Abstract
The minimum error entropy (MEE) criterion finds extensive utility across diverse applications, particularly in contexts characterized by non-Gaussian noise. However, its computational demands are notable, and are primarily attributable to the double summation operation involved in calculating the probability density function (PDF) of the error. To address this, our study introduces a novel approach, termed the fast minimum error entropy (FMEE) algorithm, aimed at mitigating computational complexity through the utilization of polynomial expansions of the error PDF. Initially, the PDF approximation of a random variable is derived via the Gram–Charlier expansion. Subsequently, we proceed to ascertain and streamline the entropy of the random variable. Following this, the error entropy inherent to the linear regression model is delineated and expressed as a function of the regression coefficient vector. Lastly, leveraging the gradient descent algorithm, we compute the regression coefficient vector corresponding to the minimum error entropy. Theoretical scrutiny reveals that the time complexity of FMEE stands at , in stark contrast to the complexity associated with MEE. Experimentally, our findings underscore the remarkable efficiency gains afforded by FMEE, with time consumption registering less than 1‰ of that observed with MEE. Encouragingly, this efficiency leap is achieved without compromising accuracy, as evidenced by negligible differentials observed between the accuracies of FMEE and MEE. Furthermore, comprehensive regression experiments on real-world electric datasets in northwest China demonstrate that our FMEE outperforms baseline methods by a clear margin.
1. Introduction
Entropy serves as a pivotal metric for quantifying the inherent uncertainty within a system, finding ubiquitous application across a multitude of domains including dimension reduction [1,2], parameter estimation [3,4], identification [5,6], feedback control [7,8], and abnormal detection [9,10,11]. The minimum error entropy (MEE) criterion stands out as a notable framework aimed at minimizing the entropy associated with estimation errors, thereby mitigating uncertainty within the estimation model. Particularly pertinent to linear regression estimation quandaries, MEE diverges from conventional least square methodologies by not only considering the variance of prediction errors, but also incorporating higher-order cumulants, rendering it adept at handling non-Gaussian noise distributions [12,13]. Given the prevalence of non-Gaussian noise in real-world scenarios, the efficacy of MEE has been duly validated across various applications, encompassing adaptive filtering [14,15,16], face recognition [17,18], sparse system identification [19,20,21], stochastic control systems [22,23], and visible light communication [24].
Furthermore, the convergence properties of MEE have been meticulously examined in the prior literature [25,26,27]. In-depth analyses delved into the convergence dynamics of fixed-point MEE methodologies [28], while investigations into the interplay between MEE and Minimum Mean-Squared Error (MMSE) [29], as well as its relationship with maximum correntropy [30], have been extensively explored. Noteworthy extensions to the conventional MEE framework include the proposal of kernel MEE variants [31], elucidations on regularization strategies for MEE implementations [32], and the development of semi-supervised and distributed adaptations [33]. Moreover, within the errors-in-variables (EIV) modeling realm, robustness analyses of MEE methodologies have been expounded upon [34], alongside the proposition of novel methodologies such as the minimum total error entropy approach [35].
The computational demands associated with MEE criterion stem from its time complexity, which scales quadratically as . Central to MEE’s computational load is the necessity for a double summation operation during the calculation of the gradient pertaining to the error probability density function (PDF), particularly when employing Parzen windowing [36] and certain types of Kernel functions. Moreover, the selection of an inappropriate Kernel function or its parameters can detrimentally impact the accuracy of the resulting PDF. To solve the problem, efforts have been made to optimize the gradient descent MEE approach, as evidenced by the normalization of the step size in [37], leveraging the power of the input entropy. Additionally, innovative methodologies such as the utilization of a quantization operator, as proposed in [38], have been instrumental in mitigating computational complexity. By mapping the error onto a series of real-valued code words, this approach effectively transforms the double summation operation into a singular form, consequently reducing the algorithm’s computational overhead.
This paper presents a novel approach, the fast minimum error entropy estimation (FMEE) algorithm, tailored specifically for linear regression tasks, leveraging the polynomial expansion technique applied to the error Probability Density Function (PDF). In contrast to the traditional minimum error entropy (MEE) methodology employing Parzen windowing for error PDF derivation, FMEE adopts the Gram–Charlier expansion method to approximate the error PDF, resulting in a notable reduction in time complexity from to . Notably, FMEE obviates the need for Kernel functions or their associated parameters. The proposed algorithm entails several key steps: firstly, the derivation of the PDF approximation for a random variable via the Gram–Charlier expansion, followed by the simplification of the entropy of the random variable facilitated by the orthogonality of the Hermite polynomials. Subsequently, the error of the linear regression model is ascertained, with the error entropy expressed as a function of the regression coefficient vector. Ultimately, the gradient descent technique is employed to deduce the regression coefficient vector corresponding to the minimum error entropy. Experimental validation underscores the efficacy of FMEE, revealing a remarkable reduction in time consumption, with a disparity of less than 1‰ compared to that of the MEE approach for identical problem settings. Importantly, minimal discrepancies are observed between the accuracy levels of FMEE and MEE methodologies.
