Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Analyses and Calculations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
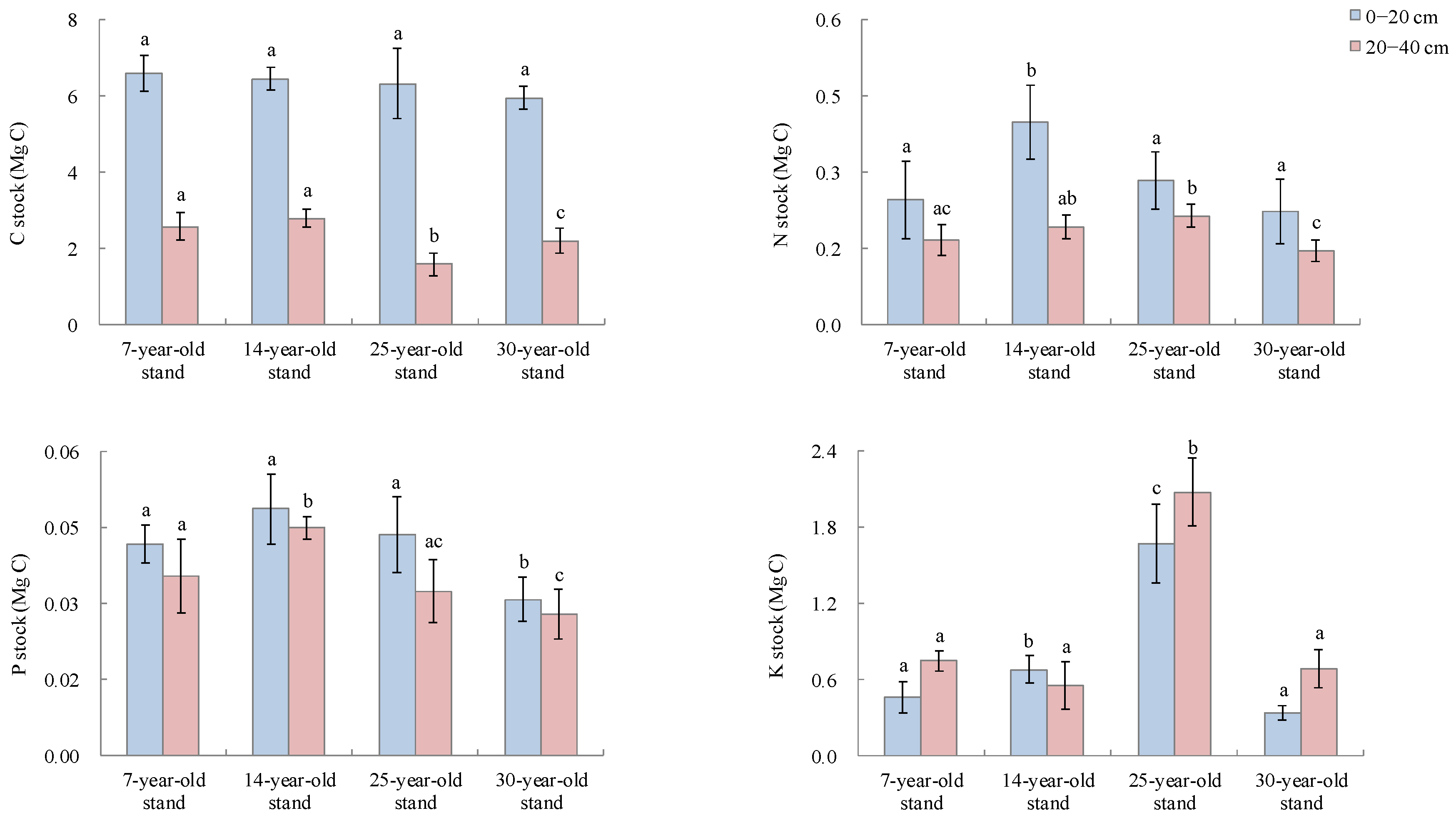
3.1. Soil Macronutrient Stocks and Allocation
3.2. Variations of Soil Macronutrient Stoichiometry
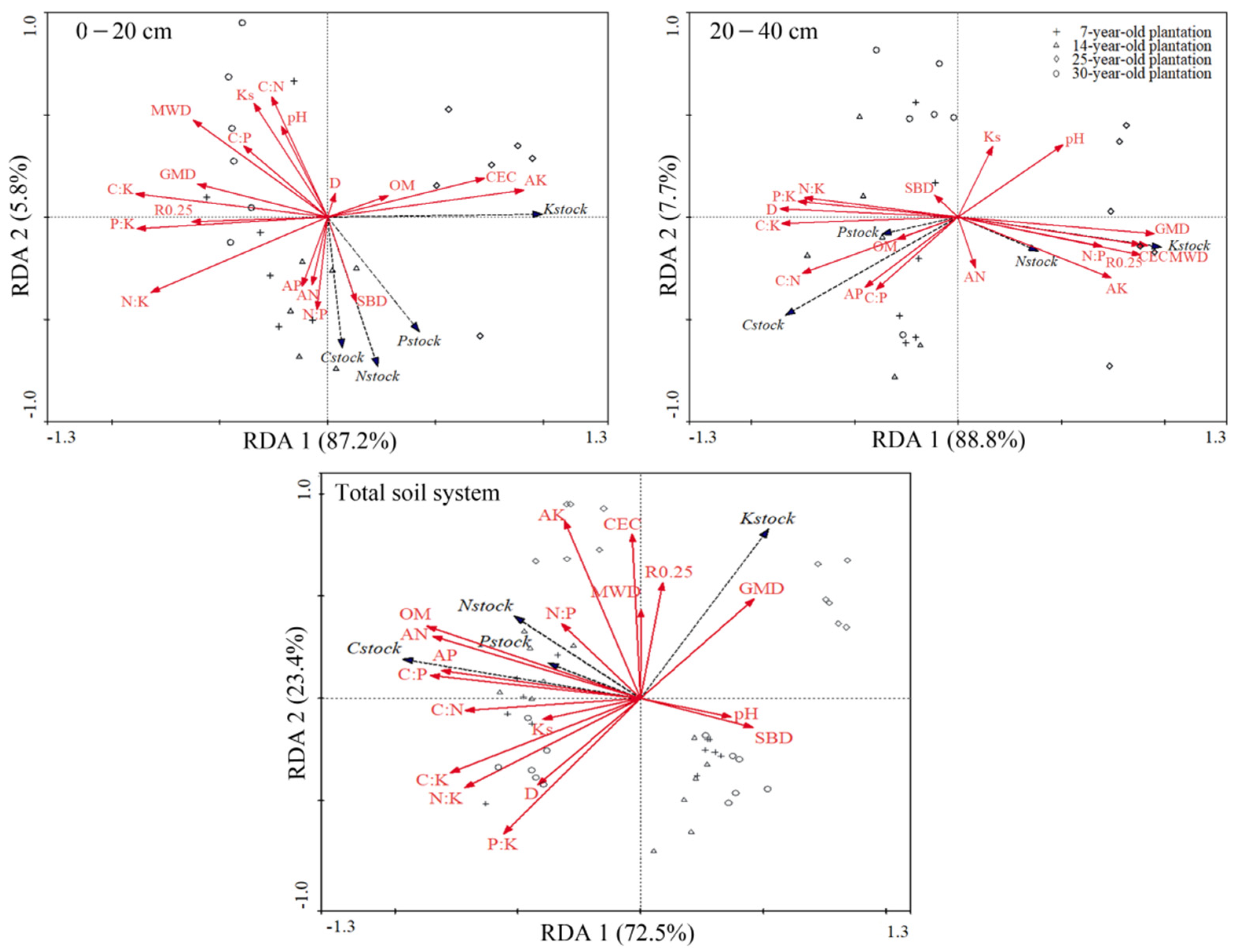
3.3. Relationships between Macronutrient Stocks and Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.3.1. Controls of Macronutrient Stocks at Various Plantations
3.3.2. Controls of Macronutrient Stocks at Various Soil Depths
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Soil Macronutrient Stocks
4.2. Factors Controlling Soil Macronutrient Stocks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węgiel, A.; Bielinis, E.; Polowy, K. Macronutrient stocks in Scots pine stands of different densities. Forests 2018, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, G.R.; Chapin, F.S. Long-Term Responses to Factorial, NPK Fertilizer Treatment by Alaskan Wet and Moist Tundra Sedge Species. Ecography 1995, 18, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, L.E.; Mielke, N.; Woodin, S.J. Phosphorus Availability Determines the Response of Tundra Ecosystem Carbon Stocks to Nitrogen Enrichment. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, C.A.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Richardson, A.E.; Wade, L.J.; Blanchard, C.; Batten, G. Stable soil organic matter: A comparison of C:N:P:S ratios in Australian and other world soils. Geoderma 2011, 163, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N.; Reynolds, J.F. Soil Carbon Stocks in Experimental Mesocosms Are Dependent on the Rate of Labile Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Inputs to Soils. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Wang, K.X.; Baoyin, T. Effects of grazing and mowing on vertical distribution of soil nutrients and their stoichiometry (C:N:P) in a semi-arid grassland of North China. Catena 2021, 206, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.; Goswami, A.J.; Ghosh, S.; Kalita, C. An indigenous strain of potassium-solubilizing bacteria Bacillus pseudomycoides enhanced potassium uptake in tea plants by increasing potassium availability in the mica waste-treated soil of North-east India. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 126, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, G.; Yue, G.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Soil moisture and texture primarily control the soil nutrient stoichiometry across the Tibetan grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, N.P.; Yu, G.R. Nitrogen storage in China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhao, L.; Kuzyakov, Y. Shrubs magnify soil phosphorus depletion in Tibetan meadows: Conclusions from C:N:P stoichiometry and deep soil profiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birendra, N.G.; Om Pal, S.K.; Ranjan, B.; Kuldeep, S.D.; Prasant, K.M. Effect of potassium on soil conservation and productivity of maize/cowpea based crop rotations in the north-west Indian Himalayas. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaszczyk, W.; Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Lukac, M. A comparison of C:N:P stoichiometry in soil and deadwood at an advanced decomposition stage. Catena 2019, 179, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lan, T.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Ling, J.; Deng, O.P.; Wang, C.Q.; Gao, X.S.; Li, Q.Q.; Tang, X.Y.; et al. Soil labile organic carbon impacts C:N:P stoichiometry in urban park green spaces depending on vegetation types and time after planting. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.W.; Qu, Q.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.Q.; Wulan, E.; Xue, S. Stocks and Stoichiometry of Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Total Phosphorus after Vegetation Restoration in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Forests 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Abdalla, M.; Espenberg, M.; Hastings, A.; Hallett, P.; Smith, P. A systematic analysis and review of the impacts of afforestation on soil quality indicators as modified by climate zone, forest type and age. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D.E.; Vergütz, L.; Valadares, S.V.; Silva, I.R.d.; Jackson, R.B. Soil nutrient stocks are maintained over multiple rotations in Brazilian Eucalyptus plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 448, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.J.; Xu, S.; Zheng, X. Conversion from temperate secondary forests into plantations (Larix spp.): Impact on belowground carbon and nutrient pools in northeastern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Hedo, J.; Cerdá, A.; Candel-Pérez, D.; Viñegla, B. Unravelling the importance of forest age stand and forest structure driving microbiological soil properties, enzymatic activities and soil nutrients content in Mediterranean Spanish black pine(Pinus nigra Ar. ssp. salzmannii) Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.P.; Chen, X.; Huang, B.; Chi, G.Y. Distribution Changes of Phosphorus in Soil–Plant Systems of Larch Plantations across the Chronosequence. Forests 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Palmer, P.I.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.X.; Bösch, H.; O’Dell, C.W.; Tang, X.P.; Yang, D.X.; Liu, L.X.; et al. Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data. Nature 2020, 586, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, T.Y.; Song, L.H.; Mei, L. Fertilization and clear-cutting effect on greenhouse gases emission of pinewood nematode damaged Masson pine plantation. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2021, 7, 1868271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.P.; He, B.H.; Zeng, Q.P.; Li, N.J.; Yang, L. Effects of seasonal variation on soil microbial community structure and enzyme activity in a Masson pine forest in Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Liu, H.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Zhang, S.G. Changes in soil carbon and nutrients and related extracellular enzymes in successive rotations of Japanese larch plantations. Catena 2021, 204, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, M.; Chettri, R.; Vineeta, V.; Shukla, G.; Bhat, J.A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Suryawanshi, A.; CabralPinto, M.; Chakravarty, S. Stand Structure, Biomass and Carbon Storage in Gmelina arborea Plantation at Agricultural Landscape in Foothills of Eastern Himalayas. Land 2021, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, M.; Avishek, S.; Krishna, G.; Jyoti, N.A.; Rattan, L.; Rosa, F. Changes in soil carbon stocks under plantation systems and natural forests in Northeast India. Ecol. Model. 2021, 446, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, F.; Wei, L.Y.; Zhang, D.K.; Jin, H.J. Carbon Sequestration of Sand-fixing Plantation of Haloxylon ammodendron in Shiyang River Basin: Storage, Rate and Potential. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yu, K.Y.; Deng, Y.B.; Zeng, Q.; Lai, Z.J.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon stocks in Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) forests in subtropical China. Catena 2019, 178, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S.; Tian, L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Tian, C. Long-term fertilization and residue return affect soil stoichiometry characteristics and labile soil organic matter fractions. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.H.; Hou, F.J. Different responses of soil C:N:P stoichiometry to stocking rate and nitrogen addition level in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, S.Z.; Cao, Y.W.; Jiang, M.; Wang, G.D.; Dong, Y.M. The effects of hummock-hollow microtopography on soil organic carbon stocks and soil labile organic carbon fractions in a sedge peatland in Changbai Mountain, China. Catena 2021, 201, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.Y.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Liu, S.R.; Cai, D.X.; Lu, L.H.; He, R.M.; Gao, Y.X.; Di, W.Z. Soil physical and chemical characteristics under different vegetation restoration patterns in China south subtropical area. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Buurman, P.; do Nascimento, D.L.; Almquist, V.; Vidal-Torrado, P. Substantial changes in podzol morphology after tree-roots modify soil porosity and hydrology in a tropical coastal rainforest. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D.; Jiang, R.F.; Yang, C.G. