Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
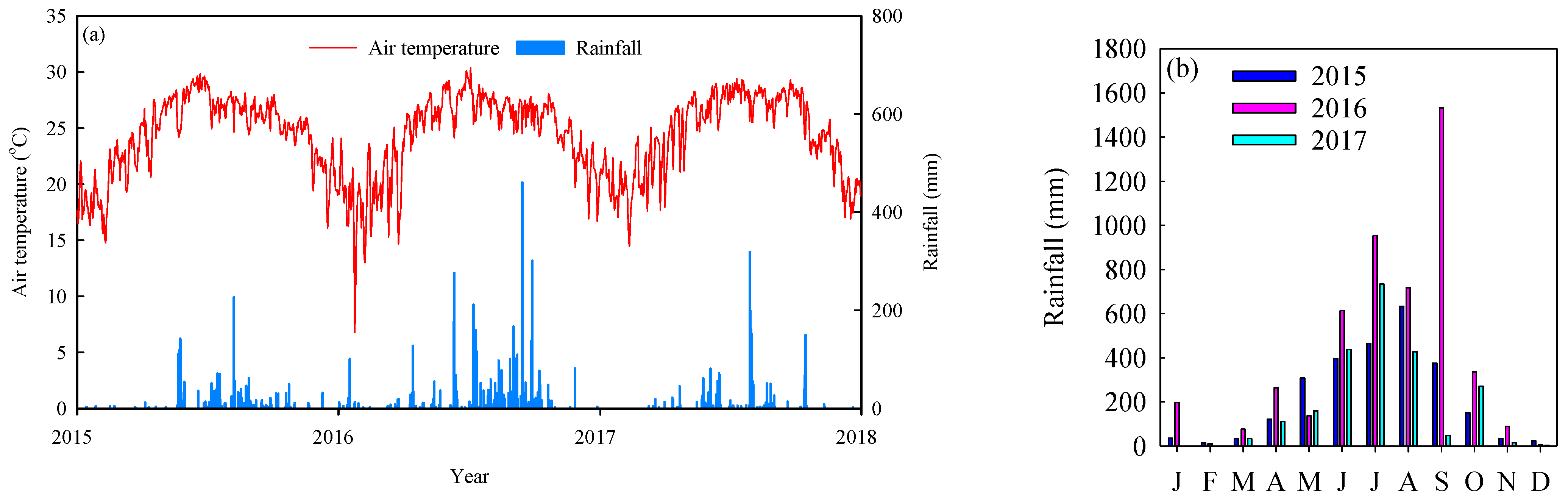
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Plot Inventory
2.3. Soil Respiration Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
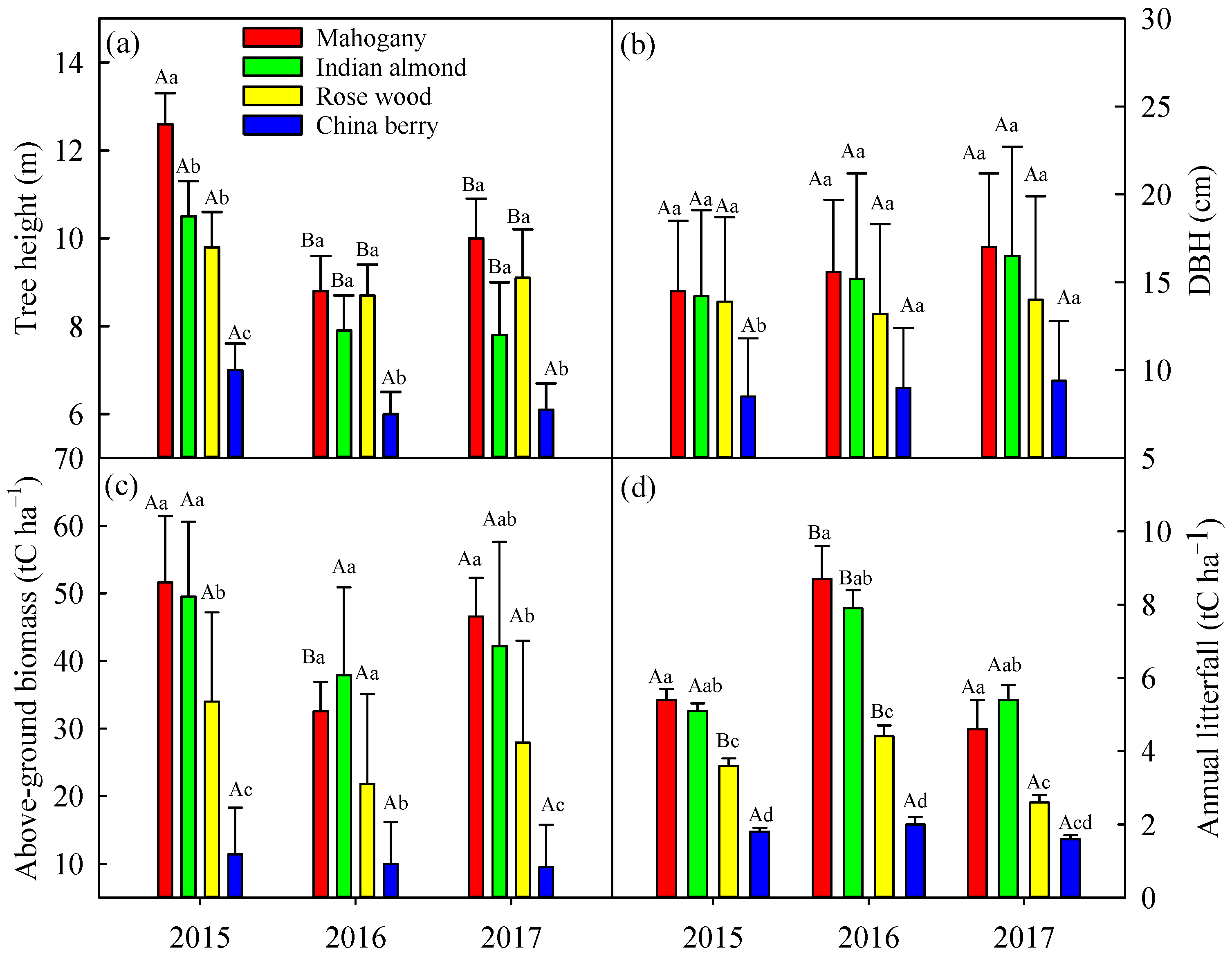
3.1. Change in the Inventory of the Four Tree Species before and after Typhoon Disturbances
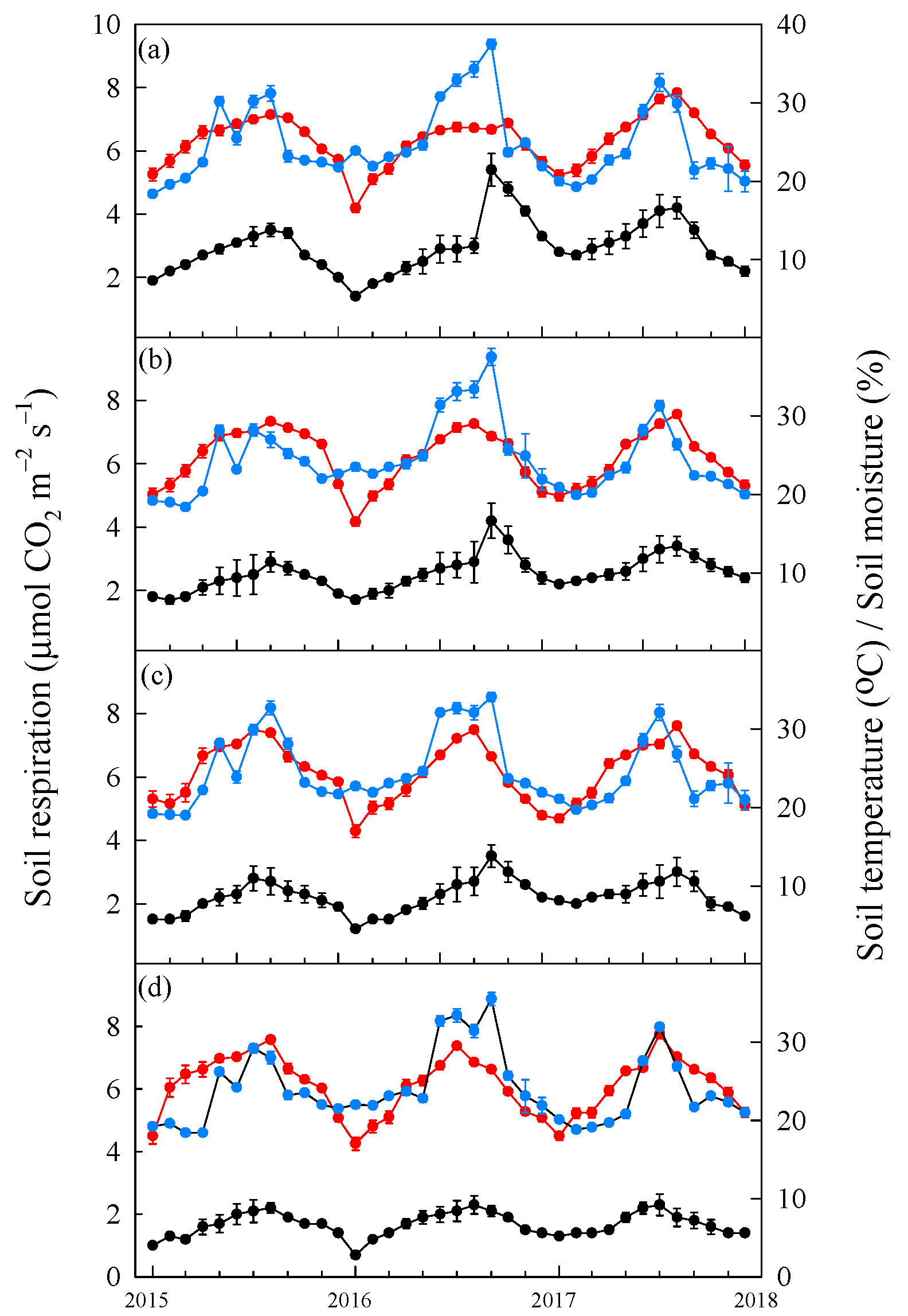
3.2. Change in Soil Respiration, Soil Temperature and Volumetric Soil Moisture before and after Typhoon Disturbances
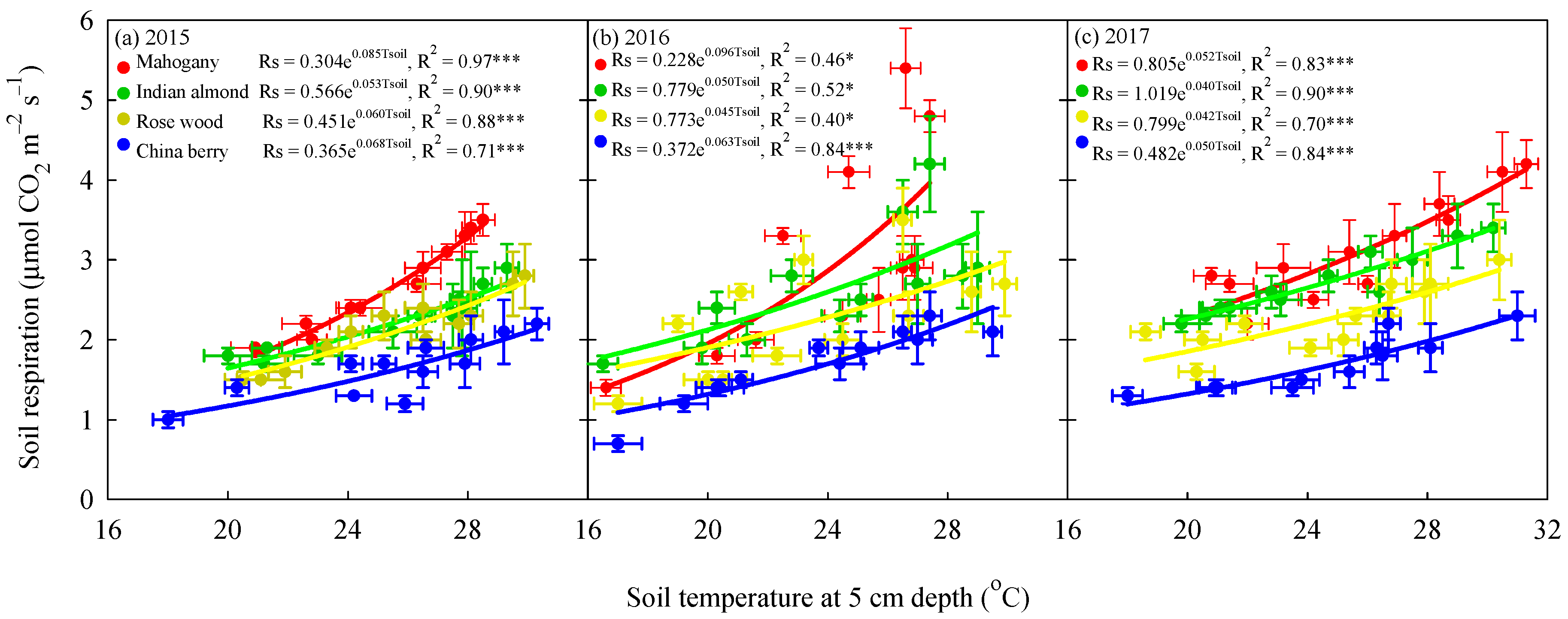
3.3. Variation in Rs with Soil Temperature, Temperature Sensitivity and Soil Moisture
3.4. Relationships between the Annual Litterfall and Annual Rs
4. Discussion
4.1. Typhoon Disturbance Impact on the Aboveground Biomass and Litterfall
4.2. Impact of Typhoon Disturbances on the Soil Temperature, Soil Moisture and Rs Response of the Four Tree Species at the Afforested Sites
4.3. Response of Aboveground Biomass Increment, Litterfall and Rs to Typhoon Disturbances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Jackson, R.B.; Collatz, G.J.; Randerson, J.T. CO2 emissions from forest loss. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global carbon budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3269–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelman, J.C.; Stehfest, E.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Tabeau, A.; Hof, A.F.; Braakhekke, M.C.; Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; van den Berg, M.; van Zeist, W.J.; Daioglou, V.; et al. Afforestation for climate change mitigation: Potentials, risks and trade-offs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.B.; Wu, Y.Q.; Cao, F.L. Afforestation and agroforestry enhance soil nutrient status and carbon sequestration capacity in eastern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastin, J.F.; Finegold, Y.; Garcia, C.; Mollicone, D.; Rezende, M.; Routh, D.; Zohner, C.M.; Crowther, T.W. The global tree restoration potential. Science 2019, 365, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, J.; Engelmann, J.; Cook-Patton, S.C.; Griscom, B.W.; Kroeger, T.; Possingham, H.; Shyamsundar, P. Potential for low-cost carbon dioxide removal through tropical reforestation. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payn, T.; Carnus, J.M.; Freer-Smith, P.; Kimberley, M.; Kollert, W.; Liu, S.R.; Orazio, C.; Rodriguez, L.; Silva, L.N.; Wingfield, M.J. Changes in planted forests and future global implications. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 352, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, P.; Korhonen, J.; Prestemon, J.P.; Cubbage, F.W. Projecting global planted forest area developments and the associated impacts on global forest product markets. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Liang, N.S.; Takahashi, Y.; Zeng, J.Y.; Saigusa, N.; Ide, R.; Zhao, X. Enhanced understory carbon flux components and robustness of net CO2 exchange after thinning in a larch forest in central Japan. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 274, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Liang, N.; Ishida, S.; Zeng, J. Long-term stimulatory warming effect on soil heterotrophic respiration in a cool-temperate broad-leaved deciduous forest in northern Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 2018, 123, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Steele, M.K.; Thomas, R.Q.; Day, S.D.; Hodges, S.C. Constraining estimates of global soil respiration by quantifying sources of variability. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4143–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.E.; Kelliher, F.M.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Anthoni, P.M.; Irvine, J.; Moore, D.; Van Tuyl, S. Spatial and temporal variation in respiration in a young ponderosa pine forests during a summer drought. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 110, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.S.; Teramoto, M.; Takagi, M.; Zeng, J.Y. Data descriptor: High-resolution data on the impact of warming on soil CO2 efflux from an Asian monsoon forest. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Liang, N.S.; Zeng, J.Y.; Saigusa, N.; Takahashi, Y. Long-term chamber measurements reveal strong impacts of soil temperature on seasonal and inter-annual variation in understory CO2 fluxes in a Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi Sarg.) forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Chiang, P.N.; Lai, Y.J.; Tsai, M.J.; Wang, Y.N. High rainfall inhibited soil respiration in an Asian monsoon forest in Taiwan. Forests 2021, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ren, C.J.; Feng, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Doughty, R.; Zhao, F.Z. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition due to shifts in soil extracellular enzymes after afforestation. Geoderma 2020, 374, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.X.; De Boeck, H.J.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.S.N.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Seasonal variations in the response of soil respiration to rainfall events in a riparian poplar plantation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.D.; Zhao, Y.; Harrison, R.D.; Monkai, J.; Li, Y.; Chau, K.; Xu, J. Soil respiration in sloping rubber plantations and tropical natural forests in Xishuangbanna, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Goldberg, S.D.; Xu, J.C.; Harrison, R.D. Spatial and seasonal variation in soil respiration along a slope in a rubber plantation and a natural forest in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Alonso, M.J.; Diaz-Pines, E.; Ortiz, C.; Rubio, A. Disentangling the effects of tree species and microclimate on heterotrophic and autotrophic soil respiration in a Mediterranean ecotone forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 430, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pinés, E.; Schindlbacher, A.; Godino, M.; Kitzler, B.; Jandl, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Rubio, A. Effects of tree species composition on the CO2 and N2O efflux of a Mediterranean mountain forest soil. Plant. Soil 2014, 384, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Liang, N.S.; Takagi, M.; Zeng, J.Y.; Grace, J. Sustained acceleration of soil carbon decomposition observed in a 6-year warming experiment in a