The Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometric Ratios as Affected by Geological Background in a Karst Graben Area, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Patterns of Soil C, N, and P in the Karst Graben Basin
3.2. Soil Nutrient Concentrations and their Stoichiometry under Different Rocky Desertification
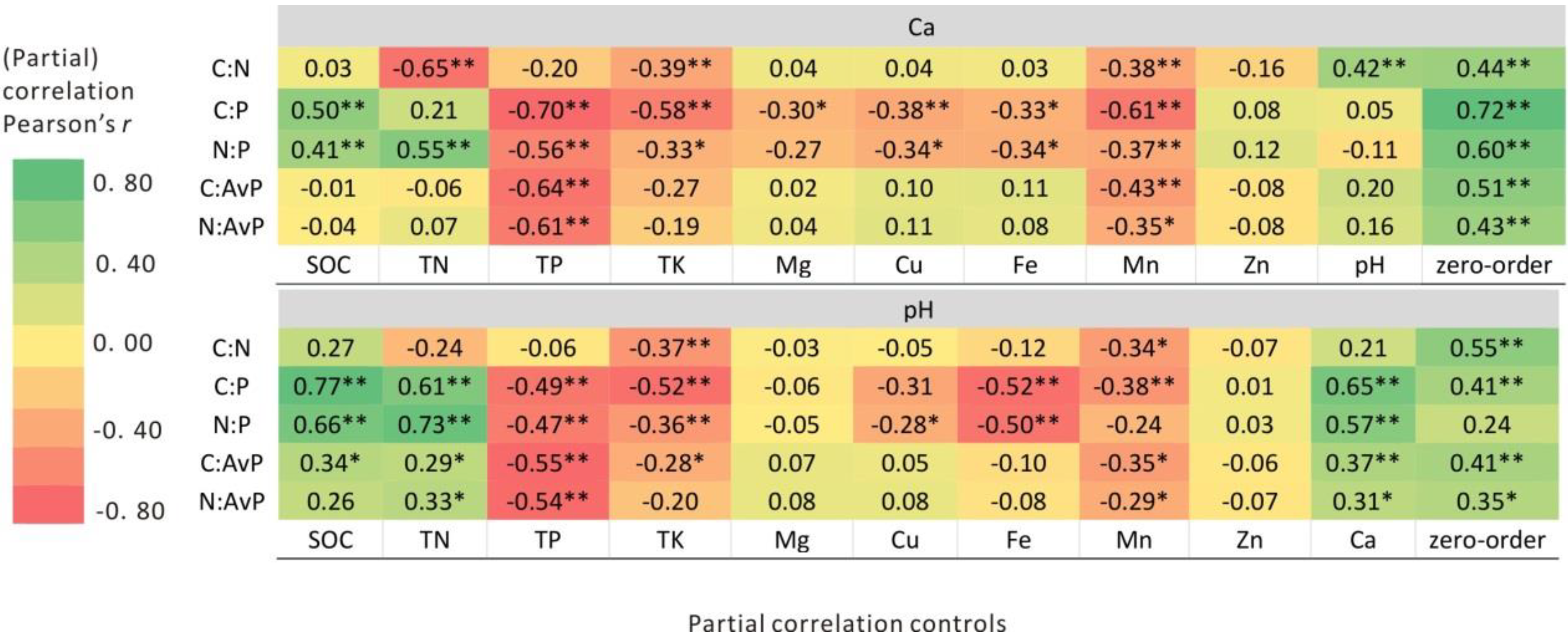
3.3. Correlations among Geochemical Variables and C, N, and P Stoichiometry
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Pattern of Eco-Stoichiometric Characteristics of C, N, and P and Analysis of Influencing Factors
4.2. Soil Ca and pH Controls on Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, X.; Deng, X.; Xiang, W.; Lei, P.; Ouyang, S.; Wen, H.; Chen, L. Calcium content and high calcium adaptation of plants in karst areas of southwestern Hunan, China. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2991–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Qin, X. Rocky desertification in Southwest China: Impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 132, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.X. Rock desertification in the subtropical Karst of South China. Z. Geomorphol. 1997, 108, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Pu, J.B.; Huang, N.; Du, H.M.; Qi, X.K.; Wang, L.; Yang, H. A research approach for ecological, environmental and geological differentiation of rocky desertification and its driving mechanism in karst graben basin. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 899–907. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.H.; Deng, Y.; Yang, H.; Pu, J.B.; Zhu, T.B.; Lan, F.N.; Huang, F.; Liang, J.H. Rocky desertification evolution, treatment technology and demonstration in Karst faulted basins, Southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7103–7108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; Oelmann, Y.; Schickhoff, U.; Böhner, J.; Scholten, T. Himalayan