Comparison of Horizontal Accuracy, Shape Similarity and Cost of Three Different Road Mapping Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
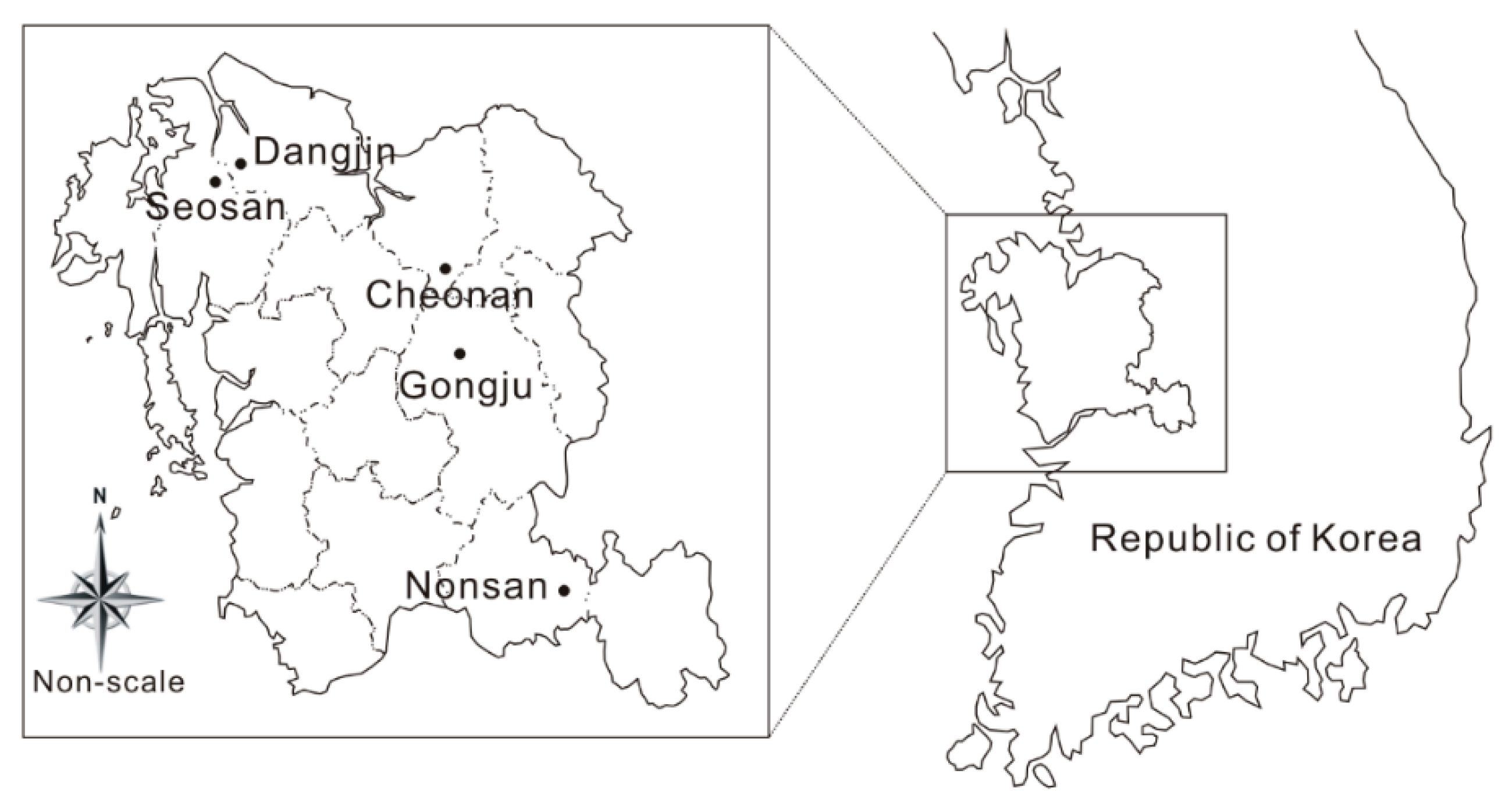
