Expression Pattern Analysis of Larch WRKY in Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material
2.2. Test Method
2.2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2.2. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
3. Results
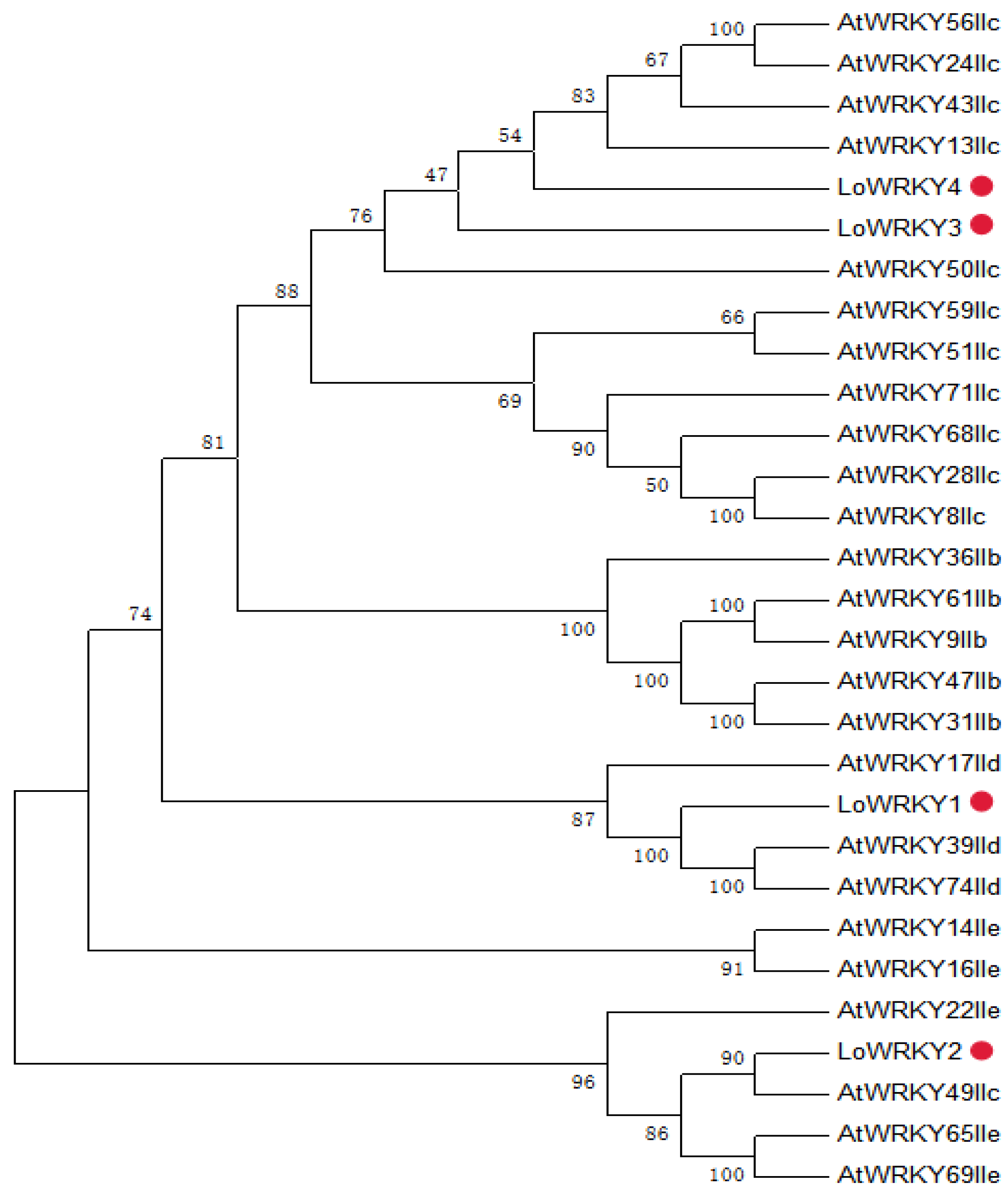
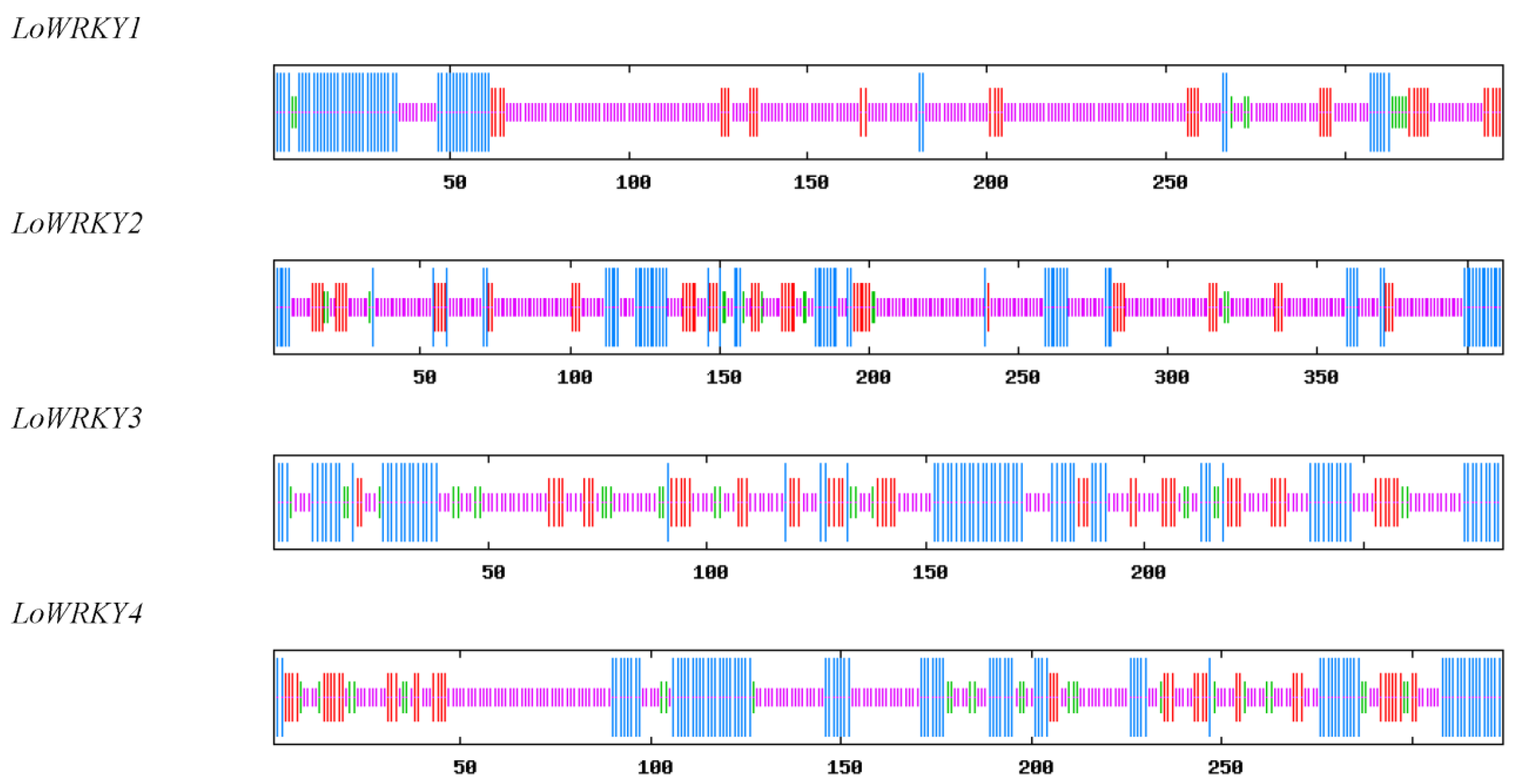
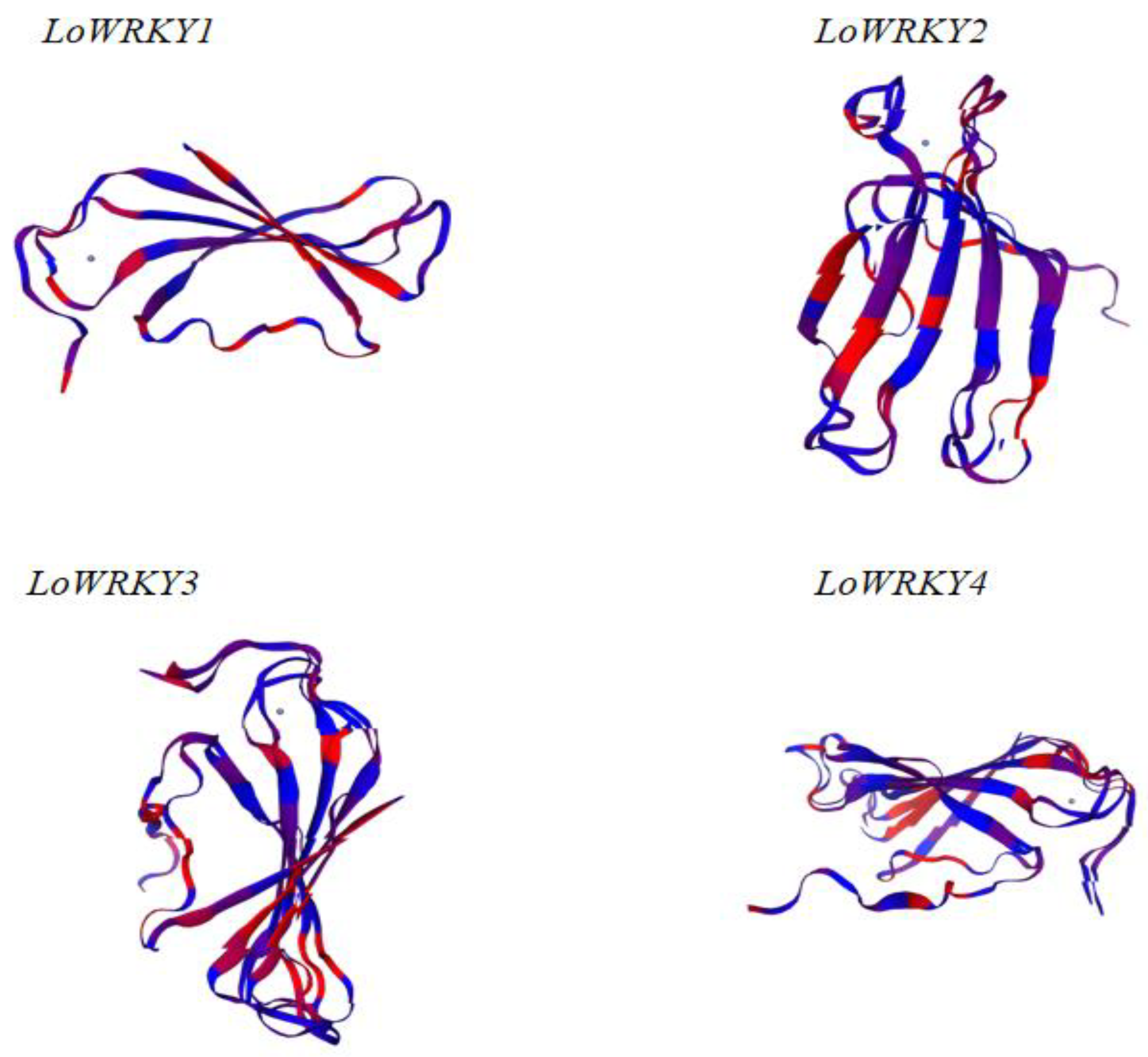
3.1. WRKY Sequence Analysis of Larix olgensis
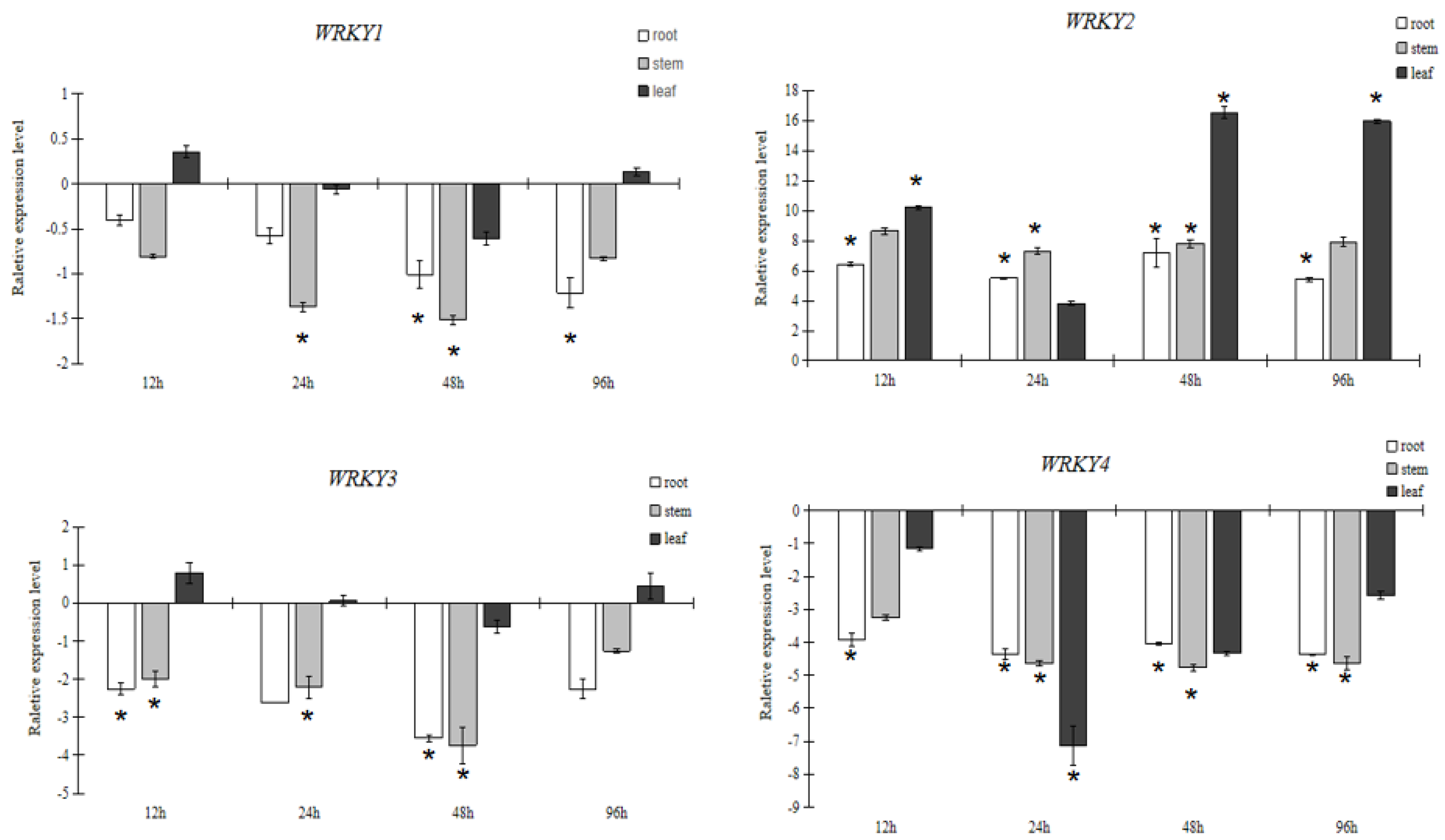
3.2. Analysis of WRKY Gene Expression Pattern of Larix Olgensis under Abiotic Stress
3.2.1. Expression Pattern Analysis of WRKY in Response to PEG6000 Stress
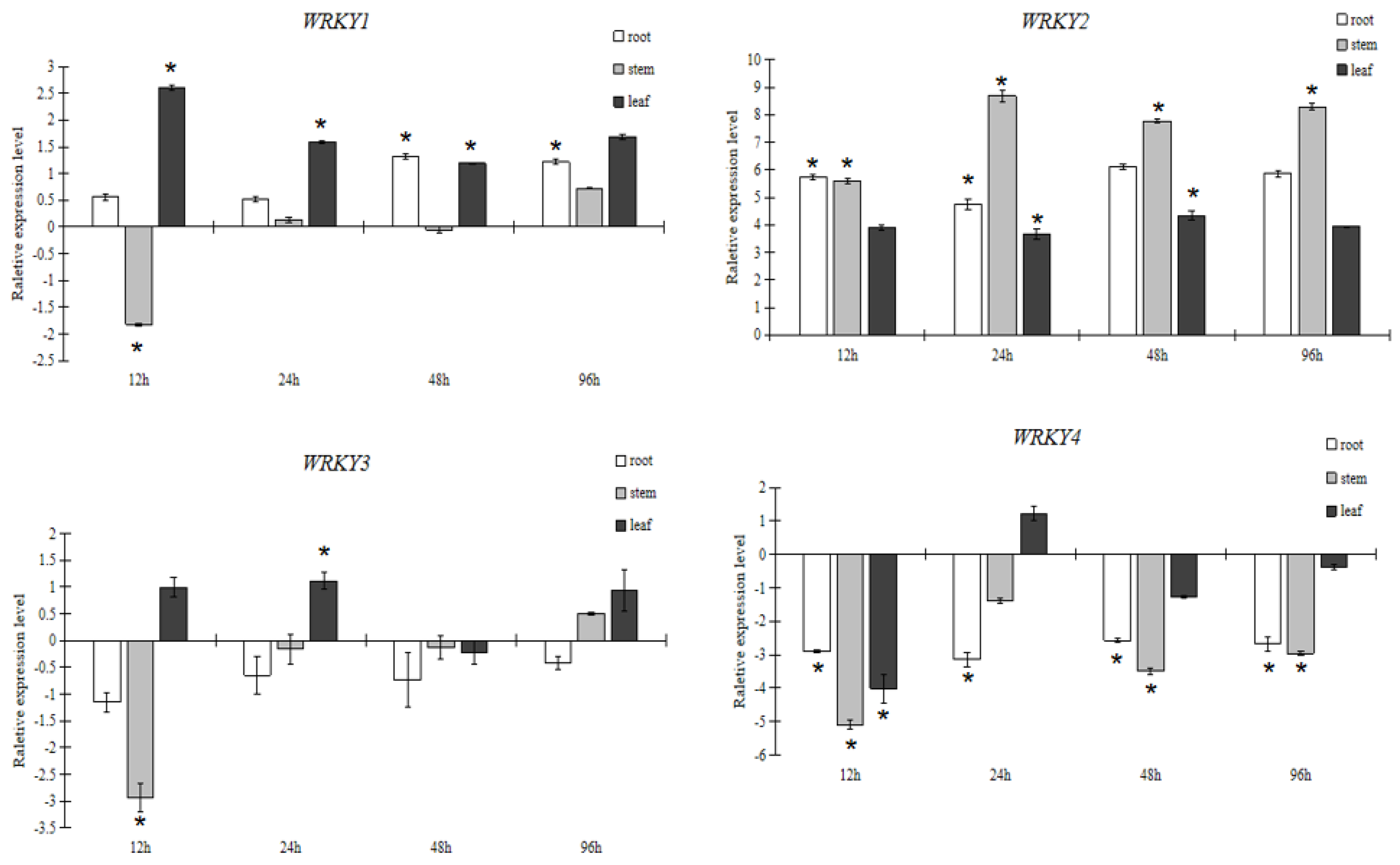
3.2.2. Expression Pattern Analysis of WRKY in Response to Salt Stress
3.2.3. Expression Pattern Analysis of WRKY in Response to NaHCO3 Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties Analysis of WRKY Gene of Larix Olgensis
4.2. Differential Expression Analysis of WRKY Gene in Larix olgensis under Abiotic Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Hybrid larch. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2009, 45, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lai, L.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Jakada, B.H.; Huang, Y.; He, Q.; Chai, M.; Niu, X.; Qin, Y. AcoMYB4, an Ananas comosus L. MYB Transcription Factor, Functions in Osmotic Stress through Negative Regulation of ABA Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; An, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Preliminary analysis of two NAC transcription factor expression patterns in Larix olgensis. J. For. Res. 2021. prepublish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Soo, K.H.; Soo, K.S.; Qian, Z.; Shuai, L.; Peiyong, M.; Zhaodong, J.; Yizhi, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, Y. Different Functions of IbRAP2.4, a Drought-Responsive AP2/ERF Transcription Factor, in Regulating Root Development between Arabidopsis and Sweetpotato. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 820450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jiang, J.; Yao, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, K.; Cheng, Z.; Han, L.; Wei, R.