Impregnation of Wood with Waste Engine Oil to Increase Water- and Bio-Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Wood Impregnation Using Spent Engine Oil
2.3. Measuring Weight Gain as a Percentage (WPG)
2.4. Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability
2.5. Moisture Absorption
2.6. Anti-Swelling Efficiency (ASE)
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.8. Determination of the Contact Angle
2.9. IR Spectroscopic Studies
2.10. Biodegradation Resistance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Measurements of Weight Percent Gain (WPG)
3.2. Dimensional Stability and Water Resistance of Wood
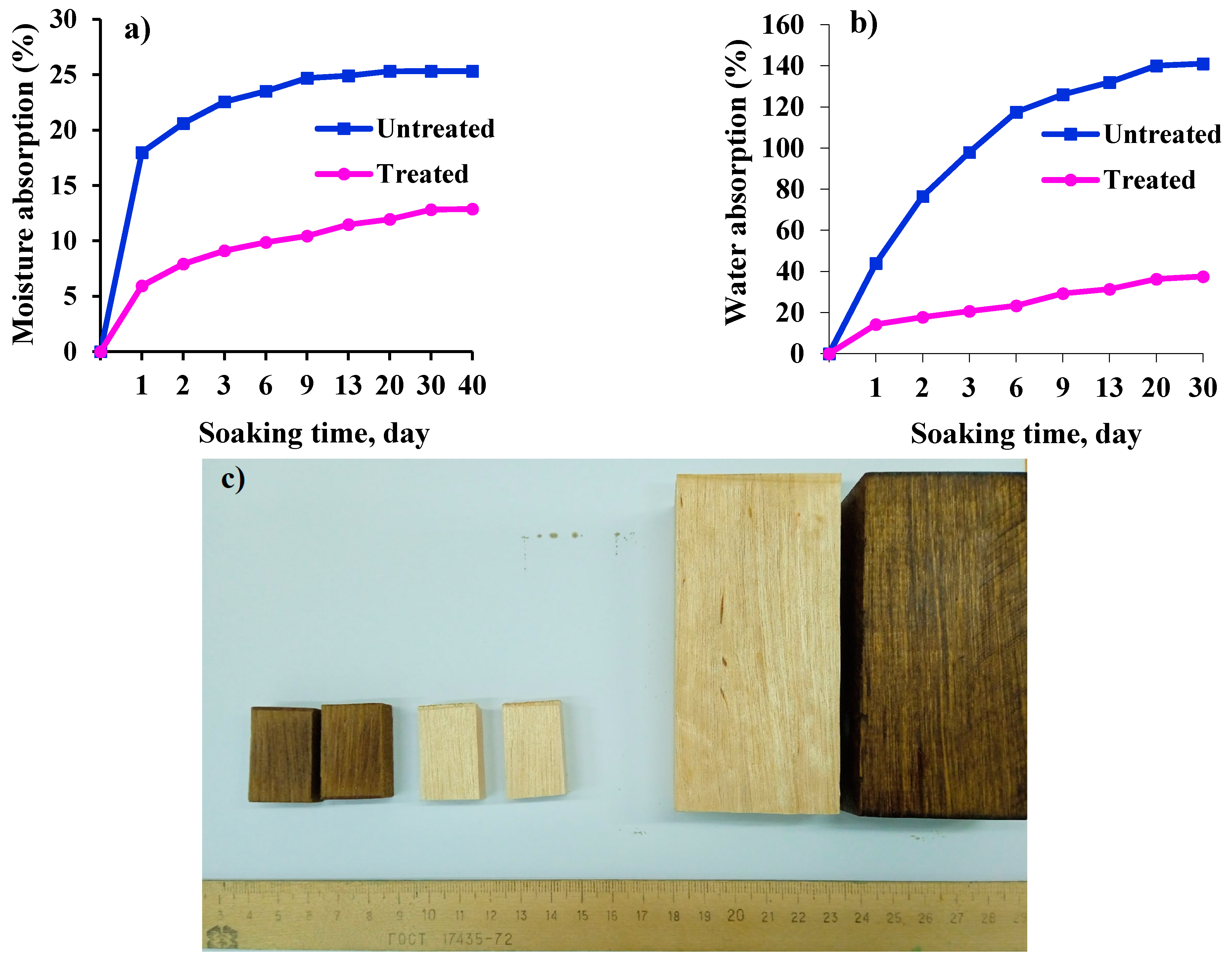
3.2.1. Water and Moisture Absorption
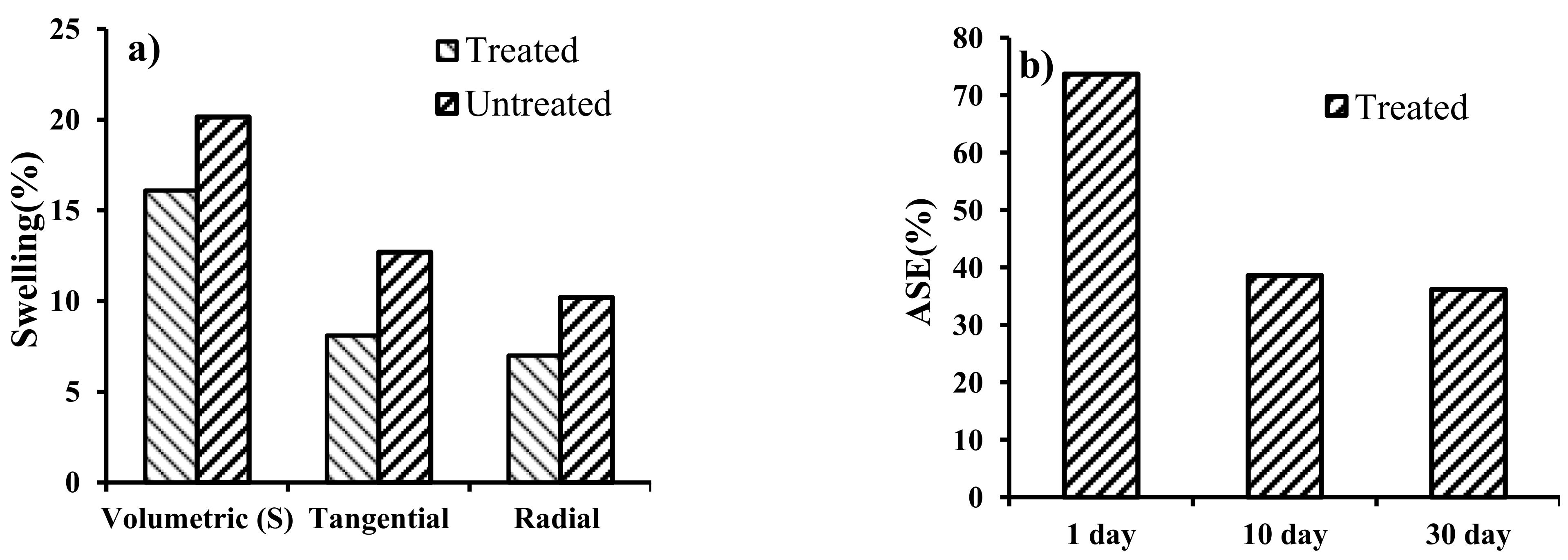
3.2.2. Swelling and Anti-Swelling Efficiency
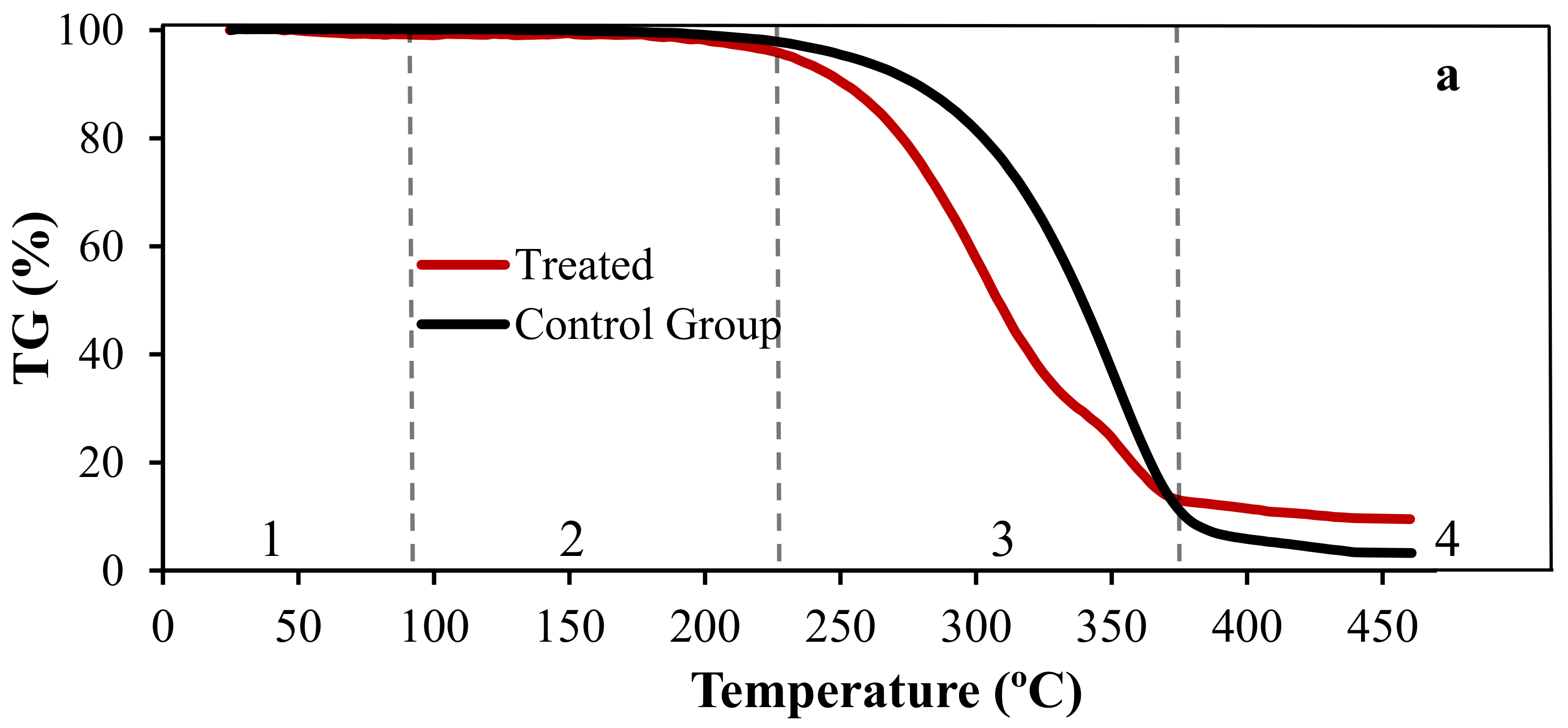
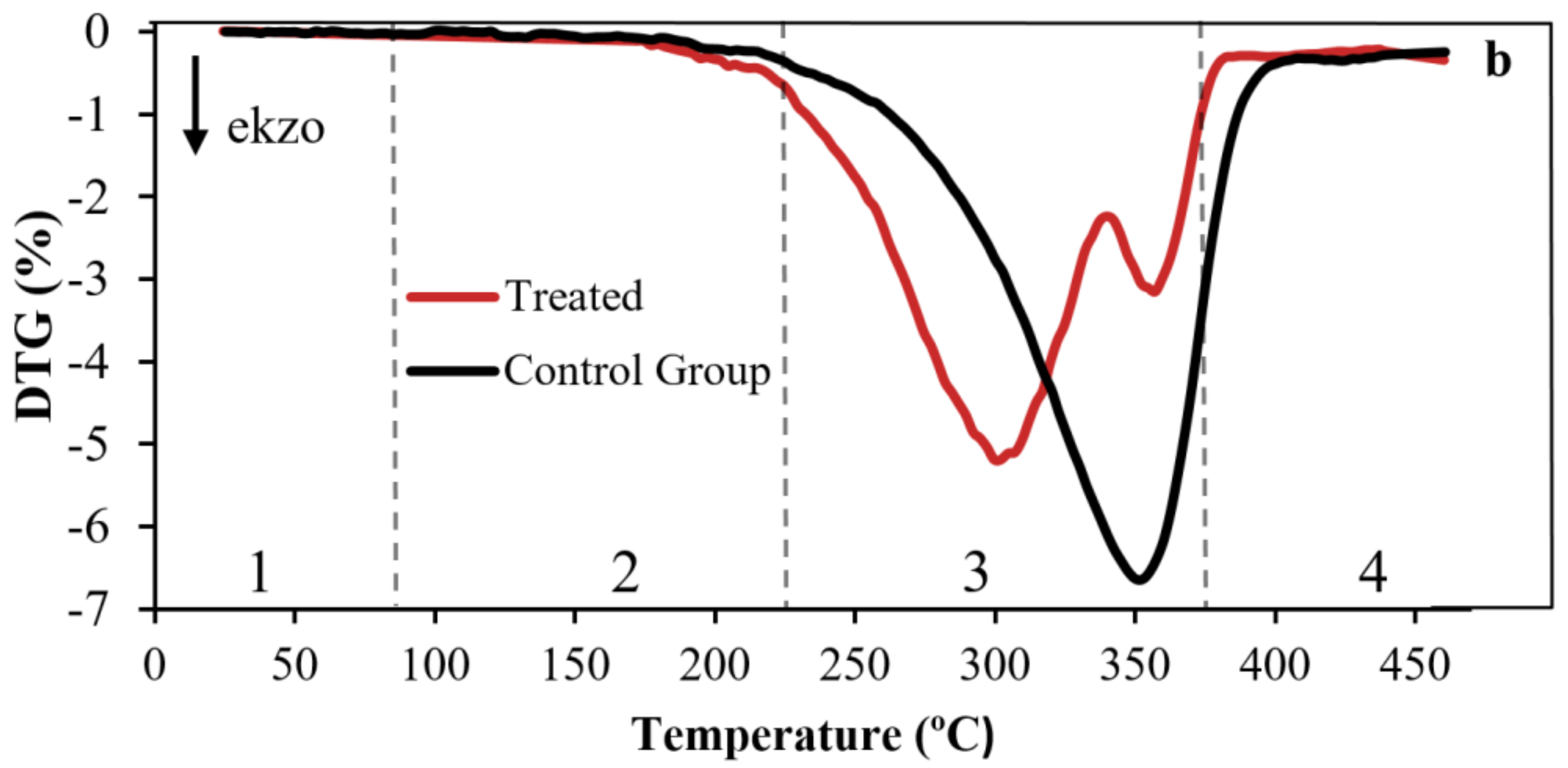
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.4. Angle of Contact
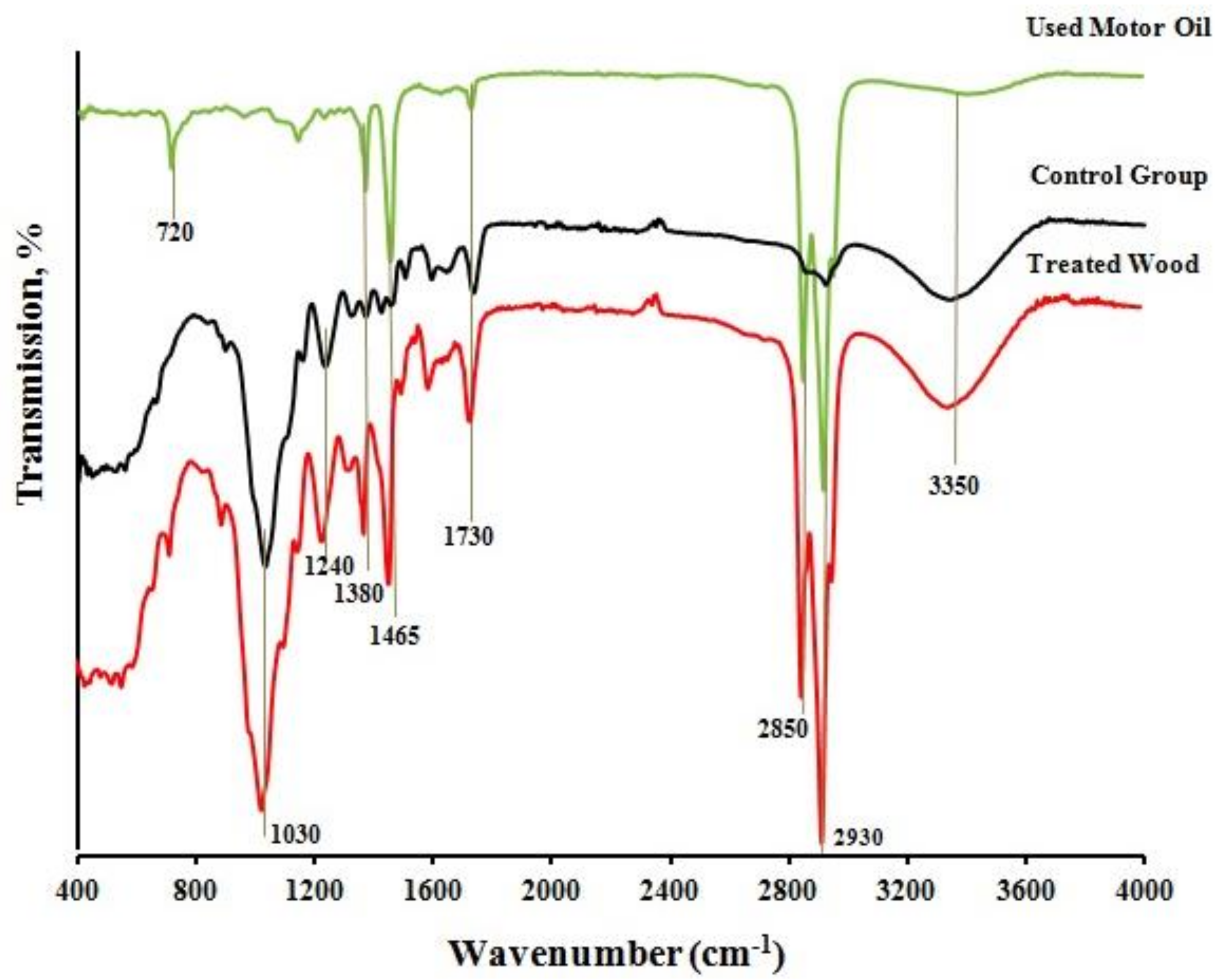
3.5. Investigation of Possibility of Intermolecular Interaction Formation (Method of IR-Fourier Spectroscopy) during Wood Impregnation
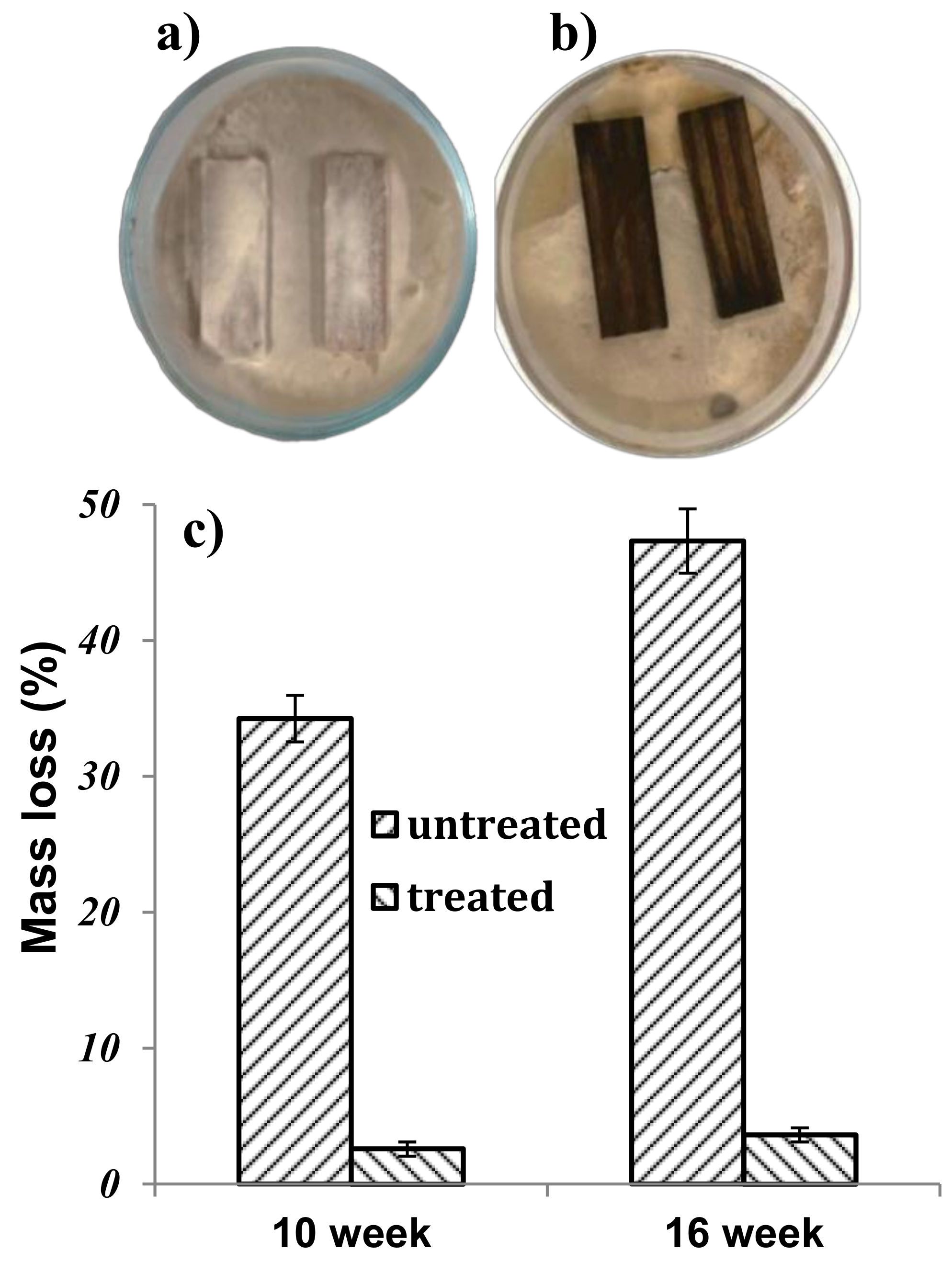
3.6. Biodurability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowell, R.; Pettersen, R.; Tshabalala, M. Cell Wall Chemistry. In Handbook of Wood Chemistry and Wood Composites, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Tokyo, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C.-M.; Popescu, M.-C. A near Infrared Spectroscopic Study of the Structural Modifications of Lime (Tilia Cordata Mill.) Wood during Hydro-Thermal Treatment. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkut, D.S.; Hiziroglu, S. Experimental Test of Heat Treatment Effect on Physical Properties of Red Oak (Quercus Falcate Michx.) and Southern Pine (Pinus Taeda L.). Materials 2014, 7, 7314–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okon, K.E.