Abstract
In this work we present a bimodal multitask network for audiovisual biometric recognition. The proposed network performs the fusion of features extracted from face and speech data through a weighted sum to jointly optimize the contribution of each modality, aiming for the identification of a client. The extracted speech features are simultaneously used in a speech recognition task with random digit sequences. Text prompted verification is performed by fusing the scores obtained from the matching of bimodal embeddings with the Word Error Rate (WER) metric calculated from the accuracy of the transcriptions. The score fusion outputs a value that can be compared with a threshold to accept or reject the identity of a client. Training and evaluation was carried out by using our proprietary database BIOMEX-DB and VidTIMIT audiovisual database. Our network achieved an accuracy of 100% and an Equal Error Rate (EER) of 0.44% for identification and verification, respectively, in the best case. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first system that combines the mutually related tasks previously described for biometric recognition.
1. Introduction
Biometric recognition is a technology that uses data from the unique physical or behavioral traits of a person to authenticate his/her identity. One of the most important advantages over traditional authentication methods such as passwords, ID cards, personal identification numbers (PIN), etc., is that biometric traits cannot get lost, forgotten, and they cannot be easily stolen, since they are inherent to a person’s body or behaviour [1,2]. The most common identity authentication tasks are verification and identification. Verification refers to a one-to-one comparison of a user claiming his/her identity with a template belonging to an enrolled client stored in the system. In that case there is a binary output, i.e., the system either accepts or rejects the identity claim. Identification is a one-to-many comparison of a client with all templates in the system [3].
In a biometric system, a classifier uses information from traits such as fingerprints, iris, facial features or speech patterns, among many others. Theses traits must have certain properties such as universality, distinctiveness, acceptability, easiness to acquire data, etc. Systems that focus on just one trait are called unimodal and have been the subject of wide research achieving remarkable results. However, despite the high performance achieved by these systems they present drawbacks that make them prone to committing mistakes, for example, decrease performance when working with noisy data, lack of universality, and spoof attacks, among others. To overcome the limitations of unimodal systems, multimodal biometrics have become a subject of extensive research. Multimodal systems are based on multiple biometric traits or multiple representations of the same trait obtained with different sensors. These systems take advantage of the multiple sources of data to create a more robust representation of the identity of an individual. For instance, if a trait fails to contribute with significant information to the final decision due to noisy samples or lack thereof, the other traits can still contribute with enough data to output a correct decision [4,5].
In order to create a multimodal system it is necessary to combine/fuse different sources of information. There are various levels of fusion depending on the stage of the biometric pipeline where the fusion process takes place. The two stages are: pre-classification and post-classification [6]. The pre-classification stage refers to data processing before matching a template stored in the system with data from a user. Information fusion can be done at sensor or feature level in that case. Post-classification combines information after the matching process; fusion levels in this stage include decision, rank, and score levels [7].
Another useful approach in multimodal biometric systems is based on Multi-task learning (MTL) models. MTL refers to the process of learning multiple related tasks while exploiting similar characteristics across them [8]. It is usually straightforward to develop multiple classifiers to perform a specific set of tasks, though this requires more computing resources and introduces the possibility of processing the same data multiple times [9]. MTL aims to increase the performance of a model’s tasks by jointly learning them, i.e., one task is regularized/improved by the others by enhancing the overall generalization of the model [10,11]. In our work we take advantage of the fact that identification and speech recognition share the speech features. Therefore, the model’s parameters related to the speech input are optimized to improve the performance in both tasks.
In this paper we make the following contributions: a bimodal biometric system comprised of a multitask network is developed to perform identification and provide the necessary information to perform text prompted verification. In order to achieve these objectives we trained the network to jointly learn identification and speech recognition tasks. Both tasks process the extracted speech features. This circumstance is used to improve the overall performance of the network via mutual regularization.
The network architecture dedicated to the identification task optimally fuses face and voice features, resulting in a bimodal embedding that stores the discriminant characteristics of a client. This embedding is fed into a softmax classifier to establish the identity of the enrolled client that most likely generated the embedding. A set of bimodal embeddings is stored to serve as representative templates of each enrolled client. The portion of the architecture dedicated to the speech recognition task aims to accurately transcribe random digit sequences uttered by a client. These sequences are intended to eliminate the need to memorize passwords and are generated by a python function each time a client makes an identity claim.
Text prompted verification is performed with an external binary classifier that combines the cosine similarity between two bimodal embeddings and the WER value of a transcribed digit sequence.
We combined two similar databases to create a virtual one that contains data with the required characteristics to train and test our model. Our experiments indicate that it is feasible to combine information from two databases to train and evaluate a multimodal model. The results of our work are compared with other approaches using a common testing criteria to ensure a fair comparison.
The rest of this work is organized as follows: a literature overview is presented in Section 2. Section 3 presents details of the development and evaluation of the models that comprise our bimodal multitask network. Section 4 discusses the experimental results of the developed models. Section 5 presents the conclusions.