treeline soil and foliar C:N:P stoichiometry indicate nutrient shortage with elevation. Geoderma 2017, 291, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.H.; Deng, Z.M.; Chen, X.S. Soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry of three dominant plant communities distributed along a small-scale elevation gradient in the East Dongting Lake. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018, 103, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, H.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Matson, P.A. Exchange of Materials Between Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Atmosphere. Science 1987, 238, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooshammer, M.; Hofhansl, F.; Frank, A.H.; Wanek, W.; Hämmerle, I.; Leitner, S.; Schnecker, J.; Wild, B.; Watzka, M.; Keiblinger, K.M.; et al. Decoupling of microbial carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycling in response to extreme temperature events. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, A.C.; Austin, A.T.; Cleland, E.E.; Frey, S.D.; Houlton, B.Z.; Wallenstein, M.D. Responses and feedbacks of coupled biogeochemical cycles to climate change: Examples from terrestrial ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques Agra Bezerra da Silva, Y.; Williams Araújo do Nascimento, C.; Jacques Agra Bezerra da Silva, Y.; Miranda Biondi, C.; Cordeiro Atanázio Cruz Silva, C.M. Rare Earth Element Concentrations in Brazilian Benchmark Soils. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo. 2016, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Yu, G.R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 3937–3947. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Shao, J.A.; Yang, H.; Bai, X.Y. The relations between land use and karst rocky desertification in a typical karst area, China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.J.