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B. Effect of Silicone Oil Heat Treatment on the Chemical Composition, Cellulose Crystalline Structure and Contact Angle of Chinese Parasol Wood. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, H.; Ren, D.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y. Wood Modification with Furfuryl Alcohol Catalysed by a New Composite Acidic Catalyst. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemsiri, P.; Hiziroglu, S.; Rimdusit, S. Characterization of Heat Treated Eastern Redcedar (Juniperus Virginiana L.). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, R.; Jiang, J. Increased Dimensional Stability of Chinese Fir through Steam-Heat Treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2012, 70, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of Peeling and Steam-Heating Treatment on Mechanical Properties and Dimensional Stability of Oriented Phyllostachys Makinoi and Phyllostachys Pubescens Scrimber Boards. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, C.; Altgen, M.; Rautkari, L. Thermal Modification of Wood—A Review: Chemical Changes and Hygroscopicity. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.; Mazela, B. Application of Methyltrimethoxysilane to Increase Dimensional Stability of Waterlogged Wood. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 25, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinprecht, L.; Vacek, V.; Grznárik, T. Enhanced Fungal Resistance of Scots Pine (Pinus Sylvestris L.) Sapwood by Treatment with Methyltrimethoxysilane and Benzalkoniumchloride. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Xiao, Z.; Che, W.; Trinh, H.M.; Xie, Y. Effects of Modification with a Combination of Styrene-Acrylic Copolymer Dispersion and Sodium Silicate on the Mechanical Properties of Wood. J. Wood Sci. 2019, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowsky, D. Influence of the Formaldehyde Content of Waterbased Melamine Formaldehyde Resins on Physical Properties of Scots Pine Impregnated Therewith. Holz Als Roh-Und Werkst. 