The Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow for Multi-SNP Analysis in Complex Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
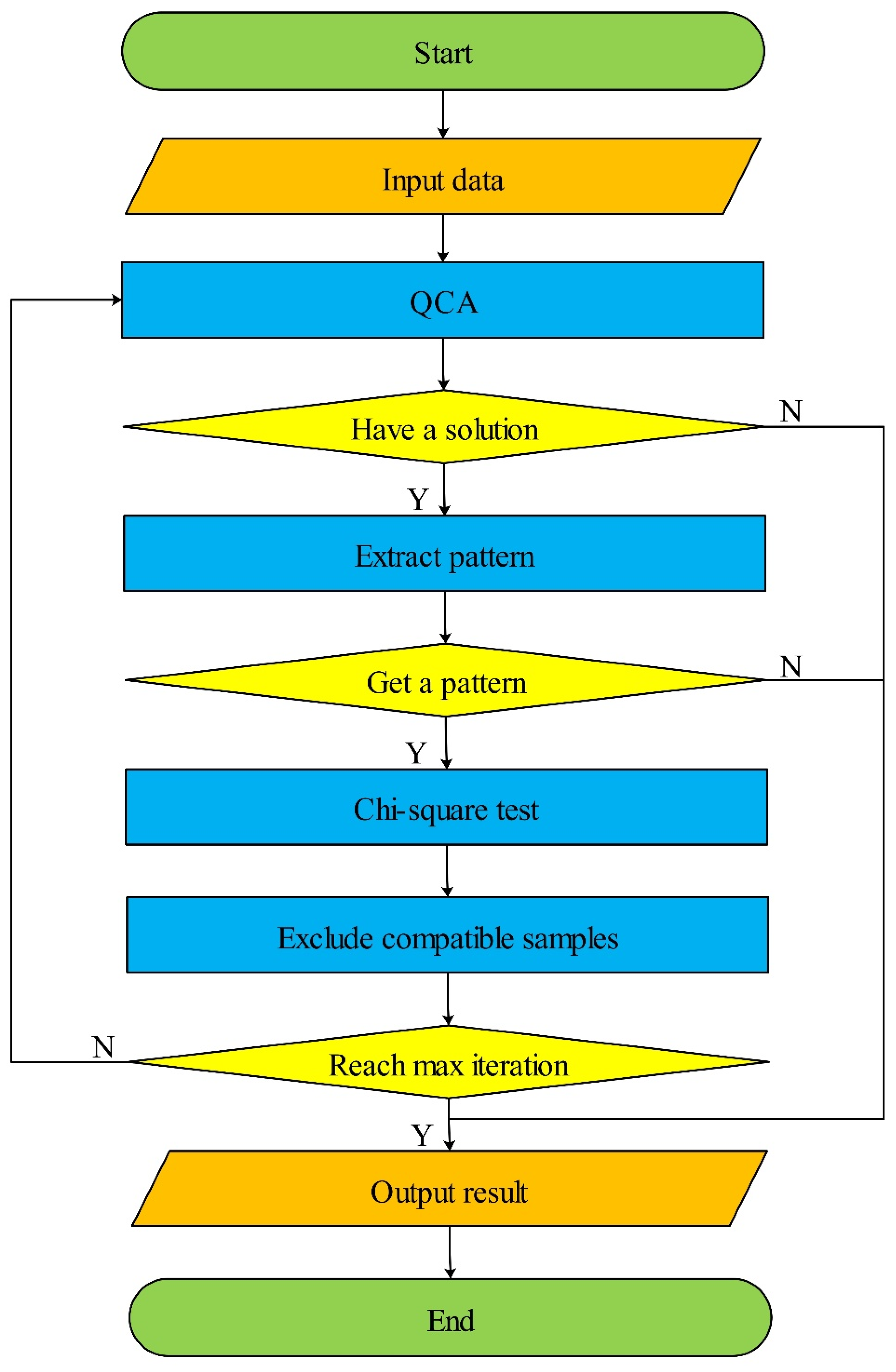
2.1. Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow
| Algorithm 1 IECS |
| Input: k: threshold of iterations; consistency threshold: threshold of consistency; U: set of samples. Output: Solution: The SNP combinations with p-value of chi-square test. 1: Solution ← ∅ 2: V ← U 3: W ← U 4: For i = 1 → k do 5: X ← qca(V) 6: If X.length == 1 then 7: Break 8: Else 9: Z ← Extractpattern(X) 10: p ← Chisquaretest(Z, W) 11: V ← Excludesamples(V) 12: Z ← Append(Z, p) 13: Solution ← Append(Solution, Z) 14: End if 15: End for |
2.2. Analysis of Necessary Conditions
2.3. Performance Measurements
2.4. Simulated Data
2.5. Alzheimer’s Disease Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulated Data Experiment
3.2. Alzheimer’s Disease Data Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komar, A.A. SNPs, Silent but Not Invisible. Science 2007, 315, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, A.; Farlow, A. The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: A review. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International SNP Map Working Group; Sachidanandam, R.; Weissman, D.; Schmidt, S.C.; Kakol, J.M.; Stein, L.D.; Marth, G.; Sherry, S.; Mullikin, J.C.; Mortimore, B.J.; et al. A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature 2001, 409, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Larson, S.R.; Hu, Z.; Palazzo, A.J.; A Jones, T.; Wang, R.R.-C.; Jensen, K.B.; Chatterton, N.J. Molecular genetic linkage maps for allotetraploid Leymus wildryes (Gramineae: Triticeae). Genome 2003, 46, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culverhouse, R.; Suarez, B.K.; Lin, J.; Reich, T. A perspective on epistasis: Limits of models displaying no main effect. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-T.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Lin, X. Joint analysis of SNP and gene expression data in genetic association studies of complex diseases. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2014, 8, 352–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtaz, R.; Ghanem, N.; El-Makky, N.; Ismail, M. Integrated analysis of SNP, CNV and gene expression data in genetic association studies. Clin. Genet. 2017, 93, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Chaffin, M.; Aragam, K.G.; Haas, M.E.; Roselli, C.; Choi, S.H.; Natarajan, P.; Lander, E.S.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, I.M.; Van Der Most, P.J.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; De Bakker, P.I.; Boezen, H.M.; Bruinenberg, M.; Franke, L.; Van Der Harst, P.; Navis, G.; Postma, D.S.; et al. Missing heritability: Is the gap closing? An analysis of 32 complex traits in the lifelines cohort study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Ponce, S.