Distribution Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along Elevation Gradients in the Southern of Taihang Mountain, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
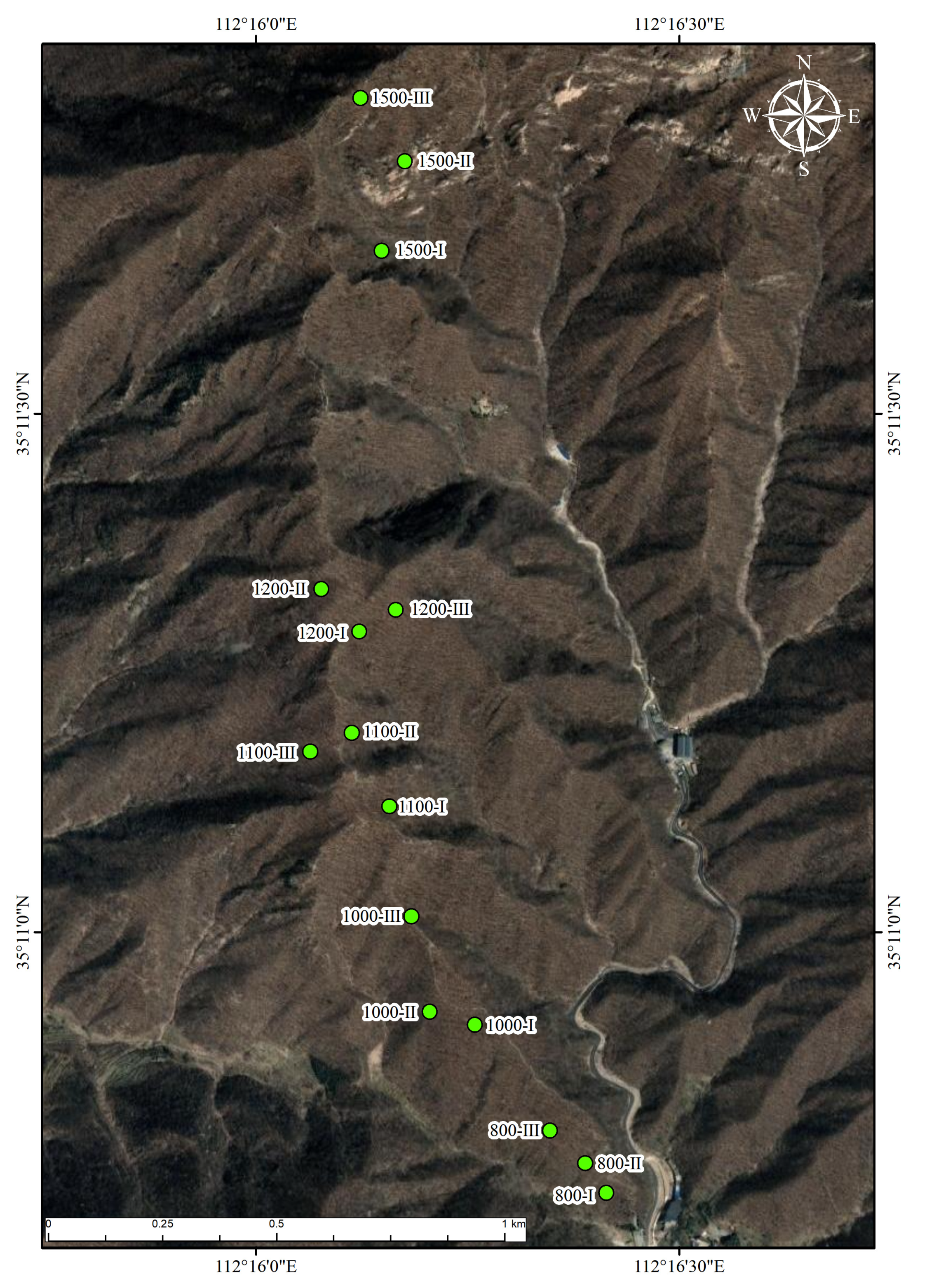
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Soil Sampling and Plant Investigation
2.3. Chemical and Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Plant Diversity and Litter Biomass
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Plant Diversity along Altitudinal Gradients
3.2. Characteristics of the Soil’s Physical and Chemical Properties
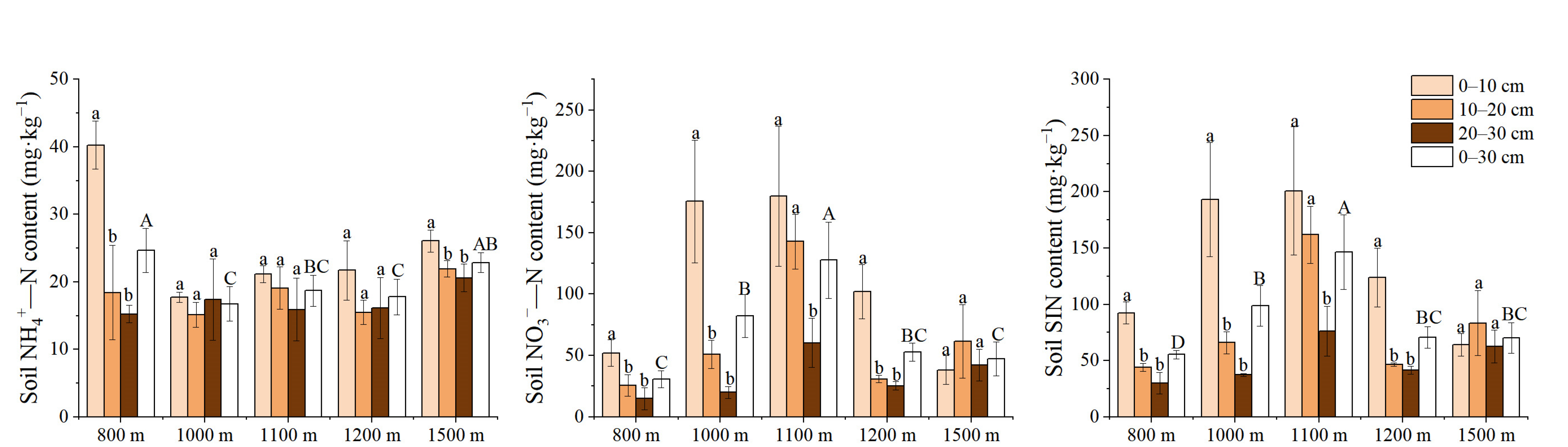
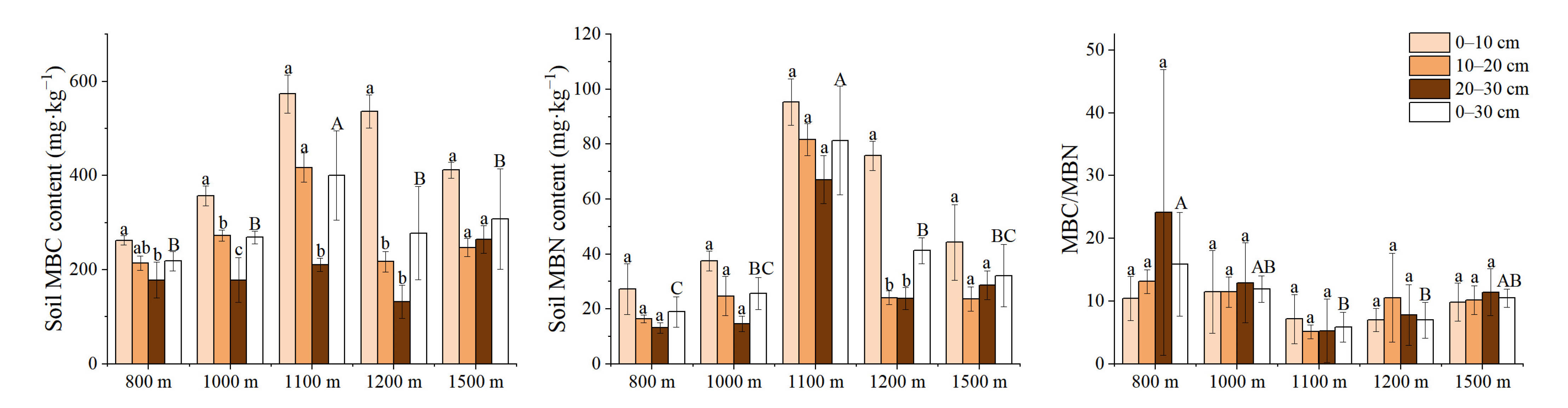
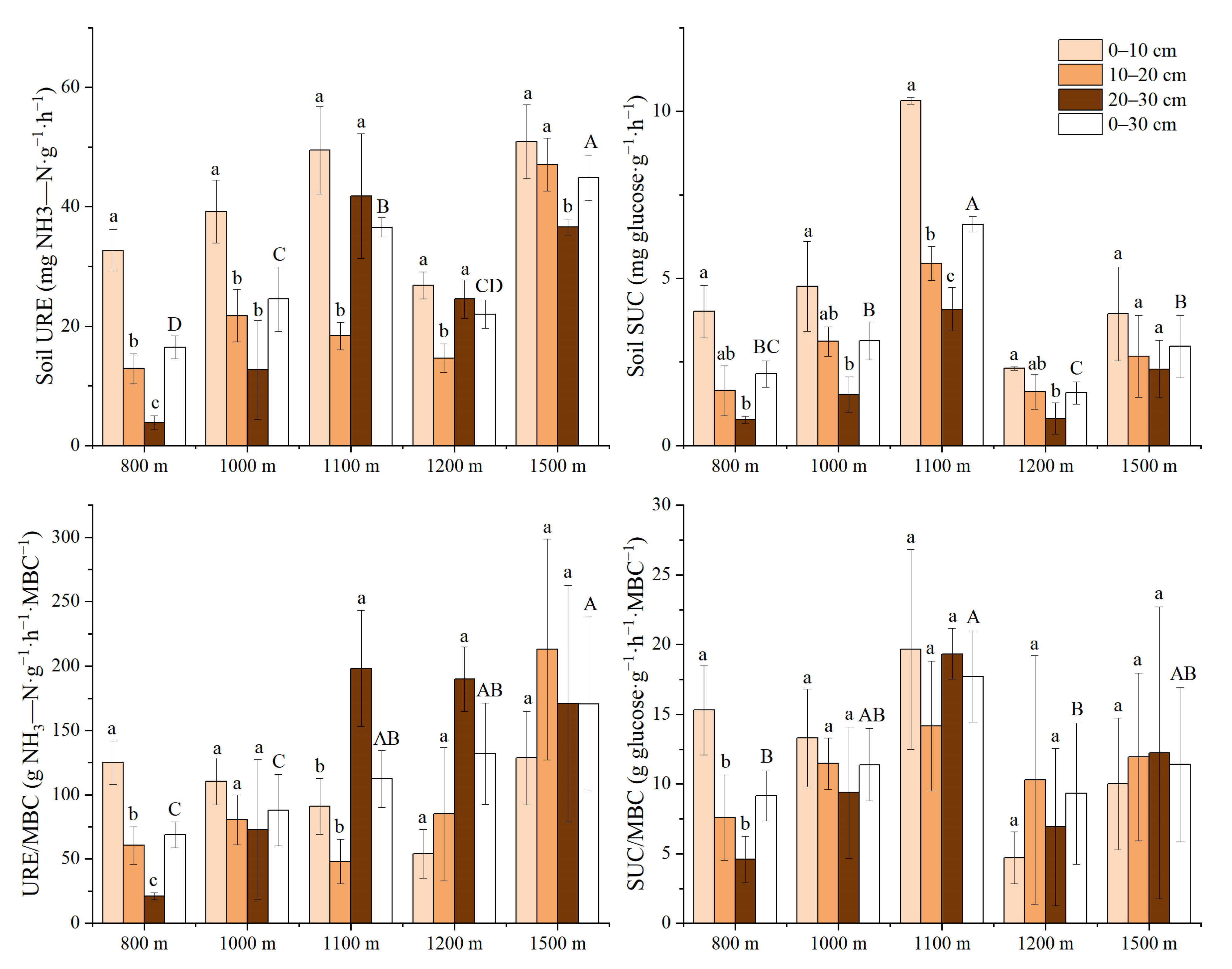
3.3. Variation Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along the Elevation Gradients
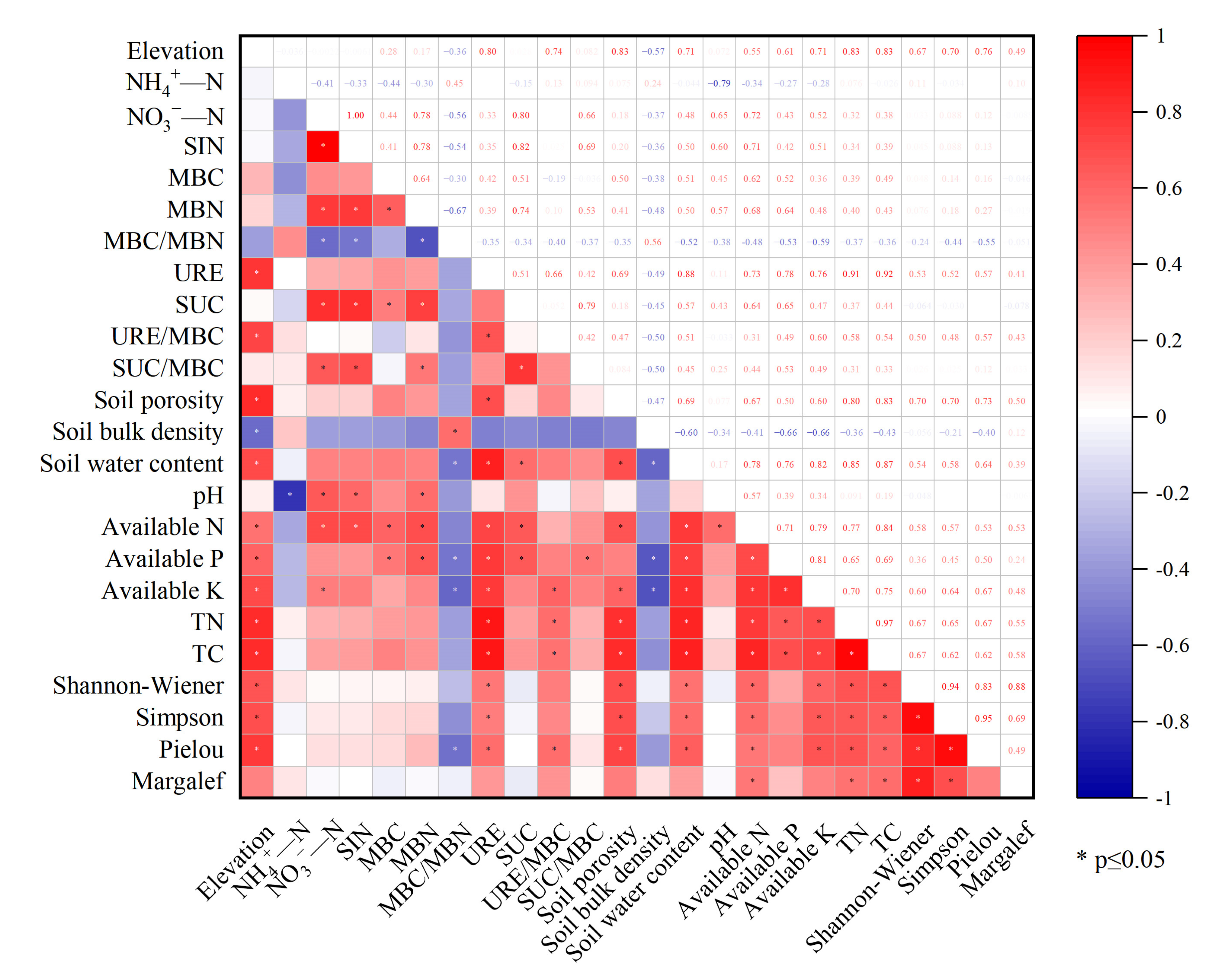
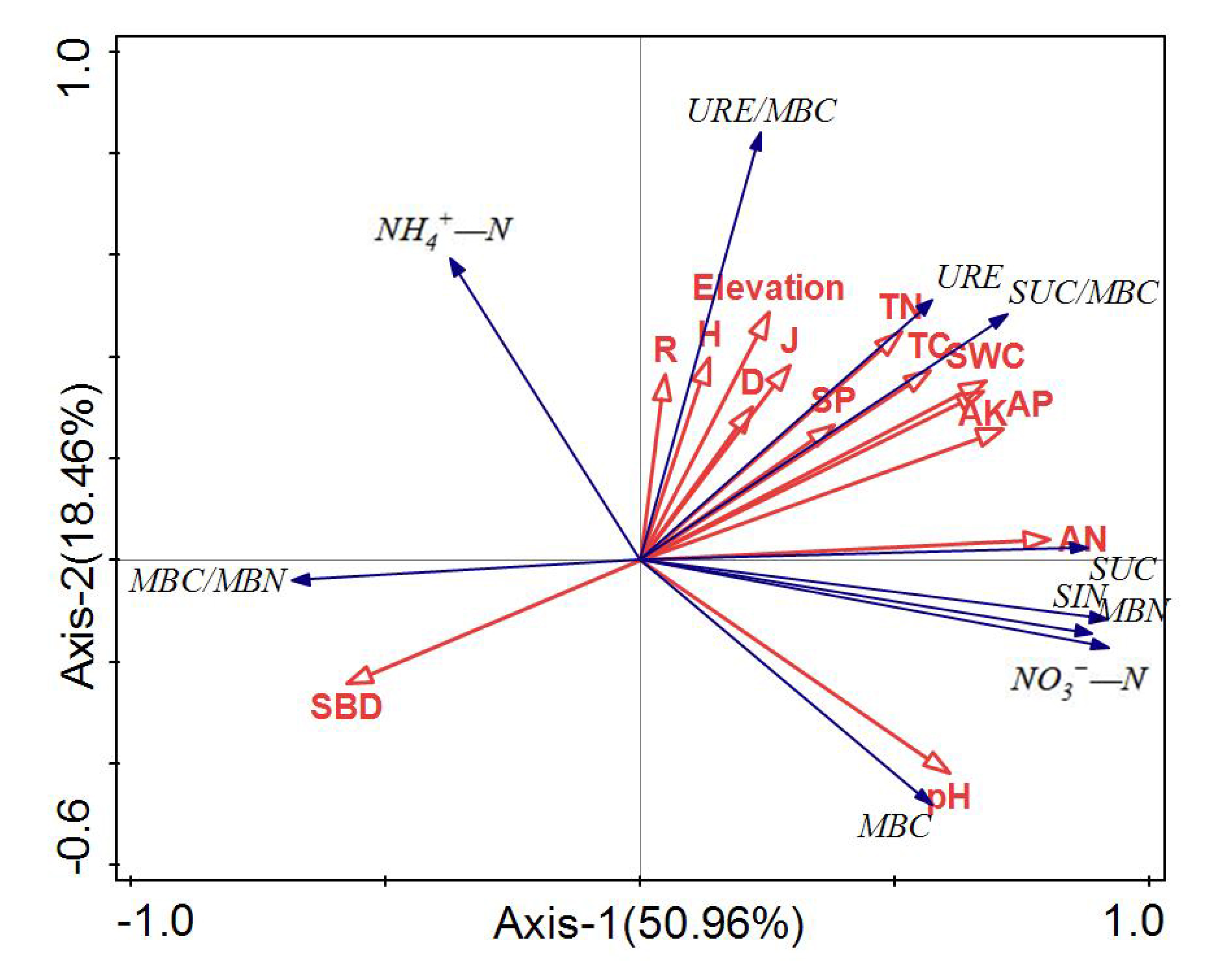
3.4. Correlation between Active Soil Substances and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, J.; Chen, A.; Peng, C.; Zhao, S.; Ci, L. Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998. Science 2001, 292, 2320–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guan, D.; Yan, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Wen, X. Water-use efficiency of forest ecosystems in eastern China and its relations to climatic variables. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrall, B.; Pickering, C.M. Alpine vegetation in the context of climate change: A global review of past research and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nottingham, A.T.; Turner, B.L.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N.J.; McNamara, N.P.; Bardgett, R.D.; Salinas, N.; Meir, P. Soil microbial nutrient constraints along a tropical forest elevation gradient: A belowground test of a biogeochemical paradigm. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 6071–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndossi, E.M.; Becker, J.N.; Hemp, A.; Dippold, M.A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Effects of land use and elevation on the functional characteristics of soil enzymes at Mt. Kilimanjaro. Eur.J.Soil Biol. 2020, 97, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G. The role of DOM sorption to mineral surfaces in the preservation of organic matter in soils. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.G.; Verburg, P.S.J.; Arnone, J.A., III. Effects of climate and vegetation on soil nutrients and chemistry in the Great Basin studied along a latitudinal-elevational climate gradient. Plant Soil 2014, 382, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, M.K.; Wardle, D.A.; Vincent, A.; Giesler, R. Contrasting nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics across an elevational gradient for subarctic tundra heath and meadow vegetation. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, R.L.; Yeates, G.W.; Ross, D.J.; Mackay, A.D.; Budding, P.J. Relationships between soil biota, nitrogen and phosphorus availability, and pasture growth under organic and conventional management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, K.; Matzner, E. Nitrogen content of forest floor Oa layers affects carbon pathways and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J.; Estiarte, M. Changes in soil enzymes related to C and N cycle and in soil C and N content under prolonged warming and drought in a Mediterranean shrubland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 39, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, G.; Ren, Z.P. Changes in soil nutrient and enzyme activities under different vegetations in the Loess Plateau area, Northwest China. Catena 2012, 92, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C.-Y. The effect of altitudinal gradient on soil microbial community activity and structure in moso bamboo plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; Cajthaml, T.; Minerbi, S.; Margesin, R. Effect of altitude and season on microbial activity, abundance and community structure in Alpine forest soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, K.; Huang, L.; Ji, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Responses of absolute and specific enzyme activity to consecutive application of composted sewage sludge in a Fluventic Ustochrept. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Soil nutrient stoichiometries and enzymatic activities along an elevational gradient in the dry-hot valley region of southwestern China. Arch. Agron.Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, J.-D. Microbial extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycling of ecosystems. J.Environ.Manage. 2017, 197, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Chen, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Han, C.; Lu, K.; Li, Y.; Rafiq, M.; Iqbal, A.; Zhao, C. Soil fungal taxonomic diversity along an elevation gradient on the semi-arid Xinglong Mountain, Northwest China. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, V.; De Feudis, M.; Fornasier, F.; Massaccesi, L.; Cocco, S.; Agnelli, A.; Weindorf, D.C.; Corti, G. Changes of topsoil under Fagus sylvatica along a small latitudinal-altitudinal gradient. Geoderma 2019, 344, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, X.; Lu, J. Pattern and drivers of soil fungal community along elevation gradient in the Abies georgei forests of Segila mountains, Southeast Tibet. Glob.Ecol.Conserv. 2022, 39, e02291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jia, X.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhao, Y. Fungal community diversity in soils along an elevation gradient in a Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forest in Qinling Mountains, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaccesi, L.; De Feudis, M.; Leccese, A.; Agnelli, A. Altitude and vegetation affect soil organic carbon, basal respiration and microbial biomass in Apennine forest soils. Forests 2020, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.; Lamprecht, A.; Pauli, H.; Illmer, P. Distribution of prokaryotic abundance and microbial nutrient cycling across a high-alpine altitudinal gradient in the Austrian Central Alps is affected by vegetation, temperature, and soil nutrients. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, P.; Li, J.; Zheng, N. Ecosystem water use efficiency in a warm-temperate mixed plantation in the North China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Feng, Z.; Qu, A.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Yong, L.; Kong, Y. Effects of land-use types on the temporal dynamics of soil active carbon and nitrogen in the rocky mountainous of North China. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Ma, N.L.; Yang, X.; Lai, Y.; Feng, Z.; Shao, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D. Examining CO2 and N2O pollution and reduction from forestry application of pure and mixture forest. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S. Soil Enzymes and their Research Methods; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 274–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Wang, W. Vertical pattern and its driving factors in soil extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry along mountain grassland belts. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, L.; Su, X.; Liu, D.; Jin, T.; Shi, S.; Li, T.; Liu, G. Effects of soil physico-chemical properties on plant species diversity along an elevation gradient over alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 822268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Qin, H. Species diversity of plant communities along an altitude gradient in Yinmachi Mountain, northwestern Shanxi, China. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 28, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, R.; Cao, H.; Shi, L.; Guo, J.; Sun, W. Response of soil enzyme activity to warming and nitrogen addition in a meadow steppe. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xia, H.; Li Za Cai Xa Fu, S. Impacts of litter and understory removal on soil properties in a subtropical Acacia mangium plantation in China. Plant Soil 2008, 304, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Miao, S.; Silva, L.C.R.; Horwath, W.R. Understory species regulate litter decomposition and accumulation of C and N in forest soils: A long-term dual-isotope experiment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 329, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.A.; Jackson, C.R. Fine scale patterns in microbial extracellular enzyme activity during leaf litter decomposition in a stream and its floodplain. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, H.; Gottfried, M.; Dullinger, S.; Abdaladze, O.; Akhalkatsi, M.; Benito Alonso, J.L.; Coldea, G.; Dick, J.; Erschbamer, B.; Fernandez Calzado, R.; et al. Recent plant diversity changes on Europe’s mountain summits. Science 2012, 336, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Nagano, H.; Watanabe, K.; Yashima, M.; Inubushi, K. Effects of land-use type and nitrogen addition on nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide production potentials in Japanese Andosols. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Duan, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, X. Effects of litter decomposition on soil N in Picea mongolica forest at different forest ages. Forests 2022, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, W.R.; Cornforth, I.S.; Rowarth, J.S. Winter soil temperature (2–15 °C) effects on nitrogen transformations in clover green manure amended or unamended soils: A laboratory and field study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, X.; Xing, X. Effects of grazing exclusion on soil net nitrogen mineralization and nitrogen availability in a temperate steppe in northern China. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Mary, B.; Zhang, J.-B.; Cai, Z.