2. Literature Overview
Face recognition approaches have relied on the use of a wide variety of feature extraction algorithms such as: Local Binary Pattern (LBP), Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG), Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Gabor filters, and frequency domain analysis, among many others. These features are used to train Machine Learning models or are matched with functions that measure their similarity or geometric distance to achieve high performance [1,12,13]. State of the art approaches have focused on extracting image features using Deep Learning Networks to improve recognition performance due to the parameter optimization at training time. Various architectures trained for image classification have been adapted to perform face recognition and have obtained outstanding performances. In Ref. [14] the authors train a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) with 5 layers for face recognition and make a comparison of performance and training time using the pre-trained architectures AlexNet with 8 layers and GoogleNet with 22 layers. Their results yield an accuracy of 100% for all networks with the face94 database, though pre-trained models achieved these results with less training iterations than their proposed DCNN. They tested their networks with noisy samples and studied how the accuracy decreased according to a parameter that controlled the noise level. Pratama et al. [15] conducted a study on the impact of different hyperparameter values on the accuracy of various Residual Networks trained and tested with a dataset that contains faces in different positions and orientations. A certain set of hyperparameters allow a particular network to achieve a 99% accuracy. Another popular network is FaceNet; in Ref. [16] a pre-trained model was fine-tuned with CASIA-Webface database and tested with other databases. In most of their cases an accuracy higher than 99% was achieved. In Ref. [17] a pre-trained DenseNet architecture is trained with the Wider Face dataset, obtaining results above 90% in most cases. Additional reports on face recognition approaches with pre-trained architectures can be found in Refs. [13,18]. In Ref. [19] LBP and CNN extracted features are fused using an adaptive weighting function. Pei et al. [20] proposed a set of image transformations to increase the amount of face images to train a CNN to recognize class attending students in a picture.
Speaker recognition (voice or speech biometric modality) has been performed with popular approaches such as Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) or Hidden Markov Models (HMM) whose parameters have been tuned with features based on Mel Frequency Cepstral Coeffients (MFCC). These approaches are combined with Universal Background Models (UBM) in order to calculate the log likelihood ratio to perform a hypothesis test [21]. A breakthrough in speaker verification came with the development of the i-vectors approach presented in Ref. [22]. The i-vector framework has also been combined with other models to improve verification results, most commonly using HMM and GMM [21,23].
Early work on Deep Learning based speaker recognition proposed the use of bottleneck features extracted from the middle layer of a Deep Neural Network (DNN) [23]. Novoselov et al. [24] created a CNN to extract deep embeddings to perform a text prompted verification task on Part 3 of the RSR2015 database using a 5 digit password. Their results show EER values lower than 10%. In recent years, X-vectors have become a widely used embedding due to the outstanding performance achieved [25]. In this framework, a DNN is trained to map variable length utterances to fixed length embeddings using a training scheme based on bank filtered features. X-vectors embeddings achieved EER values as low as 5.71 when they were evaluated on Speakers in the Wild (SITW) dataset and the Cantonese portion of NIST SRE 2016. Recent approaches such as Jung et al. [26] and Muckenhirn et al. [27] focus on processing raw speech data with convolutional layers to extract discriminant features for speaker recognition. A novel architecture called SincNet was proposed in Ref. [28]; this architecture is based on the convolutional layer of the same name. This layer convolves bandpass filters represented in time domain as sinc functions with raw audio frames. The obtained results exhibited EER values of 0.85 and 0.96 using the TIMIT and LibriSpeech databases, respectively. Tripathi et al. [29] concatenated features extracted from a SincNet layer with embeddings generated by a pre-trained X-vectors system. These new features are fed to a set of fully connected layers, achieving an EER of 3.56 in the VoxCeleb1 database. An interesting study on the effect that different softmax based loss functions can have on the performance of a SincNet model can be found in Ref. [30]. The authors present a detailed comparison on TIMIT and LibriSpeech datasets. Li et al. [9], trained a CNN, a Deep Neural Network (DNN) and two Time-delay Deep Neural Networks (TDNN) with a multitask setting for speaker verification and anti-spoofing. The first three models were trained with Crossentropy loss function and one TDNN with a modified Triplet loss function employing different cepstral speech features. Their results compared the performance of all models on both tasks employing the ASVspoof 2017 and ASVspoof 2019 databases. The models trained with Crossentropy yielded EER values below 7.5% for speaker verification, less than 14% for anti-spoofing, and a joint verification of less than 12.7%, while the TDNN with Triplet loss yielded values below 6%, 12.3%, and 10.6% respectively. A detailed overview of Deep Learning on speaker recognition is found in Ref. [31].
Mandalapu et al. [32] present a comprehensive survey on audiovisual biometric recognition and attack detection. Refs. [6,7,33] are comprehensive reviews on recently published multimodal biometric systems. Table 1 summarizes the relevant work in chronological order about multimodal biometric systems whose content was considered important to our research.

Table 1.
Overview table of relevant work related to our proposal in chronological order.
3. Structure of the Proposed Biomodal Multitask Network
The structure of our proposed system is shown in Figure 1. Details of the architecture are presented in Table 2. In the following subsections we will explain in detail each stage associated with the development of our network.
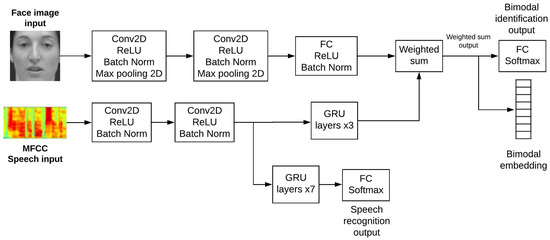
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the proposed multitask network.

