Abstract
It is known that fractional-order models can effectively represent complex high-order systems with fewer parameters. This paper focuses on the identification of a class of multiple-input single-output fractional Hammerstein models. When the commensurate order is assumed to be known, a greedy orthogonal least squares method is proposed to simultaneously identify the parameters and system orders, combined with a stopping rule based on the Bayesian information criterion. Subsequently, the commensurate order is determined by minimizing the normalized output error. The proposed method is validated by applying it to identify a CD-player arm system.
1. Introduction
The majority of real processes demonstrate intricate nonlinear dynamic behavior, which can be approximated by using nonlinear models. Due to the inherent diversity and complexity of these models, their development and identification continue to be a central focus of ongoing research efforts. Block-oriented Hammerstein nonlinear systems exhibit remarkable versatility and utility, making them highly effective for modeling a wide range of practical nonlinear dynamic systems, such as pH neutralization processes [1], heat exchangers [2], fuel cell systems [3], and wind turbines [4]. Thus, Hammerstein systems have remained a prominent and actively researched topic over the past decades.
On the other hand, numerous physical nonlinear processes exhibit fractional dynamics, characterized by hereditary properties and infinite-dimensional structures. Fractional operators are inherently capable of capturing memory effects and provide additional degrees of freedom for describing both existing and potential physical attributes of systems. This has generated significant interest among researchers across various disciplines in leveraging fractional derivatives for system modeling [5]. Fractional calculus, a natural extension of traditional integer-order calculus, has emerged as a powerful tool for constructing complex nonlinear models. Compared to integer-order systems, fractional calculus offers a more concise and accurate representation for systems with intricate dynamics [6,7]. Research on the identification of fractional systems has been particularly active, with a predominance of studies focusing on linear cases [8,9,10]. However, most real-world systems inherently exhibit nonlinear behavior to varying degrees, and their modeling remains an open research challenge due to the diversity of their structures. This paper focuses on the identification of fractional Hammerstein systems, particularly those in which the linear component exhibits fractional characteristics.
A wide range of methodologies have been proposed in the literature for the identification of classical integer-order Hammerstein systems [11,12,13,14,15]. For the fractional case, an adapted version of the simplified refined instrumental variable method has been introduced to estimate the parameters of fractional Hammerstein models under the assumption that all differentiation orders are known, with Monte Carlo simulations employed to evaluate the performance of the proposed approaches in [16]. Jin et al. derived an adaptive immune algorithm based on a global search strategy, which was employed to determine initial values for the fractional Hammerstein model’s coefficients and order, which were then refined using an auxiliary model recursive least squares method [17]. Rahmani et al. developed an iterative linear optimization algorithm integrated with Lyapunov stability theory, which was applied to determine the fractional order and parameters of a neuro-fractional Hammerstein model [18]. Meanwhile, ref. [19] utilizes principal component analysis within a subspace identification framework to identify coefficient matrices of fractional systems and employs singular value decomposition to directly estimate the parameters of the nonlinear part. A Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm is applied to determine system parameters, where the linear part is represented by a fractional transfer function [20]. However, these studies either involve matrix inversion operations, which typically result in high computational complexity, or focus solely on parameter identification while neglecting the estimation of the fractional order.
In this paper, a Householder transformation-based greedy orthogonal least squares (H-GOLS) algorithm is proposed for the identification of multi-input single-output (MISO) fractional Hammerstein models. The proposed methodology initiates by reformulating the system into a pseudo-linear regression model via over-parameterization, introducing upper bounds on the nonlinear order and regression length. The parameters are subsequently estimated using orthogonal least squares. In each iteration, the Householder transformation is applied to the information matrix, converting it into an upper triangular matrix. This approach eliminates the need for matrix inversion, thereby significantly reducing computational complexity and mitigating the risk of ill-conditioned solutions in high-dimensional matrices. The selection of columns in each iteration is simultaneously guided by a greedy criterion. Additionally, we adopt a modified stopping criterion based on the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) to determinate the sparsity level and model order. Finally, an output error criterion function is introduced to estimate the approximate fractional order.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 discusses the mathematical background on fractional differentiation, the structure of the fractional Hammerstein system with multiple inputs, and its identification problem formulation. Section 3 derives an algorithm for identifying the MISO fractional Hammerstein systems. Section 4 applies two examples to support the proposed algorithm. Finally, some conclusions are given in Section 5.
