Convolutional Neural Network with an Elastic Matching Mechanism for Time Series Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- An elastic matching mechanism is proposed to measure the similarity between the time series and convolutional kernels. This mechanism can be extended to different architectures based on the CNN.
- The experiments performed on 85 University of California, Riverside (UCR) time series datasets [11] demonstrate that the proposed mechanism improves the performance of CNN on classification tasks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Dynamic Time Warping
2.2. Dynamic Time Warping with the Convolutional Neural Network
3. Proposed Method
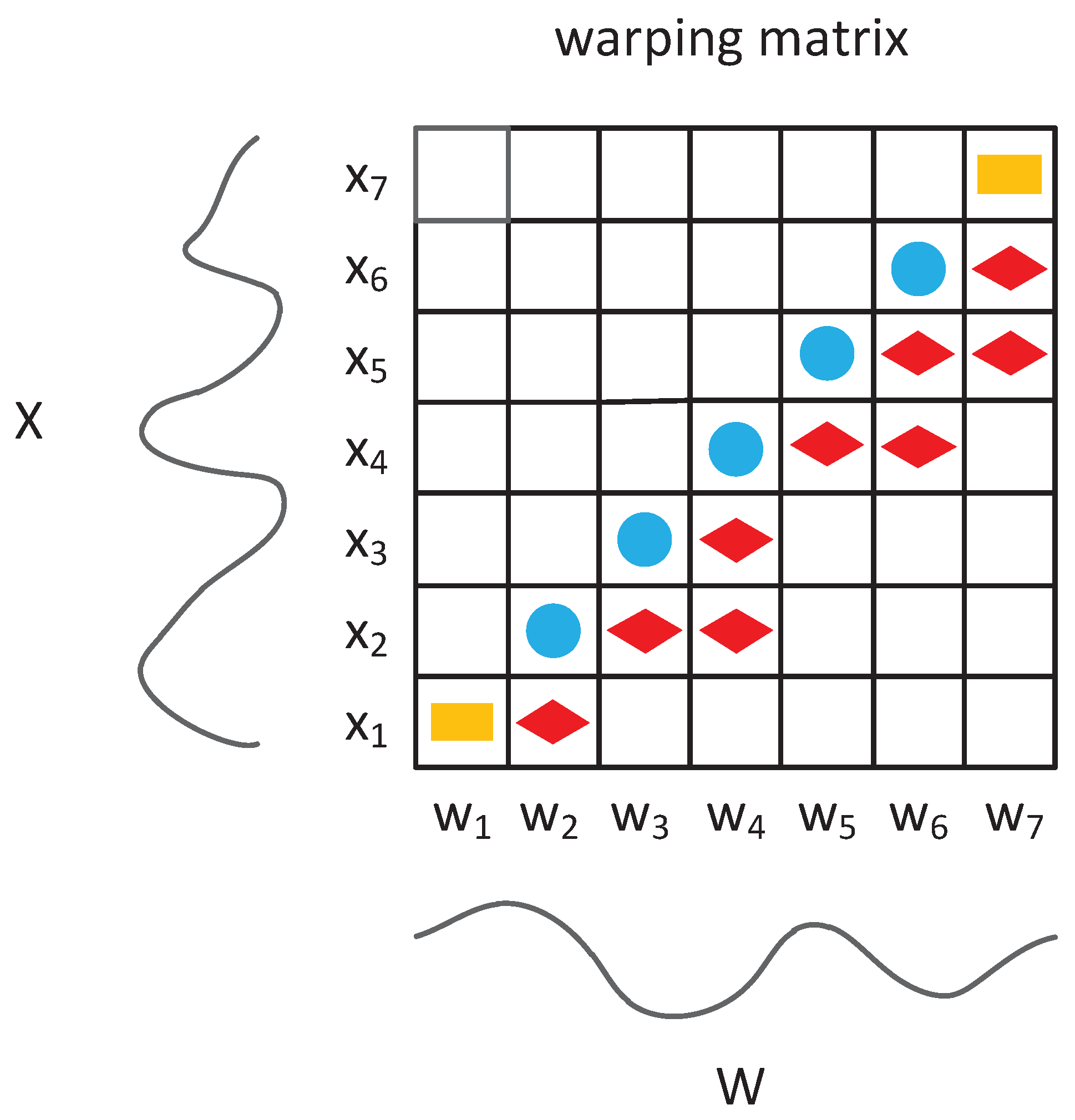
3.1. Elastic Matching in Dynamic Time Warping
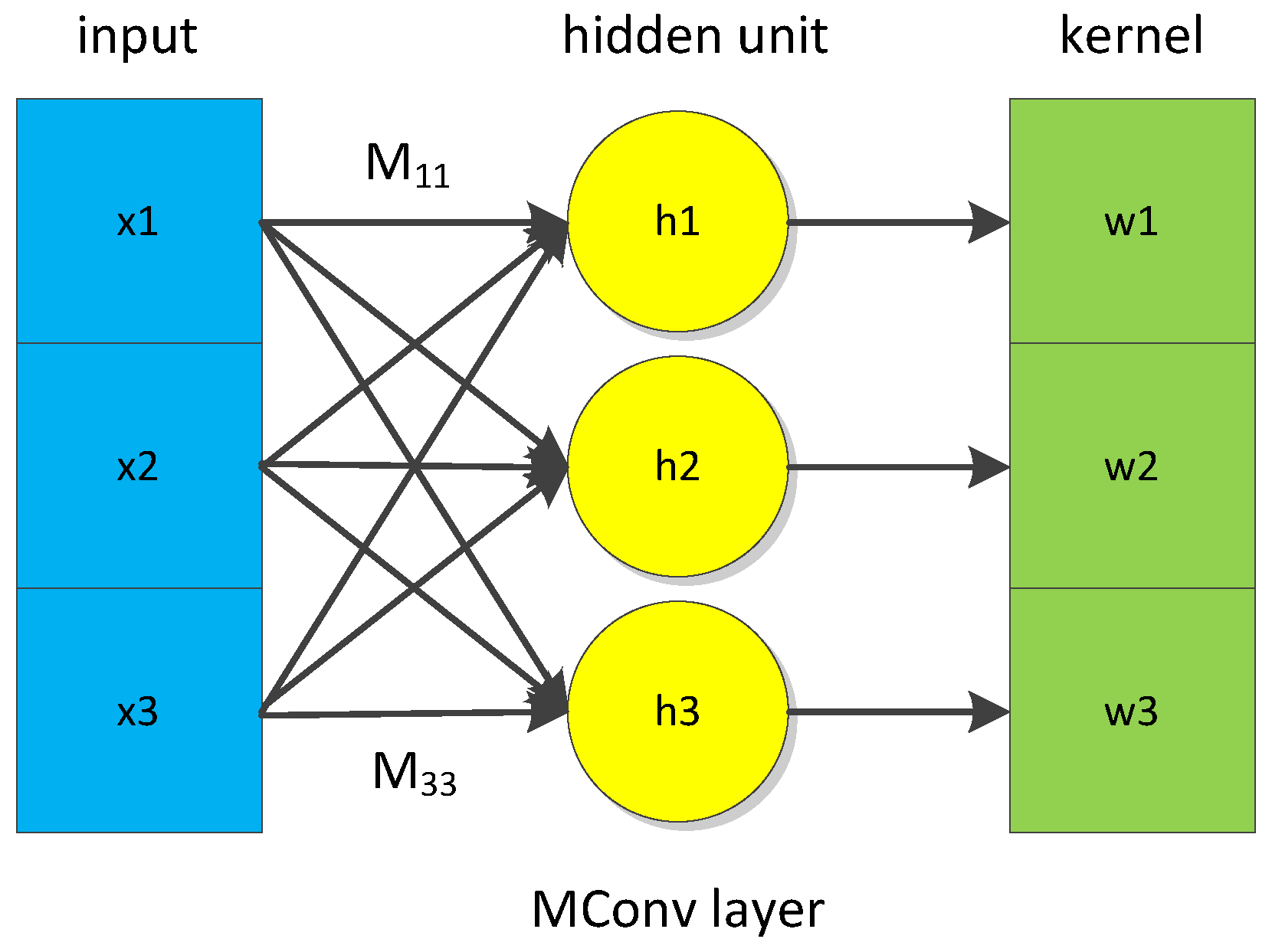
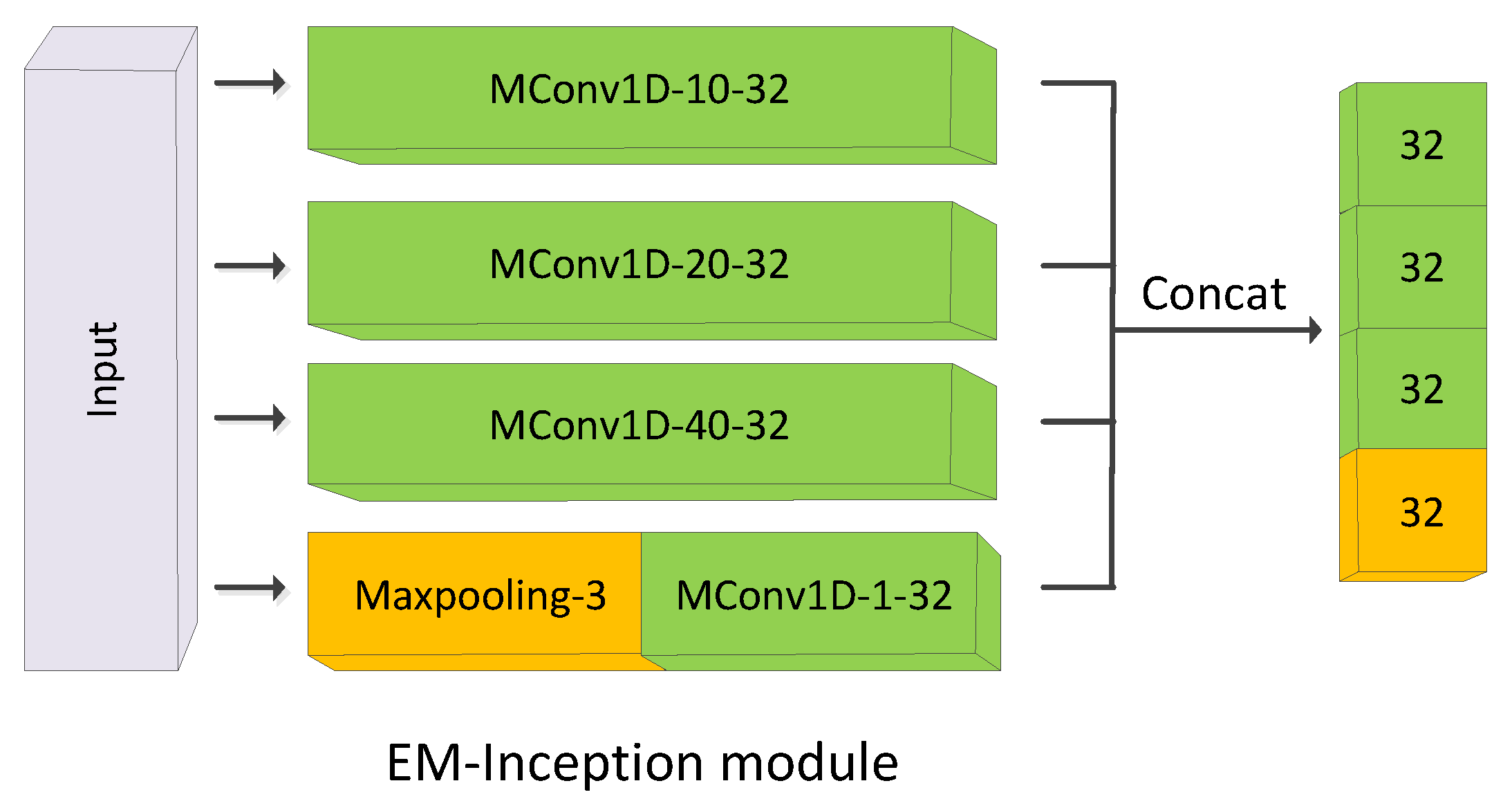
3.2. Elastic Matching in the Convolutional Neural Network
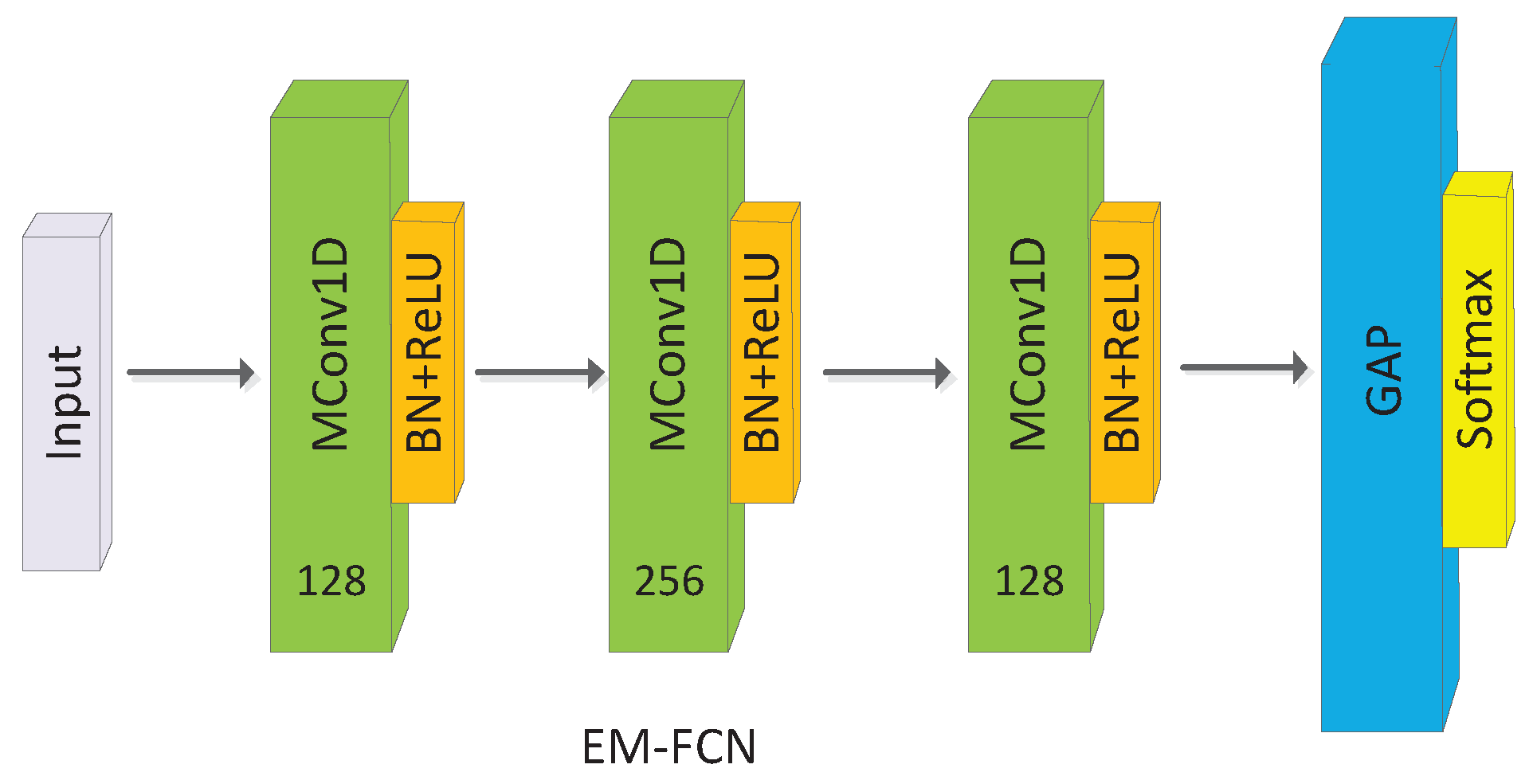
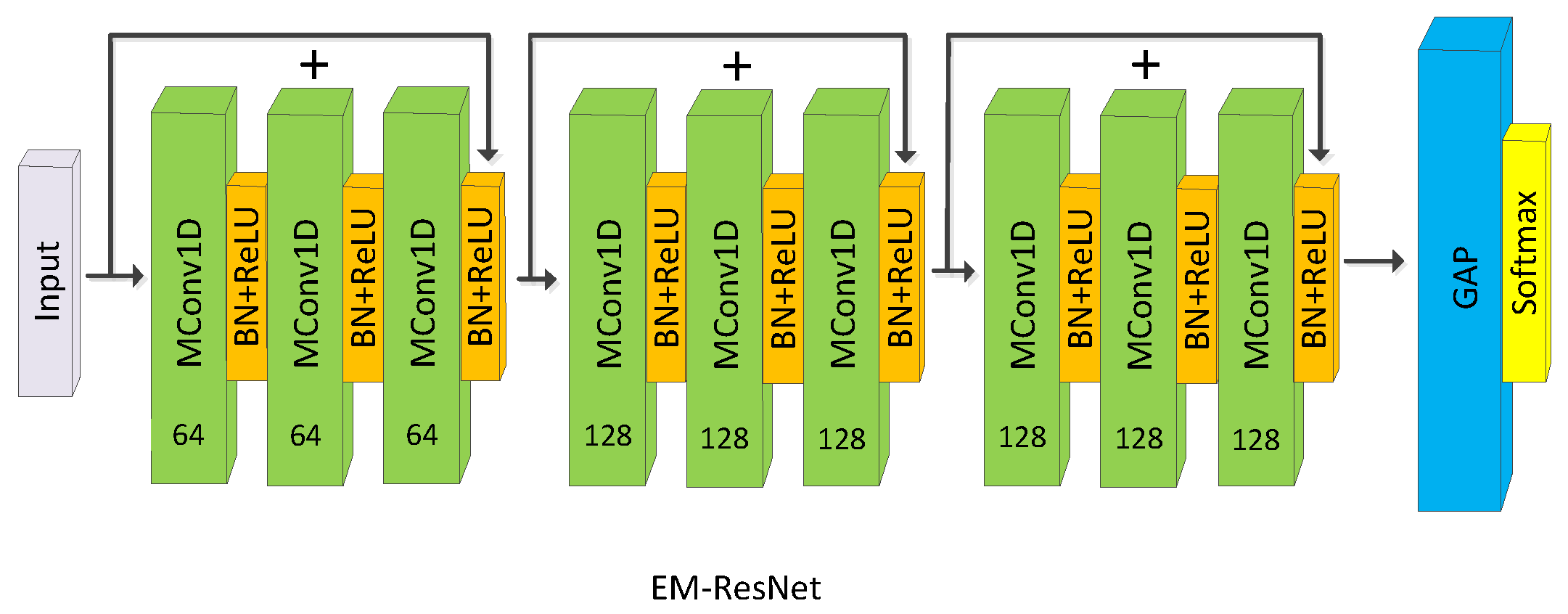
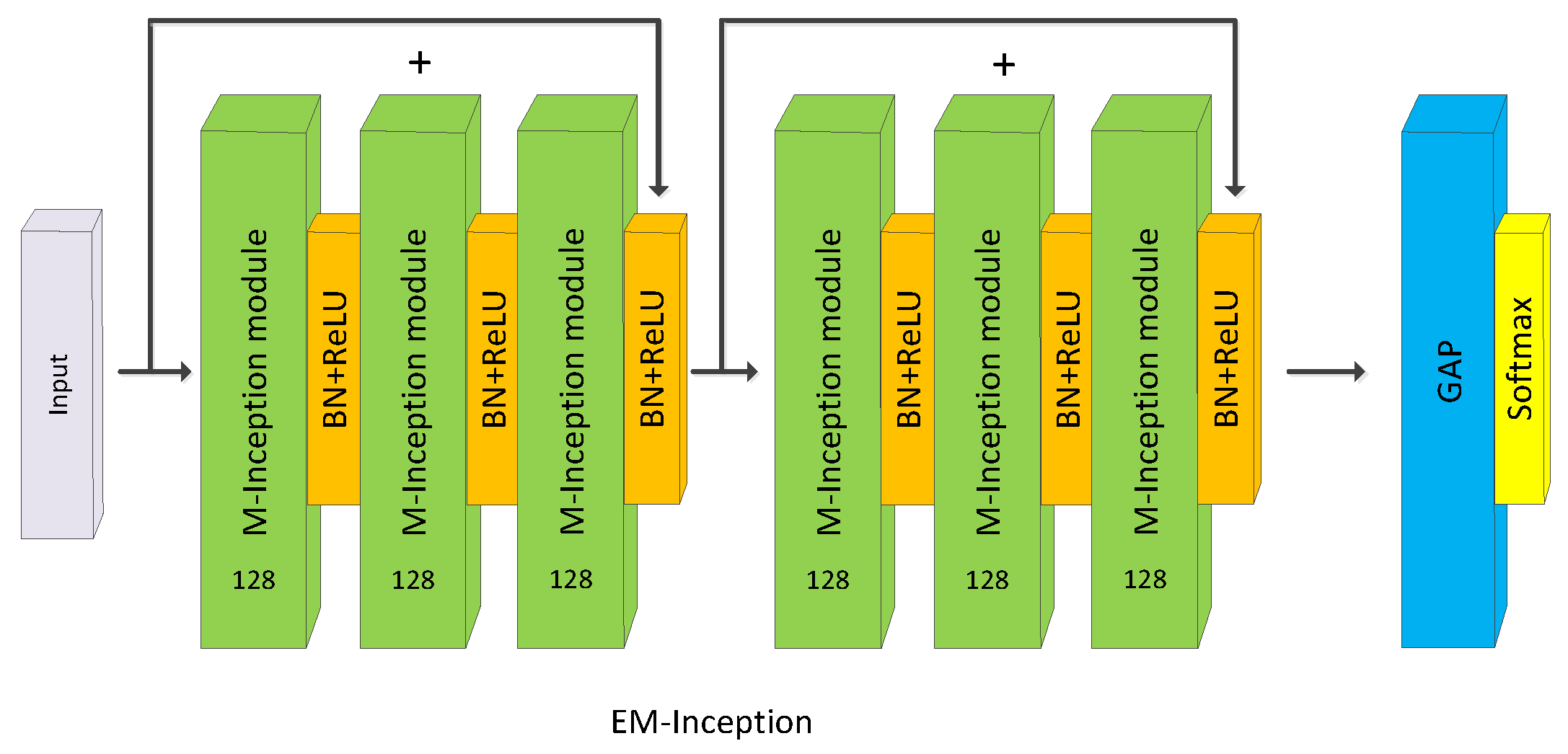
3.3. EM-CNN
4. Experiments
4.1. Hyperparameter Settings
4.2. Metrics
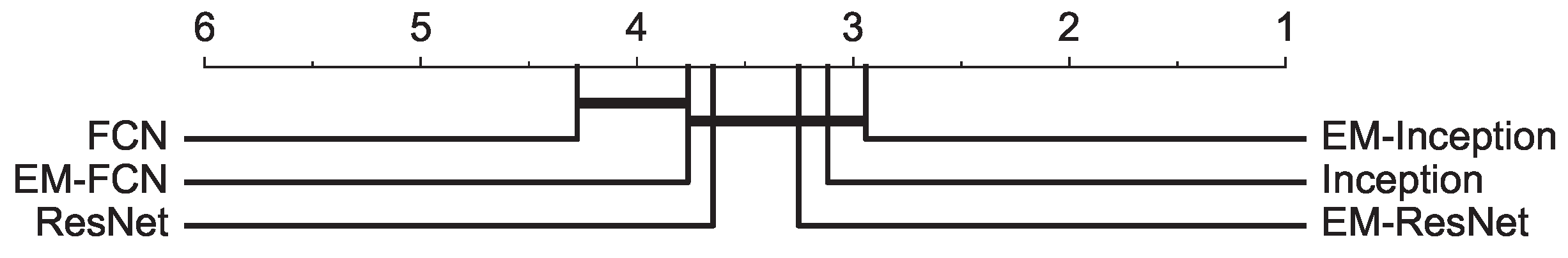
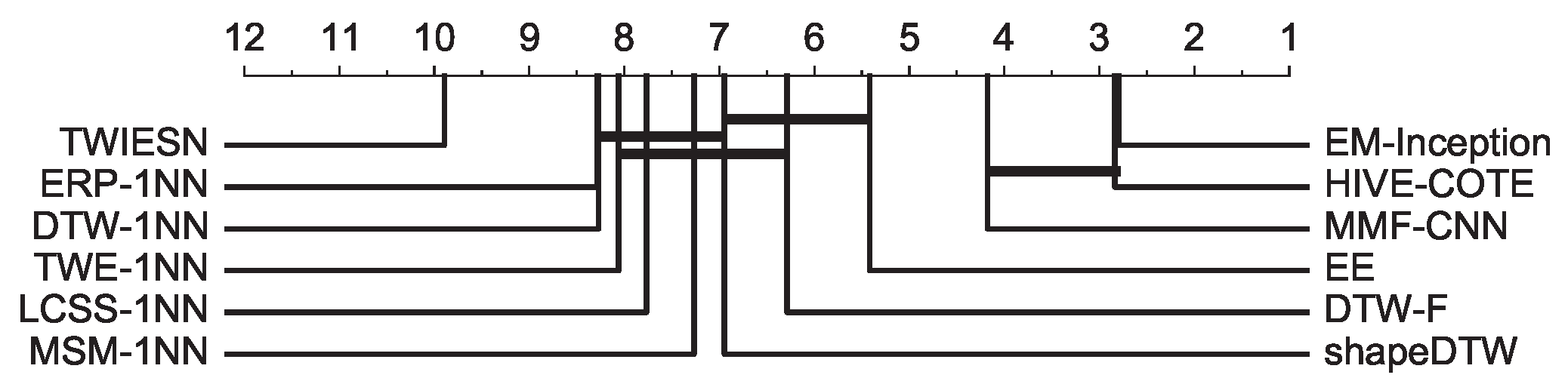
4.3. Evaluation on the UCR Archive
4.4. Effects of the Different Numbers of Layers
4.5. Effects of the Different Kernel Sizes
4.6. Effects of the Different Kernel Initialization
4.7. Computational Complexity
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.L.; Hsaio, W.H.; Tu, Y.C. Time series classification with multivariate convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 4788–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, F.J.; Roggen, D. Deep convolutional and lstm recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition. Sensors 2016, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graves, A.; Jaitly, N.; Mohamed, A. Hybrid speech recognition with deep bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 8–13 December 2013; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Übeyli, E.D. Wavelet/mixture of experts network structure for EEG signals classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Schoenberger, R.B.; Shiozawa, D.; Xu, X.; Zhan, P. Contour matching for a fish recognition and migration-monitoring system. In Two-and Three-Dimensional Vision Systems for Inspection, Control, and Metrology II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5606, pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fawaz, H.I.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.A. Deep learning for time series classification: A review. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 33, 917–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Xu, T.; Yi, J.; Huang, J.; Rajasekaran, S. DTWNet: A dynamic time warping network. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 11640–11650. [Google Scholar]
- Iwana, B.K.; Uchida, S. Time series classification using local distance-based features in multi-modal fusion networks. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 97, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; Arcos, J.L. An empirical evaluation of similarity measures for time series classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 67, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Itti, L. shapedtw: Shape dynamic time warping. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dau, H.A.; Bagnall, A.; Kamgar, K.; Yeh, C.C.M.; Zhu, Y.; Gharghabi, S.; Ratanamahatana, C.A.; Keogh, E. The UCR time series archive. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 6, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Trajcevski, G.; Scheuermann, P.; Wang, X.; Keogh, E. Querying and mining of time series data: Experimental comparison of representations and distance measures. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2008, 1, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Jeong, M.K.; Omitaomu, O.A. Weighted dynamic time warping for time series classification. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoe, H.; Chiba, S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1978, 26, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itakura, F. Minimum prediction residual principle applied to speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1975, 23, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecki, T.; Łuczak, M. Using derivatives in time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2013, 26, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passalis, N.; Tefas, A.; Kanniainen, J.; Gabbouj, M.; Iosifidis, A. Deep Adaptive Input Normalization for Time Series Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 3760–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, J.Y.; Dieuleveut, A.; Jaggi, M. Unsupervised scalable representation learning for multivariate time series. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 4650–4661. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, D.K.; Acar, D.; Mandikal, V.; Sadasivan, V.; Simhadri, H.; Saligrama, V.; Jain, P. Shallow RNNs: A method for accurate time-series classification on tiny devices. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, L.; Thome, N. Shape and time distortion loss for training deep time series forecasting models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 4189–4201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Multilevel wavelet decomposition network for interpretable time series analysis. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 2437–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, W.; Oates, T. Time series classification from scratch with deep neural networks: A strong baseline. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 1578–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Iwana, B.K.; Uchida, S. Dynamic Weight Alignment for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.06530. [Google Scholar]
- Fawaz, H.I.; Lucas, B.; Forestier, G.; Pelletier, C.; Schmidt, D.F.; Weber, J.; Webb, G.I.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.A.; Petitjean, F. Inceptiontime: Finding alexnet for time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 1936–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekar, S.; Woodworth, B.; Bhojanapalli, S.; Neyshabur, B.; Srebro, N. Implicit regularization in matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–16 February 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Rehg, J.M.; Song, L. Neural similarity learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 5025–5036. [Google Scholar]
