Abstract
Gaze estimation is a cornerstone of applications such as human–computer interaction and behavioral analysis, e.g., for intelligent transport systems. Nevertheless, existing methods predominantly rely on coarse-grained features from deep layers of visual encoders, overlooking the critical role that fine-grained details from shallow layers play in gaze estimation. To address this gap, we propose a novel Hierarchical Fine-Grained Attention Decoder (HFGAD), a lightweight fine-grained decoder that emphasizes the importance of shallow-layer information in gaze estimation. Specifically, HFGAD integrates a fine-grained amplifier MSCSA that employs multi-scale spatial-channel attention to direct focus toward gaze-relevant regions, and also incorporates a shallow-to-deep fusion module SFM to facilitate interaction between coarse-grained and fine-grained information. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of HFGAD over existing methods, achieving a remarkable 1.13° improvement in gaze estimation accuracy for in-car scenarios.
1. Introduction
Gaze estimation, which analyzes eye movements to determine a person’s visual focus [1], is a critical research area in computer vision. It has diverse applications, including human–computer interaction [2], behavioral analysis [3,4], and intelligent transportation systems [5]. In behavioral analysis, gaze estimation provides valuable insights into human attention and cognitive states. It enables the study of subtle behavioral patterns, such as understanding user intent during interactions with digital interfaces, monitoring mental fatigue, and identifying social cues in group dynamics. In intelligent transportation systems, accurately predicting a driver’s gaze direction plays a pivotal role in enhancing traffic safety and driver monitoring systems (DMS). As a result, effective gaze estimation is vital for advancing technologies that rely on understanding human attention, enabling safer transportation systems, more intuitive human–computer interactions, and deeper insights into human behavior.
In recent years, appearance-based neural networks [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] have become the leading frameworks for gaze estimation, thanks to their remarkable ability to extract and represent complex features from visual data. These methods typically employ convolutional layers [7] or transformer blocks [14] to capture intricate facial features, translating them into meaningful representations. These representations are then refined and processed through fully connected layers [7] to predict the driver’s gaze direction. While these approaches have shown excellent performance, they still face several challenges.
One key challenge in gaze estimation lies in accurately capturing the subtle features of the eye region. Unlike many high-level vision tasks that rely on coarse semantic understanding, gaze estimation depends on fine-grained, low-level visual cues—particularly those derived from the eye area—since gaze direction is primarily determined by minute movements of the eyeball, such as variations in the positions of the iris and pupil. These subtle details are often lost in deeper convolutional layers. Therefore, shallow-layer features, which retain precise spatial information, play a critical role in achieving accurate gaze prediction. However, in real-world applications, facial rotations can lead to improper capture of the eye region. For example, as shown in Figure 1a, significant prediction biases arise when the head is turned, due to the misalignment of the eyes relative to the camera’s viewpoint. Additionally, the eye region is often occluded by objects like glasses or masks, which further hinders the extraction of reliable eye features (see Figure 1b). The results indicate that the lack of effective attention to the eye region leads to significant prediction biases in challenging scenarios, such as when large portions of the face are occluded. This suggests that existing methods struggle to focus on small but gaze-relevant regions, such as the eyes. We attribute this limitation to their insufficient capacity for capturing fine-grained features, which can severely impact the accuracy of the final predictions. Such inaccuracies can severely impact applications where precise gaze estimation is critical, including tablets, smartphones [7,15], and human–machine interaction within smart cockpit environments [16], where even slight prediction errors may disrupt the system’s ability to accurately identify the user’s region of interest. This limitation stems from inadequate capacity to capture fine-grained features, which crucially affects prediction accuracy in gaze-sensitive applications. Even minor estimation errors can compromise systems’ ability to identify users’ focus areas, particularly in tablet/smartphone interfaces [7,15] and smart cockpit human–machine interaction [16], where precise gaze tracking is essential. Addressing these limitations requires developing approaches that not only preserve but also enhance fine-grained features of the eye region, enabling higher prediction accuracy and improving the robustness of gaze estimation systems in real-world environments.
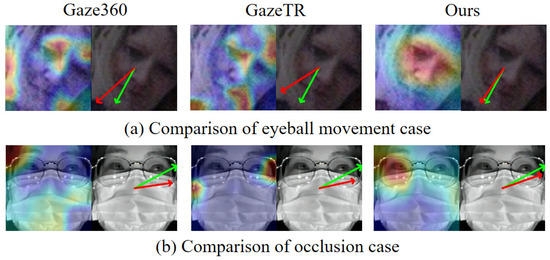
Figure 1.