2. Model and Problem Formulation
2.1. Mathematical Background of Fractional Differentiation
Generally, there are three widely used definitions of fractional calculus: the Grünwald–Letnikov (GL) definition [21], the Riemann–Liouville (RL) definition [22], and the Caputo definition [23]. Among these, the GL definition is the most frequently used due to its ease of implementation and programming. Therefore, this paper adopts the GL definition as the basis for investigation. The concept of fractional calculus can be expressed as
where denotes the floor operator, represents the differentiation operator , is the fractional order, and the binomial term is defined as
Define , when , to numerically evaluate the fractional derivative; the parameter h in Equation (1) is substituted with the sampling period, and as a result, the limit operation is dropped
In the above equation, the error term is directly related to the length of the sampling interval. Therefore, to ensure that the approximation error is negligible, the sampling interval should be sufficiently short.
Under the condition that is relaxed at ( for all ), the Laplace transform of is given by [24]. Therefore, for the following fractional mathematical model,
a symbolic representation of the above system can be established using the transfer function
Additionally, if is commensurate of order , it can be rewritten as
where and are integers; for and , we have [16]
2.2. MISO Fractional Hammerstein System
Consider a MISO fractional Hammerstein CAR model described by
where is the measured data of the unobserved output , is the noise with zero mean and variance , , and . represents the output of the memoryless nonlinear function with known basis, which serves as the input to the linear part. It can be expressed as
where denotes the r inputs at the t-th sampling instant, is the nonlinear order, is the parameter to be identified, and is a known basis function, respectively. According to Equation (3), Model (8) can be rewritten as
The above system can be expressed as the following pseudo-linear regression model:
where represents the information vector containing input–output data, which is expressed as
where is the nonlinear order bound and is the data regression length. From Equations (8) and (10), the parameter vector is given by
with
Assumption 1.
Only is known, while the parameters , ⋯, , , ⋯, , , ⋯, and , as well as the orders and , are to be identified.
Assumption 2.
From Equations (8)–(14), it is observed that for any nonzero constant ζ, the system would yield an identical output with . To ensure parameter uniqueness, it is assumed that [12].
Let and . The goal is to estimate the sparse parameter vector and then to extract the system parameters , and from the sparse structure of . Though minimizing a least squares criterion leads to a solution , it requires a large amount of sampled data, since the dimension of is high. Furthermore, the least squares method does not inherently produce sparse solutions, which poses another challenge in the identification process.
3. Identification Algorithm
The identification problem of sparse vector can be formulated as
where denotes the norm of the vector , and is the tolerance.
The Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm [25] is a typical greedy method used to solve this type of optimization problem. However, it requires computing the inverse of the information matrix in each iteration, which leads to a high computational cost, particularly when the matrix dimension is large. Additionally, using this method may result in an ill-conditioned solution. In this paper, we aim to address these problems by employing the Householder transformation strategy.
3.1. Orthogonal Least Squares Algorithm Based on Householder Transformation
We introduce a permutation matrix , which is constructed by performing k column swaps on an identity matrix . The first k columns of can be expressed as follows [26]:
where , denote the index of the chosen column in the k-th iteration, . Using the permutation matrix , the least squares criterion can be formulated as
where comprises the columns of that correspond to k non-zero parameters, and is a vector containing the k non-zero elements of . Since the sub-information matrix corresponding to is a column full-rank matrix, there must exist an orthogonal matrix and an upper triangular matrix such that
where is a zero matrix. Define
with and ; then, the criterion function (18) can be rewritten as
By minimizing (21), we obtain and . The solution can subsequently be derived using the following back-substitution method:
where denotes the i-th element of , and and denote the i-th diagonal element of and the i-th element of , respectively.