warm-temperate forest in southern Japan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Y.; Xia, H.P.; Fu, S.L.; Eisenhauer, N. Tree diversity regulates soil respiration through accelerated tree growth in a mesocosm experiment. Pedobiologia 2017, 65, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.; Fu, S.L.; Li, Z.; Xia, H.P.; Zhou, L.X. Temperature sensitivity of total soil respiration and its heterotrophic and autotrophic components in six vegetation types of subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Lin, I.R.; Kume, T.; Menyailo, O.V.; Cheng, C.H. Soil respiration patterns and rates at three Taiwanese forest plantations: Dependence on elevation, temperature, precipitation, and litterfall. Bot. Stud. 2017, 58, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.X.; Liu, T.X.; Lu, X.X.; Duan, L.M.; Singh, V.P.; Ma, L.Q. Effect of litter on soil respiration in a man-made Populus L. forest in a dune-meadow transitional region in China’s Horqin sandy land. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuille, A.; Buchmann, N.; Schulze, E.D. Carbon stocks and soil respiration rates during deforestation, grassland use and subsequent Norway spruce afforestation in the Southern Alps, Italy. Tree Physiol. 2000, 20, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Hamburg, S.P.; Lin, K.C.; Wang, L.J.; Chang, C.T.; Hsia, Y.J.; Vadeboncoeur, M.A.; McMullen, C.M.M.; Liu, C.P. Typhoon disturbance and forest dynamics: Lessons from a northwest pacific subtropical forest. Ecosystems 2011, 14, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.H.; Guan, B.T.; Chang-Yang, C.H.; Sun, I.F.; Wang, H.H.; Hsieh, C.F. Multi-stemming and size enhance survival of dominant tree species in a frequently typhoon-disturbed forest. J. Veg. Sci. 2020, 31, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Lin, T.C. Forests affected by frequent and intense typhoons challenge the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Biotropica 2019, 51, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Meehl, G.A.; Parmesan, C.; Changnon, S.A.; Karl, T.R.; Mearns, L.O. Climate extremes: Observations, modeling, and impacts. Science 2000, 289, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichstein, M.; Bahn, M.; Ciais, P.; Frank, D.; Mahecha, M.D.