Performance Optimization of a Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller Using Grey Wolf-Based Multi-Objective Algorithms and Regression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Develop a novel MOGWO-based approach for optimizing a single-stage dual-bed adsorption chiller;
- Optimize the coefficient of performance (COP), cooling capacity (), and waste heat recovery efficiency ();
- Conduct a one-at-a-time (OAT) sensitivity analysis to quantify how key decision variables influence each objective.
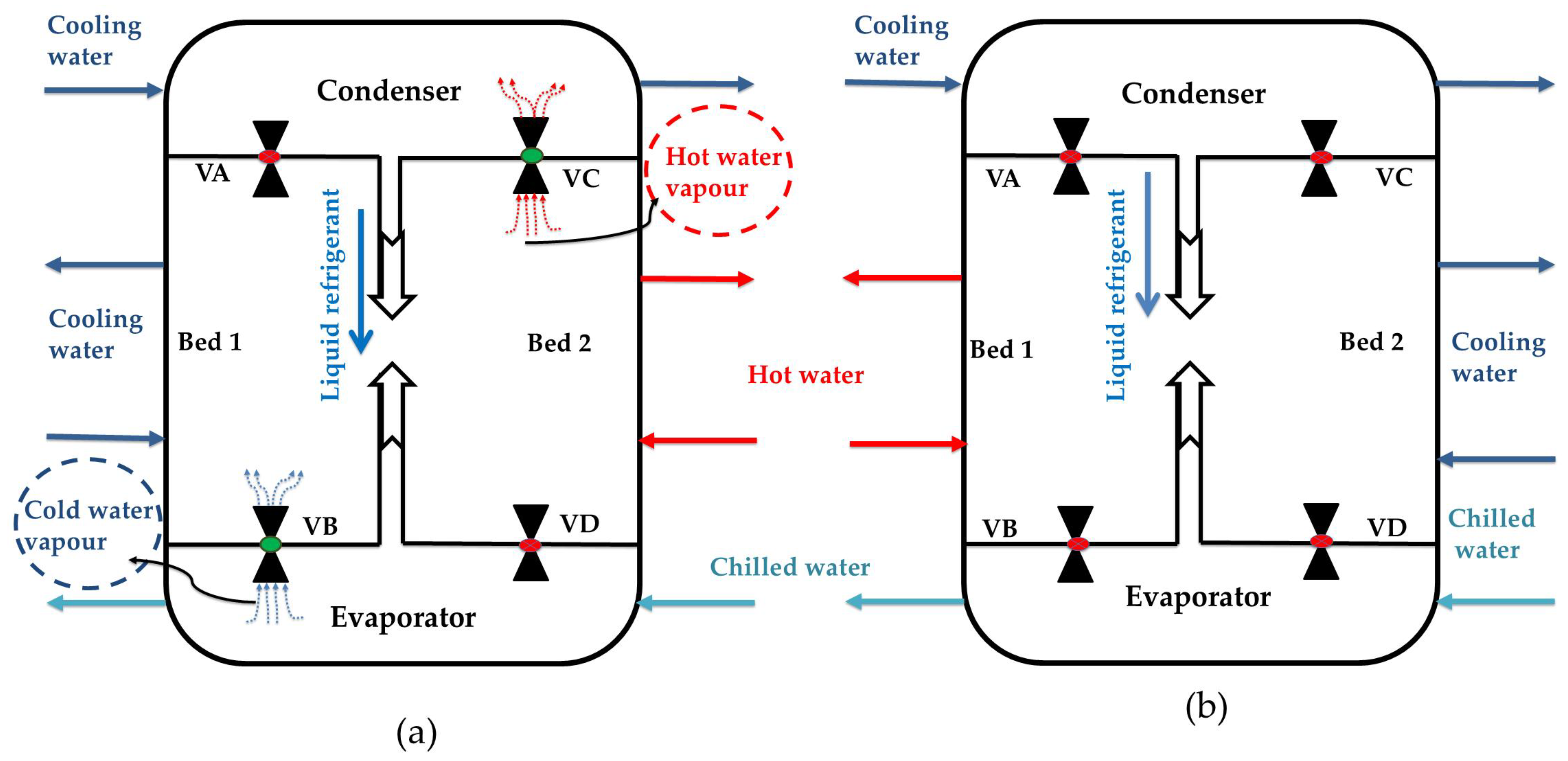
2. Materials and Methods
- 1.
- Maximize COP: For adsorption cycles, COP is a key performance indicator calculated by estimating the cooling and heating within the evaporator and condenser, respectively. The formula for the chiller’s COP can be expressed as in Equation (1) [18].
- = half cycle time;
- = chilled water mass flow rate;
- = specific heat capacity of the water;
- = chilled water inlet temperature;
- = chilled water outlet temperature;
- = hot water inlet temperature;