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, S.J.; Cheng, A.Y.; Dan, W.L. Comparison of ecological significance of landscape diversity changes in karst mountains: A case study of 4 typical karst area in Guizhou Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3882–3889. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.Q.; Peng, W.X.; Du, H.; Wang, K.L.; Zeng, F.P. Occurrence, spatial-temporal dynamics and regulation strategies of karst rocky desertification in southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5328–5341. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, K.N. Response of soil physical-chemical properties to rocky desertification succession in South China Karst. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 6303–6313. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, Y.S.; He, T.B.; Luo, H.B.; Long, J. Changes of soil quality in the process of karst rocky desertification and evaluation of impact on ecological environment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 639–644. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, D.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Two Typical Plantations in the Karst Ecosystem of Southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Biondi, C.M.; Silva, Y.J.A.B.; Accioly, A.M.; Montero, A.; Ugarte, O.M.; Estevez, J. Rare-earth-element geochemistry in soils developed in different geological settings of Cuba. Catena 2018, 162, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P. Progress and propects in research of mountain meteorogy in China during the past 25 years. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 115–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.N.; Pu, J.B.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, T.; Huo, W.J.; Yuan, D.X. Climatic chararacteristics under the influence of basin-mountain coupled topography and its influence on the ecological restoration of rocky desertification in a Mengzi karst graben basin, Southwest China. Carsol. Sin. 2019, 38, 50–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, G.L.; Olsson, T. Conditions related to solubility of rare and minor elements in forest soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.S.; Chen, J.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zheng, C.J. Study on the background contents on elements of soils in China. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 1991, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Zeng, S.; Qin, H.; Zhou, K.; Yang, H.; Lan, F.; Huang, F.; Cao, J.; Müller, C. Low nitrate retention capacity in calcareous soil under woodland in the karst region of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, L.K.; Yu, S.; Cao, J.H. Effects of different land-uses on the features of water-stable aggregates in karst and clasolite areas in Maocun, Guilin. Carsol. Sin. 2012, 31, 265–271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.N.; Su, Y.R.; He, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, J.S. The speciation and content of calcium in karst soils, and its effects on soil organic carbon in karst region of Southwest China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.H.; Yuan, D.X.; Pan, G.X. Some soil features in karst ecosystem. Adv. Earth Sci. 2003, 18, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.F.; Fu, W.L.; Zen, X.J.; Du, F.Z. Correlation between soil organic carbon and water-stable aggregate in karst area-A case study in Zhongliangshan karst valley, Chongqing. Carsol. Sin. 2009, 28, 75–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, L.K.; Cao, J.H.; Yu, S. Comparison of mineralization and chemical structure of the soil organic carbon under different land uses in Maocun karst area, Guilin. Carsol. Sin. 2011, 30, 410–416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Fu, W.L.; Lan, J.C.