Table 2.
Multitask network architecture.
3.1. Feature Extraction
One of the objectives of our proposal is fusing the face and speech data at the feature level in order to implement the bimodal part of our biometric system. The state of the art work proposes to create a module within the network architecture that optimally combines the extracted features of all biometric traits [19,44,48]. This fusion module delivers a unique feature vector that contains the most important information of the identity of an individual.
Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the proposed multitask network. The diagram indicates two streams of layers that process face and speech data independently. The speech stream is divided into two paths, represented by the GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) layers. The first path processes the feature maps that will be combined with the face features in the weighted sum module. The second path extracts the temporal information used to perform the speech recognition task.
The input of the image stream consists of face grayscale images with dimensions of 128 × 128 pixels. We employed 2 convolutional blocks comprised of 32 and 64 filters, respectively, with the ReLU activation function, a 2D max pooling operation to reduce the feature map’s dimensions and to extract important information based on a pixel’s location, and batch normalization as a feature regularizer. The extracted feature maps are fed to a fully connected layer with ReLU activation and batch normalization; this layer outputs a vector of length 512.
The input of the speech stream consists of MFCC features, which are widely used in speaker and speech recognition works [32]. These features are represented as two dimensional signals with the cepstral coefficients containing the frequency information in Mel scale located in one dimension, and the time domain in the other. No pooling layers were included to avoid a loss of temporal information.
The extracted speech feature maps are processed by two different paths of GRU layers. The first path with 3 layers extracts temporal dependencies from the feature maps and allows the network to handle maps with different temporal sizes. The last GRU layer outputs a unique feature vector of size 512 and discards the previous vectors in the sequence. The second path of 7 GRU layers extracts temporal information with more detail than the first path. The last layer outputs the complete sequence of processed vectors, which are fed to the speech recognition output.
3.2. Bimodal Data Fusion
The feature fusion module was implemented using a weighted sum controlled by a training parameter . This parameter is updated during the training stage and its value determines which modality is more representative to the identity of a user. Equation (1) shows the weighted sum used in the bimodal embedding.
where and are the speech and face vectors, respectively, and is the resulting bimodal embedding. The initial value for was 0.5.
3.3. Outputs
The output of the weighted sum module is a 512-dimensional bimodal embedding that represents the biometric identity of a client. To perform the identification task, this embedding is fed to the biometric recognition output, which is represented by a fully connected layer using a configuration commonly known as a softmax classifier. This layer includes 45 neurons that represent the number of enrolled users in the system. The output is a normalized probability distribution.
As mentioned in Section 3.1 the set of seven consecutive GRU layers outputs a sequence of vectors that contain information about the temporal dependencies of the speech features. This sequence of vectors is fed to a fully connected layer with a softmax activation that corresponds to the speech recognition output. This layer has 27 neurons that represent the characters of the alphabet including a space character. The output is a sequence of probability distributions that indicate the most probable character at each time step. However, these distributions are not enough to fully transcribe the speech features into text. The decoding process will be explained in the following subsections.
3.4. Training and Testing Data
One of the main problems that arise when building a multimodal biometric system is the lack of a database that contains enough data on multiple traits/modalities to train and test robust models. Publicly available multimodal databases may contain insufficient data for a particular trait, while private databases may not be accessible. To overcome these issues many authors resort to building their own multimodal databases that meet the requirements of their work. A large number of studies on multimodal biometric recognition are performed using virtual databases, i.e., databases created by combining datasets of specific traits and pairing their respective subjects [10,39]. Hence, we created a virtual database by combining BIOMEX-DB and VidTimit databases.
BIOMEX-DB is a multimodal database created by our research group, composed of speech, video, and electroencephalogram (EEG) biometric data. Speech data was recorded at a 16 KHz sample rate. The vocabulary is comprised of pronunciations in Spanish language of 20 random digit sequences. The first 10 sequences have a length of 10 digits, while the remaining sequences are 5 digits long. A video feed was recorded showing the faces as the volunteers pronounced their digit sequences. During the pronunciations, EEG signals were simultaneously acquired with a 14 channels Emotiv wireless headset. This database contains the biometric data of 51 subjects; 39 of them have information of the 3 modalities while the remaining 12 subjects lack video data. A complete description of the database can be found in Ref. [49]. VidTimit [50] is a database comprised of video and audio recordings of 43 subjects reciting 10 sentences from the TIMIT database. Volunteers have 10 audio recordings and several image frames extracted from their videos. The speech dataset of BIOMEX-DB has a maximum of 51 subjects, thus we used that amount as the population of our experiments. In order to complete our virtual database we pooled the image datasets from BIOMEX-DB and VidTimit. Then we randomly selected 51 subjects from the pooled set and paired them with the ones of the speech dataset. Our virtual database had a balanced gender representation: 26 males and 25 females. In the following subsections we describe the preprocessing of speech and face data.