2. The Related Algorithms
2.1. MEE
MEE minimizes the information contained in the error and maximizes the information captured by the estimated model. Usually, the second-order Renyi entropy [39] is used to measure the entropy contained in the error of the model.
where E is the error random variable of MEE, and is the entropy of E and donates the PDF of E. In this paper, donates the expectation in order to avoid misunderstanding. Then, the PDF of E can be estimated by Parzen windowing:
where n is the number of the observed data, K is the kernel function, and h is the bandwidth. Usually, the Gaussian kernel is chosen, and . Then, the empirical information of error can be calculated as:
As the logarithmic function is monotone increasing, it can be removed without any influence on the minimizing process. Then, the transformed empirical error information can be obtained as Equation (4):
For the linear regression, , the target of the model is to estimate from the limited samples. As , the corresponding empirical error information is calculated as Equation (5):
Then, the MEE estimator can be obtained by minimizing with gradient descent. The time complexity of MEE is due to the double summation operation, as shown in Equation (5). As the time consumption of MEE is quadratic to the number of the observed data, the running time of MEE would increase dramatically with the increase in the amount of the observed data.
2.2. The Hermite Polynomials
The Hermite polynomials [40] are a classical orthogonal polynomial sequence. They are defined by the derivatives of the standardized Gaussian PDF as Equation (6):
where donates the ith-order Hermite polynomial.
The Hermite polynomials forms an orthogonal system, as in Equation (7):
This paper uses the first five Hermite polynomials, shown in Equation (8):
2.3. The Gram–Charlier Expansion
The Gram–Charlier expansion obtains the approximation of the PDF of a random variable, and there is no significant loss of accuracy with this expansion, which is demonstrated in [41]. Under the assumption that the random variable is near the normal distribution with the same mean and variance as itself, the Gram–Charlier expansion of the PDF of x can be expressed as:
where and are the mean and standard deviation of x. is the Gaussian random variable whose mean and variable are the same as those of x. and are the third-order and fourth-order cumulant of x, which can also be called skewness and kurtosis. and are the third-order and fourth-order Hermite polynomials.
3. Methodology
This section derives the relation between the differential entropy and the Gram–Charlier expansion of the PDF of the error for linear regression. Moreover, the assumption that the PDF of the regression error is near the Gaussian distribution that has the same mean and variance as the error is implemented.
This integral is rather difficult to compute. However, notice that if the PDF of x is near the normal density as assumed, it can be inferred that and are very small. Then, the approximation in Equation (12) can be used:
where denotes the infinitesimal.
The details of the simplification process of Equation (14) are illustrated as follows. This part is to derive Equation (14). First, it is needed to show that
and
For Equation (15), suppose that ,
As is an even function and is an odd function, then
and Equation (15) holds.
For Equation (16), suppose that ,
Then, for Equation (13),
Notice that , then the second term of Equation (24) is 0. As it is assumed that x is close to a normal random variable, and are very small. Then, the last term of Equation (24) can be omitted as 0, as it involves third-order monomials, which are infinitely smaller than the terms only containing second-order monomials. Then, for Equation (24), take Equations (15) and (16) into consideration, and notice again that ,
So, Equation (14) holds.
For the linear regression, , the standard deviation of the error is in Equation (26):
where is the mean of y and donates the mean of .
To simplify the calculation of , let become a random variable with 0 mean:
Notice that the transformation in Equation (27) does not change the standard deviation and the entropy of as and when c is a constant number. In the rest of the paper, to keep clarity, is replaced with .
Then, the optimal for the minimum of can be obtained by the iteration scheme in Equation (35) with gradient descent:
where is the step size determined by Armijo condition [43].
To compute for FMEE in every iteration, , , , , , and are needed. From Equations (26) and (29)–(34), the time complexity of , , , , , and is , respectively. Then, the computational complexity of FMEE is . As the time complexity of MEE is due to the double summation operation, FMEE runs faster than MEE does.
