Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level during the Dedifferentiation and Cellular Competence in Coffea arabica Lines: Insights about the Different In Vitro Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
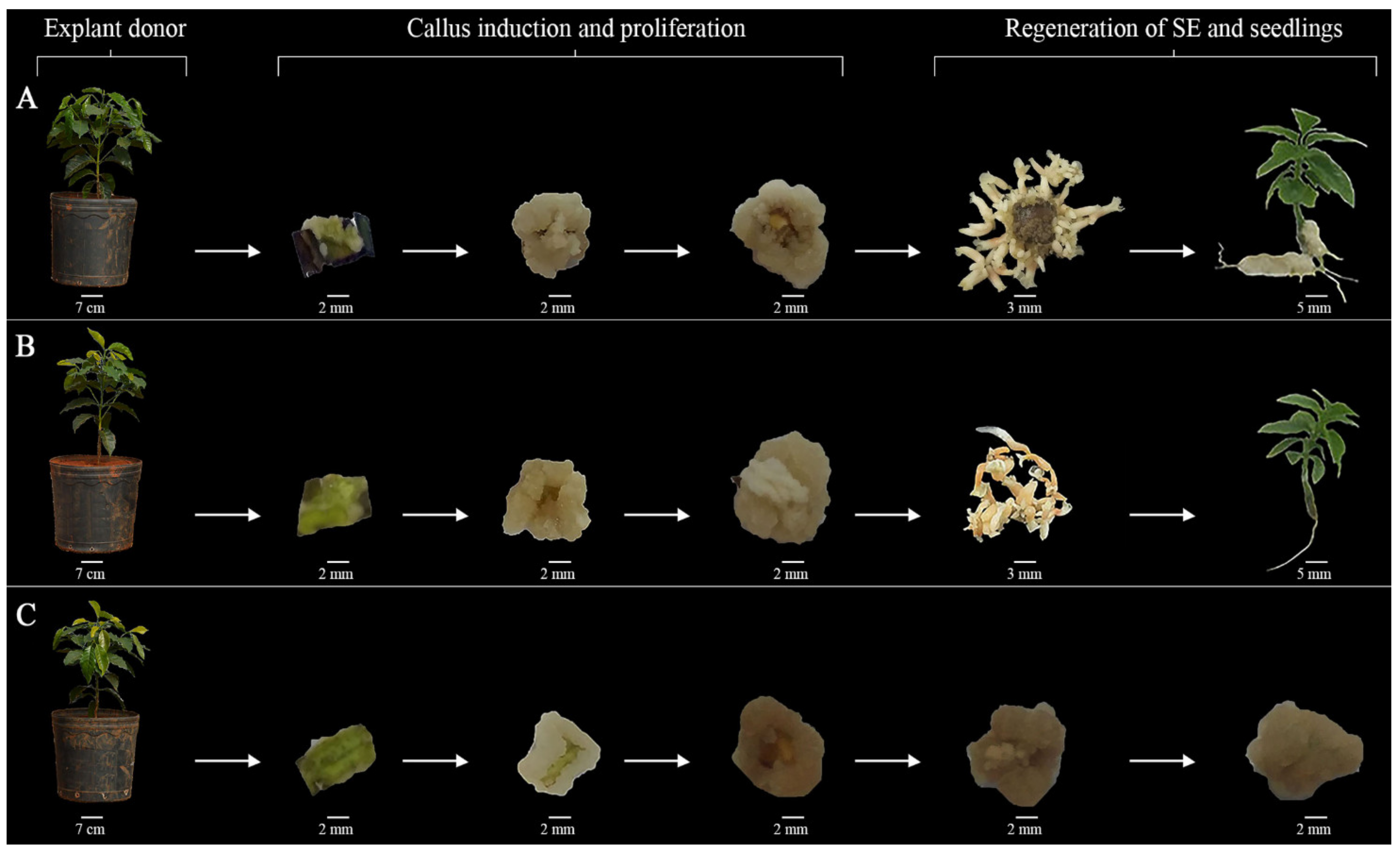
2.1. ISE Establishment
2.2. Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level
2.3. Ploidy Level Stability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
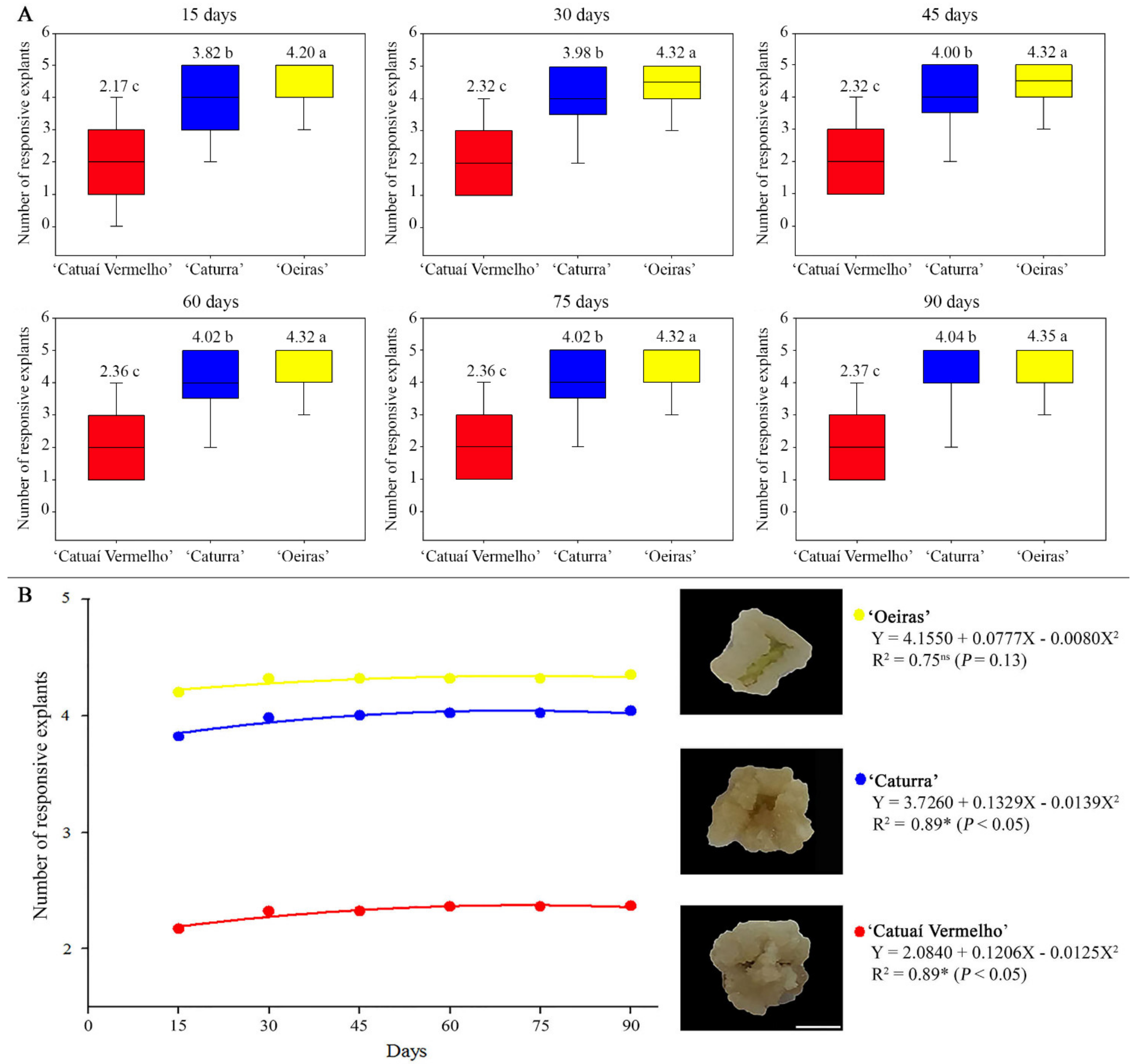
3.1. ISE Establishment
3.2. Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level
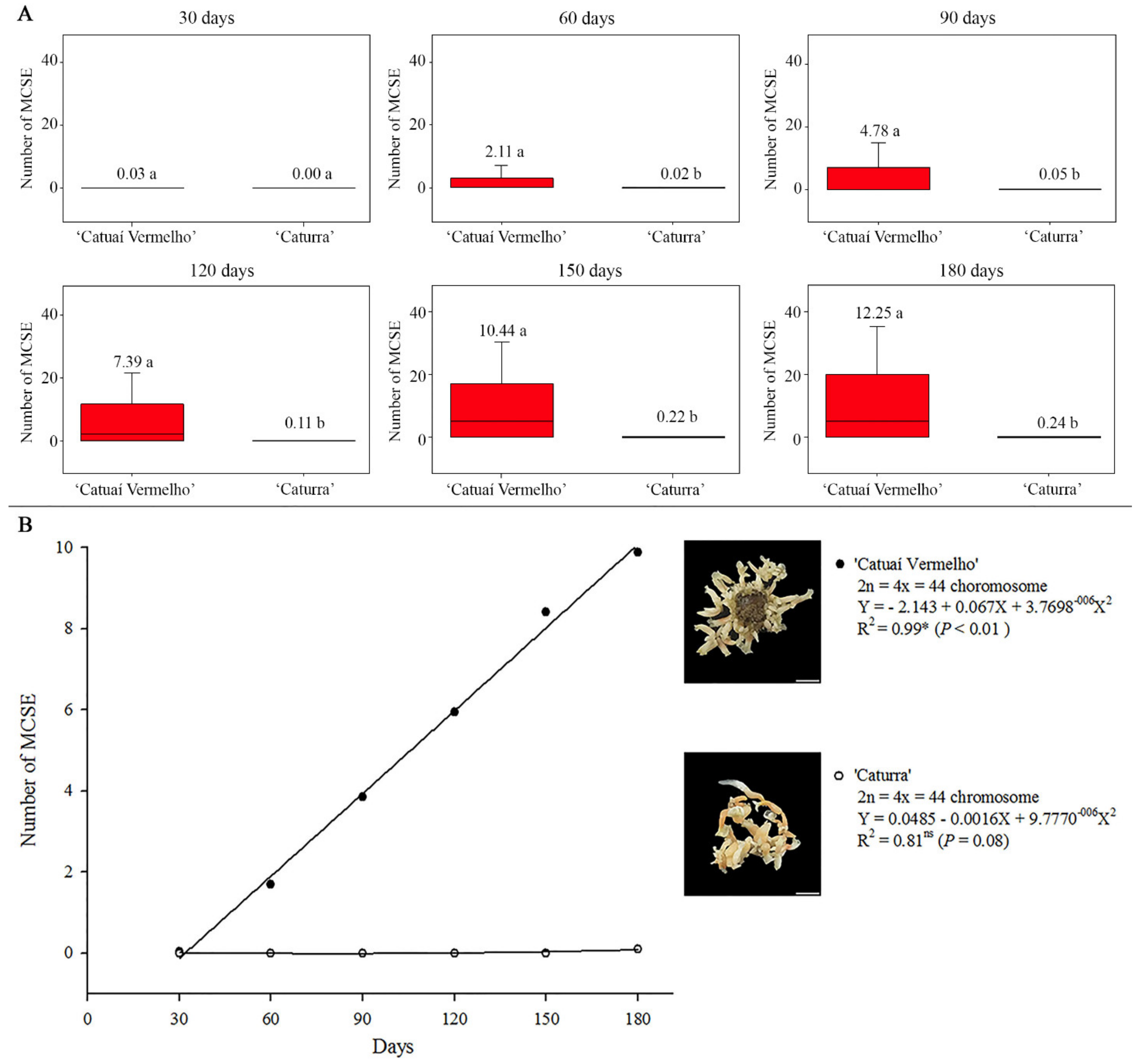
3.3. Ploidy Level Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loyola-vargas, V.M.; Avilez-Montalvo, J.R.; Avilés-Montalvo, R.N.; Marquez-Lopez, R.; Galaz-Avalos, R.; Mellado-Mojica, E. Somatic embryogenesis in Coffea spp. In Somatic Embryogenesis: Fundamental Aspects and Applications; Loyola-Vargas, V.M., Ochoa-Alejo, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 297–318. [Google Scholar]
- Los Santos-Briones, C.D.L.; Hérnandez-Sotomayor, S.M.T. Coffee biotechnology. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 18, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.A.; Panis, B.; Carpentier, S.C. Somatic Embryogenesis in Coffee: The Evolution of Biotechnology and the Integration of Omics Technologies Offer Great Opportunities. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boxtel, J.; Berthouly, M. High frequency somatic embryogenesis from coffee leaves. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 1996, 44, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanglard, N.A.; Amaral-Silva, P.M.; Sattler, M.C.; De Oliveira, S.C.; Cesário, L.M.; Ferreira, A.; Carvalho, C.R.; Clarindo, W.R. Indirect somatic embryogenesis in Coffea with different ploidy levels: A revisiting and updating study. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2018, 136, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.; Luz, J.M.Q.; Rodrigues, T.M.; Bittar, C.A.; Lino, L.D.O. Callus induction and embryo regeneration in Coffea arabica L. anthers by silver nitrate and ethylene. Revista Ciência Agronômica 2011, 42, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanglard, N.A.; Amaral-Silva, P.M.; Sattler, M.C.; De Oliveira, S.C.; Nunes, A.C.P.; Soares, T.C.B.; Carvalho, C.R.; Clarindo, W.R. From chromosome doubling to DNA sequence changes: Outcomes of an improved in vitro procedure developed for allotriploid “Híbrido de Timor” (Coffea arabica L. × Coffea canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2017, 131, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Teyer, L.F.