Extended von Bertalanffy Equation in Solow Growth Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
- the population grows at a constant rate when it is small compared to
- scarcity of resources slows population growth as it approaches
- the population growth rate approaches zero over time.
2. Constant Parameter Model
2.1. Dynamics of Population and Capital Accumulation
2.2. Constant Parameter Model Solution
- Note that, while changes over time, is a fixed number for a given scenario of the parameters. This feature is obviously inherited by (12), which becomes
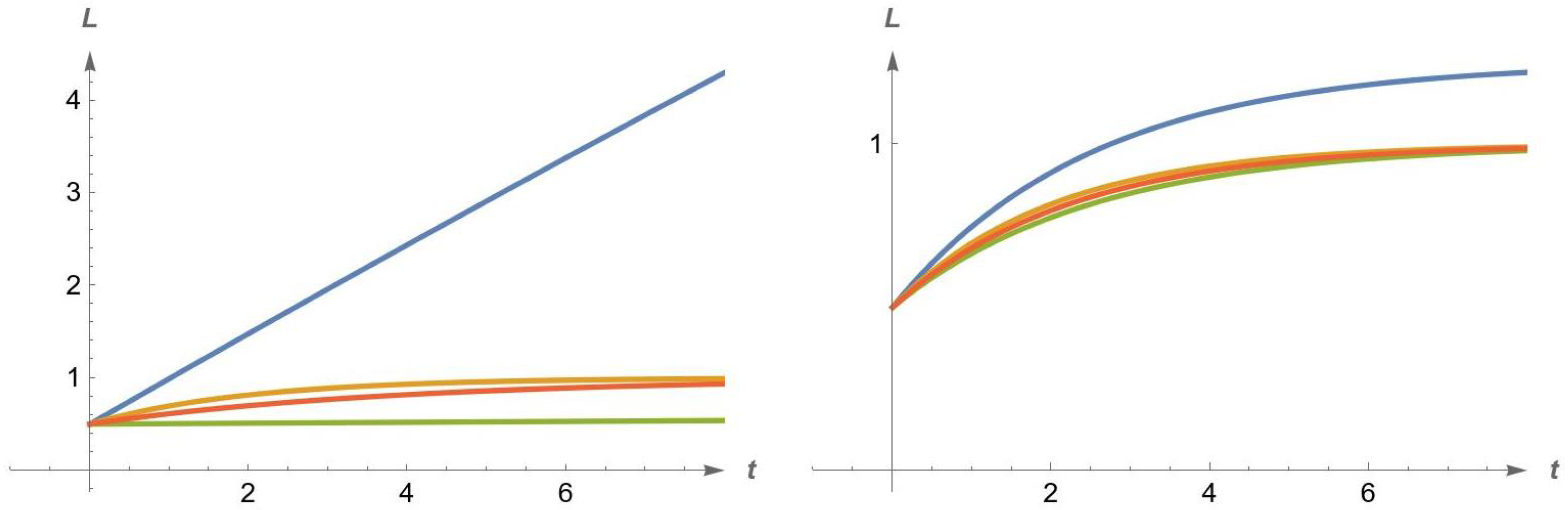
2.3. Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis
3. Model with a Time-Varying Parameter
3.1. Dynamics of Population and Capital Accumulation
3.2. Time-Varying Parameter Model Solution
- We are faced, again, with solving
- This time, though, the integral has no closed-form solution, due to the presence of the periodic perturbation. We can only compute its approximation using a numerical method of integration. At the same time, however, we can compute exactly an inferior bound and a superior bound for and show that the approximate also lies within these bounds.
3.3. Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis
- means that labour force prevails over capital, in the production function
- represents a situation of equilibrium;
- means that, in capital prevails over labour force.