-I.; Samoré, A.B.; A Dolezal, M.; Bagnato, A.; Meuwissen, T.H. Estimates of missing heritability for complex traits in Brown Swiss cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2014, 46, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidlin, B.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Gastwirth, J.L. Trend Tests for Case-Control Studies of Genetic Markers: Power, Sample Size and Robustness. Hum. Hered. 2002, 53, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Elston, R.C. A powerful method of combining measures of association and Hardy-Weinberg disequilibrium for fine-mapping in case-control studies. Stat. Med. 2006, 25, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Ng, H.K.T. Genetic model selection in two-phase analysis for case-control association studies. Biostatistics 2007, 9, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Kardia, S.; Ferrell, R.; Sing, C. A Combinatorial Partitioning Method to Identify Multilocus Genotypic Partitions That Predict Quantitative Trait Variation. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Sung, P.-Y.; Lin, P.-L.; Yu, Y.-W.; Chung, R.-H. A multi-SNP association test for complex diseases incorporating an optimal P-value threshold algorithm in nuclear families. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, H.J. Detecting gene–gene interactions that underlie human diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.J.; Zeiss, C.; Chew, E.Y.; Tsai, J.-Y.; Sackler, R.S.; Haynes, C.; Henning, A.K.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Mane, S.M.; Mayne, S.T.; et al. Complement Factor H Polymorphism in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Science 2005, 308, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, N.; Merikangas, K. The Future of Genetic Studies of Complex Human Diseases. Science 1996, 273, 1516–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, C.; Durand, G.; Thuillier, V.; Augé, F. Performance of epistasis detection methods in semi-simulated GWAS. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.D.; Hahn, L.W.; Roodi, N.; Bailey, L.R.; Dupont, W.D.; Parl, F.F.; Moore, J.H. Multifactor-dimensionality reduction reveals high-order interactions among estrogen-metabolism genes in sporadic breast cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, L.W.; Ritchie, M.D.; Moore, J.H. Multifactor dimensionality reduction software for detecting gene–gene and gene–environment interactions. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chung, Y.; Elston, R.C.; Kim, Y.; Park, T. Log-linear model-based multifactor dimensionality reduction method to detect gene–gene interactions. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2589–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Chen, G.-B.; Yan, L.; Ma, J.Z.; Zhu, J.; Elston, R.C.; Li, M.D. A Generalized Combinatorial Approach for Detecting Gene-by-Gene and Gene-by-Environment Interactions with Application to Nicotine Dependence. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaert, T.; Calle, M.L.; Dudek, S.M.; Mahachie John, J.M.; Van Lishout, F.; Urrea, V.; Ritchie, M.D.; Van Steen, K. Model-based multifactor dimensionality reduction for detecting epistasis in case-control data in the presence of noise. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2011, 75, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.S.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.A.; Himmelstein, D.S.; Park, J.P.; Jason, H.M.; Brent, T.H. Multifactor dimensionality reduction for graphics processing units enables genome-wide testing of epistasis in sporadicals. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 694–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Moore, J.H.; Williams, S.M.; Andrews, P.; Hillege, H.L.; Van Der Harst, P.; Navis, G.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. A simple and computationally effient approach to multifactor dimensionality reduction analysis of gene-gene interactions for quantitative traits. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-D.; Chuang, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-B.; Chang, H.-W. MDR-ER: Balancing Functions for Adjusting the Ratio in Risk Classes and Classification Errors for Imbalanced Cases and Controls Using Multifactor-Dimensionality Reduction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Leem, S.; Lee, S.; Park, T. A novel fuzzy set based multifactor dimensionality reduction method for detecting gene–gene interaction. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 65, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Lee, S.; Park, T. A unified model based multifactor dimensionality reduction framework for detecting gene–gene interactions. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, i605–i610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chuang, L.-Y.; Lin, Y.-D. CMDR based differential evolution identifies the epistatic interaction in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2354–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chuang, L.-Y.; Lin, Y.-D. Multiobjective multifactor dimensionality reduction to detect SNP–SNP interactions. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chan, K.C.C. Detecting gene-gene interactions for complex quantitative traits using generalized fuzzy classification. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooperberg, C.L.; LeBlanc, M. Increasing the power of identifying gene × gene interactions in genome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 32, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, C.; Steffens, M.; Brockschmidt, F.F.; Baur, M.P.; Becker, T. INTERSNP: Genome-wide interaction analysis guided by a priori information. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, Q.; Xue, H.; Fan, X.; Tang, N.L.; Yu, W. BOOST: A Fast Approach to Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions in Genome-wide Case-Control Studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H. Physical nature of higher-order mutual information: Intrinsic correlations and frustration, Physical review E, Statis-tical physics, plasmas, flids, and related interdisciplinary topics. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62 Pt A, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dong, H.; Luo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, G.; Reveille, J.D.; Xiong, M. A Novel Statistic for Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, M.; Cordell, H.J. Improved Statistics for Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Malley, J.D.; Andrew, A.S.; Karagas, M.R.; Moore, J.H. Detecting gene-gene interactions using a permutation-based random forest method. BioData Min. 2016, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Sun, J.; Dimitrov, L.; Turner, A.R.; Adams, T.S.; Meyers, D.A.; Chang, B.L.; Zheng, S.L.; Grönberg, H.; Xu, J.; et al. A support vector machine approach for detecting gene-gene interaction. Genet. Epidemiol. 2008, 32, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.D.; White, B.C.; Parker, J.S.; Hahn, L.W.; Moore, J.H. Optimization of neural network architecture using genetic programming improves detection and modeling of gene-gene interactions in studies of human diseases. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, V.; Briollais, L.; A Knight, J.; Shi, E.; Wang, Y.; Wells, S.; Li, H.; Rajendram, I.; Andrulis, I.L.; Ozcelik, H. SNP-SNP interactions in breast cancer susceptibility. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raign, C.C. The Comparative Method: Moving beyond Qualitative and Quantitative Strategies, 1st ed.; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- McAdam, D.; Boudet, H.S.; Davis, J.; Orr, R.J.; Scott, W.R.; Levitt, R.E. “Site Fights”: Explaining Opposition to Pipeline Projects in the Developing World1. Sociol. Forum 2010, 25, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, I.O.; Woodside, A.G. Fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA): Guidelines for research practice in Information Systems and marketing. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, M.; Ambühl, M. Causal modeling with multi-value and fuzzy-set Coincidence Analysis. Politi- Sci. Res. Methods 2018, 8, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Moyeed, R.; Carroll, C.; Luo, S.; Li, X. Genetic networks in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging 2020, 12, 5221–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, S.; Tang, M.; Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Han, H.; et al. Mutation screening and association study of the neprilysin gene in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese persons. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Quaddus, M.; Warren, M.; Akter, S.; Pappas, I. Are you a cyberbully on social media? exploring the personality traits using a fuzzy-set confiurational approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 66, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