The results of three ResNet18-based models under large-area occlusion are shown. (a) Grad-CAM. (b) Model predictions with green as ground truth (GT) and red as prediction. Traditional methods fail to capture gaze-relevant regions under heavy occlusion, causing prediction errors.
In this work, we propose the Hierarchical Fine-Grained Attention Decoder (HFGAD), an innovative and efficient module that effectively harnesses information from all backbone stages. Our HFGAD selectively integrates fine-grained features step-by-step from shallow to deep layers, producing refined feature representations, enhancing critical spatial details by employing a combination of channel-spatial and multi-scale attention mechanisms. Furthermore, HFGAD demonstrates exceptional performance while adhering to an ultra-lightweight design, primarily leveraging the efficiency of sparse convolution.
Specifically, our approach achieves competitive results across three benchmark datasets: 10.46° on Gaze360, 3.88° on MPIIFaceGaze, and 7.02° on IVGaze.
In summary, the main contributions of this work are as follows:
- We propose HFGAD, which introduces a multi-scale channel-spatial attention mechanism and a selective feature fusion module to address the challenges of fine-grained feature extraction and effective feature aggregation, respectively.
- HFGAD is innovatively designed with a lightweight and plug-and-play decoder, achieving an excellent balance between performance and computational efficiency.
- Extensive experimental results demonstrate the competitive advantage of HFGAD, achieving competitive performance on MPIIFaceGaze, Gaze360, and IVGaze datasets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Geometry-Based Gaze Estimation
Geometry-based gaze estimation methods can be broadly classified into 2D eye feature regression methods and 3D eye model reconstruction methods. These approaches estimate gaze direction using geometric features such as eye contours, reflection points, and eye corners. With specialized equipment like infrared cameras, geometric features can be extracted with high precision. Specifically, 2D eye feature regression methods learn a mapping function from geometric features to gaze points using polynomial regression [17,18] or neural networks [19]. In contrast, 3D eye model reconstruction methods build subject-specific geometric eye models to estimate gaze direction by fitting features such as corneal reflections [20,21], pupil centers [22], and iris contours [23]. However, these methods typically require individual calibration for each subject, as the eye model incorporates subject-specific parameters, including the corneal radius and the kappa angle.
2.2. Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation
Appearance-based gaze estimation methods estimate gaze direction by analyzing facial images or videos. Unlike traditional geometric or eye-tracking methods, these approaches rely on visual features extracted from the input images instead of precisely measuring the physical movement of the eyes. This makes them advantageous in applications such as eye-tracking systems, virtual reality, and driver monitoring, as they typically require less system resources and are easier to apply. Conventional methods extract gaze-related features from eye images [10,11,24], but these techniques are limited when it comes to addressing individual differences, head movements, and environmental factors. In recent years, appearance-based gaze estimation methods have evolved to directly learn gaze from facial images [25,26], often using deep learning techniques like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to analyze and predict gaze direction. Despite their advantages, these methods face challenges, such as sensitivity to head posture, lighting conditions, and the difficulty in capturing fine-grained eye features. For example, Cheng et al. use the Dual-View Gaze Estimation method [27] which improves accuracy by using image pairs captured by two cameras, overcoming the limitations of single-camera perspectives that do not provide complete facial information. Additionally, Biswas et al. demonstrated the effectiveness of Transformer models for gaze estimation [12,13], which have shown superior performance compared to traditional CNNs. However, these methods still struggle to meet the high-accuracy demands of certain tasks and often suffer from low real-time monitoring frame rates. In addition to CNNs and Transformers, recent studies have introduced attention-based decoder modules that aim to refine spatial and channel information for improved feature modeling. Li et al. [28] proposed a Multi-Scale Coupled Spatial Attention mechanism that jointly models inter-scale spatial correlations to enhance dense prediction accuracy. Shang et al. [29] introduced SCSA, a plug-and-play attention module that combines spatial and channel-wise attention with multi-semantic consistency enhancement. Meanwhile, Ouyang et al. [30] developed the EMA (Efficient Multi-scale Attention) module, which reduces computational overhead while maintaining robust cross-spatial interactions. In parallel, structural designs, such as the bottom-up path augmentation strategy in PANet [31], have shown the effectiveness of cross-stage feature aggregation in decoder modules. These advances demonstrate the growing importance of hierarchical and fine-grained attention, as well as bottom-up structural refinement, in decoder design—both of which directly inspire the attention mechanisms and fusion strategies used in our proposed HFGAD.