3.4.1. Speech Data Preprocessing
The BIOMEX-DB speech dataset is organized with time labels that allow segmentation of each digit utterance. In that way it is possible to create new random sequences with a variable number of digits or to rearrange the order within the existing sequences. A common strategy to increase the amount of speech data is to add different types of noise [51]. We added background noise taken from the MUSAN database [52] to our speech samples at several signal to noise ratio (SNR) values. The decibel values used in our experiments were 0, 5, 10 and 15 dB. Then, the speech data was normalized in amplitude within the range [−1, 1]. As mentioned in Section 3.1, the speech input of our network consists of MFCC features organized as two dimensional signals. These features attempt to model the human vocal tract using a frequency logarithmic scale. MFCC are calculated by applying a Mel scaled filterbank to the periodogram of the power spectrum of the speech signal. Then, the discrete cosine transform (DCT) is calculated with the filterbank energies to decorrelate the features. In many speech applications only 13 features are kept, although more features can be kept according to the obtained results. Additionally, the first and second derivatives can be calculated to increase the performance of the system. A detailed description on the calculation of MFCC can be found in Ref. [53]. In this work, MFCC were calculated by segmenting the signal into 25 ms frames with an overlap of 15 ms between them. We observed that 26 features yielded the best results during the evaluation stage. The first and second derivatives were added. The total size of the speech features is 78.
3.4.2. Face Data Preprocessing
Raw images obtained from BIOMEX-DB and VidTimit databases were pre-processed to extract the region of interest (ROI) with the corresponding face in grayscale and sized 128 × 128 pixels. This process was carried out using the scikit-image face detector based on Local Binary Pattern [54]. Data augmentation was incorporated to the image set obtained from the previous procedure. Wang et al. [20,55] describe different types of image transformations for data augmentation to train deep learning models for face recognition. However, some transformations require complex algorithms that rely on deep and machine learning models to perform them. Therefore, we decided to carry out geometric and photometric transformations that could be done with software libraries. In this work we included the following transformations: image rotation, horizontal flipping, brightness changes, and combining the aforementioned transformations. They were implemented using the IMGAUG library [56].
3.5. Network Training
The total population we considered for our experiments comprised 51 individuals, which were divided into 2 sets: 45 target clients and 6 impostors. Consequently, the biometric output layer of the network is composed of 45 fully connected neurons, as described in Table 2. After we applied the data augmentation to the voice and image datasets, we split the target clients’ data as follows: 65% for training, 5% for validation, and 30% for testing. Each target client had 100 voice samples and 150 face images. The impostors’ data was used exclusively to test the text-prompted verification task with each impostor made up of 100 voice samples and 150 face images.
Keras libraries with Tensorflow backend was used to train and test the network. We used the Adam optimizer with a 0.0001 learning rate and a training process with 1000 epochs. Data batches were created by randomly pairing MFCC features extracted from sequences of spoken digits with face images at each epoch, using a Python generator to ensure large variability. Training and validation batches were composed of 16 and 8 pairs, respectively. We configured a Keras callback that saved the parameter values only if they decreased the validation loss value in each epoch.
Joint Loss Function
Since our network is designed to perform two different tasks simultaneously, we defined a joint loss function that allows the network to learn each task. This function was defined as the sum of the Sparse Categorical Crossentropy (SCC) and Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss functions. SCC is a commonly used loss function in supervised multi-class classification [30]; it helps to reduce the error of the identification task during the training stage. CTC loss function was proposed to solve temporal classification problems, it allows to reduce the error when labelling sequences where the alignment between the input sequences and the target labels is unknown [57]. CTC aimed to reduce the error of the speech recognition task. The joint loss function has two parameters that scale the values of SCC and CTC. This scaling results in mutual regularization and may accelerate the convergence of the network [10]. The joint loss function is shown in Equations (2) and (3).
The first term corresponds to SCC function where represents the true label assigned to target client i, C is the total number of target clients in our population, and is the normalized probability distribution predicted with the softmax classifier of the biometric output given the bimodal input data belonging to target client i.
In CTC loss, represents all possible character sequences given an input of MFCC features , B is the search space of our speech recognition task, and y is the target sequence. Equation (4) describes the conditional probability that a character is predicted in the label sequence y at time t given the MFCC features , across all time steps.
The probability lt is calculated for each time step with the softmax function of the speech recognition output. The CTC loss function maps MFCC speech features to character sequences following the procedure proposed in Ref. [58]. In order to produce a refined transcription from the CTC characters sequence we employed the greedy decoder implemented in Keras. A linguistic model to decode the character sequences was not required since the vocabulary of BIOMEX-DB comprises random digit pronunciations [59].
Tao et al. [11] proposed an audiovisual approach for speech recognition and speech detection tasks. Their joint loss function was the sum of Crossentropy and CTC functions and experimented with different coefficient values to scale them. According to their results, their proposed network converged faster when both tasks had the same weight value. Following this work we experimented with different values for and . During the experiments we observed that if had a value greater than , then the network yielded better recognition results in comparison to those cases where both coefficients had the same value, or had a value greater than . The chosen values for and were 0.3 and 0.7, respectively.
4. Experimental Evaluation
Once the training stage was completed, we established the experimental conditions to evaluate the identification and text prompted verification tasks. We developed five different multitask networks with the architecture and training conditions described in previous sections. For each iteration the subjects that integrated the target clients and impostors sets were randomly chosen. After evaluating the identification and text prompted tasks of each network, we calculated the average and standard deviations of the corresponding metrics. The identification and text prompted verification results are organized according to the SNR value or image transformation associated to a speech signal and face image, respectively.
