S-EPSO: A Socio-Emotional Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Multimodal Search in Low-Dimensional Engineering Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Question
1.2. Research Contribution and Paper Organization
- The first endows the particles with socio-emotional personalities. Based on an analogy pertaining to socio-emotional relations prevailing during the mammal reproduction period, the proposed approach introduces three particle types with specific personalities. Among these, some male particles are intrepid and explore the landscapes, while others are more prudent and preserve the found optima. The interactions between the socio-emotional particles give the swarm a natural ability to locate and maintain multiple optima and completely eliminate the need for predefined niching parameters.
- The second strategy introduces a technique to help the particles visit secluded zones. This technique apportions the particles of the initial distribution to subdomains based on biased decisions. The biases reflect the subdomain’s potential to contain optima. The procedure establishes this potential from a balanced combination of the jaggedness and the mean-average interval descriptors put forward in the study.
- In addition, to control the number of particles required to populate the subdomains, the proposed investigation reduces the domain dimensionality based on a sensitivity index.
- To boost the performance of the particles, the investigation also examines an economical strategy exploiting the information provided by contours formed by surrounding particles.
2. Related Work Survey
- (1)
- Require no specification of niching parameters;
- (2)
- Must be able to locate and maintain multiple optima;
- (3)
- Must be able to locate multiple global and local optima;
- (4)
- Have low computational complexity.
3. Particle with Socio-Emotional Behavior and Model Basis
3.1. Pseudocode of the S-EPSO Algorithm
3.2. Algorithm Basis and Socio-Emotional Particle Personalities
3.3. Life Expectancy of the Particles
3.4. Boundary Crossing
3.5. Additional Information
4. A Strategy Based on a Segmentation of the Search Domain’s
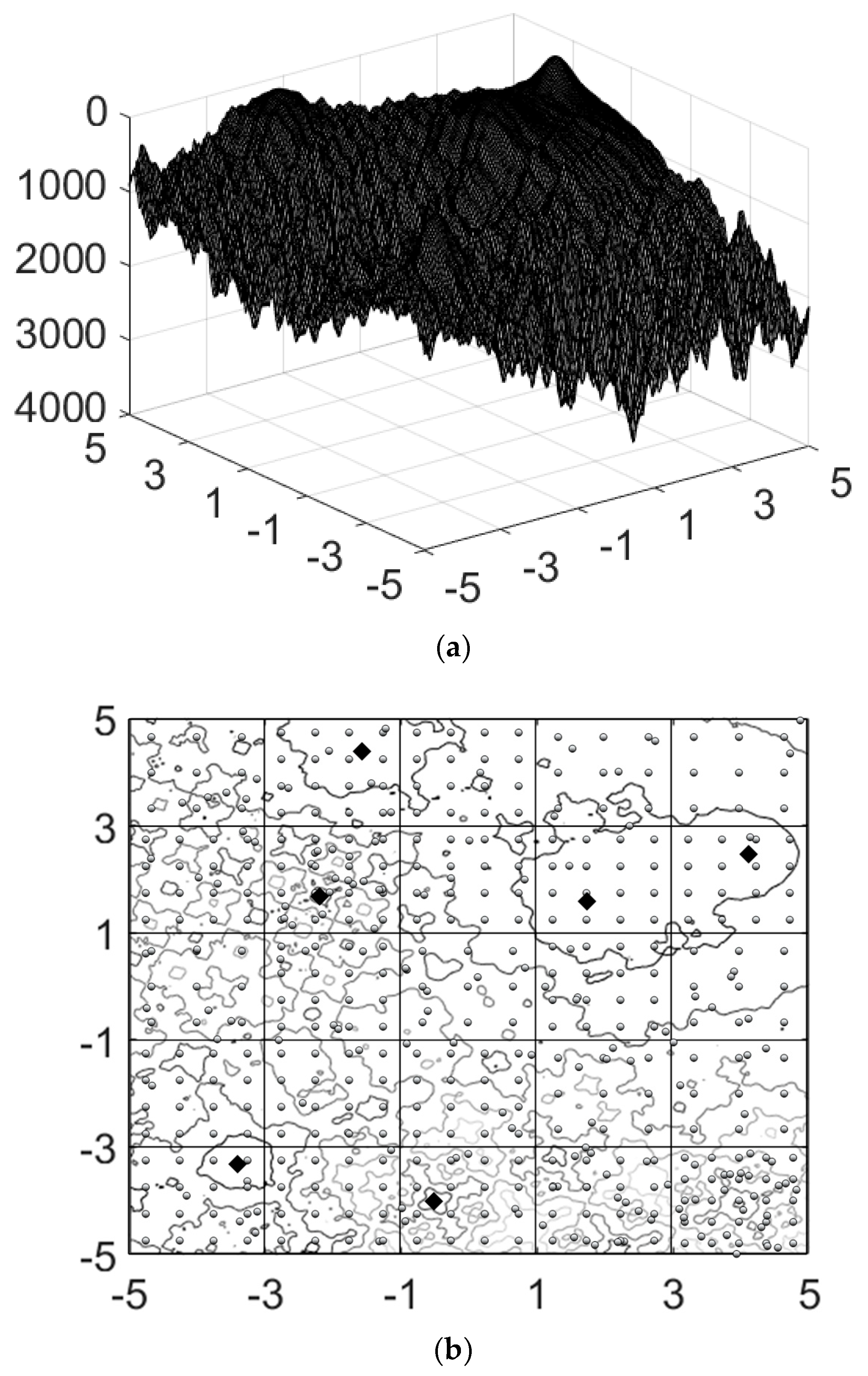
4.1. Problem Description
4.2. Evaluation of Landscapes Jaggedness
4.3. Evaluation of Subdomains Mean-Average Separation and Weight Factor Formulation
4.4. Reduction of the Domain Dimensionality
5. An Intermediate Improvement of the Particle Positions
6. Results
6.1. Multimodal-Multi-Optima Problems
6.2. Real-World Constrained Design Problems
- For the PV problem, are given by and , respectively, where represent integer values , and (See [32]).
- For the SpRe problem, , , , , , , and
- For the PV case: with , , , and (see [34]);
- For the SpRe case: with , , , , 7.7153, 3.3503 and (see [37]).
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X. Niching without niching parameters: Particle swarm optimization using a ring topology. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 14, 150–169. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Oliva, D.; Abualigah, L.; Lu, S.; Ewees, A.A. Advanced metaheuristic techniques for mechanical design problems. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 695–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, A.R.; Abderazek, H.; Mirjalili, S. A comparative study of recent non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Abderazek, H.; Yıldız, B.S.; Yildiz, A.R.; Mirjalili, S.; Sait, S.M. Comparison of metaheuristic optimization algorithms for solving constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miler, D.; Žeželj, D.; Lončar, A.; Vučković, K. Multi-objective spur gear pair optimization focused on volume and efficiency. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 125, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Sun, K. Reliability design and optimization of the planetary gear by a GA based on the DEM and Kriging model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 203, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, B.S.; Pholdee, N.; Panagant, N.; Bureerat, S.; Yildiz, A.R.; Sait, S.M. A novel chaotic Henry gas solubility optimization algorithm for solving real-world engineering problems. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Deng, W.; Showaib, E.A. Improving laser cutting quality of polymethylmethacrylate sheet: Experimental investigation and optimization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.P.; Eckert, J.J.; Silva, L.C.A.; da Silva, L.A.R.; Gutiérrez, J.C.H.; Dedini, F.G. Gear shifting optimization applied to a flex-fuel vehicle under real driving conditions. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2022, 50, 2084–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbault, R.; Lalonde, S. Tip relief designed to optimize contact fatigue life of spur gears using adapted PSO and Firefly algorithms. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epitropakis, M.G.; Plagianakos, V.P.; Vrahatis, M.N. Finding multiple global optima exploiting differential evolution’s niching capability. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Differential Evolution (SDE), Paris, France, 11–15 April 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Storn, R. On the usage of differential evolution for function optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE North American Fuzzy Information Processing, Berkeley, CA, USA, 19–22 June 1996; pp. 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential evolution—A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Suganthan, P.N. Differential evolution: A survey of the state-of-the-art. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 15, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Engelbrecht, A.; Epitropakis, M.G. Benchmark Functions for CEC’2013 Special Session and Competition on Niching Methods for Multimodal Function Optimization; Technical Report; RMIT University, Evolutionary Computation and Machine Learning Group: Melbourne, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, R. Multimodal optimization using crowding-based differential evolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2004 Congress on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8753), Portland, OR, USA, 19–23 June 2004; pp. 1382–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Zhan, Z.-H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, W.-J.; Wang, H.; Kwong, S.; Zhang, J. Automatic niching differential evolution with contour prediction approach for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 24, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieldsend, J.E. Running up those hills: Multi-modal search with the niching migratory multi-swarm optimiser. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 2593–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Corriveau, G.; Guilbault, R.; Tahan, A.; Sabourin, R. Review and study of genotypic diversity measures for real-coded representations. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2012, 16, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriveau, G.; Guilbault, R.; Tahan, A.; Sabourin, R. Review of phenotypic diversity formulations for diagnostic tool. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In Stochastic Algorithms: Foundations and Applications; SAGA 2009; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Watanabe, O., Zeugmann, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5792, pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Tuba, M.; Bacanin, N. Improved seeker optimization algorithm hybridized with firefly algorithm for constrained optimization problems. Neurocomputing 2014, 143, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Handling boundary constraints for particle swarm optimization in high-dimensional search space. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 4569–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, B. EEG analysis based on time domain properties. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1970, 29, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzé-Amady, M.; Horwat, F. Evaluation of Hjorth parameters in forearm surface EMG analysis during an occupational repetitive task. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol./Electromyogr. Mot. Control 1996, 101, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walmsley, M. On the normalized slope descriptor method of quantifying electroencephalograms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 11, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjengue, L.; Audet, C.; Ben Yahia, I. A variance-based method to rank input variables of the mesh adaptive direct search algorithm. Optim. Lett. 2014, 8, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lan, L.-K. A contour method in population-based stochastic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart, R.C.; Shi, Y. Comparing inertia weights and constriction factors in particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the Congress on Evolutionary Computation, La Jolla, CA, USA, 16–19 July 2000; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tsipianitis, A.; Tsompanakis, Y. Improved Cuckoo Search algorithmic variants for constrained nonlinear optimization. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2020, 149, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaros, N.D.; Kournoutos, M.; Kallioras, N.A.; Nordas, A.N. Constraint handling techniques for metaheuristics: A state-of-the-art review and new variants. Optim. Eng. 2023, 24, 2251–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadollah, A.; Bahreininejad, A.; Eskandar, H.; Hamdi, M. Mine blast algorithm: A new population based algorithm for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 2592–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Kumar, V. Spotted hyena optimizer: A novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, W.; Gao, Y. A particle swarm optimization algorithm based on an improved deb criterion for constrained optimization problems. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Peng, X.; Zeng, Q. Learning search algorithm: Framework and comprehensive performance for solving optimization problems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Saha, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Pal, G. Comparative performance analysis of differential evolution variants on engineering design problems. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 1140–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-H.; Tsai, J.-F.; Hu, N.-Z.; Chang, S.-C. Design optimization of a speed reducer using deterministic techniques. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 419043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. An efficient constraint handling method for genetic algorithms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 186, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Function | Dim. (D) | Optimization Domain | Number of Minima | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | Local | |||
| F1: Five-Uneven-Peak Trap | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| F2: Equal Maxima | 1 | 5 | 0 | |
| F3: Uneven Decreasing Maxi | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| F4: Himmelblau | 2 | 4 | 0 | |
| F5: Six-Hump Camel Back | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| F6: Shubert | 2 | 18 | many | |
| F7: Vincent | 2 | 36 | 0 | |
| F8: Shubert | 3 | 81 | many | |
| F9: Vincent | 3 | 216 | 0 | |
| F10: Modified Rastrigin | 2 | 12 | 0 | |
| F11: Composition function 1 | 2 | 6 | many | |
| F12: Composition function 2 | 2 | 8 | many | |
| F13: Composition function 3 | 2 | 6 | many | |
| F14: Composition function 3 | 3 | 6 | many | |