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wu, L.Z. Distribution characteristics of soil particulate organic carbon and mineral-associated organic carbon of different land use in karst mountain. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.B.; He, X.Y.; Hu, Y.J.; Su, Y.R. Characteristics and mechanisms of soil organic carbon accumulation and stability in typical karst ecosystems. Res. Agric. Mod. 2018, 39, 907–915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, J.M.; Cao, J.H. Research progress of the relationship between soil calcium and soil organic carbon in karst area. Guangxi Sci. 2018, 25, 505–514. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Chen, J.R.; Liang, J.H.; Cao, J.H. Preliminary study on the relationship between soil organic carbon and pH value and calcium species in Yaji karst region, Giulin. Geol. Rev. 2017, 63, 1117–1126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Cao, J.H.; Sun, L.; Luan, H.N.; Hou, Y.L. Fractions and distribution of inorganic phosphorus in different land use types of karst area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 135–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Ji, H.; Sun, N.; Tao, H.; Du, B.; Hui, D.; Liu, C. Imbalanced plant stoichiometry at contrasting geologic-derived phosphorus sites in subtropics: The role of microelements and plant functional group. Plant Soil 2018, 430, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, T.B.; Wang, X.H.; Pu, J.B.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, T.; Cao, J.H. Soil element contents of typical small watershed in the plateau area of karst fault basin, Yunnan. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 27, 859–865. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.Y.; Xiong, K.N.; Cui, G.Y.; Liu, Y. Plant diversity and soil physical-chemical properties in karst rocky desertification ecosystem of Guizhou, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 434–448. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bárcenas-Moreno, G.; Rousk, J.; Bååth, E. Fungal and bacterial recolonisation of acid and alkaline forest soils following artificial heat treatments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabovich, M.Y.D.G.; Churikova, V.V.; Churikov, S.N.; Korovina, T.I. Mechanisms of synthesis and utilization of oxalate inclusions in the colorless sulfur bacterium Macromonas bipunctata. Mikrobiology 1995, 64, 630–636. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, W.L.; Miya, R.K. Global patterns in root decomposition: Comparisons of climate and litter quality effects. Oecologia 2001, 129, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
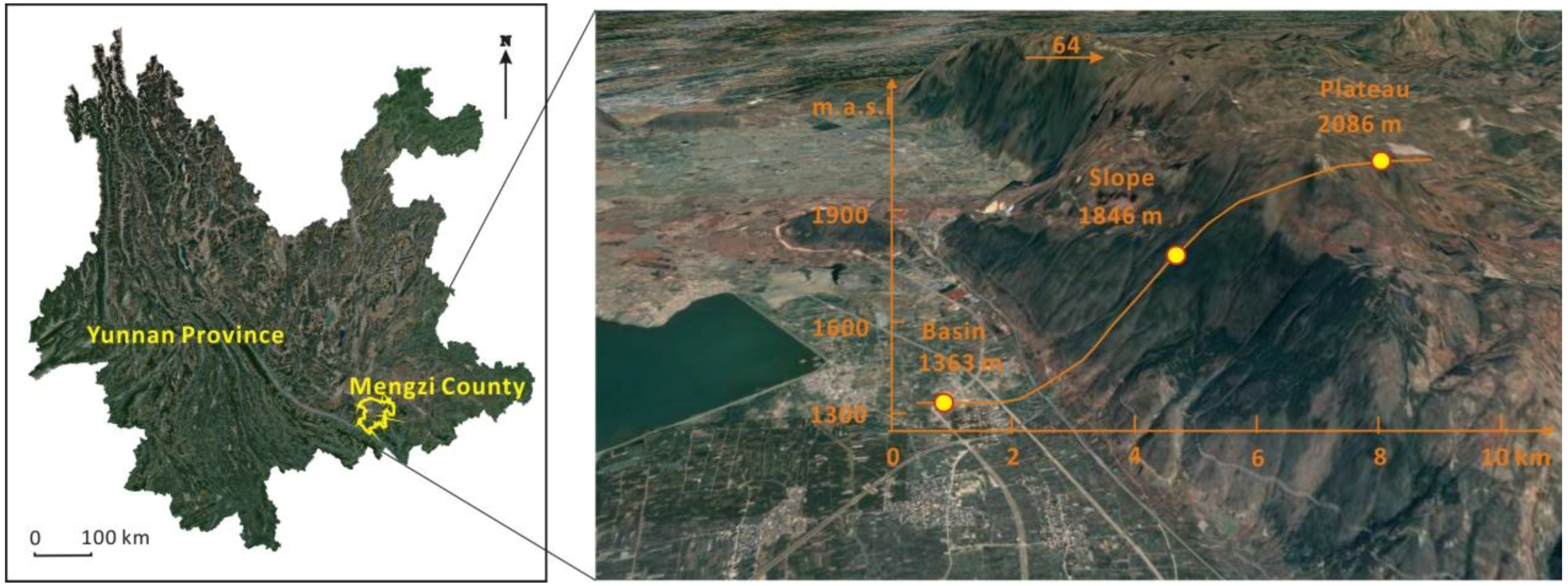
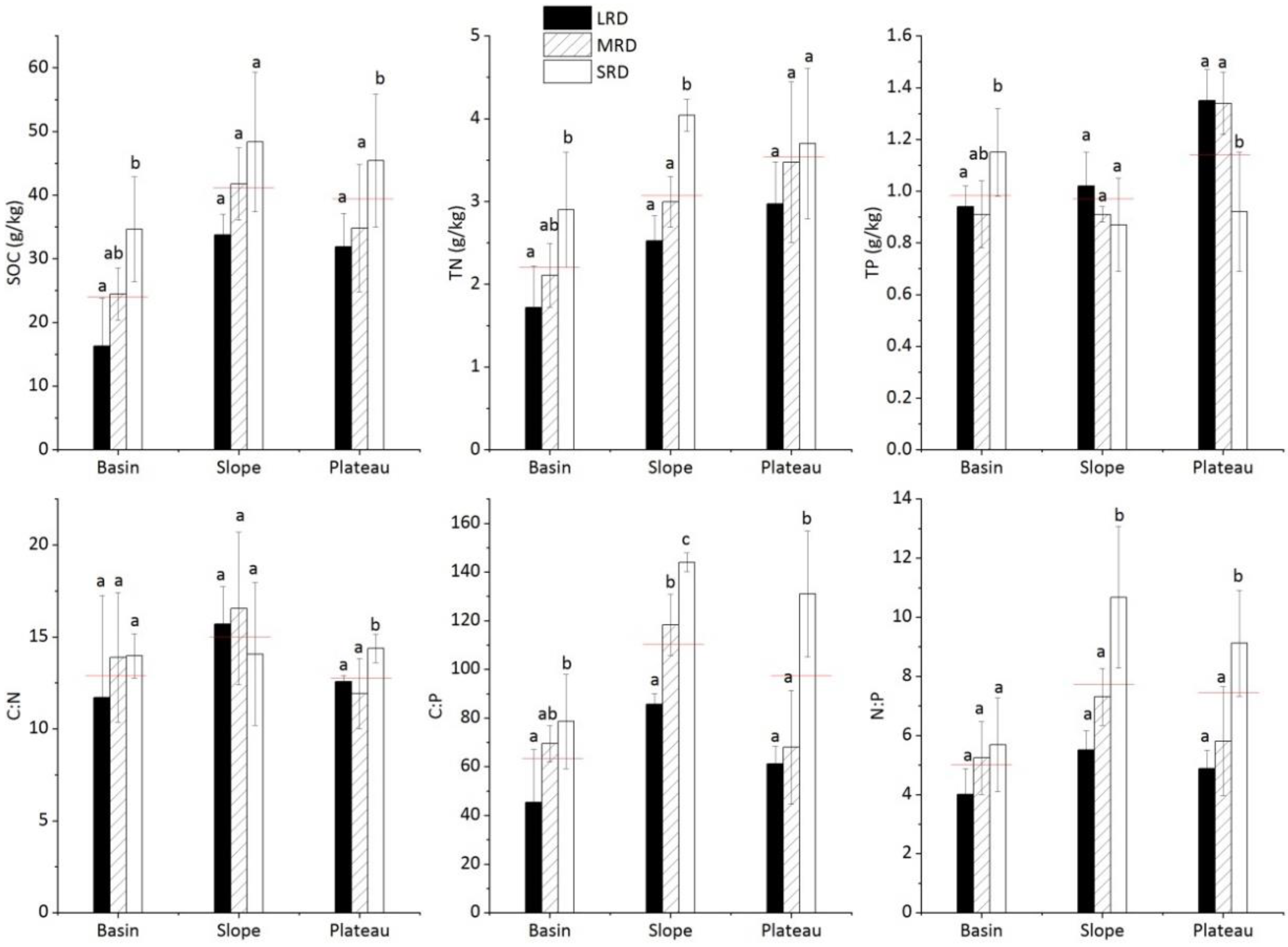
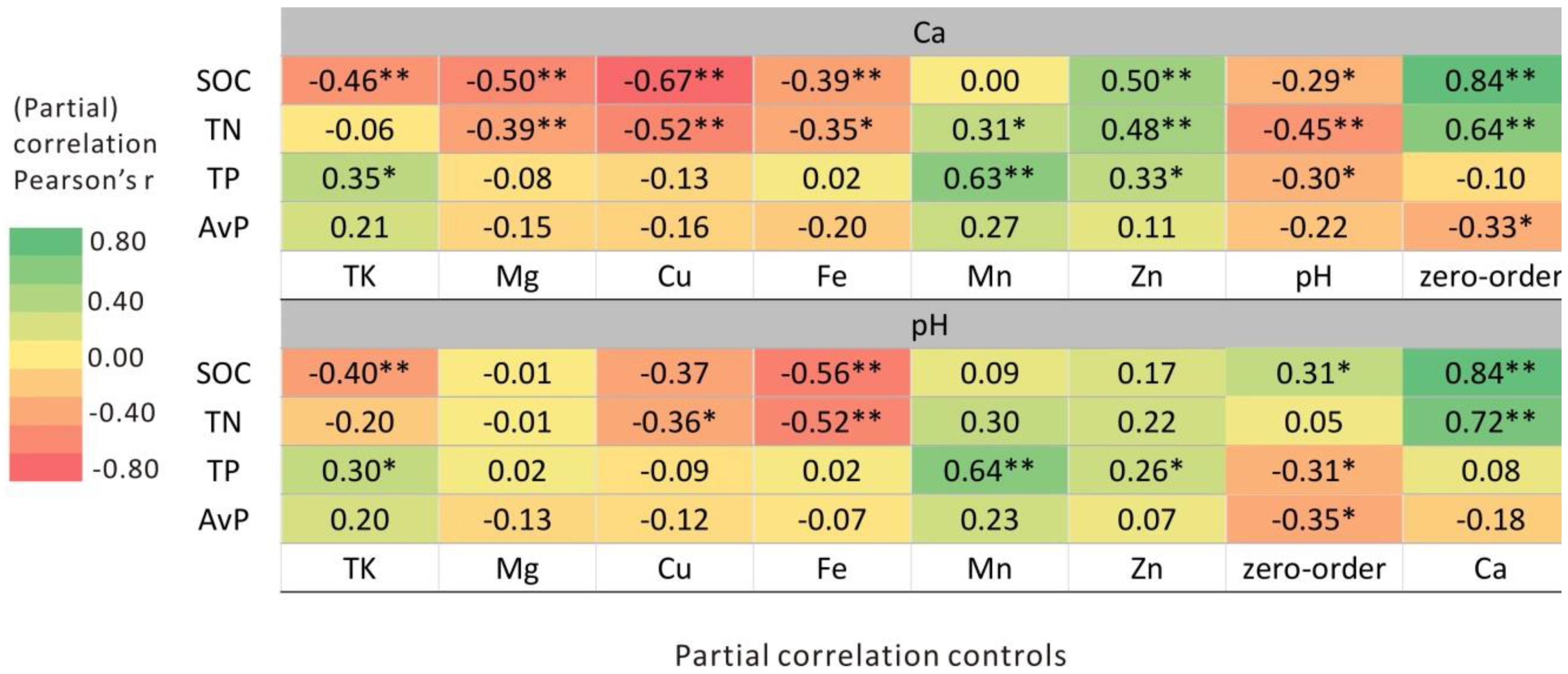
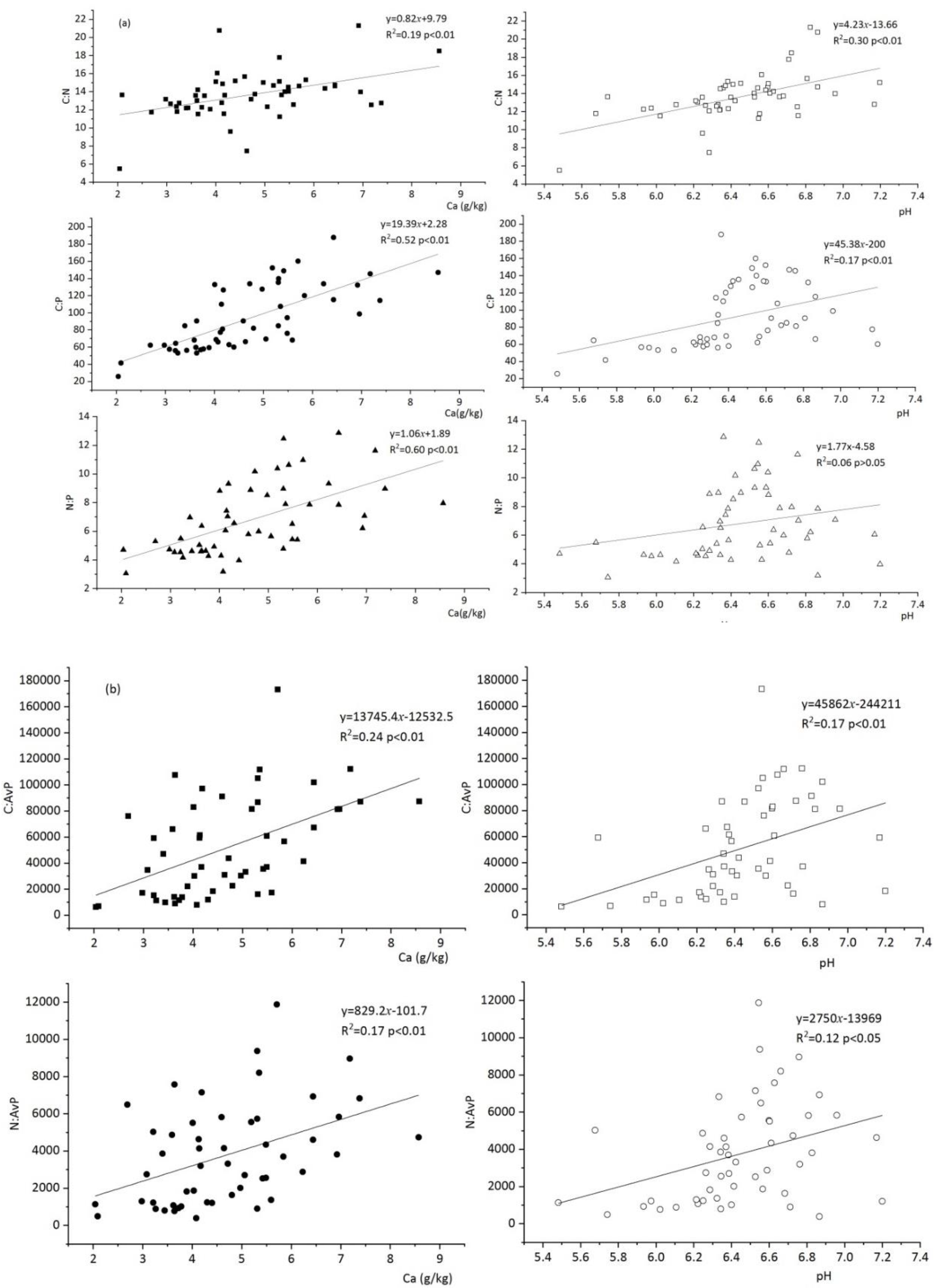
| Location | Latitude and Longitude | Altitude (m) | Rocky Desertification and Vegetation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basin | 103°23′47″E, 23°28′22″N | 1363 | LRD: Eucalyptus forest with short planting years and single community structure. The rock bareness rate was ~35%. |
| MRD: Herbs, dominated by Miscanthus. The rock bareness rate was ~55%. | |||
| SRD: Herbs, herb of Spanishneedles (Bidens bipinnata Linn.) and Canadian fleabane (Conyza canadensis (Linn.) Cronq.) was dominant specie. The rock bareness rate was >70%. | |||
| Slope | 103°26′13″E, 23°27′43″N | 1846 | LRD: Artificially planted cypress forests, with high canopy density. The rock bareness rate was ~30%. |
| MRD: Shrub, domained by Purpus Priver (Ligustrum quihoui Carr.) and Euphorbiae Pekinensis Radix (Euphorbia pekinensis Rupr). The rock bareness rate was ~50% | |||
| SRD: Ferns are the main species. The rock bareness rate was >70%. | |||
| Plateau | 103°27′09″E, 23°27′08″N | 2086 | LRD: Forest, the main vegetation types are Ligustrum quihoui Carr. and Chinese mugwort (Artemisia argyi H. Lév.) and Vaniot. The rock bareness rate was ~30%. |