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Loyola-Varga, V.M.; Infante-Herrera, D. Culture-induced variation in plants of Coffea arabica cv. Caturra rojo, regenerated by direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2003, 23, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Slater, A. Recent advances in the genetic transformation of coffee. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 580857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpke, C.; Müller, L.E.; Kohlenbach, H.W. Somatic embryogenesis and regeneration of plantlets in protoplast cultures from somatic embryos of coffee (Coffea canephora P. ex. Fr.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1987, 8, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.L.; Zarowitz, M.A. Stably Transformed Coffee Plant Cells and Plantlets. U.S. Patent No. 5,334,529, 2 August 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowska, B.; Wójcik, A.M.; Gaj, M.D. Epigenetic Regulation of Auxin-Induced Somatic Embryogenesis in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, M.; Baiton, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Pepe, M.; Torkamaneh, D.; Jones, A. Advances and Perspectives in Tissue Culture and Genetic Engineering of Cannabis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.G.; Maheswaran, G. Somatic embryogenesis: Factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 1986, 57, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A.; Pasternak, T.; Dudits, D. Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 74, 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. Somatic embryogenesis—Stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2015, 1849, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic-Can, G.I.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; De-La-Peña, C.; Alcazar-Magaña, A.; Wróbel, K.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Somatic Embryogenesis: Identified Factors that Lead to Embryogenic Repression. A Case of Species of the Same Genus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, N.; González, M.E.; Valcarcel, M.; Cantoflick, A.; Hernandez, M.M.; Fuentes-Cerda, F.J.; Barahona, F.; Mijangos-Cortés, J.; Loyolavargas, V.M. Somatic embryogenesis: A valuable alternative for propagating selected robusta coffee (Coffea canephora) clones. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2004, 40, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychappa, M.; Mishra, M.K.; Jingade, P.; Huded, A.K.C. Genomic alterations in coding region of tissue culture plants of Coffea arabica obtained through somatic embryogenesis revealed by molecular markers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2019, 139, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loschiavo, F.; Pitto, L.; Giuliano, G.; Torti, G.; Nuti-Ronchi, V.; Marazziti, D.; Vergara, R.; Orselli, S.; Terzi, M. DNA methylation of embryogenic carrot cell cultures and its variations as caused by mutation, differentiation, hormones and hypomethylating drugs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1989, 77, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic-Can, G.I.; Lopez-Torres, A.; Barredo-Pool, F.; Wrobel, K.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M.; Herrera, R.A.R.; De-La-Peña, C. New Insights into Somatic Embryogenesis: Leafy Cotyledon1, Baby Boom1 and Wuschel-Related Homeobox4 Are Epigenetically Regulated in Coffea canephora. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Silva, P.M.; Clarindo, W.R.; Guilhen, J.H.S.; Passos, A.B.R.D.J.; Sanglard, N.A.; Ferreira, A. Global 5-methylcytosine and physiological changes are triggers of indirect somatic embryogenesis in Coffea canephora. Protoplasma 2020, 258, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Seo, P.J. Dynamic Epigenetic Changes during Plant Regeneration. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Favero, D.; Sakamoto, Y.; Iwase, A.; Coleman, D.; Rymen, B.; Sugimoto, K. Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Regeneration. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.M.; Sanglard, N.A.; Ferreira, A.; Clarindo, W.R. Ploidy level, epigenetic and in vitro environment influence the indirect somatic embryogenesis of the new synthetic autoallohexaploid Coffea. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2021, 146, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, H.; Bertrand, B. Are Genetic and Epigenetic Instabilities of Plant Embryogenic Cells a Fatality? The Experience of Coffee Somatic Embryogenesis. Hum. Genet. Embryol. 2016, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landey, R.B.; Cenci, A.; Georget, F.; Bertrand, B.; Camayo, G.; Dechamp, E.; Herrera, J.C.; Santoni, S.; Lashermes, P.; Simpson, J.; et al. High Genetic and Epigenetic Stability in Coffea arabica Plants Derived from Embryogenic Suspensions and Secondary Embryogenesis as Revealed by AFLP, MSAP and the Phenotypic Variation Rate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landey, R.B.; Cenci, A.; Guyot, R.; Bertrand, B.; Georget, F.; Dechamp, E.; Herrera, J.-C.; Aribi, J.; Lashermes, P.; Etienne, H. Assessment of genetic and epigenetic changes during cell culture ageing and relations with somaclonal variation in Coffea arabica. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2015, 122, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Karmakar, J.; Ray, A.; Adhikari, S.