2.1. Study Area Description
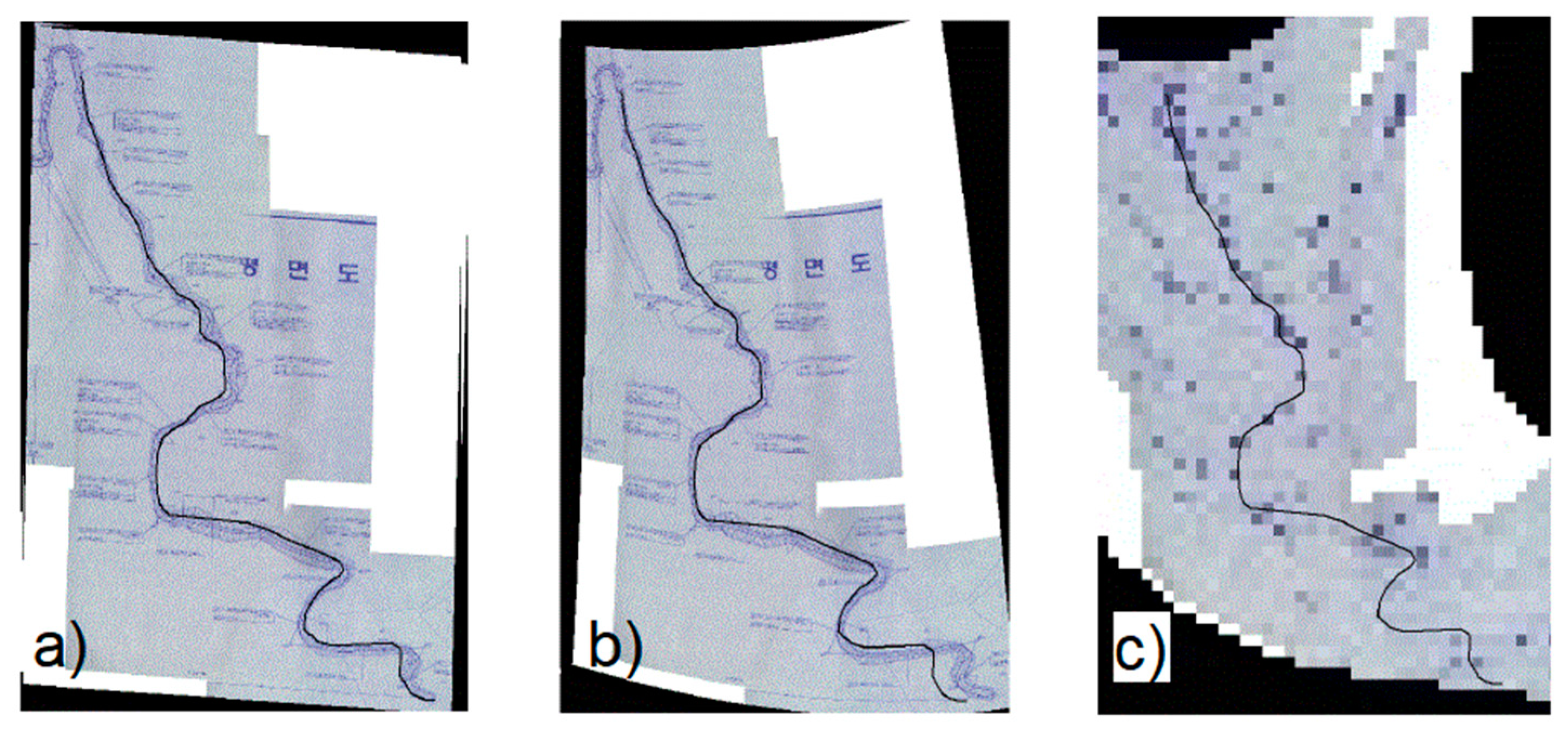
2.2. Mapping Techniques of Forest Roads
2.3. Comparison of the Horizontal Accuracy and Shape Similarity between Three Mapping Techniques
