HIPACO: An RSSI Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Division of labor and collaboration framework: we design a worker ant–soldier ant role differentiation mechanism, where worker ants perform local refinement search through pheromone-weighted learning, and soldier ants perform Gaussian perturbation-based global exploration to achieve dynamic allocation of search capabilities.
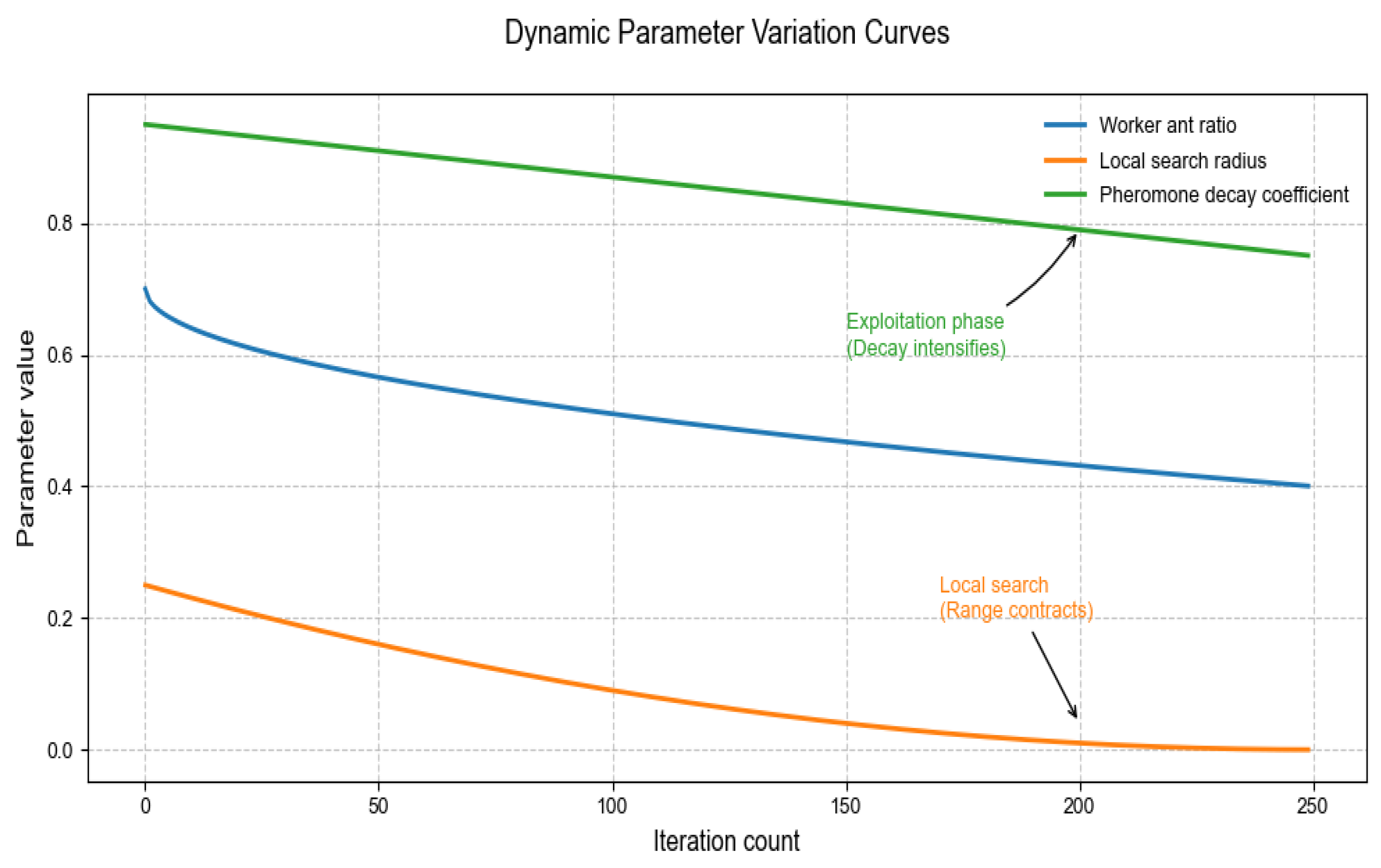
- Dynamic parameter adjustment: we establish a convergence state perception model, adaptively adjust the pheromone decay rate, learning factor, and other parameters, introduce sinusoidal modulation function to dynamically adjust the pheromone concentration in each dimension, and balance the exploration and development needs in different iteration stages.