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
We introduce our Hierarchical Fine-Grained Attention Decoder (HFGAD) for processing multi-stage features from pretrained hierarchical vision encoders in gaze estimation. As shown in Figure 2, HFGAD includes Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention (MSCSA) to enhance feature maps, Selective Fusion Modules (SFMs) to adaptively refine feature maps fusing with skip connection, Efficient Convolutional Downsamples (ECDs) to downsample enhanced features, and an Estimation Head (EH) for gaze direction prediction.
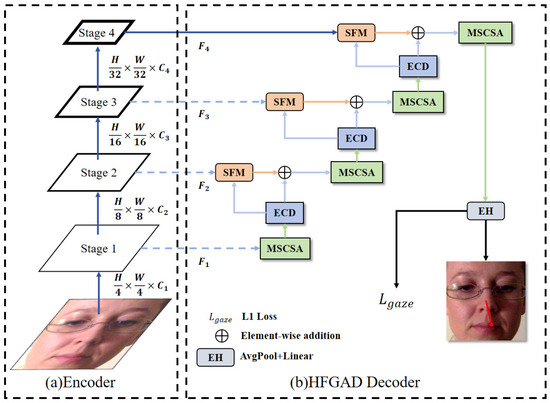
Figure 2.
Hierarchical encoder with proposed HFGAD Decoder architecture: (a) Hierarchical Encoder, (b) HFGAD Decoder. The HFGAD primarily comprises two modules: (1) Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention (MSCSA), and (2) Selective Fusion Module (SFM). The red arrows in the final output indicates the direction of the line of sight.
Specifically, we use four MSCSAs to refine the pyramid features extracted from the four stages of the encoder (i.e., , , , and in Figure 1). After the final MSCSA, the EH produces the gaze estimation results. Before reaching this stage, ECDs are employed to downsample the refined feature maps, aligning them with the feature maps of the next stage. These next-stage feature maps are then fused with the downsampled features using SFMs to generate refined outputs. The following sections detail the individual modules within our decoder.
3.2. Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention
Channel-spatial attention mechanisms (e.g., CBAM [28]) have been widely proven effective in enhancing feature representation by jointly modeling ‘what’ to focus on and ‘where’ to focus. Inspired by recent decoder-level attention modules such as SCSA [29] and ELA [32], which highlight the importance of multi-scale spatial dependencies and semantic disparity alignment, we propose our Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention (MSCSA). Unlike these approaches, MSCSA introduces two key improvements: (1) Orthogonal decoupling of spatial attention into height-wise and width-wise pathways to better capture directional priors in gaze; (2) A gated multi-scale grouped convolution module that selectively aggregates context from multiple receptive fields. This design ensures both fine-grained spatial sensitivity and computational efficiency for resource-constrained scenarios.
Given an input feature map , with B: batch size, C: channel number, H: height, and W: width. MSCSA (Figure 3) begins by aggregating global spatial information through a combination of averages along the dimensions of width and height, resulting in two intermediate descriptors: and . These descriptors are processed by a lightweight 1D convolutional layer with a kernel size of 5, which incorporates grouped convolutions () to capture fine-grained local dependencies while reducing computational complexity.
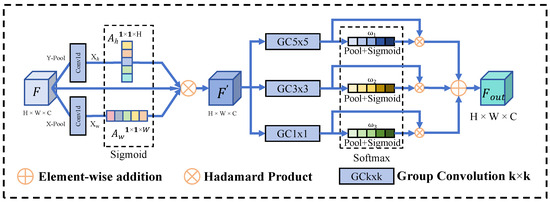
Figure 3.
Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention Module.
The convolved outputs are normalized using Group Normalization (GN) to ensure stable feature distributions and then passed through a Sigmoid activation function to generate spatial attention maps, corresponding to the height and width dimensions, respectively. These attention maps are subsequently applied to the original input feature F via element-wise multiplication ×, resulting in the final output:
A multi-scale grouped convolution is then used to enhance feature representation by dynamically aggregating information from multiple receptive fields through a gating mechanism. For the feature map , MSCSA processes the features through three parallel branches: a 1 × 1 convolution branch to preserve baseline feature representation, a 3 × 3 grouped convolution branch for mid-range feature exaction, and a 5 × 5 grouped convolution branch to capture long-range contextural infomation.
To integrate these multi-scale features, we first apply global average pooling to each branch’s output, yielding channel-wise descriptors , , ∈. The operation can be described by the formula as:
These descriptors are transformed into attention weights using a shared 1 × 1 convolution followed by a Sigmoid activation, and then concatenated and normalized with a Softmax operation, producing weights :
The final multi-scale feature output is computed by weighting each scale-specific feature map with its corresponding attention weight and summing them:
The proposed MSCSA module combines a lightweight channel-spatial attention mechanism with multi-scale grouped convolution to enhance feature representation. It refines spatial relevance and efficiently captures context from diverse receptive fields, balancing accuracy and computational cost for effective feature extraction in resource-constrained environments.
