Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Treatments
2.3. Sample Collection and Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Organic Carbon Concentration and Recalcitrance Index
3.2. Lignin Fraction Concentration
3.3. 13C Isotope Dynamics and Association with the Lignin Fraction
3.4. 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Litter Residue
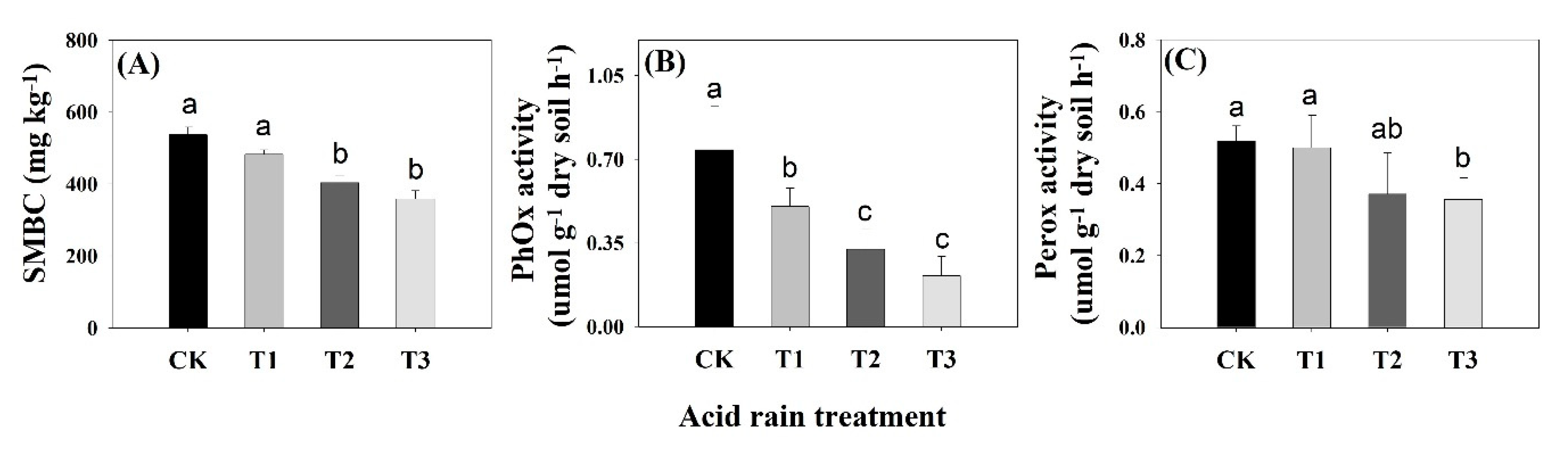
3.5. Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Ligninolytic Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of SAR on the Lignin Fraction
4.2. Effect of SAR on Soil Ligninolytic Enzymatic Activity
4.3. Effect of SAR on Soil Organic Carbon
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.X.; Xu, P.J. Research progress in precipitation chemistry in China. Prog. Chem. 2009, 21, 266–281. [Google Scholar]
- Du, E.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.; Fang, J.; Galloway, J.N.; Jiang, Y. Spatial boundary of urban ‘acid islands’ in southern China. Sci. Rep.-UK 2015, 5, 12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.X.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhang, D.Q. Effects of acidic solutions on element dynamics in the monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest at Dinghushan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 3, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.Q.; Yi, P.; Duan, N.; Zhao, D.G.; Zhao, J.M.; Cheng, K. Study on the influence factors of accurate definition of the spatial distribution of acid rain area in China. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 917–924. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.H.; Fang, Y.T.; Yu, F.M.; Liu, Q.; Li, E.R.; Peng, S.L. Soil acidification in response to acid deposition in three subtropical forests of subtropical China. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Hirai, K.; Morita, S.; Ohse, K.; Hiradate, S. Organic carbon accumulation processes on a forest floor during an early humification stage in a temperate deciduous forest in Japan: Evaluations of chemical compositional changes by 13C NMR and their decomposition rates from litterbag experiment. Geoderma 2009, 151, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.R.; Wang, J.X.; Shi, Z.M.; Lu, L.H.; Guo, W.F.; Jia, H.Y. Dynamics and speciation of organic carbon during decomposition of leaf litter and fine roots in four subtropical plantations of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 300, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Sharma, G.; Tripathi, S.K.; Singh, A.K. Litterfall, litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in a subtropical natural oak forest and managed plantation in northeastern India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 240, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.G.; Liu, Y.F.; Cui, Y.G.; Pei, Z.Y. Litter decomposition in a subtropical plantation in Qianyanzhou, China. J. For. Res. 2011, 16, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, M.; Danise, T.; D’Alessandro, F.; Curcio, E.; Fioretto, A. Dynamics of Organic Matter in Leaf Litter and Topsoil within an Italian Alder (Alnus cordata (Loisel.) Desf.) Ecosystem. Forests 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, K.; Hiradate, S.; Ohse, K.; Hirai, K. Humification processes of needle litter on forest floors in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) and Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparisobtusa) plantations in Japan. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavalli, P.P.; Palm, C.A.; Parton, C.A.; Elliott, E.T.; Frey, S.D. Soil pH and organic C dynamics in tropical forest soil: Evidence from laboratory and simulation studies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.L.; Christian, S.; Dayan, F.E.; Song, Y.Y.; Su, Y.J.; Zeng, R.S. Simulated acid accelerates litter decomposition and enhances the allelopathic potential of the invasive plant Wedelia trilobata (creeping daisy). Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.N.; Wang, C.Y.; Jia, Y.Y.; Wang, W.W.; Ma, X.; Du, J.J.; Pu, G.Z.; Tian, X.J. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on litter decomposition, soil microbial biomass, and enzyme activities in subtropical forests of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil respiration and its component in a mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest of the three gorges reservoir area in Southwest China. For. Ecosyst. 2019, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.P.; Liang, G.H.; Hui, D.F.; Deng, Q.; Xiong, X.