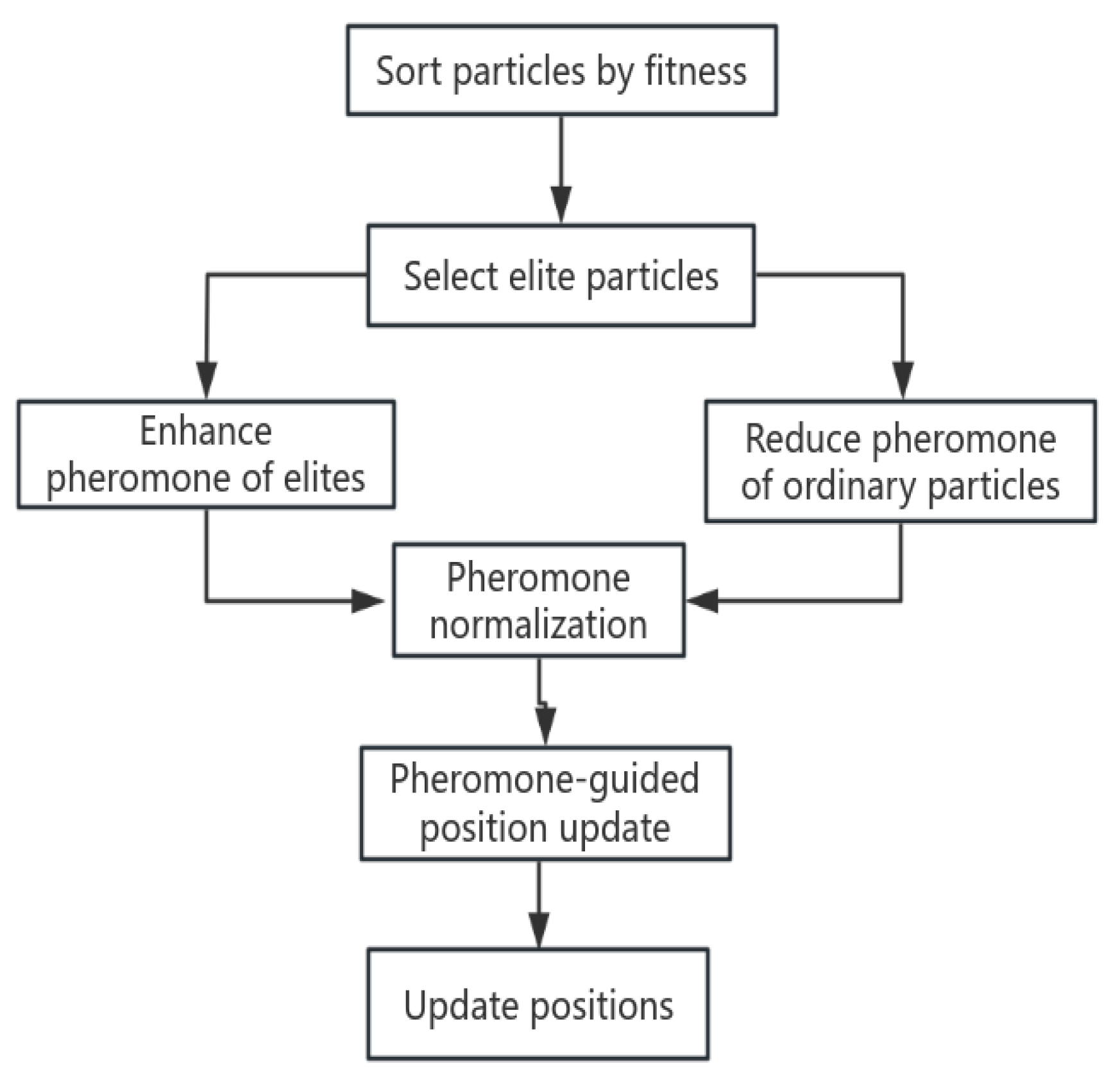
- Hybrid bootstrapping mechanism: we fuse elite particle pheromone enhancement with failed particle local search strategy to improve the algorithm robustness.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm
2.2. Positioning Techniques Based on RSSI Ranging Model
2.3. Algorithm Design
2.3.1. The Fitness Function (RMSE) and Batch Evaluation
2.3.2. Initialization Phase
2.3.3. HIPACO Algorithm Design
2.3.4. Soldier Ant Global Exploration Phase
2.3.5. Mechanisms for Updating Pheromone
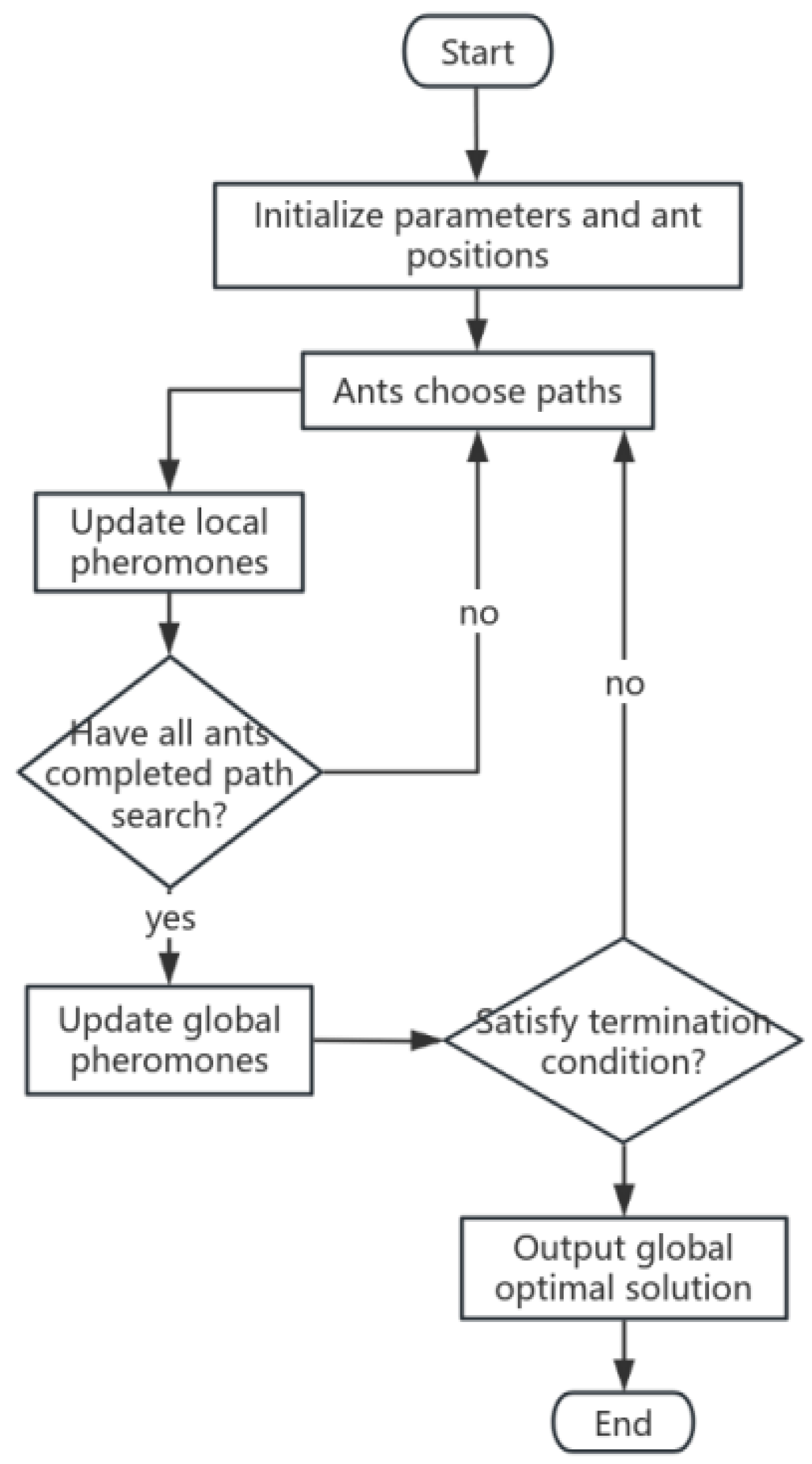
2.3.6. Algorithmic Flow
| Algorithm 1. HIPACO for RSSI Indoor Positioning. |
| Input: - 3D boundary: X_min = (,), X_max = a(,,) - Anchor nodes: B = {b1, b2, …, bm} (bj = (xja,yja,zja), m = 4~10) - RSSI data: RSSI_ij (signal strength from bj to particle i) - Hyperparameters: * Population size: n (default = 80) * Max iterations: T (default = 100) * Initial worker ratio: λ0 = 0.8 * Initial phero Φ0 = 1.0 * Base decay rate: ρ_base = 0.95 * Max failure count: k_max = 4 * Learning factors: α = 1.0, β = 2.0 Output: - Global best position: X_best = (x_best,y_best,z_best) - Minimum ALE: ALE_min # === 1. Initialization Phase === 1: Initialize particles: for i = 1 to n do `X_i(0) ← random_position(X_min, X_max) # Equation(9) boundary constraint Φ_i(0) ← Φ0 # Uniform pheromone initialization fail_counter[i] ← 0 end for 2: Evaluate initial fitness: for i = 1 to n do f_i(0) ← RMSE(X_i(0), B, RSSI) # Equation(7): fitness calculation end for 3: Set global best: X_best(0) ← argmin{f_i(0)|i ∈ [1,n]} f_best(0) ← min{f_i(0)} # === 