3.3. Selective Feature Fusion Module (SFM)
The Selective Feature Fusion Module (Figure 4) is designed to enhance the fusion of multistage features in the decoder by adaptively emphasizing different spatial regions from multiple feature maps. Inspired by the Efficient Local Attention (ELA) [32] mechanism, SFM introduces a lightweight yet effective fusion strategy that captures both global and local dependencies while preserving computational efficiency.
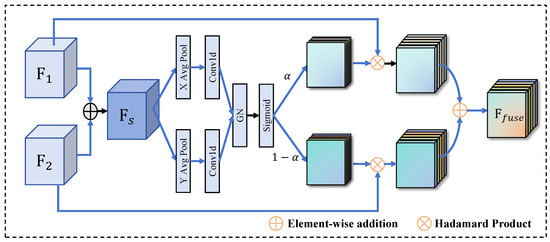
Figure 4.
The Selective Fusion Module combines shallow-stage features with the current-stage features through element-wise addition, followed by an adaptive weighting mechanism that learns the optimal combination.
Given two input features: from the current stage and an aligned feature from the previous stage, which have the same shape [B, C, H, W], SFM begins by performing an element-wise addition to combine these two features, resulting in an intermediate fused representation . To capture cross-spatial dependencies, the feature map is aggregated along the spatial dimensions (height H and width W) by performing global average pooling across each dimension.
These spatial descriptors and are then processed by a 1D grouped convolution layer with a kernel size of 5 and groups set to C/4, which allows for efficient local feature extraction while minimizing computational cost. The resulting convolved features are normalized using Group Normalization (GN), followed by a Sigmoid activation to generate spatial attention maps for the height and width dimensions, respectively. These attention maps reflect the relative importance of each spatial region in the corresponding input feature maps and are computed as:
where and have shapes and , respectively. To facilitate the feature fusion, SFM computes the complementary inverse attention maps , = 1 −, and = 1 −.
The final feature fusion is achieved by modulating the input features and using their corresponding attention maps. The fused feature is computed as:
where × represents element-wise multiplication.This dual-branch attention mechanism allows SFM to dynamically weight and fuse the features, emphasizing regions that contribute the most to the task. By adaptively combining the information from both features, SFM ensures that the decoder can effectively leverage the multiscale features while maintaining a lightweight structure. The proposed fusion strategy allows the model to focus on significant spatial regions, enabling more accurate and efficient feature extraction without introducing excessive computational complexity.
3.4. Efficient Convolutional Downsample (ECD)
Our decoder architecture extends the bottom-up feature aggregation strategy of PANet [31], which demonstrated that cross-level feature interaction improves localization accuracy. To enable effective fusion of multi-scale features from different encoder stages (Figure 2), we propose the Efficient Convolutional Downsample (ECD) module to align cross-stage feature maps via:
where denotes a depthwise convolution with stride 2 for spatial downsampling, applies spatial attention enhancement [33], and adjusts the channel dimensions. After ECD, the features from the shallow stage can be aligned with the deep features and input into the SFM module for interaction.
3.5. Estimation Head and Loss Function
Following established practices in appearance-based gaze estimation [1,9,10], we apply global average pooling (GAP) to the refined feature maps from HFGAD, converting spatial features into a 1D descriptor. A fully connected layer is used to predict the yaw and pitch angles. The EH is formulated as Equation (8):
The L1 Loss is used to supervise the training of our model [1,9,13], measuring the absolute difference between the predicted gaze vector and the ground truth (GT) gaze vector. Assuming the actual gaze vector is , and the estimated gaze vector is , the angular error can be computed as:
4. Experiments
In this section, we first describe the evaluation metrics used in our study. Next, we provide detailed information about the network implementation. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through comprehensive qualitative and quantitative results, highlighting its superior performance.
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. Gaze360 [9]
The Gaze360 dataset, comprising 238 subjects (172 with 3D gaze labels), is the largest publicly available collection for unconstrained gaze estimation. Captured in diverse environments with varying head poses and lighting, it provides normalized images and 3D gaze ground truth.
4.1.2. MPIIFaceGaze [7]
This dataset comprises gaze images collected from 15 subjects, captured in everyday settings using their personal laptops over a long period. It provides 2D gaze labels and is widely used for evaluating gaze estimation models in constrained environments. The images are normalized to a resolution of .