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-wide analysis of poplar HD-Zip family and over-expression of PsnHDZ63 confers salt tolerance in transgenic Populus simonii × P.nigra. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Pan, G.; Tao, J.; Doblin, M.S.; Zeng, W.; Pan, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chang, L.; et al. Identification of MYB genes reveals their potential functions in cadmium stress response and the regulation of cannabinoid biosynthesis in hemp. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 180, 114607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: Its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2005, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tan, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, Z. Phylogenetic analysis and drought-responsive expression profiles of the WRKY transcription factor family in maize. Agri Gene 2017, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumie Ishiguro, K.N. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel DNA-binding protein, SPF1,that recognizes SP8 sequences in the 5′upstream regions of genes coding for sporamin and β-amylase from sweet potato. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 244, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, P.J.; Macdonald, H.; Huttly, A.K.; Lazarus, C.M.; Hooley, R. Members of a new family of DNA-binding proteins bind to a conserved cis-element in the promoters of α-Amy2 genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, P.J.; Torres, J.T.; Parniske, M.; Wernert, P.; Hahlbrock, K.; Somssich, I.E. Interaction of elicitor-induced DNA-binding proteins with elicitor response elements in the promoters of parsley PR1 genes. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5690–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, S.; Ye, N.; Jiang, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J. WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, D.