-C.; Chang, S.X. Soil pH has contrasting effects on gross and net nitrogen mineralizations in adjacent forest and grassland soils in central Alberta, Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Campbell, C.D.; Qiao, X. Soil pH controls nitrification and carbon substrate utilization more than urea or charcoal in some highly acidic soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, F.; Sheng, Q. Spatial variability of soil microbial biomass and its relationships with edaphic, vegetational and climatic factors in the Three-River Headwaters region on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 95, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Jien, S.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C.-Y. Soluble organic C and N and their relationships with soil organic C and N and microbial characteristics in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) plantations along an elevation gradient in Central Taiwan. J. Soil Sediments 2014, 14, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N.; Nottingham, A.T.; Ccahuana, A.; Salinas, N.; Bardgett, R.D.; Meir, P.; McNamara, N.P. Microbial community composition explains soil respiration responses to changing carbon inputs along an Andes-to-Amazon elevation gradient. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prommer, J.; Walker, T.W.N.; Wanek, W.; Braun, J.; Zezula, D.; Hu, Y.; Hofhansl, F.; Richter, A. Increased microbial growth, biomass, and turnover drive soil organic carbon accumulation at higher plant diversity. Glob Chang Biol. 2019, 26, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, P.; Asensio, D.; Ogaya, R.; Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J. Effects of seasonal and decadal warming on soil enzymatic activity in a P-deficient Mediterranean shrubland. Global Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3698–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F.; Beheshti, A. Soil specific enzyme activity shows more clearly soil responses to paddy rice cultivation than absolute enzyme activity in primary forests of northwest Iran. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, N.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. Season-dependence of soil extracellular enzyme activities in a Pinus koraiensis forest on Changbai Mountain. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elevation/m | Canopy Density | Mean Diameter at Breast Height/cm | Litter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness/cm | Biomass/(t·ha−1) | |||