4. Experiments
In this section, a comprehensive array of experiments is undertaken, encompassing both numerical simulations and real-world scenarios. The numerical simulations serve to validate the efficacy of the FMEE approach and to scrutinize the time efficiency of both FMEE and MEE methodologies. Concurrently, practical experiments are conducted aimed at forecasting power outages within a city located in northwest China.
Regarding the numerical simulations, we consider a scenario where , with the model defined as , where and follows a normal distribution . Two distinct types of noise are examined in our experiments. Firstly, Gaussian noise is employed, while the second type comprises generalized Gaussian noise characterized by a probability density function . This heavy-tailed distribution, utilized herein, aligns with previous works, such as references [27,35]. Although FMEE is derived under the assumption of near-Gaussian noise, it is anticipated that FMEE remains effective in the presence of non-Gaussian, heavy-tailed noises. Here, denotes a constant adjusted to maintain a variance of 1 for e. For MEE, the step size is set to , and the scale parameter for the Gaussian kernel is 10, mirroring the settings adopted in Reference [27]. Across the experiments, sample sizes range from 100 to 500, with each combination of sample size and noise type repeated 100 times. The ensuing experimental results are detailed below.
Table 1 provides a comparative analysis of the time consumption between MEE and FMEE in the presence of Gaussian noise. FMEE demonstrates a notable acceleration in computational efficiency compared to MEE. Specifically, while the computational time of MEE exhibits quadratic growth relative to the sample size, FMEE’s computational overhead scales linearly with the number of samples. Notably, FMEE achieves remarkable speed, processing 500 objects in approximately 0.1 s, thereby positioning it as a highly promising candidate for time-sensitive applications.

Table 1.
The running time of MEE and FMEE for Gaussian noise.
Table 2 compares the mean squared error between MEE and FMEE in the context of Gaussian noise. Overall, MEE exhibits superior performance compared to FMEE in terms of MSE. Particularly noteworthy is MEE’s substantial advantage over FMEE, especially evident when the sample size is 100. However, as the sample size increases, the discrepancy in MSE between the two algorithms diminishes. By the time the sample size reaches 500, the difference dwindles to a mere . This observation suggests that while FMEE may lag slightly behind MEE, particularly in larger-scale datasets, such disparity remains acceptable in practical applications, given FMEE’s significantly reduced computational time compared to MEE.

Table 2.
The mean squared error of MEE and FMEE for Gaussian noise.
Table 3 analyses the iteration counts required for convergence between MEE and FMEE in the context of Gaussian noise. Notably, FMEE achieves convergence with significantly fewer iterations compared to MEE. Furthermore, it is observed that the iteration count of MEE gradually decreases as the sample size increases. Conversely, the iteration count of FMEE remains relatively constant, irrespective of variations in sample size.

Table 3.
The number of iterations of MEE and FMEE for Gaussian noise.
Table 4 provides a comparative assessment of the time consumption between MEE and FMEE in the context of non-Gaussian noise. Across all five experimental groups, FMEE consistently demonstrates a remarkable reduction in time consumption, consistently amounting to less than 1‰ of MEE’s time expenditure. Moreover, in accordance with theoretical predictions, the computational cost of MEE exhibits quadratic growth relative to the sample size, whereas FMEE’s time overhead scales linearly with the sample size.

Table 4.
The running time of MEE and FMEE for non-Gaussian noise.
Table 5 conducts a comparative evaluation of the mean squared error (MSE) between MEE and FMEE in the context of non-Gaussian noise. Generally, the disparity between the MSE values of FMEE and MEE is relatively minor. Notably, FMEE outperforms MEE when the sample size is 100 or 400, while MEE exhibits superior performance for sample sizes of 200, 300, and 500. Additionally, FMEE attains the optimal MSE across all sample sizes, except for . Furthermore, it is observed that the MSE values for non-Gaussian noise, as depicted in Table 5, span a broader range compared to those for Gaussian noise, indicating greater variability in results for both MEE and FMEE.

Table 5.
The mean squared error of MEE and FMEE for non-Gaussian noise.
Table 6 compares the number of iterations required for convergence between MEE and FMEE in the context of non-Gaussian noise. FMEE consistently demonstrates faster convergence compared to MEE. Furthermore, it is observed that the iteration count of MEE decreases as the sample size increases. In contrast, the iteration count of FMEE remains relatively stable despite variations in sample size.

Table 6.