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chu, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D. Prolonged acid rain facilitates soil organic carbon accumulation in a mature forest in Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osono, T.; Takeda, H.; Azuma, J. Carbon isotope dynamics during leaf litter decomposition with reference to lignin fractions. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel-Knabner, I. The macromolecular organic composition of plant and microbial residues as inputs to soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmitt, S.J.; Wright, D.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Jones, D.L. pH regulation of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in two agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, F.A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Knops, J.M.H.; Reich, P.B. Nitrogen deposition and plant species interact to influence soil carbon stabilization. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Jastrow, J.D. Activities of extracellular enzymes in physically isolated fractions of restored grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 3245–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, K.; Kooliyottil, R.; Joshi, A.; Pandey, A. Simultaneous production of ligninolytic enzymes by a temperature and pH tolerant strain of Aspergillus niger under different cultural conditions. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Schimel, J.; Becerra, C.A.; Blankinship, J. Estimating decay dynamics for enzyme activities in soils from different ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernoux, M.; Cerri, C.C.; Neill, C.; de Moraes, J.F.L. The use of stable carbon isotopes for estimating soil organic matter turnover rates. Geoderma 1998, 82, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, P.; Masia, A.; Canaccini, F.; Boldreghini, P.; Tonon, G. Isotopic discrimination during litter decomposition and δ13C and δ15N soil profiles in a young artificial stand and in an old floodplain forest. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2006, 42, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collister, J.W.; Rieley, G.; Stern, B.; Eglinton, G.; Fry, B. Compound-specific δ13C analyses of leaf lipids from plants with differing carbon dioxide metabolisms. Org. Geochem. 1994, 21, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, E.A.; Werner, R.A. Intramolecular, compound-specific, and bulk carbon isotope patterns in C3 and C4 plants: A review and synthesis. New Phytol. 2004, 161, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümig, A.; Rumpel, C.; Digna, M.F.; Kögel-Knabner, I. The role of lignin for the δ13C signature in C4 grassland and C3 forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClaugherty, C.A.; Berg, B. Cellulose, lignin and nitrogen concentrations as rate regulating factors in late stages of forest litter decomposition. Pedobiologia 1987, 30, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Benner, R.; Fogel, M.L.; Sprague, E.K.; Hodson, R.E. Depletion of 13C in lignin and its implications for stable carbon isotope studies. Nature 1987, 329, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X. A theoretical analysis of carbon isotope evolution of decomposing plant litters and soil organic matter. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2002, 16, 66-1–66-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M.; Trofymow, J.A.; Flanagan, L.B. Decomposition, δ13C, and the “lignin paradox”. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 86, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osono, T.; Takeda, H. Limit values for decomposition and convergence process of lignocelluloses fraction in decomposing leaf litter of 14 tree species in a cool temperate forest. Ecol. Res. 2005, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osono, T.; Hobara, S.; Koba, K.; Kameda, K.; Takeda, H. Immobilization of avian excreta-derived nutrients and reduced lignin decomposition in needle and twig litter in a temperate coniferous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, N.J.; Mao, X.A.; Xu, Z.H.; Saffigna, P.G.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Perera, M.C.S. Recent advances in the application of 13C and 15N NMR spectroscopy to soil organic matter studies. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 69–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.E.; Blumfield, T.J.; Boyd, S.; Xu, Z.H. A 13C NMR study of decomposing logging residues in an Australian hoop pine plantation. J. Soil. Sediment. 