- = hot water outlet temperature.
- = cooling water inlet temperature;
- = mass flow rate of the hot water;
- = cooling water mass flow rate of the bed;
- = cooling water mass flow rate of the condenser;
- = adsorbent bed overall thermal conductance;
- = evaporator overall thermal conductance;
- = condenser overall thermal conductance.
- 2.
- Maximize Cooling Capacity (): Cooling capacity is another primary indicator of adsorption chiller performance. Qcc is defined in Equation (3) [19].
- 3.
- Maximize waste heat recovery efficiency (): Effective heat recovery strategies are pivotal in enhancing the efficiency of ADCs, and heat recovery is shown to influence the overall system performance [19]. Thus, is defined as a performance indicator for the single-stage dual-bed ADC, according to Equation (5) [19].
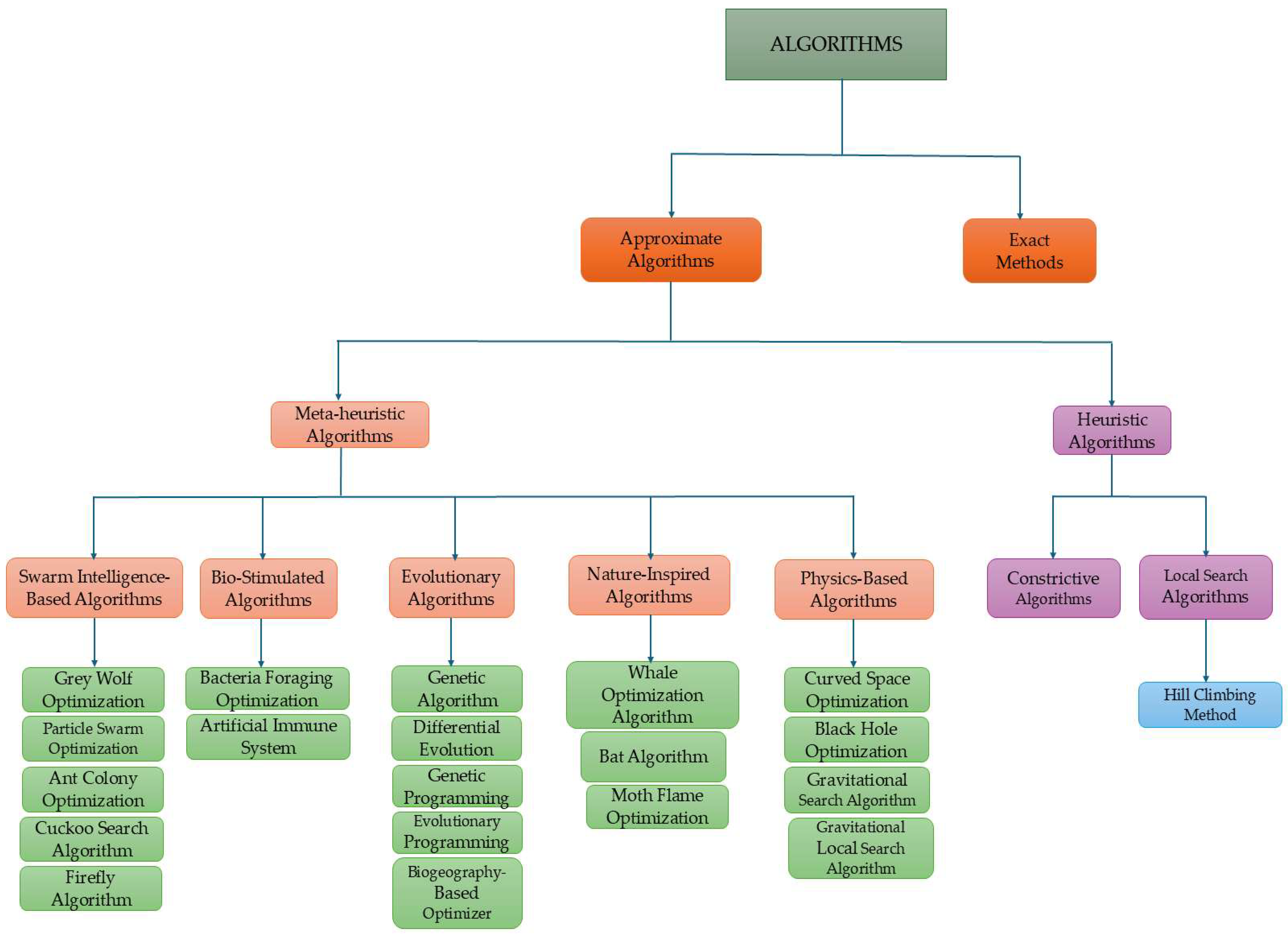
2.1. Overview of Algorithmic Techniques
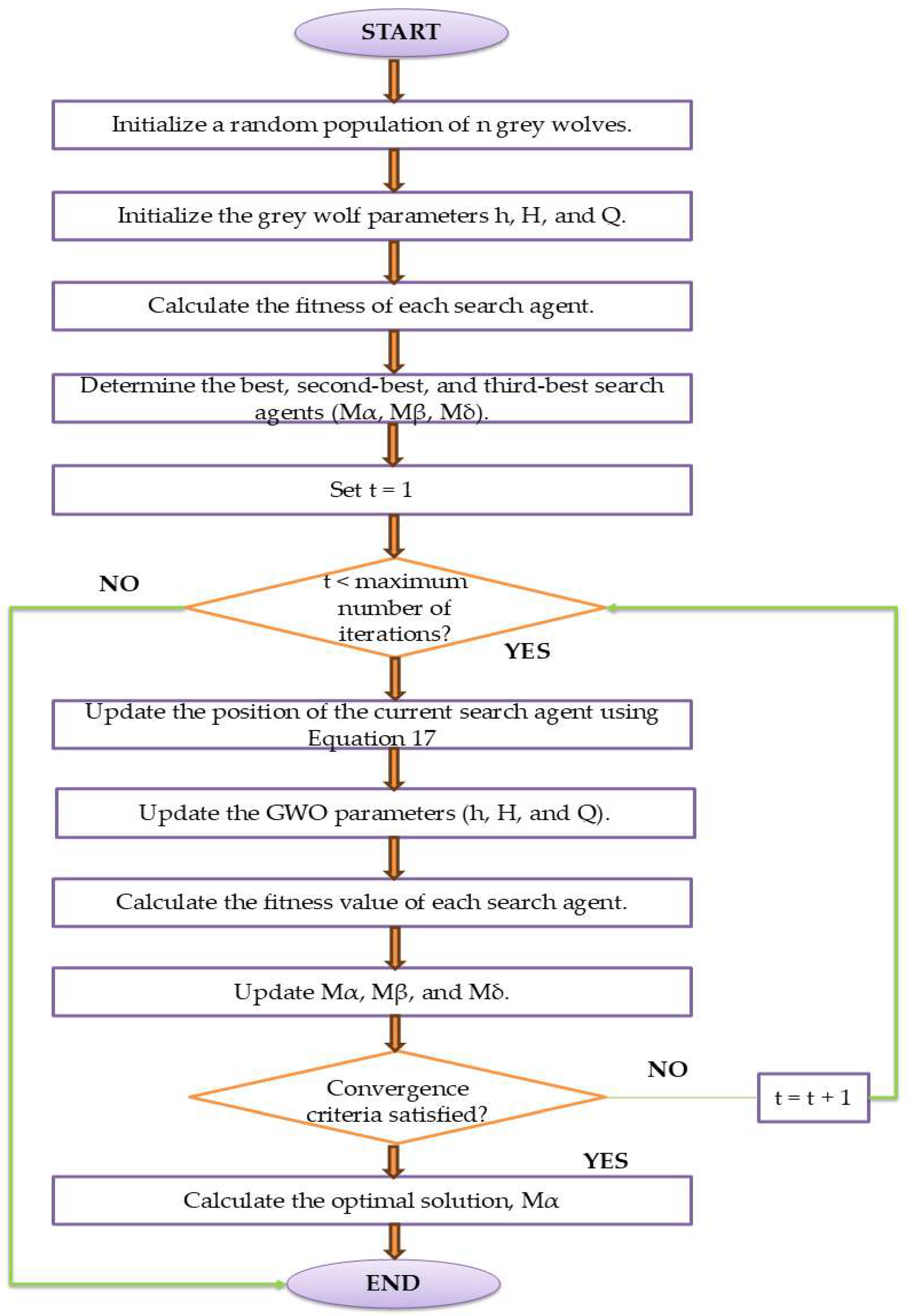
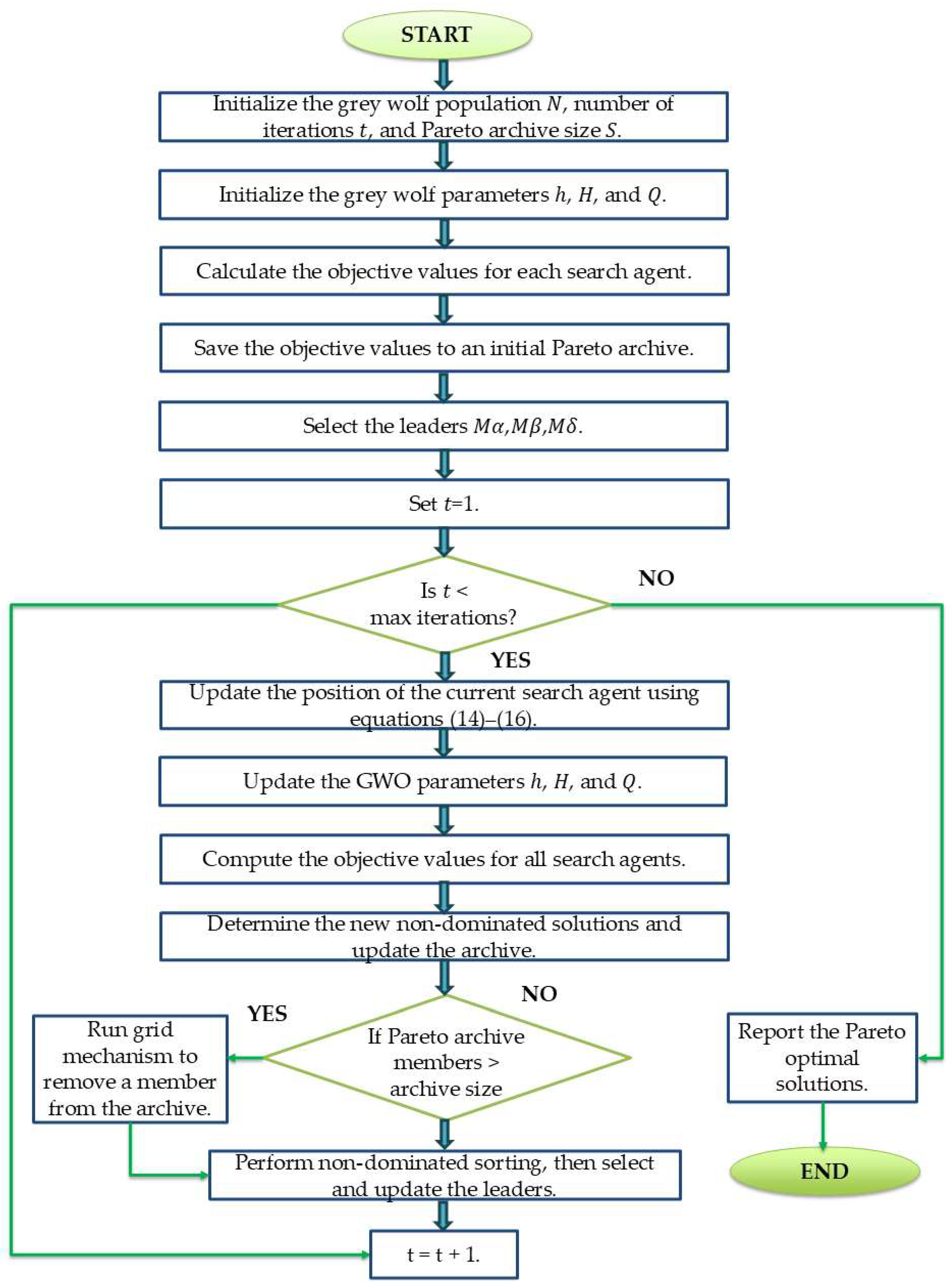
2.2. Greywolf Optimization (GWO)
- = current iteration;
- = coefficient vector;