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K. Regeneration of plantlets through somatic embryogenesis from root derived calli of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (Roselle) and assessment of genetic stability by flow cytometry and ISSR analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebeli, P.J.; Karp, A.; Kalts1Kes, P.J. Somaclonal variation from cultured immature embryos of sister lines of rye differing in heterochromatic content. Genome 1990, 33, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.L.; Kaeppler, S.; Olhoft, P. Genetic instability of plant tissue cultures: Breakdown of normal controls. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5222–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-la-Peña, C.; Nic-Can, G.I.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; Avilez-Montalvo, R.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. The role of chromatin modifications in somatic embryogenesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarindo, W.R.; Carvalho, C.R.; Mendonca, M.A.C. Cytogenetic and flow cytometry data expand knowledge of genome evolution in three Coffea species. Plant Syst. Evol. 2012, 298, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Tao, S.; Bi, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Research of total levels on DNA methylation in plant based on HPLC analysis. Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 3, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Praça-Fontes, M.M.; Carvalho, C.R.; Clarindo, W.R. C-value reassessment of plant standards: An image cytometry approach. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.J. DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA. In Methods in Cell Biology v. 33; Darzynkiewiez, Z., Crissman, H.A., Robinson, J.P., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Namasivayam, P. Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2007, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T. Biotechnology Applications of Plant Callus Cultures. Engineering 2018, 5, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.N.G.; Carvalho, G.R.; Botelho, C.E.; Fazuoli, L.C.; Silvarolla, M.B. História das primeiras cultivares de café plantadas no Brasil. In Carvalho CHS. Cultivares de Café; Embrapa Café: Brasília, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bieysse, D.; Gofflot, A.; Michaux-Ferrière, N. Effect of experimental conditions and genotypic variability on somatic embryogenesis in Coffea arabica. Can. J. Bot. 1993, 71, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, N.P.; Campa, C.; Le Gal, L.; Noirot, M.; Thomas, G.; Lokeswari, T.S.; De Kochko, A. Effect of primary culture medium composition on high frequency somatic embryogenesis in different Coffea species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2006, 86, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lang, Z.; Zhu, J.