2002, 60, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, H.; Furuno, T.; Imamura, Y. The Modification of Wood by Treatment with Low Molecular Weight Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin: A Properties Enhancement with Neutralized Phenolic-Resin and Resin Penetration into Wood Cell Walls. Wood Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N. Combined Effects of Boron and Compatibilizer on Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Properties of Wood/HDPE Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, K.B.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood–Plastic Composites Based on Recycled and Virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, C.A.; Alfieri, P.V.; Canosa, G. Decay Resistance and Dimensional Stability of Araucaria Angustifolia Using Siloxanes Synthesized by Sol–Gel Process. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 83, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, A.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Weathering Characteristics of Wood Treated with Water Glass, Siloxane or DMDHEU. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2012, 70, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candan, Z.; Korkut, S.; Unsal, O. Effect of Thermal Modification by Hot Pressing on Performance Properties of Paulownia Wood Boards. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 45, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaefe, D.; Huang, X.; Kocaefe, Y. Dimensional Stabilization of Wood. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesar, B.; Straže, A.; Humar, M. Sorption Properties of Wood Impregnated with Aqueous Solution of Boric Acid and Montan Wax Emulsion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varganici, C.-D.; Rosu, L.; Rosu, D.; Mustata, F.; Rusu, T. Sustainable Wood Coatings Made of Epoxidized Vegetable Oils for Ultraviolet Protection. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Morén, T.; Sehlstedt-Persson, M.; Blom, Å. Effect of Oil Impregnation on Water Repellency, Dimensional Stability and Mold Susceptibility of Thermally Modified European Aspen and Downy Birch Wood. J. Wood Sci. 2017, 63, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dündar, T.; Büyüksarı, Ü.; Avcı, E.; Akkılıç, H. Effect of heat treament on the physical and mechanical properties of compression and opposite wood of black pine. BioResources 2012, 7, 5009–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteves, B.; Videira, R.; Pereira, H. Chemistry and Ecotoxicity of Heat-Treated Pine Wood Extractives. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.G.; Luxton, T.P.; Rygiewicz, P.T.; Reichman, J.R.; Bollman, M.A.; King, G.A.; Storm, M.J.; Nash, M.S.; Andersen, C.P. Transformation and Release of Micronized Cu Used as a Wood Preservative in Treated Wood in Wetland Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebisch, R.; Karmann, J.; Schäferhenrich, A.; Göen, T.; Berger, M.; Poppek, U.; Roitzsch, M. Inhalation and Dermal Exposure of Workers during Timber Impregnation with Creosote and Subsequent Processing of Impregnated Wood. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolmatov, L.V.; Akhmetov, A.F.; Kutukov, I.E. Aggregative Stability and Thermal Stability of the Petroleum-Based Biocide ZhTK. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2001, 37, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnisa, S.A.; Hassanpour, M. Development Circumstances of Four Recycling Industries (Used Motor Oil, Acidic Sludge, Plastic Wastes and Blown Bitumen) in the World. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animpong, M.A.B.; Oduro, W.O.; Koranteng, J.; Ampomah-Benefo, K.; Boafo-Mensah, G.; Akufo-Kumi, K.; Tottimeh, G.O.; Amoah, J.Y. Coupling Effect of Waste Automotive Engine Oil in the Preparation of Wood Reinforced LDPE Plastic Composites for Panels. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 24, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belchinskaya, L.; Zhuzhukin, K.; Dmitrenkov, A.; Roessner, F. Studying and Imparting Moisture Absorption Qualities of the New Wood Based Bio-Composite Material. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.J.; Fei, B.H.; Lv, J.X.; Yu, H.Q.; Huang, R.F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Huang, A.M.; Cui, Y.Z. Wood Moisture Content Measuring Method. Wood—Determination of Moisture Content for Physical and Mechanical Test. MOD CN-GB GB/T. 2009. Available online: https://wenku.baidu.com/view/df6e7b14d35abe23482fb4daa58da0116d171feb.html (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Cheremisinoff, N.P.; Rosenfeld, P.E. Wood-Preserving Technology. In Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Betts, W.D. The Properties and Performance of Coal-Tar Creosote as a Wood Preservative. In The Chemistry of Wood Preservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 136–160. [Google Scholar]
- Baar, J.; Brabec, M.; Slávik, R.; Čermák, P. Effect of Hemp Oil Impregnation and Thermal Modification on European Beech Wood Properties. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesar, B.; Humar, M. Use of Wax Emulsions for Improvement of Wood Durability and Sorption Properties. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 69, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, M.; Hai, Y. Individualization of Cellulose Nanofibers from Wood Using High-Intensity Ultrasonication Combined with Chemical Pretreatments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Colin, B.; Pétrissans, A.; Quirino, R.L.; Pétrissans, M. Thermodegradation Characterization of Hardwoods and Softwoods in Torrefaction and Transition Zone between Torrefaction and Pyrolysis. Fuel 2022, 310, 122281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-J.; Colin, B.; Chen, W.