Using the permutation matrix , we can recover the parameter estimation by
The Householder transformation [27,28] is adopted for QR decomposition in Equation (19). Let denote the column of indexed by , and represent the identity matrix of dimension j. Define the Householder matrix as
with
where is an -dimensional vector with only the first element being 1 and the rest being 0. Then, we have . Let , and the orthogonal matrix can be constructed as
Therefore, the critical factor is determining the permutation matrix . The following section introduces a method to obtain using the greedy criterion of the Householder transformation.
3.2. Construction of the Permutation Matrix
Assuming that the sub-information matrix has already been constructed based on the active set , the next step involves selecting a candidate column from the remaining columns of . Let represent the candidate column selected at the k-th iteration, and define
According to Equations (24)–(26), we have
where , , and denotes the first element of . From Equations (21) and (29), we have
By substituting Equation (32) into (31), we obtain
and then we can obtain that
where . We employ the indices , , where represents the level of sparsity. The permutation matrix can be formed using Equation (17).
3.3. Determination of Sparsity Level
To determine the sparsity level, various information-theoretic criteria (ITCs) can be employed, including the Akaike information criterion (AIC) [29], the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) [29], and the Mallows Cp criterion (Cp) [30]. For the purposes of this paper, our focus will be on the BIC. Typically, the BIC is expressed as
where denotes the residual vector. The sparsity level can then be determined as
where denotes the maximum allowed level of sparsity. However, the upper bound is hard to determine. In this paper, we propose a new stopping rule based on the BIC criterion,
Given a small threshold [31], when , the iteration stops. Then, we have
By adopting this stopping criterion, the computational complexity is reduced, enabling the model to converge rapidly to an accurate sparse structure. Once the sparsity level K has been established, the following subsection explores methods for determining the model order and separating the mixed parameters based on the obtained estimates .
3.4. Identification of Orders and Separation of Parameters
Given the block sparse nature of , it becomes possible to obtain an efficient parameter estimate, denoted as , which preserves the identical sparse structure. Within this sparse structure, comprises zero blocks. Let represent the number of zeros in each zero block, where ranges from 1 to . Subsequently, the size of can be detected sequentially. Upon detecting that , the nonlinear order for each input channel can be estimated as
Based on the structure of , we can deduce that the number of elements within each non-zero block, ranging from the -th to the -th non-zero block, is constant. The linear orders can be determined by counting the number of elements in any of these non-zero blocks.
According to Equations (13)–(15), it is evident that all non-zero blocks in contain mixed parameters, with the exception of the first block. We can obtain and from the structure of . Since , the -th non-zero block corresponds to . The estimations of can be derived using the parameters from the -th to the -th non-zero block and . Notably, can be computed using any one of . Thus, the average of these computed values is taken as the estimation of , i.e.,
In order to obtain the fractional order, we introduce an output error criterion function as [16]
where , is the estimated parameter vector for the fractional order . By minimizing this criterion function over different fractional orders, we can determine the approximate fractional order .
The H-GOLS algorithm is systematically detailed in the following Algorithm 1, offering a comprehensive suite of implementation procedures.
| Algorithm 1 H-GOLS algorithm for MISO fractional Hammerstein system |
| Input: , p, l and . Output: , ⋯, , , ⋯, , , ⋯, , and .
|
4. Experimental Results and Discussions
Example 1.