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Su, W.; Que, Y. Structure, Classification, Evolution and Function of Plant WRKY Transcription Factors. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 29, 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, H.; Du, T. Research Progress in the Role of WRKY Transcription Factor in Plant Drought Response Mechanism. Chin. J. Inf. TCM 2021, 28, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Z. Isolation and characterization of two pathogen and salicylic acid-induced genes encoding WRKY DNA-binding proteins from tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 42, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pang, S.; Lu, Z.; Jin, B. Function and Mechanism of WRKY Transcription Factors in Abiotic Stress Responses of Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finatto, T.; Viana, V.E.; Woyann, L.G.; Busanello, C.; Maia, L.C.; Oliveira, A.C. Can WRKY transcription factors help plants to overcome environmental challenges? Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Reddy, M.; Chikara, J. WRKY: Its structure, evolutionary relationship, DNA-binding selectivity, role in stress tolerance and development of plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 3883–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Kracher, B.; Roccaro, M.; Somssich, I.E. Induced genome-wide binding of three Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factors during early MAMP-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yi, K.; Zhang, D. Transcription factor WRKY30 mediates resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Current status and development strategies of wood fiber raw materials for pulp and papermaking in China. World For. Res. Inst. 2003, 16, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F. Study on the Sharpness Equation of Larch Plantation; Northeast Forestry University: Harbin, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- An, P.; Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal expression and bioinformatic analyses of the HD-zip transcription factor family in Larix olgensis. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2021, 39, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Mining Myb transcription factors related to wood development in Larix olgensis. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2453–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zeng, M.; An, X. Identification of Populus trichocarpa WRKY Gene Family and Its’ Response to Drought Stress. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 41, 2160–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Qi, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y. Research Advances about Function of WRKY Family Gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Anhui Agri. Sci. 2014, 42, 1295–1297, 1301. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Niu, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y. Characterization and Stress-resistance Functional Identification of Transcription Factor Gene WRKY72 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 27, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lei, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y. Studies on WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Biological Functions in Soybean. Soybean Sci. 2019, 38, 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wei, B. Identification of WRKY Gene Family and Their Expression Analysis Under Low-temperature Stress in Melon (Cucumis melo). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Bioinformatics Analysis of VvWRKY71 Transcription Factor in Vitis vinifera L. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2013, 29, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wei, C.; Qin, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Cai, L.; Huang, J.; Gao, L.; et al. In Silico Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of EcWRKY50 Transcription Factors in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Agric. Res. Appl. 2014, 04, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, T.; Li, S.; Long, X.; Han, S. Cloning, Sequence Analysis and Prokaryotic Expression of CmWRKY from Castanea mollissima BL. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2019, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D.; Tang, Q. Molecular mechanism of WRKY12 in regulating plant development. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Ulker, B.; Somssich, I.E. WRKY transcription factors:from DNA binding towards biological function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Jing, S.; Fu, J.; Li, L.; Yu, D. Cloning and analysis of expression profile of 13 WRKY genes in rice. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.F.; Wei, W.E.I.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Tian, A.G.; Hao, Y.J.; Zhang, W.K.; Ma, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.S. Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Liang, N.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Zhan, Y. Cloning and Expression Analysis of FmWRKY40 Gene in Fraxinus mandshurica. Mol. Plant Breed. 2017, 15, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Du, G.; Fu, X. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor PpWRKY18 in Peach. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2021, 35, 1987–1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ling, H.; Liu, F.; Huang, N.; Wang, L.; Mao, H.; Li, C.; Tang, H.; Su, W.; Su, Y.; et al. Cloning and Expression Analysis of aⅡd Sub-Group WRKY Transcription Factor Gene from Sugarcane. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 4409–4423. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, R.; Zhang, X.; Su, Z.; Wei, J.; Liu, J. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor Gene HrWRKY1 in Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides). Mol. Plant Breed. 2019, 17, 5638–5643. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Partial WRKY genes expression under non-biological stress and analysis of SlWRKY50 gene silencing in tomato. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2018, 49, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Miao, H.; Liu, J.; Jin, Z.; Xu, B. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Eight WRKY Transcription Factors in Banana (Musa acuminata L.). Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2018, 39, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, N.N.; Kong, L.; Gong, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.B. Molecular characterization of 26 cotton WRKY genes that are expressed differently in tissues and are induced in seedlings under high salinity and osmotic stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 119, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Xu, Z.; Shen, X. Expression analysis of WRKY gene related to salt tolerance in Cotton under Salt Stress. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.H.; Yin, H.; Huang, Q.M.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, M.; Zhou, Y.W. An analysis of the response of the LpWRKY20 gene to abiotic stress and its role in drought resistance. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2020, 29, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Zhou, Z.; Du, M.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Yang, G. Clone and preliminary functional analysis of Malus xiaojinensis transcription factors gene WRKY48. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2020, 51, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Zou, Y.; Xie, D.; Lu, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q. Expression and functional analysis of rice OsWRKY78 transcription factor in response to salt stress. J. Yangzhou Univ. (Agric. Life Sci. Ed.) 2019, 40, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Gao, Z. Cloning and Expression Analysis of SlWRKY44 Gene in Tomato. North. Hortic. 2018, 22, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L. Cloning and Functional Analysis of HbWRKY8Transcription Factor in Hevea Brasiliensis; Hainan University: Haikou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Hu, W.; Kuang, L.; Guo, W.; Shen, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of Citrus WRKY75 genes in response to abiotic stresses. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2021, 43, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, J.; Dai, T.; Cao, W.; Pu, H.; Jiang, D. Salt stress increases content and size of glutenin macropolymers in wheat grain. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Akhar, J.; Qureshi, R.H. Na+ exclusion and salt resistance of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in saline-waterlogged conditions are improved by the development of adventitious nodal roots and cortical root aerenchyma. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, K.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Study on Growth and Physiological Response Mechanism of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge under Salt-alkali Stress. For. Res. 2021, 34, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Gao, S.; He, H.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Song, G.; et al. Expression Analysis of the Maize ZmWRKY45 Gene under the Saline-alkali Adversity Stress. J. Maize Sci. 2017, 25, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Song, X.; Li, H.; Du, J.; Li, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhu, Y. Cloning of Gene GsWRKY15 Related to Alkaline Stress and Alkaline Tolerance of Transgenic Plants. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Purpose | Software |
|---|---|
| Physical and chemical properties of protein | ExPAsy (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/) accessed on 27 August 2021. |
| Phylogenetic tree | Mega 5.0 |
| Signal peptide | SignIP (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) accessed on 27 August 2021. |
| Secondry structure | SOPMA (https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html) accessed on 27 August 2021. |
| Tertiary structure | SWISS MODEL (https://www.swissmodel.expasy.org/) accessed on 27 August 2021. |
| Subcellular localization | WOLF PSORT (http://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/) accessed on 27 August 2021. |
| Gene Name | Forward Primers (5′-3′) | Reverse Primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| LoWRKY1 | TTTCAATGCTCGGAACCAC | GAGGGGCAAAGCTTAGGAG |