The number of iterations of MEE and FMEE for non-Gaussian noise.
Based on the findings presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, it is evident that FMEE consistently yields comparable outcomes to MEE, albeit with significantly reduced time consumption and iteration counts. Notably, FMEE stands out for its remarkable efficiency, being approximately 1000 times faster than MEE and achieving convergence within approximately 0.1 s for 500 instances. Given its linear time complexity of , FMEE holds considerable promise for deployment in real-time scenarios characterized by non-Gaussian noise.
Subsequently, we embark on practical experimentation utilizing transformer characteristic data to forecast distribution network failures. The transformers are categorized into two groups based on their geographical location within distinct levels of urban activity within a specific city in northwest China. Initially, our attention is directed towards a subset of 1265 transformers situated within a smaller, less densely populated area of the aforementioned city. We undertake a random partitioning of this dataset into two segments: a training set comprising of the data, totaling 1012 instances, and a verification set encompassing the remaining , comprising 253 instances. To be more specific, the transformer dataset comprises various characteristic variables, involving the standardized heavy overload duration, maximum active load ratio, average active load ratio, mean three-phase unbalance, standardized heavy three-phase unbalance duration and so forth.
We conduct a comparative analysis, pitting our proposed FMEE against three established baseline methodologies: logistic regression, neural network, and support vector machine. The dataset comprises 1265 transformer characteristic variables associated with substantial load levels, undergoing 30 rounds of random partitioning. Subsequently, each randomly divided dataset is subjected to four distinct algorithms. The predictive efficacy of these algorithms on the verification set is assessed based on F-measure and error rate metrics.
Figure 1 depicts the F-measure evaluations stemming from 30 prediction instances conducted by four distinct algorithms. Notably, each evaluation involves consistent partitioning of the dataset across the four algorithms. A discernible trend emerges wherein all algorithms yield F-measure values surpassing 0.8. Notably, our proposed FMEE exhibits the most promising performance, boasting an average F-measure of 0.904, thereby outshining the other three baseline methodologies by a significant margin.
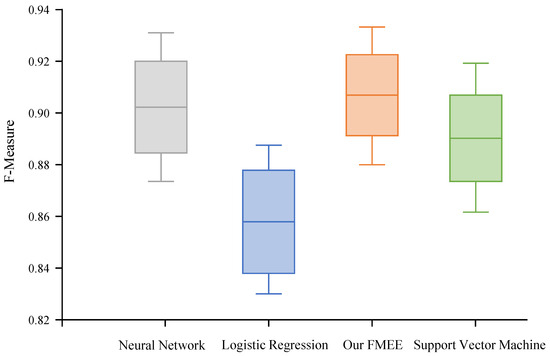
Figure 1.
The boxplot of F-measure among four algorithms for failure outage prediction results.
To facilitate a comprehensive comparison among the four algorithms, Figure 2 depicts the error rate and F-measure of fault outage prediction results in the form of line and box charts. Notably, FMEE emerges as a frontrunner, showcasing a substantial advantage over the sophisticated support vector machine in terms of error rate. Specifically, our FMEE achieves an average error rate of , surpassing the neural network, logistic regression, and support vector machine by margins of , , and , respectively. These findings underscore the clear superiority of our proposed FMEE methodology.
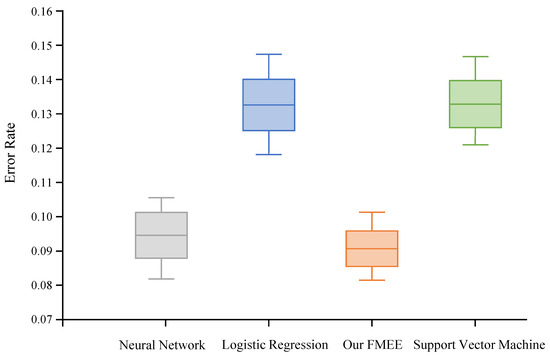
Figure 2.
The boxplot of error rate among four algorithms for failure outage prediction results.
Furthermore, we extend our experimentation to a more densely populated urban region within the northwest Chinese city. Figure 3 illustrates the F-measure evaluations derived from 30 independent tests conducted across the four comparative algorithms. On a comprehensive scale, our proposed FMEE attains an F-measure of 0.891, surpassing baseline methodologies such as neural networks, logistic regression, and support vector machines by margins of 0.013, 0.023, and 0.028, respectively.