2. Main Iteration Loop === 4: for t = 1 to T do # --- 2.1 Dynamic Parameter Update --- 5: λ(t) ← 0.7 − 0.3*(t/T)^0.5 # Worker ratio decay (Equation (8)) 6: ρ(t) ← ρ_base - 0.2*(t/T) # Pheromone decay rate # --- 2.2 Ant Grouping --- 7: n_worker ← round(n*λ(t)) 8: Worker_set ← random_sample(n_worker from [1,n]) 9: Soldier_set ← [1,n]\Worker_set # --- 2.3 Worker Ant Update (Local Exploitation) --- 10: for each i ∈ Worker_set do 11: for d ∈ {x,y,z} do 12: L(t)_{i,d} ← β * N(1,0.2) * Φ_i(t − 1)/(f_i(t − 1) + ε) # Equation (11) 13: dir ← random({−1,1}) 14: X_i(t)_d ← X_i(t − 1)_d + dir * L(t)_{i,d} ⊙ (X_best(t − 1)_d − X_i(t − 1)_d) # Equation(10) 15: end for 16: X_i(t) ← clamp(X_i(t), X_min, X_max) # Boundary check 17: f_i(t) ← RMSE(X_i(t), B, RSSI) 18: Update fail_counter[i] (increment if f_i(t) ≥ f_i(t − 1)) end for # --- 2.4 Soldier Ant Update (Global Exploration) --- 19: for each j ∈ Soldier_set do 20: Δx(t)_j ← (1 − β*(t/T)) * N(0,σ2) * Φ_j(t − 1) # Equation (13) 21: X_j(t) ← X_best(t − 1) + Δx(t)_j # Equation (12) 22: X_j(t) ← clamp(X_j(t), X_min, X_max) 23: f_j(t) ← RMSE(X_j(t), B, RSSI) 24: if f_j(t) ≥ f_j(t − 1) then 25: fail_counter[j] += 1 26: if fail_counter[j] ≥ k_max then 27: X_j(t) ← X_j(t) + N(0,2σ2) # Enhanced perturbation end if else 28: fail_counter[j] ← 0 end if end for # --- 2.5 Fitness Evaluation --- 29: f_best(t) ← min{f_i(t) | i ∈ [1,n]} 30: if f_best(t) < f_best(t − 1) then 31: X_best(t) ← argmin{f_i(t)} 32: else 33: X_best(t) ← X_best(t − 1) 34: end if # --- 2.6 Pheromone Update --- 35: Rank particles by fitness: top 20% → Elite_set, others → NonElite_set 