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.C.; He, H.Z. Effects of rehabilitation through afforestation on soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated carbon after forest fires in subtropical China. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Zhou, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.M. Carbon Sequestration Anticipation Response to land use change in a mountainous karst basin in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidoust, E.; Afyuni, M.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Mosaddeghi, M.R. Soil carbon sequestration potential as affected by soil physical and climatic factors under different land uses in a semiarid region. Catena 2018, 171, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellock, M.L.; Rashad, R.; Laperle, C.M.; Matthias, P.; Gerard, K. Changes in ecosystem carbon stocks in a grassland ash (Fraxinus excelsior) afforestation chronosequence in Ireland. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 7, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, J.X.; Pan, H.; Chen, Z.; Shang, H. Dynamics in Stoichiometric Traits and Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Pools across Three Different-Aged Picea asperata Mast. Plantations on the Eastern Tibet Plateau. Forests 2020, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Xiang, W.H.; Yang, S.O.; Xiao, W.F.; Li, S.G.; Chen, L.; Lei, P.F.; Deng, X.W.; Zeng, Y.L.; Zeng, L.X.; et al. Tree growth rate and soil nutrient status determine the shift in nutrient-use strategy of Chinese fir plantations along a chronosequence. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 460, 117896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Xiang, W.H.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.O.; Xiao, W.F.; Li, S.G.; Forrester, D.I.; Lei, P.F.; Zeng, Y.L.; Deng, X.W.; et al. Soil Phosphorus Bioavailability and Recycling Increased with Stand Age in Chinese Fir Plantations. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrer, C.; Phillips, R.P.; Hungate, B.A.; Rosende, J.; Ridge, J.P.; Craig, M.E.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Keenan, T.F.; Sulman, B.N.; Stocker, B.D.; et al. A trade-off between plant and soil carbon storage under elevated CO2. Nature 2021, 591, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.S.; Wang, G.G.; Fang, X.M.; Lin, X.F.; Wan, S.Z.; He, P. The effects of simulated deposited nitrogen on nutrient dynamics in decomposing litters across a wide quality spectrum using a 15 N tracing technique. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañón-Jiménez, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sigurdsson, B.D.; Fuchslueger, L.; Leblans, N.I.W.; Janssens, I.A. Coupled carbon and nitrogen losses in response to seven years of chronic warming in subarctic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C. N2O production pathways relate to land use type in acidic soils in subtropical China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmolovskaya, N.; Dung, V.V.; Kuchaeva, L. The role of organic acids in heavy metal tolerance in plants. Biol. Commun. 