- Demšar, J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnall, A.; Lines, J.; Bostrom, A.; Large, J.; Keogh, E. The great time series classification bake off: A review and experimental evaluation of recent algorithmic advances. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2017, 31, 606–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kate, R.J. Using dynamic time warping distances as features for improved time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2016, 30, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, M.; Kollios, G.; Gunopulos, D. Discovering similar multidimensional trajectories. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Data Engineering, San Jose, CA, USA, 26 February–1 March 2002; pp. 673–684. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Özsu, M.T.; Oria, V. Robust and fast similarity search for moving object trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–16 June 2005; pp. 491–502. [Google Scholar]
- Marteau, P.F. Time warp edit distance with stiffness adjustment for time series matching. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 31, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, A.; Athitsos, V.; Das, G. The move-split-merge metric for time series. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2012, 25, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lines, J.; Bagnall, A. Time series classification with ensembles of elastic distance measures. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2015, 29, 565–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lines, J.; Taylor, S.; Bagnall, A. Time series classification with HIVE-COTE: The hierarchical vote collective of transformation-based ensembles. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanisaro, P.; Heidemann, G. Time series classification using time warping invariant echo state networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 15th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Anaheim, CA, USA, 18–20 December 2016; pp. 831–836. [Google Scholar]
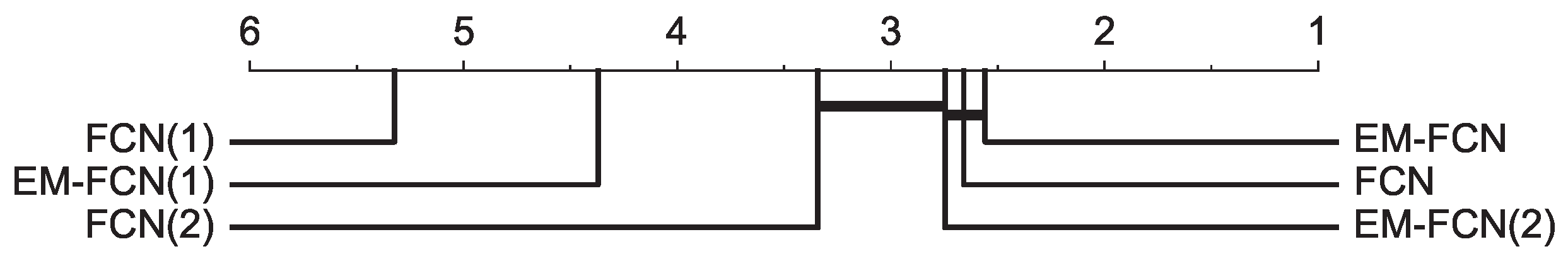
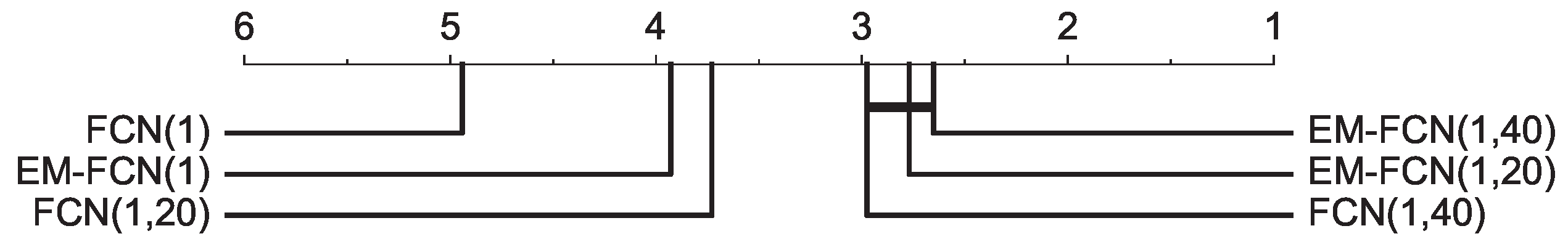
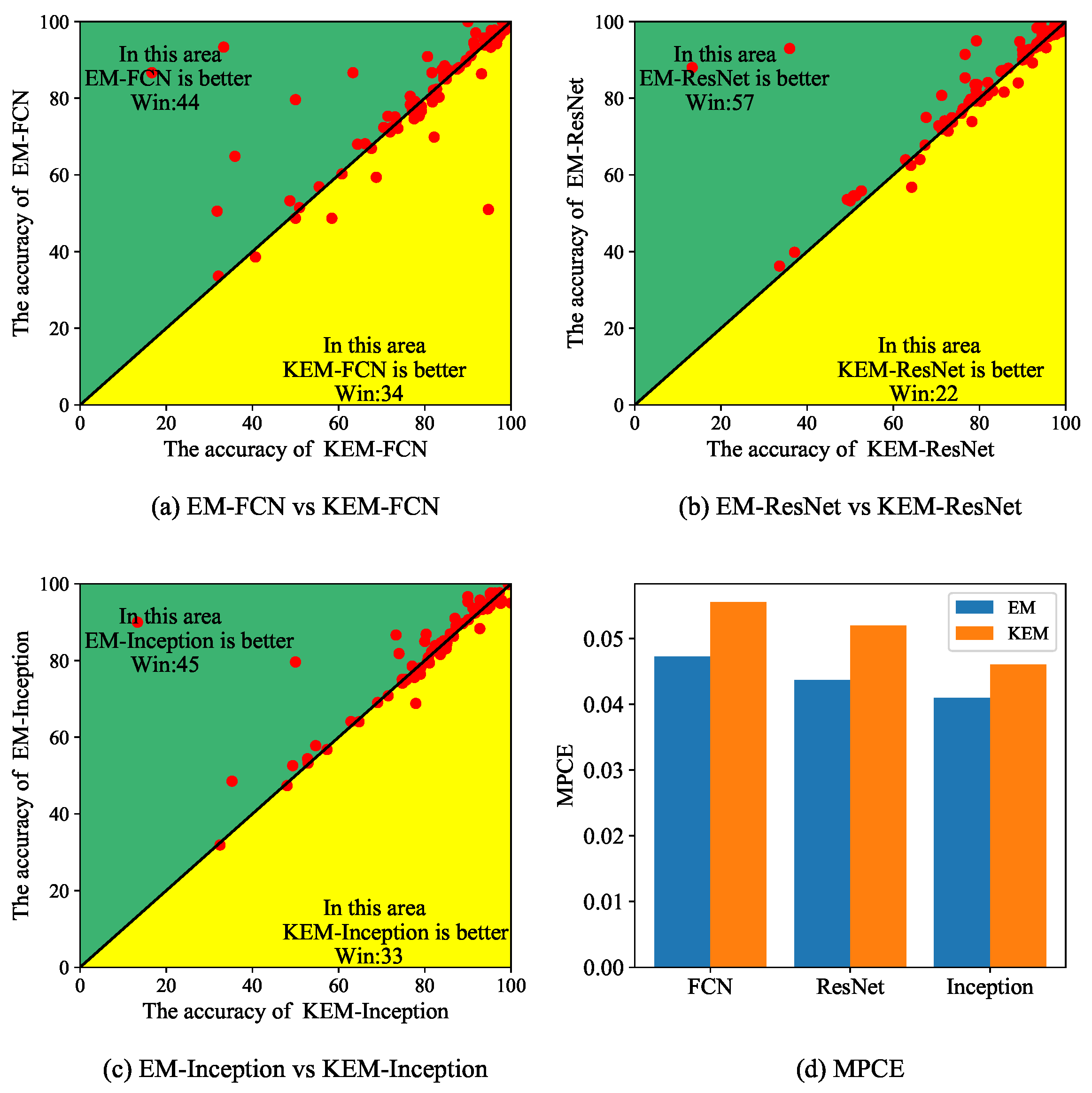
| Dataset | FCN | EM-FCN | ResNet | EM-ResNet | Inception | EM-Inception |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adiac | 0.8414 | 0.8517 | 0.8332 | 0.8159 | 0.8312 | 0.8261 |
| ArrowHead | 0.8434 | 0.8743 | 0.8377 | 0.8160 | 0.8229 | 0.8457 |
| Beef | 0.6800 | 0.8667 | 0.7533 | 0.8533 | 0.6667 | 0.8667 |
| BeetleFly | 0.9100 | 0.8500 | 0.8500 | 0.8700 | 0.7500 | 0.8500 |
| BirdChicken | 0.9400 | 1.0000 | 0.8800 | 0.9000 | 0.9500 | 0.9500 |
| Car | 0.9133 | 0.9333 | 0.9167 | 0.9266 | 0.8667 | 0.9333 |
| CBF | 0.9938 | 0.9911 | 0.9958 | 0.9989 | 0.9944 | 1.0000 |
| ChlorineConcentration | 0.8165 | 0.8237 | 0.8528 | 0.8411 | 0.8596 | 0.8898 |
| CinCECGTorso | 0.8288 | 0.9087 | 0.8378 | 0.8043 | 0.8645 | 0.8159 |
| Coffee | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Computers | 0.8192 | 0.8000 | 0.8056 | 0.8080 | 0.7800 | 0.7560 |
| CricketX | 0.7944 | 0.7641 | 0.7990 | 0.7974 | 0.8282 | 0.8436 |
| CricketY | 0.7928 | 0.7667 | 0.8103 | 0.8359 | 0.8410 | 0.8513 |
| CricketZ | 0.8097 | 0.7538 | 0.8087 | 0.8205 | 0.8333 | 0.8692 |
| DiatomSizeReduction | 0.3464 | 0.5098 | 0.9510 | 0.9641 | 0.9314 | 0.9575 |
| DistalPhalanxOutlineAgeGroup | 0.7180 | 0.7122 | 0.7180 | 0.7410 | 0.7482 | 0.7410 |
| DistalPhalanxOutlineCorrect | 0.7601 | 0.7464 | 0.7703 | 0.7391 | 0.7790 | 0.7645 |
| DistalPhalanxTW | 0.6950 | 0.6691 | 0.6633 | 0.6403 | 0.6691 | 0.6403 |
| Earthquakes | 0.7252 | 0.7410 | 0.7122 | 0.7194 | 0.7266 | 0.6906 |
| ECG200 | 0.8880 | 0.8800 | 0.8740 | 0.8400 | 0.9200 | 0.9100 |
| ECG5000 | 0.9400 | 0.9387 | 0.9351 | 0.9418 | 0.9369 | 0.9438 |
| ECGFiveDays | 0.9854 | 0.9779 | 0.9663 | 0.9733 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| ElectricDevices | 0.7065 | 0.7231 | 0.7279 | 0.7283 | 0.7021 | 0.7081 |
| FaceAll | 0.9375 | 0.9331 | 0.8667 | 0.9497 | 0.7964 | 0.8231 |