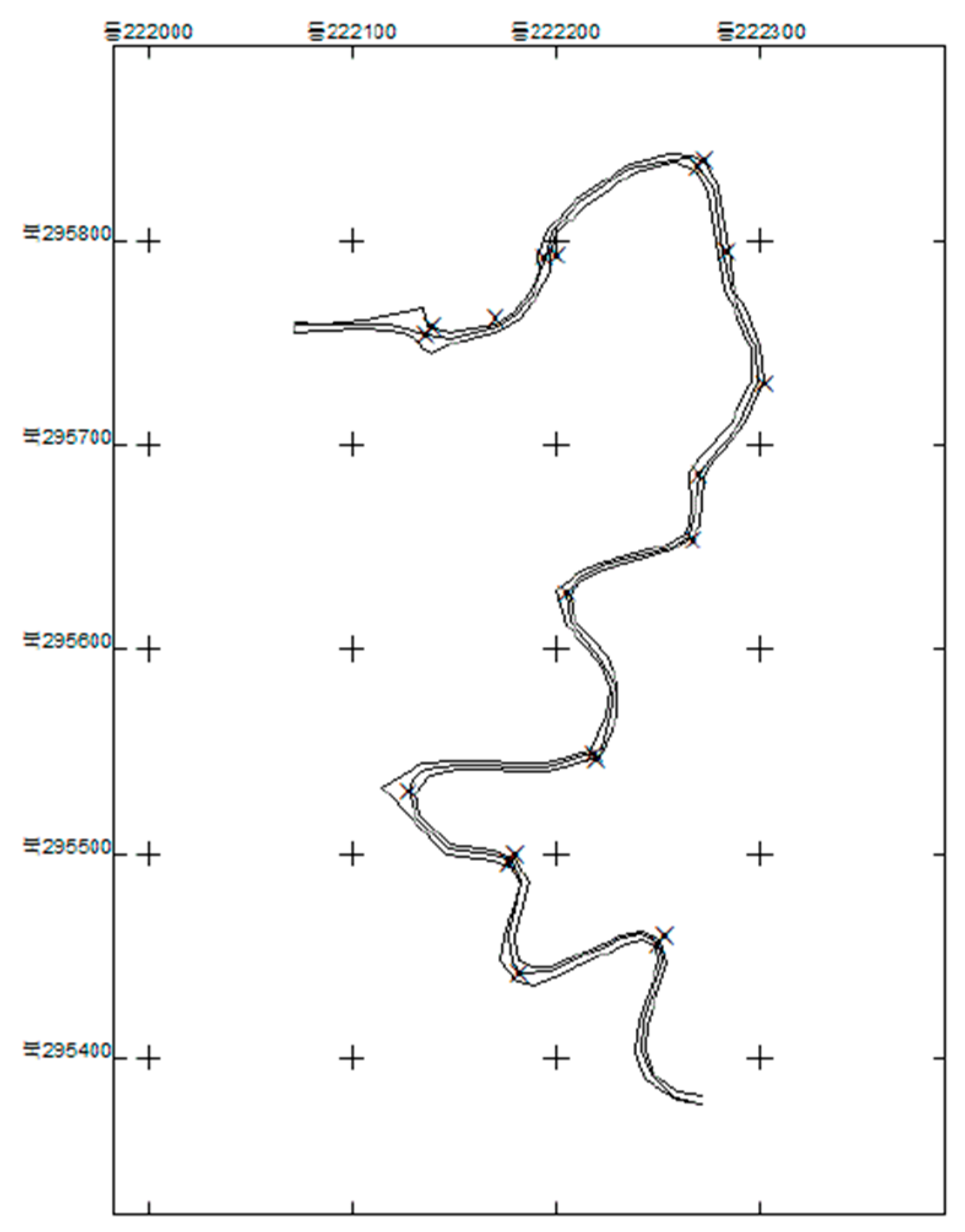
2.3.1. Point-Correspondence
- rmsex is root mean square error of x-axis,
- rmsey is root mean square error of y-axis.