2018, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, A.; Tianyi, J.; Taiki, K.; Takamitsu, K.; Kenzo, K.; Araki, K.S.; Motoki, K. Relationship among Phosphorus Circulation Activity, Bacterial Biomass, pH, and Mineral Concentration in Agricultural Soil. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Han, T.F.; Huang, J.; Asad, S.; Li, D.M.; Yu, X.H.; Huang, Q.H.; Ye, H.C.; Hu, H.W.; Zhang, H.M. Links between potassium of soil aggregates and pH levels in acidic soils under long-term fertilization regimes. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Senbayram, M.; Peiter, E. Potassium in agriculture—Status and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K. Aggregate-associated soil organic matter as an ecosystem property and a measurement tool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, A4–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Jansen, B.; Absalah, S.; van Hall, R.L.; Kalbitz, K.; Cammeraat, E.L.H. Lithology- and climate-controlled soil aggregate-size distribution and organic carbon stability in the Peruvian Andes. Soil 2020, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Ren, C.J.; Wang, X.J. C:N:P stoichiometries explain soil organic carbon accumulation during afforestation. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2020, 117, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Y.; Xu, J.M.; Wei, K.; Shi, R.Z.; Ma, L.F. Soil carbon sequestration, plant nutrients and biological activities affected by organic farming system in tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulehle, F.; Wright, R.F.; Svoboda, M.; Bače, R.; Matějka, K.; Kaňa, J.; Hruška, J.; Couture, R.-M.; Kopáček, J. Effects of Bark Beetle Disturbance on Soil Nutrient Retention and Lake Chemistry in Glacial Catchment. Ecosystems 2019, 22, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, H.Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.P.; Yu, D. Stoichiometric variation of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soils and its implication for nutrient limitation in alpine ecosystem of Eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Freschet, G.T.; Zhang, W.D.; Yu, X.; Zheng, W.H.; Guan, X.; Yang, Q.P.; Chen, L.C.; Dijkstra, F.A.; et al. Litter carbon and nutrient chemistry control the magnitude of soil priming effect. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; ShangGuan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Variations in soil aggregate stability due to land use changes from agricultural land on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2021, 200, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