| FaceFour | 0.9295 | 0.8636 | 0.9545 | 0.9318 | 0.9545 | 0.9659 |
| FacesUCR | 0.9434 | 0.9390 | 0.9542 | 0.9478 | 0.9634 | 0.9654 |
| FiftyWords | 0.6457 | 0.6813 | 0.7402 | 0.7495 | 0.8044 | 0.8462 |
| Fish | 0.9611 | 0.9771 | 0.9806 | 0.9943 | 0.9829 | 0.9714 |
| FordA | 0.9141 | 0.9705 | 0.9370 | 0.9356 | 0.9553 | 0.9545 |
| FordB | 0.7723 | 0.7914 | 0.8131 | 0.8074 | 0.8679 | 0.8630 |
| GunPoint | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9907 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Ham | 0.7067 | 0.7238 | 0.7581 | 0.7500 | 0.7238 | 0.7810 |
| HandOutlines | 0.7989 | 0.6486 | 0.9135 | 0.9297 | 0.9459 | 0.9351 |
| Haptics | 0.4896 | 0.5325 | 0.5097 | 0.5584 | 0.5649 | 0.5325 |
| Herring | 0.6438 | 0.5938 | 0.6000 | 0.6250 | 0.6719 | 0.5781 |
| InlineSkate | 0.3316 | 0.5055 | 0.3771 | 0.3982 | 0.4655 | 0.4855 |
| InsectWingbeatSound | 0.3919 | 0.3859 | 0.4993 | 0.5455 | 0.6328 | 0.6409 |
| ItalyPowerDemand | 0.9629 | 0.9602 | 0.9615 | 0.9602 | 0.9553 | 0.9689 |
| LargeKitchenAppliance | 0.9029 | 0.8987 | 0.9013 | 0.9013 | 0.9040 | 0.9067 |
| Lightning2 | 0.7344 | 0.7213 | 0.7803 | 0.7377 | 0.8033 | 0.8689 |
| Lightning7 | 0.8247 | 0.6986 | 0.8274 | 0.8356 | 0.8082 | 0.8082 |
| Mallat | 0.9671 | 0.9574 | 0.9736 | 0.9753 | 0.9429 | 0.9710 |
| Meat | 0.8033 | 0.9333 | 0.9900 | 0.9833 | 0.9167 | 0.9667 |
| MedicalImages | 0.7784 | 0.7724 | 0.7697 | 0.7724 | 0.7908 | 0.8000 |
| MiddlePhalanxOutlineAgeGroup | 0.5351 | 0.4870 | 0.5455 | 0.5325 | 0.5455 | 0.5260 |
| MiddlePhalanxOutlineCorrect | 0.7945 | 0.7904 | 0.8261 | 0.8076 | 0.8144 | 0.7938 |
| MiddlePhalanxTW | 0.5013 | 0.4870 | 0.4948 | 0.5455 | 0.5260 | 0.4740 |
| MoteStrain | 0.9358 | 0.9449 | 0.9240 | 0.9313 | 0.8826 | 0.8962 |
| NonInvasiveFetalECGThorax1 | 0.9583 | 0.9578 | 0.9414 | 0.9481 | 0.9618 | 0.9496 |
| NonInvasiveFetalECGThorax2 | 0.9531 | 0.9573 | 0.9436 | 0.9435 | 0.9588 | 0.9542 |
| OliveOil | 0.7200 | 0.8667 | 0.8467 | 0.8800 | 0.8333 | 0.9000 |
| OSULeaf | 0.9785 | 0.9421 | 0.9802 | 0.9917 | 0.9256 | 0.9463 |
| PhalangesOutlinesCorrect | 0.8177 | 0.8030 | 0.8452 | 0.8193 | 0.8380 | 0.8310 |
| Phoneme | 0.3280 | 0.3360 | 0.3334 | 0.3623 | 0.3249 | 0.3191 |