4.1.3. IVGaze [16]
This dataset focuses on in-vehicle gaze estimation, featuring data from 125 individuals across a variety of realistic driving scenarios, including urban streets, highways, and parking environments. It captures a diverse range of gaze directions and head poses, reflecting natural driver behaviors under different lighting conditions and seating positions.
In gaze estimation studies, angular error (AE) is a widely used metric to quantify the discrepancy between predicted and actual gaze directions, providing a clear measure of model performance. This study employs the Gaze360, MPIIFacegaze, and IVGaze datasets, which include ground truth gaze annotations captured using specialized eye-tracking devices. These annotations are represented by pitch and yaw angles, where pitch indicates vertical tilt (rotation around the X-axis), and yaw represents horizontal rotation (rotation around the Y-axis). Together, these angles are crucial for determining precise gaze direction [1].
Pitch and yaw are derived from the coordinates of the 3D vector extending from the eye or face center to the focal point. To compute AE, gaze directions in 2D are converted into unit vectors in 3D space using the following equations:
where x, y, and z represent the unit vector’s coordinates, while and calculate the respective trigonometric values of the pitch and yaw. The angular error (AE) is determined using the following calculation:
where G represents the predicted gaze vector and is the actual gaze vector. The magnitudes of the vectors are and . The function calculates the angle from the cosine of the vectors’ dot product, followed by a conversion from radians to degrees using .
4.2. Implementation Details
We implemented our model using the PyTorch 1.10.1 and trained it with the Adam optimizer, where and . All experiments were conducted on an NVIDIA 3090 GPU. The training process included 80 epochs, with an initial learning rate of 0.005 for most datasets, and 0.001 specifically for the IVGaze dataset. A 5-epoch warmup phase was applied, followed by the StepLR scheduler, which reduces the learning rate by a factor of 0.5 every 15 epochs.
For the MPIIFaceGaze dataset, we employed a 15-fold cross-evaluation strategy, while a 3-fold cross-evaluation was used for the IVGaze dataset. The Gaze360 dataset was trained using a standard single-run approach.
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art
We compared our proposed HFGAD-Res18 model with several state-of-the-art methods, including Gaze360, FullFace, Dilated-Net, RT-Gene, CA-Net, GazeTR, and GazePTR, on three widely used datasets: Gaze360, MPIIFaceGaze, and IVGaze. The comparative results are summarized in Table 1, where the best performance for each dataset is highlighted in bold.

Table 1.
Comparison of gaze estimation methods on Gaze360, MPIIFaceGaze, and IVGaze datasets. The best performance for each dataset is in bold.
As shown in the table, HFGAD-Res18 consistently achieves competitive performance across all three datasets. Specifically, on the Gaze360 dataset, HFGAD-Res18 obtains the best average angular error of 10.46°, surpassing GazeTR (10.62°) and Gaze360 (11.04°). This demonstrates the effectiveness of our model in handling challenging unconstrained gaze scenarios.
On the MPIIFaceGaze dataset, our model achieves an angular error of 3.88°, outperforming the previous best model, GazeTR (4.00°), by a notable margin. This result highlights the superior ability of HFGAD-Res18 to capture fine-grained gaze features from single-subject images, even in controlled environments.
For the IVGaze dataset, HFGAD-Res18 achieves an angular error of 7.02°, slightly improving upon the prior best-performing method with fewer Flops (48%↓), GazePTR of 7.04°, and improvement in the angular error compared to the Gaze360 (ResNet-18 based) on the IVGaze dataset. This demonstrates the adaptability of our model to driver monitoring systems, where variations in head poses and gaze directions are critical.
To verify our method’s ability to capture fine-grained eye features, we conduct additional experiments with 448 × 448 eye-region crops (2× higher resolution than original 224 × 224 inputs). As shown in Table 2, our method consistently achieves the lowest average angular error across all datasets and resolutions. as well as the mean performance, we report the standard deviation and 95% confidence intervals for each result to assess statistical reliability. Notably, our method yields both lower average errors and narrower confidence intervals compared to baseline methods, indicating not only better accuracy but also greater robustness. Furthermore, under the high-resolution setting (448 × 448), our model shows greater relative improvements (up to 9.2%) than competing methods such as GazeTR and Gaze360, whose gains are more limited. This suggests that HFGAD is more effective in leveraging fine-grained visual cues, especially from high-resolution facial inputs. The combination of consistently improved accuracy, reduced variance, and statistically significant margins confirms the effectiveness of our proposed design.

Table 2.
Performance comparison with statistical metrics (bold indicates best performance per metric).