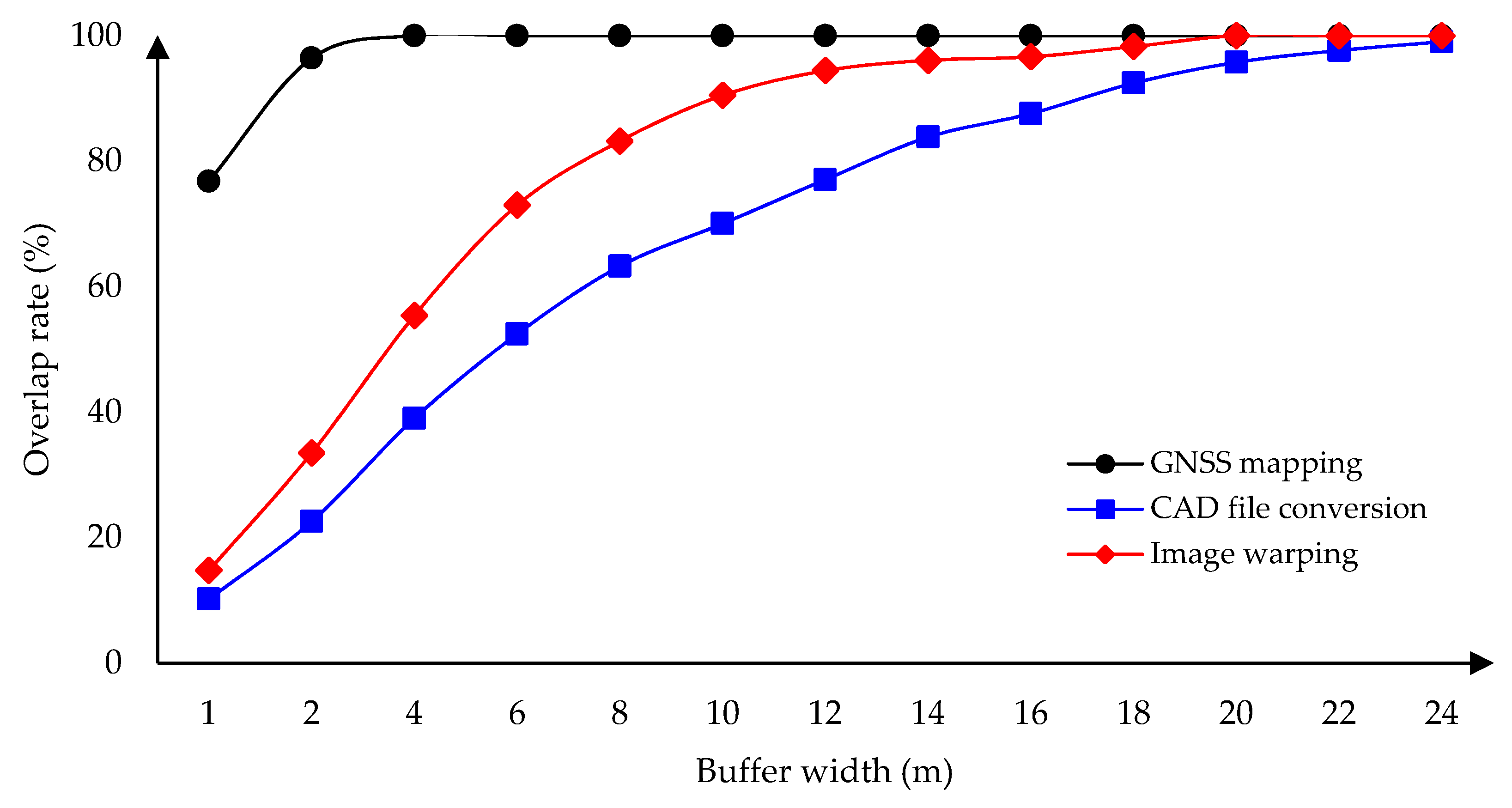
2.3.2. Buffering Analysis
2.3.3. Shape Index
- : shape index,
- p: perimeter (m),
- A: Area (m2).