- = position vector;
- = position vector of the prey.
2.3. Mathematical Formulation
- [°C];
- [°C];
- [°C];
- [kg/s];
- [kg/s];
- [kg/s];
- [kg/s];
- [W/K];
- [W/K];
- [W/K].
3. Results
3.1. Single-Objective Optimization
3.1.1. Coefficient of Performance (COP) Maximization
- Increasing , , , , and ;
- Maintaining a lower value for ;
- Moderate values for and .
3.1.2. Cooling Capacity () Maximization
- Maximizing , , , , , and ;
- Minimizing and ;
- Moderating .
3.1.3. Waste Heat Recovery Efficiency () Maximization
- Maximizing ;
- Minimizing , and ;
- Moderating , , , and .
3.1.4. Analysis of the Single-Objective Optimization Results
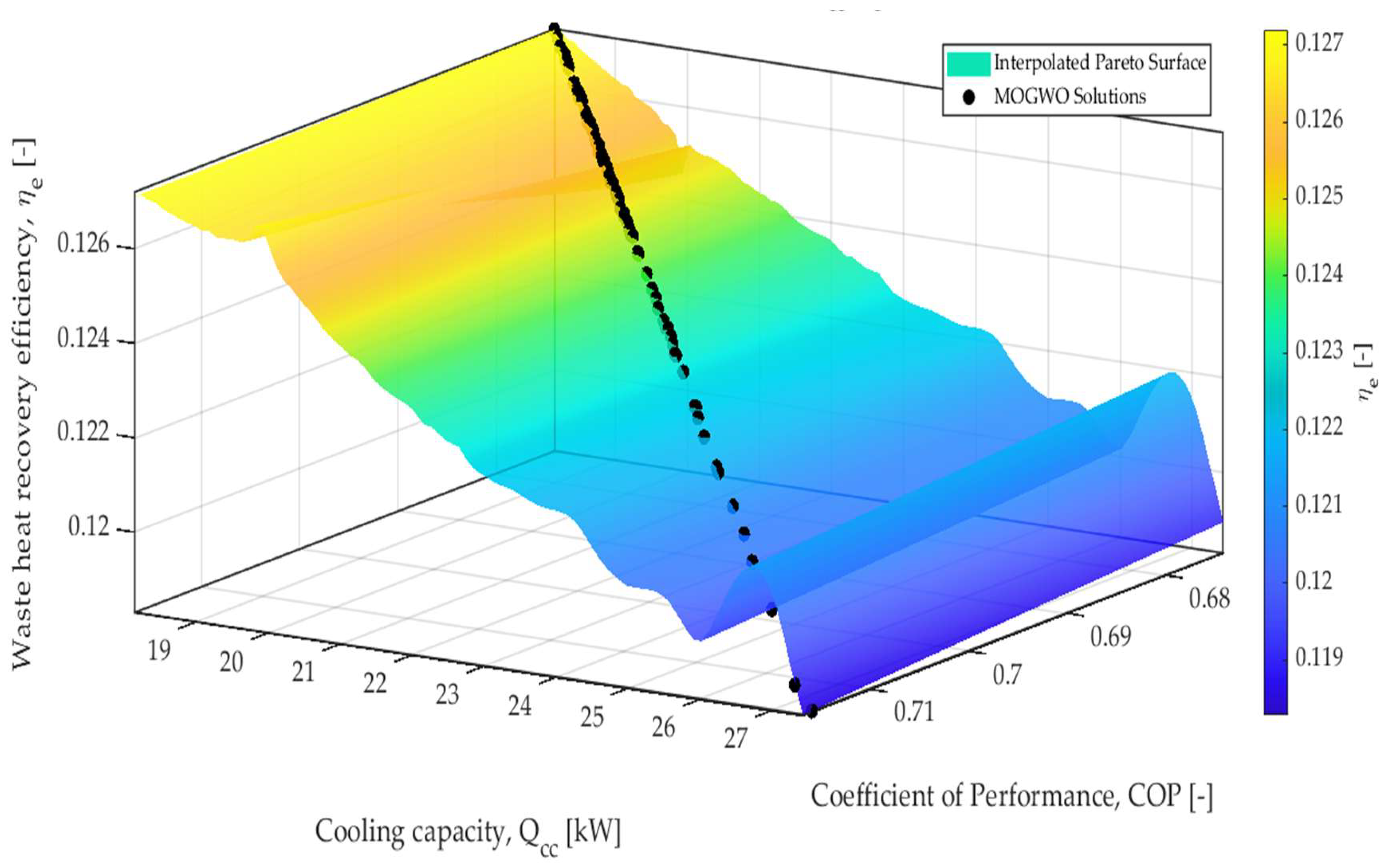
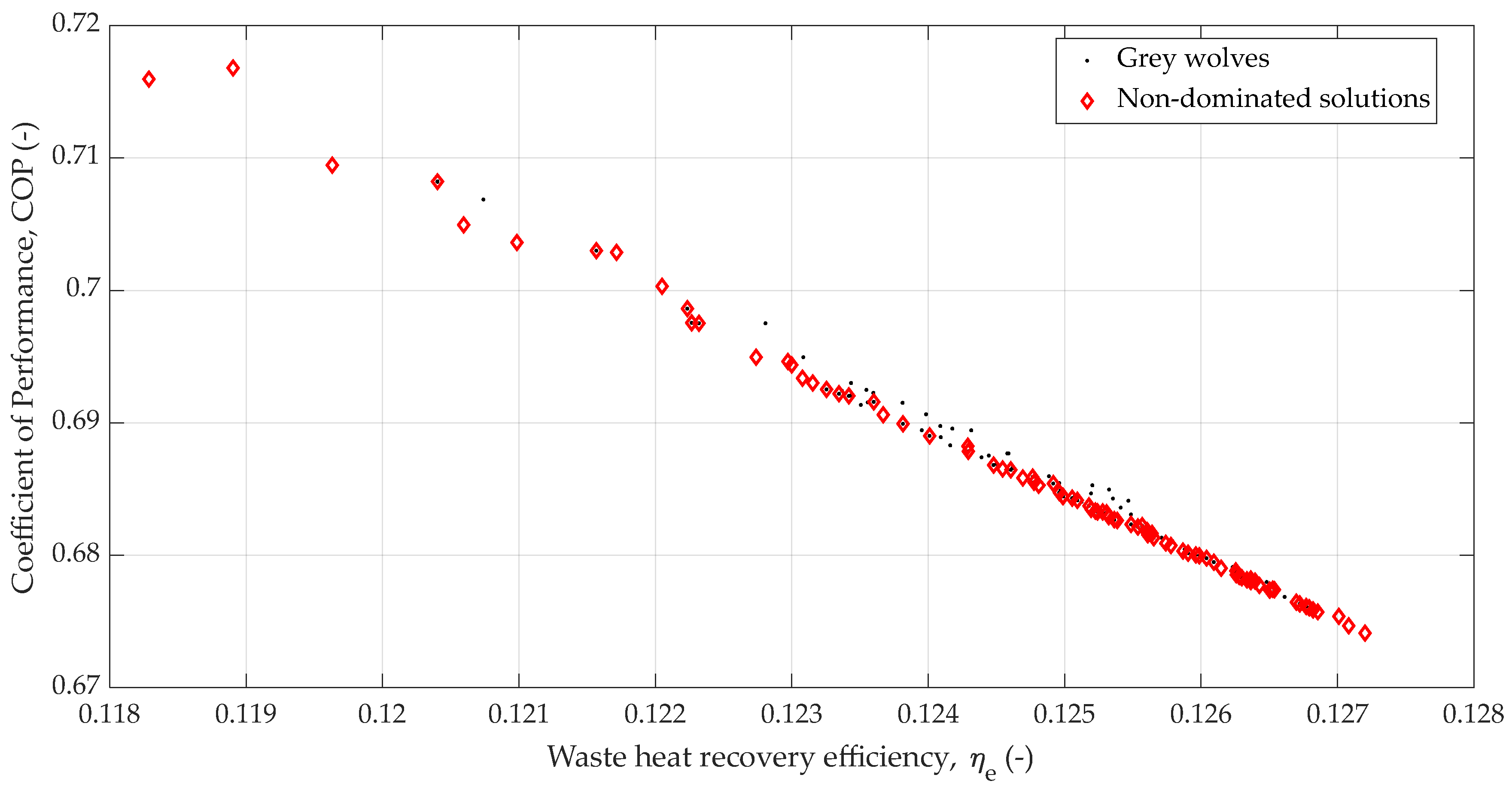
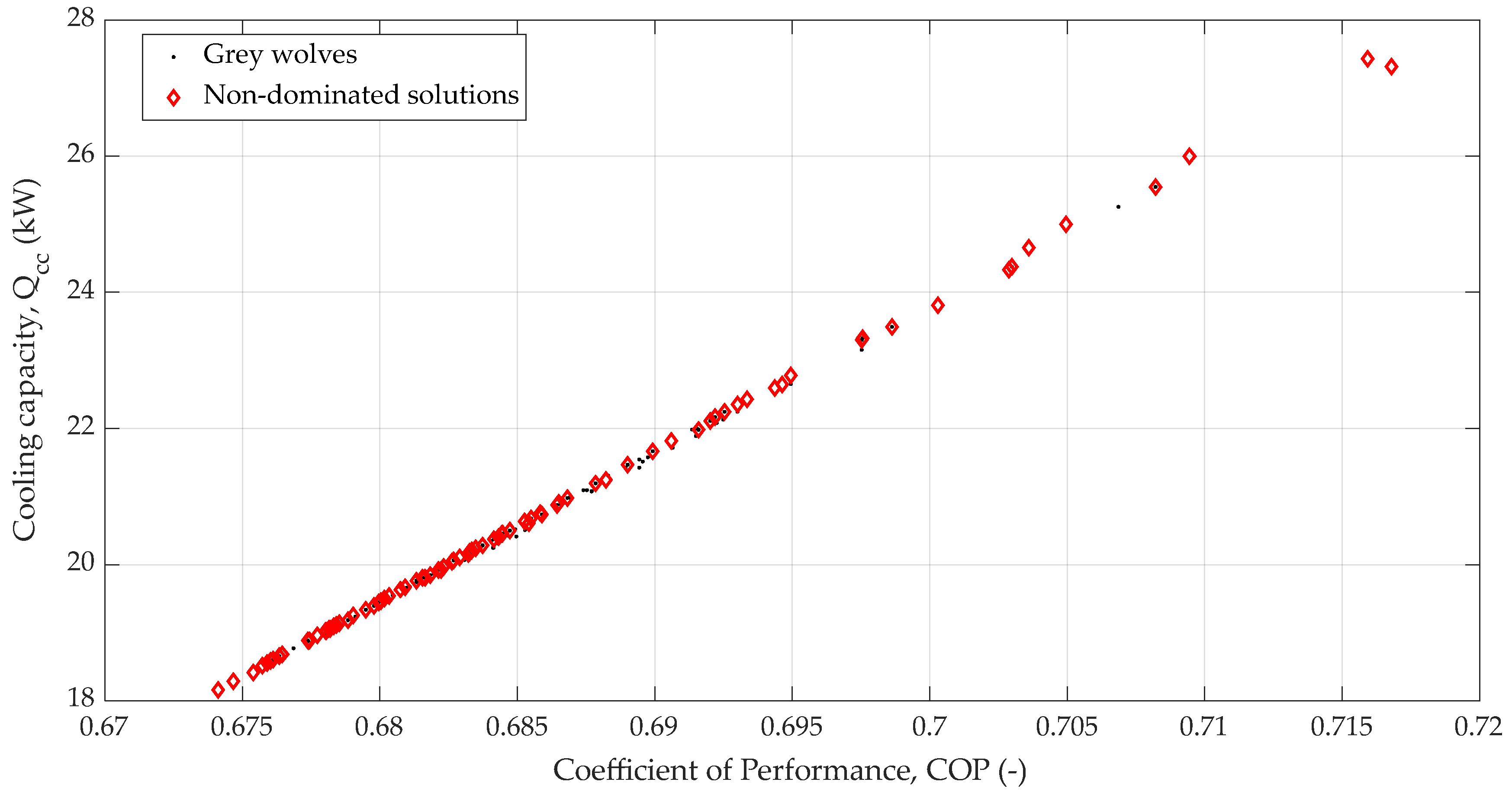
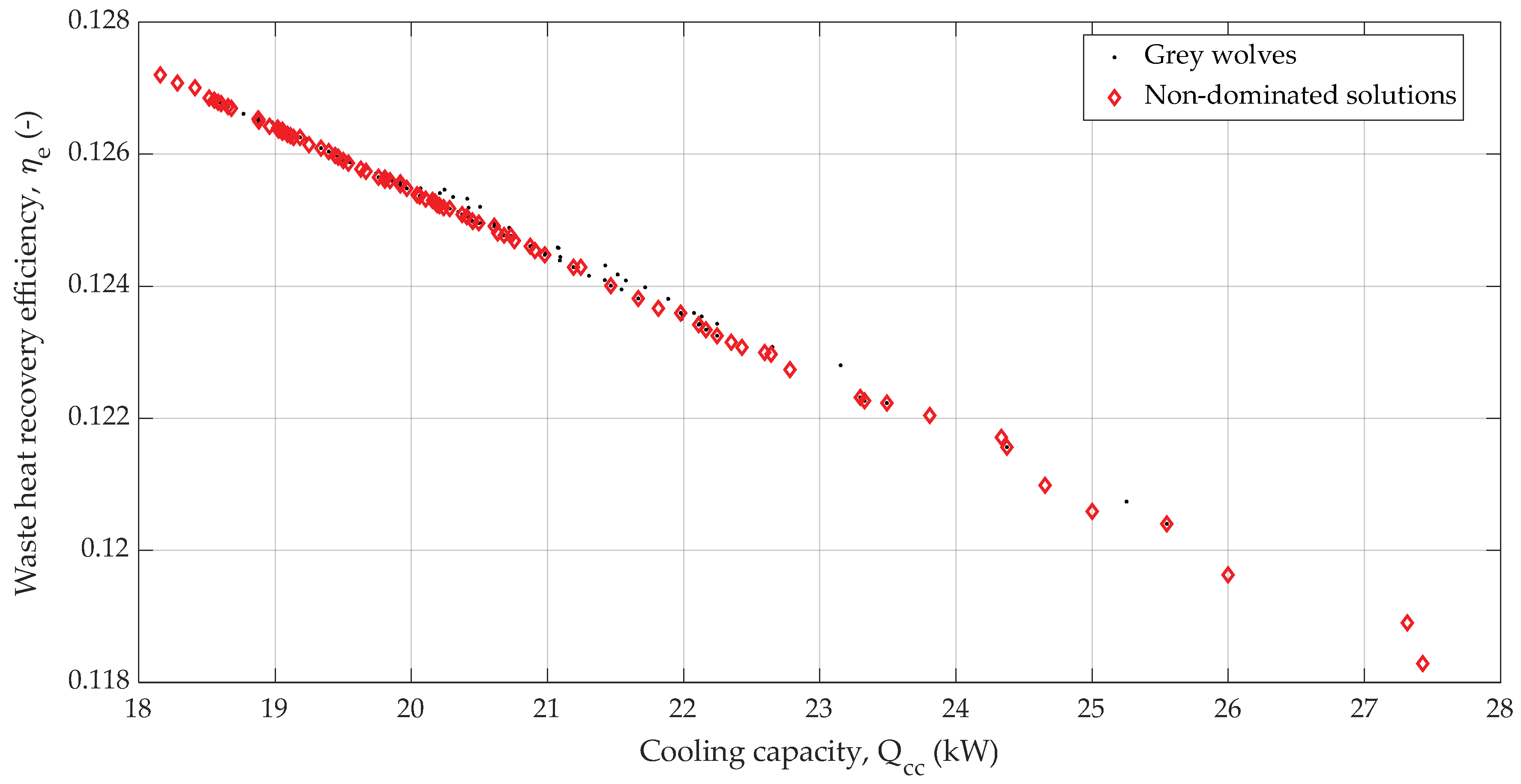
3.2. Multi-Objective Optimization
Representative Design Points and Decision Variables
3.3. Sensitivity
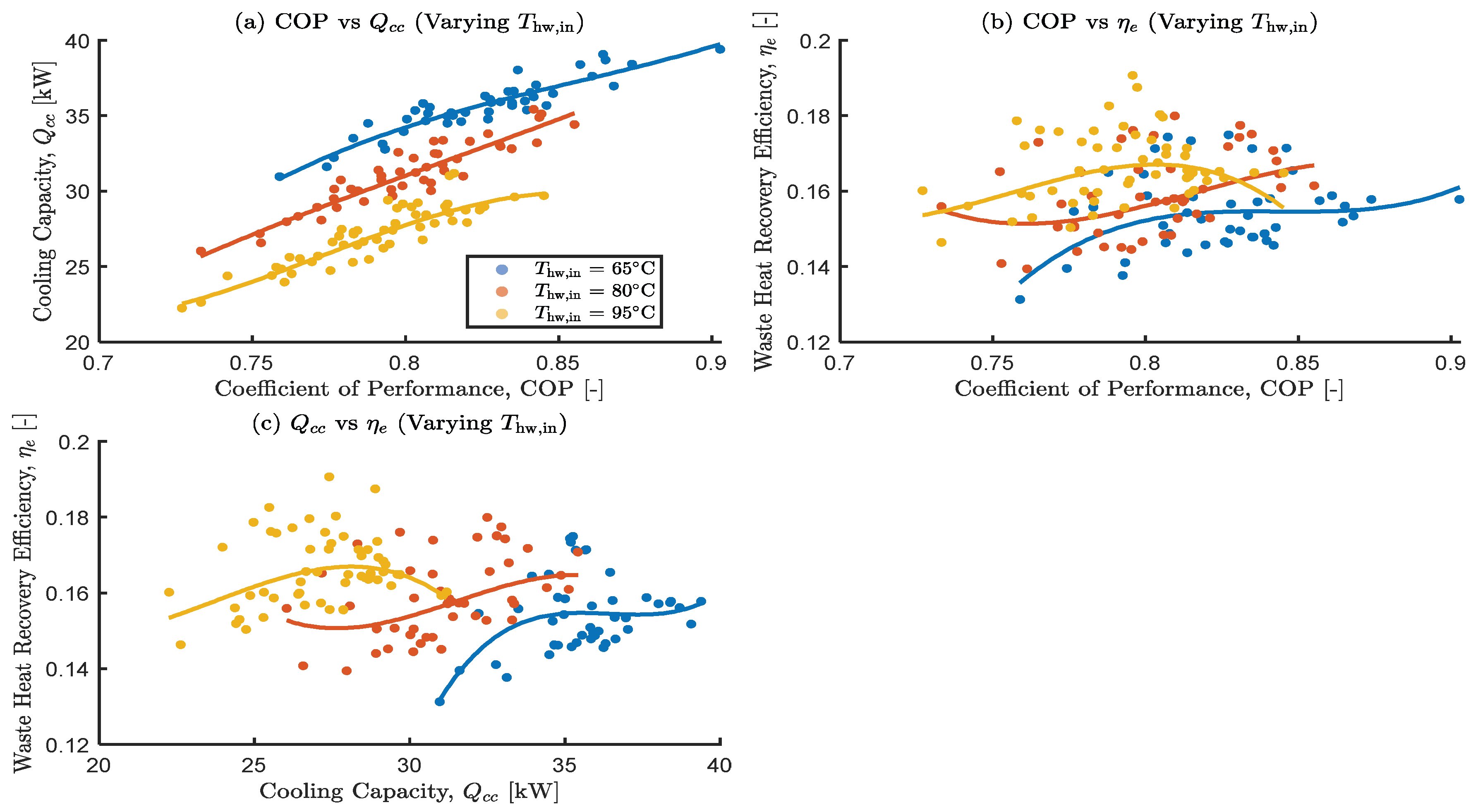
3.3.1. The Effects of Varying the Hot Water Inlet Temperature
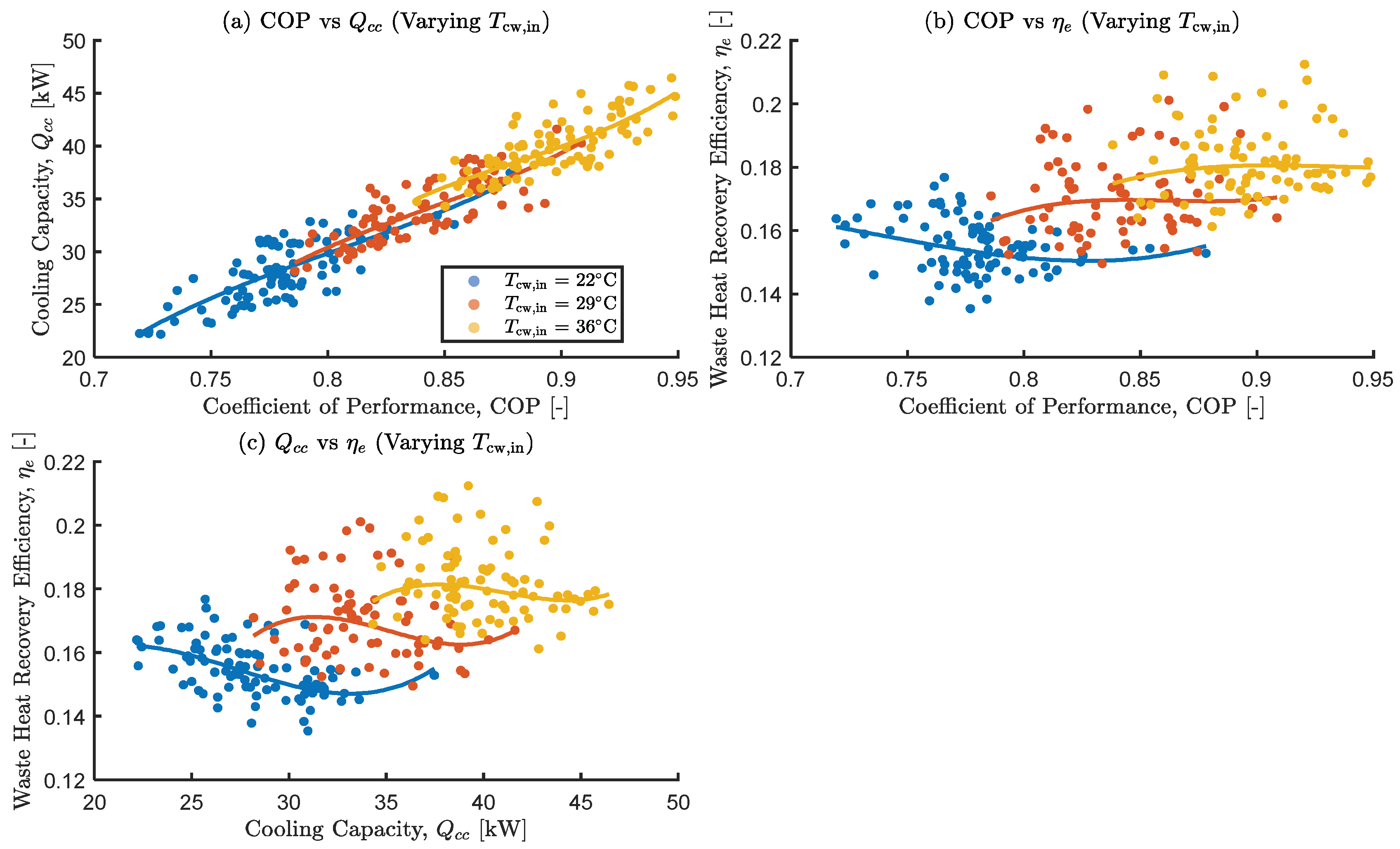