| MRD: the main vegetation types are Miscanthus. The rock bareness rate was ~50%. | |||
| SRD: Herbs, domained by Miscanthus with a small amount of Conyza canadensis (Linn.) Cronq. The rock bareness rate was >70%. |
| Landform | C:N | C:P | N:P | C:AvP | N:AvP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basin | 13.4 ± 3.5 a | 65.8 ± 18.6 a | 5.0 ± 1.3 a | 42,429 ± 28,020 a | 3292 ± 2181 a |
| Slope | 15.4 ± 3.2 b | 116.0 ± 26.2 b | 7.8 ± 2.6 b | 81,067 ± 36,628 b | 5600 ± 3079 b |
| Plateau | 13.2 ± 1.7 a | 96.3 ± 39.9 b | 7.2 ± 2.5 b | 46,285 ± 37,982 a | 3399 ± 2589 a |
| Average | 13.6 ± 2.6 | 92.6 ± 37.3 | 6.8 ± 2.5 | 51,516 ± 37,650 | 3762 ± 2682 |
| China [27] | 14.4 ± 0.4 | 136 ± 11 | 9.3 ± 0.7 | 15,810 ± 1832 | 1114 ± 115 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Cao, J. The Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometric Ratios as Affected by Geological Background in a Karst Graben Area, Southwest China. Forests 2019, 10, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10070601
Yang H, Zhang P, Zhu T, Li Q, Cao J. The Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometric Ratios as Affected by Geological Background in a Karst Graben Area, Southwest China. Forests. 2019; 10(7):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10070601
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hui, Peng Zhang, Tongbin Zhu, Qiang Li, and Jianhua Cao. 2019. "The Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometric Ratios as Affected by Geological Background in a Karst Graben Area, Southwest China" Forests 10, no. 7: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10070601
APA StyleYang, H., Zhang, P., Zhu, T., Li, Q., & Cao, J. (2019). The Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P Stoichiometric Ratios as Affected by Geological Background in a Karst Graben Area, Southwest China. Forests, 10(7), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10070601