3.4. Final Remark
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Domar, E. Capital Expansion, Rate of Growth, and Employment. Econometrica 1946, 14, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, R. A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth. Q. J. Econ. 1956, 70, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, T. Economic Growth and Capital Accumulation. Econ. Rec. 1956, 32, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, R.; Sala-i Martin, X. Economic Growth, 2nd ed.; MIT: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mingari-Scarpello, G.; Ritelli, D. The Solow model improved through the logistic manpower growth law. Annali Univ. Ferrara 2003, 49, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, J.; Maldonado, E. Closed form solutions to a generalization of the Solow growth model. Appl. Math. Sci. 2007, 1, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Donghan, C. An improved Solow-Swan model. Chin. Q. J. Math. 1998, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Ye, H.; Gu, L. A generalized Solow-Swan model. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchem Neto, J.; Claeyssen, J.; Ritelli, D.; Mingari-Scarpello, G. Closed-form solution for the Solow Model with Constant Migration. TEMA 2015, 16, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingari-Scarpello, G.; Ritelli, D. Closed form solution of a periodically forced logistic model. Ann. Univ. Ferrara 2008, 54, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, F.J. A Flexible Growth Function for Empirical Use. J. Exp. Bot. 1959, 10, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, E.; Brida, J. Re-Formulation of the Solow Economic Growth Model with the Richards Population Growth Law; Vol. RePEc 0508006, GE, Growth, Math methods; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, M. A note on the Solow economic growth model with Richards population growth law. Appl. Sci. 2011, 13, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Juchem Neto, J.; Paese, B. An intersectoral migration and growth model with distinct population growth rates. Econ. Bull. 2023, 43, 413–428. [Google Scholar]
- Juchem Neto, J.; Claeyssen, J.; Pôrto Júnior, S. Economic agglomerations and spatio-temporal cycles in a spatial growth model with capital transport cost. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 494, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchem Neto, J.; Claeyssen, J.; Pôrto Júnior, S. Returns to scale in a spatial Solow–Swan economic growth model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 533, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliano, M.; Cananà, L.; Ciano, T.; Ragni, S.; Ferrara, M. On the dynamics of a SIR model for a financial risk contagion. Qual. Quant. 2025, 59, 1177–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokye, M.; Nkangbi, S.Z.; Konadu, A.A.; Sackitey, A.L.; Mensah, J.A.; Guerrini, L.; Ferrara, M. Stability analysis of a delay logistic growth model with nonlinear harvesting. Qual. Quant. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaghy, K.P.; Federici, D.; Gandolfo, G. Continuous-time estimation of an endogenous growth model of an open economy. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2001, 35, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Ciano, T.; Gangemi, M.; Guerrini, L. Complex dynamics of a model with R& D competition. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucekkine, R.; Ruiz-Tamarit, J. Special functions for the study of economic dynamics: The case of the Lucas-Uzawa model. J. Math. Econ. 2008, 44, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard Smith, J. Models in Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- von Bertalanffy, L. A quantitative theory of organic growth (Inquiries on growth laws. II). Hum. Biol. 1938, 10, 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- WRI. Mathematica Quick Revision History. 2025. Available online: https://www.wolfram.com/mathematica/quick-revision-history.html (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Andrews, G.; Askey, R.; Roy, R. Special Functions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, H.; Erdélyi, A. Higher Transcendental Functions; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1955; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rainville, E. Special Functions; Chelsea: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Cloern, J.E.; Nichols, F.H. A von Bertalanffy growth model with a seasonally varying coefficient. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1978, 35, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essington, T.E.; Kitchell, J.F.; Walters, C.J. The von Bertalanffy growth function, bioenergetics, and the consumption rates of fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 58, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Maravelias, C.D. Modelling fish growth: Multi-model inference as a better alternative to a priori using von Bertalanffy equation. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, I.F. On a Seasonally Oscillating Growth Function; Technical Report; Division of Fisheries Research, CSIRO Marine Laboratories: Cleveland, Australia, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniou, M. Symbolic derivation of Runge–Kutta methods. J. Symbolic Comput. 1994, 18, 265–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniou, M.; Knapp, R. Advanced Numerical Differential Equation Solving in Mathematica; Wolfram Media: Champaign, IL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniou, M.; Spaletta, G. Increment formulations for rounding error reduction in the numerical solution of structured differential systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2003, 19, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniou, M.; Spaletta, G. On the construction of a new generalization of Runge–Kutta methods. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 2003, 74, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniou, M.; Spaletta, G. Hybrid Solvers for Splitting and Composition Methods. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 2006, 185, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.C. The Numerical Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations: Runge–Kutta and General Linear Methods; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, J. Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bargellini, A.E.; Ritelli, D.; Spaletta, G. Extended von Bertalanffy Equation in Solow Growth Modelling. Algorithms 2025, 18, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090565
Bargellini AE, Ritelli D, Spaletta G. Extended von Bertalanffy Equation in Solow Growth Modelling. Algorithms. 2025; 18(9):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090565
Chicago/Turabian StyleBargellini, Antonio E., Daniele Ritelli, and Giulia Spaletta. 2025. "Extended von Bertalanffy Equation in Solow Growth Modelling" Algorithms 18, no. 9: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090565
APA StyleBargellini, A. E., Ritelli, D., & Spaletta, G. (2025). Extended von Bertalanffy Equation in Solow Growth Modelling. Algorithms, 18(9), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090565