2013, 13, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preston, C.M.; Nault, J.R.; Trofymow, J.A. Chemical changes during 6 years of decomposition of 11 litters in some Canadian forest sites. Part 2. 13C abundance, solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy and the meaning of lignin. Ecosystems 2010, 12, 1078–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Hiradate, S.; Morita, S.; Hirai, K. Fate of organic carbon during decomposition of different litter types in Japan. Biogeochemistry 2013, 112, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.M.; Sandra, B.; Xue, J.H.; Fang, Y.T.; Li, Z.A. Response of litter decomposition to simulated N deposition in disturbed, rehabilitated and mature forests in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2006, 282, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; He, D.; Huang, Y. The Vegetation Map of Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve with Reference to Its Illustration. In Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem 4; Science Press: Guangzhou, China, 1986; pp. 43–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Brown, S.; Lugo, A.E. A Continental Subtropical Forest in China Compared with an Insular Subtropical Forest in the Caribbean; Gen. Tech. Rep. IIF-17, USDA, Forest Service; Institute of Tropical Forestry: Rio Piedras, PR, USA, 2001; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.H.; Liu, X.Z.; Chen, X.M.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Chu, G.W.; Liu, J.X.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhou, G.Y. Response of soil respiration to acid rain in forests of different maturity in southern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chertov, O.G.; Komarov, A.S. SOMM—A model of soil organic matter dynamics. Ecol. Model. 1997, 94, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, G.; Huang, W.; Liu, J. Increased litter input increases litter decomposition and soil respiration but has minor effects on soil organic carbon in subtropical forests. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.G.C.; Heath, G.W. The chemical analysis of small samples of leaf material and the relationship between the disappearance and composition of leaves. Pedobiologia 1967, 7, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Liang, G.; Qiu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; Chu, G.; Yan, J. Effects of precipitation on soil organic carbon fractions in three subtropical forests in southern China. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyodo, F.; Inoue, T.; Azuma, J.; Tayasu, I.; Abe, T. Role of the mutualistic fungus in lignin degradation in the fungus-growing termite Macrotermes gilvus (Isoptera; Macrotermitinae). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A.; Oades, J.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Skene, T.M.; Golchin, A.; Clarke, P. Assessing the extent of decomposition of natural organic materials using solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, R.; Marin-Spiotta, E.; Silver, W.L.; Schulten, J. Litterfall and decomposition in relation to soil carbon pools along a secondary forest chronosequence in Puerto Rico. Ecosystems 2008, 5, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, R. Current methods for measuring microbial biomass C in soil: Potentials and limitations. Biol. Fert. Soils 1995, 19, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyyemperumal, K.; Shi, W. Soil enzyme activities in two forage systems following application of different rates of swine lagoon effluent or ammonium nitrate. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connin, S.L.; Feng, X.; Virginia, R.A. Isotopic discrimination during long-term decomposition in an arid land ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem. 2001, 33, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.A.; Grierson, P.F. Stable isotopes at natural abundance in terrestrial plant ecology and ecophysiology: An update. Plant Biol. 2001, 3, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, W.S.G.; Craigie, J.S. Examinations of some soluble constituents of Sphagnum gametophytes. Can. J. Bot. 1964, 42, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, H.; Samland, J. Occurrence and metabolism of Sphagnum acid in the cell walls of bryophytes. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falappi, D.; Farini, A.; Ranalli, G.; Sorlini, C. Effects of simulated acid rain on some microbiological parameters of subacid soil. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Guo, P.; Han, G.M.; Feng, X.G.; Zhang, P.; Tian, X.J. Effect of simulated acid rain on the litter decomposition of Quercusacutissima and Pinusmassoniana in forest soil microcosms and the relationship with soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Gallo, M.; Lauber, C. Nitrogen deposition modifies soil carbon storage through changes in microbial enzymatic activity. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enowashu, E.; Poll, C.; Lamersdorf, N.; Kandeler, E. Microbial biomass and enzyme activities under reduced nitrogen deposition in a spruce forest soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 43, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, G.G.; Tang, C.; Fang, H.; Duan, J.; Yu, X. Effects of One-Year Simulated Nitrogen and Acid Deposition on Soil Respiration in a Subtropical Plantation in China. Forests 2020, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinsabaugh, R.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, W.; Ziegler, F.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Haumaier, L. Humic substances distribution and transformation in forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 117–118, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Campbell, C.A.; Jalil, A. Effects of acidity on mineralization: pH-dependence of organic matter mineralization in weakly acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | SOC (g/kg) | Alkyl C | O-alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carbonyl C | Recalcitrance Index 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 27.79 ± 2.19b | 46.70 ± 1.71 | 40.47 ± 1.05 | 2.13 ± 0.21 | 10.70 ± 0.5 | 0.96 ± 0.06b |
| T1 | 31.35 ± 2.79b | 49.37 ± 1.71 | 39.03 ± 0.71 | 1.16 ± 0.70 | 10.43 ± 0.42 | 1.02 ± 0.04ab |
| T2 | 32.04 ± 2.53ab | 48.37 ± 0.98 | 39.16 ± 1.86 | 2.10 ± 0.35 | 10.37 ± 0.68 | 1.02 ± 0.05ab |
| T3 | 36.80 ± 3.13a | 50.16 ± 1.38 | 37.77 ± 3.87 | 2.27 ± 0.83 | 9.80 ± 3.20 | 1.10 ± 0.03a |
| Lignin (%) | Lignin C/Total C (%) | δ13C (‰) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | L | 43.44 ± 1.51C | 37.05 ± 2.17C | −30.25 ± 0.07A |
| F | 45.21 ± 1.54B | 40.42 ± 4.05B | −30.93 ± 0.11B | |
| H | 52.10 ± 3.05A | 44.73 ± 2.80A | −31.43 ± 0.11C | |
| Treatment | CK | 43.55 ± 2.20b | 39.91 ± 3.50 | −30.81 ± 0.47a |
| T1 | 46.30 ± 3.55b | 40.04 ± 4.35 | −30.84 ± 0.53ab | |
| T2 | 47.23 ± 4.14ab | 41.35 ± 4.93 | −30.90 ± 0.53b | |
| T3 | 48.40 ± 5.64a | 41.63 ± 5.11 | −30.93 ± 0.55b | |
| Analysis of variance (P value) | ||||
| Layer | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment | <0.05 | 0.585 | <0.05 | |
| Layer × Treatment | 0.385 | 0.663 | 0.454 | |
| E | Alkyl C | O-alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carbonyl C | A/O-A Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | L | 19.90 ± 2.48C | 72.06 ± 2.97A | 2.58 ± 0.48B | 5.47 ± 0.87B | 0.28 ± 0.05C |
| F | 23.93 ± 2.60B | 65.80 ± 3.54B | 4.76 ± 1.39A | 5.52 ± 1.06B | 0.37 ± 0.06B | |
| H | 29.64 ± 2.79A | 57.13 ± 3.52C | 5.37 ± 1.10A | 7.86 ± 1.20A | 0.52 ± 0.08A | |
| Treatment | CK | 22.63 ± 3.35b | 67.77 ± 5.60a | 3.28 ± 1.07b | 6.32 ± 1.63 | 0.34 ± 0.08b |
| T1 | 23.61 ± 4.50b | 65.73 ± 6.42ab | 4.19 ± 1.40a | 6.47 ± 1.44 | 0.37 ± 0.11b | |
| T2 | 25.22 ± 5.03ab | 64.09 ± 7.28b | 4.67 ± 1.98a | 6.02 ± 1.64 | 0.40 ± 0.12ab | |
| T3 | 26.48 ± 5.81a | 62.40 ± 8.45b | 4.80 ± 1.59a | 6.31 ± 1.61 | 0.44 ± 0.15a | |
| Analysis of variance (P value) | ||||||
| Layer | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.86 | <0.001 | |
| Layer × Treatment | 0.134 | 0.179 | 0.111 | 0.385 | <0.05 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Deng, Q.; Hui, D.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses. Forests 2020, 11, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11111191
Wu J, Deng Q, Hui D, Xiong X, Zhang H, Zhao M, Wang X, Hu M, Su Y, Zhang H, et al. Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses. Forests. 2020; 11(11):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11111191
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jianping, Qi Deng, Dafeng Hui, Xin Xiong, Huiling Zhang, Mengdi Zhao, Xuan Wang, Minghui Hu, Yongxian Su, Hongou Zhang, and et al. 2020. "Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses" Forests 11, no. 11: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11111191
APA StyleWu, J., Deng, Q., Hui, D., Xiong, X., Zhang, H., Zhao, M., Wang, X., Hu, M., Su, Y., Zhang, H., Chu, G., & Zhang, D. (2020). Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses. Forests, 11(11), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11111191