-H.; Pétrissans, A.; Rousset, P.; Pétrissans, M. Thermal Degradation and Compositional Changes of Wood Treated in a Semi-Industrial Scale Reactor in Vacuum. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelier, K.; Chaouch, M.; Dumarçay, S.; Pétrissans, A.; Pétrissans, M.; Gérardin, P. Utilization of Thermodesorption Coupled to GC–MS to Study Stability of Different Wood Species to Thermodegradation. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 92, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastouri, A.; Efhamisisi, D.; Shirmohammadli, Y.; Oladi, R. Physicochemical Properties of Thermally Treated Poplar Wood in Silicone and Rapeseed Oils: A Comparative Study. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétrissans, A.; Younsi, R.; Chaouch, M.; Gérardin, P.; Pétrissans, M. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Wood Thermodegradation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, J.; de Jong, W.; Arvelakis, S.; Spliethoff, H.; Verkooijen, A.H.M. Quantitative and Kinetic TG-FTIR Study of Biomass Residue Pyrolysis: Dry Distiller’s Grains with Solubles (DDGS) and Chicken Manure. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kumari, U.; Turlapati, V.Y.; Siddiqi, H.; Meikap, B.C. Extensive Thermogravimetric and Thermo-Kinetic Study of Waste Motor Oil Based on Iso-Conversional Methods. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rossi, S.; Morin, H.; Bettero, A. Within-Tree Variations in the Surface Free Energy of Wood Assessed by Contact Angle Analysis. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, A.; Barboutis, I. Changes Caused by Heat Treatment in Color and Dimensional Stability of Beech (Fagus Sylvatica L.) Wood. Drv. Ind. 2014, 65, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelund, E.T.; Thygesen, L.G.; Svensson, S.; Hill, C.A.S. A Critical Discussion of the Physics of Wood–Water Interactions. Wood Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altgen, M.; Willems, W.