Consider the following MISO fractional Hammerstein model:
Set l = 30 and p = 10. The true parameter vector is
The inputs {} are white noise sequences with zero mean and unit variance , while {} is a noise sequence with zero mean and constant variance of . This example is intended to serve as a standard numerical simulation case to demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm. The parameters are not fixed and can indeed be modified as needed. For a data length of , the proposed H-GOLS algorithm along with stopping rule (37) and a threshold of , was employed. The resulting curve is illustrated in Figure 1. The algorithm converged after 21 iterations, as indicated. Consequently, the sparsity level is determined to be . The estimated non-sparse parameter vector is
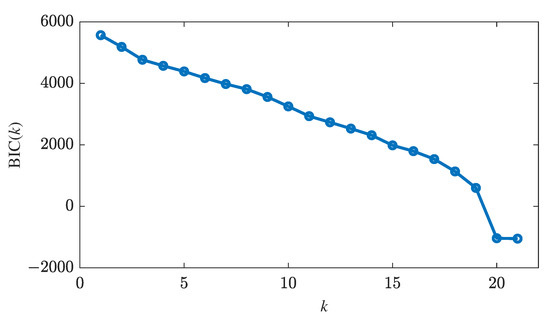
Figure 1.
The curves versus k.
Defining the parameter estimation error as , we obtain .
Based on Equations (39)–(40), the following estimates are obtained:
The curve of the output error criterion for different values of is shown in Figure 2, allowing the estimated fractional order to be determined as .
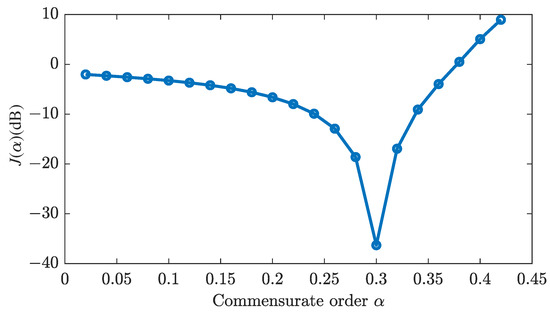
Figure 2.
Output error criterion versus the commensurate differentiation .
From the above results, it is clear that the proposed H-GOLS algorithm effectively estimates the system’s structure with limited data. Moreover, by implementing stopping rule (37), the algorithm reduces the computational burden while enhancing parameter estimation accuracy.
The H-GOLS, OMP, basis pursuit denoising (BPDN) [32], and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) [33] algorithms are employed to identify the system; Figure 3 illustrates the parameter estimation errors for varying data lengths with the noise variance . It is observed that the H-GOLS, OMP, and LASSO algorithms effectively estimate system parameters even with restricted data lengths, with the H-GOLS algorithm exhibiting a higher degree of precision compared to the other two. In cases where the data length is sufficient, all four methods are capable of accurately estimating the system parameters; however, the H-GOLS algorithm maintains the utmost estimation accuracy.
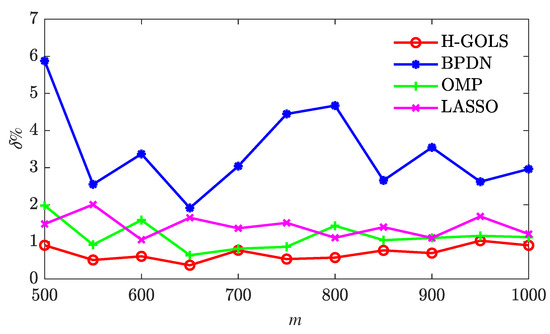
Figure 3.
The parameter estimation errors of different algorithms under different data lengths m.
With a data length fixed at , the system was characterized using the H-GOLS, BPDN, OMP, and LASSO algorithms. Figure 4 displays the parameter estimation errors across various noise variance levels. At lower noise variances, all four algorithms demonstrate effective parameter estimation capabilities, with the H-GOLS algorithm exhibiting the highest parameter estimation accuracy. Nevertheless, as the noise variance rises, both the BPDN and OMP algorithms exhibit growing parameter estimation errors, indicating that the H-GOLS algorithm not only achieves superior estimation accuracy but also exhibits better robustness against interference.