2.3.4. Turning Function Analysis
2.3.5. Estimation of Map-Making Time and Cost
3. Results
3.1. Point-correspondence
3.2. Buffering Analysis
3.3. Shape Index
3.4. Turning Function Analysis
3.5. Estimation of Map-Making Time and Cost
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdi, E.; Sisakht, L.; Goushbor, L.; Soufi, H. Accuracy assessment of GPS and surveying technique in forest road mapping. Ann. For. Res. 2012, 55, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Talebi, M.; Majnounian, B.; Ehsan, A.; Tehrani, F.B. Development a GIS database for forest road management in Arasbaran forest, Iran. For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.N.C.; Ogilvie, J.; Castonguay, M.; Zhang, C.F.; Meng, F.R.; Arp, P.A. Improving forest operations planning through high-resolution flow-channel and wet-areas mapping. For. Chron. 2008, 84, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Choi, J.; Yu, K. Development of the Digital Map Updating System using CAD Object Extracted from As-Built Drawings. J. Korean Soc. GIS 2009, 17, 13–21, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, S.; Majnounian, B.; Darvishsefat, A. Possibility of designing and evaluation of forest road network variants using GIS and field investigation. J. For. Wood Prod. 2011, 63, 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Grigolato, S.; Mologni, O.; Raffaele, C. GIS applications in forest operations and road network planning: An overview over the last two decades. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2017, 38, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ömer, M.; Ayhan, C. Accuracy and cost comparison of spatial data acquisition methods for the development of geographical information systems. J. Geogr. Regional Plan. 2009, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.A.; Dietterick, B.C.; Mastin, T.; Strohman, R. Forest roads mapped using LiDAR in steep forested terrain. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1120–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yoon, J.; Woo, C.; Lee, K.; Hong, C. Comparison of methodology and accuracy of digital mapping of forest roads. J. Geogr. Inform. Syst. Assoc. Korea 2005, 13, 195–209. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Glasbey, C.; Mardia, K. A review of image warping methods. J. Appl. Stat. 1998, 25, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kweon, H.; Choi, Y.; Yeom, I.; Lee, J. Evaluation of horizontal position accuracy in forest road completion drawing. Korean J. Agr. Sci. 2010, 37, 471–479, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Malenovský, Z.; Turner, D.; Vopěnka, P. Assessment of Forest Structure Using Two UAV Techniques: A Comparison of Airborne Laser Scanning and Structure from Motion (SfM) Point Clouds. Forests 2016, 7, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, Y.; Sekimoto, Y.; Shibasaki, R. Comparative study of positional accuracy evaluation of line data. In Proceedings of the 20th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Hong Kong, China, 22–25 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.; Hunter, G. A simple positional accuracy measure for linear features. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1997, 11, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveite, H.; Langaas, S. An accuracy assessment method for geographical line data sets based on buffering. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1999, 13, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueng, Y.; Yan, J. A locational error model for spatial features. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1998, 12, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, E.; Chew, P.; Huttenlocher, D.; Kedem, K.; Mitchel, J. An efficiently computable metric for comparing polygonal shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkamp, R.C. Shape matching: similarity measures and algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications, Genova, Italy, 7–11 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- SOKKIA KOREA. Available online: https://www.sokkia.co.kr (accessed on 15 August 2010).
- AutoCAD. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com (accessed on 15 April 2012).