36: for each i ∈ Elite_set do 37: Φ_i(t) ← Φ_i(t − 1) * [1.5 − 0.5*(t/T)] * (1 + U(−0.1,0.1)) # Equation (14) 38: end for 39: for each i ∈ NonElite_set do 40: Φ_i(t) ← Φ_i(t − 1) * ρ(t) * (1 + U(−0.05,0.05)) # Equation (15) 41: end for 42: for each i ∈ [1,n], d ∈ {x,y,z} do 43: Φ_i(t)_d ← Φ_i(t) * [1 + 0.1*sin(2πt/10)] # Equation (16): dimensional balance 44: end for 44: end for # === 3. Result Output === 45: ALE_min ← average_localization_error(X_best(T), B_test, RSSI_test) # Equations (17)–(18) 46: return X_best(T), ALE_min |
3. Experiment and Analysis of Results
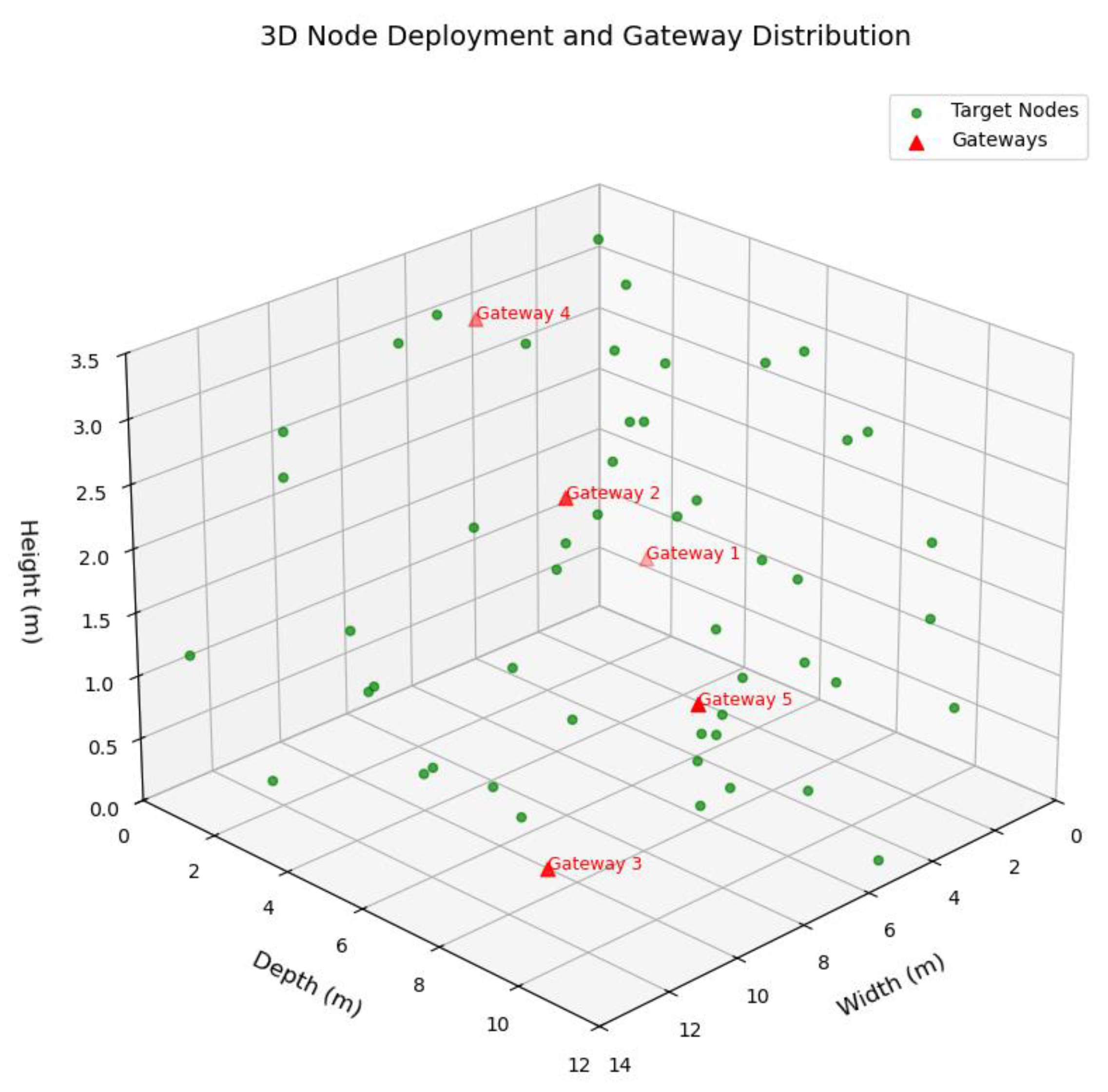
3.1. Simulation Scenario Performance Testing
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
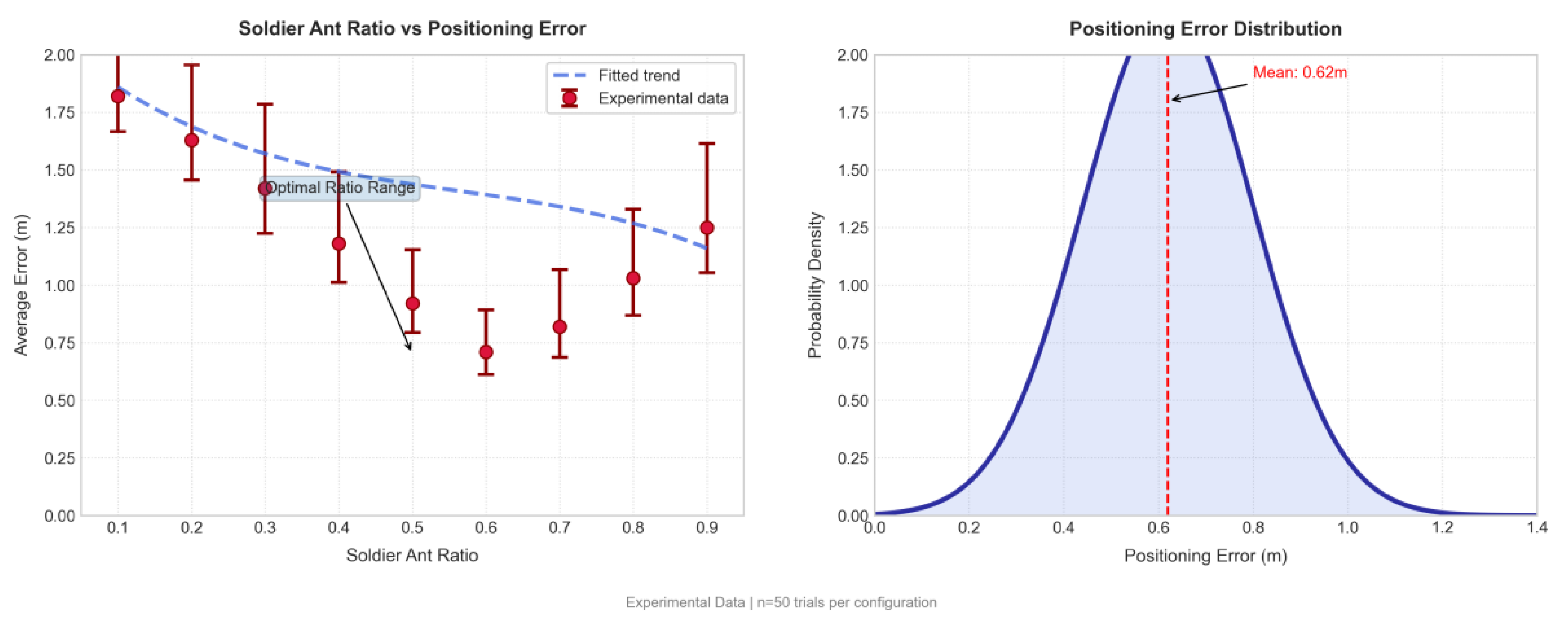
3.3. Effect of Different Soldier and Worker Ratios on Localization Error
3.4. Effect of Different Numbers of Anchor Nodes on Localization Accuracy
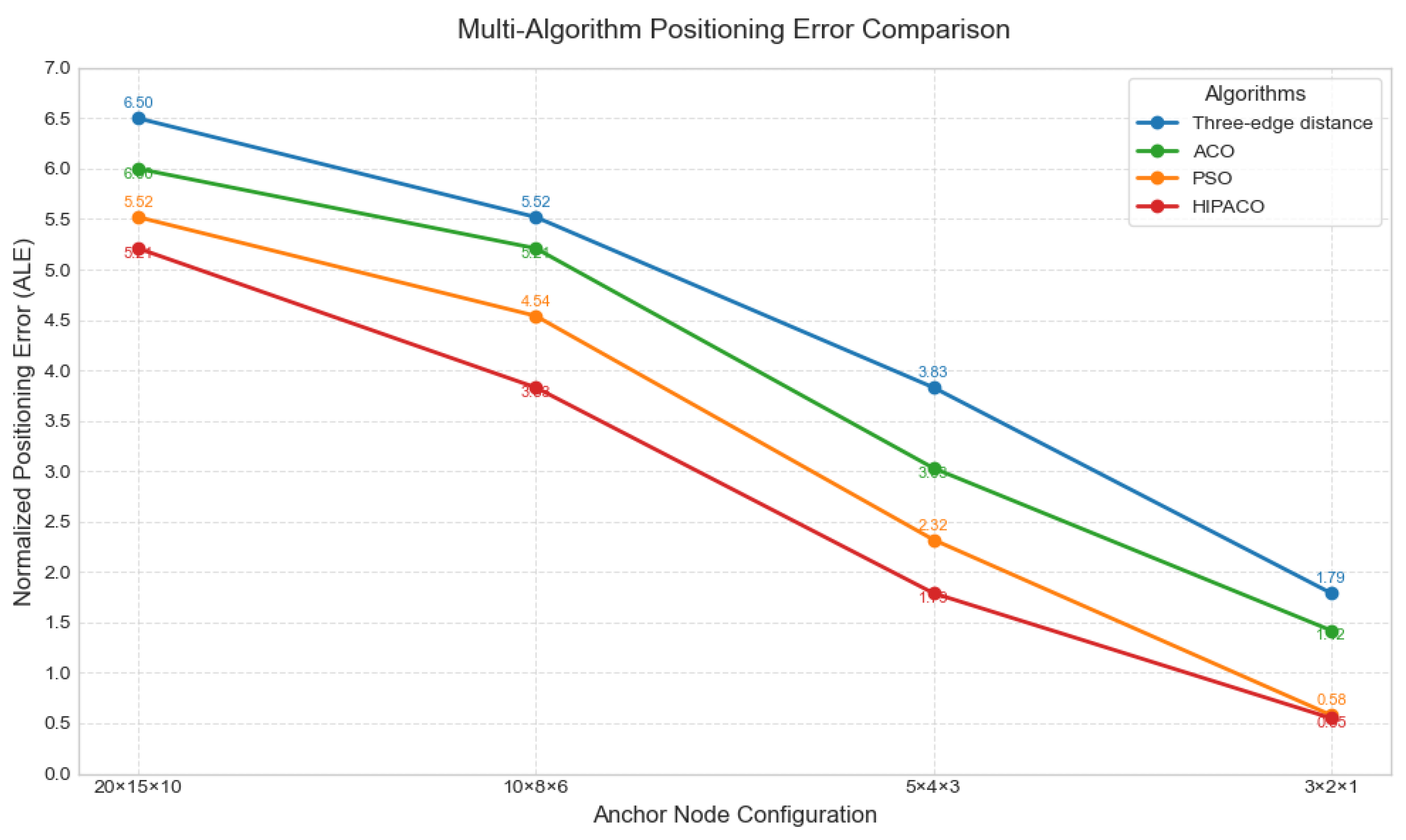
3.5. Effect of Different Site Sizes on Localization Accuracy
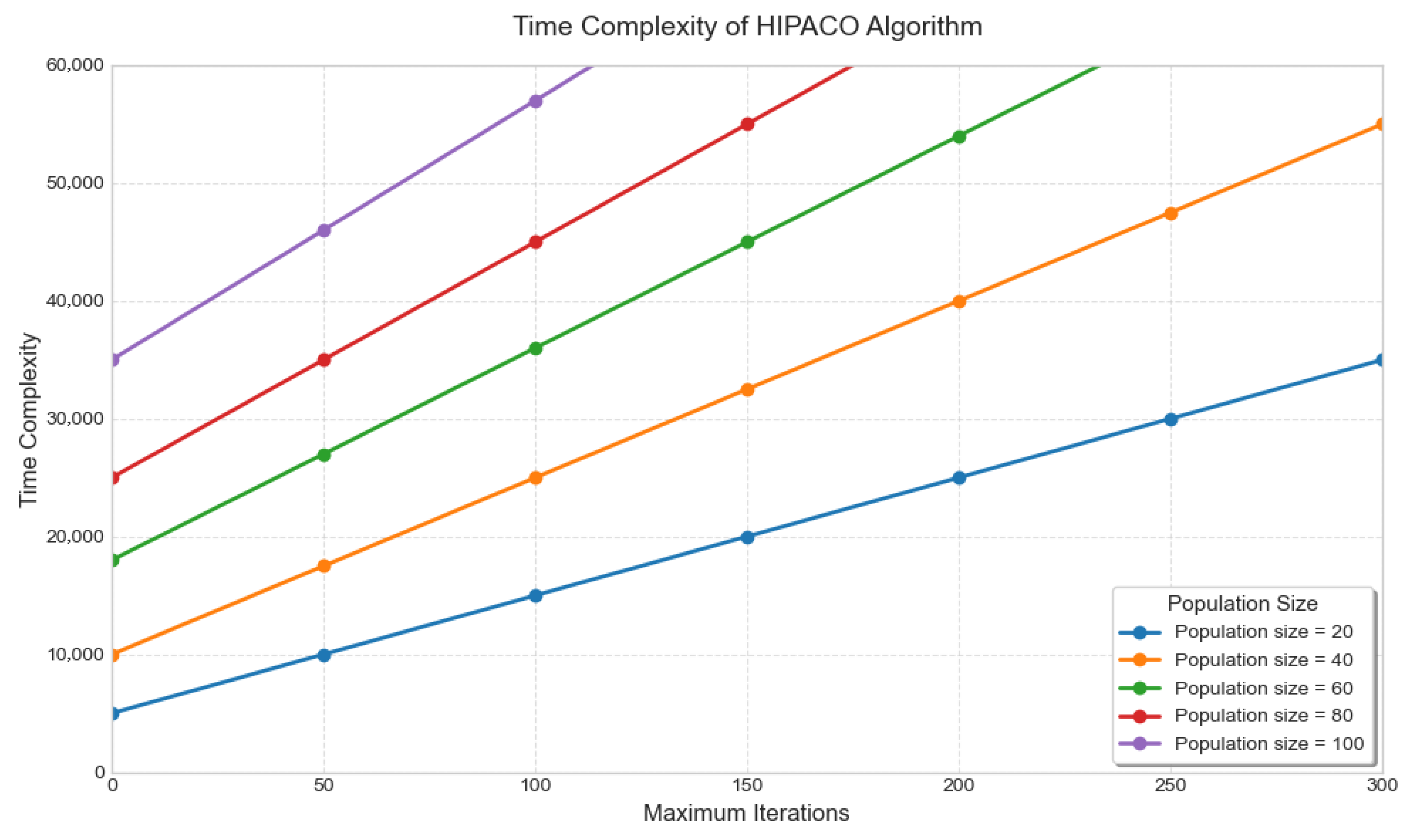
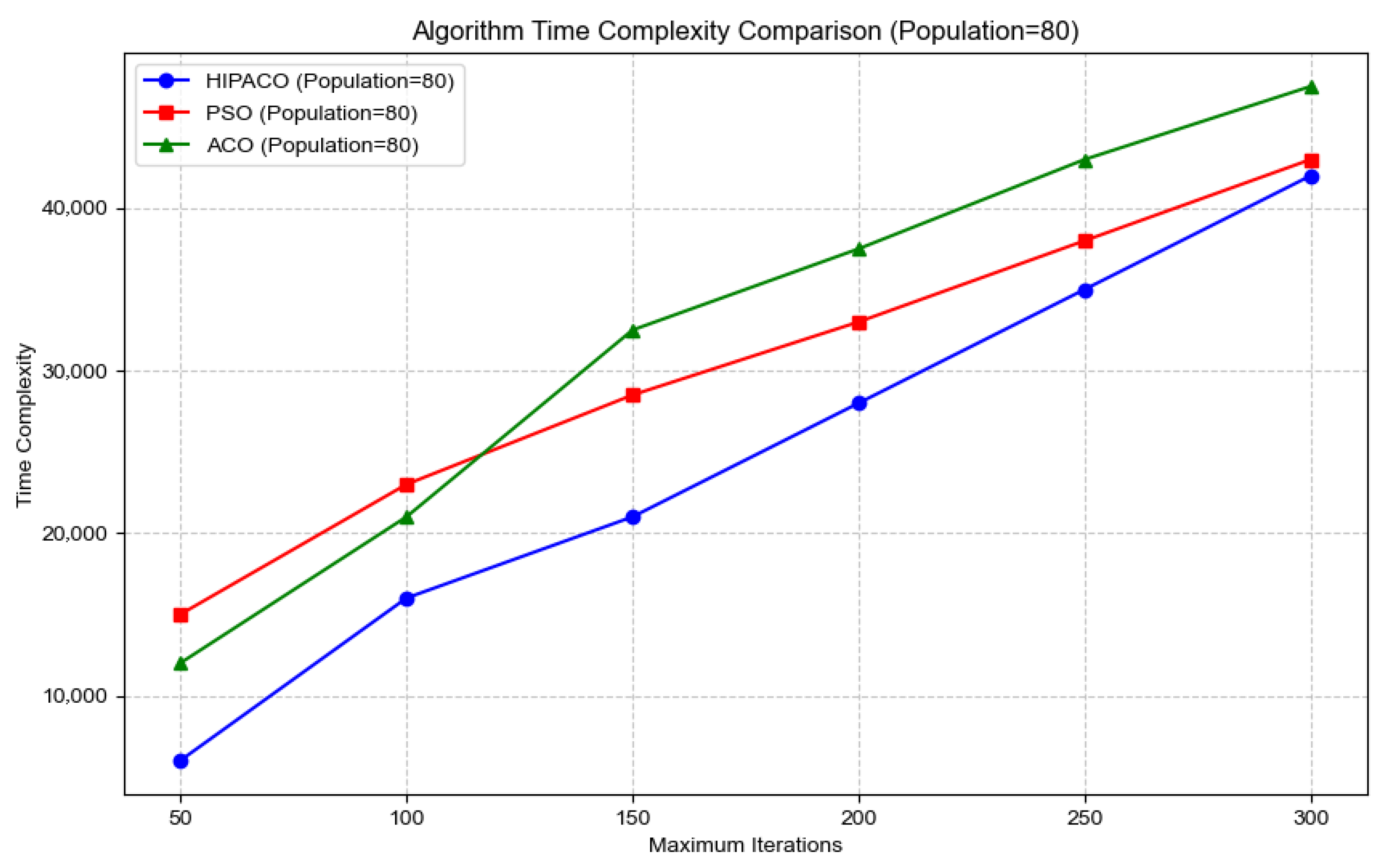
3.6. Time Complexity Analysis
3.7. Real Scenario Testing
- (1)
- Conventional laboratory scenarios: containing obstacles such as tables and chairs and interference from electronic devices such as computers;
- (2)
- Add obstacle scene: randomly adding obstacles such as large green plants on top of the regular scene;
- (3)
- People activity scenarios: introducing people walking around in regular scenarios;
- (4)