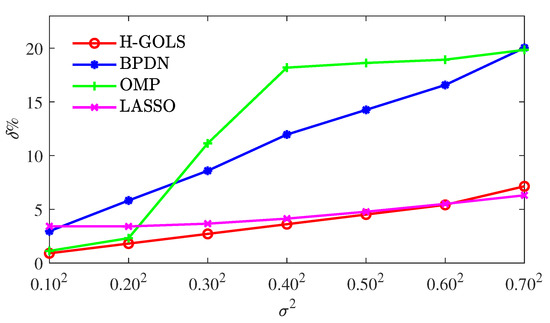
Figure 4.
The parameter estimation errors of different algorithms under different noise variances .
Computational complexity serves as a critical performance metric for algorithm evaluation, quantifying the computational resources required for execution. It is conventionally characterized by the number of floating-point operations (FLOPs), primarily encompassing multiplication and addition operations. Let ; the computational requirements for the H-GOLS, BPDN, OMP, and LASSO algorithms are listed in Table 1, where and are the given iterations for the BPDN algorithm and the LASSO algorithm, respectively. Since K is significantly smaller than n (i.e., ), the H-GOLS algorithm apparently achieves the lowest computational complexity among the four methods.

Table 1.
Comparison of computational complexity among different algorithms.
Example 2.
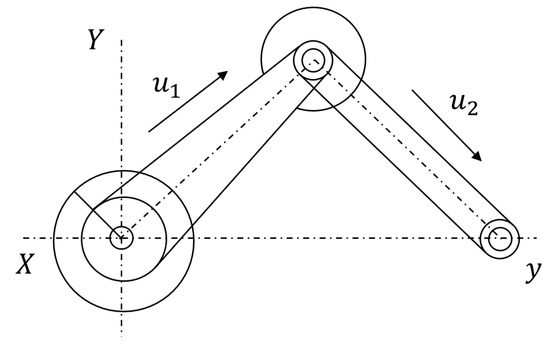
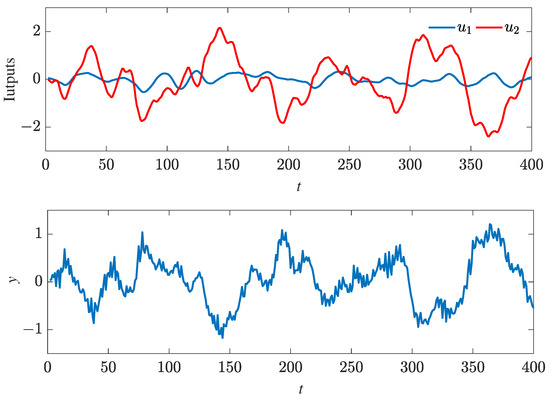
Consider the CD-player arm system depicted in Figure 5; we employed measurement data sourced from Daisy, a dedicated database for system identification [34]. A total of 400 samples were collected, with the first 200 samples used to fit the fractional Hammerstein model and remaining 200 samples reserved for validation. The inputs and represent the forces exerted by the mechanical actuators, characterized by high autocorrelation, while the output reflects the tracking accuracy of the arm. Standardized inputs and output data samples for this system are shown in Figure 6.

Figure 5.
The CD-player arm system.

Figure 6.
The inputs and output data of the CD-player arm system.
Setting , , , and , the H-GOLS algorithm is utilized to identify the following fractional Hammerstein model:
where {} is a noise sequence with zero mean and constant variance of . By using the stopping criterion (37), the process stops after completing five iterations. Therefore, the sparsity level is . The estimated parameter vector is
where . Figure 7 displays the output fittings for both the training and validation data.