4.4. Visualization Analysis
We conducted comprehensive visualizations of the outputs and attention mechanisms across the Gaze360, MPIIFaceGaze, and IVGaze datasets. These visualizations encompass two aspects: the direct outputs of HFGAD-Res18 and the Grad-CAM-based attention heatmaps compared with the baseline model GazeTR.
Figure 5 illustrates the gaze direction predictions of HFGAD-Res18 on the three datasets. The visualized results show that HFGAD-Res18 accurately aligns with the ground truth, even in challenging scenarios involving varying head poses and gaze directions. These visualizations demonstrate the robustness of our model across diverse conditions.

Figure 5.
Visualization of our gaze estimation model on three datasets. The green arrows represent the ground truth gaze directions, while the red arrows indicate the predicted gaze directions. (a) Front-facing. (b) Wearing glasses. (c) Extreme situation such as low brightness, head attitude offset, and large area occlusion.
In addition, we employed Grad-CAM to analyze the attention mechanisms of HFGAD and GazeTR (see Figure 6). The attention heatmaps of HFGAD exhibit a strong focus on the central regions of the face, particularly the eyes, which are critical for gaze estimation. In contrast, GazeTR’s attention maps are relatively dispersed, with less emphasis on gaze-relevant regions. This distinction highlights the effectiveness of HFGAD-Res18’s architectural design in prioritizing task-specific features.
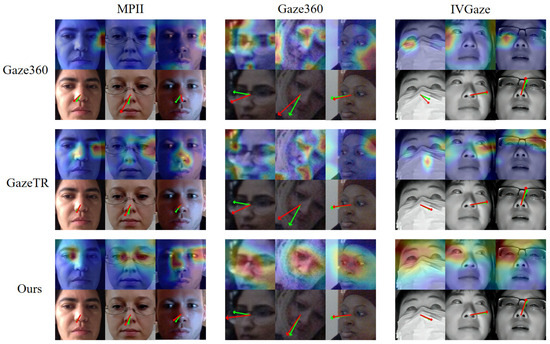
Figure 6.
Visualization of Grad-CAM [34] heatmap and gaze estimation results for GazeTR [13], Gaze360 [9], and our proposed HFGAD. The red arrow denotes the predicted gaze and the green arrow denotes the ground truth. Our model can focus on the eye area better and achieve a better prediction.
Moreover, by comparing the output visualizations and attention heatmaps side-by-side, we observe that HFGAD-Res18 not only achieves higher prediction accuracy but also demonstrates superior interpretability. Its attention maps align closely with the regions necessary for precise gaze estimation, validating the design choices in HFGAD-Res18 and its adaptability to real-world applications.
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Ablation Study of Each Module
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed components in HFGAD-Res18, we conducted an ablation study on three datasets: Gaze360, MPIIFaceGaze, and IVGaze. As shown in Table 3, we take ResNet-18 [35] as the baseline and progressively add the proposed modules—Stepwise Feature Module (SFM) and Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention (MSCSA)—to assess their individual and combined contributions in terms of both performance and computational efficiency.

Table 3.
Ablation study: Performance of HFGAD-Res18 with different modules, bold indicates the best performance in each column.
From the results, we observe that adding SFM alone reduces the average angular error across the three datasets while introducing only a minor increase in parameters (+0.206M) and FLOPs (+0.118G), demonstrating its effectiveness in feature aggregation across scales. Introducing MSCSA alone leads to further performance gains by guiding attention toward gaze-relevant regions; the parameter and FLOPs increases remain modest (+0.414M, +0.105G), while the average error drops significantly (e.g., from 10.91° to 10.65° on Gaze360).
When combining both SFM and MSCSA, the model achieves the lowest angular errors on all datasets (e.g., 10.46° on Gaze360, 3.88° on MPII, and 7.02° on IVGaze), with only 0.838M additional parameters and 0.126G extra FLOPs compared to the baseline. This confirms that the two modules are complementary: SFM improves hierarchical feature fusion, while MSCSA enhances spatial attention precision.
Moreover, as visualized in Figure 7, the encoder alone fails to focus on gaze-relevant eye regions. The SFM module refines the feature space to highlight subtle eye details, whereas MSCSA extends attention toward broader gaze-relevant regions, supporting better global–local awareness. Together, they significantly improve the model’s ability to infer accurate gaze directions.

Figure 7.
Areas of interest for each module. (a) Input image. (b) Encoder’s region of interest. (c) SFM’s region of interest. (d) MSCSA’s region of interest. (e) Model prediction (red arrow) and GT (green arrow). Encoder does not effectively focus on the eye area, whereas SFM focuses on tiny areas of the eye and MSCSA focuses on large areas of line-of-sight relevance.
