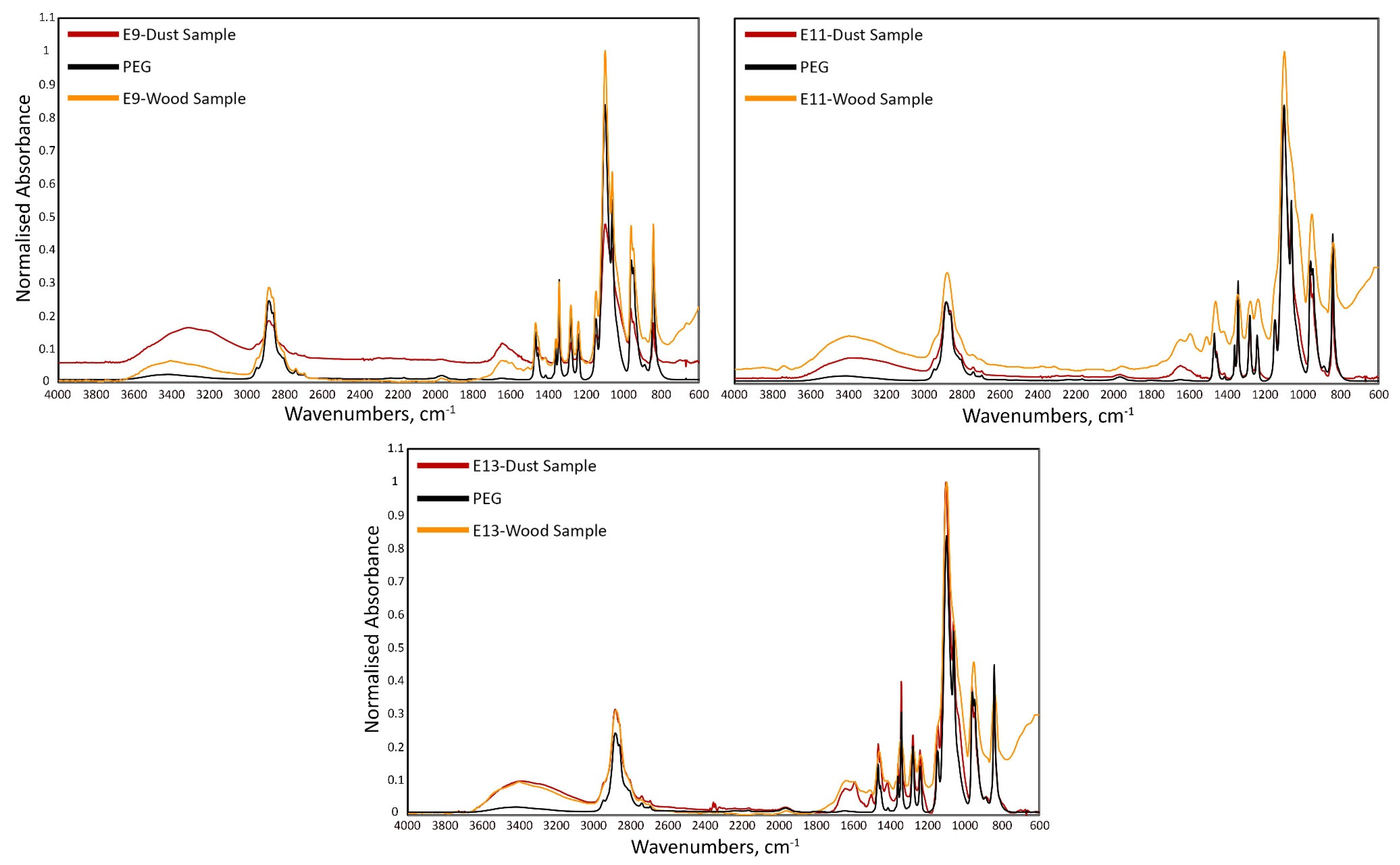
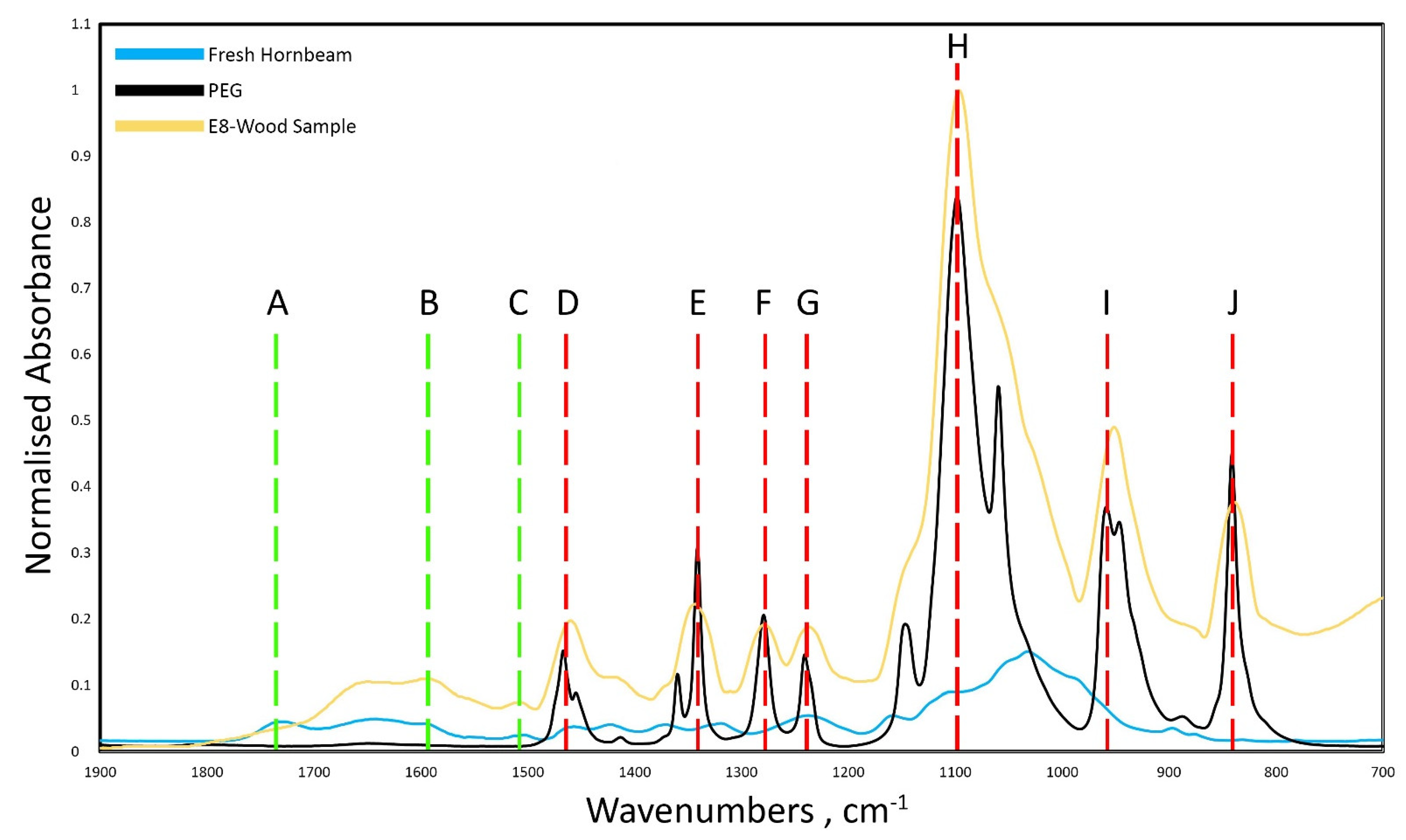

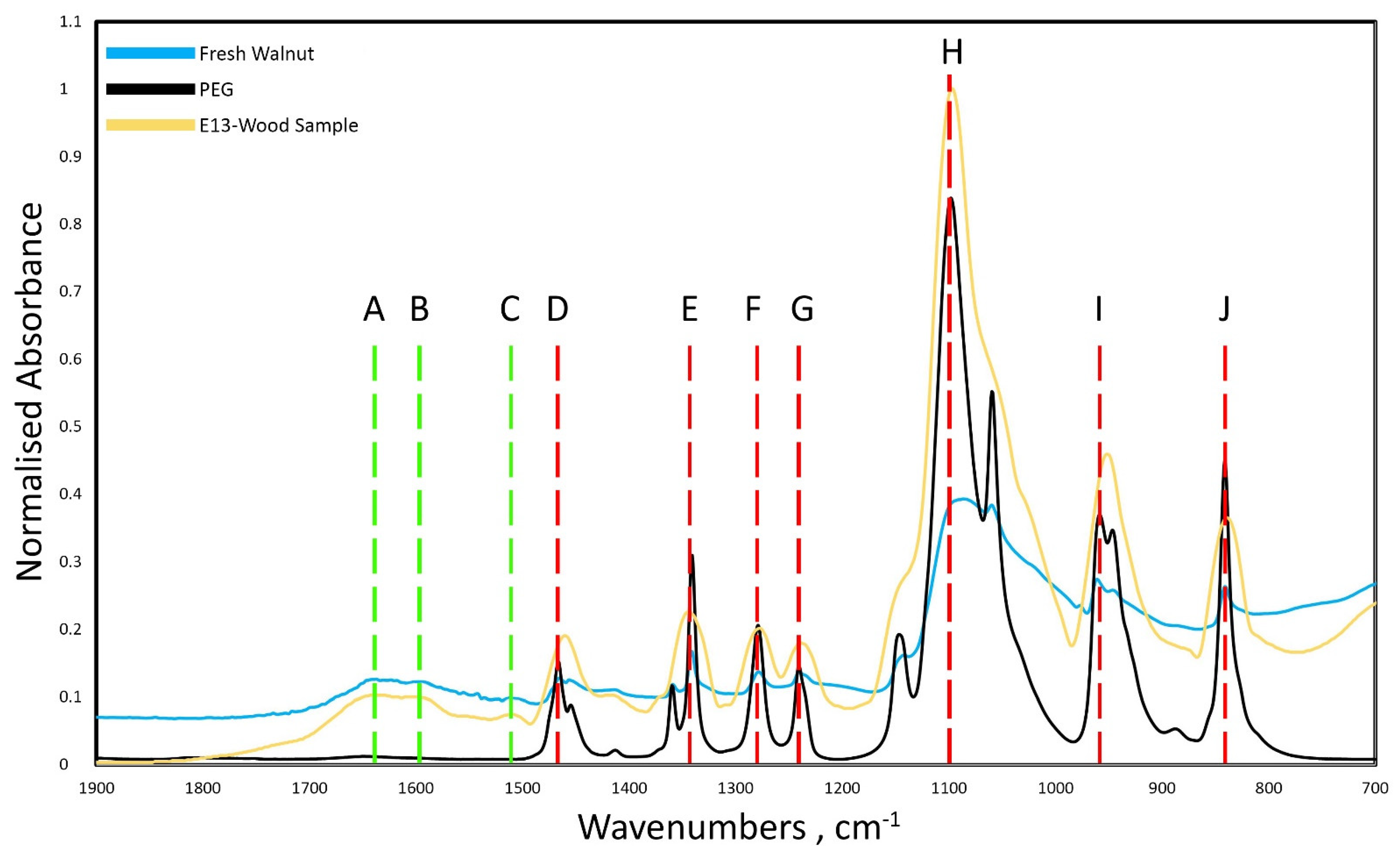
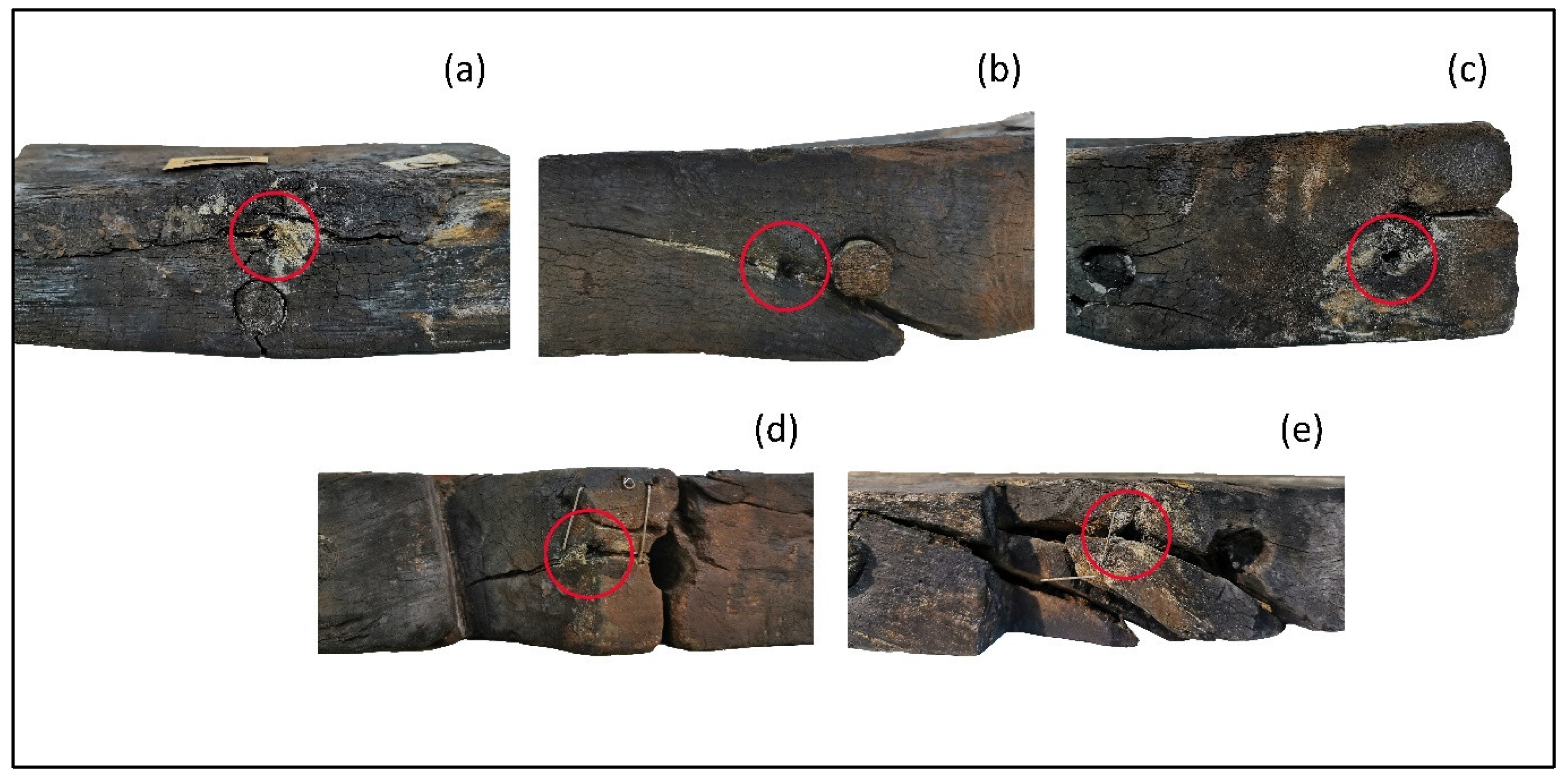
| Sample | Species |
|---|---|
| E8 | Hornbeam (Carpinus) |
| E9 | Oak (Quercus) |
| E11 | Oak (Quercus) |
| E13 | Walnut (Juglans) |
| E17 | Oak (Quercus) |
| Sample | Primary Phase | Secondary Phase |
|---|---|---|
| E8 | FeSO4·4H2O | FeSO4·7H2O |
| E9 | SiO2 | FeSO4·4H2O |