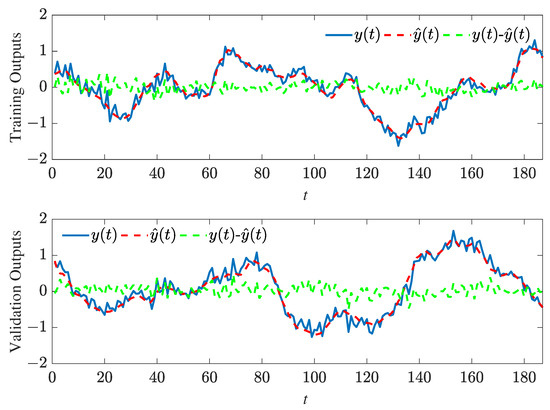
Figure 7.
Output fitting of the training data and validation data.
Figure 8 depicts the curve of the output error criterion as a function of , yielding an estimated fractional order of 0.10.
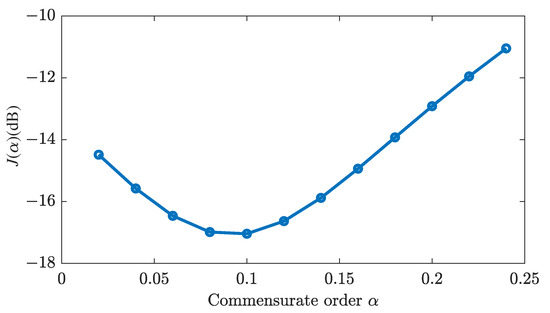
Figure 8.
Output error criterion versus the commensurate differentiation order for the CD-player arm system.
Then, the CD-player arm system can be expressed as
Table 2 presents the performance evaluation results for the fractional Hammerstein model using the H-GOLS, BPDN, OMP, and LASSO algorithms, along with results for the integer-order Hammerstein model using the H-GOLS algorithm. The results demonstrate that the fractional Hammerstein model offers a significantly more accurate representation of the CD-player arm system compared to its integer-order counterpart. Furthermore, the H-GOLS algorithm demonstrates superior performance compared to BPDN, OMP, and LASSO algorithms.

Table 2.
Comparison of the accuracy of the models established by different algorithms.
5. Conclusions
For MISO fractional Hammerstein systems, the H-GOLS algorithm is proposed for jointly identifying the model orders and parameters. This algorithm leverages the Householder transformation to triangularize the sub-information matrix, effectively addressing issues related to ill-conditioned matrices and significantly reducing computational complexity. Subsequently, the sparse parameter vector is obtained using a back-substitution approach. Compared to conventional sparse identification algorithms such as BPDN, OMP, and LASSO, the proposed H-GOLS algorithm demonstrates significant advantages in parameter estimation accuracy, noise robustness, and computational efficiency. Notably, even under limited data availability, H-GOLS maintains superior estimation precision. Furthermore, in comparison to integer-order models, fractional models offer a more accurate description of systems with complex nonlinear characteristics, such as the CD-player mechanical arm presented in this paper. Both numerical simulations and the modeling of a CD-player arm system validate the effectiveness of the proposed H-GOLS algorithm.