| 800 | 0.75 ± 0.01 B | 12.47 ± 2.27 B | 3.37 ± 0.64 B | 2.93 ± 0.24 D |
| 1000 | 0.73 ± 0.03 B | 11.53 ± 1.51 B | 3.7 ± 1.13 B | 2.94 ± 0.26 D |
| 1100 | 0.81 ± 0.04 A | 18.03 ± 2.61 A | 7 ± 1.00 A | 5.39 ± 0.44 B |
| 1200 | 0.78 ± 0.02 AB | 14.4 ± 1.41 B | 7.3 ± 0.58 A | 6.73 ± 0.50 A |
| 1500 | 0.81 ± 0.04 A | 12.87 ± 1.87 B | 4.7 ± 0.58 B | 4.52 ± 0.32 C |
| Elevation/m | Shannon–Wiener Index | Simpson Index | Pielou Index | Margalef Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 1.51 ± 0.31 B | 0.66 ± 0.13 B | 0.64 ± 0.12 B | 2.34 ± 0.16 A |
| 1000 | 1.90 ± 0.33 AB | 0.73 ± 0.10 AB | 0.67 ± 0.09 B | 3.34 ± 0.83 A |
| 1100 | 1.81 ± 0.51 AB | 0.75 ± 0.11 AB | 0.74 ± 0.09 AB | 2.68 ± 1.01 A |
| 1200 | 1.85 ± 0.31 AB | 0.77 ± 0.05 AB | 0.78 ± 0.01 AB | 2.59 ± 0.86 A |
| 1500 | 2.47 ± 0.22 A | 0.89 ± 0.02 A | 0.86 ± 0.02 A | 3.93 ± 0.91 A |
| Soil Variables | Soil Layer | 800 m | 1000 m | 1100 m | 1200 m | 1500 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil porosity/% | 0–10 cm | 44.67 ± 5.59 a | 54.87 ± 6.79 a | 62.01 ± 5.56 a | 66.73 ± 9.83 a | 78.06 ± 10.86 a |
| 10–20 cm | 45.54 ± 7.43 a | 48.26 ± 6.98 a | 61.32 ± 5.72 a | 58.75 ± 7.94 a | 67.71 ± 6.65 a | |
| 20–30 cm | 48.12 ± 4.46 a | 50.63 ± 5.47 a | 65.33 ± 4.39 a | 56.28 ± 9.22 a | 76.31 ± 6.23 a | |
| 0–30 cm | 46.11 ± 5.80 C | 51.25 ± 6.36 BC | 62.89 ± 5.19 AB | 60.59 ± 8.99 B | 74.03 ± 7.91 A | |
| Soil bulk density /(g·cm−3) | 0–10 cm | 1.78 ± 0.10 a | 1.53 ± 0.09 a | 1.33 ± 0.09 a | 1.18 ± 0.13 b | 1.39 ± 0.11 a |
| 10–20 cm | 1.71 ± 0.15 a | 1.63 ± 0.11 a | 1.39 ± 0.18 a | 1.40 ± 0.10 ab | 1.45 ± 0.10 a | |
| 20–30 cm | 1.65 ± 0.09 a | 1.58 ± 0.16 a | 1.24 ± 0.12 a | 1.49 ± 0.13 a | 1.43 ± 0.13 a | |
| 0–30 cm | 1.71 ± 0.11 A | 1.58 ± 0.12 AB | 1.32 ± 0.13 C | 1.36 ± 0.12 C | 1.42 ± 0.11 BC | |
| Soil water contents/% | 0–10 cm | 26.5 ± 0.08 a | 33.78 ± 0.05 a | 39.82 ± 0.04 a | 32.51 ± 0.03 a | 36.77 ± 0.02 a |
| 10–20 cm | 15.16 ± 0.05 b | 19.35 ± 0.03 b | 34.16 ± 0.05 a | 18.07 ± 0.01 b | 32.54 ± 0.01 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 13.31 ± 0.02 b | 15.36 ± 0.02 b | 21.71 ± 0.06 b | 15.53 ± 0.01 b | 19.69 ± 0.01 c | |
| 0–30 cm | 18.32 ± 3.72 B | 22.83 ± 2.29 B | 31.90 ± 3.65 A | 22.04 ± 1.69 B | 33.00 ± 0.48 A | |
| pH | 0–10 cm | 4.67 ± 0.39 a | 5.63 ± 0.25 a | 5.72 ± 0.11 b | 5.57 ± 0.31 a | 4.93 ± 0.09 b |
| 10–20 cm | 4.90 ± 0.38 a | 5.67 ± 0.40 a | 5.87 ± 0.12 b | 5.73 ± 0.48 a | 5.11 ± 0.19 ab | |
| 20–30 cm | 5.13 ± 0.10 a | 5.75 ± 0.29 a | 6.09 ± 0.09 a | 5.64 ± 0.49 a | 5.37 ± 0.10 a | |