These results collectively demonstrate that each proposed module contributes positively and efficiently to gaze estimation, and their integration yields the best balance of accuracy and efficiency across all benchmarks.
Furthermore, we visualize the performance distribution of each variant using box plots (Figure 8). As the modules are incrementally added, the angular error distribution becomes progressively narrower and shifts toward lower values, confirming that each module contributes not only to reducing the mean error but also to improving prediction stability.
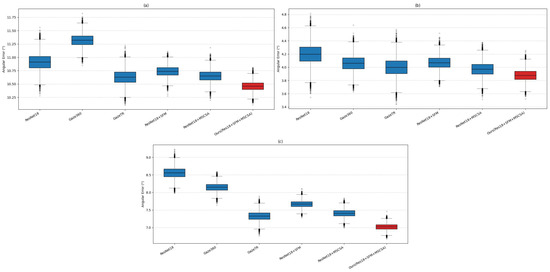
Figure 8.
Boxplot of angular error distributions for the baseline models and ablation variants of our proposed method across three datasets: (a) Gaze360, (b) MPIIFaceGaze, and (c) IVGaze.
Overall, the ablation study confirms that every component proposed in HFGAD plays a distinct and effective role in enhancing gaze estimation performance.
4.5.2. Generalization of HFGAD Across Different Backbones
To demonstrate the effectiveness and adaptability of the proposed HFGAD framework, we evaluated its performance on two distinct types of backbone architectures: a convolutional neural network (ResNet-18 [35]) and vision transformers (PVTv2-B0 and PVTv2-B2 [36]). This evaluation highlights the capability of HFGAD to generalize across different model paradigms.
As presented in Table 4, the baseline backbones achieve angular errors of 11.32°, 10.63°, and 10.91° for PVTv2-B0, PVTv2-B2, and ResNet-18, respectively, on the Gaze360 dataset. By incorporating HFGAD, the performance improves consistently across all backbones, reducing angular errors to 11.00° for PVTv2-B0, 10.24° for PVTv2-B2, and 10.46° for ResNet-18. These improvements underline the effectiveness of HFGAD in leveraging both CNN and ViT-based feature representations to enhance gaze estimation accuracy.

Table 4.
Performance of different backbones with and without HFGAD on Gaze360, bold indicates the best performance in each column.
This analysis confirms the robustness of HFGAD as a decoder that can seamlessly integrate with different backbone architectures, fully demonstrating its versatility and practical applicability across a wide range of gaze estimation tasks.
4.6. Performance Distribution
To provide deeper insights into the performance characteristics of our model, we conduct an angle-wise error analysis based on the IVGaze dataset. Compared to MPIIFaceGaze, IVGaze offers a wider variety of head poses, and compared to Gaze360, it provides clearer facial imagery. Moreover, as an in-vehicle dataset, IVGaze aligns well with our goal of developing a practical Driver Monitoring System (DMS), making it particularly suitable for distributional analysis.
Following the evaluation protocol proposed in the original IVGaze paper, we categorize samples based on the angle between the gaze direction and the frontal reference vector . The gaze angles are divided into four intervals: , , , and . For each interval, we calculate the average gaze estimation error of four representative models: the ResNet-18 baseline, Gaze360, GazeTR, and our proposed HFGAD.
The results are illustrated in Figure 9. Our method consistently achieves the lowest error across all angular ranges, especially under extreme head pose variations, demonstrating its superior generalization ability under challenging gaze conditions. Notably, HFGAD shows a substantial improvement in the – interval compared to other models. According to the IVGaze dataset analysis, this range often corresponds to situations where the gaze target is close to the subject, prompting them to rely more on eye movement than head rotation. Thanks to its multi-level feature aggregation and fine-grained attention mechanisms, HFGAD effectively captures these subtle eye movements, resulting in more accurate gaze predictions.
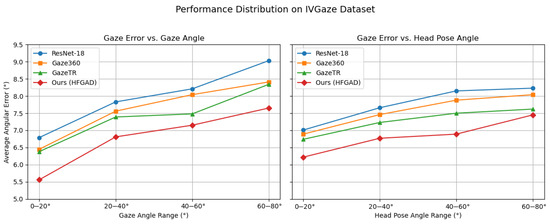
Figure 9.
Average angular error across different gaze and head pose angle ranges on the IVGaze dataset. Each sample is categorized based on its angular deviation from the frontal direction .
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented HFGAD, a lightweight and efficient gaze estimation decoder designed to balance prediction accuracy with computational efficiency. By incorporating innovative attention mechanisms and hierarchical feature fusion strategies, HFGAD enhances task-relevant focus across scales, enabling superior performance with minimal parameter overhead.