| LoWRKY2 | TCTAGTCGCCTAGATTCACTAGG | CTTCCTGCGTTTTGAATCAG |
| LoWRKY3 | TTCCCAGAGTGATAATTCCG | CCACGTTGAGAGTCGTTATATTC |
| LoWRKY4 | GGATTAAGCAGCTCAAAACCTC | CAGGACATTTCAGTCATCTGATC |
| Component | Volume |
|---|---|
| Template | 1 μL |
| Forward Primer | 1 μL |
| Reverse Primer | 1 μL |
| 2 × TransStart Top Green qPCR SuperMix | 10 μL |
| Passive Reference Dye (50×) (optional) | 1 μL |
| ddH2O | 6 μL |
| Total volume | 20 μL |
| Gene | Size (bp) | Molecular Weight (Da) | Theoretical PI | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Instability Index | Signal Peptide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoWRKY1 | 1035 | 37,385.39 | 9.36 | 61.54 | −0.544 | 47.68 | Non-signal peptide |
| LoWRKY2 | 1239 | 44,904.72 | 6.28 | 62.01 | −0.807 | 38.84 | |
| LoWRKY3 | 849 | 32,314.77 | 6.55 | 57.34 | −0.873 | 55.74 | |
| LoWRKY4 | 975 | 36,799.79 | 9.07 | 52.93 | −0.953 | 58.85 |
| Gene | Alpha Helix (Hh) | Extended Strand (Ee) | Beta Turn (Tt) | Random Coil (Cc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoWRKY1 | 17.15% | 10.17% | 2.91% | 69.77% |
| LoWRKY2 | 17.48% | 13.35% | 3.16% | 66.02% |
| LoWRKY3 | 29.43% | 18.44% | 8.51% | 43.62% |
| LoWRKY4 | 28.09% | 12.96% | 8.33% | 50.62% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Expression Pattern Analysis of Larch WRKY in Response to Abiotic Stress. Forests 2022, 13, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13122123
Wang C, Zhao Q, Zhang L, Zhang H. Expression Pattern Analysis of Larch WRKY in Response to Abiotic Stress. Forests. 2022; 13(12):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13122123
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Qingrong Zhao, Lei Zhang, and Hanguo Zhang. 2022. "Expression Pattern Analysis of Larch WRKY in Response to Abiotic Stress" Forests 13, no. 12: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13122123
APA StyleWang, C., Zhao, Q., Zhang, L., & Zhang, H. (2022). Expression Pattern Analysis of Larch WRKY in Response to Abiotic Stress. Forests, 13(12), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13122123