3.3.2. The Effects of Varying the Cooling Water Inlet Temperature
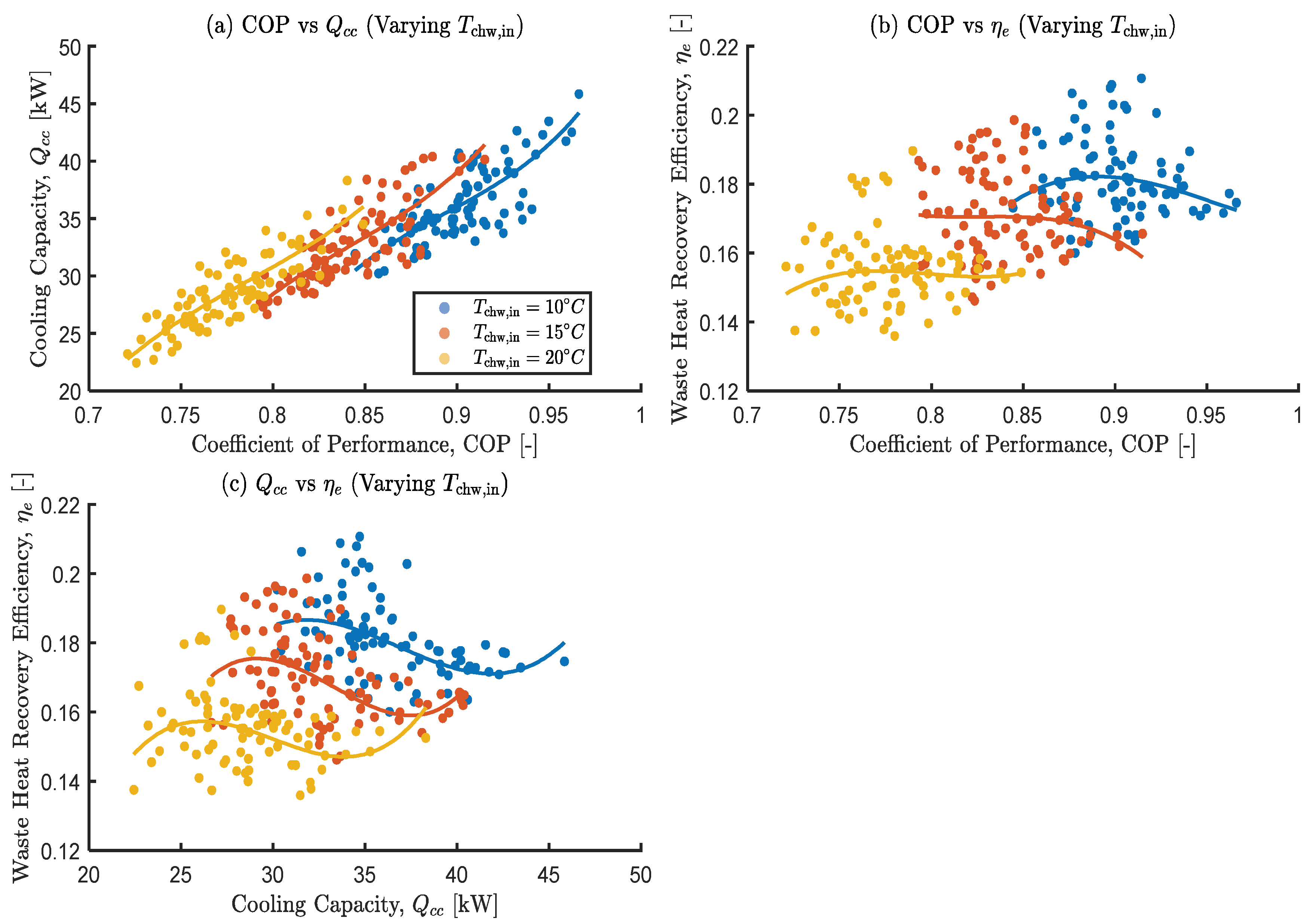
3.3.3. The Effects of Varying the Chilled Water Inlet Temperature
3.3.4. The Effects of Varying the Bed Cooling Water Mass Flow Rate
3.3.5. The Effects of Varying the Hot Water Mass Flow Rate
3.3.6. The Effects of Varying the Chilled Water Mass Flow Rate
3.3.7. The Effects of Varying the Condenser Cooling Water Mass Flow Rate
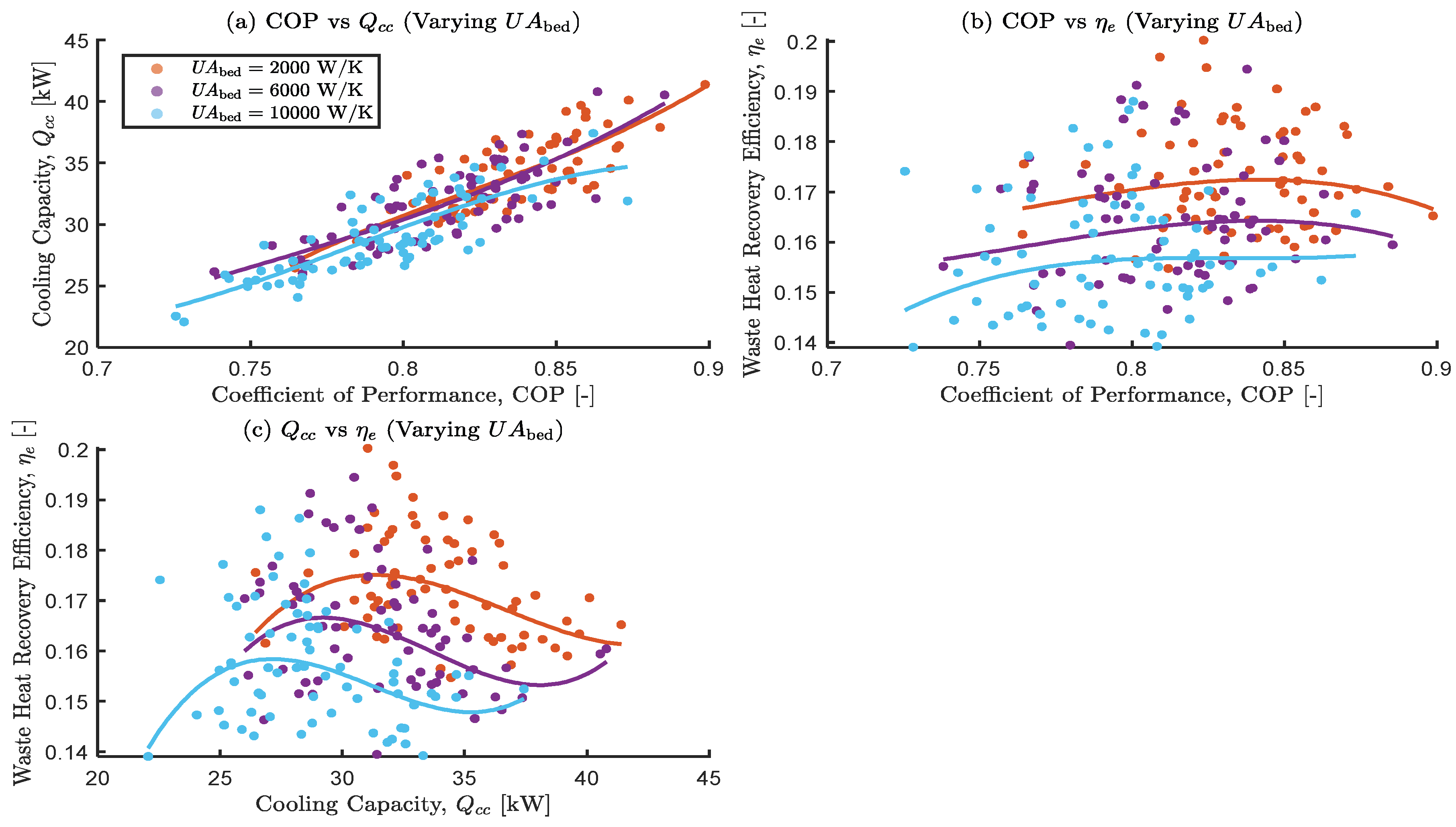
3.3.8. The Effects Varying the Adsorbent Bed Overall Thermal Conductance
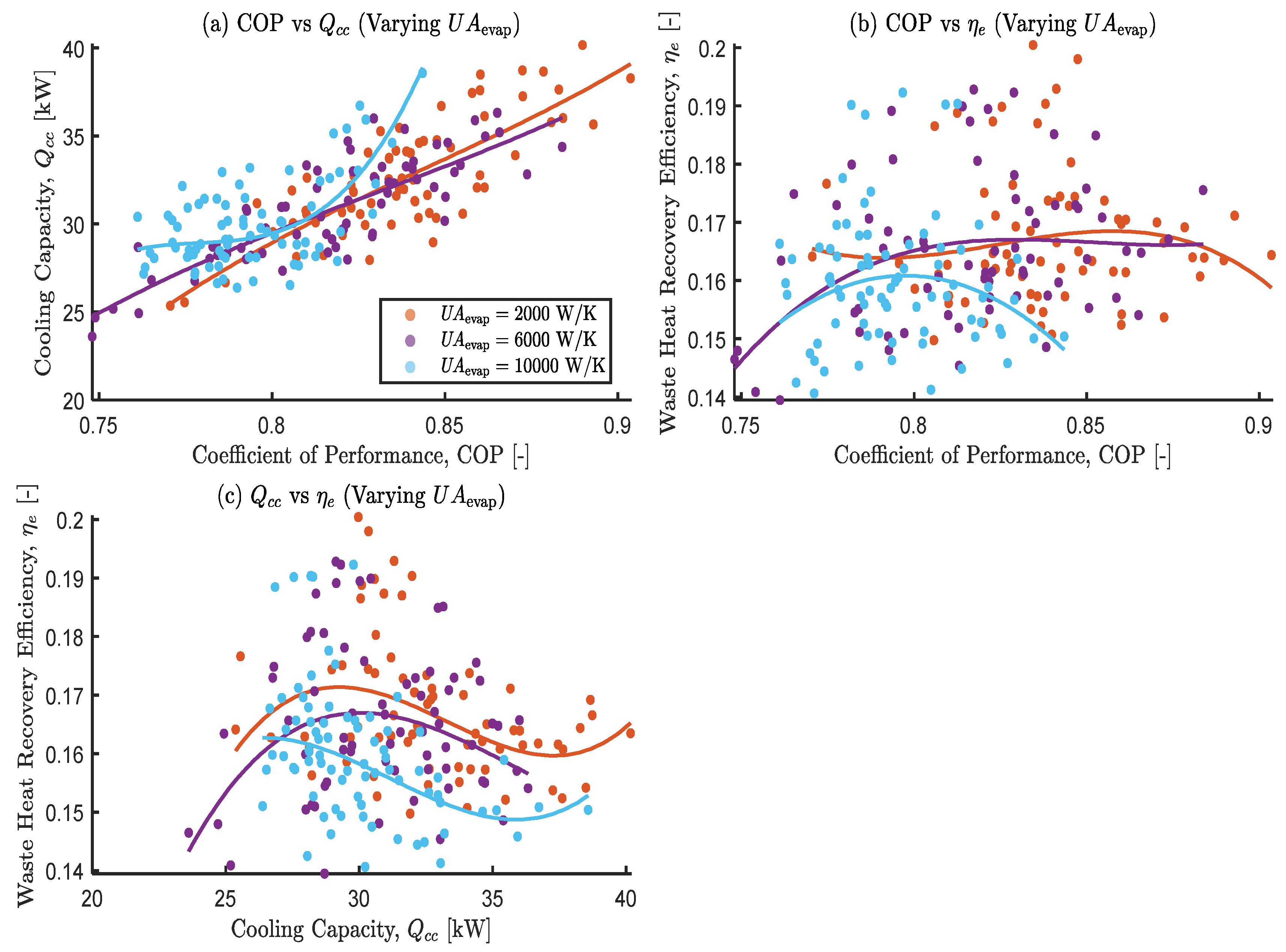
3.3.9. The Effects of Varying the Evaporator Overall Thermal Conductance
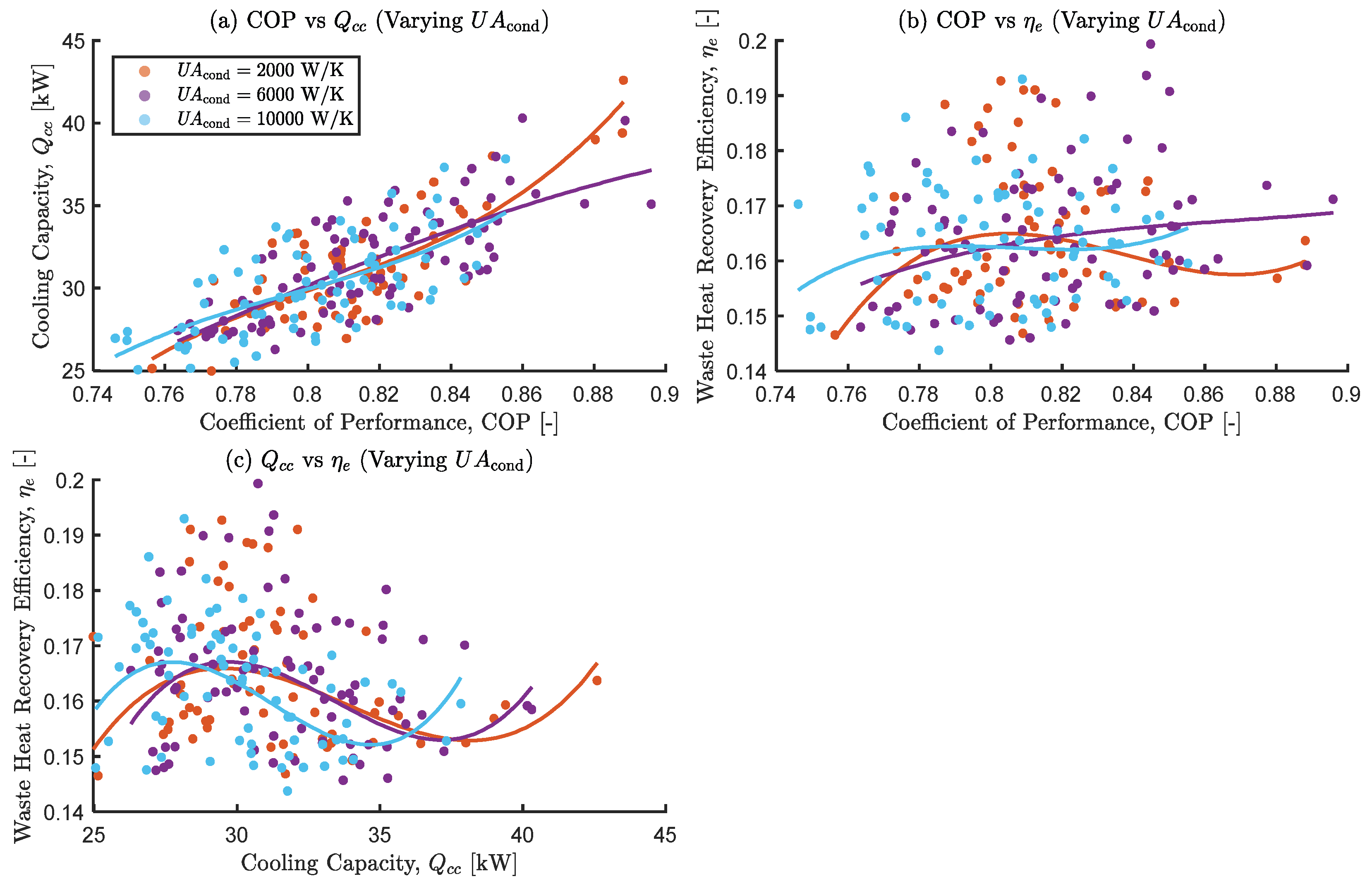
3.3.10. The Effects of Varying Condenser Overall Thermal Conductance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- A multi-objective optimization approach based on MOGWO was used to identify Pareto-optimal sets of decisions (inlet temperatures, mass flow rates, and overall thermal conductance) for a single-stage dual-bed ADC. Instead of a single “best” solution, this approach generated a set of trade-off solutions.
- The MOGWO front exhibits COP values ranging from 0.5123 to 0.6859 and values from 12.45 to 20.73 kW, both surpassing Chua, Ng, and Saha’s [30] reported ranges of 0.50–0.65 COP and 6–10 kW at = 90 °C and = 25 °C. The attained values between 0.0824 and 0.1248 (8.24–12.48%) align well with the qualitatively reported range of approximately 10–12% by Chua, Ng, and Saha [30]. All MOGWO-selected decision variables fall within experimentally validated ranges, confirming the predictive accuracy of the regression models.
- Rather than a typical trade-off, the Pareto front for COP and showed a strong positive correlation, indicating the existence of a suitable thermodynamic synergy where both objectives co-improve.
- Table 7 shows a detailed description of how specific combinations of decision variables can maximize individual objectives (COP, , ) or offer a balanced compromise. This is to equip designers with actionable knowledge on the generated representative Pareto-optimal variable sets.