- Parkhomenko, A.S. Affine transformation. In Encyclopedia of Mathematics; Hazewinkel, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Available online: http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Affine_transformation&oldid=17980 (accessed on 9 September 2018).
- ESRI. Available online: http://support.esri.com (accessed on 15 August 2010).
- Trimble Korea. Available online: https://geospatial.trimble.com (accessed on 15 June 2010).
- Van Niel, T.G.; McVicar, T.R. Experimental evaluation of positional accuracy estimates from a linear network using point-and line-based testing methods. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2002, 16, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.R.; Ali, T. Progress in metrics development to measure positional accuracy of spatial data. In Proceedings of the 21st International Cartographic Conference, Durban, South Africa, 10–16 August 2003; pp. 1763–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Godron, M. Landscape Ecology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Velkamp, R.C.; Hagedoorn, M. Shape similarities, properties, and constructions. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, Lyan, France, 2–4 November 2000; pp. 467–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Ahn, D. Landscape ecological analysis of urban parks –analysis of index of patch shape and the dispersion of patches. J. Korean Inst. Landsc. Archit. 1996, 23, 12–19, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Korea Engineering and Consulting Association (KENCA). Available online: https://www.etis.or.kr/webs/statistics/statistics_board.jsp?leftParam=1&topParam=3&boardId=TOTALBBS&categorygroup2=TB050 (accessed on 6 May 2019).
- KEB Hanabank. Available online: https://www.kebhana.com (accessed on 14 January 2019).
- Pirti, A. Accuracy analysis of GPS positioning near the forest environment. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2008, 29, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Yosimura, T.; Hasegawa, H. Comparing the precision and accuracy of GPS positioning in forested areas. J. For. Res. 2003, 8, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W. A generic statistical approach for modelling error of geometric features in GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 1998, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckham, M.; Drummond, J. Assessment of error in digital vector data using fractal geometry. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2000, 14, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veregin, H. Quantifying positional error induced by line simplification. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2000, 14, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, Z.; Najafi, A.; Sadeghian, S. Forest road detection using LiDAR data. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.M.; Yoon, H.C.; Lee, J.D.; Park, J.K. Analysis of economical efficiency of digital map in production cost by aerial LiDAR surveying. J. KOGSIS 2007, 15, 67–73, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B. Republic of Korea, Nation Map Book II; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, National Geographic Information Institute: Suwon, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 2016. Available online: http://map.ngii.go.kr/ms/pblictn/nationMapBook.do (accessed on 17 September 2018).



| Location | Length (m) 1 | Construction Year | Altitude (m) | Forest Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.P. 2 | E.P. 3 | Max. | Min. | ||||
| Dangjin | 1417 | 2009 | 147 | 190 | 190 | 143 | Hardwood-forest |
| Seosan | 1275 | 2008 | 116 | 98 | 124 | 97 | Softwood-forest |
| Nonsan | 1012 | 2009 | 151 | 154 | 175 | 151 | Mixed forest |
| Choenan | 1020 | 2007 | 174 | 197 | 197 | 167 | Mixed forest |