- Mixed scenarios: simultaneously adding obstacles and people walking.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Liu, T. Review and development prospect of indoor positioning technology. Digit. Commun. World 2024, 2024, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q. Research on Indoor Mobile Robot Navigation Technology Based on Improved Ant Colony Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.T.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Y.J. An improved ant colony algorithm for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles route planning. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Li, X.P. A research review of improved ant colony algorithm. Inf. Comput. (Theor. Ed.) 2021, 33, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Châari, I.; Koubaa, A.; Bennaceur, H.; Trigui, S.; Al-Shalfan, K. smartPATH: A hybrid ACO-GA algorithm for robot path planning. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopov, A.S. MBHGA: A Matrix-Based Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Solving an Agent-Based Model of Controlled Trade Interactions. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 26843–26863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.B.; Fang, T.T. A Hybrid Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm Enhanced with Mutation and Metabolism. J. Dali Univ. 2025, 10, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.C.; Tian, L.Q.; Wu, W.X. A review on the application of ant colony algorithm in solving the traveler problem. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2023, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Improved ant colony algorithm for AGV path planning in automated container terminals. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 76348–76358. [Google Scholar]
- Gutjahr, W.J. ACO algorithms with guaranteed convergence to the optimal solution. Inf. Process. Lett. 2002, 82, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Tseng, H.W.; Jan, Y.G.; Chuang, M.H. Study of characteristics of RSSI signal. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Chengdu, China, 21–24 April 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.T.; Fu, J.Q. A hybrid RSSI and AoA indoor positioning approach with adapted confidence evaluator. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 154, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniş, F.S. Live RSSI filtering for indoor positioning with Bluetooth Low-Energy. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Beijing, China, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 46, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, S.; Spachos, P. RSSI-based indoor localization with the internet of things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 30149–30161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?–Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payton, D.; Daily, M.; Estowski, R.; Howard, M.; Lee, C. Pheromone robotics. Auton. Robots 2001, 11, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y. Decoupled parameter control for hybrid PSO-ACO: A quantum entanglement inspired approach. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGEVO Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation (GECCO), Boston, MA, USA, 9–13 July 2022; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Joe, P.I.R. A hybrid PSO-ACO algorithm to facilitate software project scheduling. Int. J. Eng. Comput. 2022, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoemphon, S.; Leelathakul, N.; So-In, C. An enhanced node segmentation and distance estimation scheme with a reduced search space boundary and improved PSO for obstacle-aware wireless sensor network localization. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2024, 221, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, S.; Dashti, M.; Claussen, H.; Perez-Cruz, F. Wireless RSSI fingerprinting localization. Signal Process. 2017, 131, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, W.N.; Gu, T.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. ACO-A*: Ant colony optimization plus A* for 3-D traveling in environments with dense obstacles. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2018, 23, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhan, F.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H. A distributed robust economic dispatch strategy for integrated energy system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, D.; Walendziuk, W.; Sadowski, M.; Zankiewicz, A.; Konopko, K.; Slowik, M.; Gulewicz, M. Indoor positioning based on Bluetooth RSSI mean estimator for the evacuation supervision system application. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 5584–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

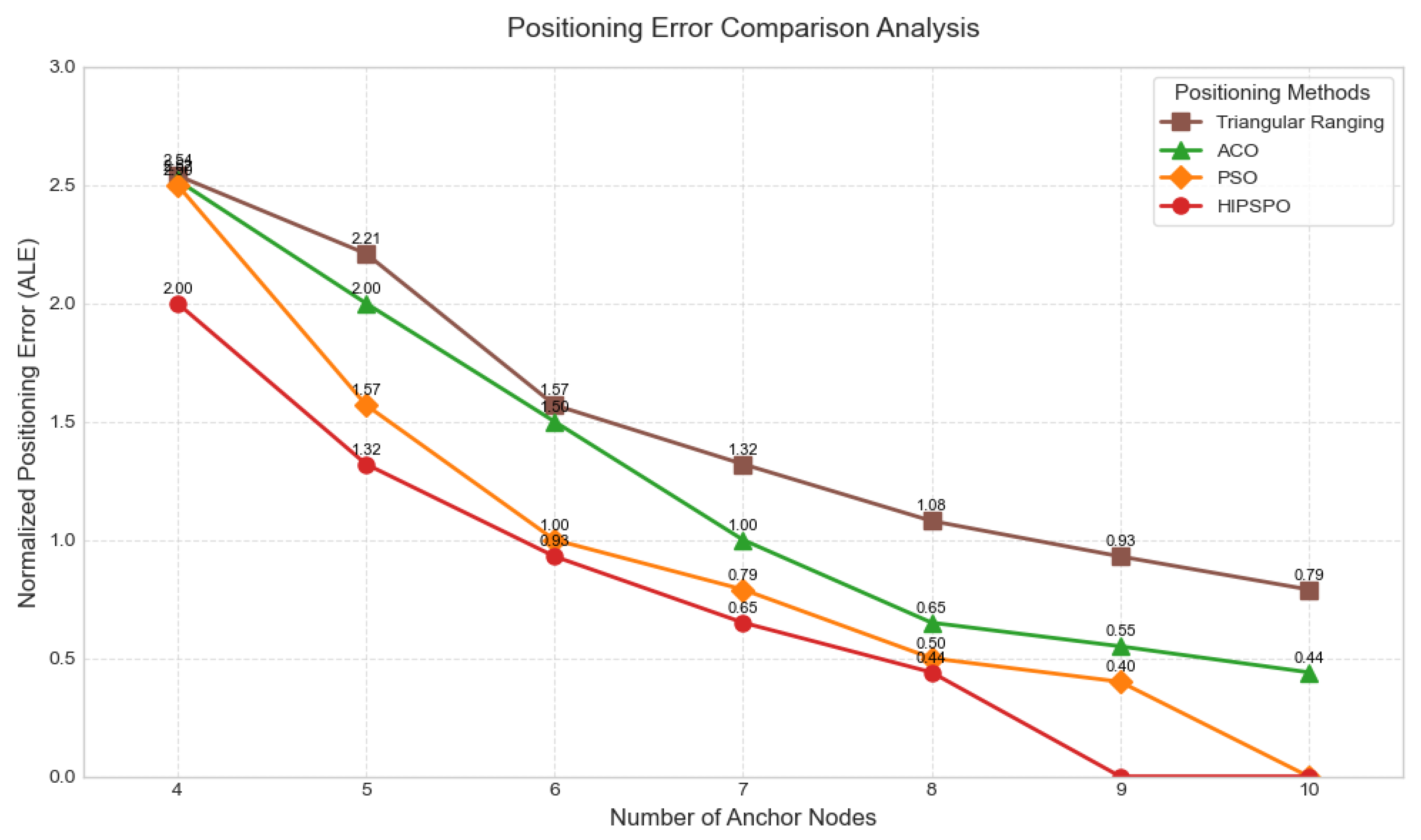


| Localization Algorithm | Mean Value of Normalized Positioning Error |