- Results from the one-at-a-time (OAT) sensitivity analysis showed that higher hot water inlet temperatures and mass flow rates are crucial for maximizing , while lower cooling and chilled water inlet temperatures are beneficial for COP and . These confirm complex trade-offs and the non-monotonic influences of decision variables.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADCs | adsorption Chillers |
| MVC | mechanical vapour compression |
| COP | coefficient of performance |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| MOGWO | Multi-Objective Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| HFC | hydrofluorocarbon |
| HCFC | hydrochlorofluorocarbon |
| RAC | refrigeration and air conditioning |
| GHG | greenhouse gas |
| SEER | seasonal energy efficiency ratio |
| KPI | key performance indicators |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization |
| Symbols | |
| half cycle time | |
| chilled water mass flow rate | |
| cpw | specific heat capacity of the water |
| chilled water inlet temperature | |
| chilled water outlet temperature | |
| hot water inlet temperature | |
| hot water outlet temperature | |
| cooling water inlet temperature | |
| mass flow rate of the hot water | |
| cooling water mass flow rate of the bed | |
| cooling water mass flow rate of the condenser | |
| adsorbent bed overall thermal conductance | |
| evaporator overall thermal conductance | |
| condenser overall thermal conductance | |
| current iteration (in GWO algorithm) | |
| coefficient vector (in GWO algorithm) | |
| N | position vector (in GWO algorithm) |
| position vector of the prey (in GWO algorithm) | |
| H | coefficient vector (in GWO algorithm) |
| random value between 0 and 1 (in GWO algorithm) | |
| random value between 0 and 1 (in GWO algorithm) | |
| h | value decreasing linearly from 2 to 0 during the iterative optimization process (in GWO algorithm) |
| distance and direction of the current search agent (wolf) to the alpha (α) wolf | |
| distance and direction of the current search agent (wolf) to the beta (β) wolf | |
| distance and direction of the current search agent (wolf) to the delta (δ) wolf | |
| position of the alpha wolf | |
| position of the beta wolf | |
| position of the delta wolf | |
| next position of the search agent according to the influence of the alpha wolf | |
| next position of the search agent according to the influence of the beta wolf | |
| next position of the search agent according to the influence of the delta wolf | |
| coefficient vector (in GWO algorithm) | |
| coefficient vector (in GWO algorithm) | |
| coefficient vector (in GWO algorithm) |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Climate Change: Heat and Health (Fact Sheet); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Coulomb, D.; Dupont, J.-L. The Impact of the Refrigeration Sector on Climate Change; International Institute of Refrigeration/Institut International du Froid: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency. The Future of Cooling: Opportunities for Energy-Efficient Air Conditioning; IEA: Paris, France, 2018; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency. Net Zero Emissions Guide: Space Cooling (Part of Net Zero Roadmap); IEA: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Graff Zivin, J.; Neidell, M. Temperature and the Allocation of Time: Implications for Climate Change. J. Labor Econ. 2014, 32, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.L.; Domanski, P.; Lebrun, P.; Ziegler, F. 38th Note on Refrigeration Technologies: The Role of Refrigeration in the Global Economy; International Institute of Refrigeration: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, M.J.; Shapiro, H.N.; Boettner, D.D.; Bailey, M.B. Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, 8th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 1-118-82044-4. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Baredar, P.; Mittal, A.; Siddiqui, A.R. Adsorption Refrigeration Technology—An Overview of Theory and Its Solar Energy Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1389–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnier, D.; Goetz, V. Energy Storage Comparison of Sorption Systems for Cooling and Refrigeration. Sol. Energy 2001, 71, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Choudhury, B.; Das, R.K. Study of a Two-Bed Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller: Performance Analysis. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywanski, J.; Grabowska, K.; Sosnowski, M.; Zylka, A.; Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Wojcik, T.; Nowak, W. An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Model of a Re-Heat Two-Stage Adsorption Chiller. Therm. Sci. 2019, 23, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheniti, M.B.; Hassab, M.A.; Attia, A.-E. Examination of Effects of Operating and Geometric Parameters on the Performance of a Two-Bed Adsorption Chiller. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 146, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorowski, M.; Pyrka, P.; Rogala, Z.; Czupryński, P. Experimental Study of Performance Improvement of 3-Bed and 2-Evaporator Adsorption Chiller by Control Optimization. Energies 2019, 12, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, M.; Elgendy, E.; Elsayed, K.; Fatouh, M. Performance Enhancement of an Adsorption Chiller by Optimum Cycle Time Allocation at Different Operating Conditions. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019884780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, N.U.; Said, S.A.M.; Mansour, R.B.; Imran, H.; Khan, M. Performance Comparison of a Two-Bed Solar-Driven Adsorption Chiller with Optimal Fixed and Adaptive Cycle Times Using a Silica Gel/Water Working Pair. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, N.U.; Xu, Z.Y.; Pan, Q.W.; Said, S.A.M.; Mansour, R.B.; Akhtar, K. Performance Prediction of a Two-Bed Solar-Powered Adsorption Chiller with Heat and Mass Recovery Cycles and Adaptive Cycle Time—A First Step towards the Design of Fully Autonomous Commercial-Scale Adsorption Chillers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 192, 116950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, E.G.; Koronaki, I.P.; Papaefthimiou, V.D. Parametric Study of a Single-Stage Two-Bed Adsorption Chiller. J. Energy Eng. 2017, 143, 04016068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Akisawa, A. The Influence of Heat Exchanger Parameters on the Optimum Cycle Time of Adsorption Chillers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, I.I.; AbdelMeguid, H.; Saha, B.B. Towards an Optimal Performance of Adsorption Chillers: Reallocation of Adsorption/Desorption Cycle Times. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 63, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Linear Regression. In An Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer Texts in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 59–128. ISBN 978-1-0716-1417-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Lekhraj, L.; Kumar, A. Weighted Grey Wolf Optimizer with Improved Convergence Rate in Training Multi-Layer Perceptron to Solve Classification Problems. Jordanian J. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic Algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, K.; Goldberg, D.E. Control System Optimization Using Genetic Algorithms. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1992, 15, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Coelho, L.D.S. Multi-Objective Grey Wolf Optimizer: A Novel Algorithm for Multi-Criterion Optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 47, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO). 2024. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/44974-grey-wolf-optimizer-gwo (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-0-471-87339-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S. Multi-Objective Grey Wolf Optimizer (MOGWO) 2025. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/55979-multi-objective-grey-wolf-optimizer-mogwo (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Chua, H.T.; Ng, K.C.; Wang, W.; Yap, C.; Wang, X.L. Transient Modeling of a Two-Bed Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.T.; Ng, K.C.; Malek, A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Akisawa, A.; Saha, B.B. Modeling the Performance of Two-Bed, Sillica Gel-Water Adsorption Chillers. Int. J. Refrig. 1999, 22, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henig, M.I.; Buchanan, J.T. Tradeoff Directions in Multiobjective Optimization Problems. Math. Program. 1997, 78, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Manoharan, P.; Sinha, D.K.; Jangir, P.; Abualigah, L.; Alghamdi, T.A.H. Multi-Objective Resistance-Capacitance Optimization Algorithm: An Effective Multi-Objective Algorithm for Engineering Design Problems. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj Deepak, S.N.; Seiler, C.; Monahan, A.H. A Global Sensitivity Analysis of Parameter Uncertainty in the Classic Model. Atmosphere-Ocean 2024, 62, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roka, R.; Figueiredo, A.; Vieira, A.; Cardoso, C. A Systematic Review of Sensitivity Analysis in Building Energy Modeling: Key Factors Influencing Building Thermal Energy Performance. Energies 2025, 18, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Pulido, G.T.; Lechuga, M.S. Handling Multiple Objectives with Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Computat. 2004, 8, 256–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, A.; Rodríguez, D.; Garzón, W.; Gómez, D.F.; Al Sumaiti, A.; Rivera, S. Algorithms for Bidding Strategies in Local Energy Markets: Exhaustive Search through Parallel Computing and Metaheuristic Optimization. Algorithms 2021, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Shieh, C.-C. Experimental Study of a Solid Adsorption Cooling System Using Flat-Tube Heat Exchangers as Adsorption Bed. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlinda, M.; Uyun, A.S.; Miyazaki, T.; Ueda, Y.; Akisawa, A. Performance Analysis of a Double-Effect Adsorption Refrigeration Cycle with a Silica Gel/Water Working Pair. Energies 2010, 3, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Puri, I.K. Waste Heat Recovery in a Data Center with an Adsorption Chiller: Technical and Economic Analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 245, 114576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarayreh, A.A.; Al-Maaitah, A.; Attarakih, M.; Bart, H.-J. Energy and Exergy Analyses of Adsorption Chiller at Various Recooling-Water and Dead-State Temperatures. Energies 2021, 14, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheniti, M.B.; Abd El-Hamid, A.T.; El- Samni, O.A.; Elsherbiny, S.M.; Elsayed, E. Experimental Evaluation of a Solar Two-Bed Lab-Scale Adsorption Cooling System. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Sur, A.; Sarma, N.D.; Chaurasiya, S.P. Comparative Study on Performances of Waste Heat Driven Adsorption Cooling System Using Silica Gel/Methanol and Silica Gel/Water Working Pair. J. Eur. Syst. Autom. 2024, 57, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, A.M.S.; Erkek, T.Ü.; Jaber, M.W.K.; Güngör, A. Performance Prediction of a Two-Bed Adsorption Chiller Considering the Impact of Hot and Cooling Water Temperatures and Hot Water Mass Flow Rate. In Proceedings of the AES 2021 Symposium Abstract Book, Trabzon, Turkey, 24 March 2021; pp. 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Baudouy, B. Heat Transfer and Cooling Techniques at Low Temperature. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1501.07153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishugah, F.T.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z. Performance Improvement of an Adsorption Chiller Using Composite Adsorbent, Silica Gel Impregnated with Lithium Chloride, Paired with Methanol as the Adsorbate. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 2014, 22, 1440003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çengel, Y.A.; Boles, M.A. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-07-339817-4. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, G.P.; Henry, W.; Thuillard, M. Improving Campus Chilled Water Systems with Intelligent Control Valves: A Field Study. In Proceedings of the AEI 2013, State College, PA, USA, 5 April 2013; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- ARANER. How to Improve a Chilled Water Refrigeration System. Available online: https://www.araner.com/blog/chilled-water-refrigeration-system (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Vartolomei, H.M. Theoretical Analysis of the Entropy Flow Generated by the Fluid Flow with Friction and Heat Exchange. AMM 2014, 659, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, E.I.; Jasem, B. Influence of Irreversibility and Entropy Production Produced by Nanofluid on the Performance of Heat Exchanger. In Proceedings of the Volume 10: Mechanics of Solids, Structures, and Fluids; Micro- and Nano-Systems Engineering and Packaging, Portland, Oregon, USA, 17 November 2024; p. V010T13A021. [Google Scholar]
- Stefański, S.; Mika, Ł.; Sztekler, K.; Kalawa, W.; Lis, Ł.; Nowak, W. Adsorption Bed Configurations for Adsorption Cooling Application. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 108, 01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkar, S.; Mulukh, R.; Narhari, G.; Kulkarni, S. Department of Chemical Engineering, Gharda Institute of Technology, Lavel, Khed, 415708, INDIA Intensification of Temperature Swing Adsorption. J. Sustain. Mater. Process. Manag. 2022, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppi, T.; Villa, T.; Vasta, S.; Mittelbach, W.; Freni, A. Testing of a Falling-Film Evaporator for Adsorption Chillers. Energies 2022, 15, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.I.; Alam, K.C.A.; Saha, B.B.; Hamamoto, Y.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Parametric Study of a Two-Stage Adsorption Chiller Using Re-Heat—The Effect of Overall Thermal Conductance and Adsorbent Mass on System Performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2006, 45, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Park, M.Y.; Duong, X.Q.; Cao, N.V.; Chung, J.D. Effects of Evaporator and Condenser in the Analysis of Adsorption Chillers. Energies 2020, 13, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvålseth, T.O. Cautionary Note about R2. Am. Stat. 1985, 39, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