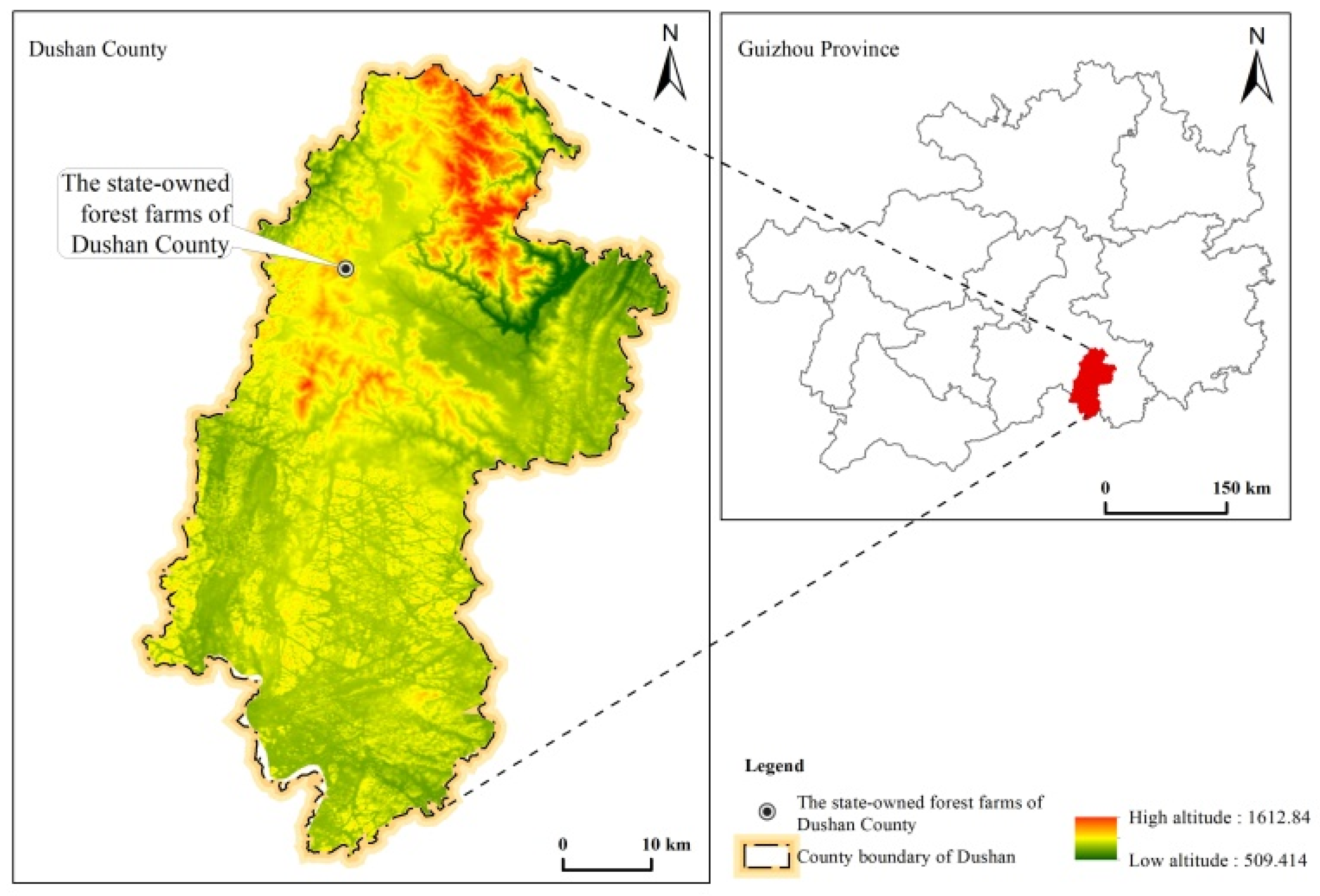

| Stand Age (a) | Slope Direction | Slope (°) | Elevation (m) | Soil Type | Bulk Density (g/cm−3) | Carbon (g/kg) | Nitrogen (g/kg) | Phosphorus (g/kg) | Canopy Density | Average Diameter at Breast Height (cm) | Average Tree Height (m) | Main Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | NW 35° | 28 | 1072~1076 | yellow soil | 1.28 | 20.46 | 0.93 | 0.17 | 0.5 | 3.25 | 2.78 | Dicranopteris linearis, Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv., Miscanthus floridulus (Lab.) Warb. ex Schum. et Laut., Nandina domestica |
| 14 | NE 13° | 35 | 1063~1066 | yellow soil | 1.12 | 23.19 | 1.54 | 0.24 | 0.7 | 11.03 | 10.67 | |
| 25 | NE 10° | 25 | 1075~1080 | yellow soil | 1.12 | 20.23 | 1.25 | 0.19 | 0.8 | 14.07 | 12.6 | |
| 30 | NE 45° | 30 | 1067~1068 | yellow soil | 1.08 | 22.80 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.9 | 25.10 | 15.43 |
| Plantations | Equation | Adjusted R2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7-year-old plantation | Cstock = −0.861 + 3.281AP + 2.282MWD − 0.051OM | 0.975 | 0.000 |
| Nstock = 0.091 + 0.001AN | 0.428 | 0.012 | |
| Pstock = 0.02 + 0.00044AK | 0.338 | 0.028 | |
| Kstock = −0.288 − 0.049WSA > 0.25 mm + 0.783pH + 0.552AP − 0.207D − 0.005OM | 0.980 | 0.000 | |
| 14-year-old plantation | Cstock = −2.110 + 0.161WSA > 0.25 mm | 0.975 | 0.000 |
| Nstock = −1.924 + 0.012WSA > 0.25 mm + 0.319SBD + 0.288pH | 0.930 | 0.000 | |
| Pstock = −0.007 + 0.015Ks + 0.035SBD + 0.000441CEC | 0.804 | 0.001 | |
| Kstock = 0.401 + 0.491GMD | 0.268 | 0.049 | |
| 25-year-old plantation | Cstock = 12.499 − 0.119WSA > 0.25 mm | 0.934 | 0.000 |
| Nstock = 0.191 + 0.004OM −0.083AP | 0.792 | 0.000 | |
| Pstock = 0.029 + 0.000258OM | 0.528 | 0.004 | |
| Kstock = 4.891 − 1.183D | 0.424 | 0.013 | |
| 30-year-old plantation | Cstock = −6.606 + 0.053WSA > 0.25 mm + 0.214CEC + 1.128pH | 0.990 | 0.000 |
| Nstock = 0.122 + 0.004OM − 0.078AP | 0.830 | 0.000 | |
| Pstock = 0.021 + 0.000296AK | 0.460 | 0.009 | |
| Kstock = 0.767 − 0.150MWD | 0.740 | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Dai, Q.; Xu, F.; Yan, Y.; Peng, X. Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations. Forests 2022, 13, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010017
He J, Dai Q, Xu F, Yan Y, Peng X. Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations. Forests. 2022; 13(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jie, Quanhou Dai, Fengwei Xu, Youjin Yan, and Xudong Peng. 2022. "Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations" Forests 13, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010017
APA StyleHe, J., Dai, Q., Xu, F., Yan, Y., & Peng, X. (2022). Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations. Forests, 13(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010017