| F15: Composition function 4 | 3 | 8 | many | |
| F16: Composition function 3 | 5 | 6 | many | |
| F17: Composition function 4 | 5 | 8 | many | |
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | 0 | Offset in Equation (7c) |
| m | 1.5 | Curvature control in Equation (7c) |
| c2 | 1.495 | Acceleration constants in Equation (8) |
| c3 | 1.0 | Constant for subdomains selection |
| c4 | 4.0 | Constant in Equation (18) |
| c5 | 10 | Constant in Equation (21) |
| Ch | 1 or 2 | Constant in Equation (7a): 1 for sage males 2 for intrepid males |
| cnb | 4 | Neighbour number in Equation (27) |
| D* | 3 | Reduced domain dimension number |
| fp | 0.25 | Fraction of improved particles |
| k0 | 1.5 | Constant in Equation (9) |
| k1 | 20 | Constant in Equation (9) |
| Scrt | 10% | Improved particles/added func. Evalua. |
| or | Constant in Equations (7a) and (7b): for F1 to F5 and for F6 to F17 | |
| W | 0.729 | Weight of particle record in Equation (8) |
| κ | 0.5 | Proportion of adventurous male particles |
| 0.4 | Constant proportion in Equation (26) | |
| 0.8 | Life duration of short-lived males | |
| ζ | 0.42 | Proportion of female particles |
| Functions | Particle Numbers |
|---|---|
| F1 | 30 |
| F2 | 30 |
| F3 | 30 |
| F4 | 100 |
| F5 | 100 |
| F6 | 1000 |
| F7 | 1000 |
| F8 | 2000 |
| F9 | 2000 |
| F10 | 500 |
| F11 | 1000 |
| F12 | 1000 |
| F13 | 1000 |
| F14 | 2000 |
| F15 | 2000 |
| F16 | 2000 |
| F17 | 2000 |
| S-EPSO | ANDE | NMMSO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | SR | PR | SR | PR | SR | ||
| F1 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F4 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F5 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F6 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.960 | |
| 0.999 | 0.980 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.960 | ||
| 0.996 | 0.920 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.960 | ||
| 0.980 | 0.660 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.940 | ||
| 0.896 | 0.080 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| F7 | 0.947 | 0.100 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 0.882 | 0.020 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 0.754 | 0.000 | 0.936 | 0.176 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 0.651 | 0.000 | 0.933 | 0.176 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 0.607 | 0.000 | 0.941 | 0.196 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F8 | 0.494 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.984 | 0.260 | |
| 0.308 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.984 | 0.220 | ||
| 0.202 | 0.000 | 0.947 | 0.078 | 0.983 | 0.180 | ||
| 0.162 | 0.000 | 0.944 | 0.078 | 0.981 | 0.180 | ||
| 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.948 | 0.039 | 0.980 | 0.180 | ||
| F9 | 0.477 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.930 | 0.020 | |
| 0.380 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.922 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.355 | 0.000 | 0.616 | 0.000 | 0.920 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.321 | 0.000 | 0.512 | 0.000 | 0.917 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.203 | 0.000 | 0.506 | 0.000 | 0.913 | 0.000 | ||
| F10 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F11 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| F12 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.980 | |
| 0.995 | 0.96 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| 0.985 | 0.88 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| 0.970 | 0.76 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| 0.960 | 0.68 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.980 | ||
| F13 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 0.993 | 0.960 | |
| 1.000 | 1.000 | -- | -- | 0.993 | 0.960 | ||
| 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.771 | 0.078 | 0.990 | 0.940 | ||