| 0–30 cm | 4.90 ± 0.28 B | 5.68 ± 0.25 A | 5.89 ± 0.03 A | 5.65 ± 0.39 A | 5.14 ± 0.11 B | |
| AvailableN /(mg·kg−1) | 0–10 cm | 97.31 ± 12.17 a | 169.17 ± 23.76 a | 170.41 ± 19.99 a | 113.67 ± 18.23 a | 145.46 ± 9.67 a |
| 10–20 cm | 29.78 ± 9.17 b | 74.08 ± 14.32 b | 100.97 ± 15.13 b | 71.37 ± 11.69 b | 105.29 ± 15.66 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 18.42 ± 4.73 b | 42.58 ± 15.55 b | 91.74 ± 12.39 b | 42.25 ± 8.61 c | 69.26 ± 11.17 c | |
| 0–30 cm | 48.50 ± 8.68 D | 95.28 ± 5.42 BC | 121.04 ± 15.82 A | 75.76 ± 12.84 C | 106.67 ± 12.13 AB | |
| Available P /(mg·kg−1) | 0–10 cm | 1.40 ± 0.44 a | 3.06 ± 0.95 a | 3.85 ± 1.34 a | 2.62 ± 0.38 a | 3.67 ± 1.06 a |
| 10–20 cm | 0.76 ± 0.59 ab | 0.85 ± 0.23 b | 2.11 ± 0.77 ab | 1.27 ± 0.03 b | 1.86 ± 0.72 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 0.21 ± 0.03 b | 0.22 ± 0.24 b | 1.83 ± 0.36 b | 0.99 ± 0.09 b | 1.31 ± 0.60 b | |
| 0–30 cm | 0.79 ± 0.29 C | 1.37 ± 0.35 C | 2.60 ± 0.44 A | 1.63 ± 0.10 BC | 2.28 ± 0.77 AB | |
| Available K /(mg·kg−1) | 0–10 cm | 98.79 ± 27.34 a | 204.70 ± 35.66 a | 238.42 ± 53.37 a | 202.89 ± 20.95 a | 230.95 ± 42.47 a |
| 10–20 cm | 38.83 ± 32.92 b | 108.30 ± 16.63 b | 224.84 ± 33.14 a | 118.03 ± 56.93 b | 160.80 ± 34.75 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 13.71 ± 11.22 b | 98.12 ± 16.20 b | 58.74 ± 11.57 b | 85.44 ± 35.17 b | 141.34 ± 20.24 b | |
| 0–30 cm | 50.44 ± 20.71 B | 137.04 ± 22.53 A | 174.00 ± 29.97 A | 135.45 ± 37.41 A | 177.70 ± 32.29 A | |
| TN /(g·kg−1) | 0–10 cm | 4.04 ± 0.67 a | 6.08 ± 0.20 a | 5.89 ± 1.13 a | 4.63 ± 0.15 a | 8.92 ± 0.90 a |
| 10–20 cm | 1.32 ± 0.59 b | 3.32 ± 1.44 b | 5.73 ± 0.97 a | 3.16 ± 0.75 b | 6.36 ± 1.31 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 0.87 ± 0.05 b | 1.04 ± 0.28 c | 3.47 ± 0.75 b | 1.50 ± 0.07 c | 5.58 ± 0.49 b | |
| 0–30 cm | 2.08 ± 0.15 D | 3.48 ± 0.44 C | 5.03 ± 0.95 B | 3.09 ± 0.32 CD | 6.95 ± 0.89 A | |
| TC /(g·kg−1) | 0–10 cm | 47.90 ± 6.80 a | 78.13 ± 5.39 a | 74.27 ± 5.75 a | 55.53 ± 3.51 a | 95.42 ± 8.30 a |
| 10–20 cm | 11.92 ± 5.51 b | 46.42 ± 10.01 b | 63.56 ± 4.70 a | 40.51 ± 3.15 b | 68.56 ± 6.75 b | |
| 20–30 cm | 9.58 ± 1.53 b | 11.03 ± 5.32 c | 43.07 ± 7.51 b | 15.70 ± 1.53 c | 66.30 ± 6.20 b | |
| 0–30 cm | 23.13 ± 3.60 D | 45.20 ± 2.08 C | 60.30 ± 5.98 B | 37.25 ± 2.72 C | 76.76 ± 7.08 A |
| Parameters | Elevation | Soil Layer | Elevation × Soil Layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| NH4+—N | 8.436 | <0.001 *** | 24.922 | <0.001 *** | 6.636 | <0.001 *** |