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Zscheischler, J.; Beer, C.; Buchmann, N.; Frank, D.C.; et al. Climate extremes and the carbon cycle. Nature 2013, 500, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.C.; Hamburg, S.P.; Wang, L.X.; Duh, C.T.; Huang, C.M.; Chang, C.T.; Lin, T.C. Impacts of increasing typhoons on the structure and function of a subtropical forest: Reflections of a changing climate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, S.F.; Lin, K.C.; Shaner, P.J.; Lin, T.C. Litterfall and element fluxes in a natural hardwood forest and a Chinese-fir plantation experiencing frequent typhoon disturbance in central Taiwan. Biotropica 2013, 45, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Q.; Mo, Q.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Li, Y.W.; Li, Y.X.; Zou, B.; Xia, H.P.; Jun, W.; Li, Z.A.; Wang, F.M. Effects of seasonal precipitation change on soil respiration processes in a seasonally dry tropical forest. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H. Typhoons affecting Taiwan: Current understanding and future challenges. Bulletin Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, N. The development of the use of interflow water in the barren land/l creation process of Wan-long farm of Taiwan sugar Co., Ltd. Irrig. Taiwan 1936, 6, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-I.; Wang, Y.-N.; Lih, H.-W.; Yu, J.-C. Three-year study on diurnal and seasonal CO2 sequestration of a young Fraxinus griffithii plantation in southern Taiwan. Forests 2016, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneke-Fiegenbaum, F.; Santos, S.H.; Klemm, O.; Yu, J.C.; Chiang, P.N.; Lai, Y.J. Carbon dioxide fluxes of a young deciduous afforestation under the influence of seasonal precipitation patterns and frequent typhoon occurrence. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 2021, 126, e005996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Taylor, J.A. On the Temperature-Dependence of Soil Respiration. Funct. Ecol. 1994, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.W.; Chiang, J.M.; McEwan, R.; Lin, T.C. The effect of typhoon-related defoliation on the ecology of gap dynamics in a subtropical rain forest of Taiwan. J. Veg. Sci. 2015, 26, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W. Temporal Variability of soil respiration in experimental tree plantations in lowland Costa Rica. Forests 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon-dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus B 1992, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendenmann, L.; Veldkamp, E.; Brenes, T.; O’Brien, J.J.; Mackensen, J. Spatial and temporal variation in soil CO2 efflux in an old-growth neotropical rain forest, La Selva, Costa Rica. Biogeochemistry 2003, 64, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Chu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hui, D. Changing rainfall frequency rather than drought rapidly alters annual soil respiration in a tropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Baishya, R. Interactive effects of soil moisture and temperature on soil respiration under native and non-native tree species in semi-arid forest of Delhi, India. Trop. Ecol. 2019, 60, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechet, L.M.; Lopez-Sangil, L.; George, C.; Birkett, A.J.; Baxendale, C.; Castro Trujillo, B.; Sayer, E.J. Distinct responses of soil respiration to experimental litter manipulation in temperate woodland and tropical forest. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 3787–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machmuller, M.B.; Ballantyne, F.; Markewitz, D.; Thompson, A.; Wurzburger, N.; Frankson, P.T.; Mohan, J.E. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in a low-latitude forest ecosystem varies by season and habitat but is unaffected by experimental warming. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Bekku, Y.S.; Konuma, A.; Kadir, W.R.; Okuda, T.; Koizumi, H. Required sample size for estimating soil respiration rates in large areas of two tropical forests and of two types of plantation in Malaysia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 210, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Chaudhry, S. Dependency of rate of soil respiration on soil parameters and climatic factors in different tree plantations at Kurukshetra, India. Trop. Ecol. 2017, 58, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Barbhuiya, A.R.; Arunachalam, A.; Nath, P.C.; Khan, M.L.; Arunachalam, K. Leaf litter decomposition of dominant tree species of Namdapha National Park, Arunachal Pradesh, northeast India. J. For. Res. 2008, 13, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Bird, M.I. Temperature sensitivity of tropical forest soil respiration increase along an altitudinal gradient with ongoing decomposition. Geoderma 2012, 187–188, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Davies, K.; Zimmermann, V.; Bird, M. Impact of temperature and moisture on heterotrophic soil respiration along a moist tropical forest gradient in Australia. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Hirano, T.; Liang, N.S.; Hirata, R.; Fujinuma, Y. Carbon dioxide exchange of a larch forest after a typhoon disturbance. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.H.; McEwan, R.W.; Chang, C.T.; Zheng, C.Y.; Yang, Z.J.; Chiang, J.M.; Lin, T.C. Typhoon disturbance mediates elevational patterns of forest structure, but not species diversity, in humid monsoon Asia. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréchet, L.; Ponton, S.; Roy, J.; Freycon, V.; Coûteaux, M.-M.; Bonal, D.; Epron, D. Do tree species characteristics influence soil respiration in tropical forests? A test based on 16 tree species planted in monospecific plots. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
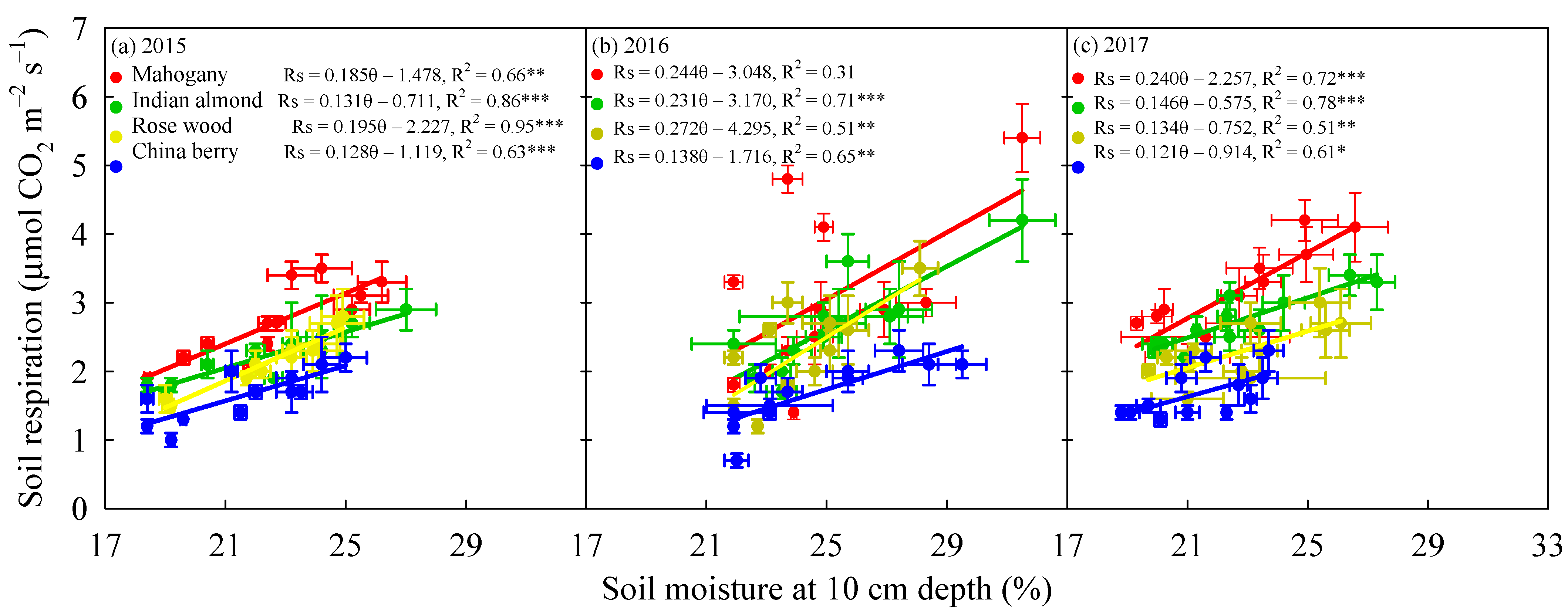
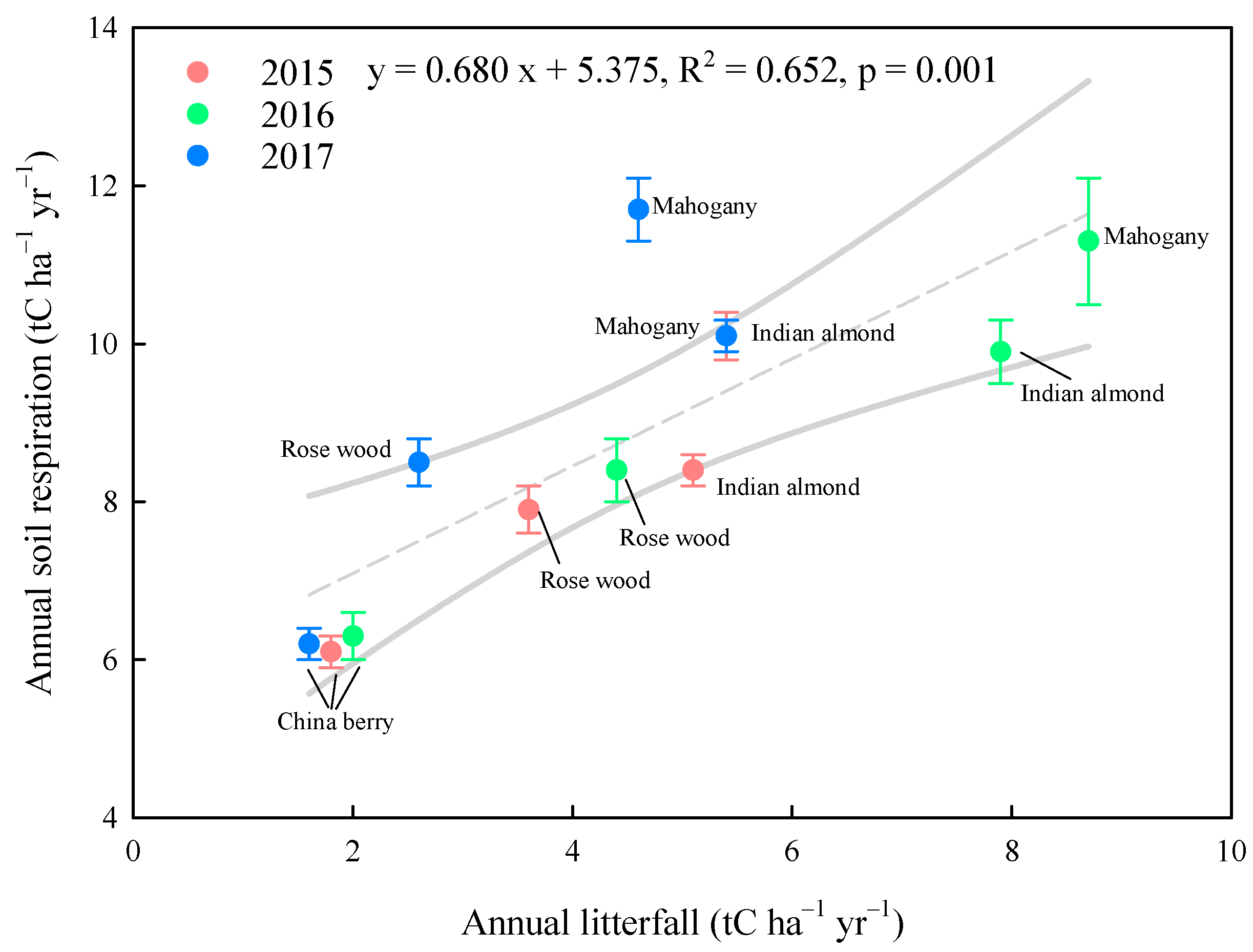
| Year | Annual Mean Soil Temperature (°C) | Annual Mean Volumetric Soil Moisture (%) | Annual Mean Soil Respiration (tC ha−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Mahogany | 24.5 ± 2.8 Aa | 24.2 ± 3.3 Aa | 25.7 ± 3.5 Aa | 22.5 ± 2.3 Ba | 24.9 ± 2.8 Aa | 22.5 ± 2.2 Ba | 9.1 ± 0.6 Aa | 11.3 ± 1.2 Ba | 11.7 ± 0.6 Ba |
