Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy for Multiagent Cooperation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel method, called MA-HCDP, is proposed to promote cooperation behaviors in environments with many agents.
- A hierarchical group network based on prior knowledge is designed to extract high-dimensional group-level state representation.
- A cognition difference network based on a variational autoencoder is designed to allow each agent to choose its neighbors adaptively to communicate.
- The effectiveness of MA-HCDP is evaluated in different tasks including cooperative navigation and group containment. Compared with existing methods, MA-HCDP shows a significant improvement in all the tasks, especially for the tasks with numerous agents.
2. Related Works
3. Background
3.1. Partially Observable Markov Games
3.2. Reinforcement Learning
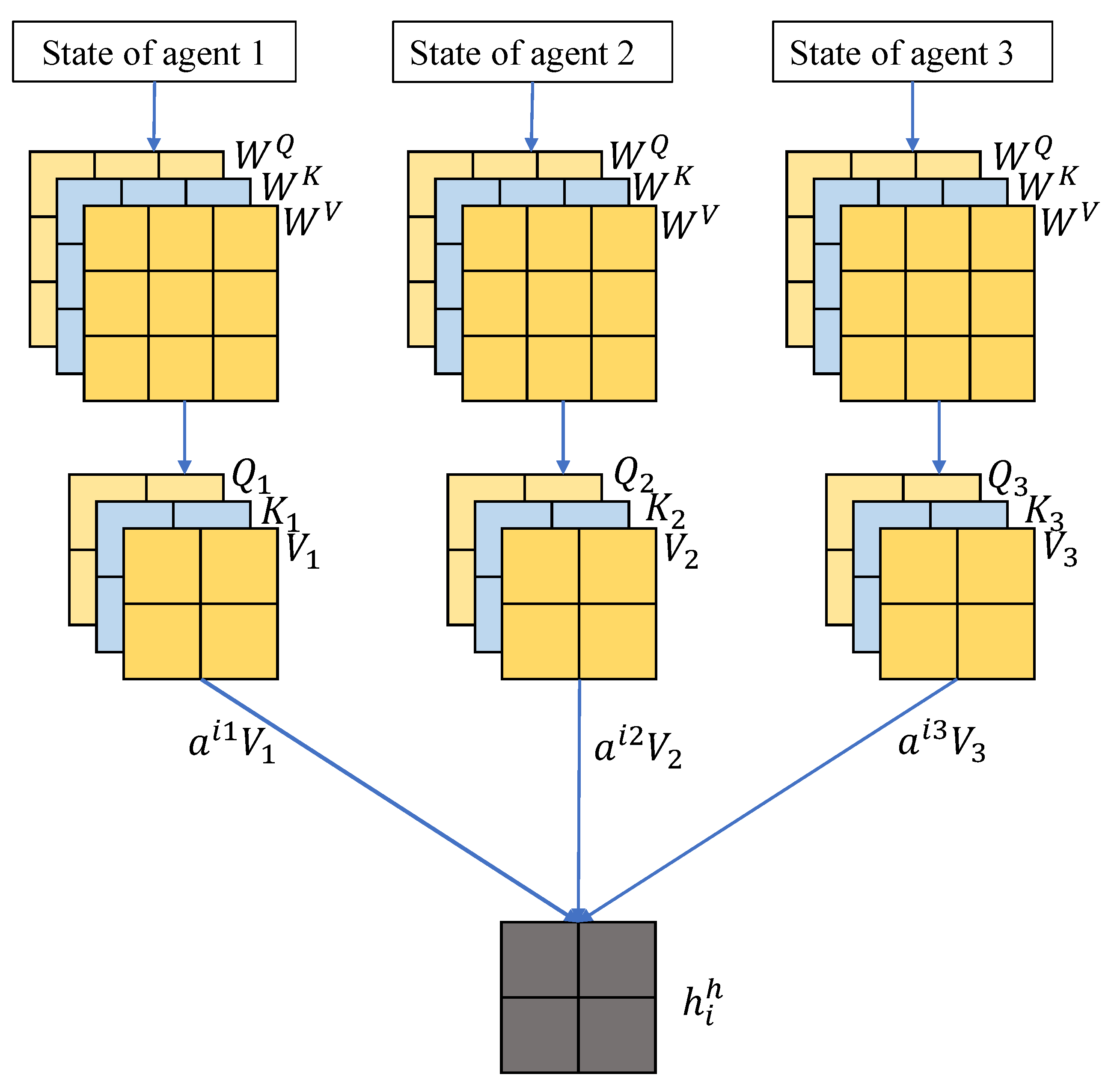
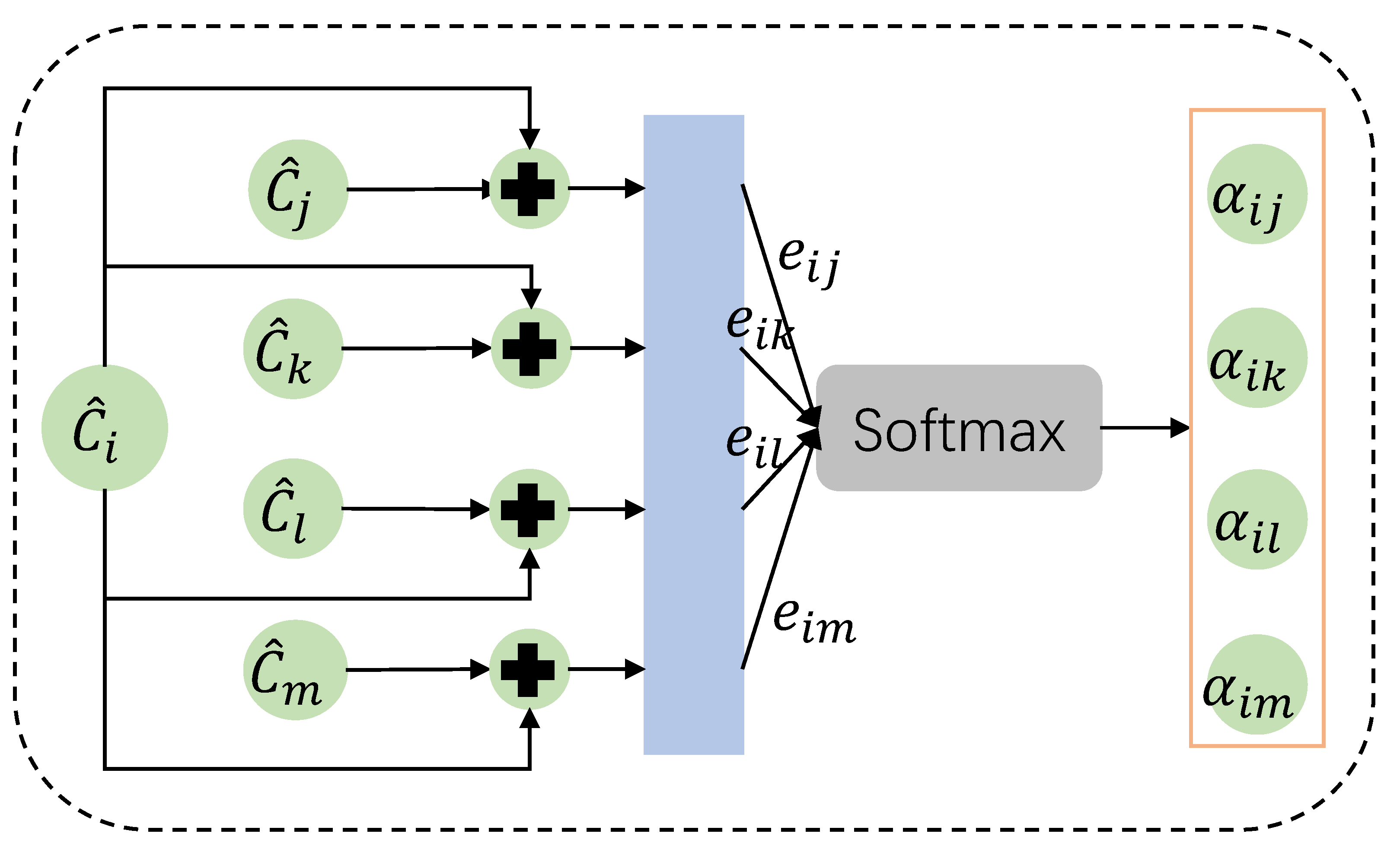
3.3. Attention Mechanism
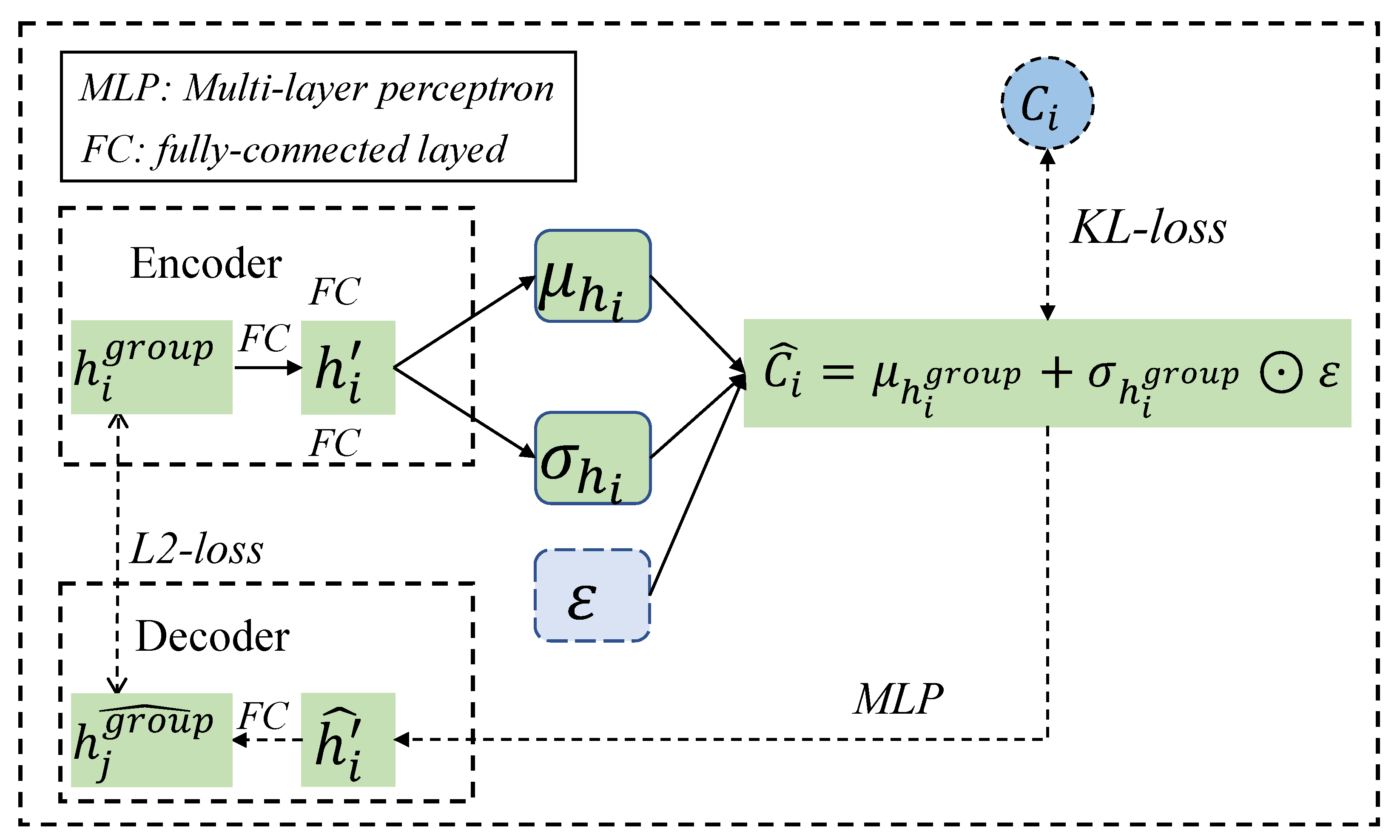
3.4. Variational Autoencoder
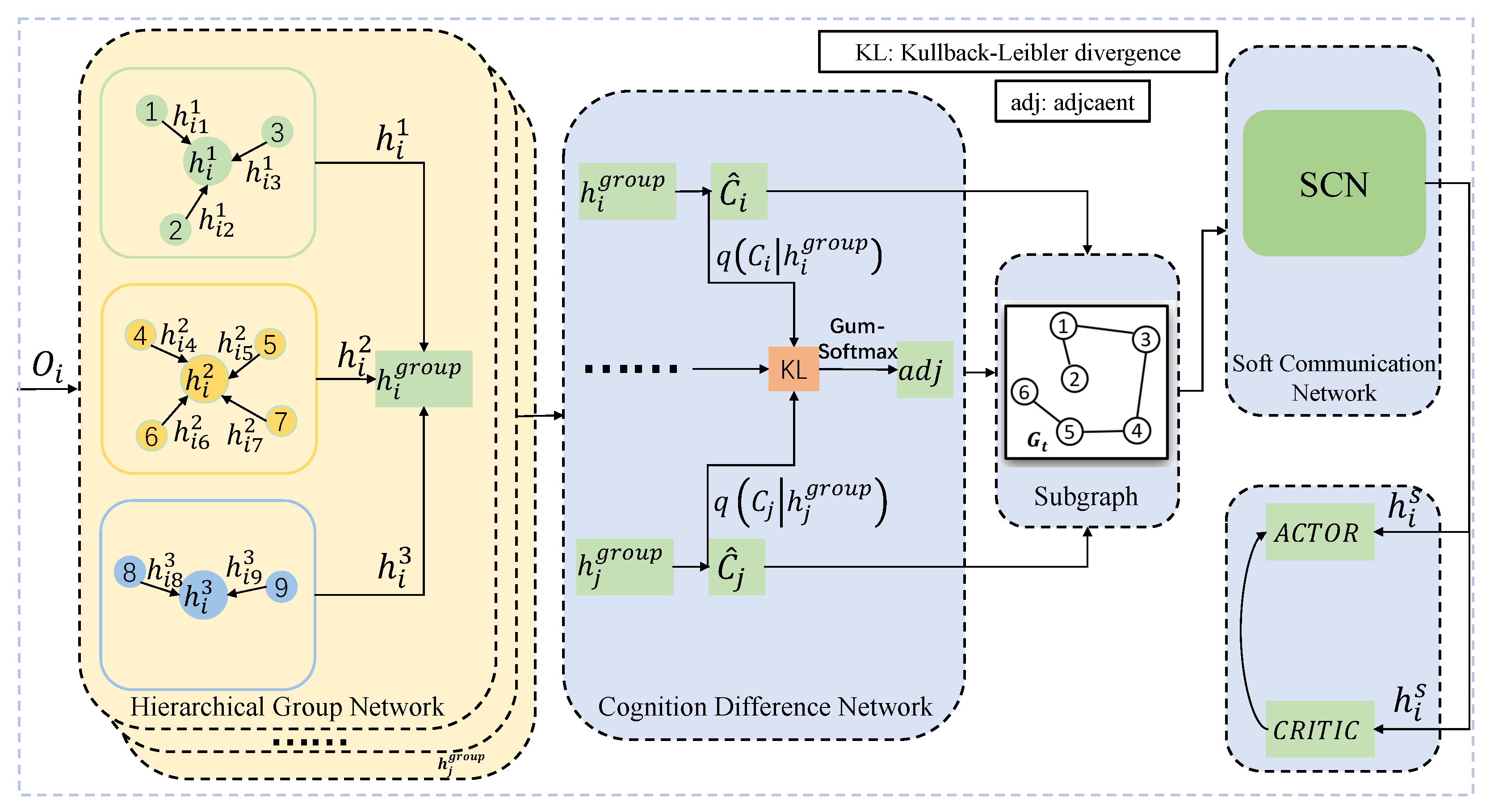
4. Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy
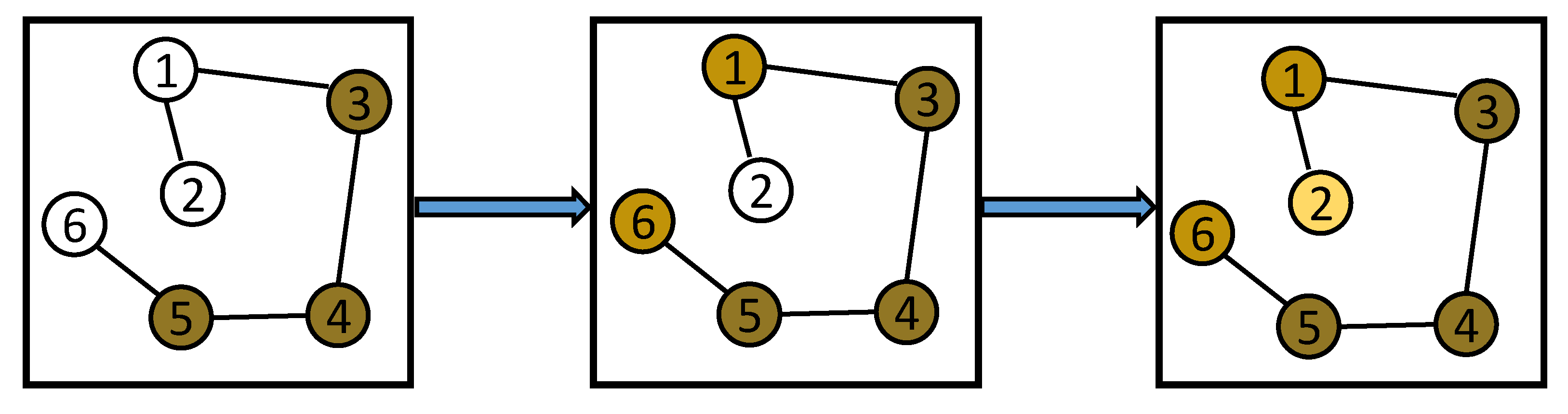
4.1. Hierarchical Group Network
4.2. Cognition Difference Network
