An O(log2N) Fully-Balanced Resampling Algorithm for Particle Filters on Distributed Memory Architectures
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Problem Definition and Related Work
- All cores perform the same pre-agreed tasks (i.e., no central unit(s) are involved) to balance the workload evenly;
- The number of messages for the load balancing is data-independent in order to guarantee a stable run-time, as often required in real-time applications;
- The redistribution of the particles is performed globally in order to ensure the same output of sequential redistribution and that no speed–accuracy trade-off is made when the DOP increases.
1.3. Our Results
2. Sequential Importance Resampling
| Algorithm 1 Sequential Redistribution (S-R) |
| Input:, , N |
| Output: |
|
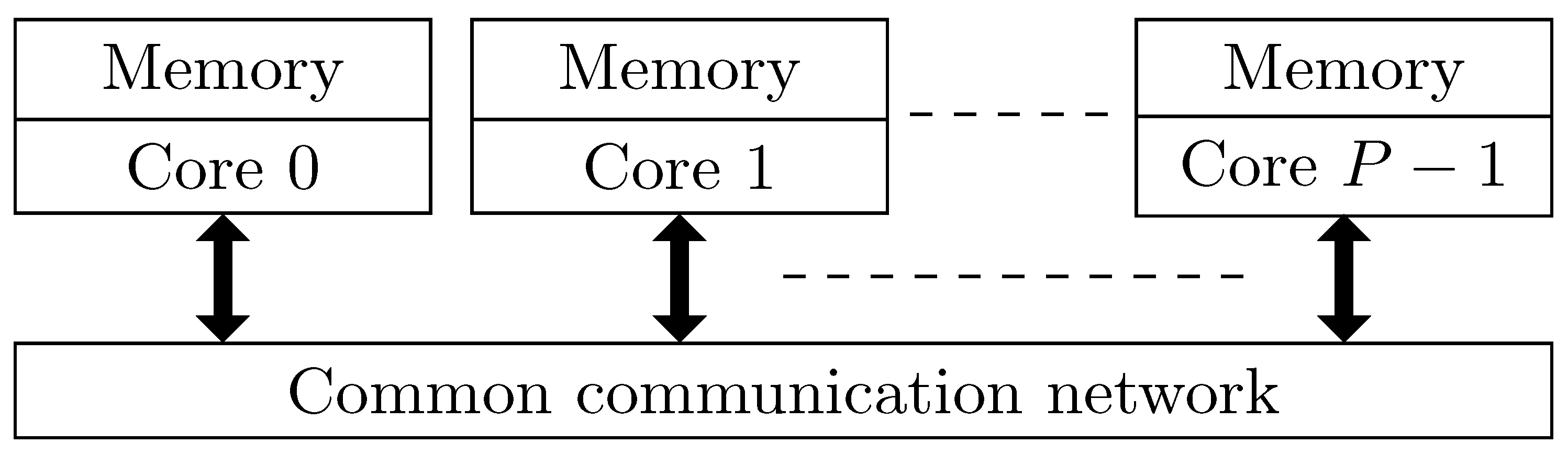
3. Distributed Memory Architectures
4. Novel Fully-Balanced Redistribution
| Algorithm 2 Rotational Nearly Sort |
| Input:, , N, P, , p |
| Output:, |
|
| Algorithm 3 Sequential Nearly Sort (S-NS) |
| Input:, , n |
| Output:, , |
|
| Algorithm 4 Rotational Split |
| Input:, , N, P, , p |
| Output:, |
|
| Algorithm 5 Rotational Nearly Sort and Split (RoSS) Redistribution |
| Input:, , N, P, , p |
| Output: |
4.1. General Overview
4.2. Algorithmic Details and Theorems
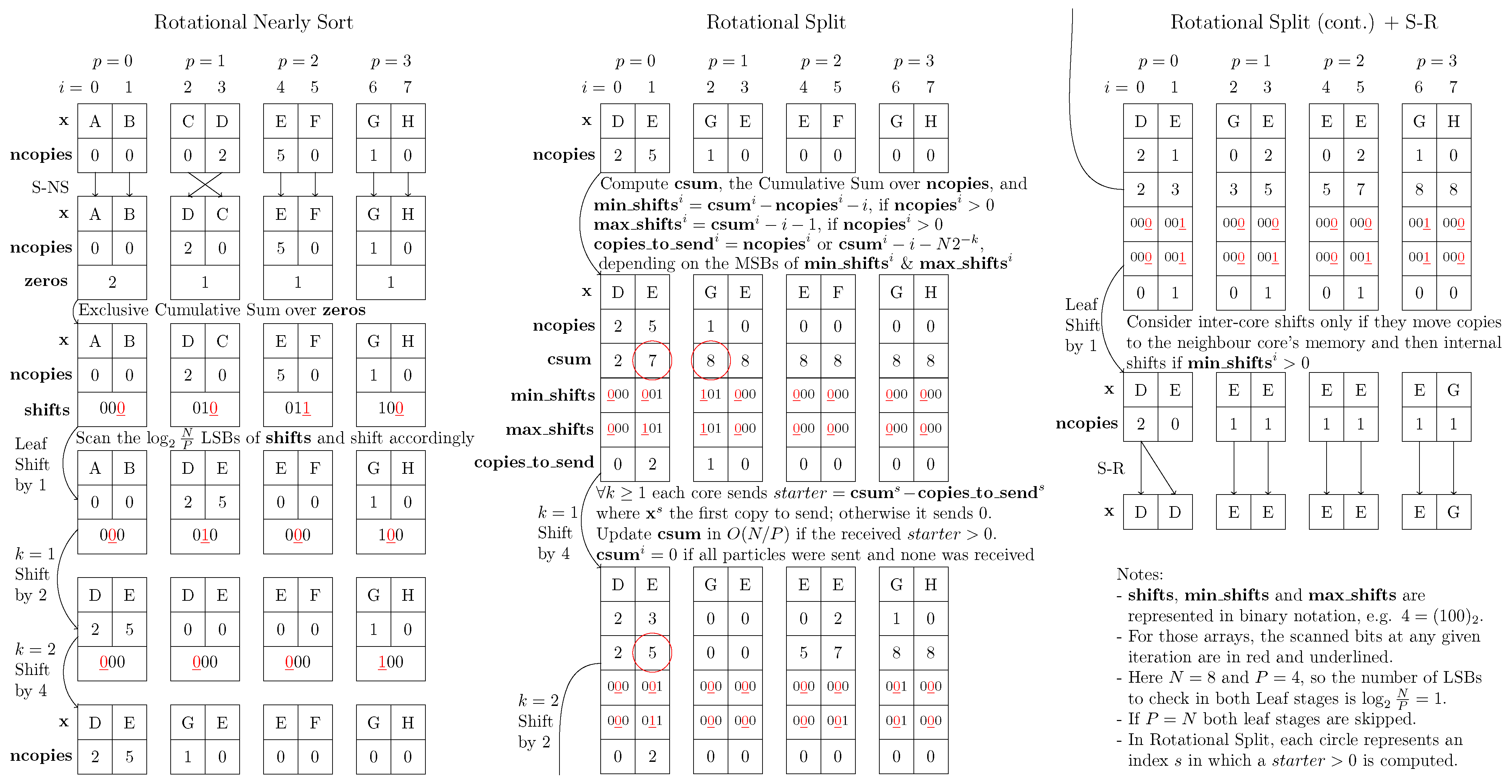
4.2.1. Rotational Nearly Sort
4.2.2. Rotational Split
- None of its copies must move;
- All of them must rotate;
- Some must split and shift, and the others must not move.
- 1.
- There are one or more zeros between i and j;
- 2.
- There are no zeros between i and j.