Extensive experiments conducted on three challenging gaze datasets demonstrate that HFGAD outperforms existing baselines in both accuracy and robustness. In particular, it shows strong generalization under diverse head poses and gaze directions, which is critical for practical applications such as driver monitoring systems (DMS). Beyond driver monitoring, the proposed approach could be extended to AR/VR gaze tracking, social attention modeling, and human–computer interaction. Future work may explore more diverse scale configurations and integration with temporal modeling for improved robustness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H. and T.W.; methodology, S.H., T.W. and H.X.; software, S.H.; validation, S.H., T.W.; formal analysis, H.X.; investigation, S.H.; resources, J.S., G.C. and H.X.; data curation, S.H., G.C. and H.X.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H. and T.W.; writing—review and editing, S.H., Y.P., J.S. and H.X.; visualization, S.H. and T.W.; supervision, W.L. and J.S.; project administration, H.X., J.S.; funding acquisition, H.X., J.S., G.C. and Y.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China, under Grant 2023J01803 and 2025J01345; in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Xiamen, China, under Grant 3502Z202371019, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 42371457.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because all data used in this study are from public datasets.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DMS | Driver Monitoring Systems |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| HFGAD | Hierarchical Fine-Grained Attention Decoder |
| MSCSA | Multi-Scale Channel-Spatial Attention |
| SFM | Selective Fusion Module |
| ECD | Efficient Convolutional Downsample |
| EH | Estimation Head |
| GC | Group Convolution |
| GN | Group Normalization |
References
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Lu, F. Appearance-based gaze estimation with deep learning: A review and benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 7509–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steil, J.; Huang, M.X.; Bulling, A. Fixation detection for head-mounted eye tracking based on visual similarity of gaze targets. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications, Warsaw, Poland, 14–17 June 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi, A.; Abati, D.; Solera, F.; Cucchiara, R. Predicting the driver’s focus of attention: The dr (eye) ve project. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1720–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Vora, S.; Yuen, K.; Trivedi, M.M. Dynamics of Driver’s Gaze: Explorations in Behavior Modeling and Maneuver Prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2018, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Xiong, L. Driver Distraction Behavior Recognition for Autonomous Driving: Approaches, Datasets and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 8000–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Lu, F. A coarse-to-fine adaptive network for appearance-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10623–10630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. It’s written all over your face: Full-face appearance-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. Rt-gene: Real-time eye gaze estimation in natural environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 334–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kellnhofer, P.; Recasens, A.; Stent, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Gaze360: Physically unconstrained gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6912–6921. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, X. Appearance-based gaze estimation via evaluation-guided asymmetric regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 100–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, F.; Sato, Y. Gaze estimation by exploring two-eye asymmetry. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5259–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P. Appearance-based gaze estimation using attention and difference mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3143–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F. Gaze estimation using transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montréal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 3341–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Appearance-Based Driver 3D Gaze Estimation Using GRM and Mixed Loss Strategies. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 38410–38424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Sabharwal, A. Tabletgaze: Dataset and analysis for unconstrained appearance-based gaze estimation in mobile tablets. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2017, 28, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hao, H.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.J. What Do You See in Vehicle? Comprehensive Vision Solution for In-Vehicle Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 1556–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, C.H.; Mimica, M.R. Eye gaze tracking techniques for interactive applications. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2005, 98, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampe, D.M. Heuristic filtering and reliable calibration methods for video-based pupil-tracking systems. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1993, 25, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yang, X. Real-time eye, gaze, and face pose tracking for monitoring driver vigilance. Real-Time Imaging 2002, 8, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guestrin, E.D.; Eizenman, M. General theory of remote gaze estimation using the pupil center and corneal reflections. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Ji, Q. Novel eye gaze tracking techniques under natural head movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 2246–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, R.; Sebe, N.; Gevers, T. Combining head pose and eye location information for gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberto Funes Mora, K.; Odobez, J.M. Geometric generative gaze estimation (g3e) for remote rgb-d cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1773–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Spurr, A.; Hilliges, O. Deep pictorial gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 721–738. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Zeng, J.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Source-free adaptive gaze estimation by uncertainty reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22035–22045. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Bao, Y.; Lu, F. Puregaze: Purifying gaze feature for generalizable gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F. Dvgaze: Dual-view gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 20632–20641. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yan, H.; Shi, L. Multi-scale coupled attention for visual object detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, X. SCSA: A Plug-and-Play Semantic Continuous-Sparse Attention for Arbitrary Semantic Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 13051–13060. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wan, Y. ELA: Efficient Local Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).