| E11 | FeSO4·4H2O | FeSO4·7H2O |
| E13 | FeSO4·4H2O | FeSO4·7H2O |
| E17 | FeSO4·4H2O | FeSO4·7H2O |
| Sample | Average pH |
|---|---|
| E8 | 5 |
| E9 | 6 |
| E11 | 4 |
| E13 | 4 |
| E17 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kılıç, A.G.; Kılıç, N.; Arnold, D.C. Analyses of Sulfur and Iron in Waterlogged Archaeological Wood: The Case of Polyethylene-Glycol-Treated Yenikapı 12 Shipwreck. Forests 2023, 14, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030530
Kılıç AG, Kılıç N, Arnold DC. Analyses of Sulfur and Iron in Waterlogged Archaeological Wood: The Case of Polyethylene-Glycol-Treated Yenikapı 12 Shipwreck. Forests. 2023; 14(3):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030530
Chicago/Turabian StyleKılıç, Aslı Gökçe, Namık Kılıç, and Donna C. Arnold. 2023. "Analyses of Sulfur and Iron in Waterlogged Archaeological Wood: The Case of Polyethylene-Glycol-Treated Yenikapı 12 Shipwreck" Forests 14, no. 3: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030530
APA StyleKılıç, A. G., Kılıç, N., & Arnold, D. C. (2023). Analyses of Sulfur and Iron in Waterlogged Archaeological Wood: The Case of Polyethylene-Glycol-Treated Yenikapı 12 Shipwreck. Forests, 14(3), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030530