| Indian almond | 24.8 ± 3.5 Aa | 24.1 ± 3.9 Aa | 24.4 ± 3.5 Aa | 23.3 ± 2.4 Ba | 25.2 ± 2.6 Aa | 22.6 ± 2.4 Ba | 8.1 ± 0.5 Aab | 9.9 ± 0.7 Ba | 10.1 ± 0.4 Bab |
| Rose wood | 24.5 ± 3.8 Aa | 23.3 ± 4.0 Aa | 24.7 ± 3.6 Aa | 22.0 ± 2.1 Ba | 24.1 ± 1.8 Aa | 22.7 ± 2.1 Ba | 7.5 ± 0.5 Ab | 8.4 ± 0.7 Aab | 8.5 ± 0.4 Ab |
| China berry | 24.7 ± 3.4 Aa | 23.5 ± 3.8 Aa | 24.4 ± 3.7 Aa | 21.7 ± 2.1 Ba | 24.6 ± 2.7 Aa | 21.4 ± 1.7 Ba | 5.9 ± 0.4 Ac | 6.3 ± 0.5 Ab | 6.2 ± 0.3 Ac |
| Year | Annual Mean Soil Temperature (°C) | Annual Mean Volumetric Soil Moisture (%) | Annual Mean Soil Respiration (t C ha−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Mahogany | 0.984 ± 0.061 | 1.047 ± 0.041 *** | 1.112 ± 0.103 ** | 1.003 ± 0.032 | 1.242 ± 0.405 * | 1.310 ± 0.192 *** |
| Indian almond | 0.967 ± 0.047 * | 0.984 ± 0.032 | 1.131 ± 0.085 *** | 1.011 ± 0.047 | 1.231 ± 0.241 ** | 1.272 ± 0.096 *** |
| Rose wood | 0.948 ± 0.048 ** | 1.007 ± 0.048 | 1.098 ± 0.058 *** | 1.035 ± 0.044 * | 1.107 ± 0.232 | 1.152 ± 0.178 ** |
| China berry | 0.948 ± 0.047 *** | 0.985 ± 0.040 | 1.132 ± 0.06 *** | 0.985 ± 0.053 | 1.051 ± 0.127 | 1.066 ± 0.104 * |
| Species | Q10 Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Mahongany | 2.34 Aa | 2.61 Aa | 1.68 Ba |
| Indian almond | 1.70 Ab | 1.65 ABb | 1.49 Bb |
| Rose wood | 1.82 Ab | 1.57 Bb | 1.52 Bb |
| China berry | 1.79 ABb | 1.88 Ab | 1.65 Bac |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiang, P.-N.; Yu, J.-C.; Lai, Y.-J. Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences. Forests 2021, 12, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060787
Chiang P-N, Yu J-C, Lai Y-J. Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences. Forests. 2021; 12(6):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060787
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiang, Po-Neng, Jui-Chu Yu, and Yen-Jen Lai. 2021. "Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences" Forests 12, no. 6: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060787
APA StyleChiang, P.-N., Yu, J.-C., & Lai, Y.-J. (2021). Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences. Forests, 12(6), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12060787