-K. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, T.; Dudits, D. Epigenetic Clues to Better Understanding of the Asexual Embryogenesis in planta and in vitro. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, K.C.; Guimarães, P.D.S.; Bazioli, J.M.; Martinati, J.C.; Dos Santos, M.M.; Padilha, L.; Filho, O.G.; Maluf, M.P. Effects of somatic embryogenesis on gene expression of cloned coffee heterozygous hybrids. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Aké, F.; De-La-Peña, C. Epigenetic Advances in Somatic Embryogenesis in Sequenced Genome Crops. In Somatic Embryogenesis: Fundamental Aspects and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Van Staden, J. New insights into plant somatic embryogenesis: An epigenetic view. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, M.G.; Lisch, D. Perspective: Transposable Elements, Parasitic DNA, and Genome Evolution. Evolution 2001, 55, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, J.P.d.M.; Sanglard, N.A.; Ferreira, A.; Clarindo, W.R. Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level during the Dedifferentiation and Cellular Competence in Coffea arabica Lines: Insights about the Different In Vitro Responses. Forests 2021, 12, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111536
Oliveira JPdM, Sanglard NA, Ferreira A, Clarindo WR. Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level during the Dedifferentiation and Cellular Competence in Coffea arabica Lines: Insights about the Different In Vitro Responses. Forests. 2021; 12(11):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111536
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, João Paulo de Morais, Natália Arruda Sanglard, Adésio Ferreira, and Wellington Ronildo Clarindo. 2021. "Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level during the Dedifferentiation and Cellular Competence in Coffea arabica Lines: Insights about the Different In Vitro Responses" Forests 12, no. 11: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111536
APA StyleOliveira, J. P. d. M., Sanglard, N. A., Ferreira, A., & Clarindo, W. R. (2021). Genomic Methylated Cytosine Level during the Dedifferentiation and Cellular Competence in Coffea arabica Lines: Insights about the Different In Vitro Responses. Forests, 12(11), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111536