| Plane | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| ProximalPhalanxOutlineAgeGroup | 0.8254 | 0.8585 | 0.8468 | 0.8732 | 0.8537 | 0.8390 |
| ProximalPhalanxOutlineCorrect | 0.9065 | 0.9107 | 0.9196 | 0.9141 | 0.9347 | 0.9244 |
| ProximalPhalanxTW | 0.7610 | 0.7659 | 0.7727 | 0.7902 | 0.7854 | 0.7854 |
| RefrigerationDevices | 0.4965 | 0.5147 | 0.5301 | 0.5360 | 0.5413 | 0.5440 |
| ScreenType | 0.6219 | 0.6027 | 0.6155 | 0.5680 | 0.5707 | 0.5680 |
| ShapeletSim | 0.7056 | 0.8667 | 0.7822 | 0.9144 | 0.9833 | 0.8833 |
| ShapesAll | 0.8940 | 0.8950 | 0.9263 | 0.9183 | 0.9150 | 0.9367 |
| SmallKitchenAppliances | 0.7771 | 0.7787 | 0.7813 | 0.7920 | 0.7680 | 0.7653 |
| SonyAIBORobotSurface1 | 0.9584 | 0.9584 | 0.9607 | 0.9271 | 0.8502 | 0.9534 |
| SonyAIBORobotSurface2 | 0.9803 | 0.9643 | 0.9754 | 0.9664 | 0.9454 | 0.9423 |
| StarLightCurves | 0.9650 | 0.9745 | 0.9723 | 0.9745 | 0.9789 | 0.9492 |
| Strawberry | 0.9751 | 0.9757 | 0.9800 | 0.9703 | 0.9811 | 0.9568 |
| SwedishLeaf | 0.9674 | 0.9776 | 0.9626 | 0.9648 | 0.9472 | 0.9760 |
| Symbols | 0.9554 | 0.9548 | 0.8931 | 0.9759 | 0.9829 | 0.9769 |
| SyntheticControl | 0.9887 | 0.9933 | 0.9967 | 1.0000 | 0.9933 | 1.0000 |
| ToeSegmentation1 | 0.9614 | 0.9561 | 0.9570 | 0.9649 | 0.9561 | 0.9737 |
| ToeSegmentation2 | 0.8892 | 0.8846 | 0.8938 | 0.8923 | 0.9462 | 0.9462 |
| Trace | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| TwoLeadECG | 0.9995 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9956 | 0.9991 |
| TwoPatterns | 0.8705 | 0.8758 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| UWaveGestureLibraryX | 0.7538 | 0.7831 | 0.7812 | 0.7929 | 0.8130 | 0.8275 |
| UWaveGestureLibraryY | 0.6425 | 0.6801 | 0.6658 | 0.6778 | 0.7501 | 0.7493 |
| UWaveGestureLibraryZ | 0.7267 | 0.7515 | 0.7486 | 0.7607 | 0.7482 | 0.7510 |
| UWaveGestureLibraryAll | 0.8179 | 0.8210 | 0.8608 | 0.8783 | 0.9422 | 0.9764 |
| Wafer | 0.9972 | 0.9982 | 0.9981 | 0.9989 | 0.9982 | 0.9977 |
| Wine | 0.6111 | 0.7963 | 0.7222 | 0.7370 | 0.7593 | 0.7963 |
| WordSynonyms | 0.5611 | 0.5690 | 0.6166 | 0.6395 | 0.7320 | 0.7508 |