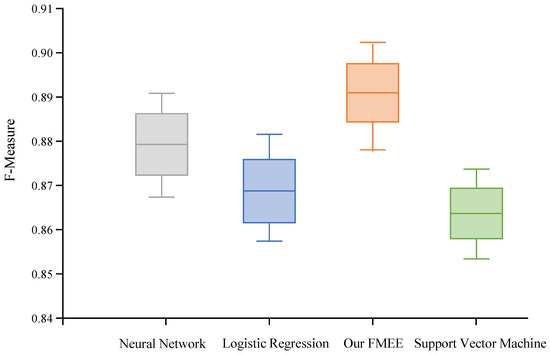
Figure 3.
The boxplot of F-measure of four algorithms for failure outage prediction results.
Finally, we report the error rate of F-measure concerning fault outage prediction results derived from four comparative algorithms, represented through line and box charts. As shown in Figure 4, our proposed FMEE achieves an average error rate of , showcasing a notable superiority over three baseline methodologies. These findings robustly underscore the efficacy of our algorithm in addressing regression problems.
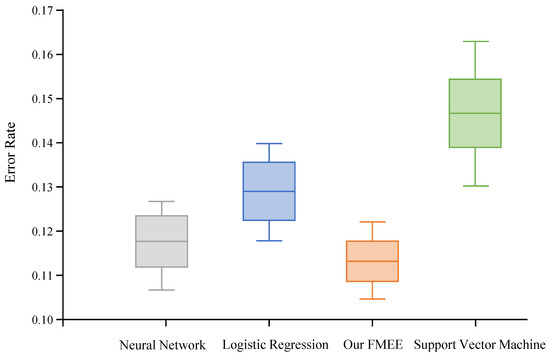
Figure 4.
The boxplot of error rate of four algorithms for failure outage prediction results.
5. Conclusions
This study introduces a rapid minimum error entropy algorithm tailored for linear regression. Several notable conclusions emerge from our investigation. Firstly, the proposed FMEE exhibits significantly faster convergence, requiring fewer iterations compared to MEE. Secondly, while FMEE does not surpass traditional MEE in performance for Gaussian noise and yields comparable results for non-Gaussian noise as measured by mean squared error, its computational efficiency is strikingly superior, consuming less than 1‰ of the time required by MEE. Thirdly, despite being derived under the assumption of noise proximity to Gaussian distribution, FMEE demonstrates efficacy in handling non-Gaussian, heavy-tailed noise distributions. Fourthly, owing to its exceptional time efficiency, FMEE holds promise for real-time applications in scenarios featuring non-Gaussian noise. Moving forward, further analysis of FMEE’s convergence conditions and exploration of noise approximation methods for arbitrary distributions represent avenues for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.L. and X.L.; methodology, Q.L.; software, W.C.; validation, Q.L., X.L. and W.C.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, X.L.; resources, Q.L.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.G.; writing—review and editing, H.C.; visualization, Q.G.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, W.C.; funding acquisition, Q.L. and H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the State Grid Information and Telecommunication Group scientific and technological innovation projects “Research on Power Digital Space Technology System and Key Technologies” (Grant no: SGIT0000XMJS2310456).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the special significance of the electrical power system used in the experimental process, which involve privacy in some research fields, it is not convenient to fully disclose their data.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors (Qiang Li, Xiao Liao, Wei Cui, and Ying Wang) were employed by the State Grid Information & Telecommunication Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Baggenstoss, P.M. Maximum Entropy PDF Design Using Feature Density Constraints: Applications in Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 11, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, X.; Yuan, D.; Yu, C.; San, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ye, J. Cu-based high-entropy two-dimensional oxide as stable and active photothermal catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisikalo, O.; Kharchenko, V.; Kovtun, V.; Krak, I.; Pavlov, S. Parameterization of the stochastic model for evaluating variable small data in the Shannon entropy basis. Entropy 2023, 25, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Su, L.; Lin, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. State Parameter Fusion Estimation for Intelligent Vehicles Based on IMM-MCCKF. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, F.P.; Chen, T.; Ljung, L. Maximum entropy kernels for system identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 62, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, M.; Zhou, Z. From Single Metals to High-Entropy Alloys: How Machine Learning Accelerates the Development of Metal Electrocatalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 1, 2401887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.T.; Ge, S.S.; Lee, T.H. Persistent Dwell-Time Switched Nonlinear Systems: Variation Paradigm and Gauge Design. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Chesi, G. Stabilization and Entropy Reduction via SDP-Based Design of Fixed-Order Output Feedback Controllers and Tuning Parameters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, H.X. Spatiotemporal entropy for abnormality detection and localization of Li-ion battery packs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 12851–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Yao, L.; Cai, Y.; Lin, T.; Zhang, J.; Dong, H. Intelligent fault detection scheme for constant-speed wind turbines based on improved multiscale fuzzy entropy and adaptive chaotic Aquila optimization-based support vector machine. ISA Trans. 2023, 138, 582–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshpazhouh, A.; Sami, A. Entropy-based outlier detection using semi-supervised approach with few positive examples. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2014, 49, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B.; Dong, H. Decentralized dynamic state estimation for multi-machine power systems with non-Gaussian noises: Outlier detection and localization. Automatica 2023, 153, 111010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, G.; Peng, B.; He, J.; Zhang, K. Novel robust minimum error entropy wasserstein distribution kalman filter under model uncertainty and non-gaussian noise. Signal Process. 