In this study, the fractional-order is estimated by first obtaining parameter estimates and then computing the system’s output error across various values. This approach is computationally intensive. In future studies, we aim to investigate methods for simultaneously estimating the parameters and the fractional-order during the identification process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y. and Y.L.; methodology, X.Y. and Y.L.; software, X.Y.; validation, X.Y. and Y.L.; formal analysis, X.Y.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, X.Y. and Y.L.; data curation, X.Y. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; visualization, X.Y. and Y.L.; supervision, X.Y. and Y.L.; project administration, X.Y. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61973137), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20201339), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2022M711361), and the 111 project (B23008).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Huang, K.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Yang, C.; Gui, W. Knowledge-informed neural network for nonlinear model predictive control with industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man-Cybern. Syst. 2023, 4, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, P.; Novak, N.; Vojislav, F.; Ljubisa, D. Multilinear model of heat exchanger with Hammerstein structure. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jhao, D. Control of a direct internal reforming molten carbonate fuel cell system using wavelet network-based Hammerstein models. J. Process Control 2012, 22, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, G.; Wingerden, J.W.; Verhaegen, M. Global identification of wind turbines using a Hammerstein identification method. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 4, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Roy, P.K.; Banerjee, S. Adaptive fractional-order sliding-mode disturbance observer-based robust theoretical frequency controller applied to hybrid wind-diesel power system. ISA Trans. 2023, 133, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Yusuf, A.; Shaikh, A.A.; Inc, M.; Baleanu, D. Fractional modeling of blood ethanol concentration system with real data application. Chaos 2019, 29, 013143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajarmi, A.; Baleanu, D. On the fractional optimal control problems with a general derivative operator. Asian J. Control 2021, 23, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y. Modulating function based identification for fractional order systems. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. An innovative parameter estimation for fractional-order systems in the presence of outliers. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamah, T.; Bettayeb, M.; Djennoune, S. Identification of multivariable fractional order systems. Asian J. Control 2013, 15, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.; Lin, G. Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2011, 21, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.; Chu, J. Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 2013, 7, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Cheng, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Pan, X. A high-accuracy CO2 carbon isotope sensing system using subspace identification of Hammerstein model for geochemical application. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, E.; Fu, M. A blind approach to Hammerstein model identification. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, P.; Fan, L. Identification of MISO Hammerstein system using sparse multiple kernel-based hierarchical mixture prior and variational Bayesian inference. ISA Trans. 2023, 137, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, S.; Malti, R.; Garnier, H.; Oustaloup, A. Parameter and differentiation order estimation in fractional models. Automatica 2013, 49, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z. Recursive identification for MIMO fractional-order Hammerstein model based on AIAGS. Mathmatics 2022, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.R.; Farrokhi, M. Identification of neuro-fractional Hammerstein systems: A hybrid frequency-/time-domain approach. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 8097–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y. Subspace identification for fractional order Hammerstein systems based on instrumental variables. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2012, 10, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, M.; Malti, R.; Cois, O.; Oustaloup, A. System identification using fractional Hammerstein models. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2002, 35, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.J.; Hamed, M.; Mohammad, T. Recursive identification of multiple-input single-output fractional-order Hammerstein model with time delay. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 70, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ge, W.; He, Y. Nonlinear modeling of PEMFC based on fractional order subspace identification. Asian J. Control 2020, 22, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Lin, X.; Zheng, Y. System identification with measurement noise compensation based on polynomial modulating function for fractional-order systems with a known time-delay. ISA Trans. 2018, 79, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, G. Chaos in the fractional order unified system and its synchronization. J. Frankl. Inst. 2008, 345, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, L.; Ji, Y.; Yan, Y. Model recovery for Hammerstein systems using the auxiliary model based orthogonal matching pursuit method. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 54, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Joint parameter and time-delay estimation for a class of Wiener models based on a new orthogonal least squares algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 12159–12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, A.; Darve, E. Hierarchical orthogonal factorization: Sparse least squares problems. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 91, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H. QR factorization-based sampling set selection for bandlimited graph signals. Signal Process. 2021, 179, 107847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Hastie, T.; Johnstone, I.; Tibshirani, R. Least angle regression. Ann. Stat. 2004, 32, 407–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, S.L.; Proctor, J.L.; Kutz, J.N. Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3932–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, J. A novel identification method for a class of closed-loop systems based on basis pursuit de-noising. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 99648–99654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ling, B.; Xie, L.; Dai, Q. Using LASSO for formulating constraint of least-squares programming for solving one-norm equality constrained problem. Signal Image Video Process. 2017, 11, 179–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moor, B.L.R. DDaisy: Database for the Identification of Systems; Department of Electrical Engineering, Ed.; ESAT/STADIUS; KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).