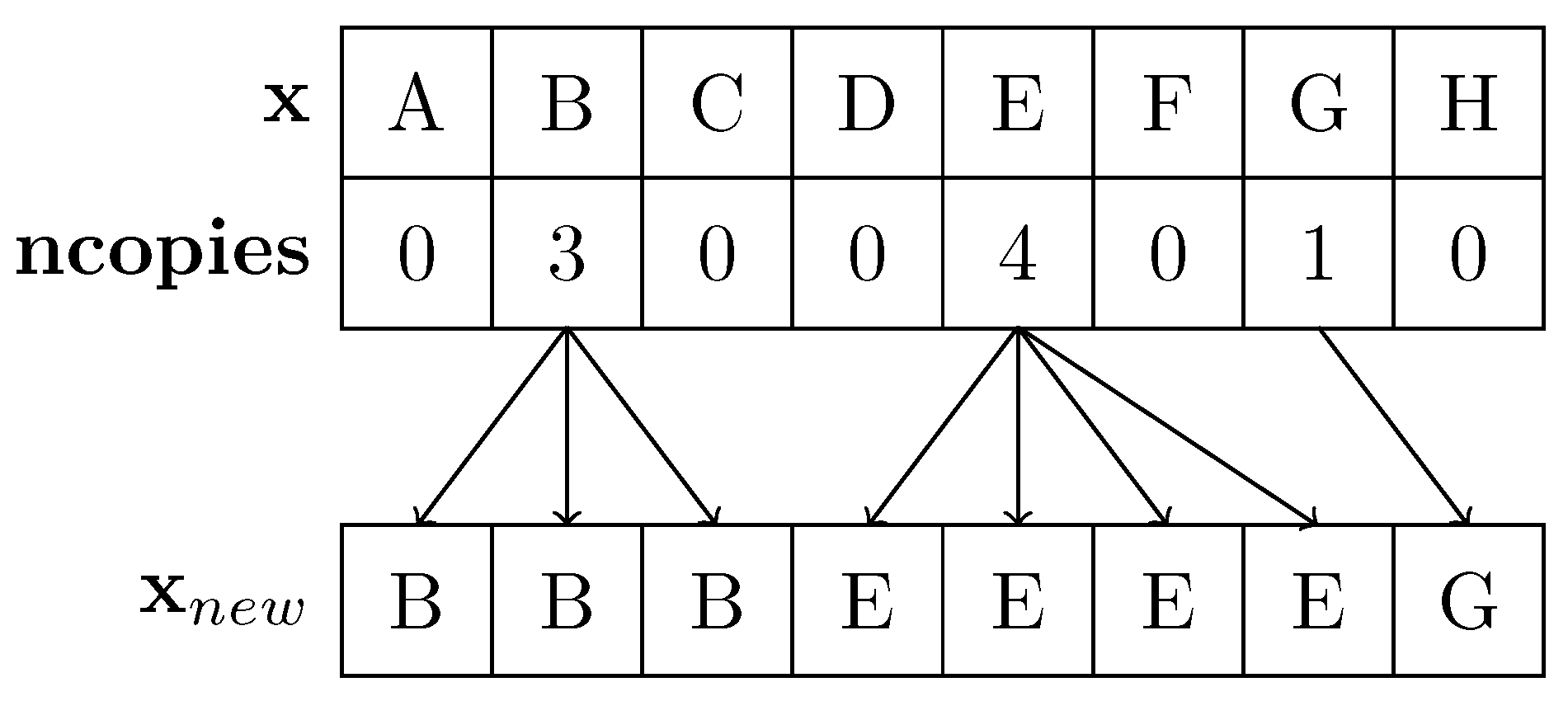
4.2.3. Rotational Nearly Sort and Split Redistribution
4.3. Implementation on MPI
5. Experimental Results
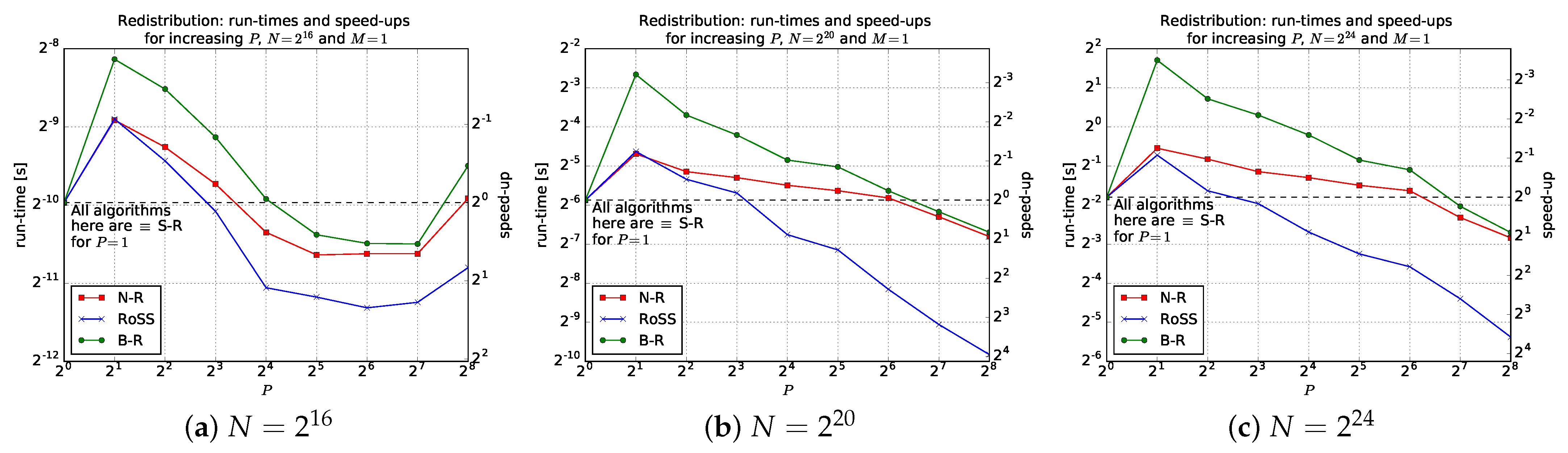
5.1. RoSS vs. B-R and N-R
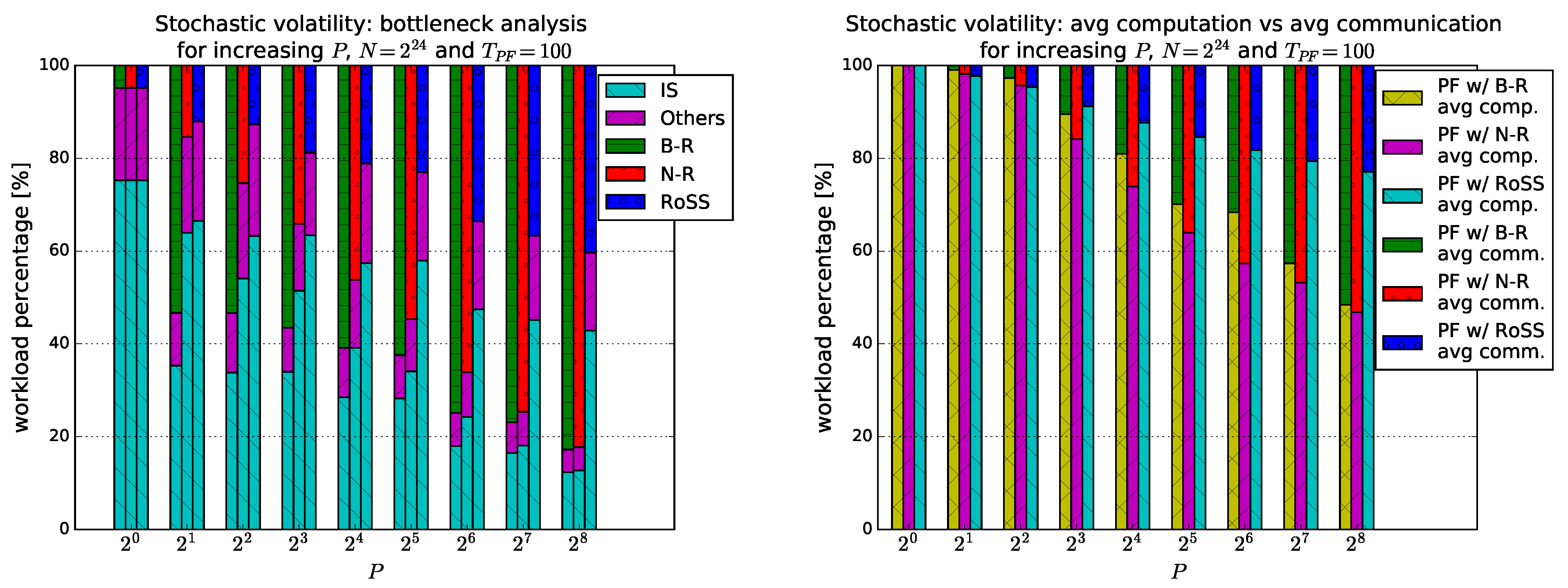
5.2. Stochastic Volatility
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. O((log 2 N) 2 ) Fully-Balanced Redistribution
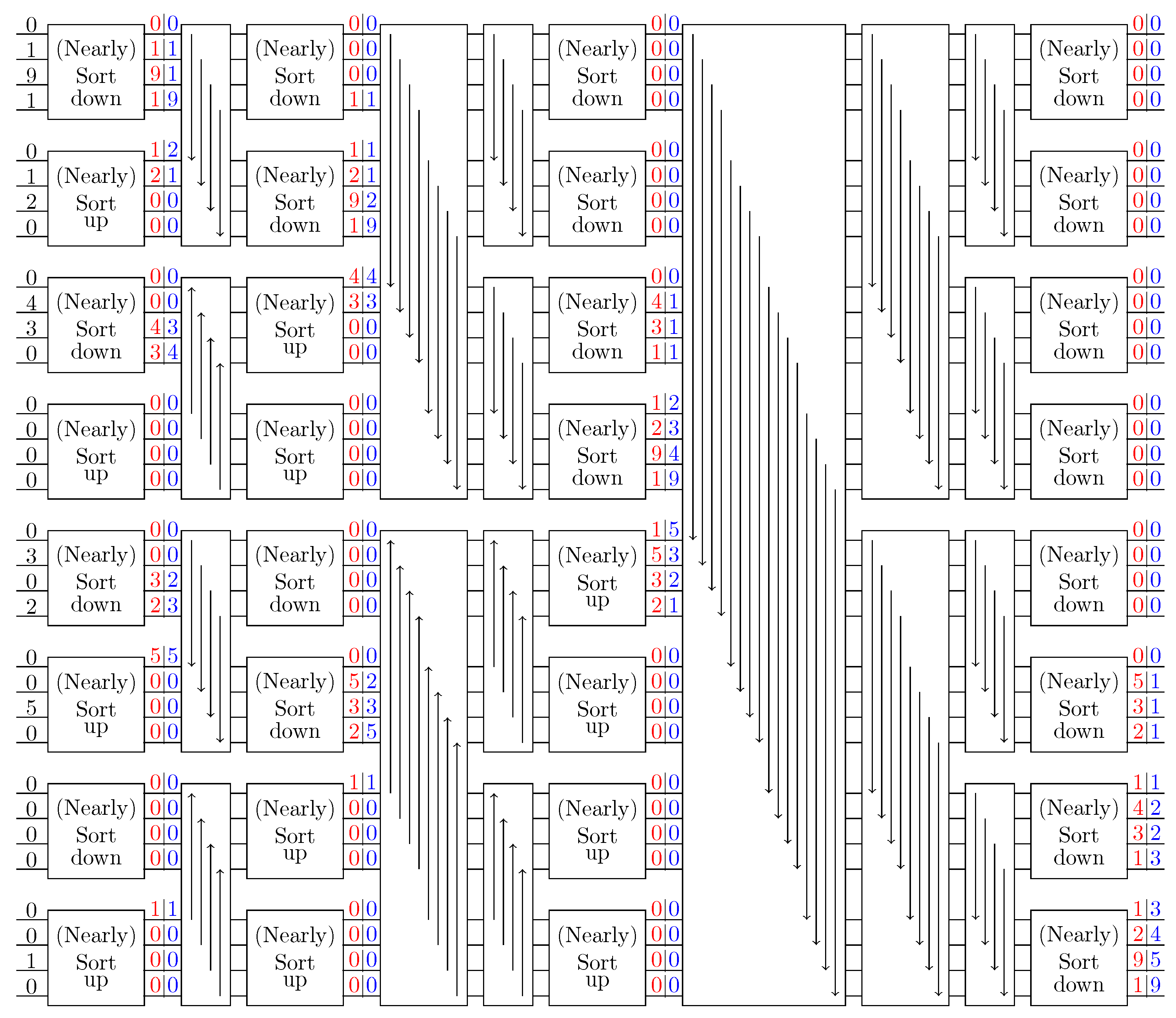

| Algorithm A1 Bitonic/Nearly-Sort-Based Redistribution (B-R/N-R) |
| Input:, , N, P, |
| Output: |
|
Appendix B. Stochastic Volatility Model
References
- Arulampalam, M.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A Tutorial on Particle Filters for Online Nonlinear/Non–Gaussian Bayesian Tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Karkus, P.; Hsu, D.; Lee, W.S. Particle Filter Recurrent Neural Networks. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 5101–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; Orlande, H.; Campos Velho, H.; Pinho, S.; Dulikravich, G.; Cotta, R.; Cunha Neto, S. Estimation of Tumor Size Evolution Using Particle Filters. J. Comput. Biol. A J. Comput. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 22, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liang, S.Y. Degradation Trend Prediction for Rotating Machinery Using Long-Range Dependence and Particle Filter Approach. Algorithms 2018, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.J.; Künsch, H.R.; Nerger, L.; Potthast, R.; Reich, S. Particle Filters for High-Dimensional Geoscience Applications: A Review. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 2335–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. A Particle Filter Track-Before-Detect Algorithm Based on Hybrid Differential Evolution. Algorithms 2015, 8, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsi, A.; Kekempanos, L.; Thiyagalingam, J.; Maskell, S. A Single SMC Sampler on MPI that Outperforms a Single MCMC Sampler. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10252. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, E.; Madigan, M. astroABC: An Approximate Bayesian Computation Sequential Monte Carlo Sampler for Cosmological Parameter Estimation. Astron. Comput. 2017, 19, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Particle Probability Hypothesis Density Filter Based on Pairwise Markov Chains. Algorithms 2019, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesseth, C.A.; Lindsten, F.; Schön, T.B. High-Dimensional Filtering Using Nested Sequential Monte Carlo. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 4177–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, H. Distributed Multi-Sensor Particle Filter for Bearings-Only Tracking. Int. J. Electron. 2012, 99, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, F.; Zhang, L.; Beaman, J.; Mok, A. Implementation of a Particle Filter on a GPU for Nonlinear Estimation in a Manufacturing Remelting Process. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Besançon, France, 8–11 July 2014; pp. 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, F.; Zhang, L.; Mok, A.; Beaman, J. Particle Filtering on GPU Architectures for Manufacturing Applications. Comput. Ind. 2015, 71, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuger, K.; Osgood, N. Particle Filtering Using Agent-Based Transmission Models. In Proceedings of the 2015 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; Johansen, A. A Tutorial on Particle Filtering and Smoothing: Fifteen Years Later. Handb. Nonlinear Filter. 2009, 12, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Djuric, P.M.; Lu, T.; Bugallo, M.F. Multiple Particle Filtering. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing—ICASSP ’07, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–20 April 2007; Volume 3, pp. III-1181–III-1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, O.; Smal, I.; Niessen, W.; Meijering, E.; Sbalzarini, I. PPF—A Parallel Particle Filtering Library. In Proceedings of the IET Conference on Data Fusion Target Tracking 2014: Algorithms and Applications (DF TT 2014), Liverpool, UK, 30 April 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.M.; Lee, A.; Jacob, P.E. Parallel Resampling in the Particle Filter. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2016, 25, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsi, A.; Taylor, J.; Kekempanos, L.; Pyzer Knapp, E.; Maskell, S. A Fast Parallel Particle Filter for Shared Memory Systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolic, M.; Djuric, P.M.; Hong, S. Resampling Algorithms and Architectures for Distributed Particle Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Long, Y.; Zeng, Y.; An, W. Parallel Particle PHD Filter Implemented on Multicore and Cluster Systems. Signal Process. 2016, 127, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Gu, F.; Hu, X.; Guo, S. Particle Routing in Distributed Particle Filters for Large-Scale Spatial Temporal Systems. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2016, 27, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, K.; Whiteley, N.; Cemgil, A. Parallelizing Particle Filters With Butterfly Interactions. Scand. J. Stat. 2020, 47, 361–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutharsan, S.; Kirubarajan, T.; Lang, T.; Mcdonald, M. An Optimization-Based Parallel Particle Filter for Multitarget Tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 1601–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsi, A.; Kekempanos, L.; Thiyagalingam, J.; Maskell, S. Parallelising Particle Filters with Deterministic Runtime on Distributed Memory Systems. In Proceedings of the IET 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Signal Processing (ISP 2017), London, UK, 4–5 December 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskell, S.; Alun-Jones, B.; Macleod, M. A Single Instruction Multiple Data Particle Filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nonlinear Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Cambridge, UK, 13–15 September 2006; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batcher, K.E. Sorting Networks and Their Applications. In Proceedings of the Spring Joint Computer Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 30 April–2 May 1968; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1968. AFIPS ’68 (Spring). pp. 