4.3. Soft Communication Network
4.4. Training Method
| Algorithm 1 MA-HCDP. |
| Input: agent’s state Initialization: Initialize actor , critic , and old actor network
|
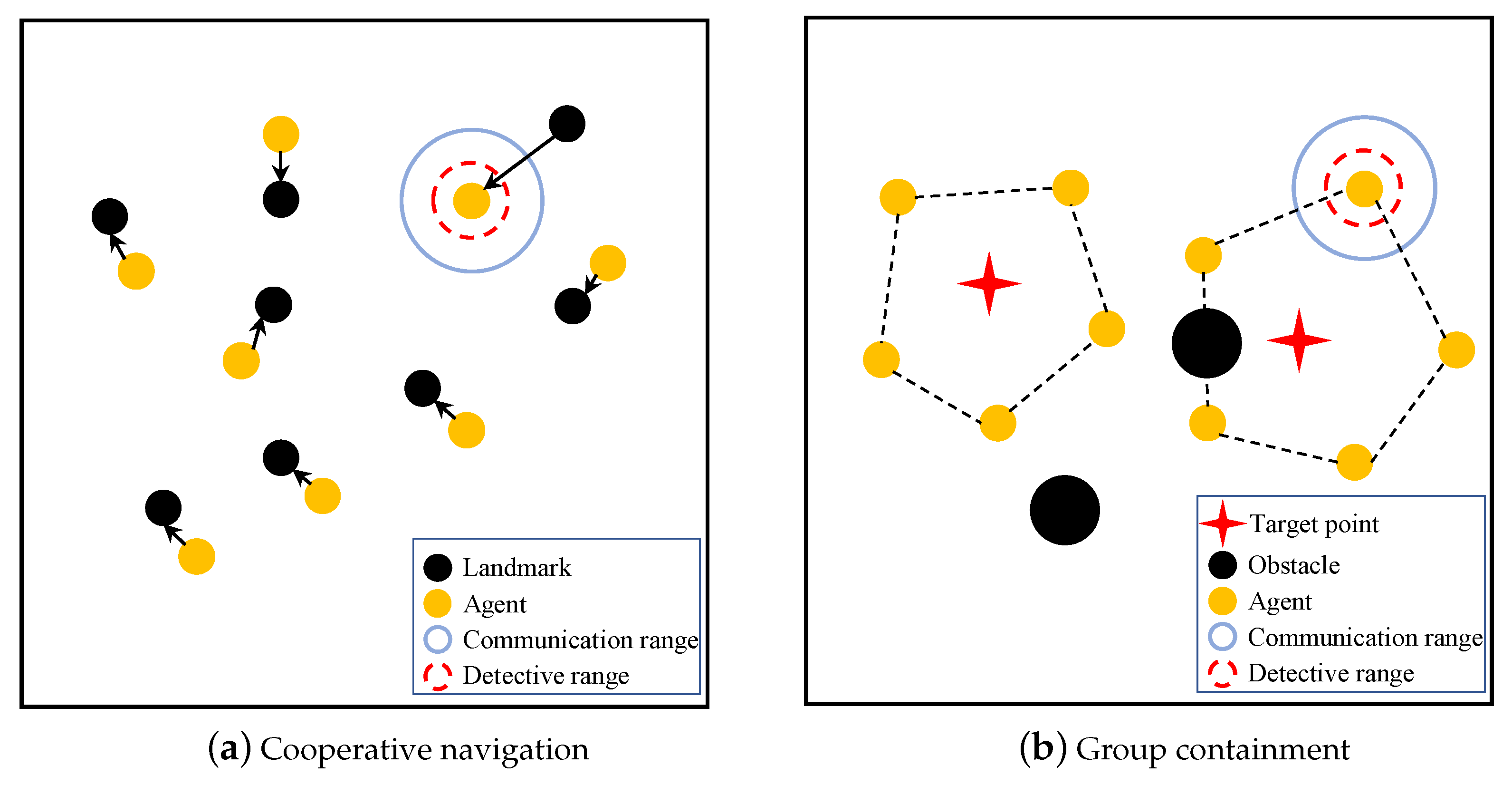
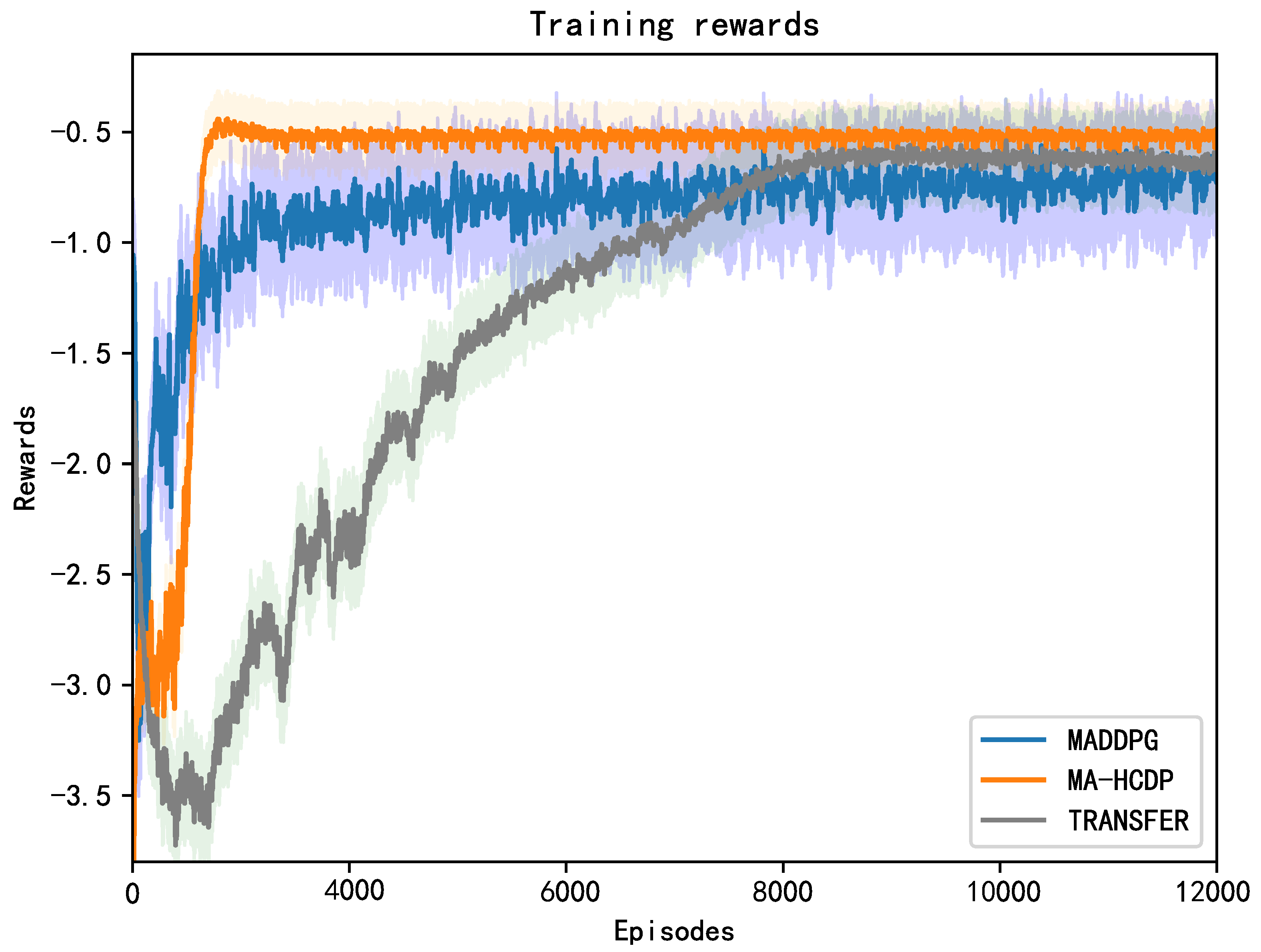
5. Simulation Results and Analysis
5.1. Simulation Settings
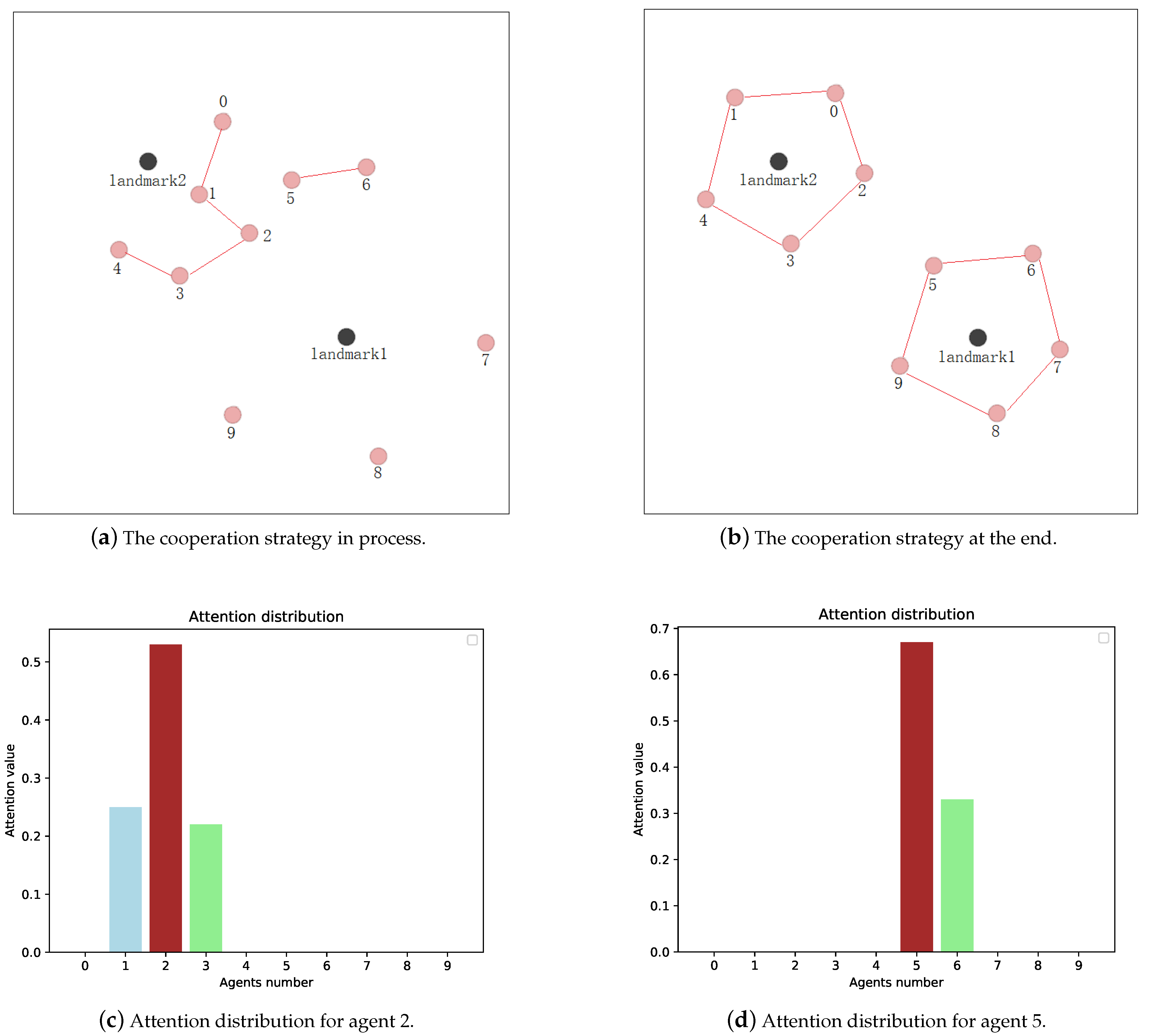
5.2. Cooperative Navigation
5.3. Group Containment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MA-HCDP | Multiagent hierarchical cognition difference policy |
| HGN | Hierarchical group network |
| CDN | Cognition difference network |
| SCN | Soft communication network |
| VAE | Variational autoencoder |
| GNN | Graph neural networks |
| PPO | Proximal policy optimization |
| POMG | Partially observable Markov games |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
References
- Yang, Y.; Hao, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Fan, C.; Strbac, G. Recurrent Deep Multiagent Q-Learning for Autonomous Brokers in Smart Grid. IJCAI 2018, 18, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Bian, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, T.Y. A Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework for Resource Balancing in Complex Logistics Network. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Babuschkin, I.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Mathieu, M.; Dudzik, A.; Chung, J.; Choi, D.H.; Powell, R.; Ewalds, T.; Georgiev, P.; et al. Grandmaster level in StarCraft II using multi-agent reinforcement learning. Nature 2019, 575, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Chen, G.; Zhao, P.; Qiu, F.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; et al. Supervised Learning Achieves Human-Level Performance in MOBA Games: A Case Study of Honor of Kings. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnih, V.; Badia, A.P.; Mirza, M.; Graves, A.; Lillicrap, T.; Harley, T.; Silver, D.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 1928–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Holly, E.; Lillicrap, T.; Levine, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robotic Manipulation with Asynchronous Off-Policy Updates. arXiv 2016, arXiv:cs.RO/1610.00633. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Abbeel, O.P.; Mordatch, I. Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02275. [Google Scholar]
- Foerster, J.N.; Farquhar, G.; Afouras, T.; Nardelli, N.; Whiteson, S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Mean Field Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 5567–5576. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.; Shin, H.; Park, J. Multi-agent actor-critic with hierarchical graph attention network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 7236–7243. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Pu, Z.; Yi, J.; Wang, H. Multi-agent Cooperation and Competition with Two-Level Attention Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Bangkok, Thailand, 18–22 November 2020; pp. 524–535. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhbaatar, S.; Szlam, A.; Fergus, R. Learning multiagent communication with backpropagation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 2244–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Kumar, S.; Sycara, K.; Lewis, M. Learning Transferable Cooperative Behavior in Multi-Agent Teams. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–13 May 2020; pp. 1741–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, Z. Learning attentional communication for multi-agent cooperation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 7254–7264. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Sha, F. Actor-Attention-Critic for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 2961–2970. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Gervet, T.; Romoff, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Rabbat, M.; Pineau, J. TarMAC: Targeted Multi-Agent Communication. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 1538–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, P.; Wen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, Z.; Long, H.; Wang, J. Multiagent bidirectionally-coordinated nets: Emergence of human-level coordination in learning to play starcraft combat games. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.10069. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Xin, B.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y. Revisiting the Master-Slave Architecture in Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:cs.AI/1712.07305. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2014, arXiv:stat.ML/1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Kullback, S. Information Theory and Statistics; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Littman, M.L. Markov games as a framework for multi-agent reinforcement learning. In Machine Learning Proceedings 1994; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Hao, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y. Multi-agent game abstraction via graph attention neural network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 7211–7218. [Google Scholar]
- Malysheva, A.; Kudenko, D.; Shpilman, A. MAGNet: Multi-agent Graph Network for Deep Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 XVI International Symposium “Problems of Redundancy in Information and Control Systems” (REDUNDANCY), Moscow, Russia, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Kucukelbir, A.; McAuliffe, J.D. Variational Inference: A Review for Statisticians. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2017, 112, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Gu, S.; Poole, B. Categorical Reparameterization with Gumbel-softmax. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01144. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning rate | |
| Max gradient normalization | 2 |
| Discount factor | 0.99 |
| Coefficient of value loss function | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of policy loss function | 1 |
| Coefficient of entropy | 0.01 |
| Coefficient of VAE loss function | 0.01 |
| Episode | 20,000 |
| Batch size | 64 |
| PPO epoch | 4 |
| Number of attention heads in HGN | 3 |
| Method | Scenario (a) with 6 Agents | Scenario (b) with 15 Agents | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | Steps | Rewards | Success Rate | Steps | Rewards | ||