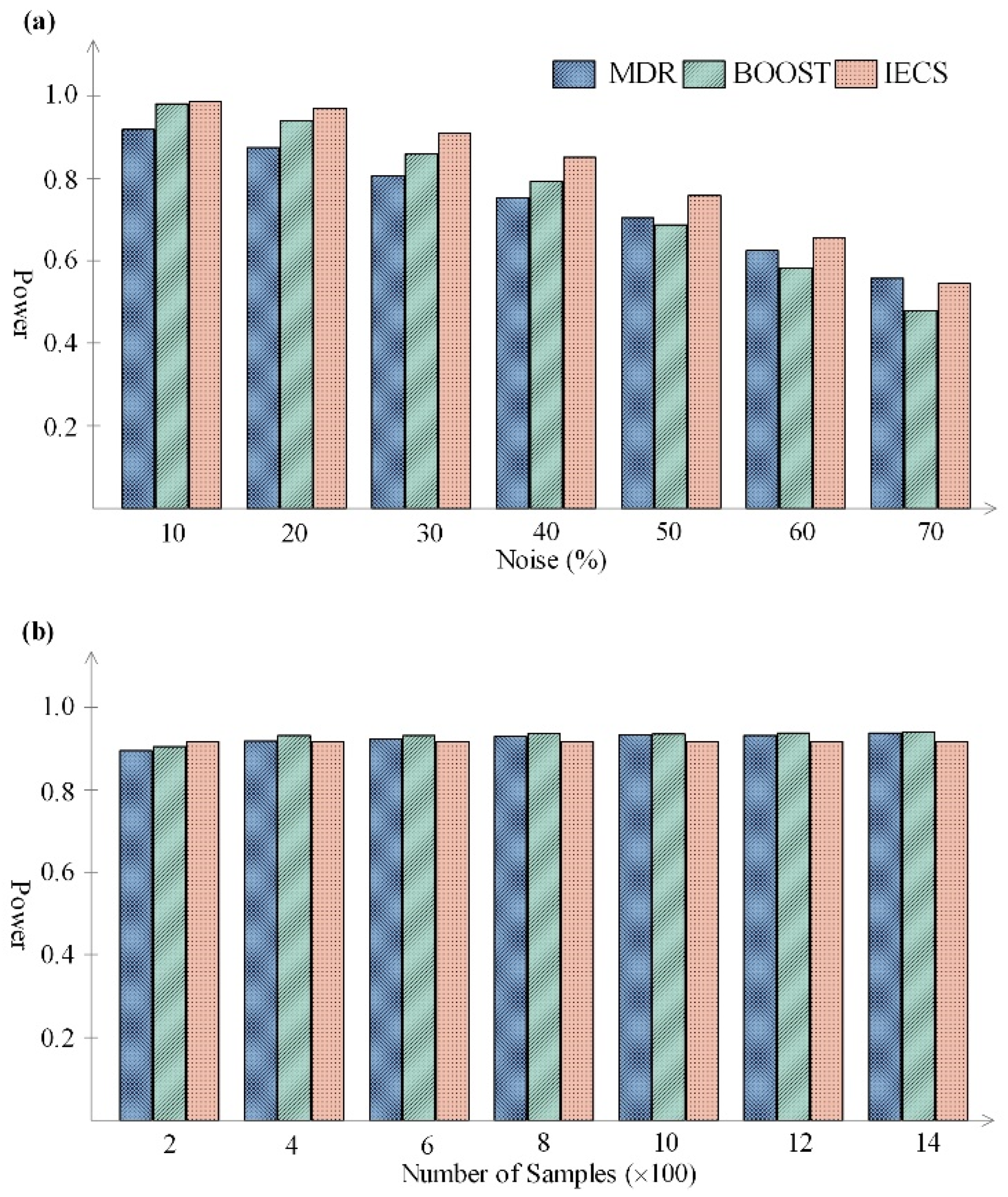

| Noise (%) | Runtime (Seconds) | Samples | Runtime (Seconds) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR | BOOST | IECS | MDR | BOOST | IECS | ||
| 10 | 14.258 | 0.056 | 0.962 | 200 | 13.783 | 0.056 | 0.953 |
| 20 | 14.241 | 0.056 | 1.034 | 400 | 17.243 | 0.059 | 1.013 |
| 30 | 14.238 | 0.056 | 1.069 | 600 | 20.658 | 0.063 | 1.070 |
| 40 | 14.221 | 0.056 | 1.040 | 800 | 24.159 | 0.074 | 1.151 |
| 50 | 14.104 | 0.056 | 0.969 | 1000 | 26.810 | 0.068 | 1.162 |
| 60 | 12.393 | 0.056 | 0.783 | 1200 | 30.203 | 0.071 | 1.229 |
| 70 | 11.990 | 0.058 | 0.651 | 1400 | 33.574 | 0.075 | 1.288 |
| Configuration | Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 3 | Round 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −204 G > C | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| IVS3 + 106 T > G | ○ | ● | ○ | |
| c.401 A > G | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| IVS10-5 C > T | ○ | ○ | ● | ○ |
| IVS15 + 144 T > A | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| IVS17-294 C > T | ● | ○ | ○ | |
| IVS22 + 36 C > A | ● | ○ | ○ | ● |
| 3′UTR159 C > T | ● | ○ | ● | ○ |
| Raw coverage | 9.73% | 2.71% | 1.96% | 1.51% |
| Consistency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Method | Result | p-Value | Runtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| IECS | IVS22 + 36 C > A * 3′UTR159 C > T | 0.007 | 4..496 s |
| IVS17-294 C > T | 0.026 | ||
| IVS22 + 36 C > A | 0.002 | ||
| MDR | IVS22 + 36 C > A * 3′UTR159 C > T | 0 | 42.591 s |
| BOOST | IVS10-5 C > T * IVS22 + 36 C > A | 0.153 | 0.368 s |
| Condition | Consistency | Coverage | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~−204 G > C | 0.969 | 0.530 | 0.008 |
| ~c.401 A > G | 0.961 | 0.510 | 0.130 |
| ~IVS10-5 C > T | 0.911 | 0.518 | 0.711 |
| ~IVS15 + 144 T > A | 0.926 | 0.528 | 0.082 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J. The Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow for Multi-SNP Analysis in Complex Diseases. Algorithms 2023, 16, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16100480
Xu W, Zhu X, Zhang L, Gao J. The Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow for Multi-SNP Analysis in Complex Diseases. Algorithms. 2023; 16(10):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16100480
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wei, Xunhong Zhu, Liping Zhang, and Jun Gao. 2023. "The Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow for Multi-SNP Analysis in Complex Diseases" Algorithms 16, no. 10: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16100480
APA StyleXu, W., Zhu, X., Zhang, L., & Gao, J. (2023). The Iterative Exclusion of Compatible Samples Workflow for Multi-SNP Analysis in Complex Diseases. Algorithms, 16(10), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16100480