| Worms | 0.7818 | 0.8052 | 0.7610 | 0.7273 | 0.7532 | 0.8182 |
| WormsTwoClass | 0.7429 | 0.7532 | 0.7481 | 0.7143 | 0.7922 | 0.6883 |
| Yoga | 0.8372 | 0.8760 | 0.8667 | 0.8720 | 0.9053 | 0.9237 |
| Number of Win | 9 | 17 | 10 | 21 | 24 | 35 |
| AVG-AR | 4.1529 | 3.6235 | 3.4588 | 3.0588 | 2.8941 | 2.7177 |
| AVG-GR | 3.6715 | 3.0460 | 3.0936 | 2.5862 | 2.3412 | 2.1272 |
| MPCE | 0.0515 | 0.0480 | 0.0453 | 0.0443 | 0.0428 | 0.0417 |
| DTW-1NN | ERP-1NN | LCSS-1NN | MSM-1NN | TWE-1NN | DTW-F | |
| Number of Win | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| AVG-AR | 7.9412 | 7.9412 | 7.5529 | 7.0353 | 7.7529 | 6.0706 |
| AVG-GR | 7.3666 | 7.2010 | 6.8627 | 6.3174 | 7.1856 | 5.2437 |
| MPCE | 0.0692 | 0.0672 | 0.0695 | 0.0660 | 0.0686 | 0.0592 |
| EE | HIVE-COTE | TWIESN | MMF-CNN | shapeDTW | EM-Inception | |
| Number of Win | 6 | 30 | 1 | 26 | 5 | 33 |
| AVG-AR | 5.1294 | 2.5647 | 9.8471 | 4.0706 | 6.8118 | 2.5647 |
| AVG-GR | 4.5357 | 2.0672 | 9.1362 | 2.7990 | 5.5298 | 1.9884 |
| MPCE | 0.0598 | 0.0411 | 0.0821 | 0.0426 | 0.0596 | 0.0417 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, K.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y. Convolutional Neural Network with an Elastic Matching Mechanism for Time Series Classification. Algorithms 2021, 14, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14070192
Ouyang K, Hou Y, Zhou S, Zhang Y. Convolutional Neural Network with an Elastic Matching Mechanism for Time Series Classification. Algorithms. 2021; 14(7):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14070192
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Kewei, Yi Hou, Shilin Zhou, and Ye Zhang. 2021. "Convolutional Neural Network with an Elastic Matching Mechanism for Time Series Classification" Algorithms 14, no. 7: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14070192
APA StyleOuyang, K., Hou, Y., Zhou, S., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Convolutional Neural Network with an Elastic Matching Mechanism for Time Series Classification. Algorithms, 14(7), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14070192