| MADDPG | mean | 0 | 50 | −1.34 | 0 | 50 | −2.2 |
| t-test | N/A(+) | −557.9873(+) | 94.2665(+) | N/A(+) | −522.7875(+) | 181.5395(+) | |
| TRANSFER | mean | 100 | 14.2 | −0.52 | 97 | 17.18 | −0.61 |
| t-test | N/A(=) | −1.2035(=) | 1.2131(=) | 1.0801(=) | −5.7893(+) | 6.3189(+) | |
| MA-HCDP | mean | 100 | 14.01 | −0.49 | 99 | 14.82 | −0.53 |
| t-test | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Method | Scenario (c) with 20 agents | Scenario (d) with 29 agents | |||||
| Success rate | Steps | Rewards | Success rate | Steps | Rewards | ||
| MADDPG | mean | 0 | 50 | −3.48 | 0 | 50 | −3.91 |
| t-test | N/A(+) | −472.6488(+) | 322.5309(+) | N/A(+) | −413.4042(+) | 373.1337(+) | |
| TRANSFER | mean | 98 | 20.11 | −0.72 | 96 | 25.2 | −0.86 |
| t-test | 0.9201(=) | −21.1968(+) | 9.2276(+) | 1.1241(=) | −38.0417(+) | 42.0352(+) | |
| MA-HCDP | mean | 99 | 17.05 | −0.64 | 98 | 20.06 | −0.69 |
| t-test | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Method | Scenario (a) with 6 Agents | Scenario (b) with 10 Agents | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | Steps | Rewards | Success Rate | Steps | Rewards | ||
| MADDPG | mean | 0 | 80 | −1.68 | 0 | 80 | −4.12 |
| t-test | N/A (+) | −583.7586 (+) | 252.3061 (+) | N/A (+) | −662.4380 (+) | 749.1802 (+) | |
| TRANSFER | mean | 93 | 16.3 | −0.66 | 91 | 14.28 | −0.82 |
| t-test | 87.3064 (+) | −38.9224 (+) | 32.3495 (+) | 103.8512 (+) | −33.4683 (+) | 36.2515 (+) | |
| MA-HCDP | mean | 100 | 14.2 | −0.56 | 100 | 12.9 | −0.68 |
| t-test | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yi, J.; Pu, Z. Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy for Multiagent Cooperation. Algorithms 2021, 14, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030098
Wang H, Liu Z, Yi J, Pu Z. Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy for Multiagent Cooperation. Algorithms. 2021; 14(3):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030098
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huimu, Zhen Liu, Jianqiang Yi, and Zhiqiang Pu. 2021. "Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy for Multiagent Cooperation" Algorithms 14, no. 3: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030098
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, Z., Yi, J., & Pu, Z. (2021). Multiagent Hierarchical Cognition Difference Policy for Multiagent Cooperation. Algorithms, 14(3), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14030098