4.1. Identification Evaluation
Performance in the identification mode of our proposed network is evaluated according to the accuracy metric shown in Equation (5).
where TP are the true positive cases correctly classified, i.e., the number of instances where the prediction and the correct label are equal, and N is the number of total instances [60]. Our identification task is done in closed-set modality so only true positive cases are counted to calculate the accuracy.
4.2. Speech Recognition Evaluation
The performance metric used to measure the accuracy of the transcriptions is the Word Error Rate (WER) defined in Equation (6).
where S stands for substitution, i.e., a word is replaced by another, I are the insertions of words, i.e., a word that was not pronounced was added to the transcription, D is a deletion, i.e., a word was left out of the transcription, and N is the number of words in the reference label. After evaluating the speech recognition task, we observed that transcriptions with a WER of less than 10% (0.1) had a few misspellings and the text was still understandable. Based on this observation we decided that a WER value less than 0.1 may be considered as a correct pronunciation, otherwise it is incorrect. The results of this task are presented in Section 5.
4.3. Text Prompted Verification
Text prompted verification was done with an external binary classifier following the next procedure: a client provides samples of speech and face data; with these samples the network produces a bimodal embedding and a transcription of the speech data; the bimodal embedding is matched with a previously stored template to generate a verification score; the WER value is calculated from the transcription; and, finally, the verification score and WER are fed to the binary classifier, which decides whether to accept or reject the identity claim. This framework reinforces the security because the identity verification is based on the characteristics of two biometric traits and whether a client correctly uttered a digit sequence that acts as a randomly generated password or not. This way the system makes it difficult for an impostor to use prerecorded audio to falsely authenticate his/her identity [32].
4.3.1. Bimodal Embeddings Matching
We followed the d-vector verification framework to carry out the embeddings matching [31]. This approach requires that each target client has a representative template that can be matched with an embedding that was generated during an identity claim. Matching a template with an embedding allows us to establish how similar they are and whether the client that made the identity claim is the same person as the target client who owns the template or not. In order to generate the template of a target client we picked 25 pairs of speech and face data; these pairs represented the combinations of 5 SNR values and the 5 image transformations. The pairs were fed to the multitask network and the resulting bimodal embeddings were averaged to obtain the template.
The verification score is obtained using the cosine similarity defined in Equation (7) as the matching function:
where T is a template belonging to a target client and E is the embedding produced by a client during an identity claim.
4.3.2. Binary Classifier
The cosine similarity scores and the WER values are combined using a perceptron that will work as the binary classifier. Since we are combining two sources of information it is possible to distinguish four cases: a target client that correctly uttered a digit sequence, a target client that incorrectly uttered a digit sequence, an impostor that correctly uttered a digit sequence, and an impostor that incorrectly uttered a digit sequence. However, verification is a binary classification problem and it is necessary to reduce the previous cases to two classes. That condition is achieved by assigning the case of a target client pronouncing a correct utterance in the accepted class and the remaining cases in the rejected one.
A new dataset to train and test the binary classifier composed of cosine similarity scores and WER values was generated. Both scores were calculated using the test data split of each target client and all samples of the impostors set. The calculation of WER values corresponding to incorrect utterances was done by introducing substitutions, insertions, and deletions to the spoken sequences. In this manner we simulate the realistic situation in which a client makes a mistake when uttering the prompted digit sequence. The similarity scores and WER values were randomly paired until we obtained 2550 samples; half of them belonged to the accepted class and the other half to the rejected one. Each class was divided into three sets according to the following percentages: 65% for training, 5% for validation, and 30% for testing. Training was carried out in 20 epochs using Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) with a learning rate of 0.001 and binary crossentropy as a loss function. A sigmoid activation function in the perceptron allowed the system to provide an output score in the range [0, 1].
4.3.3. Verification Evaluation
A common performance measure for verification is the Equal Error Rate (EER), which is defined as the case when the false acceptance rate (FAR) and the false rejection rate (FRR) are of equal value [61]. FAR is the likelihood that the biometric system will incorrectly accept an identity claimed by an unauthorized client; FRR is the likelihood that the system will incorrectly reject an identity claimed by an authorized client. The lower the EER value, the higher the accuracy of the biometric system.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Identification Results
Table 3 presents the results of the identification evaluation. The results show an average accuracy above 90% for almost all cases except for those involving a combination of image transformations. It can be seen that noisy speech samples do not have a great impact on the accuracy since the accuracy does not change significantly at different decibel values. It is also noted that the image transformations had a significant impact on the identification performance because of the difference of accuracy values between them.

Table 3.
Bimodal multitask network identification results in terms of accuracy (%).
5.2. Speech Recognition Results
The obtained results corresponding to speech recognition performance are presented in Table 4. It can be seen that the average WER values did not exceed 5% even in noisy conditions and the standard deviation values were below 1%. This suggests that speech recognition performance is not significantly affected by noise.

Table 4.
Speech recognition results in terms of WER (%).
5.3. Text Prompted Verification Results
The text prompted verification results are shown in Table 5. Average EER values were below 4%. It can be noticed that the noise level in speech signals does not considerably affect the system performance, however similarly to the identification evaluation, image transformations involving rotation and combinations yielded the worst results.