| 0.997 | 0.980 | 0.686 | 0.000 | 0.990 | 0.940 | ||
| 0.997 | 0.980 | 0.686 | 0.000 | 0.990 | 0.940 | ||
| F14 | 0.923 | 0.560 | -- | -- | 0.770 | 0.080 | |
| 0.883 | 0.380 | -- | -- | 0.740 | 0.060 | ||
| 0.873 | 0.320 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.713 | 0.020 | ||
| 0.853 | 0.240 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.710 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.847 | 0.200 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.703 | 0.000 | ||
| F15 | 0.750 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.673 | 0.000 | |
| 0.728 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.673 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.678 | 0.000 | 0.645 | 0.000 | 0.673 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.673 | 0.000 | 0.632 | 0.000 | 0.670 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.665 | 0.000 | 0.632 | 0.000 | 0.668 | 0.000 | ||
| F16 | 0.667 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 1.000 | 0.000 | |
| 0.667 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.703 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.653 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.653 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.633 | 0.000 | ||
| F17 | 0.728 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.553 | 0.000 | |
| 0.625 | 0.000 | -- | -- | 0.548 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.615 | 0.000 | 0.397 | 0.000 | 0.543 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.588 | 0.000 | 0.397 | 0.000 | 0.538 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.515 | 0.000 | 0.397 | 0.000 | 0.238 | 0.000 | ||
| S-EPSO | Tie | ANDE and NMMSO |
|---|---|---|
| 39 | 59 | 38 |
| 28.7% | 43.4% | 27.9% |
| PR | SR | PR | SR | PR | SR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F7 | 0.947 | 0.100 | 0.942 | 0.060 | 0.987 | 0.580 | |
| 0.882 | 0.020 | 0.867 | 0.000 | 0.972 | 0.360 | ||
| 0.754 | 0.000 | 0.758 | 0.000 | 0.863 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.651 | 0.000 | 0.690 | 0.000 | 0.754 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.607 | 0.000 | 0.654 | 0.000 | 0.603 | 0.000 | ||
| Problem | Variable | -20,000 | -0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV | Best | 6059.714336 | 6059.714336 |
| Worst | 6059.714336 | 6059.714336 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 0.437500 | 0.437500 | ||
| 0.812500 | 0.812500 | ||
| 176.636596 | 176.636596 | ||
| 42.098446 | 42.098446 | ||
| S SpRe R | Best | 2994.554224 | 2994.554224 |
| Worst | 2994.554224 | 2994.554224 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 3.5000 | 3.5000 | ||
| 0.7000 | 0.7000 | ||
| 17 | 17 | ||
| 7.3000 | 7.3000 | ||
| 7.715320 | 7.715320 | ||
| 3.350541 | 3.350541 | ||
| 5.286654 | 5.286654 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guilbault, R. S-EPSO: A Socio-Emotional Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Multimodal Search in Low-Dimensional Engineering Applications. Algorithms 2025, 18, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18060341
Guilbault R. S-EPSO: A Socio-Emotional Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Multimodal Search in Low-Dimensional Engineering Applications. Algorithms. 2025; 18(6):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18060341
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuilbault, Raynald. 2025. "S-EPSO: A Socio-Emotional Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Multimodal Search in Low-Dimensional Engineering Applications" Algorithms 18, no. 6: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18060341
APA StyleGuilbault, R. (2025). S-EPSO: A Socio-Emotional Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Multimodal Search in Low-Dimensional Engineering Applications. Algorithms, 18(6), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18060341