|---|---|
| Trilateral ranging method | 2.247 |
| ACO Positioning Method | 1.44 |
| PSO positioning method | 1.13 |
| HIPACO localization method | 0.822 |
| localization Algorithm | Mean Value of Normalized Positioning Error |
|---|---|
| Trilateral ranging method | 3.2225 |
| ACO Positioning Method | 2.5775 |
| PSO positioning method | 2.6975 |
| HIPACO localization method | 1.2275 |
| Arithmetic | Computational Complexity (n = 80) |
|---|---|
| PSO | 300,000 ops |
| ACO | 320,000 ops |
| HIPACO | 248,000 ops |
| Positioning Program | Maximum Values | Minimum Value | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Option 1 | 2.323 | 0.329 | 1.326 |
| Option 2 | 2.424 | 0.436 | 1.430 |
| The algorithms in this paper | 1.493 | 0.213 | 0.853 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Jin, B. HIPACO: An RSSI Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Algorithms 2025, 18, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18100654
Zhao Y, Jin B. HIPACO: An RSSI Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Algorithms. 2025; 18(10):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18100654
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yiying, and Baohua Jin. 2025. "HIPACO: An RSSI Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm" Algorithms 18, no. 10: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18100654
APA StyleZhao, Y., & Jin, B. (2025). HIPACO: An RSSI Indoor Positioning Algorithm Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Algorithms, 18(10), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18100654