Table 5.
Text prompted verification results in terms of EER (%).
5.4. Comparison of Results with Other Approaches
We compared the best results obtained by our proposed network in identification and verification modes with other systems using well known face and speaker recognition approaches. The considered unimodal systems were implemented, trained, and evaluated with our virtual database following similar conditions for a fair comparison. The results are presented as the average and standard deviation of the performance indicators obtained from a collection of five experiments in each case.
The face recognition systems considered in the comparison were: a reduced ResNet model with 4 residual blocks [62], which we called Face ResNet, Eigenfaces, and Fisherfaces. The last two approaches are based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), respectively; they are used for feature extraction and dimension reduction. These methods were implemented using the OpenCV library with the parameter values presented in Ref. [63]. The implemented speaker recognition systems were: a SincNet architecture described in Ref. [28] and x-vectors [25].
5.4.1. Identification
The face recognition identification results are presented in Table 6. In the first three conditions our network yielded better results than the other approaches, although there is a slight difference of accuracy values between the models in some cases. The last two conditions showed a performance gap between the deep learning models and th statistical approaches; the multitask network and Face ResNet gave competitive results close or above 90% while Eigenfaces and Fisherfaces presented a considerable performance drop. This indicates that statistical models have difficulties recognizing faces that present variations during the acquisition process. The standard deviation values obtained from Fisherfaces are considerably greater than those obtained from deep learning approaches and Eigenfaces. Regarding speaker identification, the best results of our approach obtained a 100% accuracy in most cases with almost no dispersion. Although SincNet delivers competitive results comparable to our proposed system, its performance is greatly affected by noisy speech samples. Moreover, x-vectors yielded the lowest values, which were slightly greater than 90% and presented a performance drop comparable to SincNet when dealing with noisy speech samples.

Table 6.
Comparison of results for the identification task in terms of accuracy (%).
5.4.2. Verification
We compared the results of our text prompted verification task with those delivered by the same approaches described in the identification case. Table 7 presents the comparison of verification results. Regarding the face modality, our bimodal network delivered the best results in all cases with EER values close to or below 3%. Face ResNet delivered results comparable to our proposal while statistical models had considerably greater EER values in each transformation case in comparison to the deep learning models. Standard deviation remained at low values for both deep learning networks and Eigenfaces despite its poor performance. Fisherfaces obtained the worst values in this regard, which is consistent with the results obtained in the identification case. In the speaker verification case our model also achieved the best EER values, equal to or below to 1%. These values are significantly lower in comparison to those obtained by SincNet and X-vectors. Contrary to the identification results, the verification performances of SincNet and X-vectors were more affected by noise, regardless of its SNR value.

Table 7.
Comparison of the verification results in terms of EER (%).
The Detection Error Tradeoff (DET) plots shown in Figure 2 present a visual comparison of the verification performance delivered by the considered biometric systems presented in this work. The curves were plot by pooling the verification scores of all data augmentation conditions generated by the best iteration of each system. The EER of each biometric system was calculated from their corresponding scores, obtaining the following values: BiMultNet 1.92%, Face ResNet 2.79%, Eigenfaces 25.84%, Fisherfaces 19.73%, Sincnet 7.24%, and Xvectors 2.9%. These results indicate that our proposed bimodal text prompted verification framework provided better results compared to unimodal biometric systems, regardless of the conditions presented by speech and facial data.
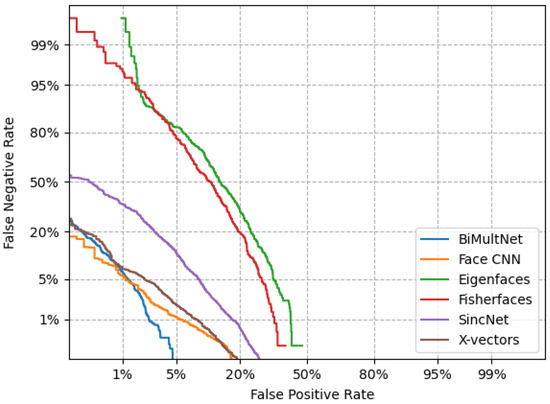
Figure 2.
DET curves of the biometric systems.
6. Conclusions
In this paper we proposed a novel multitask network to carry out bimodal biometric recognition using face and speech modalities. The proposed network was trained using a virtual database created with our locally developed BIOMEX-DB database and complemented with face data obtained from VidTimit. We incremented the data by adding noise to the speech signals at different SNR values and by performing different transformations on the face images. The data augmentation framework allowed us to establish several performance evaluation conditions.
The identification task was carried out using a fusion module that combined the feature vectors of face and speech modalities through a weighted sum providing a bimodal embedding. The values of the weights were optimized during the training stage. Text prompted verification was carried out by fusing the scores obtained from the matching of two bimodal embeddings with cosine similarity function and the WER metric with a perceptron. The score generated by it contains information of the biometric identity of a client and whether he/she correctly uttered a digit sequence prompted by the system. The text prompted modality prevents the use of prerecorded speech to gain access to the biometric system.