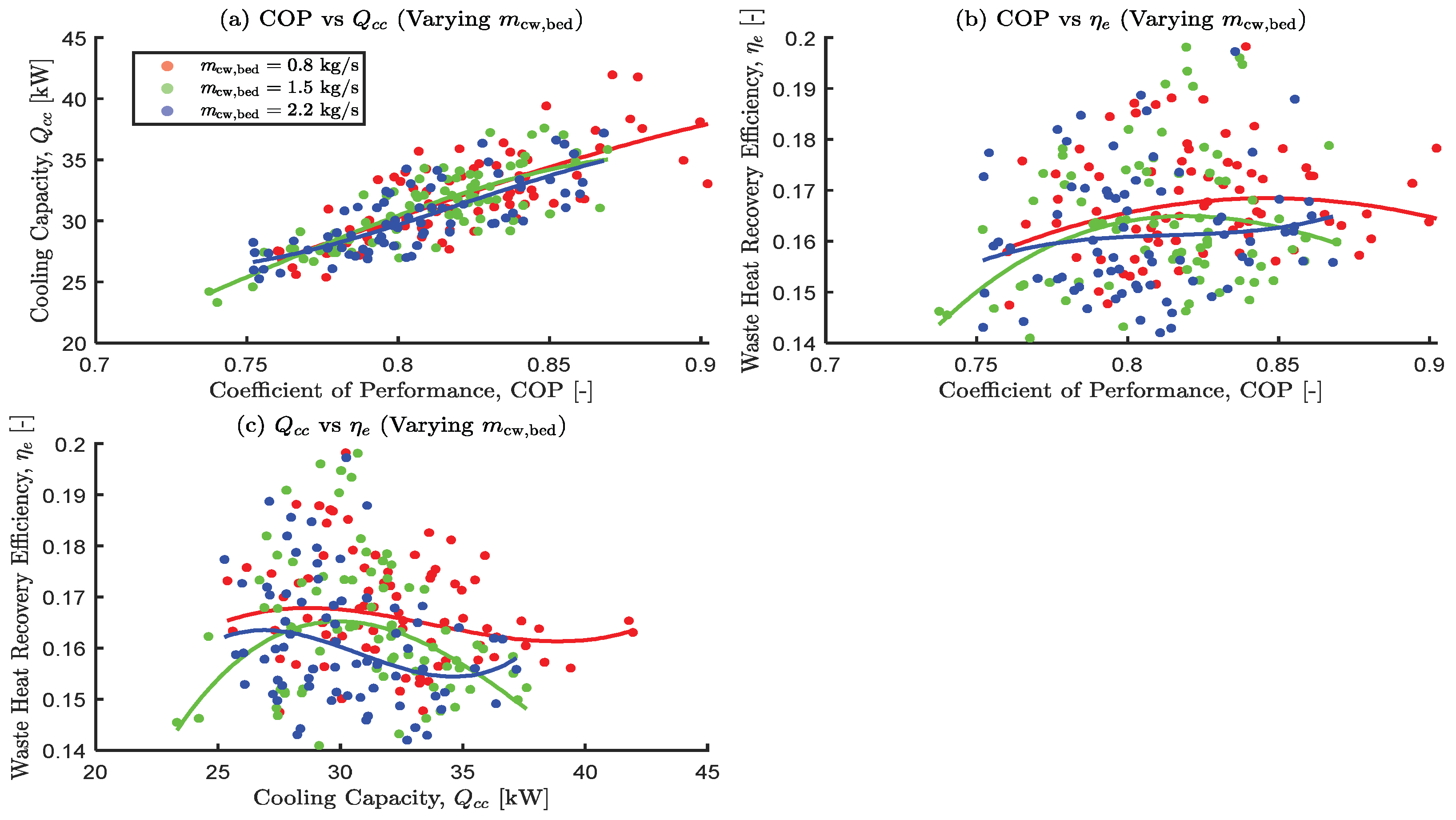
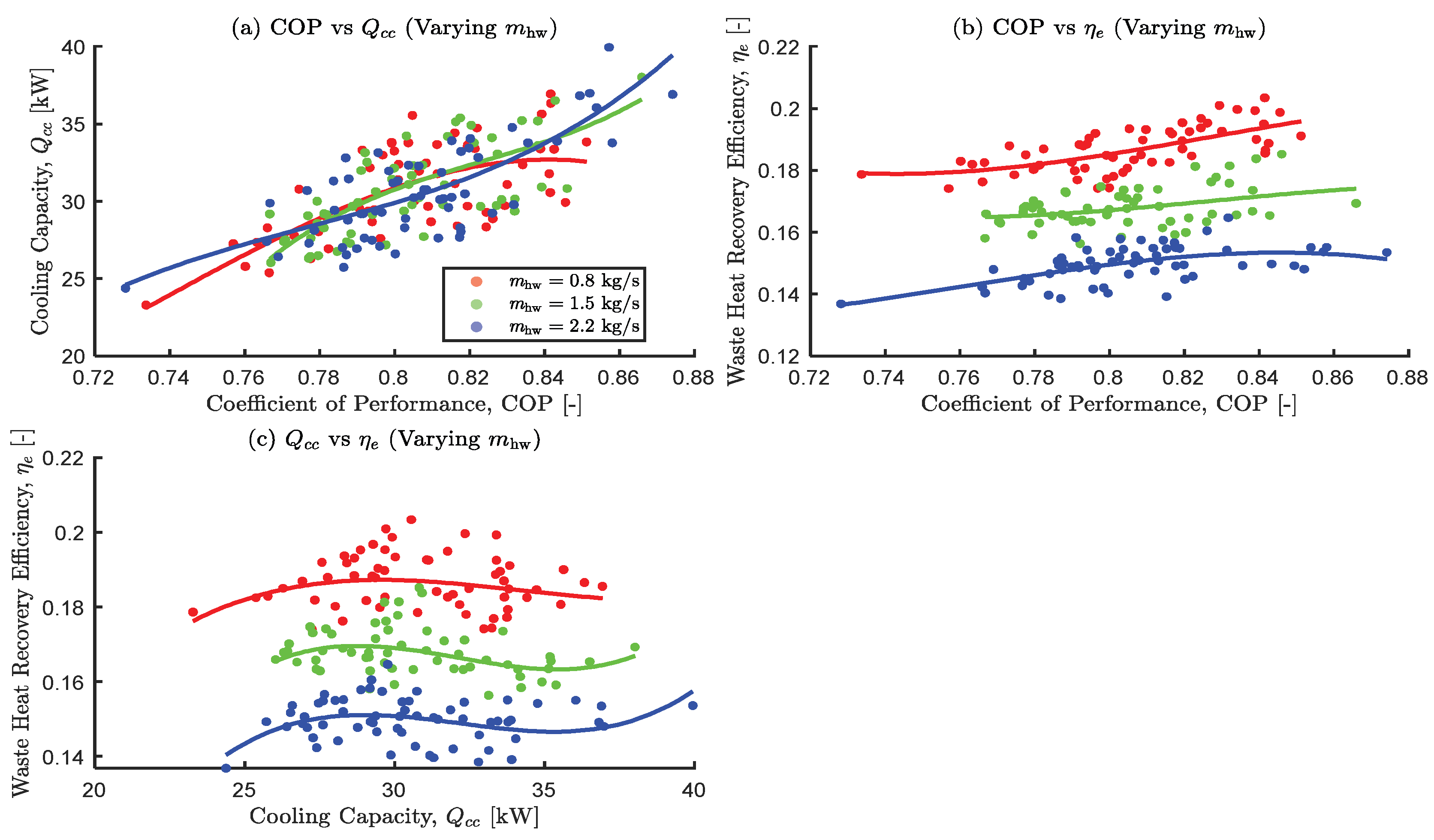
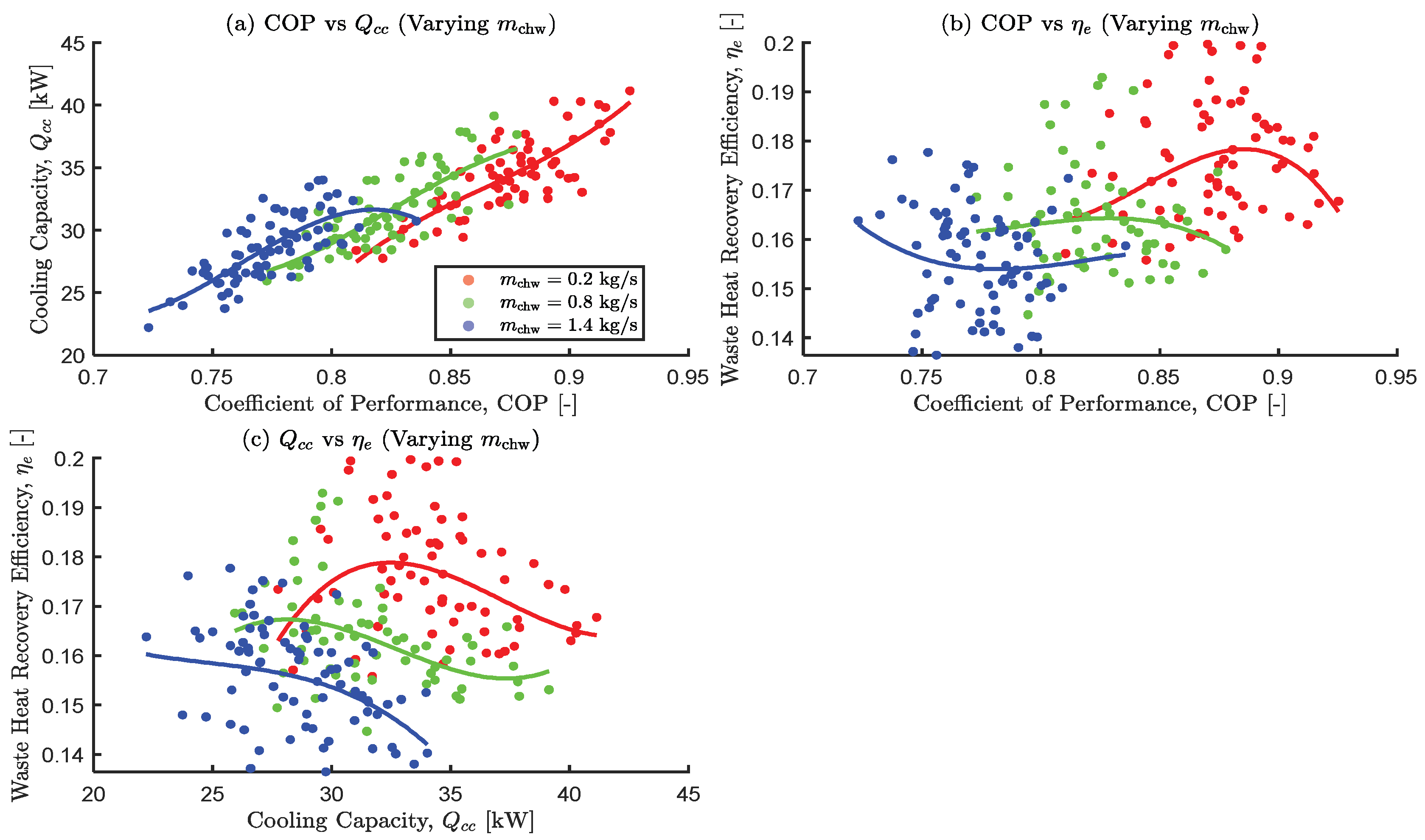
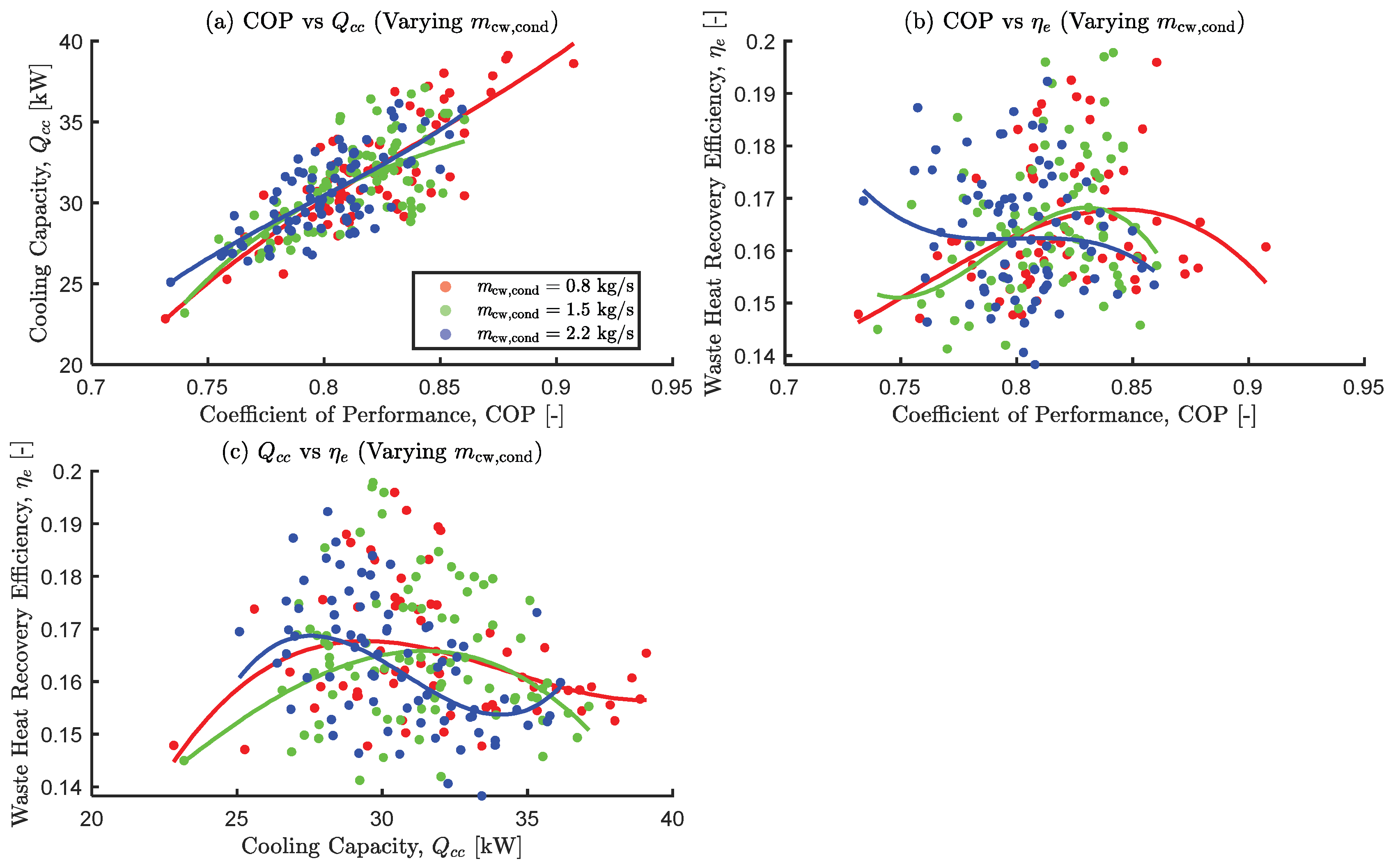
| Study | System Type | Working Pair | Heat Source |
Cycle Configuration | KPIs Evaluated | Reported Performance | Optimization Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sah et al. [10] | Two-bed ADC | Silica gel–Water | Hot Water (85 °C) | Fixed Cycle (1600 s) | COP, | = 5.95 kW at = 85 °C, = 25 °C, = 14 °C | No |
| Krzywanski et al. [11] | Re-heat Two-Stage ADC | Silica gel–Water | Hot Water | AI/ANFIS-based | Cooling Capacity | No explicit value(s) reported; ANFIS-based parametric modelling | Yes |
| Elsheniti et al. [12] | Two-bed ADC | Silica gel–Water | Hot Water | Geometry Variation | COP, SCC, | COP ↑ 68% and SCC ↑ 42% under turbulent regime | No |
| Chorowski et al. [13] | Three-bed, Two-evap ADC | — | Hot Water | Switching control (cooperation unit) | COP, Operational Noise | Improved control strategy led to COP increase | No |
| Gado et al. [14] | Two-bed ADC | Silica gel–Water | Hot Water | Optimized Cycle Time | Qcc, Enhancement Ratio | ↑ 15.6% at = 95 °C, = 40 °C, = 10 °C | No |
| Qadir et al. [15] | Two-bed, Solar ADC | Silica gel–Water | Solar | Adaptive vs. Fixed | COP, SCP | Adaptive cycle ↑ SCP by 19% and COP by 66%; min = 0.7 °C | No |
| Qadir et al. [16] | Two-bed Solar ADC | Silica gel–Water | Solar | Optimal Fixed vs. Adaptive | SCP, COP | Adaptive cycle ↑ SCP by 19% and COP by 66%; min = 0.7 °C | No |
| Present Study | Dual-bed, Single-stage ADC | Silica gel–Water | Waste Heat | MOGWO + Sensitivity | COP, , ηₑ | COP = 0.69, Qcc = 20.76 kW, = 0.125 | Yes (MOO + SA) |
| Variable Description | Symbol | Range | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot water inlet temperature | 65–95 | °C | |
| Cooling water inlet temperature | 22–36 | °C | |
| Chilled water inlet temperature | 10–20 | °C | |
| Hot water mass flow rate | 0.8–2.2 | kg/s | |
| Bed cooling water mass flow rate | 0.8–2.2 | kg/s | |
| Chilled water mass flow rate | 0.2–1.4 | kg/s | |
| Condenser cooling water mass flow rate | 0.8–2.2 | kg/s | |
| Adsorbent bed overall thermal conductance | 2000–10,000 | W/K | |
| Evaporator overall thermal conductance | 2000–10,000 | W/K | |
| Condenser overall thermal conductance | 10,000–24,000 | W/K |
| Decision Variable | Symbol | Optimal Value (Maximum COP) | Optimal Value (Maximum ) | Optimal Value (Maximum ) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot water inlet temperature | 95.00 | 95.00 | 65.00 | °C | |
| Cooling water inlet temperature | 22.00 | 22.00 | 22.00 | °C | |
| Chilled water inlet temperature | 20.00 | 19.99 | 19.98 | °C | |
| Hot water mass flow rate | 1.051 | 1.198 | 2.198 | kg/s | |
| Bed cooling water mass flow rate | 1.388 | 1.750 | 1.658 | kg/s | |
| Chilled water mass flow rate | 1.400 | 1.390 | 1.396 | kg/s | |
| Condenser cooling water mass flow rate | 1.364 | 1.126 | 1.244 | kg/s | |
| Adsorbent bed overall thermal conductance | 9830.45 | 9890.71 | 9882.41 | W/K | |
| Evaporator overall thermal conductance | 9931.11 | 7677.01 | 6501.39 | W/K | |
| Condenser overall thermal conductance | 14,157.87 | 11,495.20 | 12,386.87 | W/K | |
| Maximized objective value | — | 0.69695 | 20.7589 | 0.12527 | —/kW/— |
| Decision Variable | COP | Conflict | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ≠ | |
| ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ✓ | |
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | |
| ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ≠ | |
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | |
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | |
| ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ≠ | |
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | |
| ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ≠ | |
| ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Grid inflation parameter, alpha | 0.1 |
| Leader selection pressure parameter, beta | 4 |
| Gamma | 2 |
| Archive size | 100 |
| Number of agents | 100 |
| Maximum iterations | 50 |
| Number of grids per dimension (nGrid) | 100 |
| Final a | 0 |
| Random seed | 42 |
| Leader selection | Roulette wheel based on hypercube crowding |
| Crowding distance | Crowding handled through a hypercube grid and the “DeleteFromRep” function |
| Parameter | Chua, Ng, and Saha [29,30] | MOGWO—This Work |
|---|---|---|
| COP Range | 0.50–0.65 (at = 90 °C and = 25 °C) | 0.5123–0.6859 (at = 86.77 °C and ) = 22.01 °C) |
| Cooling Capacity (Qcc) | 6–10 kW (depending on cycle time and ) | 12.45–20.73 Kw |
| Waste-Heat Recovery Efficiency (ηₑ) | ≈ 0.10–0.12 (i.e., 10–12% of heat input converted to cooling at 90 °C/25 °C) | 0.0824–0.1248 (i.e., 8.24–12.48% of heat input recovered) |
| Operating Conditions | = 70–95 °C (optimal near 90 °C), = 20–30 °C (focus 25 °C); two beds, ~1 kg/bed; finned-tube UA (~103 W/K) | = 86.77 °C, = 22.01 °C; two beds; = 6000 W/K, = 17,000 W/K |
| Variable/Metric | Max COP Point | Point | Max ηₑ Point | Balanced Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | 95.00 | 95.00 | 65.00 | 80.00 |
| (°C) | 22.00 | 22.00 | 22.00 | 29.00 |
| (°C) | 20.00 | 19.99 | 19.98 | 15.00 |
| (kg/s) | 1.051 | 1.198 | 2.198 | 1.500 |
| (kg/s) | 1.388 | 1.750 | 1.658 | 1.500 |
| (kg/s) | 1.400 | 1.390 | 1.396 | 0.800 |
| (kg/s) | 1.364 | 1.126 | 1.244 | 1.500 |
| (W/K) | 9830.45 | 9890.71 | 9882.41 | 6000.00 |
| (W/K) | 9931.11 | 7677.01 | 6501.39 | 6000.00 |
| (W/K) | 14,157.87 | 11,495.20 | 12,386.87 | 17,000.00 |
| Achieved COP (-) | 0.69695 | 0.6000 | 0.5123 | 0.6000 |
| (kW) | 12.45 | 20.7589 | 15.00 | 16.00 |
| (-) | 0.0824 | 0.0900 | 0.12527 | 0.1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwakye-Boateng, P.; Tartibu, L.; Tien-Chien, J. Performance Optimization of a Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller Using Grey Wolf-Based Multi-Objective Algorithms and Regression Analysis. Algorithms 2025, 18, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090542
Kwakye-Boateng P, Tartibu L, Tien-Chien J. Performance Optimization of a Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller Using Grey Wolf-Based Multi-Objective Algorithms and Regression Analysis. Algorithms. 2025; 18(9):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090542
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwakye-Boateng, Patricia, Lagouge Tartibu, and Jen Tien-Chien. 2025. "Performance Optimization of a Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller Using Grey Wolf-Based Multi-Objective Algorithms and Regression Analysis" Algorithms 18, no. 9: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090542
APA StyleKwakye-Boateng, P., Tartibu, L., & Tien-Chien, J. (2025). Performance Optimization of a Silica Gel–Water Adsorption Chiller Using Grey Wolf-Based Multi-Objective Algorithms and Regression Analysis. Algorithms, 18(9), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18090542