| Gongju | 1105 | 2009 | 401 | 412 | 447 | 397 | Mixed forest |
| Area | No. of IP 1 (ea) | Total Station (m) | CAD File Conversion (m) | Image Warping (m) | GNSS Mapping (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dangjin | 11 | 1398 | 1417 (△19) | 1438 (△40) | 1396 (▽2) |
| Seosan | 19 | 1209 | 1275 (△66) | 1280 (△71) | 1211 (△2) |
| Nonsan | 12 | 985 | 1012 (△27) | 1040 (△55) | 986 (△1) |
| Cheonan | 13 | 1048 | 1020 (▽28) | 1123 (△75) | 1047 (▽1) |
| Gongju | 23 | 1022 | 1105 (△83) | 1101 (△79) | 1027 (△5) |
| Total | 78 | 5662 | 5829 (△167) | 5982 (△320) | 5667 (△5) |
| Mapping Technique | Total | Dangjin | Seosan | Nonsan | Cheonan | Gongju | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD 1 | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| CAD file conversion | 13.35 a | 7.36 | 14.78 c | 9.38 | 14.51 c | 6.25 | 11.04 c | 4.52 | 13.07 c | 6.86 | 14.01 c | 7.68 |
| Image warping | 7.13 b | 3.75 | 8.79 b | 3.34 | 8.97 b | 3.66 | 5.63 b | 2.49 | 5.66 b | 3.06 | 6.46 b | 4.16 |
| GNSS mapping | 1.28 c | 0.86 | 1.99 a | 0.63 | 0.81 a | 0.48 | 1.08 a | 0.64 | 1.16 a | 0.82 | 1.36 a | 1.00 |
| F | 79.89 | 11.10 | 24.28 | 22.08 | 17.08 | 14.14 | ||||||
| P | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | ||||||
| Route Location | Mapping Technique | Area (m2) | Length (m) | Shape Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dangjin | CAD file conversion | 11,715 | 2839.7 | 7.4 |
| Image warping | 5548 | 2852.8 | 10.8 | |
| GNSS mapping | 1624 | 2800.0 | 19.6 | |
| Seosan | CAD file conversion | 11,884 | 2506.6 | 6.5 |
| Image warping | 6733 | 2503.9 | 8.6 | |
| GNSS mapping | 557 | 2422.0 | 28.9 | |
| Nonsan | CAD file conversion | 6040 | 2019.4 | 7.3 |
| Image warping | 3517 | 2037.1 | 9.7 | |
| GNSS mapping | 554 | 1974.0 | 23.7 | |
| Cheonan | CAD file conversion | 6942 | 2123.8 | 7.2 |
| Image warping | 4582 | 2194.1 | 9.1 | |
| GNSS mapping | 479 | 2099.0 | 27.0 | |
| Gongju | CAD file conversion | 8612 | 2165.4 | 6.6 |
| Image warping | 7169 | 2164.2 | 7.2 | |
| GNSS mapping | 681 | 2042.0 | 22.1 |
| Route Location | Mapping Technique | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD File Conversion | Image Warping | GNSS Mapping | |
| Dangjin | 8661 | 7972 | 3357 |
| Seosan | 19,633 | 16,984 | 3230 |
| Nonsan | 14,211 | 13,994 | 2814 |
| Cheonan | 23,588 | 19,331 | 4130 |
| Gongju | 27,845 | 26,256 | 4949 |
| Mapping Technique | Average Working Time (min/km) | Production Cost (US$/km) 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Field Survey 1 | Map-making 2 | Total | ||
| CAD file conversion | - | 99 | 99 | 40.90 |
| Image warping | 31 | 149 | 180 | 81.84 |
| GNSS mapping | 175 | 61 | 236 | 139.64 |
| Total station | 195 | 120 | 315 | 180.66 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kweon, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.-W.; Seo, J.I.; Rhee, H. Comparison of Horizontal Accuracy, Shape Similarity and Cost of Three Different Road Mapping Techniques. Forests 2019, 10, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050452
Kweon H, Kim M, Lee J-W, Seo JI, Rhee H. Comparison of Horizontal Accuracy, Shape Similarity and Cost of Three Different Road Mapping Techniques. Forests. 2019; 10(5):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050452
Chicago/Turabian StyleKweon, Hyeongkeun, Myeongjun Kim, Joon-Woo Lee, Jung Il Seo, and Hakjun Rhee. 2019. "Comparison of Horizontal Accuracy, Shape Similarity and Cost of Three Different Road Mapping Techniques" Forests 10, no. 5: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050452
APA StyleKweon, H., Kim, M., Lee, J.-W., Seo, J. I., & Rhee, H. (2019). Comparison of Horizontal Accuracy, Shape Similarity and Cost of Three Different Road Mapping Techniques. Forests, 10(5), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050452