2023, 203, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Davies, M.E.; Proudler, I.K.; Hopgood, J.R. Adaptive kernel Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lin, H.; Hu, B.; Tan, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.Z. Beyond homophily and homogeneity assumption: Relation-based frequency adaptive graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 8497–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, H. Minimum entropy filtering for multivariate stochastic systems with non-Gaussian noises. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Li, L. Minimum error entropy based sparse representation for robust subspace clustering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep face recognition: A survey. Neurocomputing 2021, 429, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Cheng, C.; Peng, Z.; Dong, X.; Qu, Y.; Meng, G. Nonlinear dynamical system identification using the sparse regression and separable least squares methods. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 505, 116141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Peng, S.; Ma, W.; Chen, B.; Principe, J.C. Minimum error entropy algorithms with sparsity penalty constraints. Entropy 2015, 17, 3419–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tran, T.D. Sparse signal recovery via generalized entropy functions minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Wang, H. Minimum entropy control of closed-loop tracking errors for dynamic stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2003, 48, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Minimum entropy control of non-Gaussian dynamic stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2002, 47, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Bhatia, V. Minimum error entropy criterion based channel estimation for massive-MIMO in VLC. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogmus, D.; Principe, J.C. Convergence properties and data efficiency of the minimum error entropy criterion in adaline training. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Kernel minimum error entropy algorithm. Neurocomputing 2013, 121, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, D.X. Convergence of gradient descent for minimum error entropy principle in linear regression. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 6571–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Principe, J.C. Convergence of a fixed-point minimum error entropy algorithm. Entropy 2015, 17, 5549–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M. On optimal estimations with minimum error entropy criterion. J. Frankl. Inst. 2010, 347, 545–558. [Google Scholar]
- Heravi, A.R.; Hodtani, G.A. A new information theoretic relation between minimum error entropy and maximum correntropy. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 921–925. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Tan, J.; Chen, B. Robust spike-based continual meta-learning improved by restricted minimum error entropy criterion. Entropy 2022, 24, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Ma, W.; Ren, P. Robust power system state estimation with minimum error entropy unscented Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8797–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, T. Semi-Supervised Minimum Error Entropy Principle with Distributed Method. Entropy 2018, 20, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Xu, B.; Zhao, H.; Principe, J.C. Insights into the robustness of minimum error entropy estimation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 29, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Li, C. Minimum total error entropy method for parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 4079–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, P.; Kreiss, S.; Alahi, A. Human trajectory forecasting in crowds: A deep learning perspective. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 7386–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kwon, K. Normalized Minimum Error Entropy Algorithm with Recursive Power Estimation. Entropy 2016, 18, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ma, R.; Yu, S.; Du, S.; Qin, J. Granger causality analysis based on quantized minimum error entropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, M.; Santos, L.F.; Cory, D.G. Experimental detection of the correlation Rényi entropy in the central spin model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 080401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; San Kim, D.; Jang, L.C.; Lee, H.; Kim, H. Representations of degenerate Hermite polynomials. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 2022, 139, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, J.E. The valid regions of Gram–Charlier densities with high-order cumulants. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 407, 113945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, R.; Brandão, H.; Nobre, I.; Da Silva, S. Differential entropy estimation with a Paretian kernel: Tail heaviness and smoothing. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2024, 1, 129850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, C.; Galarce, C.; Rubio, F.; Pineda, F.; Anguita, J.; Barros, R.; Parragué, M.; Daille, L.K.; Aguirre, J.; Armijo, F.; et al. Testing the test: A comparative study of marine microbial corrosion under laboratory and field conditions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13496–13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).