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Rautkari, L. Hydroxyl Accessibility and Dimensional Changes of Scots Pine Sapwood Affected by Alterations in the Cell Wall Ultrastructure during Heat-Treatment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 152, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Z.; Furuno, T.; Katoh, S. Dimensional Stability and Flame Resistance of Silicate-Acetylated and -Propionylated Wood Composites. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2000, 20, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Li, L.; Xi, X.; Tian, M.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B. Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood. Coatings 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Huang, B.; Bowers, B.F.; Zhao, S. Infrared Spectra and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Cement Containing Waste Engine Oil Residues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Peng, A.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.B. Waste Engine Oil Influences on Chemical and Rheological Properties of Different Asphalt Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.; Velez Marques, A.; Domingos, I.; Pereira, H. Chemical Changes of Heat Treated Pine and Eucalypt Wood Monitored by FTIR. Maderas. Cienc. y Tecnol. 2013, 15, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Duan, H.; Jin, Y.; Jia, D.; Cheng, B.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Motor Oil Degradation during Urban Cycle Road Tests. Friction 2021, 9, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Ren, H.; Hao, X.; Song, X.; Liu, Z. A Novel Co-Treatment Scheme for Waste Motor Oil and Low Rank Coal Slime: Waste Dispose Waste. Fuel 2021, 292, 120275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicator | Unit | Test Method | Measured Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinematic viscosity at 40 °C | mm2/s | ASTM D 445 | 82.6 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 100 °C | mm2/s | ASTM D 445 | 13.7 |
| Viscosity index | - | ASTM D 2270 | 170 |
| TBN (Total Base Number) | mg, KOH | ASTM D 4739 | 8.28 |
| TAN (Total Acid Number) | mg, KOH | ASTM D 664 | 2.08 |
| pH | - | ASTM D 664 | 5.8 |
| Water content | IR Units | ASTM E 2412 | <0.1 |
| Colloidal carbon content | 0.1 | ||
| Oxidation product content | 11 | ||
| Oil content | <0.1 | ||
| Content of nitration products | 8 |
| Before Impregnation, g. | After Impregnation, g. | WPG,% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight of the specimen | 2.12 ± 0.14 | 3.36 ± 0.16 | 58.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belchinskaya, L.; Zhuzhukin, K.V.; Ishchenko, T.; Platonov, A. Impregnation of Wood with Waste Engine Oil to Increase Water- and Bio-Resistance. Forests 2021, 12, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12121762
Belchinskaya L, Zhuzhukin KV, Ishchenko T, Platonov A. Impregnation of Wood with Waste Engine Oil to Increase Water- and Bio-Resistance. Forests. 2021; 12(12):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12121762
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelchinskaya, Larisa, Konstantin Viktorovich Zhuzhukin, Tatiana Ishchenko, and Aleksey Platonov. 2021. "Impregnation of Wood with Waste Engine Oil to Increase Water- and Bio-Resistance" Forests 12, no. 12: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12121762
APA StyleBelchinskaya, L., Zhuzhukin, K. V., Ishchenko, T., & Platonov, A. (2021). Impregnation of Wood with Waste Engine Oil to Increase Water- and Bio-Resistance. Forests, 12(12), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12121762