| NO3−—N | 22.315 | <0.001 *** | 38.646 | <0.001 *** | 6.845 | <0.001 *** |
| SIN | 19.393 | <0.001 *** | 46.36 | <0.001 *** | 6.146 | <0.001 *** |
| MBC | 3.99 | 0.01 * | 21.452 | <0.001 *** | 1.867 | 0.103 |
| MBN | 12.443 | <0.001 *** | 6.883 | 0.003 ** | 0.665 | 0.718 |
| MBC/MBN | 2.506 | 0.063 | 0.763 | 0.475 | 0.674 | 0.71 |
| URE | 46.826 | <0.001 *** | 52.583 | <0.001 *** | 9.032 | <0.001 *** |
| SUC | 58.87 | <0.001 *** | 66.812 | <0.001 *** | 5.497 | <0.001 *** |
| URE/MBC | 7.149 | <0.001 *** | 2.641 | 0.088 | 5.814 | <0.001 *** |
| SUC/MBC | 4.969 | 0.003 ** | 0.628 | 0.054 | 1.269 | 0.296 |
| Impact Factors | Explains/% | F | P | Impact Factors | Explains/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available N | 34.4 | 6.8 | 0.002 | Available P | 2.6 | 1 | -- |
| Elevation | 14.5 | 3.4 | 0.004 | Soil water contents | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.73 |
| Soil bulk density | 10.3 | 2.8 | 0.03 | Shannon–Wiener | 1.8 | 0.6 | 0.678 |
| TN | 8.2 | 2.5 | -- | Simpson | 5 | 2 | 0.256 |
| Margalef | 5.9 | 2 | 0.098 | Pielou | 1.5 | 0.5 | -- |
| TC | 4.9 | 1.8 | 0.14 | Available K | 1 | 0.2 | 0.818 |
| Soil porosity | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.256 | pH | 5.1 | <0.1 | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, E.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Distribution Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along Elevation Gradients in the Southern of Taihang Mountain, China. Forests 2023, 14, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020370
Feng E, Zhang L, Kong Y, Xu X, Wang T, Wang C. Distribution Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along Elevation Gradients in the Southern of Taihang Mountain, China. Forests. 2023; 14(2):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020370
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Erpeng, Liwei Zhang, Yuhua Kong, Xingkai Xu, Ting Wang, and Caifeng Wang. 2023. "Distribution Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along Elevation Gradients in the Southern of Taihang Mountain, China" Forests 14, no. 2: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020370
APA StyleFeng, E., Zhang, L., Kong, Y., Xu, X., Wang, T., & Wang, C. (2023). Distribution Characteristics of Active Soil Substances along Elevation Gradients in the Southern of Taihang Mountain, China. Forests, 14(2), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020370