The obtained results indicate an EER of 0.44% and an accuracy of 100% for verification and identification, respectively, in the best case. Our studies provide evidence that noisy speech samples did not have a significant impact on performance; however, image conditions demonstrated to have an important effect on recognition results. We compared the best results of our model with popular unimodal approaches trained with the same data and evaluated under the same conditions. The results indicated a better performance by the proposed bimodal approach in terms of accuracy and EER in almost all conditions despite the observed effect that image conditions had on the results. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first system that combines the mutually related tasks previously described for biometric recognition.
The described work can be improved by doing additional experiments with an increased number of enrolled clients, evaluating the impact in recognition performance. The possibility of adding or removing target clients as needed should also be explored. Alternatives of liveness detection could also be included to increase the security of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.A. and J.M.R.; methodology, J.C.A. and J.C.M.; software, J.C.A.; validation, J.C.A. and J.C.M.; formal analysis, J.C.A. and J.C.M.; investigation, J.C.A. and J.C.M.; resources, J.C.A.; data curation, J.C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.A. and J.C.M.; writing—review and editing, J.C.M.; visualization, J.C.A.; supervision, J.C.M.; project administration, J.C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Information consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study. All the participants were informed about the purpose of the data collection.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The database BIOMEX-DB is available in the Mendeley Data repository: http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/s7chktmb6x.1. Accessed on 17 November 2022. VidTimit database can be found here: https://www.conradsanderson.id.au/vidtimit. Accessed on 17 November 2022.
Acknowledgments
First and second author acknowledge CONACYT (National Council of Science and Technology-Mexico) the financial support to pursue doctoral studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to this work.
References
- Minaee, S.; Abdolrashidi, A.; Su, H.; Bennamoun, M.; Zhang, D. Biometrics recognition using deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.00271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, S.K.S.; Jha, V.K. Multibiometric fusion strategy and its applications: A review. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 174–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabhanayagam, T.; Venkatesan, V.P.; Senthamaraikannan, K. A comprehensive survey on various biometric systems. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 2276–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Dahea, W.; Fadewar, H. Multimodal biometric system: A review. Int. J. Res. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2018, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dinca, L.M.; Hancke, G.P. The fall of one, the rise of many: A survey on multi-biometric fusion methods. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6247–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Camacho, D. Multiple classifiers in biometrics. part 1: Fundamentals and review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 44, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, R.; Ross, A. A comprehensive overview of biometric fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 52, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Castro, F.M.; Guil, N.; De la Torre, F.; Medina-Carnicer, R. Deep multi-task learning for gait-based biometrics. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Joint decision of anti-spoofing and automatic speaker verification by multi-task learning with contrastive loss. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7907–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Alkeem, E.; Yeun, C.Y.; Yun, J.; Yoo, P.D.; Chae, M.; Rahman, A.; Asyhari, A.T. Robust deep identification using ECG and multimodal biometrics for industrial internet of things. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2021, 121, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Busso, C. End-to-end audiovisual speech recognition system with multitask learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortli, Y.; Jridi, M.; Al Falou, A.; Atri, M. Face recognition systems: A survey. Sensors 2020, 20, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuad, M.T.H.; Fime, A.A.; Sikder, D.; Iftee, M.A.R.; Rabbi, J.; Al-Rakhami, M.S.; Gumaei, A.; Sen, O.; Fuad, M.; Islam, M.N. Recent advances in deep learning techniques for face recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 99112–99142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiarasi, P.; Esther Rani, P. A Comparative Analysis of AlexNet and GoogLeNet with a Simple DCNN for Face Recognition. In Advances in Smart System Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 655–668. [Google Scholar]
- Pratama, Y.; Ginting, L.M.; Nainggolan, E.H.L.; Rismanda, A.E. Face recognition for presence system by using residual networks-50 architecture. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 11, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, I.; Rachmawanto, E.H.; Santoso, H.A.; Sari, C.A. Face recognition using facenet (survey, performance test, and comparison). In Proceedings of the 2019 fourth international conference on informatics and computing (ICIC), Semarang, Indonesia, 16–17 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nandy, A. A densenet based robust face detection framework. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gwyn, T.; Roy, K.; Atay, M. Face recognition using popular deep net architectures: A brief comparative study. Future Internet 2021, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Niu, H. Feature extraction based on deep-convolutional neural network for face recognition. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, 1-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, Y.H. Face recognition via deep learning using data augmentation based on orthogonal experiments. Electronics 2019, 8, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.K.; Tan, Z.H. Incorporating pass-phrase dependent background models for text-dependent speaker verification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2018, 47, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehak, N.; Kenny, P.J.; Dehak, R.; Dumouchel, P.; Ouellet, P. Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 2010, 19, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Johnson, M.T. Comparison of multiple features and modeling methods for text-dependent speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Okinawa, Japan, 16–20 December 2017; pp. 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Novoselov, S.; Kudashev, O.; Shchemelinin, V.; Kremnev, I.; Lavrentyeva, G. Deep cnn based feature extractor for text-prompted speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5334–5338. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-vectors: Robust dnn embeddings for speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Heo, H.; Yang, I.; Yoon, S.; Shim, H.; Yu, H. D-vector based speaker verification system using Raw Waveform CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (Anit 2017), Bangkok, Thailand, 2–3 December 2017; Volume 150, pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Muckenhirn, H.; Doss, M.M.; Marcell, S. Towards directly modeling raw speech signal for speaker verification using CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4884–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Ravanelli, M.; Bengio, Y. Speaker recognition from raw waveform with sincnet. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 1021–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Singh, D.; Susan, S. Speaker recognition using SincNet and X-vector fusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Zakopane, Poland, 12–14 October 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, L.; Zunair, H.; Mohammed, N. Robust deep speaker recognition: Learning latent representation with joint angular margin loss. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, X.L. Speaker recognition based on deep learning: An overview. Neural Netw. 2021, 140, 65–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalapu, H.; PN, A.R.; Ramachandra, R.; Rao, K.S.; Mitra, P.; Prasanna, S.M.; Busch, C. Audio-visual biometric recognition and presentation attack detection: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 37431–37455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, R.; Yeom, S.; Kim, S.H.; Herbert, D. Continuous multimodal biometric authentication schemes: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34541–34557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talreja, V.; Valenti, M.C.; Nasrabadi, N.M. Multibiometric secure system based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global conference on Signal and Information Processing (globalSIP), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 November 2017; pp. 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Kong, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Gao, M.; Zhao, C.; Xu, X. Multimodal feature-level fusion for biometrics identification system on IoMT platform. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 21418–21426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazabal, O.; Gofman, M.; Bai, Y.; Choi, Y.; Sandico, N.; Mitra, S.; Pham, K. Multimodal biometrics for enhanced iot security. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NA, USA, 7–9 January 2019; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q. LVID: A multimodal biometrics authentication system on smartphones. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alay, N.; Al-Baity, H.H. Deep learning approach for multimodal biometric recognition system based on fusion of iris, face, and finger vein traits. Sensors 2020, 20, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.; Asfour, S.S. Multimodal biometrics recognition from facial video with missing modalities using deep learning. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 6–29. [Google Scholar]
- mehdi Cherrat, E.; Alaoui, R.; Bouzahir, H. Convolutional neural networks approach for multimodal biometric identification system using the fusion of fingerprint, finger-vein and face images. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2020, 6, e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, D.; Jia, P.; Dai, Y.; Xu, X. An efficient android-based multimodal biometric authentication system with face and voice. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 102757–102772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, M.; Memon, S.; Dhomeja, L.D.; Jalbani, A.H.; Chandio, A.A. Deep feature fusion of fingerprint and online signature for multimodal biometrics. Computers 2021, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Lee, K.A.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, C.; Dang, J. Exploring Deep Learning for Joint Audio-Visual Lip Biometrics. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08510. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y. A deep feature fusion network based on multiple attention mechanisms for joint iris-periocular biometric recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iula, A.; Micucci, M. Multimodal Biometric Recognition Based on 3D Ultrasound Palmprint-Hand Geometry Fusion. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 7914–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, V.; Predić, B.; Saracevic, M.; Elhoseny, M.; Karabasevic, D.; Stanujkic, D.; Jayapaul, P. Enhanced multimodal biometric recognition approach for smart cities based on an optimized fuzzy genetic algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, M.; Indumathi, G. Deep belief network-based hybrid model for multimodal biometric system for futuristic security applications. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2021, 58, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Tan, T. Deep feature fusion for iris and periocular biometrics on mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Rodriguez, J.C.; Atenco-Vazquez, J.C.; Ramirez-Cortes, J.M.; Arechiga-Martinez, R.; Gomez-Gil, P.; Fonseca-Delgado, R. BIOMEX-DB: A Cognitive Audiovisual Dataset for Unimodal and Multimodal Biometric Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 111267–111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, C.; Lovell, B.C. Multi-region probabilistic histograms for robust and scalable identity inference. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Alghero, Italy, 2–5 June 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.; Peddinti, V.; Povey, D.; Seltzer, M.L.; Khudanpur, S. A study on data augmentation of reverberant speech for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 5220–5224. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Chen, G.; Povey, D. Musan: A music, speech, and noise corpus. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.08484. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.; Utku, K. Speech recognition based on convolutional neural networks and MFCC algorithm. Adv. Artif. Intell. Res. 2021, 1, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T.; the Scikit-Image Contributors. scikit-image: Image processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Lian, S. A survey on face data augmentation for the training of deep neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 15503–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.B.; Wada, K.; Crall, J.; Tanaka, S.; Graving, J.; Reinders, C.; Yadav, S.; Banerjee, J.; Vecsei, G.; Kraft, A.; et al. Imgaug. Available online: https://github.com/aleju/imgaug (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Amodei, D.; Ananthanarayanan, S.; Anubhai, R.; Bai, J.; Battenberg, E.; Case, C.; Casper, J.; Catanzaro, B.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, G.; et al. Deep speech 2: End-to-end speech recognition in english and mandarin. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zenkel, T.; Sanabria, R.; Metze, F.; Niehues, J.; Sperber, M.; Stüker, S.; Waibel, A. Comparison of decoding strategies for ctc acoustic models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.04469. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.M.; Wang, H.C. A method of estimating the equal error rate for automatic speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing, Singapore, 13–16 December 2006; pp. 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyu, I.; Bomoi, M.A.; Maishanu, M. A Comparative Study of Eigenface and Fisherface Algorithms Based on OpenCV and Sci-kit Libraries Implementations. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2022, 14, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).