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.; Verosky, N.; Newhall, T. A CUDA-MPI Hybrid Bitonic Sorting Algorithm for GPU Clusters. In Proceedings of the 2012 41st International Conference on Parallel Processing Workshops, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 10–13 September 2012; pp. 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddar, S.; Batcher, K. Designing Sorting Networks: A New Paradigm; SpringerLink: Bücher; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagalingam, J.; Kekempanos, L.; Maskell, S. MapReduce Particle Filtering with Exact Resampling and Deterministic Runtime. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2017, 2017, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hol, J.D.; Schon, T.B.; Gustafsson, F. On Resampling Algorithms for Particle Filters. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Nonlinear Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Cambridge, UK, 13–15 September 2006; pp. 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, M.; Komlós, J.; Szemerédi, E. An 0(N Log N) Sorting Network. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Boston, MA, USA, 25–27 April 1983; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1983. STOC ’83. pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, M.S. Improved Sorting Networks With O(logN) Depth. Algorithmica 1990, 5, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiferas, J. Sorting Networks of Logarithmic Depth, Further Simplified. Algorithmica 2009, 53, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ladner, R.E.; Fischer, M.J. Parallel Prefix Computation. J. ACM 1980, 27, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.E. Optimal and Efficient Algorithms for Summing and Prefix Summing on Parallel Machines. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2002, 62, 517–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropp, W.; Lusk, E.; Skjellum, A. Using MPI: Portable Parallel Programming with the Message-Passing Interface; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Liang, T.Y.; Chiu, J.Y. A Compound OpenMP/MPI Program Development Toolkit for Hybrid CPU/GPU Clusters. J. Supercomput. 2013, 66, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Task Name (Parallelization Strategy) | Details | Sequential Time Complexity | Parallel Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| IS (embarrassingly parallel) | Equations (1) and (2) | ||
| Normalize (reduction) | Equation (3) | ||
| ESS (reduction) | Equation (4) | ||
| MVR (cumulative sum) | Equations (6) and (7) | ||
| Redistribution (RoSS) | Algorithm 5 | ||
| Reset (embarrassingly parallel) | |||
| Estimate (reduction) | Equation (8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varsi, A.; Maskell, S.; Spirakis, P.G. An O(log2N) Fully-Balanced Resampling Algorithm for Particle Filters on Distributed Memory Architectures. Algorithms 2021, 14, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14120342
Varsi A, Maskell S, Spirakis PG. An O(log2N) Fully-Balanced Resampling Algorithm for Particle Filters on Distributed Memory Architectures. Algorithms. 2021; 14(12):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14120342
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarsi, Alessandro, Simon Maskell, and Paul G. Spirakis. 2021. "An O(log2N) Fully-Balanced Resampling Algorithm for Particle Filters on Distributed Memory Architectures" Algorithms 14, no. 12: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14120342
APA StyleVarsi, A., Maskell, S., & Spirakis, P. G. (2021). An O(log2N) Fully-Balanced Resampling Algorithm for Particle Filters on Distributed Memory Architectures. Algorithms, 14(12), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/a14120342






